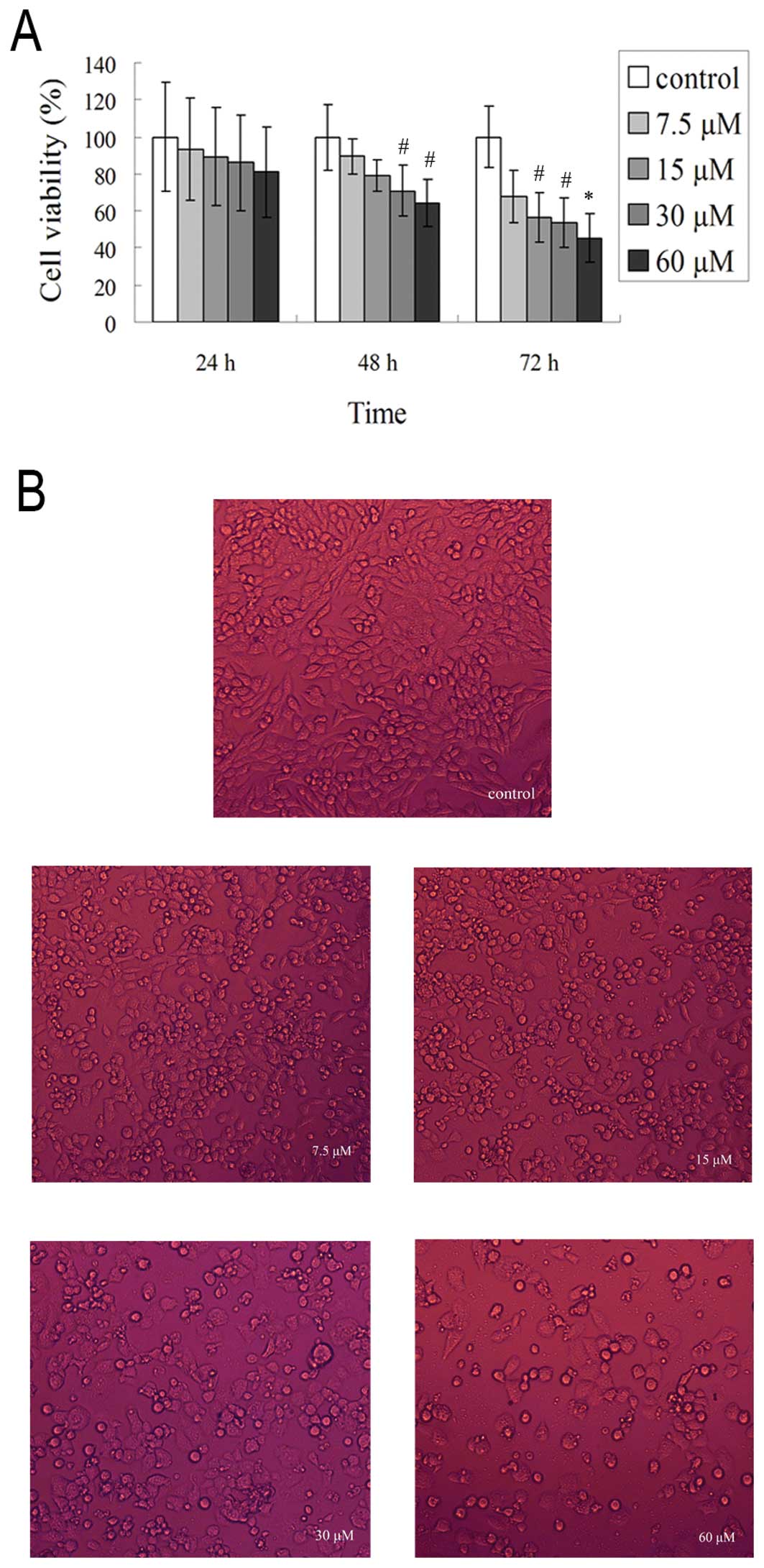
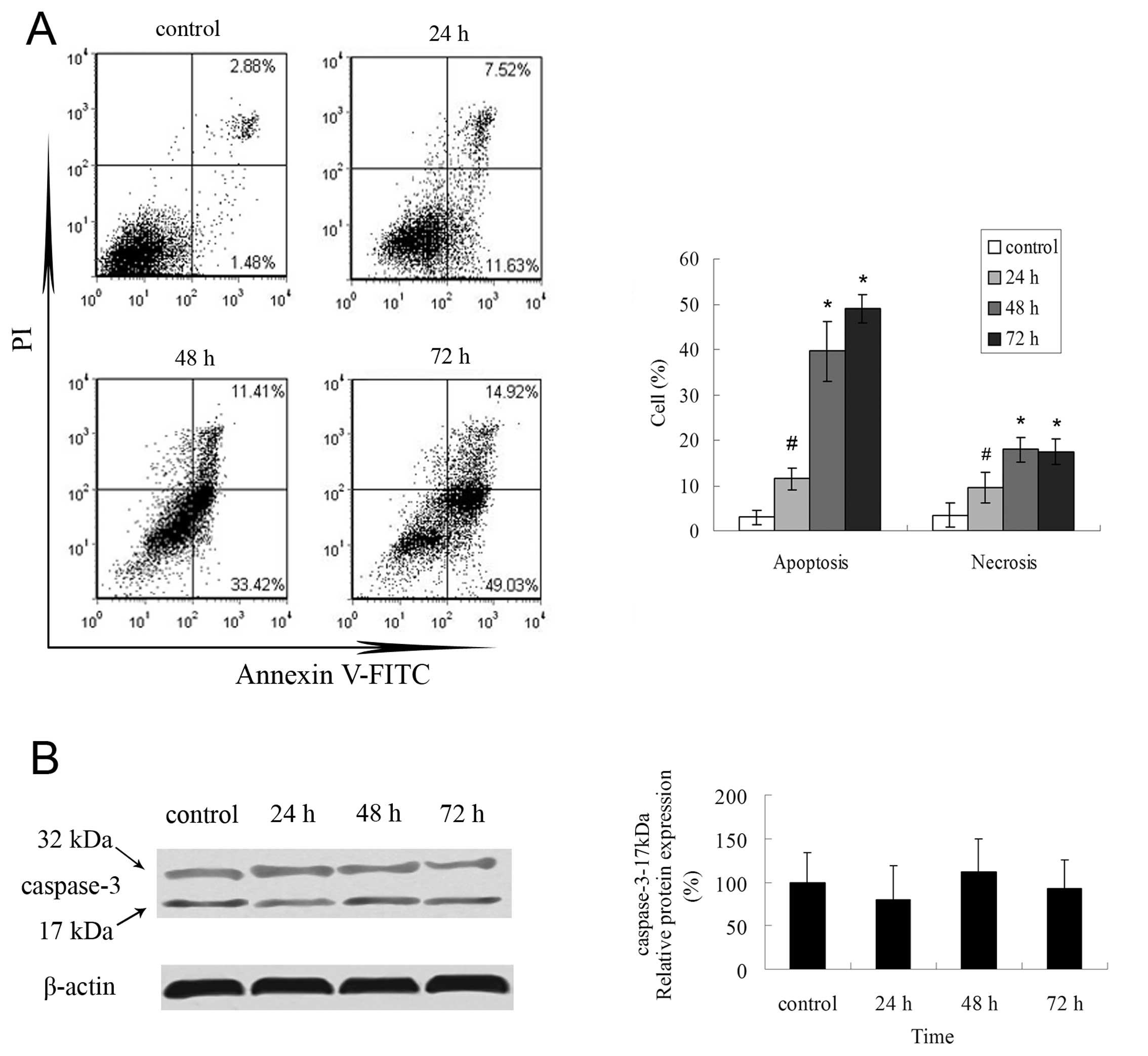
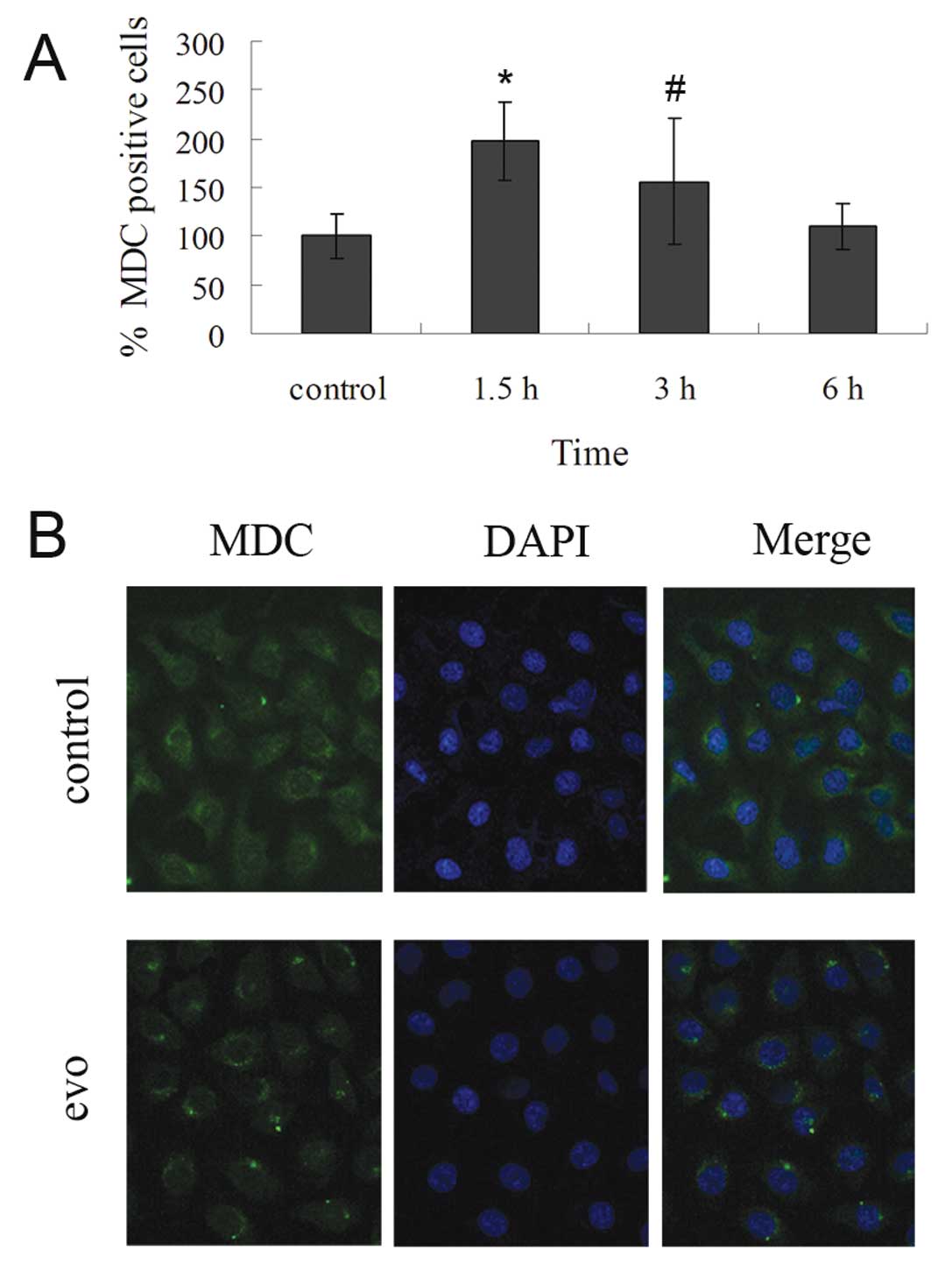
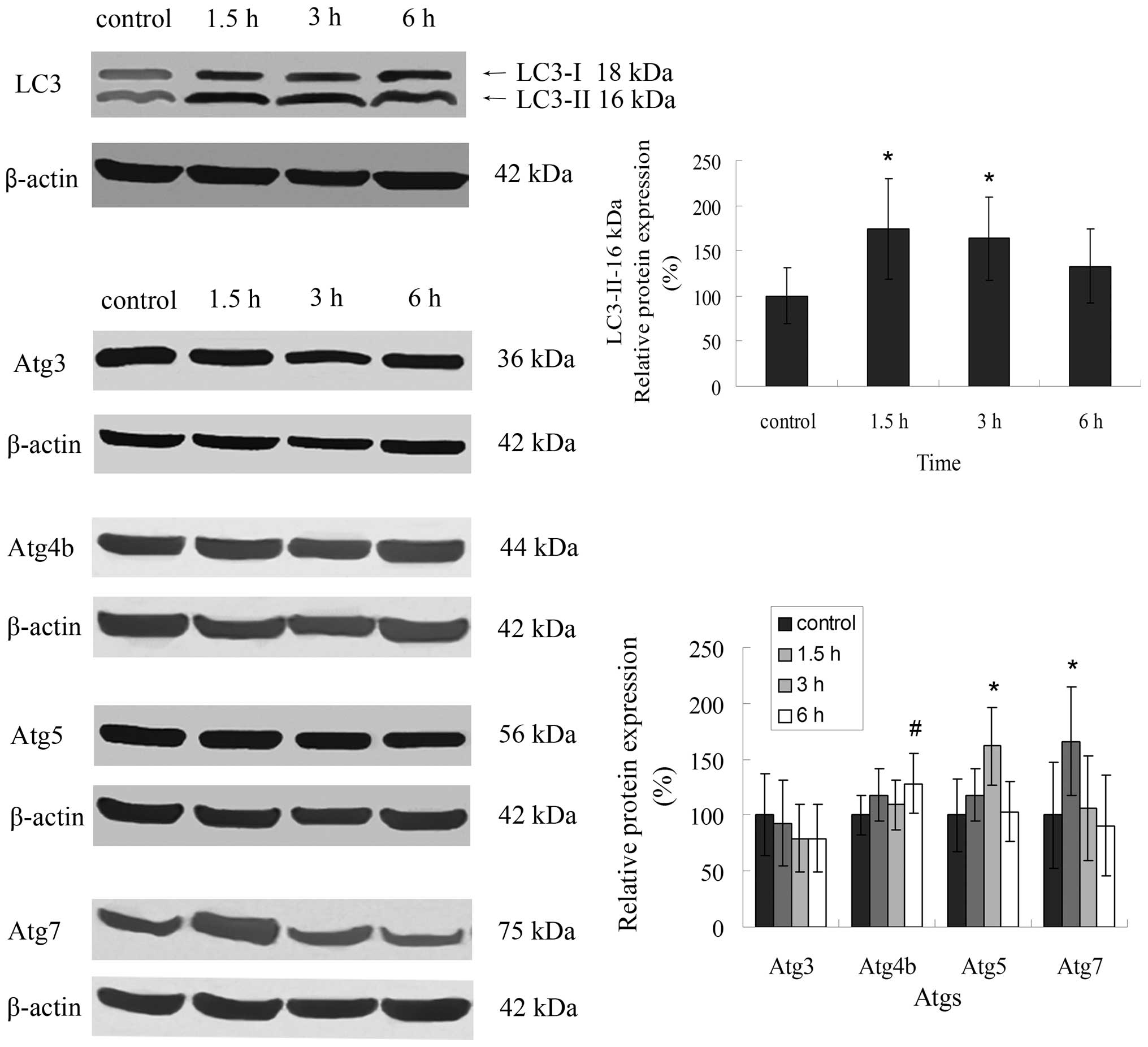
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Petty RD, Nicolson MC, Kerr KM, et al:
Gene expression profiling in non-small cell lung cancer: from
molecular mechanisms to clinical application. Clin Cancer Res.
10:3237–3248. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Erridge SC, Moller H, Price A, et al:
International comparisons of survival from lung cancer: pitfalls
and warnings. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 4:570–577. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang TY, Wu JB, Hwang TL, et al: A new
quinolone and other constituents from the fruits of Tetradium
ruticarpum: effects on neutrophil pro-inflammatory responses. Chem
Biodivers. 7:1828–1834. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu YN, Pan SL, Liao CH, et al: Evodiamine
represses hypoxia-induced inflammatory proteins expression and
hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha accumulation in RAW264.7. Shock.
32:263–269. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang T, Wang Y and Yamashita H: Evodiamine
inhibits adipogenesis via the EGFR-PKCalpha-ERK signaling pathway.
FEBS Lett. 583:3655–3659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu CL, Hung CR, Chang FY, et al: Effects
of evodiamine on gastrointestinal motility in male rats. Eur J
Pharmacol. 457:169–176. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang C, Fan X, Xu X, et al: Evodiamine
induces caspase-dependent apoptosis and S phase arrest in human
colon lovo cells. Anticancer Drugs. 21:766–776. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang J, Wu LJ, Tashino S, et al: Protein
tyrosine kinase pathway-derived ROS/NO productions contribute to
G2/M cell cycle arrest in evodiamine-treated human cervix carcinoma
HeLa cells. Free Radic Res. 44:792–802. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang C, Li S and Wang MW:
Evodiamine-induced human melanoma A375-S2 cell death was mediated
by PI3K/Akt/caspase and Fas-L/NF-kappaB signaling pathways and
augmented by ubiquitin-proteasome inhibition. Toxicol In Vitro.
24:898–904. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chen MC, Yu CH, Wang SW, et al:
Anti-proliferative effects of evodiamine on human thyroid cancer
cell line ARO. J Cell Biochem. 110:1495–1503. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang XN, Han X, Xu LN, et al: Enhancement
of apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells
through synergy of berberine and evodiamine. Phytomedicine.
15:1062–1068. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kan SF, Yu CH, Pu HF, et al:
Anti-proliferative effects of evodiamine on human prostate cancer
cell lines DU145 and PC3. J Cell Biochem. 101:44–56. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ogasawara M, Matsunaga T, Takahashi S, et
al: Anti-invasive and metastatic activities of evodiamine. Biol
Pharm Bull. 25:1491–1493. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meijer AJ and Codogno P: Regulation and
role of autophagy in mammalian cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
36:2445–2462. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang YP, Liang ZQ, Gao B, et al: Dynamic
effects of autophagy on arsenic trioxide-induced death of human
leukemia cell line HL60 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:123–134.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ogier-Denis E and Codogno P: Autophagy: a
barrier or an adaptive response to cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1603:113–128. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu D, Yang Y and Liu Q: Inhibition of
autophagy by 3-MA potentiates cisplatin-induced apoptosis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Med Oncol. 28:105–111.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Longo L, Platini F, Scardino A, et al:
Autophagy inhibition enhances anthocyanin-induced apoptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:2476–2485. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li J, Hou N, Faried A, et al: Inhibition
of autophagy by 3-MA enhances the effect of 5-FU-induced apoptosis
in colon cancer cells. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:761–771. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li J, Hou N, Faried A, et al: Inhibition
of autophagy augments 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy in human colon
cancer in vitro and in vivo model. Eur J Cancer. 46:1900–1909.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang J, Wu LJ, Tashino S, et al: Reactive
oxygen species and nitric oxide regulate mitochondria-dependent
apoptosis and autophagy in evodiamine-treated human cervix
carcinoma HeLa cells. Free Radic Res. 42:492–504. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lowe SW and Lin AWA: Apoptosis in cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 21:485–495. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: a review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Van Gurp M, Festjens N, Van Loo G, et al:
Mitochondrial intermembrane proteins in cell death. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 304:487–497. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev Cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kuma A, Mizushima N, Ishihara N, et al:
Formation of the approximately 350-kDa Apg12-Apg5. Apg16 multimeric
complex, mediated by Apg16 oligomerization, is essential for
autophagy in yeast. J Biol Chem. 277:18619–18625. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fujita N, Itoh T, Omori H, et al: The
Atg16L complex specifies the site of LC3 lipidation for membrane
biogenesis in autophagy. Mol Biol Cell. 19:2092–2100. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, et al: LC3,
a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome
membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hemelaar J, Lelyveld VS, Kessler BM and
Ploegh HL: A single protease, Apg4B, is specific for the
autophagy-related ubiquitin-like proteins GATE-16, MAP1-LC3,
GABARAP, and Apg8L. J Biol Chem. 278:51841–51850. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Suzuki K, Kirisako T, Kamada Y, et al: The
pre-autophagosomal structure organized by concerted functions of
APG genes is essential for autophagosome formation. EMBO J.
20:5971–5981. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mizushima N, Yamamoto A, Hatano M, et al:
Dissection of autophagosome formation using Apg5-deficient mouse
embryonic stem cells. J Cell Biol. 152:657–668. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Seglen PO and Gordon PB: 3-Methyladenine:
specific inhibitor of autophagic/lysosomal protein degradation in
isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 79:1889–1892.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Petiot A, Ogier-Denis E and Blommaart EF:
Distinct classes of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinases are involved in
signaling pathways that control macroautophagy in HT-29 cells. J
Biol Chem. 275:992–998. 2000.
|
|
35
|
Maiuri MC, Criollo A and Kroemer G:
Crosstalk between apoptosis and autophagy within the Beclin 1
interactome. EMBO J. 29:515–516. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gozuacik D and Kimchi A: Autophagy as a
cell death and tumor suppressor mechanism. Oncogene. 23:2891–2906.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Laane E, Tamm KP, Buentke E, et al: Cell
death induced by dexamethasone in lymphoid leukemia is mediated
through initiation of autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 16:1018–1029.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Herman-Antosiewicz A, Johnson DE and Singh
SV: Sulforaphane causes autophagy to inhibit release of cytochrome
C and apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res.
66:5828–5835. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Aoki H, Takada Y, Kondo S, et al: Evidence
that curcumin suppresses the growth of malignant gliomas in vitro
and in vivo through induction of autophagy: role of Akt and
extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathways. Mol
Pharmacol. 72:29–39. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cui Q, Tashiro S, Onodera S, et al:
Autophagy preceded apoptosis in oridonin-treated human breast
cancer MCF-7 cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:859–864. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu YC, Wu WK, Li Y, et al: Inhibition of
macroautophagy by bafilomycin A1 lowers proliferation and induces
apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
382:451–456. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hsu KF, Wu CL, Huang SC, et al: Cathepsin
L mediates resveratrol-induced autophagy and apoptotic cell death
in cervical cancer cells. Autophagy. 5:451–460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Bialik S, Simon HU, et
al: Life and death partners: apoptosis, autophagy and the
cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ. 16:966–975. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ito S, Koshikawa N, Mochizuki S, et al:
3-Methyladenine suppresses cell migration and invasion of HT1080
fibrosarcoma cells through inhibiting phosphoinositide 3-kinases
independently of autophagy inhibition. Int J Oncol. 31:261–268.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Goswami A, Ranganathan P and Rangnekar VM:
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt1/Par-4 axis: a cancer-selective
therapeutic target. Cancer Res. 66:2889–2892. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Opipari AW Jr, Tan L, Boitano AE, et al:
Resveratrol-induced autophagocytosis in ovarian cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 64:696–703. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Trincheri NF, Follo C, Nicotra G, et al:
Resveratrol-induced apoptosis depends on the lipid kinase activity
of Vps34 and on the formation of autophagolysosomes.
Carcinogenesis. 29:381–389. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|