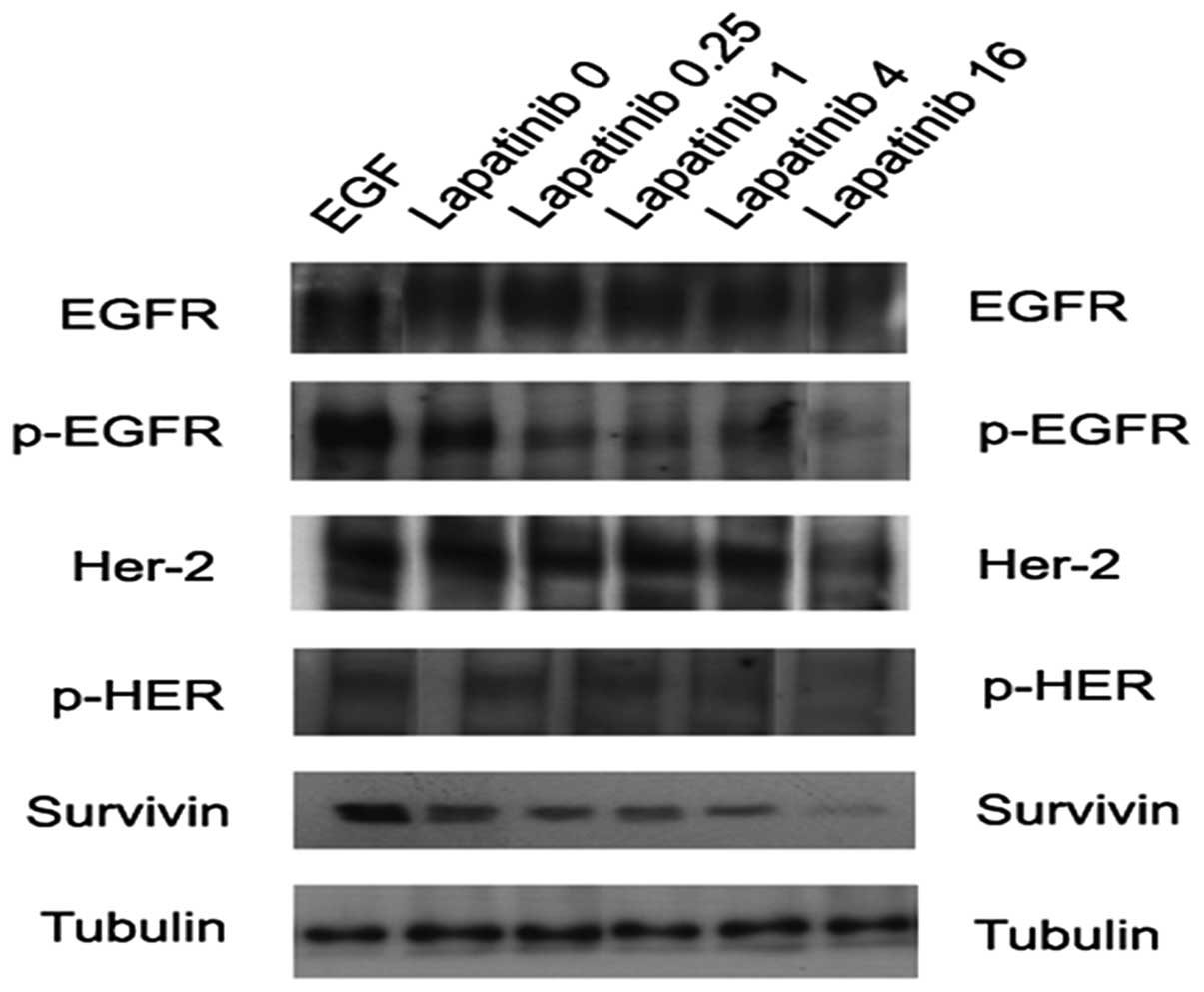
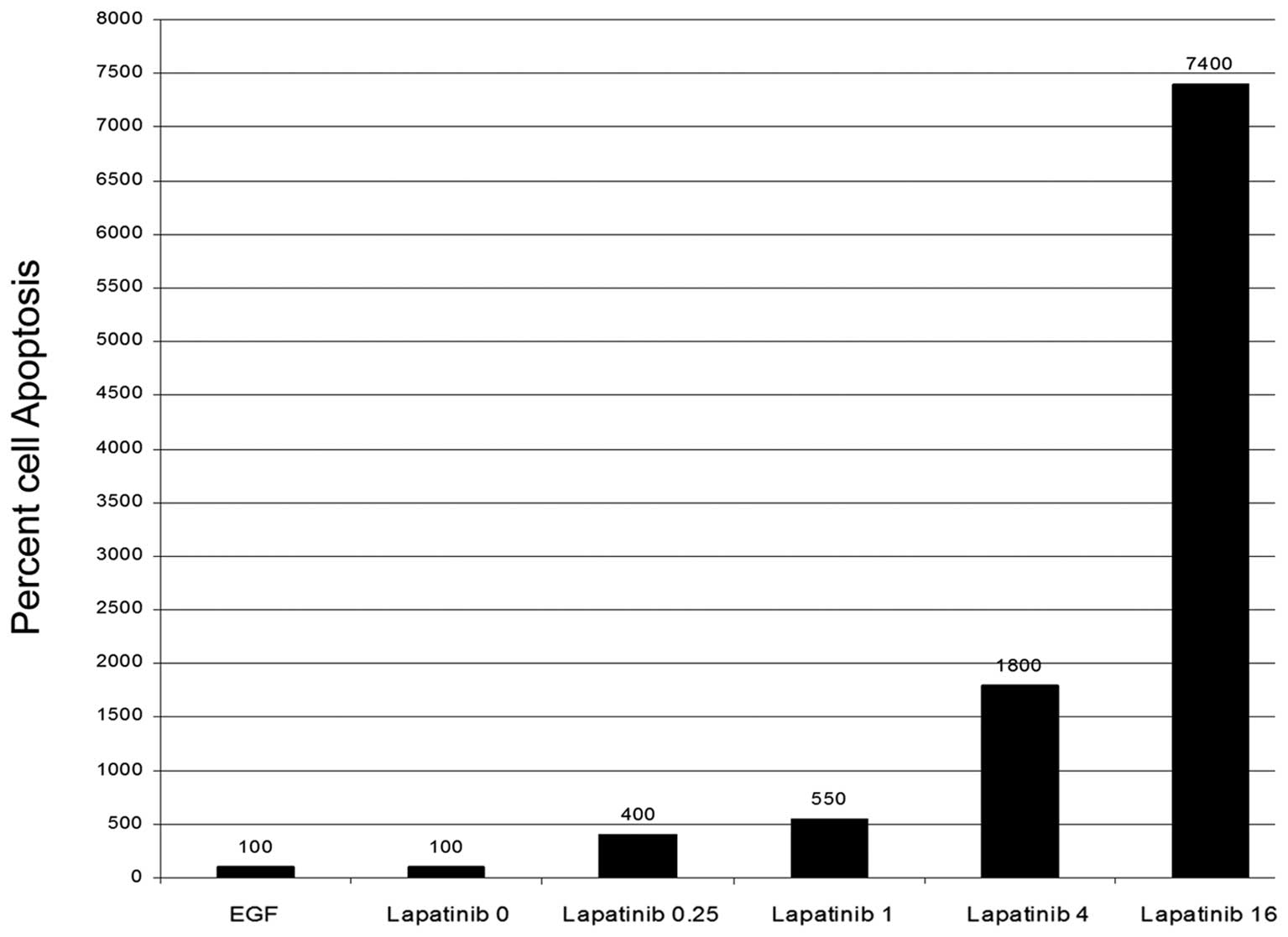
|
1
|
Nelson NJ: Pancreatic cancer research
matures. J Natl Cancer Inst. 99:1432–1434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hidalgo M: Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J
Med. 362:1605–1617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li J and Saif MW: Any progress in the
management of advanced pancreatic cancer? JOP. 10:361–365.
2009.
|
|
4
|
Zhu CP, Shi J, Chen YX, Xie WF and Lin Y:
Gemcitabine in the chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced
pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol. 99:108–113.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Heinemann V, Boeck S, Hinke A, Labianca R
and Louvet C: Meta-analysis of randomized trials: evaluation of
benefit from gemcitabine-based combination chemotherapy applied in
advanced pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer. 8:822008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yip D, Karapetis C, Strickland A, Steer CB
and Goldstein D: Chemotherapy and radiotherapy for inoperable
advanced pancreatic cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
3:CD0020932006.
|
|
7
|
Rivera F, Lopez-Tarruella S, Vega-Villegas
ME and Salcedo M: Treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer: from
gemcitabine single agent to combinations and targeted therapy.
Cancer Treat Rev. 35:335–339. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Philip PA, Benedetti J, Corless CL, et al:
Phase III study comparing gemcitabine plus cetuximab versus
gemcitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma:
Southwest Oncology Group-directed intergroup trial S0205. J Clin
Oncol. 28:3605–3610. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Fountzilas G, Bobos M, Kalogera-Fountzila
A, et al: Gemcitabine combined with gefitinib in patients with
inoperable or metastatic pancreatic cancer: a phase II Study of the
Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group with biomarker evaluation.
Cancer Invest. 26:784–793. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, et al:
National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group.
Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in
patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the
National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin
Oncol. 25:1960–1966. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Safran H, Iannitti D, Ramanathan R, et al:
Herceptin and gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancers that
overexpress ERBB2/neu. Cancer Invest. 22:706–712. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mendelsohn J and Baselga J: The EGF
receptor family as targets for cancer therapy. Oncogene.
19:6550–6565. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Riese DJ II and Stern DF: Specificity
within the EGF family/ErbB receptor family signaling network.
Bioessays. 20:41–48. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ueda S, Ogata S, Tsuda H, et al: The
correlation between cytoplasmic overexpression of epidermal growth
factor receptor and tumor aggressiveness: poor prognosis in
patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas. 29:e1–e8.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dancer J, Takei H, Ro JY and
Lowery-Nordberg M: Coexpression of ERBB1 and ERBB2 in pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma: a comparative study using
immunohistochemistry correlated with gene amplification by
fluorescencent in situ hybridization. Oncol Rep. 18:151–155.
2007.
|
|
16
|
Tobita K, Kijima H, Dowaki S, et al:
Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in human pancreatic
cancer: significance for liver metastasis. Int J Mol Med.
11:305–309. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Scaltriti M, Rojo F, Ocana A, et al:
Expression of p95HER2, a truncated form of the HER2 receptor, and
response to anti-HER2 therapies in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 99:628–638. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Konecny GE, Pegram MD, Venkatesan N, et
al: Activity of the dual kinase inhibitor lapatinib (GW572016)
against HER-2-overexpressing and trastuzumab-treated breast cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 66:1630–1639. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
O’Brien NA, Browne BC, Chow L, et al:
Activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT signaling confers
resistance to trastuzumab but not lapatinib. Mol Cancer Ther.
9:1489–1502. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, et al:
FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N
Engl J Med. 364:1817–1825. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mehta SP: Palliative chemotherapy for
pancreatic malignancies. Surg Clin North Am. 90:365–375. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Muthuswamy SK, Gilman M and Brugge JS:
Controlled dimerization of ErbB receptors provides evidence for
differential signaling by homo- and heterodimers. Mol Cell Biol.
19:6845–6857. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zwick E, Hackel PO, Prenzel N and Ullrich
A: The EGF receptor as central transducer of heterologous
signalling systems. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 20:408–412. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sorkin A, Helin K, Waters CM, Carpenter G
and Beguinot L: Multiple autophosphorylation sites of the epidermal
growth factor receptor are essential for receptor kinase activity
and internalization. Contrasting significance of tyrosine 992 in
the native and truncated receptors. J Biol Chem. 267:8672–8678.
1992.
|
|
25
|
Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, Plescia J,
Tognin S, Marchisio PC and Altieri DC: Control of apoptosis and
mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature. 396:580–584. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu BB and Wang WH: Survivin and
pancreatic cancer. World J Clin Oncol. 2:164–168. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Theodoropoulos GE, Michalopoulos NV,
Panoussopoulos SG, Taka S and Gazouli M: Effects of caspase-9 and
survivin gene polymorphisms in pancreatic cancer risk and tumor
characteristics. Pancreas. 39:976–980. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shen YM, Yang XC, Song ML, Qin CH, Yang C
and Sun YH: Growth inhibition induced by short hairpin RNA to
silence survivin gene in human pancreatic cancer cells.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 9:69–77. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, et
al: MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer
by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 316:1039–1043. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nagy P, Friedlander E, Tanner M, Kapanen
AI, Carraway KL, Isola J and Jovin TM: Decreased accessibility and
lack of activation of ErbB2 in JIMT-1, a herceptin-resistant,
MUC4-expressing breast cancer cell line. Cancer Res. 65:473–482.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xia W, Liu LH, Ho P and Spector NL:
Truncated ErbB2 receptor (p95ErbB2) is regulated by heregulin
through heterodimer formation with ErbB3 yet remains sensitive to
the dual EGFR/ErbB2 kinase inhibitor GW572016. Oncogene.
23:646–653. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xia W, Mullin RJ, Keith BR, et al:
Anti-tumor activity of GW572016: a dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor
blocks EGF activation of EGFR/erbB2 and downstream Erk1/2 and AKT
pathways. Oncogene. 21:6255–6263. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Song Z, Yao X and Wu M: Direct interaction
between survivin and Smac/DIABLO is essential for the
anti-apoptotic activity of survivin during taxol-induced apoptosis.
J Biol Chem. 278:23130–23140. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Z, Fukuda S and Pelus LM: Survivin
regulates the p53 tumor suppressor gene family. Oncogene.
23:8146–8153. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Desplanques G, Hulin P, Juin P and
Barille-Nion S: Survivin Protects Breast Cancer Cells from DNA
Damage during Mitosis (abstract). In: Thirty-Second Annual
CTRC-AACR San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium; Dec 10–13; San
Antonio, TX. pp. 2009Cancer Res. 69(Suppl 3)2009, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Boussen H, Cristofanilli M, Zaks T,
DeSilvio M, Salazar V and Spector N: Phase II study to evaluate the
efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant lapatinib plus paclitaxel in
patients with inflammatory breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:3248–3255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
LoRusso PM, Jones SF, Koch KM, et al:
Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of lapatinib and docetaxel in
patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol. 26:3051–3056. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cameron D, Casey M, Press M, et al: A
phase III randomized comparison of lapatinib plus capecitabine
versus capecitabine alone in women with advanced breast cancer that
has progressed on trastuzumab: updated efficacy and biomarker
analyses. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 112:533–543. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Johnston S, Pippen J Jr, Pivot X, et al:
Lapatinib combined with letrozole versus letrozole and placebo as
first-line therapy for postmenopausal hormone receptor-positive
metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:5538–5546. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Siegel-Lakhai WS, Beijnen JH, Vervenne WL,
et al: Phase I pharmacokinetic study of the safety and tolerability
of lapatinib (GW572016) in combination with
oxaliplatin/fluorouracil/leucovorin (FOLFOX4) in patients with
solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4495–4502. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Midgley RS, Kerr DJ, Flaherty KT, et al: A
phase I and pharmacokinetic study of lapatinib in combination with
infusional 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin and irinotecan. Ann Oncol.
18:2025–2029. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|