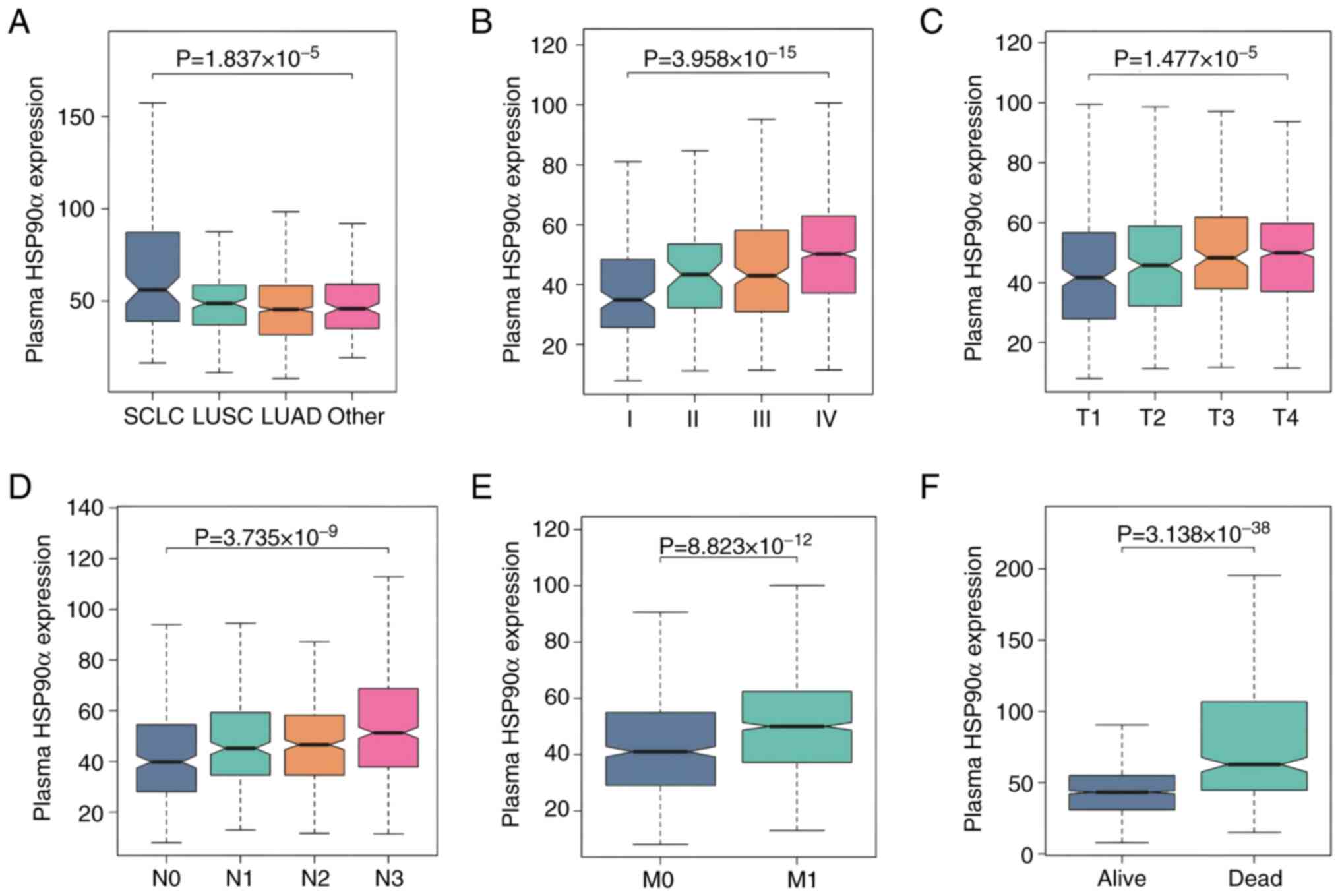
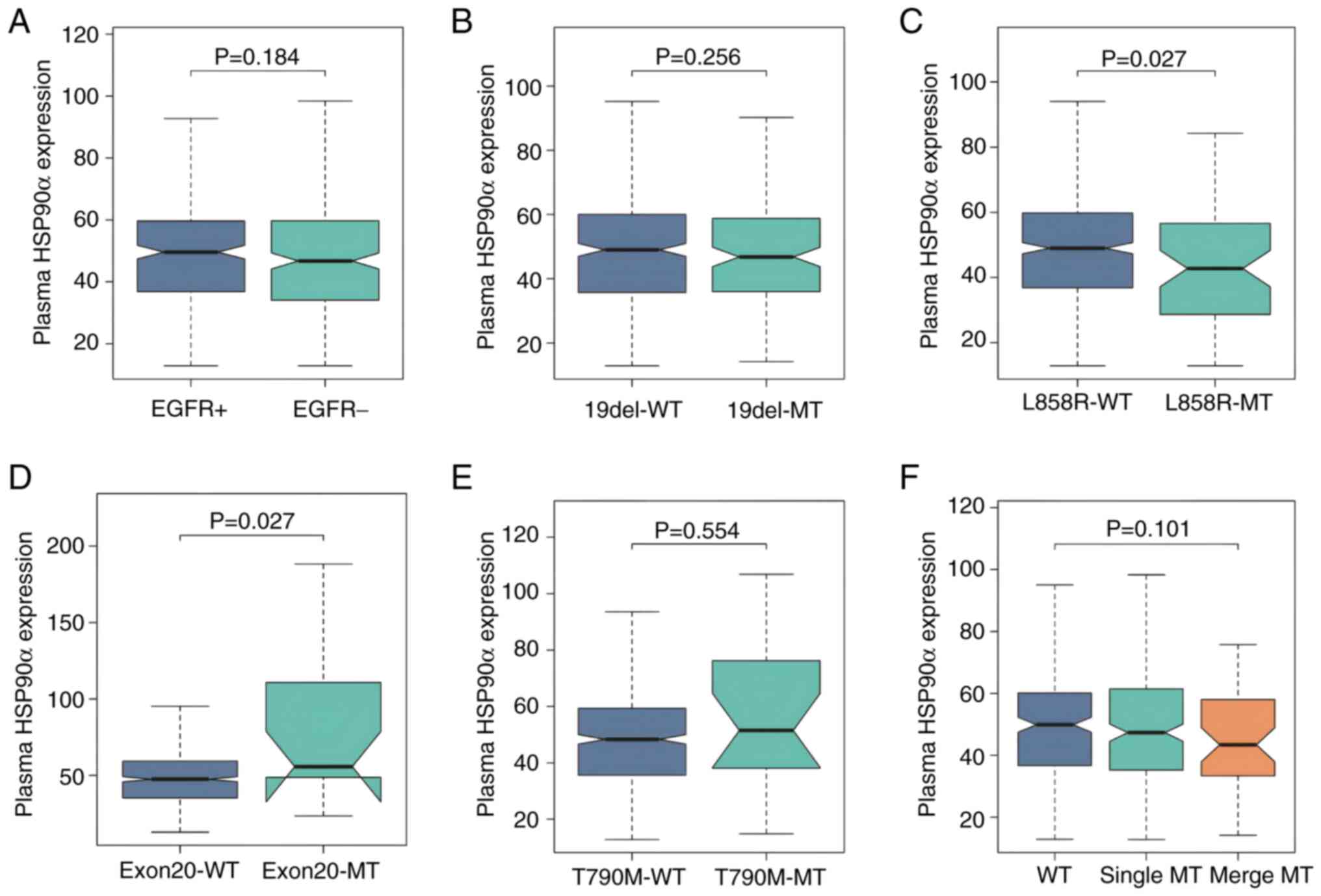
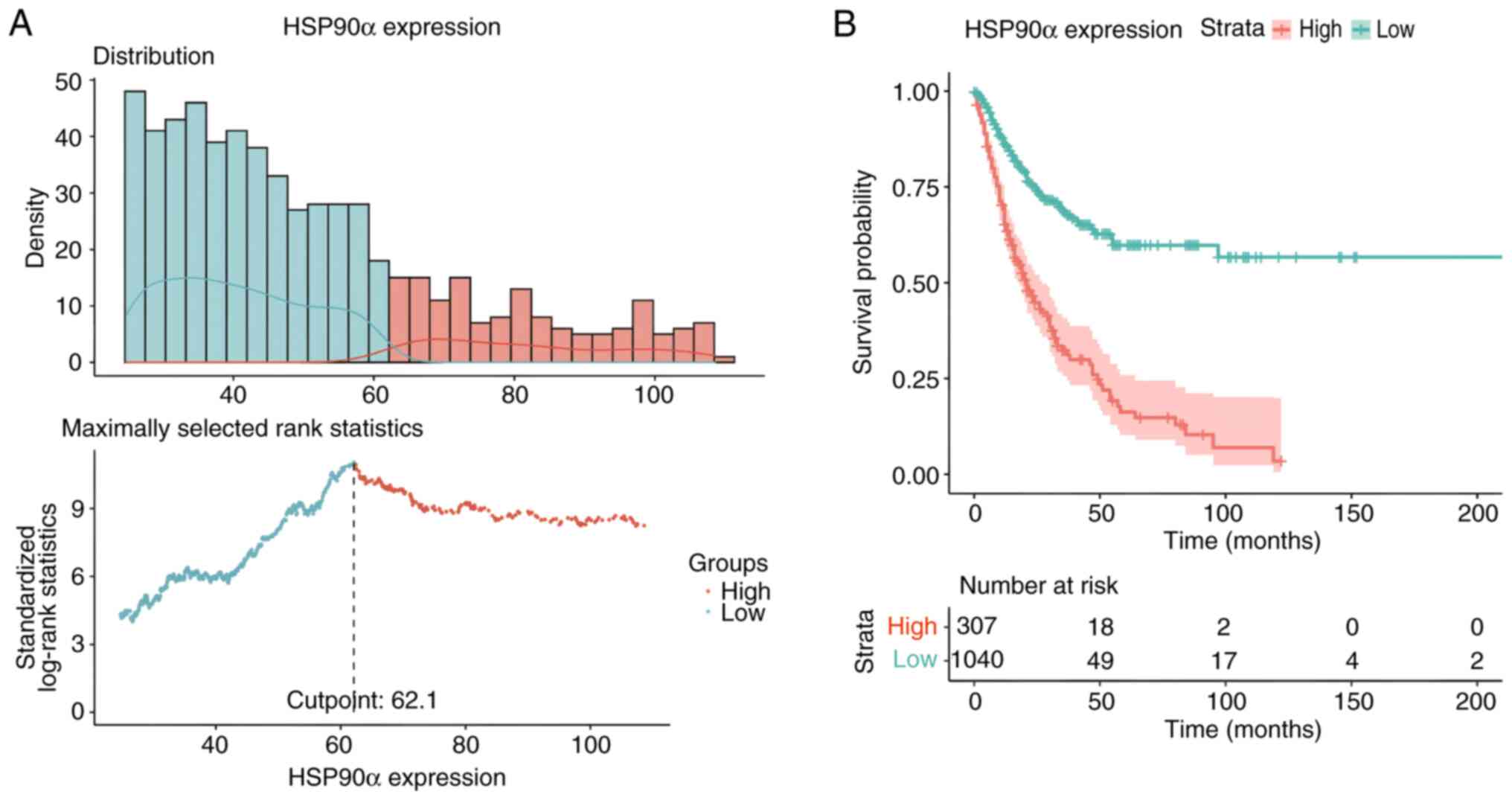
|
1
|
Khanali J and Kolahi AA: National and
subnational cancer incidence for 22 cancer groups, 2000 to 2016: A
study based on cancer registration data of Iran. J Cancer
Epidemiol. 2021:66766662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cheng L, Alexander RE, Maclennan GT,
Cummings OW, Montironi R, Lopez-Beltran A, Cramer HM, Davidson DD
and Zhang S: Molecular pathology of lung cancer: Key to
personalized medicine. Mod Pathol. 25:347–369. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang CY, Yang JC and Yang PC: Precision
management of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Annu Rev Med.
71:117–136. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
He J, Huang Z, Han L, Gong Y and Xie C:
Mechanisms and management of 3rd-generation EGFR-TKI resistance in
advanced non-small cell lung cancer (Review). Int J Oncol.
59:902021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mok TS: Personalized medicine in lung
cancer: What we need to know. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 8:661–668. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Paola U and Stefano I: Liquid biopsies in
cancer diagnosis, monitoring and prognosis. Biomedicines.
10:27482022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Frydman J: Folding of newly translated
proteins in vivo: The role of molecular chaperones. Annu Rev
Biochem. 70:603–647. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Condelli V, Crispo F, Pietrafesa M,
Lettini G, Matassa DS, Esposito F, Landriscina M and Maddalena F:
HSP90 molecular chaperones, metabolic rewiring, and epigenetics:
Impact on tumor progression and perspective for anticancer therapy.
Cells. 8:5322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ahsan A, Ramanand SG, Whitehead C, Hiniker
SM, Rehemtulla A, Pratt WB, Jolly S, Gouveia C, Truong K, Van Waes
C, et al: Wild-type EGFR is stabilized by direct interaction with
HSP90 in cancer cells and tumors. Neoplasia. 14:670–677. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Flannery PJ and Spurney RF:
Transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by
angiotensin II in glomerular podocytes. Nephron Exp Nephrol.
103:e109–e118. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou G, Pu Y, Zhao K, Chen Y and Zhang G:
Heat shock proteins in non-small-cell lung cancer-functional
mechanism. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 28:562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
AL Elaimy A, Ahsan A, Ray D, Lawrence TS
and Nyati MK: Role of Hsp90 in the stability of EGFR from radiation
and cisplatin-induced degradation. Cancer Res. 73:10282013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sui Y, Shen Z, Pan R, Ma R, Si R, Feng J
and Zhou G: AHSA1-HSP90AA1 complex stabilized IFI6 and TGFB1
promotes mitochondrial stability and EMT in EGFR-mutated lung
adenocarcinoma under Osimertinib pressure. Cell Death Dis.
16:2982025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ercan D, Zejnullahu K, Yonesaka K, Xiao Y,
Capelletti M, Rogers A, Lifshits E, Brown A, Lee C, Christensen JG,
et al: Amplification of EGFR T790M causes resistance to an
irreversible EGFR inhibitor. Oncogene. 29:2346–2356. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wei W, Zhou J, Chen L, Liu H, Zhang F, Li
J, Ning S, Li S, Wang C, Huang Y, et al: plasma levels of heat
shock protein 90 alpha associated with colorectal cancer
development. Front Mol Biosci. 8:6848362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu H, Zhang Z, Huang Y, Wei W, Ning S, Li
J, Liang X, Liu K and Zhang L: Plasma HSP90AA1 predicts the risk of
breast cancer onset and distant metastasis. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:6395962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fu Y, Xu X, Huang D, Cui D, Liu L, Liu J,
He Z, Liu J, Zheng S and Luo Y: Plasma heat shock protein 90alpha
as a biomarker for the diagnosis of liver cancer: An official,
large-scale, and multicenter clinical trial. EBioMedicine.
24:56–63. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shi Y, Liu X, Lou J, Han X, Zhang L, Wang
Q, Li B, Dong M and Zhang Y: Plasma levels of heat shock protein 90
alpha associated with lung cancer development and treatment
responses. Clin Cancer Res. 20:6016–6022. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Su K, Liu Y, Wang P, He K, Wang F, Chi H,
Rao M, Li X, Wen L, Song Y, et al: Heat-shock protein 90α is a
potential prognostic and predictive biomarker in hepatocellular
carcinoma: A large-scale and multicenter study. Hepatol Int.
16:1208–1219. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Van Schil PE, Rami-Porta R and Asamura H:
The 8th TNM edition for lung cancer: A critical analysis. Ann
Transl Med. 6:872018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shimamura T, Li D, Ji H, Haringsma HJ,
Liniker E, Borgman CL, Lowell AM, Minami Y, McNamara K, Perera SA,
et al: Hsp90 inhibition suppresses mutant EGFR-T790M signaling and
overcomes kinase inhibitor resistance. Cancer Res. 68:5827–5838.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jorge SE, Lucena-Araujo AR, Yasuda H,
Piotrowska Z, Oxnard GR, Rangachari D, Huberman MS, Sequist LV,
Kobayashi SS and Costa DB: EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations display
sensitivity to Hsp90 inhibition in preclinical models and lung
adenocarcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 24:6548–6555. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shimamura T, Lowell AM, Engelman JA and
Shapiro GI: Epidermal growth factor receptors harboring kinase
domain mutations associate with the heat shock protein 90 chaperone
and are destabilized following exposure to geldanamycins. Cancer
Res. 65:6401–6408. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin Y, Wang X and Jin H: EGFR-TKI
resistance in NSCLC patients: Mechanisms and strategies. Am J
Cancer Res. 4:411–435. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hong S, Gao F, Fu S, Wang Y, Fang W, Huang
Y and Zhang L: Concomitant genetic alterations with response to
treatment and epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitors in patients with EGFR-Mutant advanced non-small cell
lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. 4:739–742. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Attili I, Passaro A, Pisapia P, Malapelle
U and de Marinis F: Uncommon EGFR compound mutations in non-small
cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A systematic review of available
evidence. Curr Oncol. 29:255–266. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kitadai R and Okuma Y: Treatment
strategies for non-small cell lung cancer harboring common and
uncommon EGFR mutations: Drug sensitivity based on exon
classification, and structure-function analysis. Cancers (Basel).
14:25192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ou SI, Lin HM, Hong JL, Yin Y, Jin S, Lin
J, Mehta M, Nguyen D and Neal J: Real-world response and outcomes
in patients with NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. JTO
Clin Res Rep. 4:1005582023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang JC, Sequist LV, Geater SL, Tsai CM,
Mok TS, Schuler M, Yamamoto N, Yu CJ, Ou SH, Zhou C, et al:
Clinical activity of afatinib in patients with advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring uncommon EGFR mutations: A
combined post-hoc analysis of LUX-Lung 2, LUX-Lung 3, and LUX-Lung
6. Lancet Oncol. 16:830–838. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Eustace BK, Sakurai T, Stewart JK,
Yimlamai D, Unger C, Zehetmeier C, Lain B, Torella C, Henning SW,
Beste G, et al: Functional proteomic screens reveal an essential
extracellular role for hsp90 alpha in cancer cell invasiveness. Nat
Cell Biol. 6:507–514. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhou X, Wen Y, Tian Y, He M, Ke X, Huang
Z, He Y, Liu L, Scharf A, Lu M, et al: Heat shock protein
90α-dependent B-cell-2-associated transcription factor 1 promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation by regulating MYC
Proto-Oncogene c-MYC mRNA stability. Hepatology. 69:1564–1581.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Du Y, Wu J and Luo L: Secreted heat shock
protein 90α attenuated the effect of anticancer drugs in small-cell
lung cancer cells through AKT/GSK3β/β-Catenin signaling. Cancer
Control. 25:10732748188044892018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu W, Li J, Zhang P, Hou Q, Feng S, Liu
L, Cui D, Shi H, Fu Y and Luo Y: A novel pan-cancer biomarker
plasma heat shock protein 90alpha and its diagnosis determinants in
clinic. Cancer Sci. 110:2941–2959. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Smith DL, Acquaviva J, Sequeira M, Jimenez
JP, Zhang C, Sang J, Bates RC and Proia D: The HSP90 inhibitor
ganetespib potentiates the antitumor activity of EGFR tyrosine
kinase inhibition in mutant and wild-type non-small cell lung
cancer. Target Oncol. 10:235–245. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen S, Yu Q and Zhou S: Plasmatic levels
of HSP90α at diagnosis: A novel prognostic indicator of clinical
outcome in advanced lung cancer patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1
inhibitors plus chemotherapy. Front Oncol. 11:7651152021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Proia DA, Sang J, He S, Smith DL, Sequeira
M, Zhang C, Liu Y, Ye S, Zhou D, Blackman RK, et al: Synergistic
activity of the Hsp90 inhibitor ganetespib with taxanes in
non-small cell lung cancer models. Invest New Drugs. 30:2201–2209.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Magwenyane AM, Ugbaja SC, Amoako DG,
Somboro AM, Khan RB and Kumalo HM: Heat shock protein 90 (HSP90)
inhibitors as anticancer medicines: A review on the computer-aided
drug discovery approaches over the past five years. Comput Math
Methods Med. 2022:21477632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wan X, Fang Y, Du J, Cai S and Dong H:
GW4869 can inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
extracellular HSP90α in gefitinib-sensitive NSCLC cells. Onco
Targets Ther. 16:913–922. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Saarenheimo J, Andersen H, Eigeliene N and
Jekunen A: Gene-Guided treatment decision-making in non-small cell
lung cancer-a systematic review. Front Oncol. 11:7544272021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang Y, Barghi SM, Yang Y and
Akhavan-Sigari R: Value of HSP90α in lung cancer diagnosis and
recurrence prediction: A cohort study. Oncol Res Treat. 44:583–589.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fang Y, Yuan Z, Zhang H, Wang P and Hao J:
Predictive value of serum heat shock protein 90α on the prognosis
of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. J Inflamm Res. 16:1183–1193.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li Y, Jin Y, Wang Y, Liu W, Jia W and Wang
J: MR-based radiomics predictive modelling of EGFR mutation and
HER2 overexpression in metastatic brain adenocarcinoma: A
two-centre study. Cancer Imaging. 24:652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ruiz MI, Floor K, Roepman P, Rodriguez JA,
Meijer GA, Mooi WJ, Jassem E, Niklinski J, Muley T, van Zandwijk N,
et al: Integration of gene dosage and gene expression in non-small
cell lung cancer, identification of HSP90 as potential target. PLoS
One. 3:e00017222008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fang L, Barekati Z, Zhang B, Liu Z and
Zhong X: Targeted therapy in breast cancer: What's new? Swiss Med
Wkly. 141:w132312011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tsai YC, Leu SY, Chen SY, Kung CW, Lee YM,
Liu YP, Yen MH and Cheng PY: 17-DMAG, an Hsp90 inhibitor,
ameliorates ovariectomy-induced obesity in rats. Life Sci.
232:1166722019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen L, Fan H, Chu H, Du F, Chen Y, Hu L,
Li Z, Wang W, Hou X and Yang L: The HSP90 inhibitor 17-DMAG
alleviates primary biliary cholangitis via cholangiocyte
necroptosis prevention. J Cell Biochem. 123:1857–1872. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hu C, Yang J, Qi Z, Wu H, Wang B, Zou F,
Mei H, Liu J, Wang W and Liu Q: Heat shock proteins: Biological
functions, pathological roles, and therapeutic opportunities.
MedComm (2020). 3:e1612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liao Y, Liu Y, Yu C, Lei Q, Cheng J, Kong
W, Yu Y, Zhuang X, Sun W, Yin S, et al: HSP90β impedes
STUB1-induced ubiquitination of YTHDF2 to drive sorafenib
resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Adv Sci (Weinh).
10:e23020252023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Qi S, Yi G, Yu K, Feng C and Deng S: The
role of hsp90 inhibitors in the treatment of cardiovascular
diseases. Cells. 11:34442022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chadli A, Felts SJ and Toft DO: GCUNC45 is
the first Hsp90 co-chaperone to show alpha/beta isoform
specificity. J Biol Chem. 283:9509–9512. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Prince TL, Kijima T, Tatokoro M, Lee S,
Tsutsumi S, Yim K, Rivas C, Alarcon S, Schwartz H, Khamit-Kush K,
et al: Client proteins and small molecule inhibitors display
distinct binding preferences for constitutive and stress-induced
HSP90 isoforms and their conformationally restricted mutants. PLoS
One. 10:e01417862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang C, Zhang Y, Guo K, Wang N, Jin H, Liu
Y and Qin W: Heat shock proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma:
Molecular mechanism and therapeutic potential. Int J Cancer.
138:1824–1834. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Dimas DT, Perlepe CD, Sergentanis TN,
Misitzis I, Kontzoglou K, Patsouris E, Kouraklis G, Psaltopoulou T
and Nonni A: The prognostic significance of Hsp70/Hsp90 expression
in breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Anticancer
Res. 38:1551–1562. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang S, Guo S, Li Z, Li D and Zhan Q:
High expression of HSP90 is associated with poor prognosis in
patients with colorectal cancer. PeerJ. 7:e79462019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu K, Kang M, Li J, Qin W and Wang R:
Prognostic value of the mRNA expression of members of the HSP90
family in non-small cell lung cancer. Exp Ther Med. 17:2657–2665.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ding Q, Sun Y, Zhang J, Yao Y, Huang D and
Jiang Y: Utility and specificity of plasma heat shock protein 90
alpha, CEA, and CA199 as the diagnostic test in colorectal cancer
liver metastasis. J Gastrointest Oncol. 13:2497–2504. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhao Q, Miao C, Lu Q, Wu W, He Y, Wu S,
Liu H and Lian C: Clinical significance of monitoring circulating
free DNA and plasma heat shock protein 90alpha in patients with
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 13:2223–2234.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Riely GJ, Wood DE, Ettinger DS, Aisner DL,
Akerley W, Bauman JR, Bharat A, Bruno DS, Chang JY, Chirieac LR, et
al: Non-small cell lung cancer, version 4.2024, NCCN clinical
practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
22:249–274. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wang T, Zhang J, Wang S, Sun X, Wang D,
Gao Y, Zhang Y, Xu L, Wu Y, Wu Y, et al: The exon 19-deleted EGFR
undergoes ubiquitylation-mediated endocytic degradation via dynamin
activity-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Cell Commun Signal.
16:402018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bian Y, Liu H, Huang J, Feng Z, Lin Y, Li
J and Zhang L: eHSP90α in front-line therapy in EGFR exon 19
deletion and 21 Leu858Arg mutations in advanced lung
adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer. 241:8352024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Xu W, Soga S, Beebe K, Lee MJ, Kim YS,
Trepel J and Neckers L: Sensitivity of epidermal growth factor
receptor and ErbB2 exon 20 insertion mutants to Hsp90 inhibition.
Br J Cancer. 97:741–744. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|