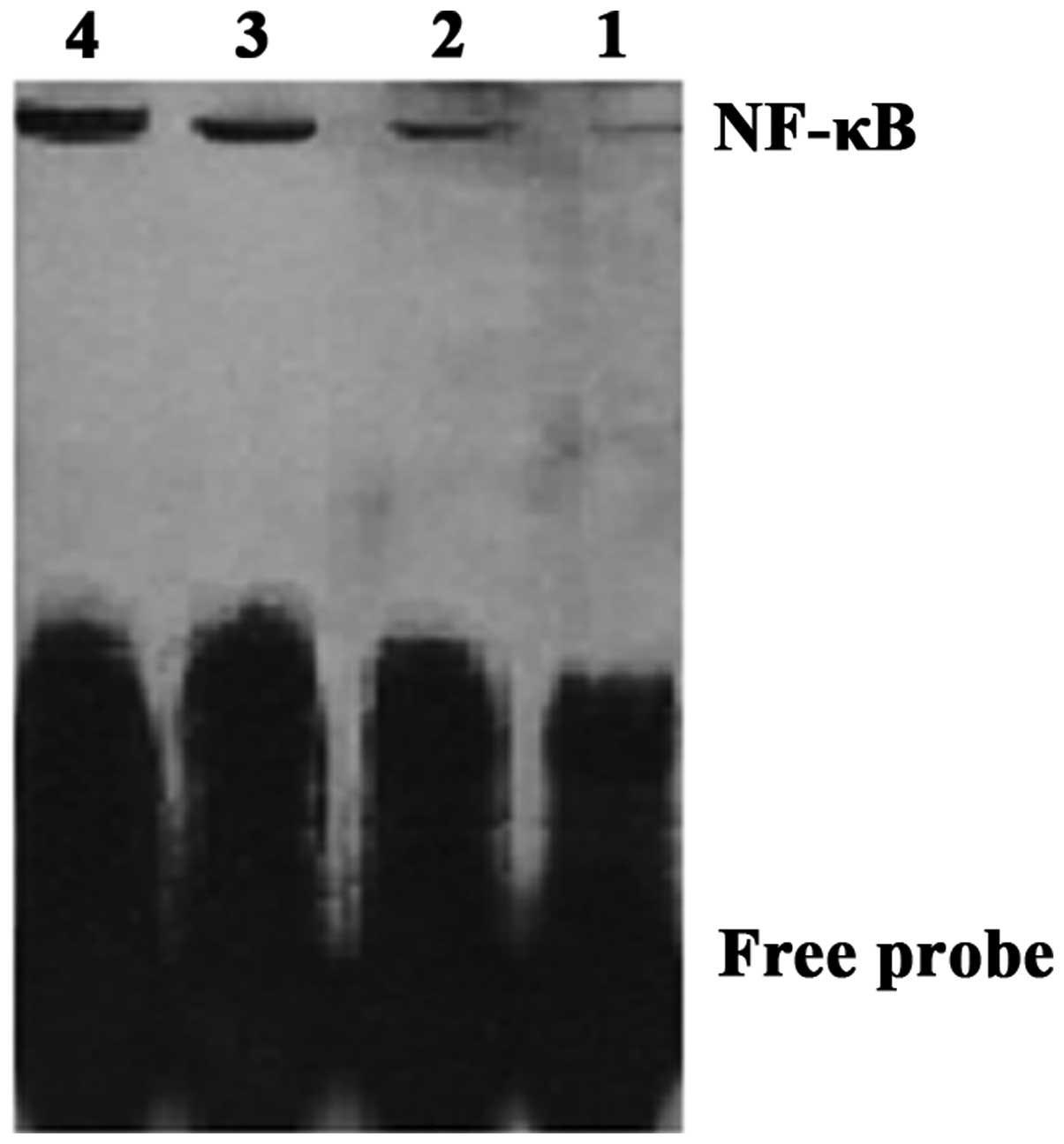
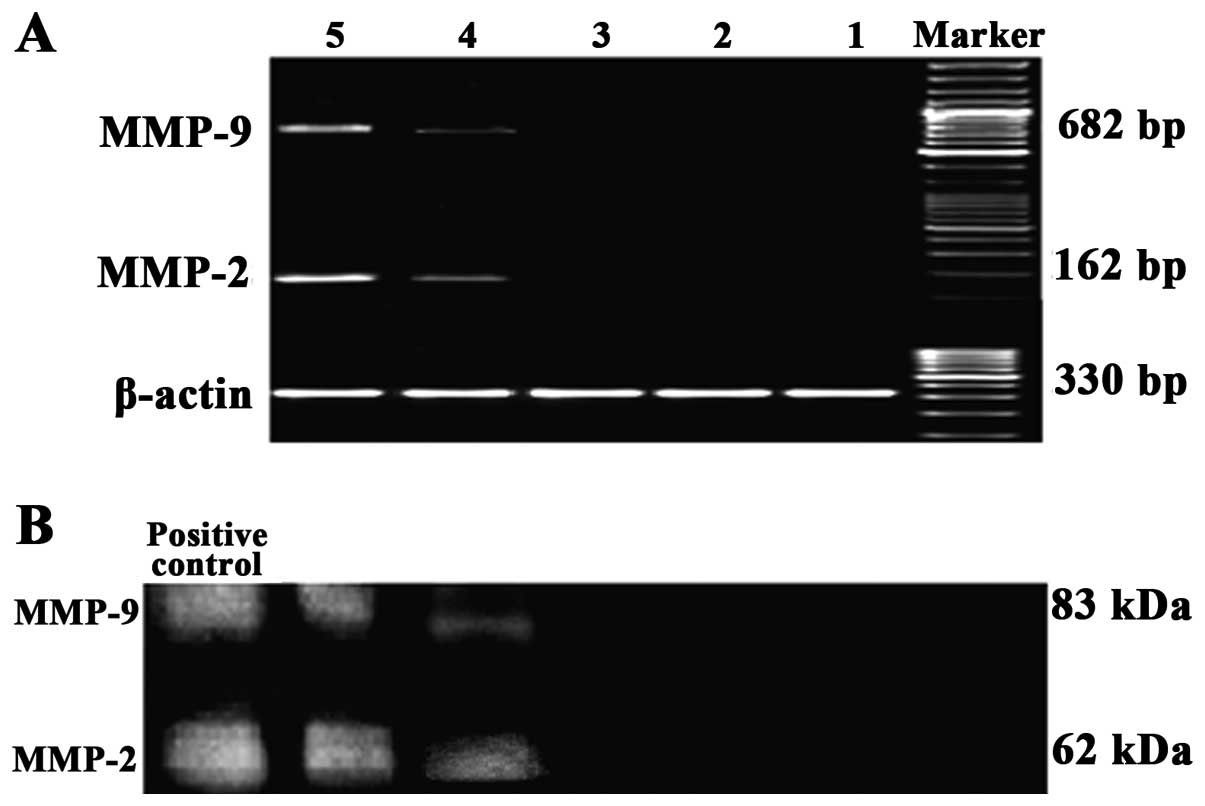
|
1
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
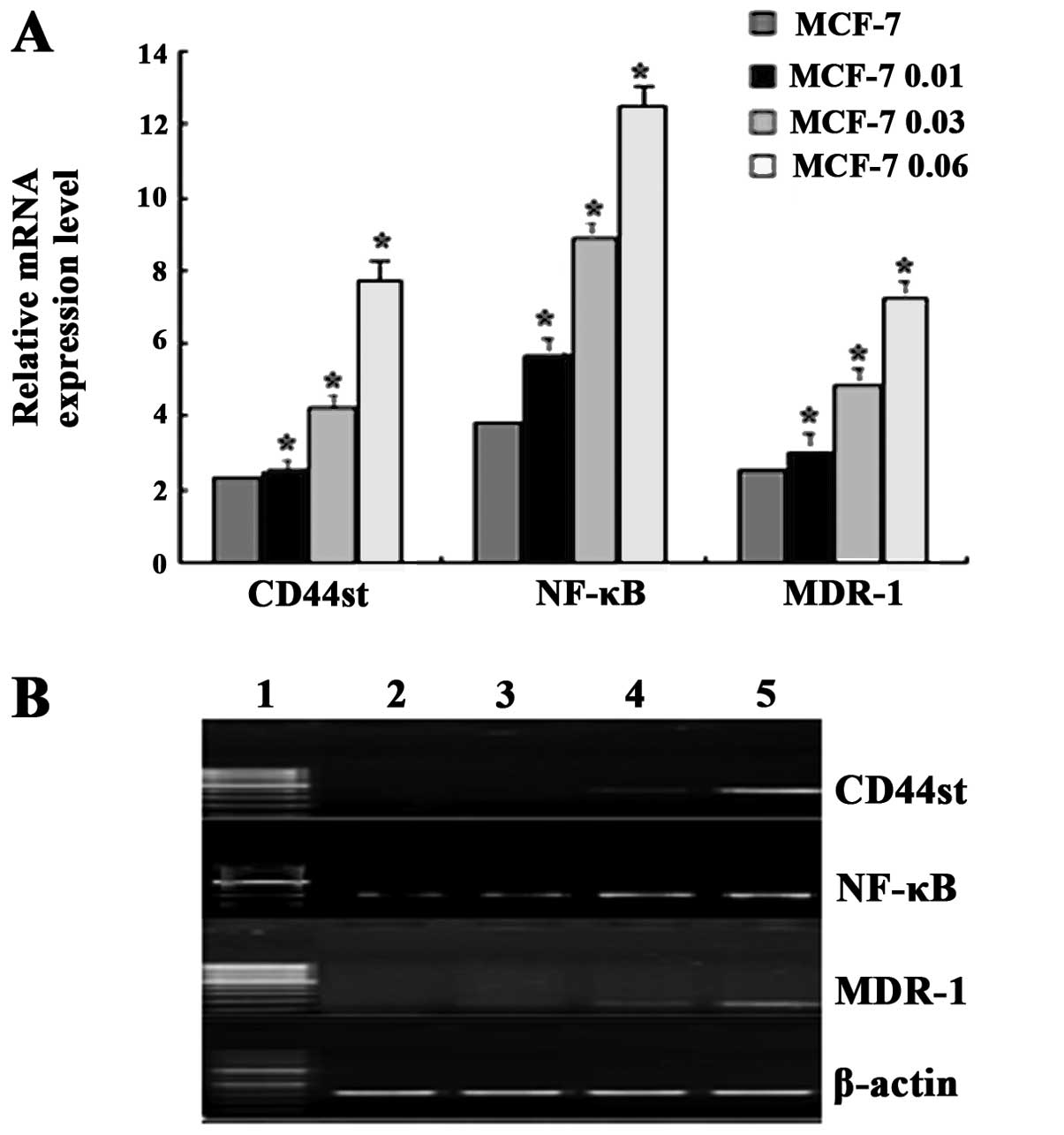
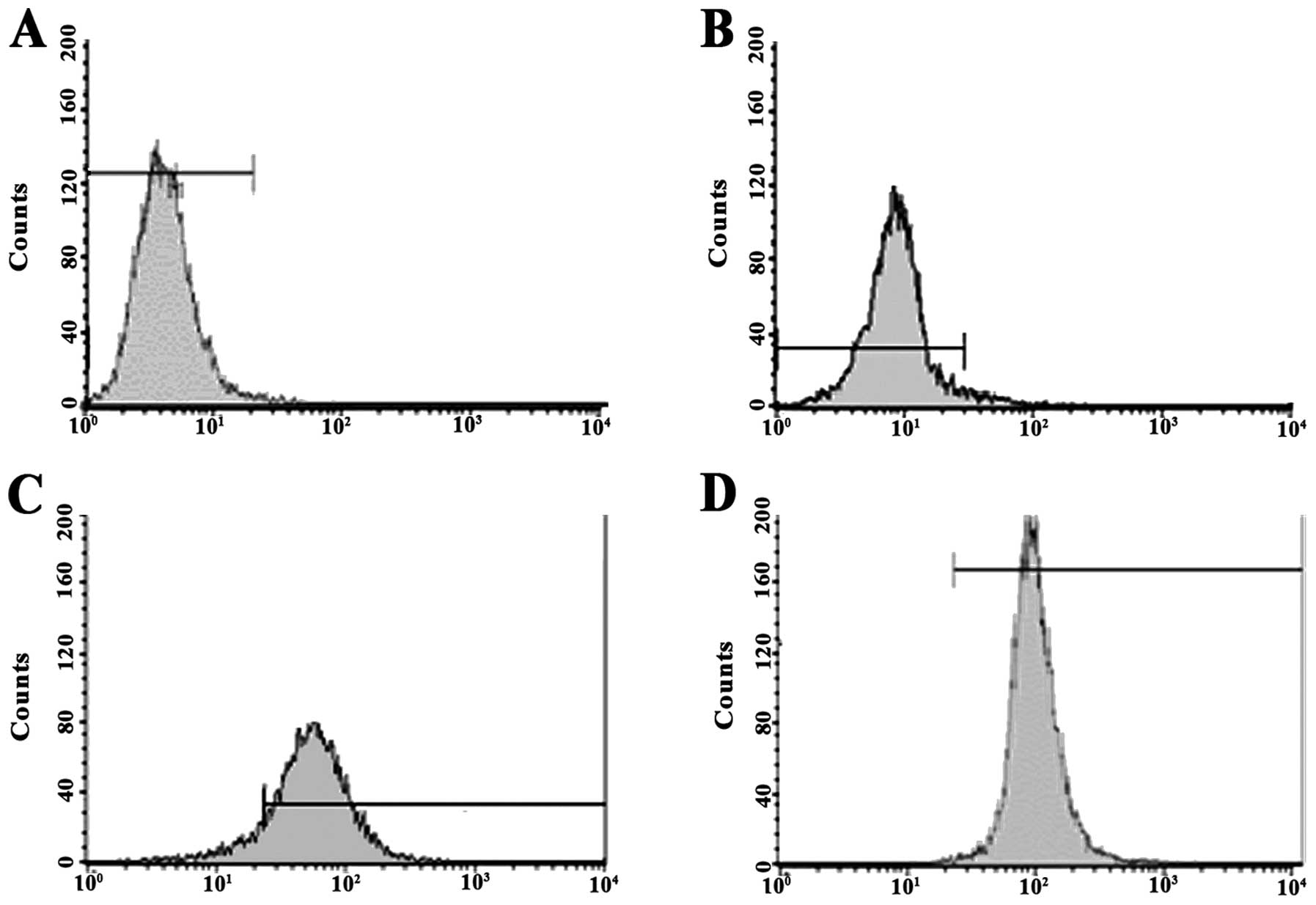
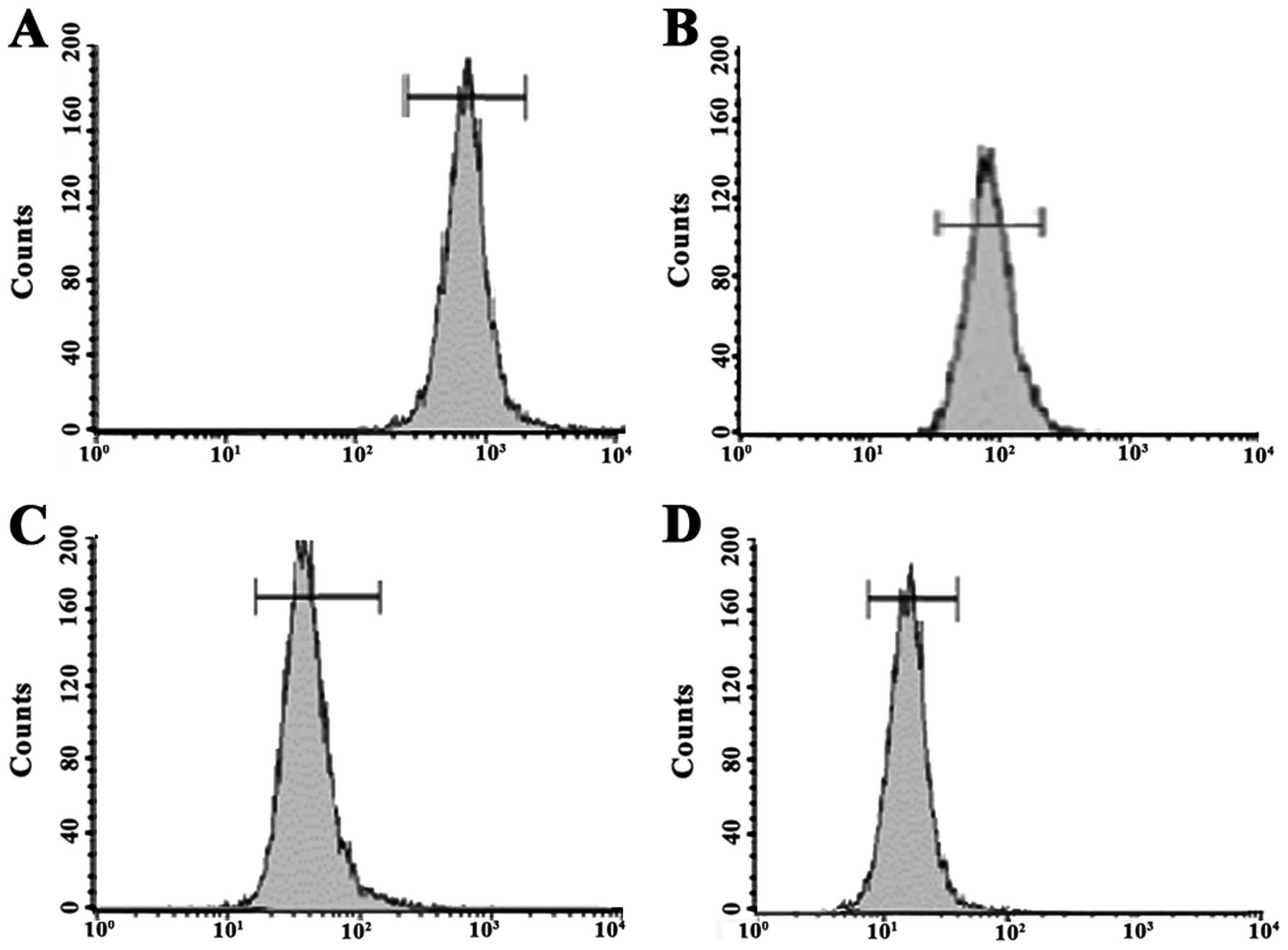
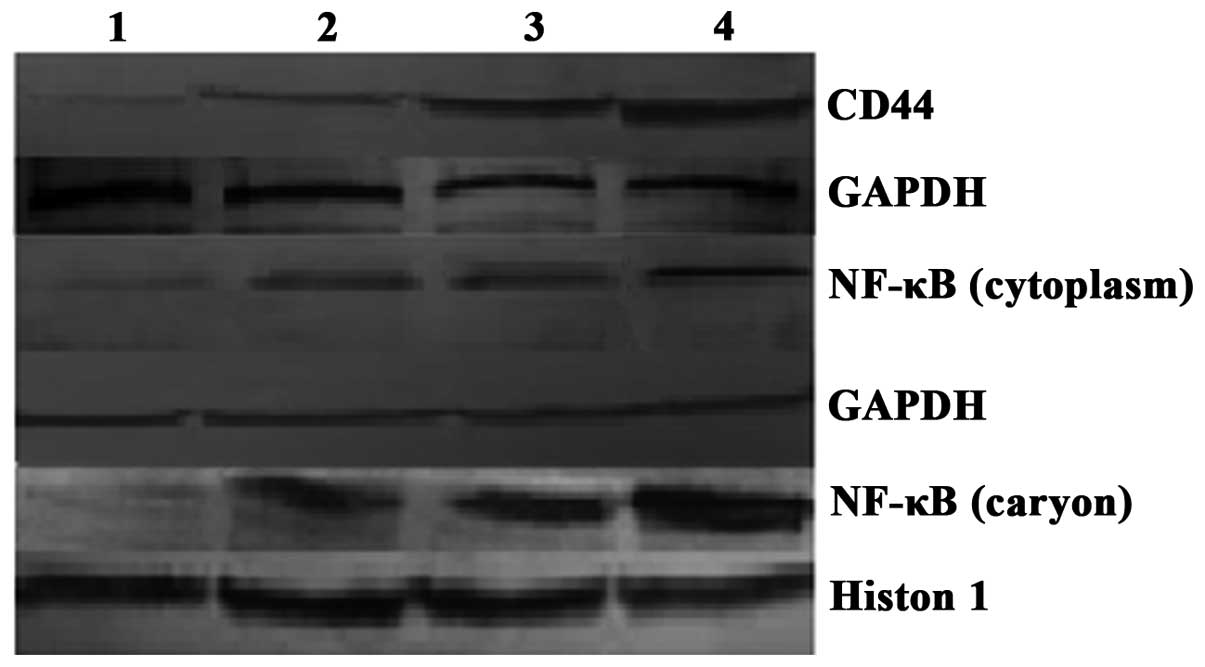
Fang XJ, Jiang H, Zhao XP and Jiang WM:
The role of a new CD44st in increasing the invasion capability of
the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. BMC Cancer. 11:2902011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang J, Lu M, Zhou F, Sun H, Hao G, Wu X
and Wang G: Key role of nuclear factor-κB in the cellular
pharmacokinetics of adriamycin in MCF-7/Adr cells: the potential
mechanism for synergy with 20(S)-ginsenoside Rh2. Drug Metab
Dispos. 40:1900–1908. 2012.
|
|
4
|
Sun J, Yeung CA, Co NN, et al: Clitocine
reversal of P-glycoprotein associated multi-drug resistance through
down-regulation of transcription factor NF-κB in R-HepG2 cell line.
PLoS One. 7:e407202012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xia Q, Wang ZY, Li HQ, et al: Reversion of
p-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in human leukemic cell
line by diallyl trisulfide. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2012:7198052012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Damm S, Koefinger P, Stefan M, et al:
HGF-promoted motility in primary human melanocytes depends on
CD44v6 regulated via NF-kappa B, Egr-1, and C/EBP-beta. J Invest
Dermatol. 130:1893–1903. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu Y, Zhang X, Zhou H, et al: Factor VIIa
regulates the expression of caspase-3, MMP-9, and CD44 in SW620
colon cancer cells involving PAR2/MAPKs/NF-κB signaling pathways.
Cancer Invest. 31:7–16. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bourguignon LY, Peyrollier K, Xia W and
Gilad E: Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction activates stem cell marker
Nanog, Stat-3-mediated MDR1 gene expression, and ankyrin-regulated
multidrug efflux in breast and ovarian tumor cells. J Biol Chem.
283:17635–17651. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bourguignon LY, Spevak CC, Wong G, Xia W
and Gilad E: Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction with protein kinase Cɛ
promotes oncogenic signaling by the stem cell marker Nanog and the
production of microRNA-21, leading to down-regulation of the tumor
suppressor protein PDCD4, anti-apoptosis, and chemotherapy
resistance in breast tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 284:26533–26546.
2009.
|
|
10
|
Fang XJ, Xu WL, Gong JL, Chen C, Fang LL
and Chen QY: CD44 variant increases the invasive ability of human
breast cancer cell line MCF-7 cells. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi.
32:22–28. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Fang XJ, Wu XL, Zhang X, Qian H, Chen C,
Fang LL and Chen QY: Construction of human CD44 eukaryotic
expression vector and its expression in mammary carcinoma cells. J
Jiangsu Univ Med Ed. 19:102–106. 2009.
|
|
12
|
Zou W, Yang H, Hou X, Zhang W, Chen B and
Xin X: Inhibition of CD147 gene expression via RNA interference
reduces tumor cell invasion, tumorigenicity and increases
chemosensitivity to paclitaxel in HO-8910pm cells. Cancer Lett.
248:211–218. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kuang YH, Chen X, Su J, et al: RNA
interference targeting the CD147 induces apoptosis of multi-drug
resistant cancer cells related to XIAP depletion. Cancer Lett.
276:189–195. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li QQ, Wang WJ, Xu JD, Cao XX, Chen Q,
Yang JM and Xu ZD: Up-regulation of CD147 and matrix
metalloproteinase-2, -9 induced by P-glycoprotein substrates in
multidrug resistant breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 98:1767–1774.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Weinstein RS, Jakate SM, Dominguez JM, et
al: Relationship of the expression of the multidrug resistance gene
product (P-glycoprotein) in human colon carcinoma to local tumor
aggressiveness and lymphnode metastasis. Cancer Res. 51:2720–2726.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Radenkovic S, Konjevic G, Jurisic V, et
al: Values of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in tumor tissue of basal-like breast
cancer patients. Cell Biochem Biophys. 68:143–152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kung CI, Chen CY, Yang CC, Lin CY, Chen TH
and Wang HS: Enhanced membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase
expression by hyaluronan oligosaccharides in breast cancer cells
facilitates CD44 cleavage and tumor cell migration. Oncol Rep.
28:1808–1814. 2012.
|
|
18
|
Golshani R, Lopez L, Estrella V, Kramer M,
Iida N and Lokeshwar VB: Hyaluronic acid synthase-1 expression
regulates bladder cancer growth, invasion, and angiogenesis through
CD44. Cancer Res. 68:483–491. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu R, Wang X, Chen GY, Dalerba P, Gurney
A, Hoey T, Sherlock G, Lewicki J, Shedden K and Clarke MF: The
prognostic role of a gene signature from tumorigenic breast-cancer
cells. N Engl J Med. 356:217–226. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Charafe-Jauffret E, Ginestier C and
Birnbaum D: Breast cancer stem cells: tools and models to rely on.
BMC Cancer. 9:2022009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park D, Kim Y, Kim H, et al: Hyaluronic
acid promotes angiogenesis by inducing RHAMM-TGFβ receptor
interaction via CD44-PKCδ. Mol Cells. 33:563–574. 2012.
|
|
22
|
Lin Y, Zhong Y, Guan H, Zhang X and Sun Q:
CD44+/CD24− phenotype contributes to
malignant relapse following surgical resection and chemotherapy in
patients with invasive ductal carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
31:592012.
|
|
23
|
Bourquiqnon LY: Hyaluronan-mediated CD44
activation of RhoGTPase signaling and cytoskeleton function
promotes tumor progression. Semin Cancer Biol. 18:251–259. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Palafox M, Ferrer I, Pellegrini P, Vila S,
Hernandez-Ortega S, Urruticoechea A, Climent F, Soler MT, Muñoz P,
Viñals F, Tometsko M, Branstetter D, Dougall WC and González-Suárez
E: RANK induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness in
human mammary epithelial cells and promotes tumorigenesis and
metastasis. Cancer Res. 72:2879–2888. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Park SY, Lee HE, Li H, Shipitsin M, Gelman
R and Polyak K: Heterogeneity for stem cell-related markers
according to tumor subtype and histologic stage in breast cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 16:876–887. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ricardo S, Vieira AF, Gerhard R, Leitão D,
Pinto R, Cameselle-Teijeiro JF, Milanezi F, Schmitt F and Paredes
J: Breast cancer stem cell markers CD44, CD24 and ALDH1: expression
distribution within intrinsic molecular subtype. J Clin Pathol.
64:937–946. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gong JL, Xu WL, Li J, Yang J, Wu XJ and
Chen QY: Expression of the new CD44 variant (CD44v17) and its
clinical significance in breast cancer tissues. J Jiangsu Univ Med
Ed. 20:248–252. 2010.
|