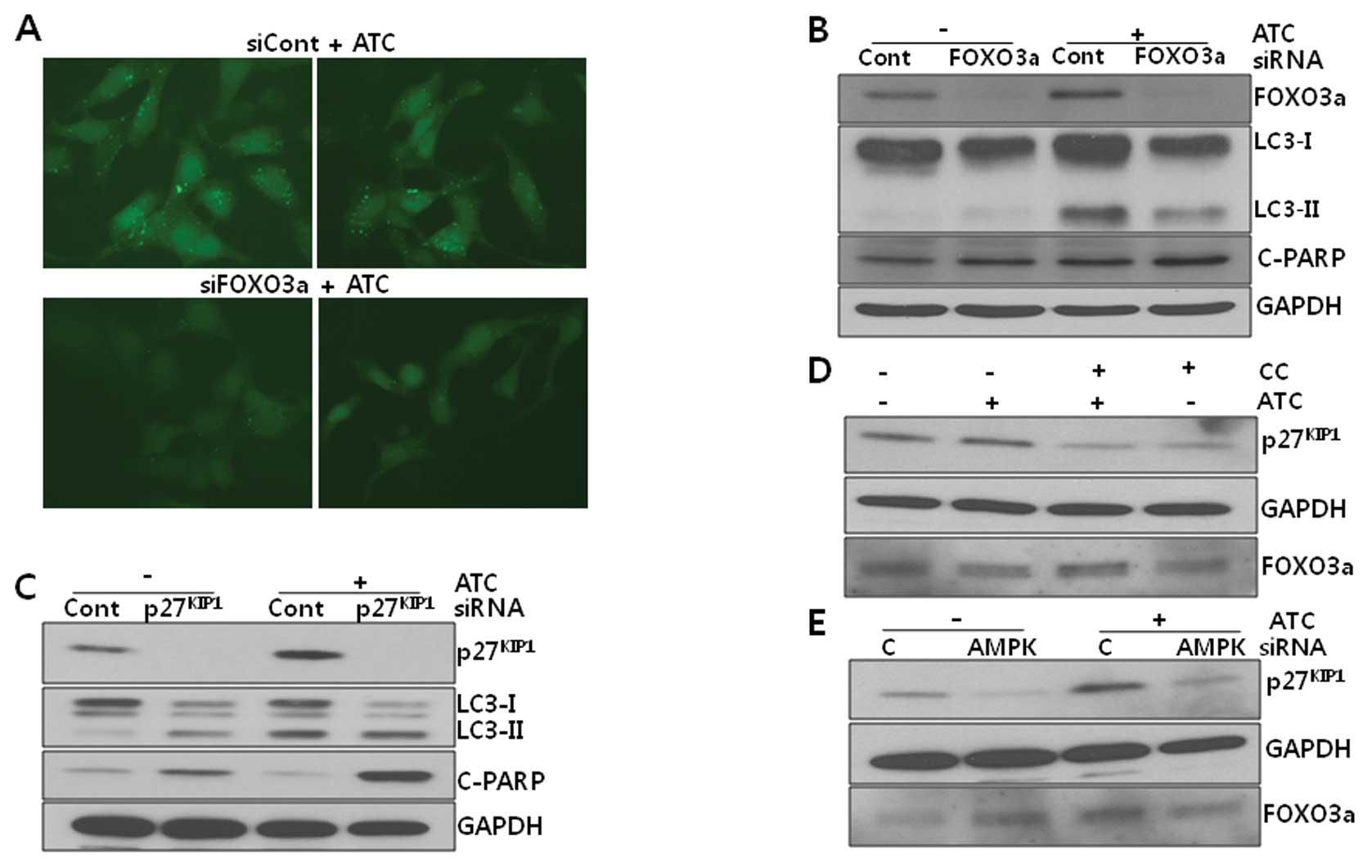
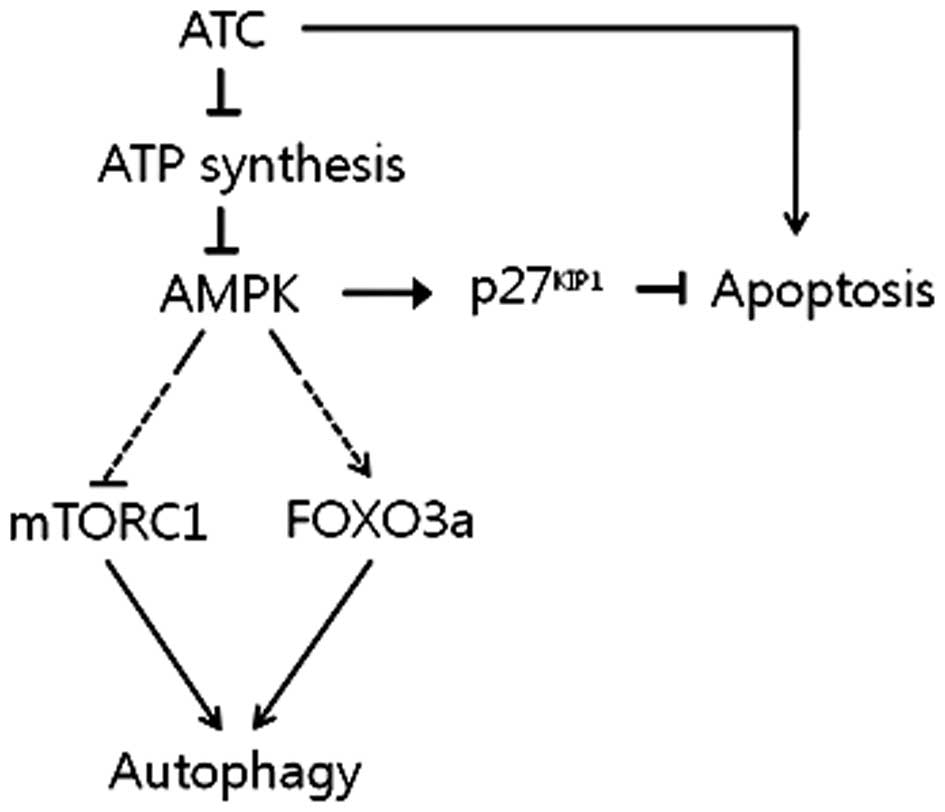
|
1
|
Yeh CT and Yen GC: Induction of apoptosis
by the anthocyanidins through regulation of Bcl-2 gene and
activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase cascade in hepatoma cells. J
Agric Food Chem. 53:1740–1749. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shin DY, Lee WS, Lu JN, et al: Induction
of apoptosis in human colon cancer HCT-116 cells by anthocyanins
through suppression of Akt and activation of p38-MAPK. Int J Oncol.
35:1499–1504. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shih PH, Yeh CT and Yen GC: Effects of
anthocyanidin on the inhibition of proliferation and induction of
apoptosis in human gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Food Chem Toxicol.
43:1557–1566. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee SH and Park SM and Park SM: Induction
of apoptosis in human leukemia U937 cells by anthocyanins through
down-regulation of Bcl-2 and activation of caspases. Int J Oncol.
34:1077–1083. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Reddivari L, Vanamala J, Chintharlapalli
S, et al: Anthocyanin fraction from potato extracts is cytotoxic to
prostate cancer cells through activation of caspase-dependent and
caspase-independent pathways. Carcinogenesis. 28:2227–2235. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hou DX, Fujii M, Terahara N and Yoshimoto
M: Molecular mechanisms behind the chemopreventive effects of
anthocyanins. J Biomed Biotechnol. 5:321–325. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tsoyi K, Park HB, Kim YM, et al:
Anthocyanins from black soybean seed coats inhibit UVB-induced
inflammatory cylooxygenase-2 gene expression and PGE2
production through regulation of the nuclear factor-κB and
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Agric Food Chem.
56:8969–8974. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sautebin L, Rossi A, Serraino I, et al:
Effect of anthocyanins contained in a blackberry extract on the
circulatory failure and multiple organ dysfunction caused by
endotoxin in the rat. Planta Med. 70:745–752. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shin DY, Lu JN, Kim GY, et al:
Anti-invasive activities of anthocyanins through modulation of
tight junctions and suppression of matrix metalloproteinase
activities in HCT-116 human colon carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep.
25:567–572. 2011.
|
|
10
|
Matsubara K, Kaneyuki T, Miyake T and Mori
M: Antiangiogenic activity of nasunin, an antioxidant anthocyanin,
in eggplant peels. J Agric Food Chem. 53:6272–6275. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang LS, Hecht SS, Carmella SG, et al:
Anthocyanins in black raspberries prevent esophageal tumors in
rats. Cancer Prev Res. 2:84–93. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thomasset S, Berry DP, Cai H, et al: Pilot
study of oral anthocyanins for colorectal cancer chemoprevention.
Cancer Prev Res. 2:625–633. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Longo L, Platini F, Scardino A, Alabiso O,
Vasapollo G and Tessitore L: Autophagy inhibition enhances
anthocyanin-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol
Cancer Ther. 7:2476–2485. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim YK, Yoon HH, Lee YD, et al:
Anthocyanin extracts from black soybean (Glycine max L.)
protect human glial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation by
promoting autophagy. Biomol Ther. 20:68–74. 2012.
|
|
15
|
Hardie DG: AMP-activated protein kinase:
an energy sensor that regulates all aspects of cell function. Genes
Dev. 25:1895–1908. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yun H and Ha J: AMP-activated protein
kinase modulators: a patent review (2006–2010). Expert Opin Ther
Pat. 21:983–1005. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Alers S, Löffler AS, Wesselborg S and
Stork B: Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the regulation of autophagy:
cross talk, shortcuts, and feedbacks. Mol Cell Biol. 32:2–11. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Egan DF, Shackelford DB, Mihaylova MM, et
al: Phosphorylation of ULK1 (hATG1) by AMP-activated protein kinase
connects energy sensing to mitophagy. Science. 331:456–461. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liang J, Shao SH, Xu ZX, et al: The energy
sensing LKB1-AMPK pathway regulates p27KIP1
phosphorylation mediating the decision to enter autophagy or
apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 9:218–224. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Greer EL, Oskoui PR, Banko MR, et al: The
energy sensor AMP-activated protein kinase directly regulates the
mammalian FOXO3 transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 282:30107–30119.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shi J, Zhang L, Shen A, et al: Clinical
and biological significance of forkhead class box O 3a expression
in glioma: mediation of glioma malignancy by transcriptional
regulation of p27KIP1. J Neurooncol. 98:57–69. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gopinath S, Malla RR, Gondi CS, et al:
Co-depletion of cathepsin B and uPAR induces G0/G1 arrest in glioma
via FOXO3a mediated p27 upregulation. PLoS One. 5:e116682010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee YK, Lee WS, Kim GS and Park OJ:
Anthocyanins are novel AMPKα1 stimulators that suppress tumor
growth by inhibiting mTOR phosphorylation. Oncol Rep. 24:1471–1477.
2010.
|
|
24
|
Jang H, Ha US, Kim SJ, Yoon BI, Han DS,
Yuk SM and Kim SW: Anthocyanin extracted from black soybean reduces
prostate weight and promotes apoptosis in the prostatic
hyperplasia-induced rat model. J Agric Food Chem. 58:12686–12691.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee JH, Kang NS, Shin SO, et al:
Characterization of anthocyanins in the black soybean (Glycine
max L.) by HPLC-DAD-ESI/MS analysis. Food Chem. 112:226–231.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jang JY, Kim MK, Jeon YK, Joung YK, Park
KD and Kim CW: Adenovirus adenine nucleotide translocator-2 shRNA
effectively induces apoptosis and enhances chemosensitivity by the
down-regulation of ABCG2 in breast cancer stem-like cells. Exp Mol
Med. 44:251–259. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hawley Simon A, Ross Fiona A, Chevtzoff
Cyrille, et al: Use of cells expressing γ subunit variants to
identify diverse mechanisms of AMPK activation. Cell Metab.
11:554–565. 2010.
|
|
28
|
Jones RG, Plas DR, Kubek S, et al:
AMP-activated protein kinase induces a p53-dependent metabolic
checkpoint. Mol Cell. 18:283–293. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Imamura K, Ogura T, Kishimoto A, Kaminishi
M and Esumi H: Cell cycle regulation via p53 phosphorylation by a
5′-AMP activated protein kinase activator,
5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-D-ribofuranoside, in a human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
287:562–567. 2001.
|
|
30
|
Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Giuliano S, et al:
Targeting cancer cell metabolism: The combination of metformin and
2-deoxyglucose induces p53-dependent apoptosis in prostate cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 70:2465–2475. 2010.
|
|
31
|
Chen MB, Shen WX, Yang Y, Wu XY, Gu JH and
Lu PH: Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase is involved in
vincristine-induced cell apoptosis in B16 melanoma cell. J Cell
Physiol. 226:1915–1925. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim HS, Hwang JT, Yun H, et al: Inhibition
of AMP-activated protein kinase sensitizes cancer cells to
cisplatin-induced apoptosis via hyper-induction of p53. J Biol
Chem. 283:3731–3742. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chhipa RR, Wu Y and Ip C: AMPK-mediated
autophagy is a survival mechanism in androgen-dependent prostate
cancer cells subjected to androgen deprivation and hypoxia. Cell
Signal. 23:1466–1472. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Karantza-Wadsworth V, Patel S, Kravchuk O,
et al: Autophagy mitigates metabolic stress and genome damage in
mammary tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 21:1621–1635. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim JW and Dang CV: Cancer's molecular
sweet tooth and the Warburg effect. Cancer Res. 66:8927–8930.
2006.
|
|
36
|
Levine AJ and Puzio-Kuter AM: The control
of the metabolic switch in cancers by oncogenes and tumor
suppressor genes. Science. 330:1340–1344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cleary MP and Grossman ME: Minireview:
obesity and breast cancer - the estrogen connection. Endocrinology.
150:2537–2542. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Goodwin PJ and Stambolic V: Obesity and
insulin resistance in breast cancer - Chemoprevention strategies
with a focus on metformin. Breast. S3:S31–S35. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mathew R, Karantza-Wadsworth V and White
E: Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:961–967. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Bialik S, Simon HU and
Kimchi A: Life and death partners: apoptosis, autophagy and the
cross-talk between them. Cell Death Diff. 16:966–975. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|