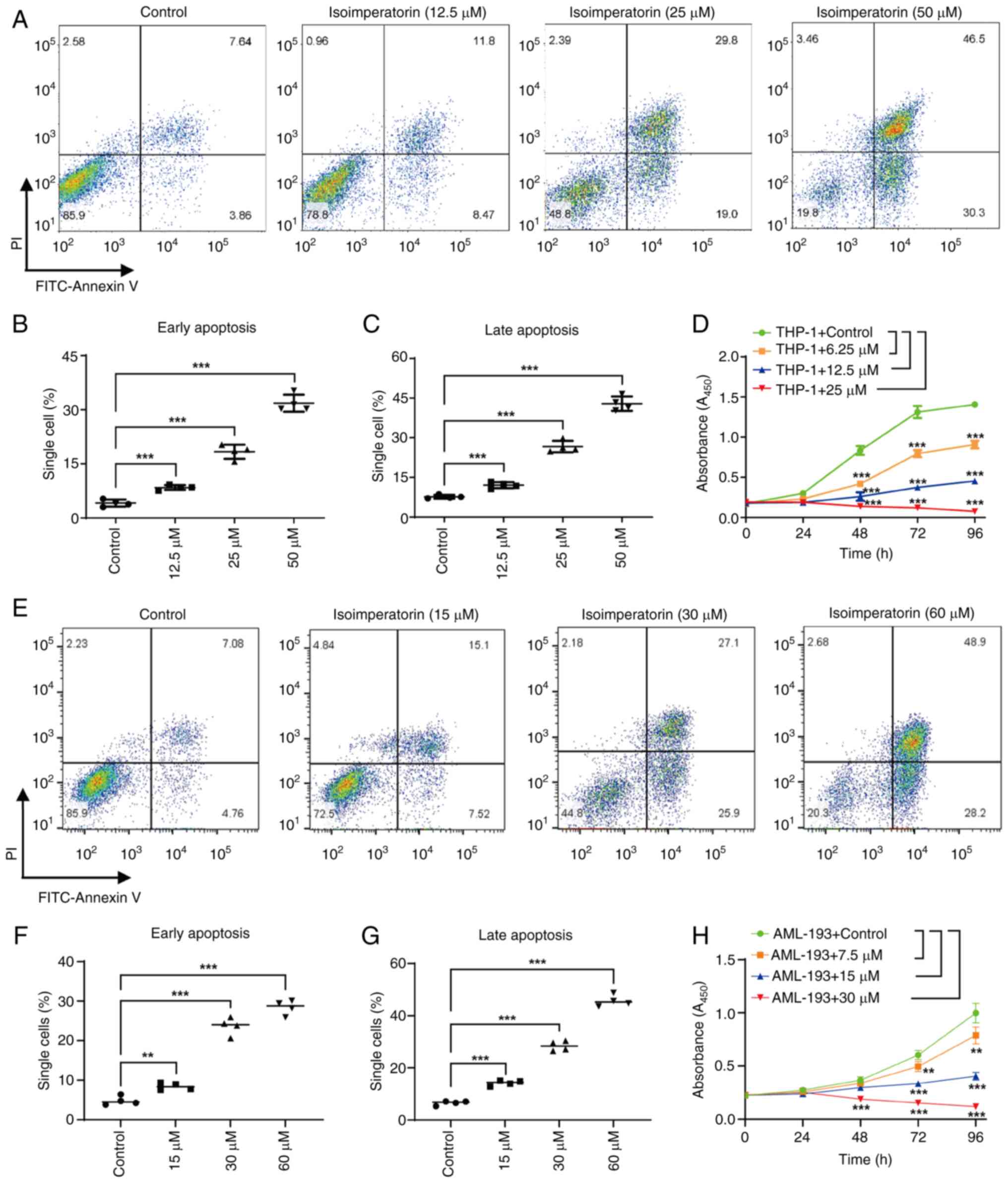
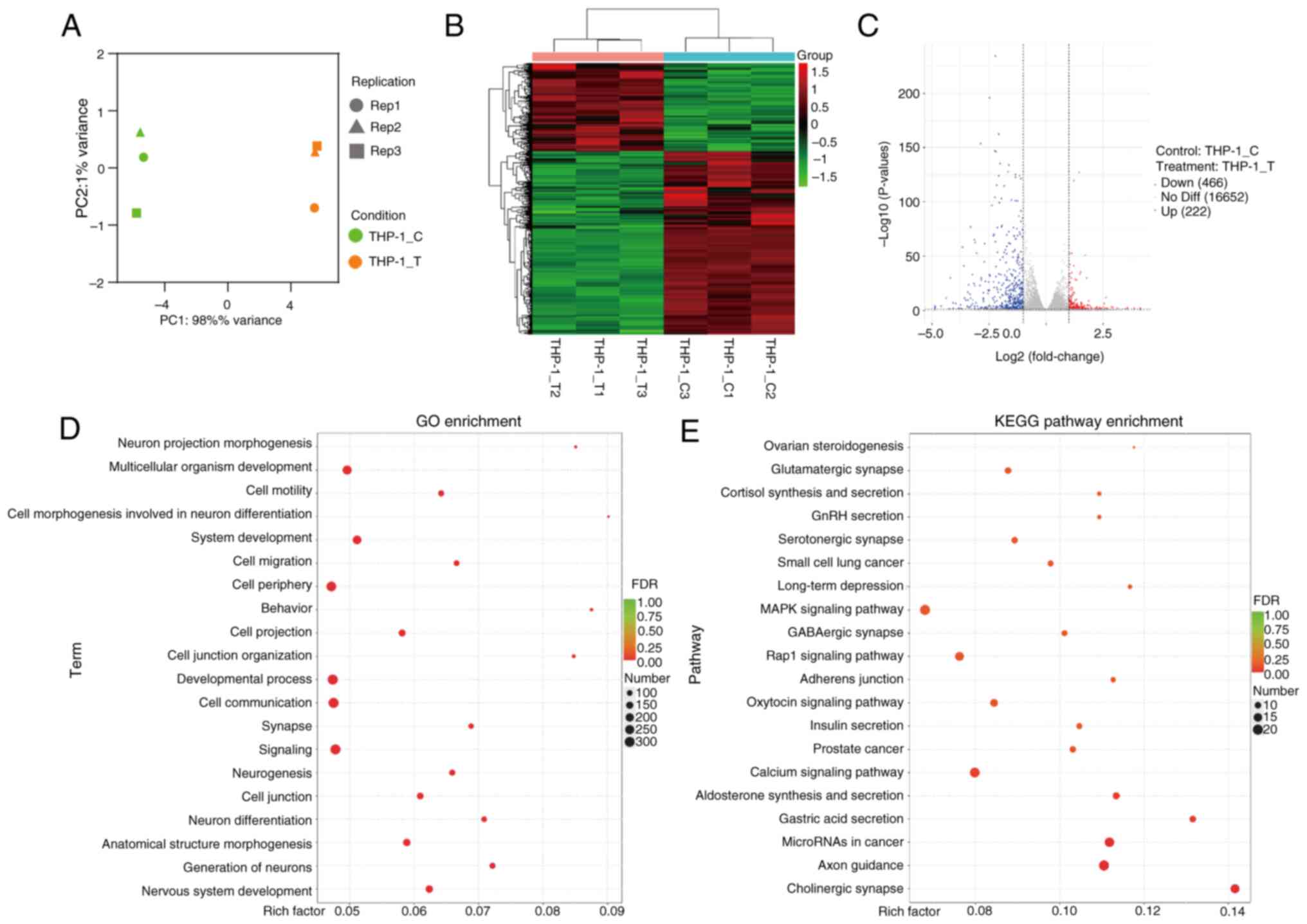
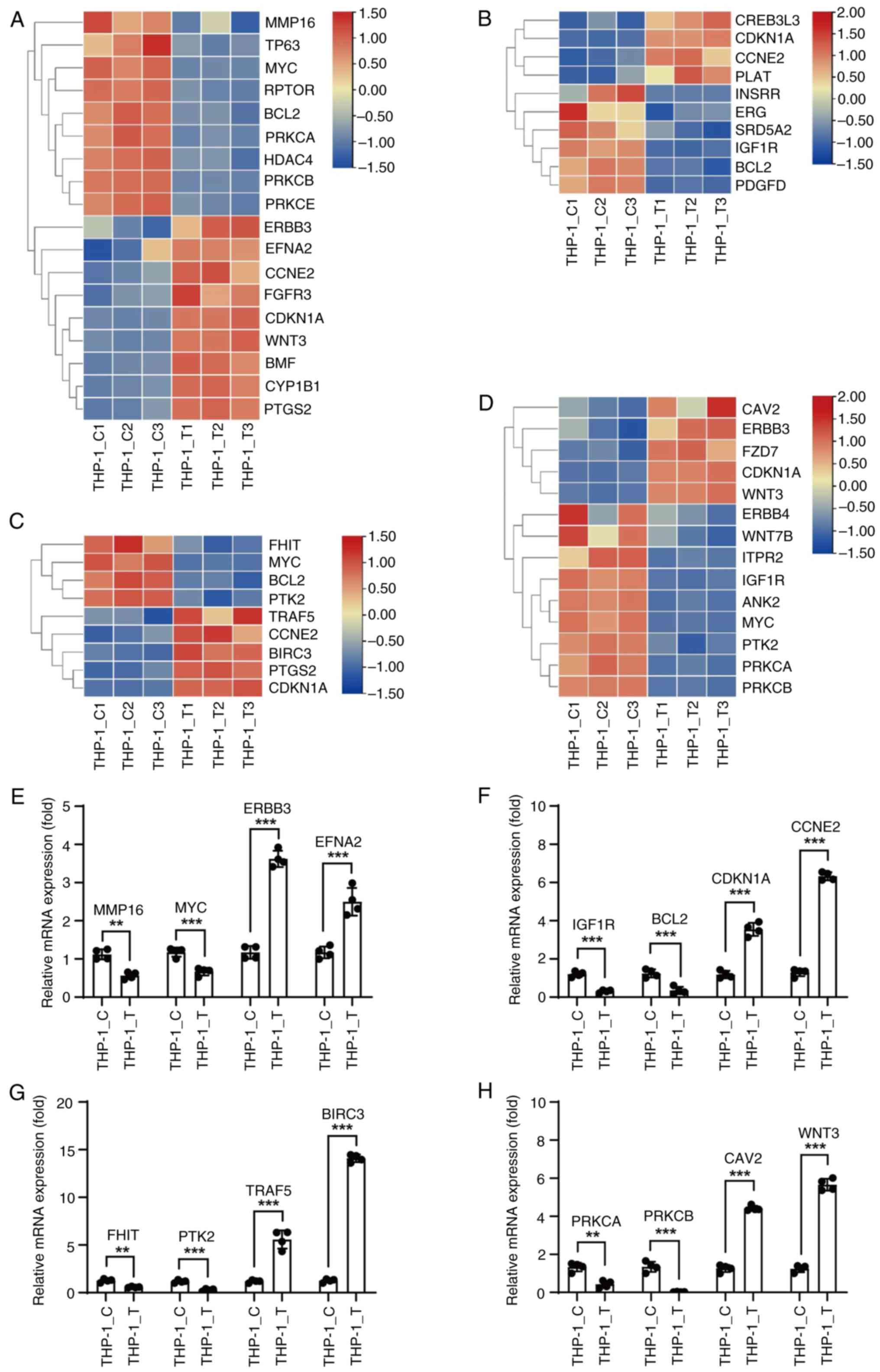
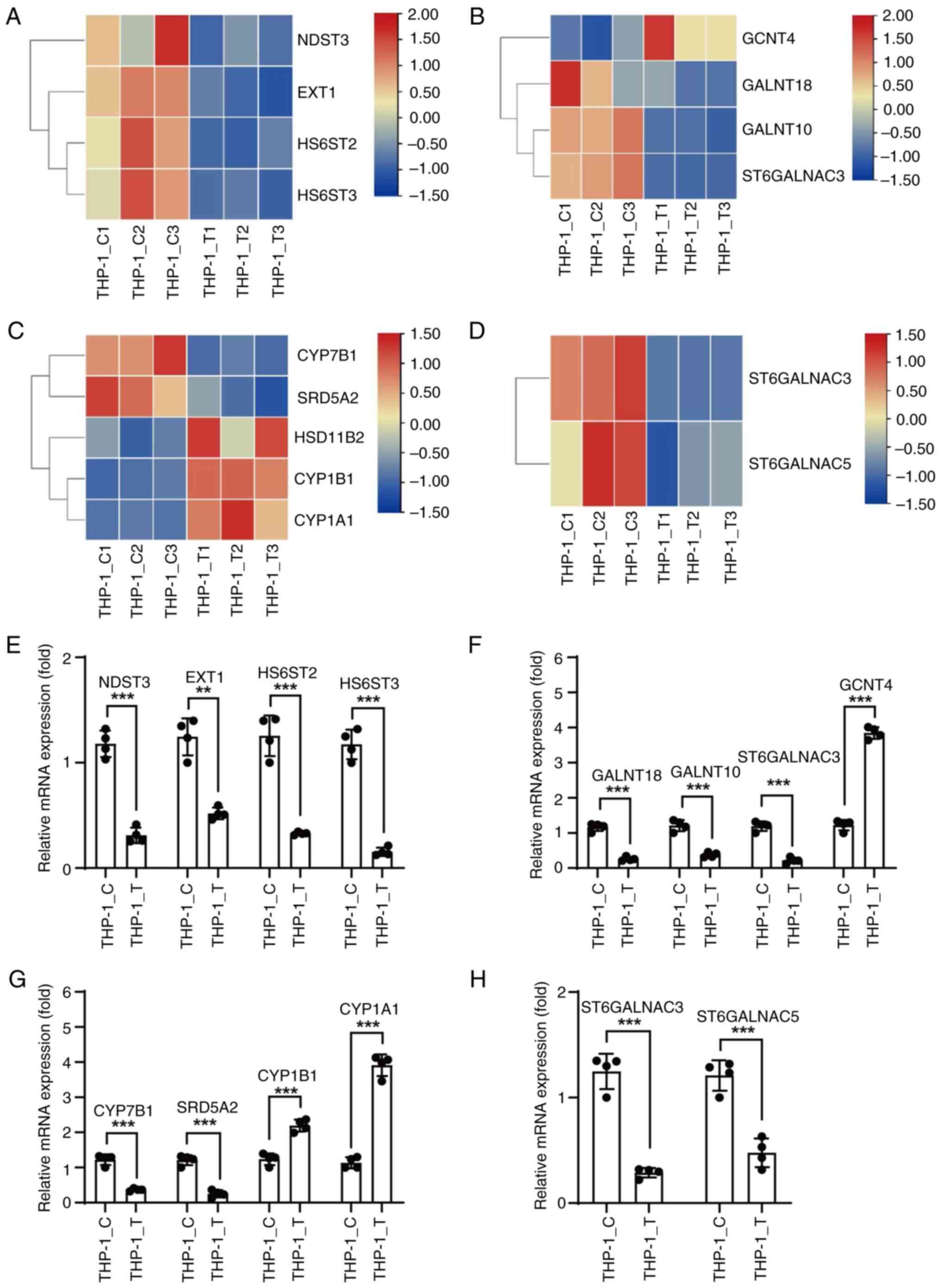
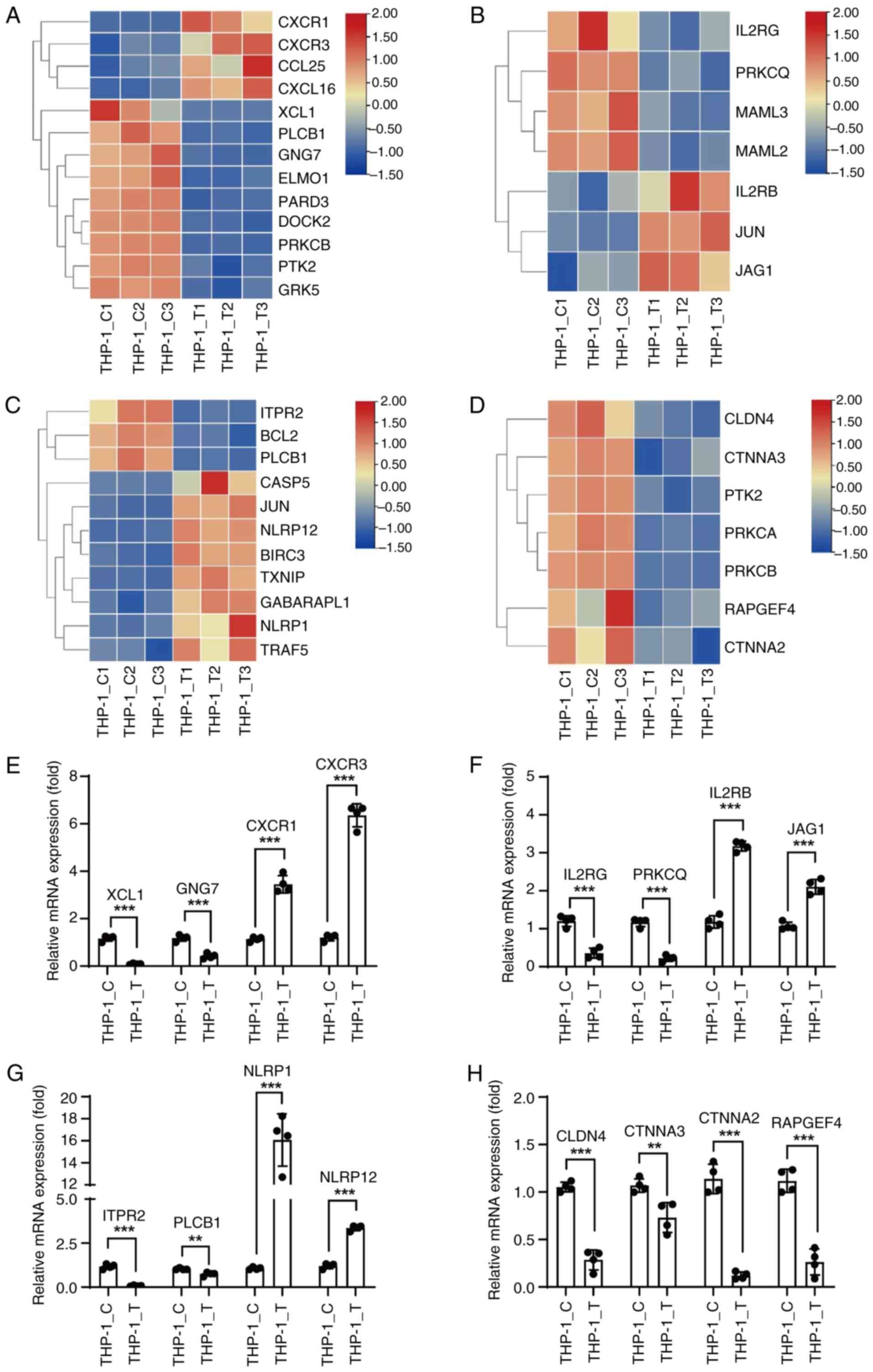
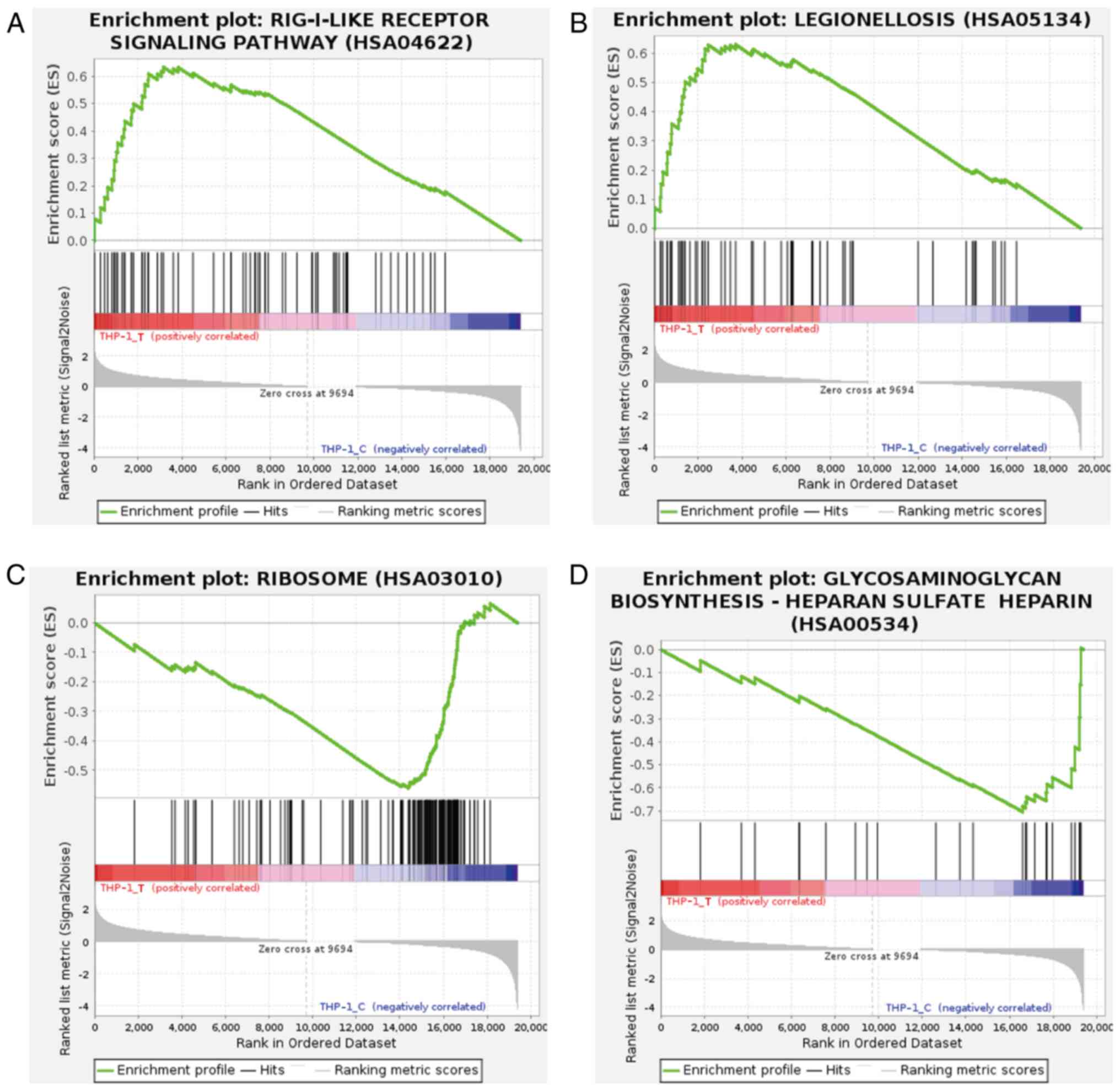
|
1
|
Whiteley AE, Price TT, Cantelli G and
Sipkins DA: Leukaemia: A model metastatic disease. Nat Rev Cancer.
21:461–475. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kantarjian HM, DiNardo CD, Kadia TM, Daver
NG, Altman JK, Stein EM, Jabbour E, Schiffer CA, Lang A and Ravandi
F: Acute myeloid leukemia management and research in 2025. CA
Cancer J Clin. 75:46–67. 2025.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Villeneuve P, Kim DT, Xu W, Brandwein J
and Chang H: The morphological subcategories of acute monocytic
leukemia (M5a and M5b) share similar immunophenotypic and
cytogenetic features and clinical outcomes. Leuk Res. 32:269–273.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Botta L, Gatta G, Capocaccia R, Stiller C,
Cañete A, Dal Maso L, Innos K, Mihor A, Erdmann F, Spix C, et al:
Long-term survival and cure fraction estimates for childhood cancer
in Europe (EUROCARE-6): Results from a population-based study.
Lancet Oncol. 23:1525–1536. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu WJ, Sun YQ, Xu LP, Zhang XH, Liu KY,
Huang XJ and Wang Y: Comparison of outcomes for patients with acute
myeloid leukemia undergoing haploidentical stem cell
transplantation in first and second complete remission. Ann
Hematol. 102:2241–2250. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Saliba RM, Kanakry CG, Gadalla S, Kebriaei
P, Rezvani K, Champlin RE, Shpall EJ, Weisdorf D and Mehta RS:
Effect of donor age in patients with acute myeloid leukemia
undergoing haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation vary
by conditioning intensity and recipient age. Am J Hematol.
99:38–47. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peroni E, Randi ML, Rosato A and Cagnin S:
Acute myeloid leukemia: from NGS, through scRNA-seq, to CAR-T.
dissect cancer heterogeneity and tailor the treatment. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 42:2592023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gabellier L, Bosetta E, Heiblig M and
Sarry JE: Metabolism and therapeutic response in acute myeloid
leukemia with IDH1/2 mutations. Trends Cancer. 11:475–490. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Soleimani Samarkhazan H, Zehtabcheh S,
Seraji HR, Beqaj SH, Tayefeh S, Mohammadi MH and Aghaei M:
Unveiling the potential of CLL-1: A promising target for AML
therapy. Biomark Res. 13:282025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brivio E, Baruchel A, Beishuizen A,
Bourquin JP, Brown PA, Cooper T, Gore L, Kolb EA, Locatelli F,
Maude SL, et al: Targeted inhibitors and antibody immunotherapies:
Novel therapies for paediatric leukaemia and lymphoma. Eur J
Cancer. 164:1–17. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Roas M, Vick B, Kasper MA, Able M, Polzer
H, Gerlach M, Kremmer E, Hecker JS, Schmitt S, Stengl A, et al:
Targeting FLT3 with a new-generation antibody-drug conjugate in
combination with kinase inhibitors for treatment of AML. Blood.
141:1023–1035. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huls GA, Woolthuis CM and Schuringa JJ:
Menin inhibitors in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
145:561–566. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Venugopal S and Sekeres MA: Contemporary
management of acute myeloid leukemia: A review. JAMA Oncol.
10:1417–1425. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu RH, Zhu CY, Yu PH, Ma Y, Hussain L,
Naranmandura H and Wang QQ: The landscape of novel strategies for
acute myeloid leukemia treatment: Therapeutic trends, challenges,
and future directions. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 473:1165852023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Peroni E, Gottardi M, D'Antona L, Randi
ML, Rosato A and Coltro G: Hematologic Neoplasms associated with
down syndrome: Cellular and molecular heterogeneity of the
diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 24:153252023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Martinez TC and McNerney ME:
Haploinsufficient transcription factors in myeloid neoplasms. Annu
Rev Pathol. 19:571–598. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mishra SK, Millman SE and Zhang L:
Metabolism in acute myeloid leukemia: Mechanistic insights and
therapeutic targets. Blood. 141:1119–1135. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Smoljo T, Tomic B, Lalic H, Dembitz V,
Batinic J, Bedalov A and Visnjic D: Bone marrow stromal cells
reduce low-dose cytarabine-induced differentiation of acute myeloid
leukemia. Front Pharmacol. 14:12581512023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thuy NTT, Lee JE, Yoo HM and Cho N:
Antiproliferative pterocarpans and coumestans from lespedeza
bicolor. J Nat Prod. 82:3025–3032. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fan L, Li Z, Gao L, Zhang N and Chang W:
Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis
by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways. Open Life Sci.
18:202205412023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ko HJ, Park SY, Sim DY, Kim SH, Hur S, Lee
JH and Kim Y: Apoptotic effect of isoimpertorin via inhibition of
c-Myc and SIRT1 signaling axis. Int J Mol Sci. 25:42482024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim NY, Jung YY, Yang MH, Um JY, Sethi G
and Ahn KS: Isoimperatorin down-regulates epithelial mesenchymal
transition through modulating NF-κB signaling and CXCR4 expression
in colorectal and hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Signal.
99:1104332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou Y, Huang G, Cai X, Liu Y, Qian B and
Li D: Global, regional, and national burden of acute myeloid
leukemia, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the global burden of
disease study 2021. Biomark Res. 12:1012024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gaur T, Ali A, Sharma D, Gupta SK, Gota V,
Bagal B, Platzbeckar U, Mishra R, Dutt A, Khattry N, et al:
Mitocurcumin utilizes oxidative stress to upregulate JNK/p38
signaling and overcomes Cytarabine resistance in acute myeloid
leukemia. Cell Signal. 114:1110042024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu M and Li S: The opportunities and
challenges of using PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors for leukemia treatment.
Cancer Lett. 593:2169692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu Q, Guan Y and Li S: Programmed death
receptor (PD-)1/PD-ligand (L)1 in urological cancers: The
‘all-around warrior’ in immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. 23:1832024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Alsouqi A, Geramita E and Im A: Treatment
of acute myeloid leukemia in older adults. Cancers (Basel).
15:54092023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Buchrits S and Wolach O: Non-immunotherapy
approaches for Relapsed or Refractory AML: An update for 2024. Acta
Haematol. 147:159–174. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiao X, Wang P, Zhang W, Wang J, Cai M,
Jiang H, Wu Y and Shan H: GNF-7, a novel FLT3 inhibitor, overcomes
drug resistance for the treatment of FLT3-ITD acute myeloid
leukemia. Cancer Cell Int. 23:3022023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen J, Zhou X, Fu L and Xu H: Natural
product-based screening for lead compounds targeting SARS CoV-2
Mpro. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 16:7672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yao L, Cai W, Chen S, Wang A, Wang X, Zhao
C, Shou C and Jia Y: Design, syntheses and biological evaluation of
natural product aiphanol derivatives and analogues: Discovery of
potent anticancer agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 90:1293262023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rajendran P, Althumairy D, Bani-Ismail M,
Bekhet GM and Ahmed EA: Isoimperatorin therapeutic effect against
aluminum induced neurotoxicity in albino mice. Front Pharmacol.
14:11039402023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Skwarska A and Konopleva M: BCL-xL
targeting to induce apoptosis and to eliminate chemotherapy-induced
senescent tumor cells: From navitoclax to platelet-sparing BCL-xL
PROTACs. Cancer Res. 83:3501–3503. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu J, He L, Hu J, Li K, Zhou F, Hu M, Luo
J, Song L and He Y: Isoimperatorin induces apoptosis of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via the MAPK/ERK1/2 signaling
pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020:21381862020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gruszka AM, Valli D, Restelli C and
Alcalay M: Adhesion deregulation in acute myeloid leukaemia. Cells.
8:662019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pereira RS, Kumar R, Cais A, Paulini L,
Kahler A, Bravo J, Minciacchi VR, Krack T, Kowarz E, Zanetti C, et
al: Distinct and targetable role of calcium-sensing receptor in
leukaemia. Nat Commun. 14:62422023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xiao J, Zhang B, Yin S, Xie S, Huang K,
Wang J, Yang W, Liu H, Zhang G, Liu X, et al: Quercetin induces
autophagy-associated death in HL-60 cells through CaMKKβ/AMPK/mTOR
signal pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 54:1244–1256.
2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lewuillon C, Laguillaumie MO, Quesnel B,
Idziorek T, Touil Y and Lemonnier L: Put in a ‘Ca2+ll’ to acute
myeloid leukemia. Cells. 11:5432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Apáti A, Jánossy J, Brózik A, Bauer PI and
Magócsi M: Calcium induces cell survival and proliferation through
the activation of the MAPK pathway in a human hormone-dependent
leukemia cell line, TF-1. J Biol Chem. 278:9235–9243. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lyakh LA, Koski GK, Telford W, Gress RE,
Cohen PA and Rice NR: Bacterial lipopolysaccharide, TNF-alpha, and
calcium ionophore under serum-free conditions promote rapid
dendritic cell-like differentiation in CD14+ monocytes through
distinct pathways that activate NK-kappa B. J Immunol.
165:3647–3655. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kurinna S, Konopleva M, Palla SL, Chen W,
Kornblau S, Contractor R, Deng X, May WS, Andreeff M and Ruvolo PP:
Bcl2 phosphorylation and active PKC alpha are associated with poor
survival in AML. Leukemia. 20:1316–1319. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cassinelli G, Torri G and Naggi A:
Non-anticoagulant heparins as heparanase inhibitors. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1221:493–522. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang M, Pan W, Xu Y, Zhang J, Wan J and
Jiang H: Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation: A potential target
for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. J Inflamm Res.
15:3083–3094. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Blöchl C, Wang D, Madunić K,
Lageveen-Kammeijer GSM, Huber CG, Wuhrer M and Zhang T: Integrated
N- and O-glycomics of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell lines.
Cells. 10:30582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Corcoran A, Bermudez MA, Seoane S,
Perez-Fernandez R, Krupa M, Pietraszek A, Chodyński M, Kutner A,
Brown G and Marcinkowska E: Biological evaluation of new vitamin D2
analogues. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 164:66–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu J, Wei Y, Jia W, Can C, Wang R, Yang
X, Gu C, Liu F, Ji C and Ma D: Chenodeoxycholic acid suppresses AML
progression through promoting lipid peroxidation via ROS/p38
MAPK/DGAT1 pathway and inhibiting M2 macrophage polarization. Redox
Biol. 56:1024522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ung J, Tan SF, Fox TE, Shaw JJP, Vass LR,
Costa-Pinheiro P, Garrett-Bakelman FE, Keng MK, Sharma A, Claxton
DF, et al: Harnessing the power of sphingolipids: Prospects for
acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Rev. 55:1009502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
van Galen P, Hovestadt V, Wadsworth Ii MH,
Hughes TK, Griffin GK, Battaglia S, Verga JA, Stephansky J, Pastika
TJ, Lombardi Story J, et al: Single-Cell RNA-Seq Reveals AML
Hierarchies Relevant to Disease Progression and Immunity. Cell.
176:1265–1281.e24. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kittang AO, Kordasti S, Sand KE,
Costantini B, Kramer AM, Perezabellan P, Seidl T, Rye KP, Hagen KM,
Kulasekararaj A, et al: Expansion of myeloid derived suppressor
cells correlates with number of T regulatory cells and disease
progression in myelodysplastic syndrome. Oncoimmunology.
5:e10622082016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Blokland SLM, Kislat A, Homey B, Smithson
GM, Kruize AA, Radstake T and van Roon JAG: Decreased circulating
CXCR3 + CCR9+T helper cells are associated with elevated levels of
their ligands CXCL10 and CCL25 in the salivary gland of patients
with Sjögren's syndrome to facilitate their concerted migration.
Scand J Immunol. 91:e128522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yuan Y, Tan S, Wang H, Zhu J, Li J, Zhang
P, Wang M and Zhang F: Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal
miRNA-222-3p increases Th1/Th2 ratio and promotes apoptosis of
acute myeloid leukemia cells. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst).
2023:40248872023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang F, Zhu K, Liu L, Zhu J, Li J, Zhang
P, Hu Z and Yuan Y: IRF2-INPP4B axis inhibits apoptosis of acute
myeloid leukaemia cells via regulating T helper 1/2 cell
differentiation. Cell Biochem Funct. 38:582–590. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Marsland BJ and Kopf M: T-cell fate and
function: PKC-theta and beyond. Trends Immunol. 29:179–185. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yu D, Peng X and Li P: The correlation
between Jun N-terminal kinase pathway-associated phosphatase and
Th1 cell or Th17 cell in sepsis and their potential roles in
clinical sepsis management. Ir J Med Sci. 190:1173–1181. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Panuciak K, Margas M, Makowska K and
Lejman M: Insights into modern therapeutic approaches in pediatric
acute leukemias. Cells. 11:1392022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang P, Wang T, Cui G, Ye R, Wan W, Liu
T, Zheng Y and Zhong Z: Systemic multifunctional nanovaccines for
potent personalized immunotherapy of acute myeloid leukemia. Adv
Mater. 36:e24071892024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gharagozloo M, Mahvelati TM, Imbeault E,
Gris P, Zerif E, Bobbala D, Ilangumaran S, Amrani A and Gris D: The
nod-like receptor, Nlrp12, plays an anti-inflammatory role in
experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroinflammation.
12:1982015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Puig-Kröger A, López-Rodriguez C, Relloso
M, Sánchez-Elsner T, Nueda A, Muñoz E, Bernabéu C and Corbi AL:
Polyomavirus enhancer-binding protein 2/core binding factor/acute
myeloid leukemia factors contribute to the cell type-specific
activity of the CD11a integrin gene promoter. J Biol Chem.
275:28507–28512. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Feng W, Chen J, Huang W, Wang G, Chen X,
Duan L, Yin Y, Chen X, Zhang B, Sun M, et al: HMGB1-mediated
elevation of KLF7 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression
and metastasis through upregulating TLR4 and PTK2. Theranostics.
13:4042–4058. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Pham TND, Perez White BE, Zhao H,
Mortazavi F and Tonetti DA: Protein kinase C α enhances migration
of breast cancer cells through FOXC2-mediated repression of
p120-catenin. BMC Cancer. 17:8322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|