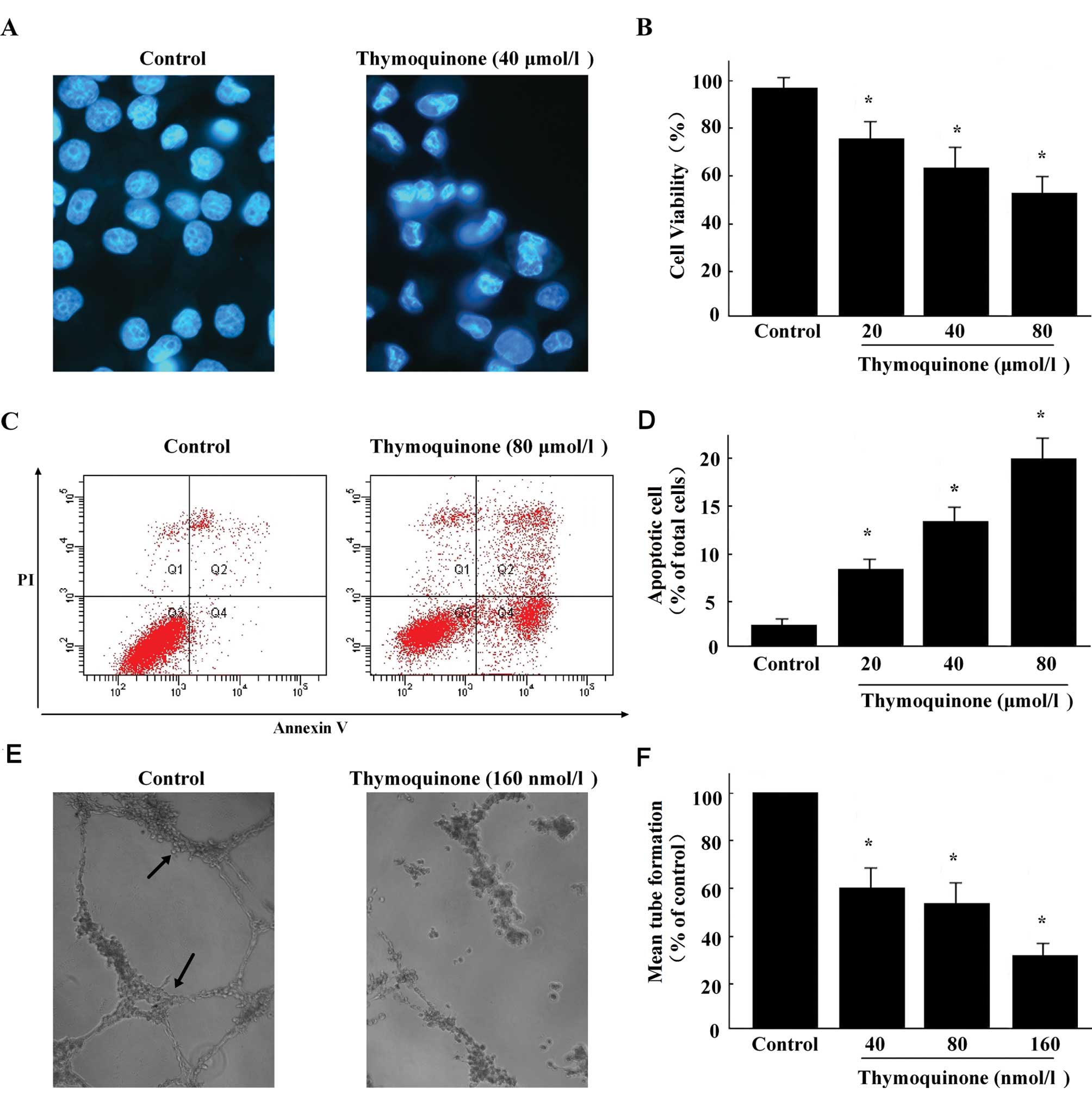
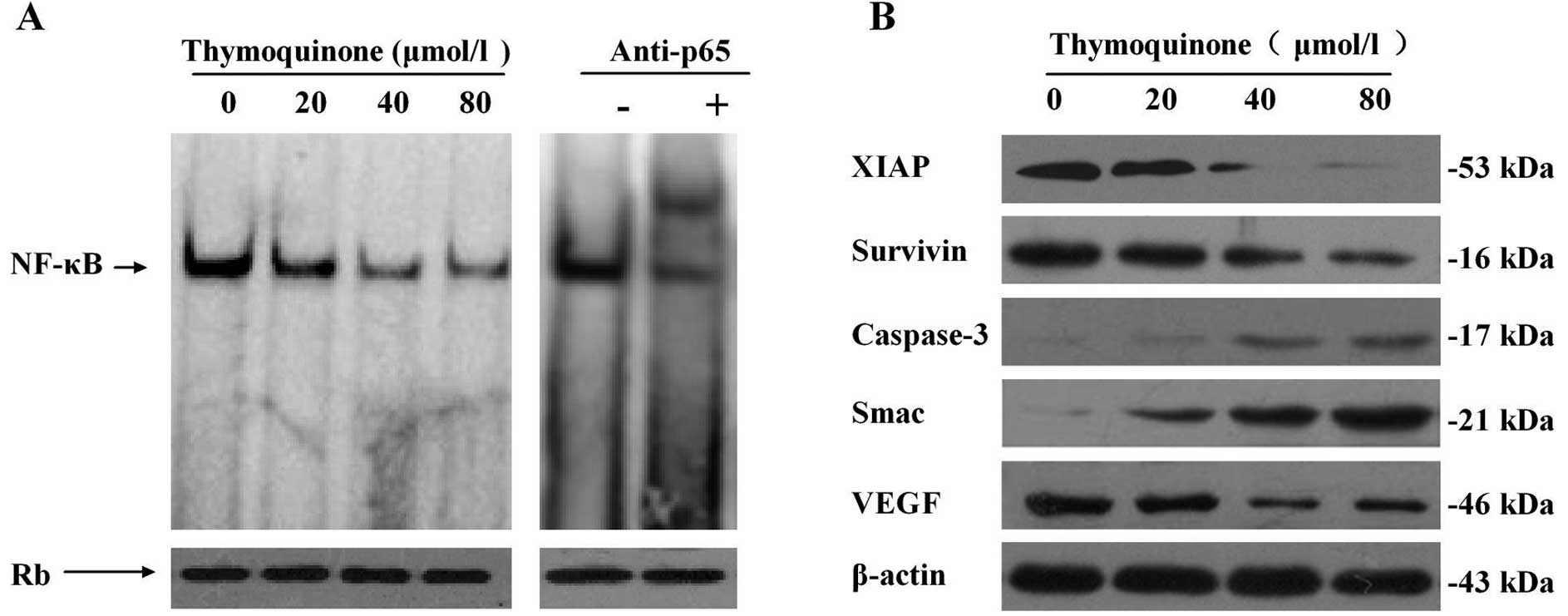
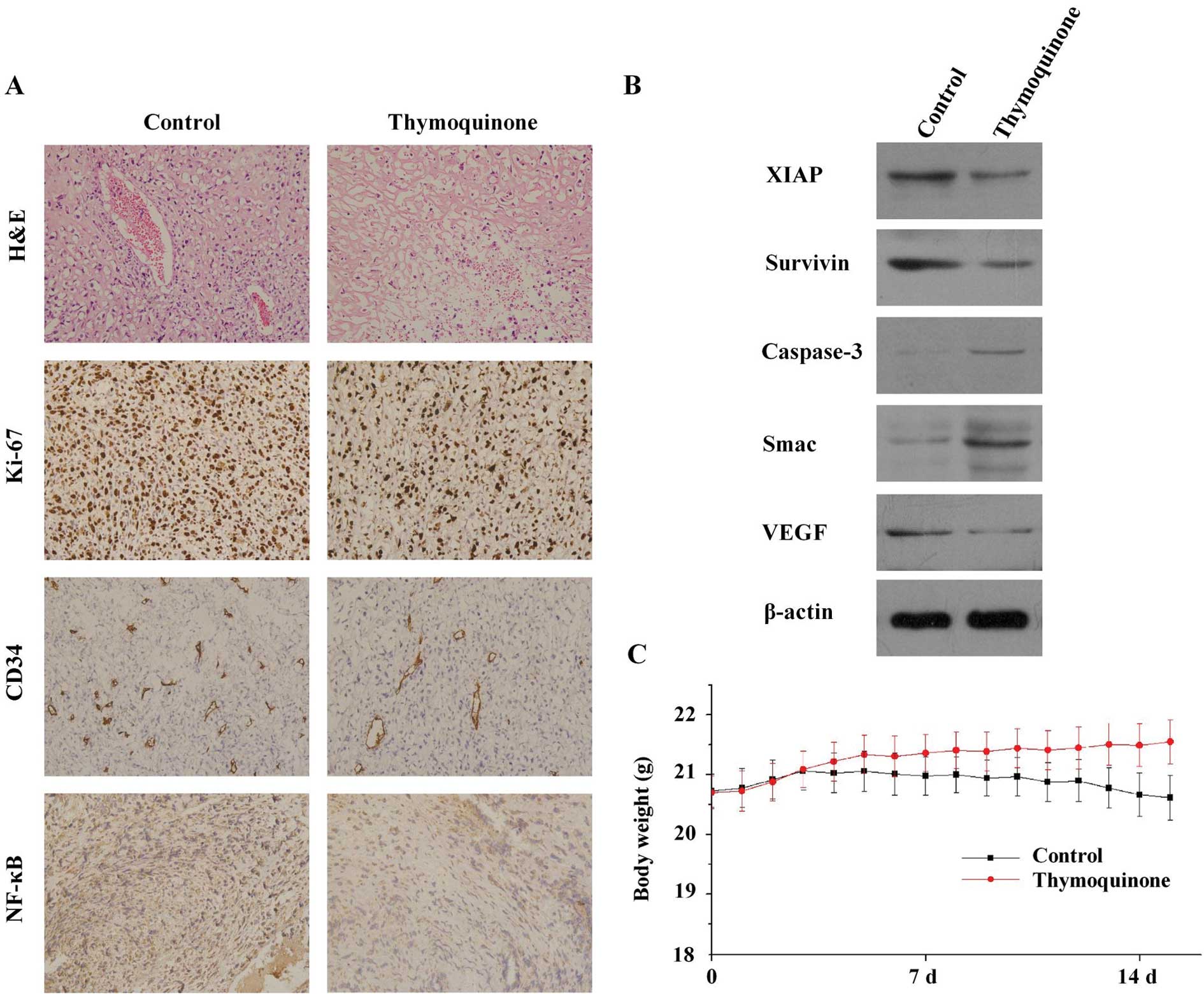
|
1
|
DuBois S and Demetri G: Markers of
angiogenesis and clinical features in patients with sarcoma.
Cancer. 109:813–819. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee JA, Kim MS, Kim DH, et al: Relative
tumor burden predicts metastasis-free survival in pediatric
osteosarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 50:195–200. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bacci G, Ferrari S, Mercuri M, et al:
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for osteosarcoma of the extremities in
patients aged 41–60 years - outcome in 34 cases treated with
adriamycin, cisplatinum and ifosfamide between 1984 and 1999. Acta
Orthop. 78:377–384. 2007.
|
|
4
|
Chou AJ, Merola PR, Wexler LH, et al:
Treatment of osteosarcoma at first recurrence after contemporary
therapy: the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center experience.
Cancer. 104:2214–2221. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Worthen DR, Ghosheh OA and Crooks PA: The
in vitro anti-tumor activity of some crude and purified components
of blackseed, Nigella sativa L. Anticancer Res. 18:1527–1532.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ali BH and Blunden G: Pharmacological and
toxicological properties of Nigella sativa. Phytother Res.
17:299–305. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gali-Muhtasib H, Diab-Assaf M, Boltze C,
et al: Thymoquinone extracted from black seed triggers apoptotic
cell death in human colorectal cancer cells via a p53-dependent
mechanism. Int J Oncol. 25:857–866. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jafri SH, Glass J, Shi RH, Zhang SL,
Prince M and Kleiner-Hancock H: Thymoquinone and cisplatin as a
therapeutic combination in lung cancer: in vitro and in vivo. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 29:872010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
El-Mahdy MA, Zhu QZ, Wang QE, Wani G and
Wani AA: Thymoquinone induces apoptosis through activation of
caspase-8 and mitochondrial events in p53-null myeloblastic
leukemia HL-60 cells. Int J Cancer. 117:409–417. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kaseb AO, Chinnakannu K, Chen D, et al:
Androgen receptor- and E2F-1-targeted thymoquinone therapy for
hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 67:7782–7788. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Banerjee S, Kaseb AO, Wang ZW, et al:
Antitumor activity of gemcitabine and oxaliplatin is augmented by
thymoquinone in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 69:5575–5583. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yi TF, Cho SG, Yi ZF, et al: Thymoquinone
inhibits tumor angiogenesis and tumor growth through suppressing
AKT and extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathways.
Mol Cancer Ther. 7:1789–1796. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sethi G, Ahn KS and Aggarwal BB: Targeting
nuclear factor-kappa B activation pathway by thymoquinone: Role in
suppression of antiapoptotic gene products and enhancement of
apoptosis. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1059–1070. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chehl N, Chipitsyna G, Gong QK, Yeo CJ and
Arafat HA: Anti-inflammatory effects of the Nigella sativa
seed extract, thymoquinone, in pancreatic cancer cells. HPB.
11:373–381. 2009.
|
|
15
|
Roepke M, Diestel A, Bajbouj K, et al:
Lack of p53 augments thymoquinone-induced apoptosis and caspase
activation in human osteosarcoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther.
6:160–169. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Al-Romaih K, Somers GR, Bayani J, et al:
Modulation by decitabine of gene expression and growth of
osteosarcoma U2OS cells in vitro and in xenografts: identification
of apoptotic genes as targets for demethylation. Cancer Cell Int.
7:142007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Srinivasula SM and Ashwell JD: IAPs:
what’s in a name? Mol Cell. 30:123–135. 2008.
|
|
18
|
Yang YL and Li XM: The IAP family:
endogenous caspase inhibitors with multiple biological activities.
Cell Res. 10:169–177. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, et al:
Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes
apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell.
102:43–53. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Du CY, Fang M, Li YC, Li L and Wang XD:
Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent
caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell. 102:33–42.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Srinivasula SM, Hegde R, Saleh A, et al: A
conserved XIAP-interaction motif in caspase-9 and Smac/DIABLO
regulates caspase activity and apoptosis. Nature. 410:112–116.
2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bergers G and Benjamin LE: Tumorigenesis
and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:401–410. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cooney MM, van Heeckeren W, Bhakta S,
Ortiz J and Remick SC: Drug insight: vascular disrupting agents and
angiogenesis - novel approaches for drug delivery. Nat Clin Pract
Oncol. 3:682–692. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu HG, Yu LL, Yang YN, et al: Increased
expression of RelA/nuclear factor-kappa B protein correlates with
colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncology. 65:37–45. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Guha S, Krishnan S,
Diagaradjane P, Gelovani J and Aggarwal BB: Curcumin potentiates
antitumor activity of gemcitabine in an orthotopic model of
pancreatic cancer through suppression of proliferation,
angiogenesis, and inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B-regulated
gene products. Cancer Res. 67:3853–3861. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Erdurmus M, Yagci R, Yilmaz B, et al:
Inhibitory effects of topical thymoquinone on corneal
neovascularization. Cornea. 26:715–719. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lamoureux F, Picarda G, Rousseau J, et al:
Therapeutic efficacy of soluble receptor activator of nuclear
factor-kappa B-Fc delivered by nonviral gene transfer in a mouse
model of osteolytic osteosarcoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3389–3398.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Aggarwal BB: Nuclear factor-kappa-B: the
enemy within. Cancer Cell. 6:203–208. 2004.
|
|
29
|
Banerjee S, Zhang YX, Wang ZW, et al: In
vitro and in vivo molecular evidence of genistein action in
augmenting the efficacy of cisplatin in pancreatic cancer. Int J
Cancer. 120:906–917. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Adachi S, Kokura S, Okayama T, et al:
Effect of hyperthermia combined with gemcitabine on apoptotic cell
death in cultured human pancreatic cancer cell lines. Int J
Hyperthermia. 25:210–219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|