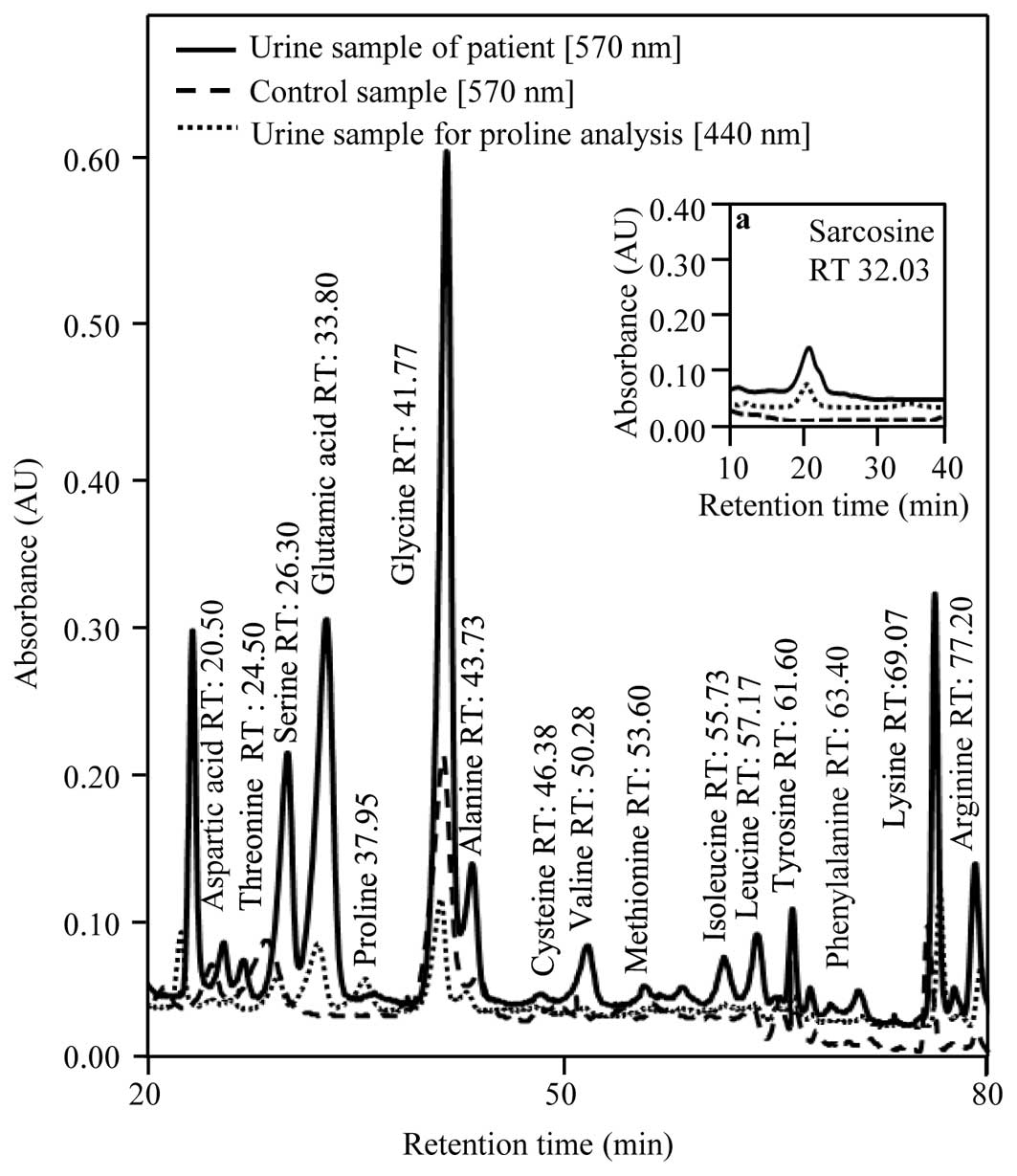
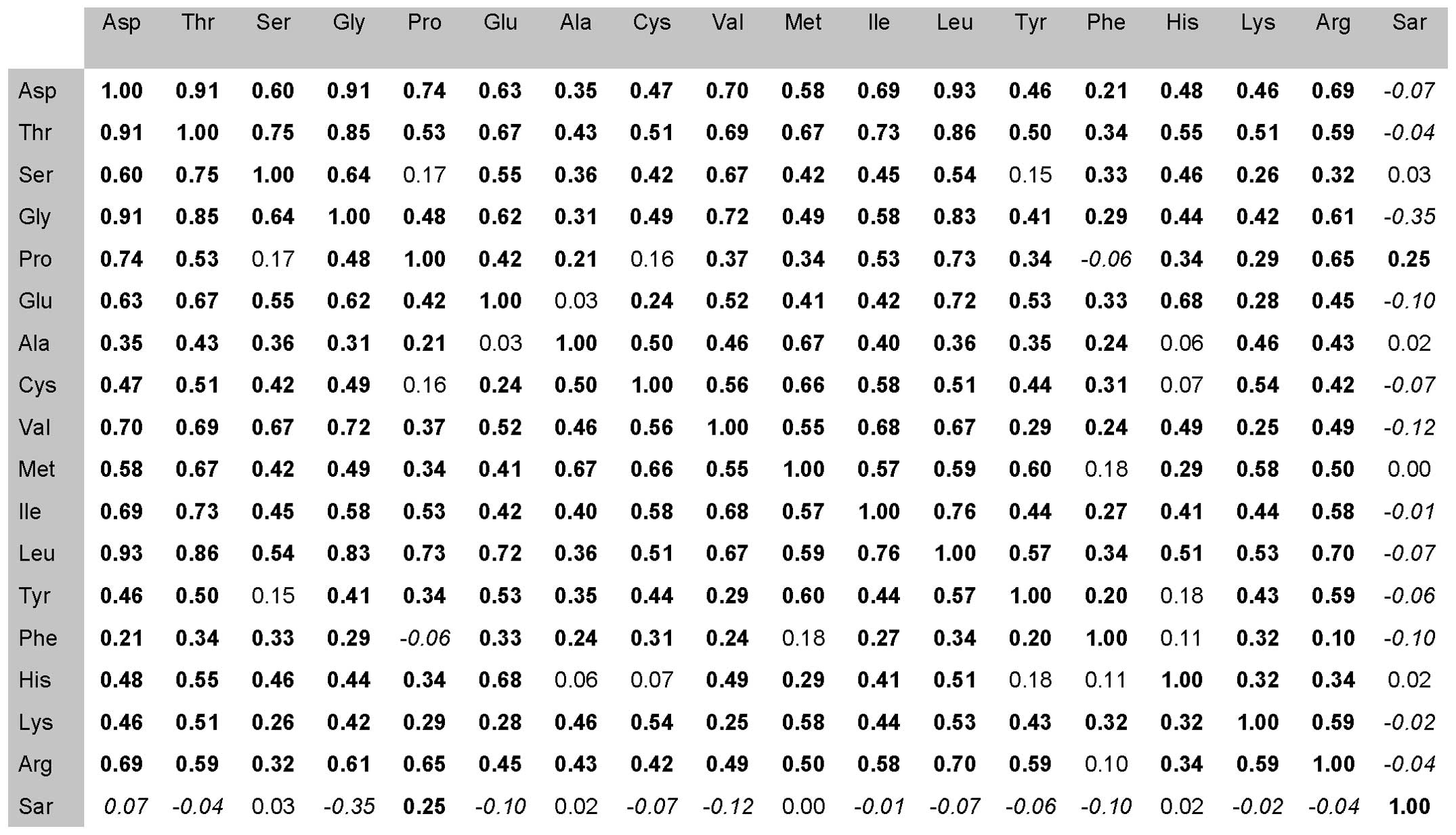
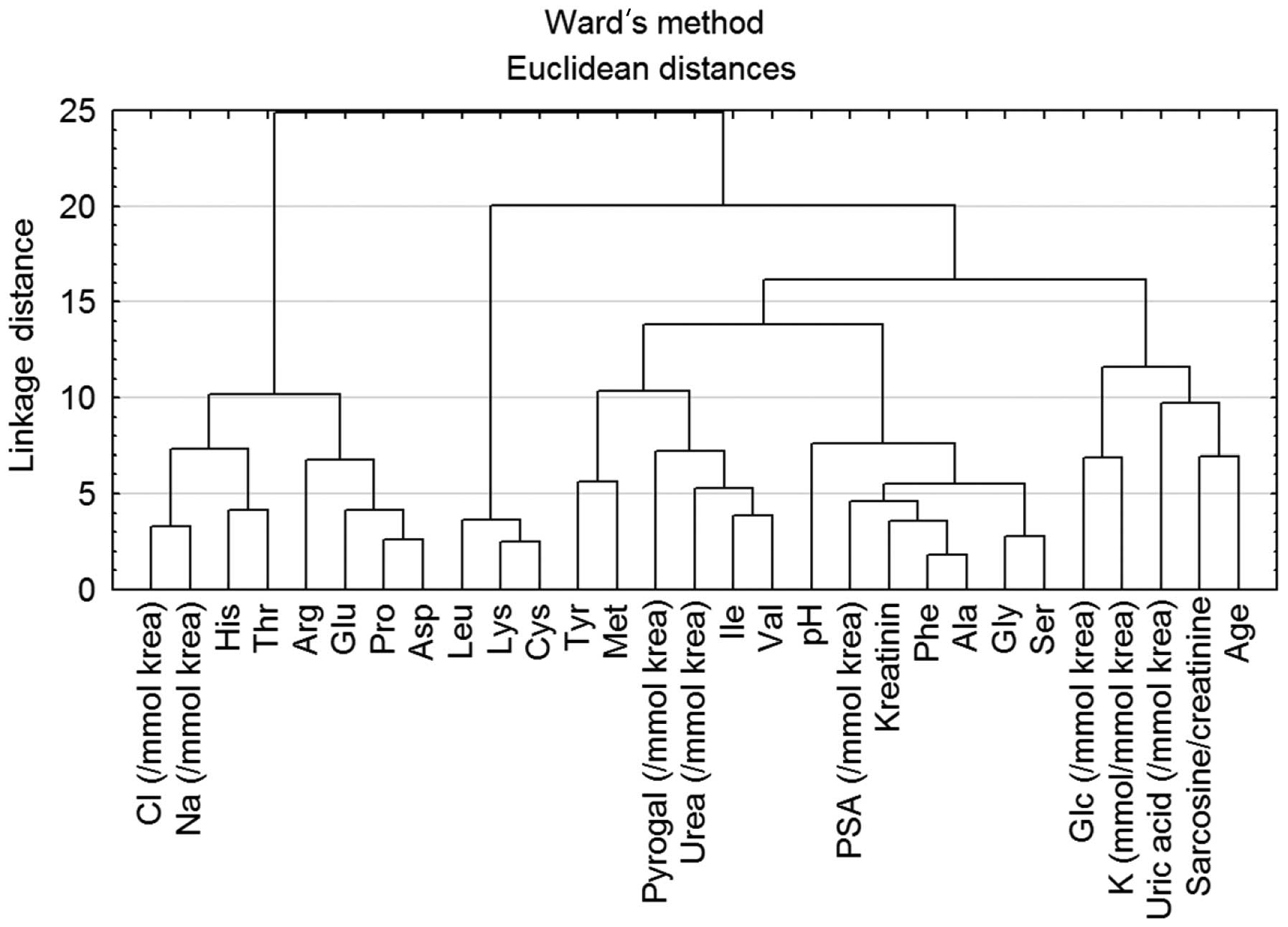
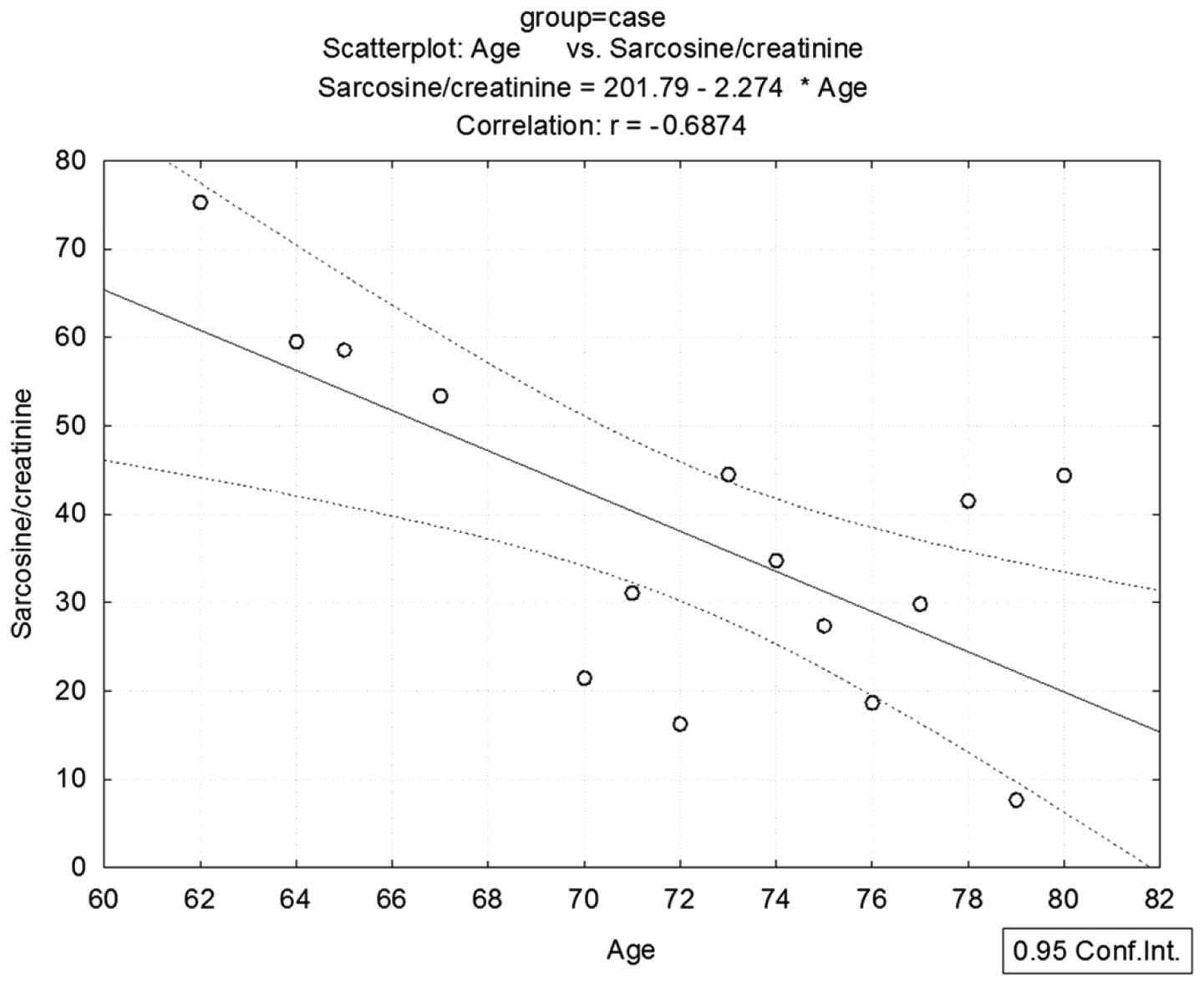
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ding ZH, Wu CJ, Chu GC, et al:
SMAD4-dependent barrier constrains prostate cancer growth and
metastatic progression. Nature. 470:269–273. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Boyle P and Ferlay J: Cancer incidence and
mortality in Europe, 2004. Ann Oncol. 16:481–488. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Armstrong AJ, Eisenberger MA, Halabi S, et
al: Biomarkers in the management and treatment of men with
metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol.
61:549–559. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Prensner JR, Rubin MA, Wei JT and
Chinnaiyan AM: Beyond PSA: the next generation of prostate cancer
biomarkers. Sci Transl Med. 4:1–12. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lattanzi J, McNeely S, Hanlon A, Das I,
Schultheiss TE and Hanks GE: Daily CT localization for correcting
portal errors in the treatment of prostate cancer. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 41:1079–1086. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
van Vugt HA, Roobol MJ, Busstra M, et al:
Compliance with biopsy recommendations of a prostate cancer risk
calculator. BJU Int. 109:1480–1488. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schoder H and Larson SM: Positron emission
tomography for prostate, bladder, and renal cancer. Semin Nucl Med.
34:274–292. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fukushima K, Satoh T, Baba S and Yamashita
K: α 1,2-Fucosylated and β-N-acetylgalactosaminylated
prostate-specific antigen as an efficient marker of prostatic
cancer. Glycobiology. 20:452–460. 2010.
|
|
10
|
Page ST, Hirano L, Gilchriest J, et al:
Dutasteride reduces prostate size and prostate-specific antigen in
older hypogonadal men with benign prostatic hyperplasia undergoing
testosterone replacement therapy. J Urol. 186:191–197. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zitka O, Cernei N, Heger Z, et al:
Microfluidic chip coupled with modified paramagnetic particles for
sarcosine isolation in urine. Electrophoresis. 34:2639–2647. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Berger MF, Lawrence MS, Demichelis F, et
al: The genomic complexity of primary human prostate cancer.
Nature. 470:214–220. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cao DL, Ye DW, Zhang HL, Zhu Y, Wang YX
and Yao XD: A multiplex model of combining gene-based,
protein-based, and metabolite-based with positive and negative
markers in urine for the early diagnosis of prostate cancer.
Prostate. 71:700–710. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rigau M, Morote J, Mir MC, et al: PSGR and
PCA3 as biomarkers for the detection of prostate cancer in urine.
Prostate. 70:1760–1767. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Crawford ED, Rove KO, Trabulsi EJ, et al:
Diagnostic performance of PCA3 to detect prostate cancer in men
with increased prostate specific antigen: a prospective study of
1,962 cases. J Urol. 188:1726–1731. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jamaspishvili T, Kral M, Khomeriki I,
Student V, Kolar Z and Bouchal J: Urine markers in monitoring for
prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 13:12–19. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pin E, Fredolini C and Petricoin EF: The
role of proteomics in prostate cancer research: biomarker discovery
and validation. Clin Biochem. 46:524–538. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vesprini D, Liu S and Nam R: Predicting
high risk disease using serum and DNA biomarkers. Curr Opin Urol.
23:252–260. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM, et
al: Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in
prostate cancer progression. Nature. 457:910–914. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cavaliere B, Macchione B, Monteleone M,
Naccarato A, Sindona G and Tagarelli A: Sarcosine as a marker in
prostate cancer progression: a rapid and simple method for its
quantification in human urine by solid-phase microextraction-gas
chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal
Chem. 400:2903–2912. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Petersen LF, Brockton NT, Bakkar A, et al:
Elevated physiological levels of folic acid can increase in
vitro growth and invasiveness of prostate cancer cells. BJU
Int. 109:788–795. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lucarelli G, Fanelli M, Larocca AMV, et
al: Serum sarcosine increases the accuracy of prostate cancer
detection in patients with total serum PSA less than 4.0 ng/ml.
Prostate. 72:1611–1621. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cernei N, Heger Z, Gumulec J, et al:
Sarcosine as a potential prostate cancer biomarker: a review. Int J
Mol Sci. 14:13893–13908. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen JL, Tang HQ, Hu JD, Fan J, Hong J and
Gu JZ: Metabolomics of gastric cancer metastasis detected by gas
chromatography and mass spectrometry. World J Gastroenterol.
16:5874–5880. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hirayama A, Kami K, Sugimoto M, et al:
Quantitative metabolome profiling of colon and stomach cancer
microenvironment by capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass
spectrometry. Cancer Res. 69:4918–4925. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Slupsky CM, Steed H, Wells TH, et al:
Urine metabolite analysis offers potential early diagnosis of
ovarian and breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 16:5835–5841. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim K, Taylor SL, Ganti S, Guo LN, Osier
MV and Weiss RH: Urine metabolomic analysis identifies potential
biomarkers and pathogenic pathways in kidney cancer. OMICS.
15:293–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Phang JM: The regulatory functions of
proline and pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid. Curr Top Cell Regul.
25:91–132. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pandhare J, Cooper SK and Phang JM:
Proline oxidase, a proapoptotic gene, is induced by troglitazone:
evidence for both peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
γ-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Biol Chem.
281:2044–2052. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pandhare J, Donald SP, Cooper SK and Phang
JM: Regulation and function of proline oxidase under nutrient
stress. J Cell Biochem. 107:759–768. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Polyak K, Xia Y, Zweier K, Kinzler W and
Vogelstein B: A model for p53-induced apoptosis. Nature.
389:300–305. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Donald SP, Sun XY, Hu CAA, et al: Proline
oxidase, encoded by p53-induced gene-6, catalyzes the generation of
proline-dependent reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res.
61:1810–1815. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu Y, Borchert GL, Surazynski A, Hu CA
and Phang JM: Proline oxidase activates both intrinsic and
extrinsic pathways for apoptosis: the role of ROS/superoxides, NFAT
and MEK/ERK signaling. Oncogene. 25:5640–5647. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu W, Le A, Hancock C, et al:
Reprogramming of proline and glutamine metabolism contributes to
the proliferative and metabolic responses regulated by oncogenic
transcription factor c-MYC. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:8983–8988.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Phang JM and Liu W: Proline metabolism and
cancer. Front Biosci. 17:1835–1845. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Liu W, Zabirnyk O, Wang H, et al: miR-23b*
targets proline oxidase, a novel tumor suppressor protein in renal
cancer. Oncogene. 29:4914–4924. 2010.
|
|
37
|
Liu Y, Borchert GL, Surazynski A and Phang
JM: Proline oxidase, a p53-induced gene, targets
COX-2/PGE2 signaling to induce apoptosis and inhibit
tumor growth in colorectal cancers. Oncogene. 27:6729–6737. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ianni M, Porcellini E, Carbone I, et al:
Genetic factors regulating inflammation and DNA methylation
associated with prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
16:56–60. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Luka Z, Cerone R, Phillips JA, Mudd SH and
Wagner C: Mutations in human glycine N-methyltransferase give
insights into its role in methionine metabolism. Hum Genet.
110:68–74. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pelzer AE, Volgger H, Bektic J, et al: The
effect of percentage free prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level on
the prostate cancer detection rate in a screening population with
low PSA levels. BJU Int. 96:995–998. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sirovich BE, Schwartz LM and Woloshin S:
Screening men for prostate and colorectal cancer in the United
States: does practice reflect the evidence? JAMA. 289:1414–1420.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Seo HS and Lee NK: Predictors of PSA
screening among men over 40 years of age who had ever heard about
PSA. Korean J Urol. 51:391–397. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Demers LM, Costa L, Chinchilli VM, Gaydos
L, Curley E and Lipton A: Biochemical markers of bone turnover in
patients with metastatic bone disease. Clin Chem. 41:1489–1494.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Catalona WJ, Partin AW, Slawin KM, et al:
Use of the percentage of free prostate-specific antigen to enhance
differentiation of prostate cancer from benign prostatic disease: a
prospective multicenter clinical trial. JAMA. 279:1542–1547. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lapi F, Azoulay L, Niazi T, Yin H,
Benayoun S and Suissa S: Androgen deprivation therapy and risk of
acute kidney injury in patients with prostate cancer. JAMA.
310:289–296. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nariculam J, Murphy DG, Jenner C, et al:
Nephrostomy insertion for patients with bilateral ureteric
obstruction caused by prostate cancer. Br J Radiol. 82:571–576.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Panis C, Victorino VJ, Herrera ACSA, et
al: Differential oxidative status and immune characterization of
the early and advanced stages of human breast cancer. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 133:881–888. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xu XL, Rao GS, Groh V, et al: Major
histocompatibility complex class I-related chain A/B (MICA/B)
expression in tumor tissue and serum of pancreatic cancer: role of
uric acid accumulation in gemcitabine-induced MICA/B expression.
BMC Cancer. 11:1942011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Burgaz S, Torun M, Yardim S, Sargin H,
Orman MN and Ozdamar NY: Serum carotenoids and uric acid levels in
relation to cancer. J Clin Pharm Ther. 21:331–336. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kolonel LN, Yoshizawa C, Nomura AMY and
Stemmermann GN: Relationship of serum uric-acid to cancer
occurrence in a prospective male cohort. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 3:225–228. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Koyner JL, Vaidya VS, Bennett MR, et al:
Urinary biomarkers in the clinical prognosis and early detection of
acute kidney injury. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 5:2154–2165. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chen CH and Lin MS: A novel structural
specific creatinine sensing scheme for the determination of the
urine creatinine. Biosens Bioelectron. 31:90–94. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Elsberger B, Lankston L, McMillan DC,
Underwood MA and Edwards J: Presence of tumoural C-reactive protein
correlates with progressive prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer
Prostatic Dis. 14:122–128. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Grases F, Costa-Bauza A and Prieto RM:
Renal lithiasis and nutrition. Nutr J. 5:1–7. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Montrose DC, Zhou XK, Kopelovich L, et al:
Metabolic profiling, a noninvasive approach for the detection of
experimental colorectal neoplasia. Cancer Prev Res. 5:1358–1367.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Green T, Chen XF, Ryan S, Asch AS and
Ruiz-Echevarria MJ: TMEFF2 and SARDH cooperate to modulate
one-carbon metabolism and invasion of prostate cancer cells.
Prostate. 73:1561–1575. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Khan AP, Rajendiran TM, Ateeq B, et al:
The role of sarcosine metabolism in prostate cancer progression.
Neoplasia. 15:491–501. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Isaacs WB: Inherited susceptibility for
aggressive prostate cancer. Asian J Androl. 14:415–418. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Powell IJ, Bock CH, Ruterbusch JJ and Sakr
W: Evidence supports a faster growth rate and/or earlier
transformation to clinically significant prostate cancer in black
than in white American men, and influences racial progression and
mortality disparity. J Urol. 183:1792–1796. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|