|
1
|
Xu Y, Wu W, Han Q, Wang Y, Li C, Zhang P
and Xu H: Post-translational modification control of RNA-binding
protein hnRNPK function. Open Biol. 9:1802392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huang T, Song X, Xu D, Tiek D, Goenka A,
Wu B, Sastry N, Hu B and Cheng SY: Stem cell programs in cancer
initiation, progression, and therapy resistance. Theranostics.
10:8721–8743. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu W, Meng J, Su R, Shen C, Zhang S, Zhao
Y, Liu W, Du J, Zhu S, Li P, et al: SP1-mediated up-regulation of
lncRNA TUG1 underlines an oncogenic property in colorectal cancer.
Cell Death Dis. 13:4332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun X, Xiao C, Wang X, Wu S, Yang Z, Sui B
and Song Y: Role of post-translational modifications of Sp1 in
cancer: State of the art. Front Cell Dev Biol. 12:14124612024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu XW, Pan CW, Yang XM, Zhou L, Zheng ZQ
and Li DC: SP1 reduces autophagic flux through activating p62 in
gastric cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 17:4633–4638. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang L, Pan J, Wang M, Yang J, Zhu S, Li
L, Hu X, Wang Z, Pang L, Li P, et al: Chronic stress-induced and
tumor derived SP1+ exosomes polarizing IL-1β+ neutrophils to
increase lung metastasis of breast cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh).
12:e23102662025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dynan WS and Tjian R: The
promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream
sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 35:79–87. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lai YH, Kuo C, Kuo MT and Chen HH:
Modulating chemosensitivity of tumors to platinum-based antitumor
drugs by transcriptional regulation of copper homeostasis. Int J
Mol Sci. 19:14862018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Crossley M, Whitelaw E, Perkins A,
Williams G, Fujiwara Y and Orkin SH: Isolation and characterization
of the cDNA encoding BKLF/TEF-2, a major CACCC-box-binding protein
in erythroid cells and selected other cells. Mol Cell Biol.
16:1695–1705. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shields JM and Yang VW: Identification of
the DNA sequence that interacts with the gut-enriched Krüppel-like
factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 26:796–802. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Samson S and Wong N: Role of Sp1 in
insulin regulation of gene expression. J Mol Endocrinol.
29:265–279. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bouwman P and Philipsen S: Regulation of
the activity of Sp1-related transcription factors. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 195:27–38. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Briggs MR, Kadonaga JT, Bell SP and Tjian
R: Purification and biochemical characterization of the
promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 234:47–52.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Safe S: Specificity proteins (sp) and
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 24:51642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang JF, Zhou ZY, Liu YZ, Wu L, Nie BB,
Huang L and Zhang C: Role of Sp1 in atherosclerosis. Mol Biol Rep.
49:9893–9902. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Orzechowska-Licari EJ, LaComb JF, Mojumdar
A and Bialkowska AB: SP and KLF transcription factors in cancer
metabolism. Int J Mol Sci. 23:99562022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hata J, Matsuda K, Ninomiya T, Yonemoto K,
Matsushita T, Ohnishi Y, Saito S, Kitazono T, Ibayashi S, Iida M,
et al: Functional SNP in an Sp1-binding site of AGTRL1 gene is
associated with susceptibility to brain infarction. Hum Mol Genet.
16:630–639. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou Y, Zeng L, Cai L, Zheng W, Liu X,
Xiao Y, Jin X, Bai Y, Lai M, Li H, et al: Cellular
senescence-associated gene IFI16 promotes HMOX1-dependent evasion
of ferroptosis and radioresistance in glioblastoma. Nat Commun.
16:12122025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shan L, Wang W, Du L, Li D, Wang Y, Xie Y,
Li H, Wang J, Shi Z, Zhou Y, et al: SP1 undergoes phase separation
and activates RGS20 expression through super-enhancers to promote
lung adenocarcinoma progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
121:e24018341212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang X, Jiang A, Meng Q, Jiang T, Lu H,
Geng X, Song Z, Hu X, Yu Z, Xu W, et al: Aberrant phase separation
drives membranous organelle remodeling and tumorigenesis. Mol Cell.
85:1852–1867. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chuang J, Lo W, Ko C, Chou SY, Chen RM,
Chang KY, Hung JJ, Su WC, Chang WC and Hsu TI: Upregulation of
CYP17A1 by Sp1-mediated DNA demethylation confers temozolomide
resistance through DHEA-mediated protection in glioma. Oncogenesis.
6:e339. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lo WL, Hsu TI, Yang WB, Kao TJ, Wu MH,
Huang YN, Yeh SH and Chuang JY: Betulinic acid-mediated tuning of
PERK/CHOP signaling by Sp1 inhibition as a novel therapeutic
strategy for glioblastoma. Cancers (Basel). 12:9812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lan T, Gao F, Cai Y, Lv Y, Zhu J, Liu H,
Xie S, Wan H, He H, Xie K, et al: The protein circPETH-147aa
regulates metabolic reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
to remodel immunosuppressive microenvironment. Nat Commun.
16:3332025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Emili A, Greenblatt J and Ingles CJ:
Species-specific interaction of the glutamine-rich activation
domains of Spl with the TATA box-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol.
14:1582–1593. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vellingiri B, Iyer M, Subramaniam MD,
Jayaramayya K, Siama Z, Giridharan B, Narayanasamy A, Dayem AA and
Cho SG: Understanding the role of the transcription factor Sp1 in
ovarian cancer: From theory to practice. Int J Mol Sci.
21:11532020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Billon N, Carlisi D, Datto MB, van
Grunsven LA, Watt A, Wang XF and Rudkin B: Cooperation of Sp1 and
p300 in the induction of the CDK inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1 during
NGF-mediated neuronal differentiation. Oncogene. 18:2872–2882.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pascal E and Tjian R: Different activation
domains of Sp1 govern formation of multimers and mediate
transcriptional synergism. Genes Dev. 5:1646–1656. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Su W, Jackson S, Tjian R and Echols H: DNA
looping between sites for transcriptional activation:
self-association of DNA-bound Sp1. Genes Dev. 5:820–826. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Eni-Aganga I: Kruppel-Like Factor 6
Promotes Specificity Protein 1-Mediated Prolidase Transcription
During Transforming Growth Factor-β1 Signaling. ProQuest LLC;
Hamburg: pp. 1–24. 2024
|
|
30
|
Ström AC, Forsberg M, Lillhager P and
Westin G: The transcription factors Sp1 and Oct-1 interact
physically to regulate human U2 snRNA gene expression. Nucleic
Acids Res. 24:1981–1986. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lim K and Chang HI: O-GlcNAc modification
of Sp1 inhibits the functional interaction between Sp1 and Oct1.
FEBS Lett. 583:512–520. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Porter W, Saville B, Hoivik D and Safe S:
Functional synergy between the transcription factor Sp1 and the
estrogen receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 11:1569–1580. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jin Z, Zhou S, Ye H, Jiang S, Yu K and Ma
Y: The mechanism of SP1/p300 complex promotes proliferation of
multiple myeloma cells through regulating IQGAP1 transcription.
Biomed Pharmacother. 119:1094342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
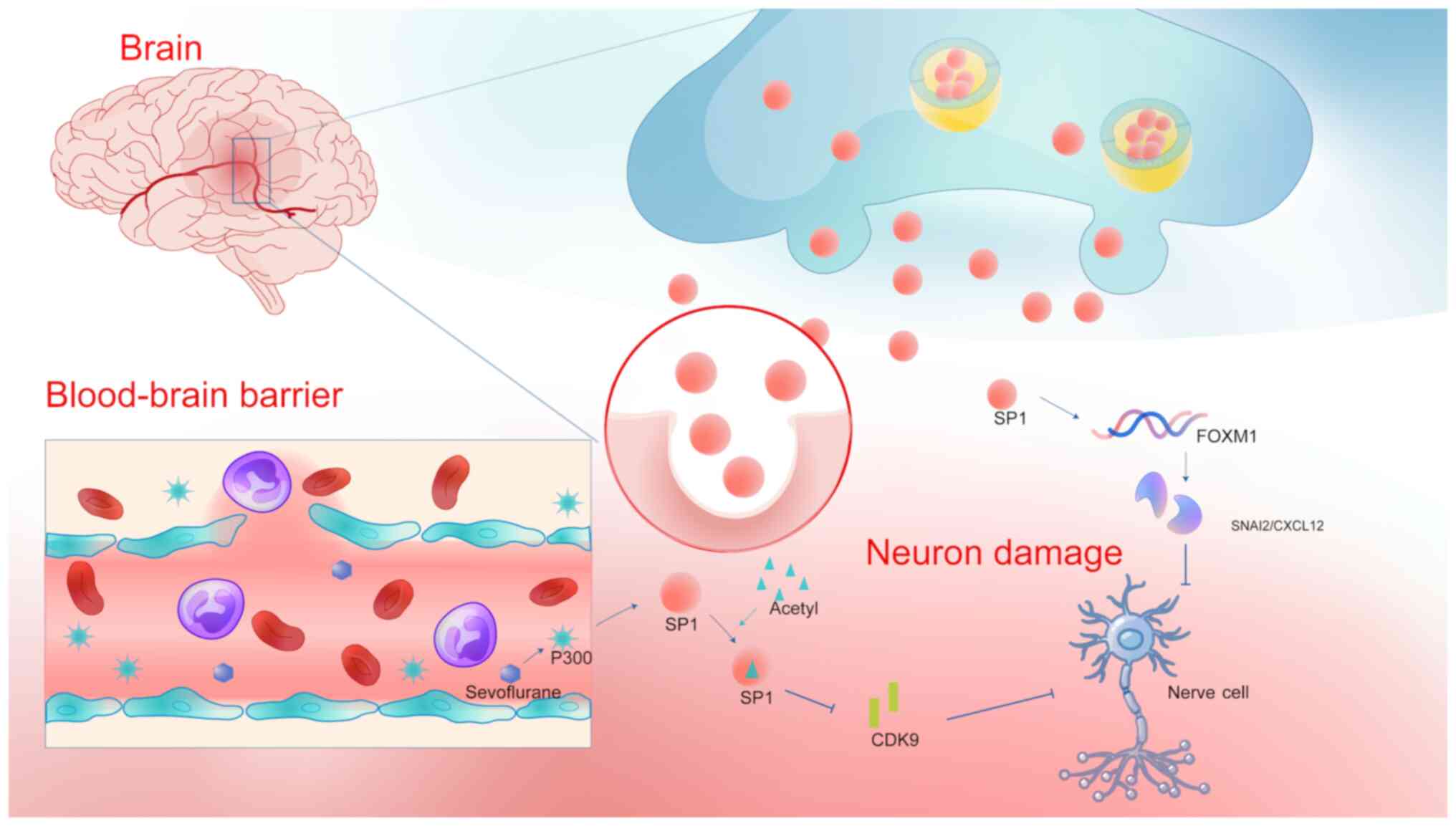
Zhou X, Liu C and Xia D:
Sevoflurane-induced P300 promotes neuron apoptosis via Sp1/CDK9
pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 50:541–553. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dong L and Gao L: SP1-Driven FOXM1
upregulation induces dopaminergic neuron injury in Parkinson's
disease. Mol Neurobiol. 61:5510–5524. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen Z, Guan D, Wang Z, Li X, Dong S,
Huang J and Zhou W: Microbiota in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and
therapeutic interventions. MedComm (2020). 4:e4172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Young MJ, Chen YC, Wang SA, Chang HP, Yang
WB, Lee CC, Liu CY, Tseng YL, Wang YC, Sun HS, et al:
Estradiol-mediated inhibition of Sp1 decreases miR-3194-5p
expression to enhance CD44 expression during lung cancer
progression. J Biomed Sci. 29:32022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jungert K, Buck A, von Wichert G, Adler G,
König A, Buchholz M, Gress TM and Ellenrieder V: Sp1 is required
for transforming growth factor-β-induced mesenchymal transition and
migration in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 67:1563–1570.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ashaie MA and Chowdhury EH: Cadherins: The
superfamily critically involved in breast cancer. Curr Pharm Des.
22:616–638. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ripple MJ, Struckhoff AP, Trillo-Tinoco J,
Li L, Margolin DA, McGoey R and Del Valle L: Activation of c-Myc
and cyclin D1 by JCV T-antigen and β-catenin in colon cancer. PLoS
One. 9:e1062572014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fang Y, Tang W, Qu S, Li Z, Zhang X, Miao
Y, Zeng Z and Huang H: RBBP7, regulated by SP1, enhances the
Warburg effect to facilitate the proliferation of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells via PI3K/AKT signaling. J Transl Med. 22:1702024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Qiu W, Guo Q, Guo X, Wang C, Li B, Qi Y,
Wang S, Zhao R, Han X, Du H, et al: Mesenchymal stem cells, as
glioma exosomal immunosuppressive signal multipliers, enhance MDSCs
immunosuppressive activity through the miR-21/SP1/DNMT1 positive
feedback loop. J Nanobiotechnology. 21:2332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hu Z, You L, Hu S, Yu L, Gao Y, Li L and
Zhang S: Hepatocellular carcinoma cell-derived exosomal miR-21-5p
promotes the polarization of tumor-related macrophages (TAMs)
through SP1/XBP1 and affects the progression of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int Immunopharmacol. 126:1111492024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tian X, Wang T, Shen H and Wang S: Tumor
microenvironment, histone modifications, and myeloid-derived
suppressor cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 74:108–121. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Su X, Liang C, Chen R and Duan S:
Deciphering tumor microenvironment: CXCL9 and SPP1 as crucial
determinants of tumor-associated macrophage polarity and prognostic
indicators. Mol Cancer. 23:132024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu Y, Xun Z, Ma K, Liang S, Li X, Zhou S,
Sun L, Liu Y, Du Y, Guo X, et al: Identification of a tumour immune
barrier in the HCC microenvironment that determines the efficacy of
immunotherapy. J Hepatol. 78:770–782. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shentu J, Su X, Yu Y and Duan S: Unveiling
the role of taurine and SLC6A6 in tumor immune evasion:
Implications for gastric cancer therapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
176:1066612024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Oleksiewicz U, Kuciak M, Jaworska A,
Adamczak D, Bisok A, Mierzejewska J, Sadowska J, Czerwinska P and
Mackiewicz AA: The roles of H3K9me3 writers, readers, and erasers
in cancer immunotherapy. Int J Mol Sci. 25:114662024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Pan J, Li Y, Gao W, Jiang Q, Geng L, Ding
J, Li S and Li J: Transcription factor Sp1 transcriptionally
enhances GSDME expression for pyroptosis. Cell Death Dis.
15:662024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huang MD, Chen WM, Qi FZ, Sun M, Xu TP, Ma
P and Shu YQ: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 is up-regulated in
hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cell growth and apoptosis by
epigenetically silencing of KLF2. Mol Cancer. 14:1–12. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zhang W, Yang H, Wang Z, Wu Y, Wang J,
Duan G, Guo Q and Zhang Y: miR-320a/SP1 negative reciprocal
interaction contributes to cell growth and invasion in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 21:1–13. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li J, Peng W, Yang P, Chen R, Gu Q, Qian
W, Ji D, Wang Q, Zhang Z, Tang J and Sun Y: MicroRNA-1224-5p
inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
colorectal cancer by targeting SP1-mediated NF-κB signaling
pathways. Front Oncol. 10:2942020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Xu W, Lou W and Mei L: A key regulatory
loop AK4P1/miR-375/SP1 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Epigenetics.
18:21484332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yu S, Wang D, Shao Y, Zhang T, Xie H,
Jiang X, Deng Q, Jiao Y, Yang J, Cai C and Sun L: SP1-induced
lncRNA TINCR overexpression contributes to colorectal cancer
progression by sponging miR-7-5p. Aging (Albany NY). 11:1389–1403.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen X, Zeng K, Xu M, Hu X, Liu X, Xu T,
He B, Pan Y, Sun H and Wang S: SP1-induced lncRNA-ZFAS1 contributes
to colorectal cancer progression via the miR-150-5p/VEGFA axis.
Cell Death Dis. 9:9822018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sun W, Wang X, Li J, You C, Lu P, Feng H,
Kong Y, Zhang H, Liu Y, Jiao R, et al: MicroRNA-181a promotes
angiogenesis in colorectal cancer by targeting SRCIN1 to promote
the SRC/VEGF signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 9:4382018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wu S, Meng Q, Zhang C, Sun H, Lu R, Gao N,
Yang H, Li X, Aschner M and Chen R: DR4 mediates the progression,
invasion, metastasis and survival of colorectal cancer through the
Sp1/NF1 switch axis on genomic locus. Int J Cancer. 143:289–297.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhang X, Yao J, Shi H, Gao B, Zhou H,
Zhang Y, Zhao D, Gao S, Wang C and Zhang L: Hsa_circ_0026628
promotes the development of colorectal cancer by targeting SP1 to
activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Death Dis. 12:8022021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yu Y, Peng K, Li H, Zhuang R, Wang Y, Li
W, Yu S, Liang L, Xu X and Liu T: SP1 upregulated FoxO3a promotes
tumor progression in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 39:2235–2242.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Shi S and Zhang ZG: Role of Sp1 expression
in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis.
Oncol Lett. 18:4126–4135. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Chen JJ, Ren YL, Shu CJ, Zhang Y, Chen MJ,
Xu J, Li J, Li AP, Chen DY, He JD, et al: JP3, an antiangiogenic
peptide, inhibits growth and metastasis of gastric cancer through
TRIM25/SP1/MMP2 axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:1–14. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
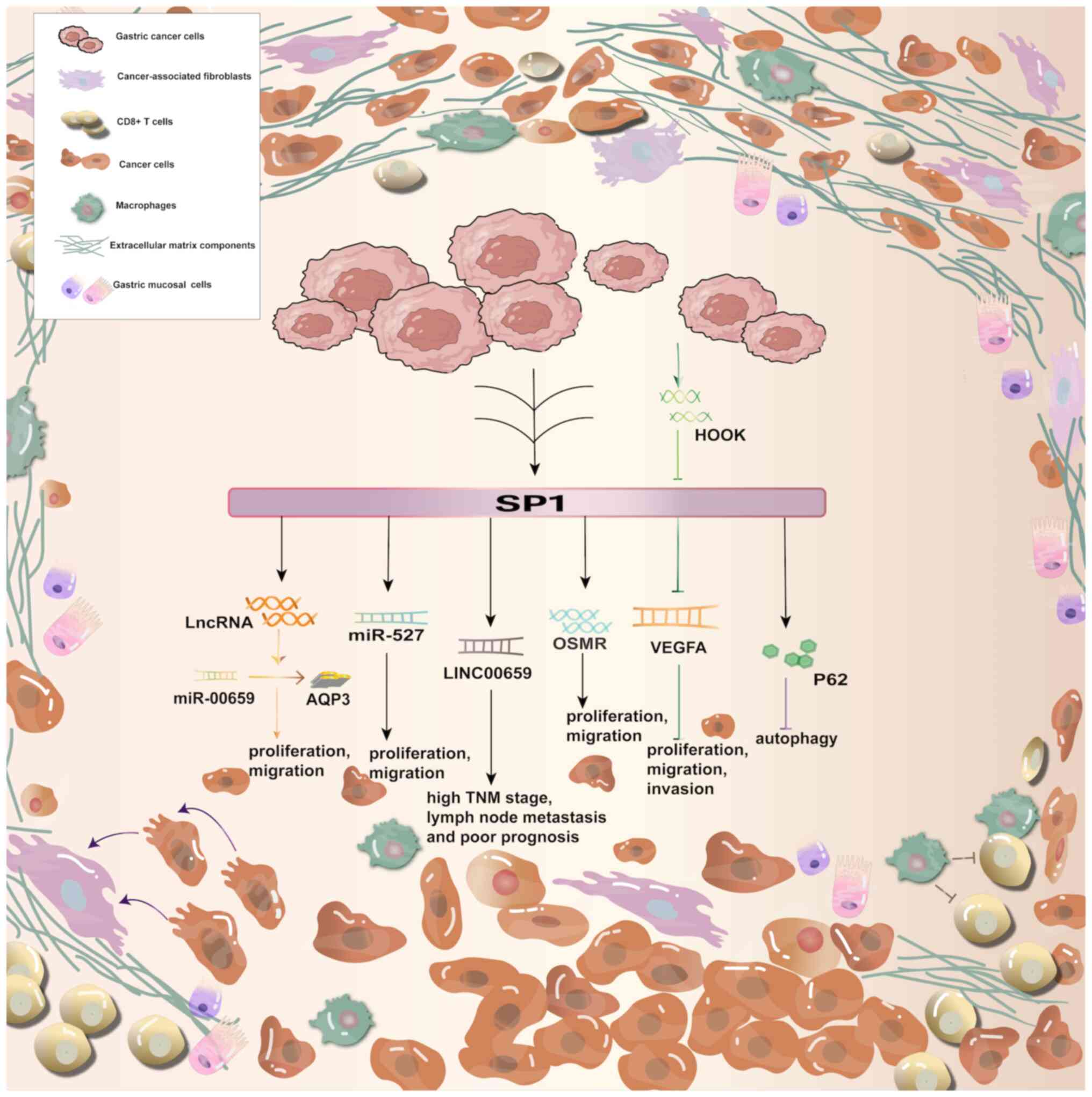
Wang Y, Guo Y, Zhuang T, Xu T and Ji M:
SP1-induced upregulation of lncRNA LINC00659 promotes tumour
progression in gastric cancer by regulating miR-370/AQP3 axis.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:9360372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhang X, Yang H, Jia Y, Xu Z, Zhang L, Sun
M and Fu J: circRNA_0005529 facilitates growth and metastasis of
gastric cancer via regulating miR-527/Sp1 axis. BMC Mol Cell Biol.
22:1–15. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yu Z, Li Z, Wang C, Pan T, Chang X, Wang
X, Zhou Q, Wu X, Li J, Zhang J, et al: Oncostatin M receptor,
positively regulated by SP1, promotes gastric cancer growth and
metastasis upon treatment with Oncostatin M. Gastric Cancer.
22:955–966. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yang K, Li J, Zhu J, Chen Y, He Y, Wang J,
Shen K, Wang K, Shi T and Chen W: HOOK3 suppresses proliferation
and metastasis in gastric cancer via the SP1/VEGFA axis. Cell Death
Discov. 10:332024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Liu Y, Du Y, Hu X, Zhao L and Xia W:
Up-regulation of ceRNA TINCR by SP1 contributes to tumorigenesis in
breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 18:1–11. 2018.
|
|
67
|
Monteleone E, Orecchia V, Corrieri P,
Schiavone D, Avalle L, Moiso E, Savino A, Molineris I, Provero P
and Poli V: SP1 and STAT3 functionally synergize to induce the RhoU
small GTPase and a subclass of non-canonical WNT responsive genes
correlating with poor prognosis in breast cancer. Cancers (Basel).
11:1012019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Li X, Zou ZZ, Wen M, Xie YZ, Peng KJ, Luo
T, Liu SY, Gu Q, Li JJ and Luo ZY: ZLM-7 inhibits the occurrence
and angiogenesis of breast cancer through miR-212-3p/Sp1/VEGFA
signal axis. Mol Med. 26:1092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Li G, Xie Q, Yang Z, Wang L, Zhang X, Zuo
B, Zhang S, Yang A and Jia L: Sp1-mediated epigenetic dysregulation
dictates HDAC inhibitor susceptibility of HER2-overexpressing
breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 145:3285–3298. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Cai F, Chen L, Sun Y, He C, Fu D and Tang
J: MiR-539 inhibits the malignant behavior of breast cancer cells
by targeting SP1. Biochem Cell Biol. 98:426–433. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhang S, Huang P, Dai H, Li Q, Hu L, Peng
J, Jiang S, Xu Y, Wu Z, Nie H, et al: TIMELESS regulates
sphingolipid metabolism and tumor cell growth through Sp1/ACER2/S1P
axis in ER-positive breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 11:8922020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhang X, Li F, Zhou Y, Mao F, Lin Y, Shen
S, Li Y, Zhang S and Sun Q: Long noncoding RNA AFAP1-AS1 promotes
tumor progression and invasion by regulating the miR-2110/Sp1 axis
in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 12:6272021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wang XX, Guo GC, Qian XK, Dou DW, Zhang Z,
Xu XD, Duan X and Pei XH: miR-506 attenuates methylation of lncRNA
MEG3 to inhibit migration and invasion of breast cancer cell lines
via targeting SP1 and SP3. Cancer Cell Int. 18:1712018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Shao W, Li Y, Chen F, Jia H, Jia J and Fu
Y: Long non-coding RNA DLEU1 contributes to the development of
endometrial cancer by sponging miR-490 to regulate SP1 expression.
Pharmazie. 73:379–385. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bai Z, Wu Y, Bai S, Yan Y, Kang H, Ma W,
Zhang J, Gao Y, Hui B, Ma H, et al: Long non-coding RNA SNGH7 Is
activated by SP1 and exerts oncogenic properties by interacting
with EZH2 in ovarian cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 24:7479–7489. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Cui JW, Li Y, Yang Y, Yang HK, Dong JM,
Xiao ZH, He X, Guo JH, Wang RQ, Dai B and Zhou ZL: Tumor
immunotherapy resistance: Revealing the mechanism of
PD-1/PD-L1-mediated tumor immune escape. Biomed Pharmacother.
171:1162032024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Kong L, Xu F, Yao Y, Gao Z, Tian P, Zhuang
S, Wu D, Li T, Cai Y and Li J: Ascites-derived CDCP1+ extracellular
vesicles subcluster as a novel biomarker and therapeutic target for
ovarian cancer. Front Oncol. 13:11427552023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Wang S, Li X, Li J, Wang A, Li F, Hu H,
Long T, Pei X, Li H, Zhong F and Zhu F: Inhibition of
cisplatin-induced Acsl4-mediated ferroptosis alleviated ovarian
injury. Chem Biol Interact. 387:1108252024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Shen HT, Chien PJ, Chen SH, Sheu GT, Jan
MS, Wang BY and Chang W: BMI1-mediated pemetrexed resistance in
non-small cell lung cancer cells is associated with increased SP1
activation and cancer stemness. Cancers (Basel). 12:20692020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Hu L, Chen Q, Wang Y, Zhang N, Meng P, Liu
T and Bu Y: Sp1 mediates the constitutive expression and repression
of the PDSS2 gene in lung cancer cells. Genes (Basel). 10:9772019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Li X, Fu Y, Xia X, Zhang X, Xiao K, Zhuang
X and Zhang Y: Knockdown of SP1/Syncytin1 axis inhibits the
proliferation and metastasis through the AKT and ERK1/2 signaling
pathways in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Med. 8:5750–5759.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Sun Y, Xu K, He M, Fan G and Lu H:
Overexpression of glypican 5 (GPC5) inhibits prostate cancer cell
proliferation and invasion via suppressing Sp1-mediated EMT and
activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncol Res. 26:5652018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Wang ZY, Duan Y and Wang P: SP1-mediated
upregulation of lncRNA SNHG4 functions as a ceRNA for miR-377 to
facilitate prostate cancer progression through regulation of ZIC5.
J Cell Physiol. 235:3916–3927. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhang L, Liu SK, Song L and Yao HR:
SP1-induced up-regulation of lncRNA LUCAT1 promotes proliferation,
migration and invasion of cervical cancer by sponging miR-181a.
Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47:555–563. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Deng YR, Chen XJ, Chen W, Wu LF, Jiang HP,
Lin D, Wang LJ, Wang W and Guo SQ: Sp1 contributes to
radioresistance of cervical cancer through targeting G2/M cell
cycle checkpoint CDK1. Cancer Manag Res. 11:5835–5844. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Lin CL, Ying TH, Yang SF, Lin CL, Chiou HL
and Hsieh YH: Magnolin targeting of the JNK/Sp1/MMP15 signaling
axis suppresses cervical cancer microenvironment and metastasis via
microbiota modulation. Cancer Lett. 583:2165842024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wang P, Song Y, Li H, Zhuang J, Shen X,
Yang W, Mi R, Lu Y, Yang B, Ma M and Shen H: SIRPA enhances
osteosarcoma metastasis by stabilizing SP1 and promoting
SLC7A3-mediated arginine uptake. Cancer Lett. 576:2164122023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Wang W and Wang B: KDM3A-mediated SP1
activates PFKFB4 transcription to promote aerobic glycolysis in
osteosarcoma and augment tumor development. BMC Cancer. 22:5622022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Mi LD, Sun CX, He SW and Du GY:
SP1-induced upregulation of lncRNA LINC00514 promotes tumor
proliferation and metastasis in osteosarcoma by regulating miR-708.
Cancer Manag Res. 3311–3322. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Hu XH, Dai J, Shang HL, Zhao ZX and Hao
YD: SP1-mediated upregulation of lncRNA ILF3-AS1 functions a ceRNA
for miR-212 to contribute to osteosarcoma progression via
modulation of SOX5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 511:510–517. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Moreira J, Almeida J, Saraiva L, Cidade H
and Pinto M: Chalcones as promising antitumor agents by targeting
the p53 pathway: An overview and new insights in drug-likeness.
Molecules. 26:37372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhang B, Song L, Cai J, Li L, Xu H, Li M,
Wang J, Shi M, Chen H, Jia H and Hou Z: The LIM protein Ajuba/SP1
complex forms a feed forward loop to induce SP1 target genes and
promote pancreatic cancer cell proliferation. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 8:1–11. 2019.
|
|
93
|
Malsy M, Graf B, Bruendl E, Maier-Stocker
C and Bundscherer A: Effect of NFATc2-and Sp1-mediated TNFalpha
regulation on the proliferation and migration behavior of
pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 20:706–711.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Cai LJ, Tu L, Li T, Yang XL, Ren YP, Gu R,
Zhang Q, Yao H, Qu X, Wang Q and Tian JY: Up-regulation of
microRNA-375 ameliorates the damage of dopaminergic neurons,
reduces oxidative stress and inflammation in Parkinson's disease by
inhibiting SP1. Aging (Albany NY). 12:672–689. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Dong X, Wu L, Gong L, Huang D, Guo J, Ma
M, Xiao L, Xu S, Chang J, Che X and Hang J: PPP3CB inhibits
pancreatic cancer progression by promoting ATOH8 translocation and
transcriptionally regulating Sp1. Life Sci. 12:36312025.
|
|
96
|
Yang J, Wang J, Zhang H, Li C, Chen C and
Zhu T: Transcription factor Sp1 is upregulated by PKCι to drive the
expression of YAP1 during pancreatic carcinogenesis.
Carcinogenesis. 42:344–356. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Gao Y, Zhou Y, Wang C, Sample KM, Yu X and
Ben-David Y: Propofol mediates pancreatic cancer cell activity
through the repression of ADAM8 via SP1. Oncol Rep. 46:2492021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Shi X, Wang X and Hua Y: LncRNA GACAT1
promotes gastric cancer cell growth, invasion and migration by
regulating MiR-149-mediated of ZBTB2 and SP1. J Cancer.
9:3715–3722. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Liu Y, Chen P, Fei H, Li M, Li X and Li T:
Natural killer cells contributed to recurrent miscarriage by
SP1-CASP3-PARP1. Int Immunopharmacol. 93:1074242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Bernacchioni C, Capezzuoli T, Vannuzzi V,
Malentacchi F, Castiglione F, Cencetti F, Ceccaroni M, Donati C,
Bruni P and Petraglia F: Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors are
dysregulated in endometriosis: Possible implication in transforming
growth factor β-induced fibrosis. Fertil Steril. 115:501–511. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Lin M, Xu H and Qiu J: Inflammation in
recurrent miscarriage-a comprehensive perspective from uterine
microenvironment and immune cell imbalance to therapeutic
strategies. Ginekol Pol. 95:266–275. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Shen L, Hong X, Liu Y, Zhou W and Zhang Y:
The miR-25-3p/Sp1 pathway is dysregulated in ovarian endometriosis.
J Int Med Res. Apr 17–2020.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Chen Z: The role of specificity protein 1
(SP1) in bladder cancer progression through PTEN-mediated AKT/mTOR
pathway. Urol Int. 107:848–856. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Zhu J, Lu Z, Ke M and Cai X: Sp1 is
overexpressed and associated with progression and poor prognosis in
bladder urothelial carcinoma patients. Int Urol Nephrol.
54:1505–1512. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Yan H, Li J, Ying Y, Xie H, Chen H, Xu X
and Zheng X: MIR-300 in the imprinted DLK1-DIO3 domain suppresses
the migration of bladder cancer by regulating the SP1/MMP9 pathway.
Cell Cycle. 17:2790–2801. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Fernández-Guizán A, Mansilla S, Barceló F,
Vizcaíno C, Núñez LE, Morís F, González S and Portugal J: The
activity of a novel mithramycin analog is related to its binding to
DNA, cellular accumulation, and inhibition of Sp1-driven gene
transcription. Chem Biol Interact. 219:123–132. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Ke X, Fei F, Chen Y, Xu L, Zhang Z, Huang
Q, Zhang H, Yang H, Chen Z and Xing J: Hypoxia upregulates CD147
through a combined effect of HIF-1α and Sp1 to promote glycolysis
and tumor progression in epithelial solid tumors. Carcinogenesis.
33:1598–1607. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Chu PC, Lin PC, Wu HY, Lin KT, Wu C,
Bekaii-Saab T, Lin YJ, Lee CT, Lee JC and Chen CS: Mutant KRAS
promotes liver metastasis of colorectal cancer, in part, by
upregulating the MEK-Sp1-DNMT1-miR-137-YB-1-IGF-IR signaling
pathway. Oncogene. 37:3440–3455. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Liu H, Shi Y and Qian F: Opportunities and
delusions regarding drug delivery targeting pancreatic
cancer-associated fibroblasts. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 172:37–51. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Yoon BK, Hwang N, Chun KH, Lee Y, Duarte
TPM and Kim JW, Kim TH, Cheong JH, Fang S and Kim JW: Sp1-induced
FNBP1 drives rigorous 3D cell motility in EMT-type gastric cancer
cells. Int J Mol Sci. 22:67842021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Shishodia S: Molecular mechanisms of
curcumin action: gene expression. Biofactors. 39:37–55. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Nangia V, Siddiqui FM, Caenepeel S,
Timonina D, Bilton SJ, Phan N, Gomez-Caraballo M, Archibald HL, Li
C, Fraser C, et al: Exploiting MCL1 dependency with combination
MEK+ MCL1 inhibitors leads to induction of apoptosis and tumor
regression in KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer
Discov. 8:1598–1613. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Moon Hr, Du Y, Choi SR, et al: DNA
origami-cyanine nanocomplex for precision imaging of KRAS-mutant
pancreatic cancer cells. Advanced Science. 24102782025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Hu L and Chen L, Xiao Z, Zheng X, Chen Y,
Xian N, Cho C, Luo L, Huang G and Chen L: Ablation of T
cell-associated PD-1H enhances functionality and promotes adoptive
immunotherapy. JCI insight. 7:e1482472022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Ryu H, Lee J, Olofsson BA, Mwidau A,
Dedeoglu A, Escudero M, Flemington E, Azizkhan-Clifford J, Ferrante
RJ and Ratan RR: Histone deacetylase inhibitors prevent oxidative
neuronal death independent of expanded polyglutamine repeats via an
Sp1-dependent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:4281–4286. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Zang X, He XY, Xiao CM, Lin Q, Wang MY,
Liu CY, Kong LY, Chen Z and Xia YZ: Circular RNA-encoded oncogenic
PIAS1 variant blocks immunogenic ferroptosis by modulating the
balance between SUMOylation and phosphorylation of STAT1. Mol
Cancer. 23:2072024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Zhang N, Zhao SS, Zhang YX, Wang YC, Shao
RG, Wang JX and He HW: A novel biphenyl compound IMB-S7 ameliorates
hepatic fibrosis in BDL rats by suppressing Sp1-mediated integrin
αv expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 41:661–669. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Liu Y, He M, Ke X, Chen Y, Zhu J, Tan Z
and Chen J: Centrosome amplification-related signature correlated
with immune microenvironment and treatment response predicts
prognosis and improves diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma by
integrating machine learning and single-cell analyses. Hepatol Int.
18:108–130. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Lu H, Yuan P, Ma X, Jiang X, Liu S, Ma C,
Philipsen S, Zhang Q, Yang J, Xu F, et al: Angiotensin-converting
enzyme inhibitor promotes angiogenesis through Sp1/Sp3-mediated
inhibition of notch signaling in male mice. Nat Commun. 14:7312023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Gao Y, Gan K, Liu K, Xu B and Chen M: SP1
expression and the clinicopathological features of tumors: A
meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis. Pathol Oncol Res.
27:5819982021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Blume S, Snyder R, Ray R, Thomas S, Koller
C and Miller D: Mithramycin inhibits SP1 binding and selectively
inhibits transcriptional activity of the dihydrofolate reductase
gene in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest. 88:1613–1621. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Ran XH, Zhu JW, Ni RZ, Zheng YT, Chen YY,
Zheng WH and Mu D: TRIM5α recruits HDAC1 to p50 and Sp1 and
promotes H3K9 deacetylation at the HIV-1 LTR. Nat Commun.
14:33432023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Dopler A, Alkan F, Malka Y, van der Kammen
R, Hoefakker K, Taranto D, Kocabay N, Mimpen I, Ramirez C, Malzer
E, et al: P-stalk ribosomes act as master regulators of
cytokine-mediated processes. Cell. 187:6981–6993. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Wang JS, Zeng QF, Feng DY, Hu YB and Wen
JF: Expression and role of nuclear transcription factor Sp1 in
macrophages stimulated by silicon dioxide. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei
Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 24:518–522. 2006.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Yuan X, Li D, Chen X, Han C, Xu L, Huang
T, Dong Z and Zhang M: Extracellular vesicles from human-induced
pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells
(hiPSC-MSCs) protect against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via
delivering specificity protein (SP1) and transcriptional activating
of sphingosine kinase 1 and inhibiting necroptosis. Cell Death Dis.
8:32002017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Gao Y, Zhao J, Huang Z, Zhao H, Guo Z, Ma
S, Tang X, Song W and Chen X: In Situ Reprogramming of tumors for
activating the OX40/OX40 ligand checkpoint pathway and boosting
antitumor immunity. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 9:4108–4116. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Ye JC and Heng HH: The new era of cancer
cytogenetics and cytogenomics. Methods Mol Biol. 2825:3–37. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|