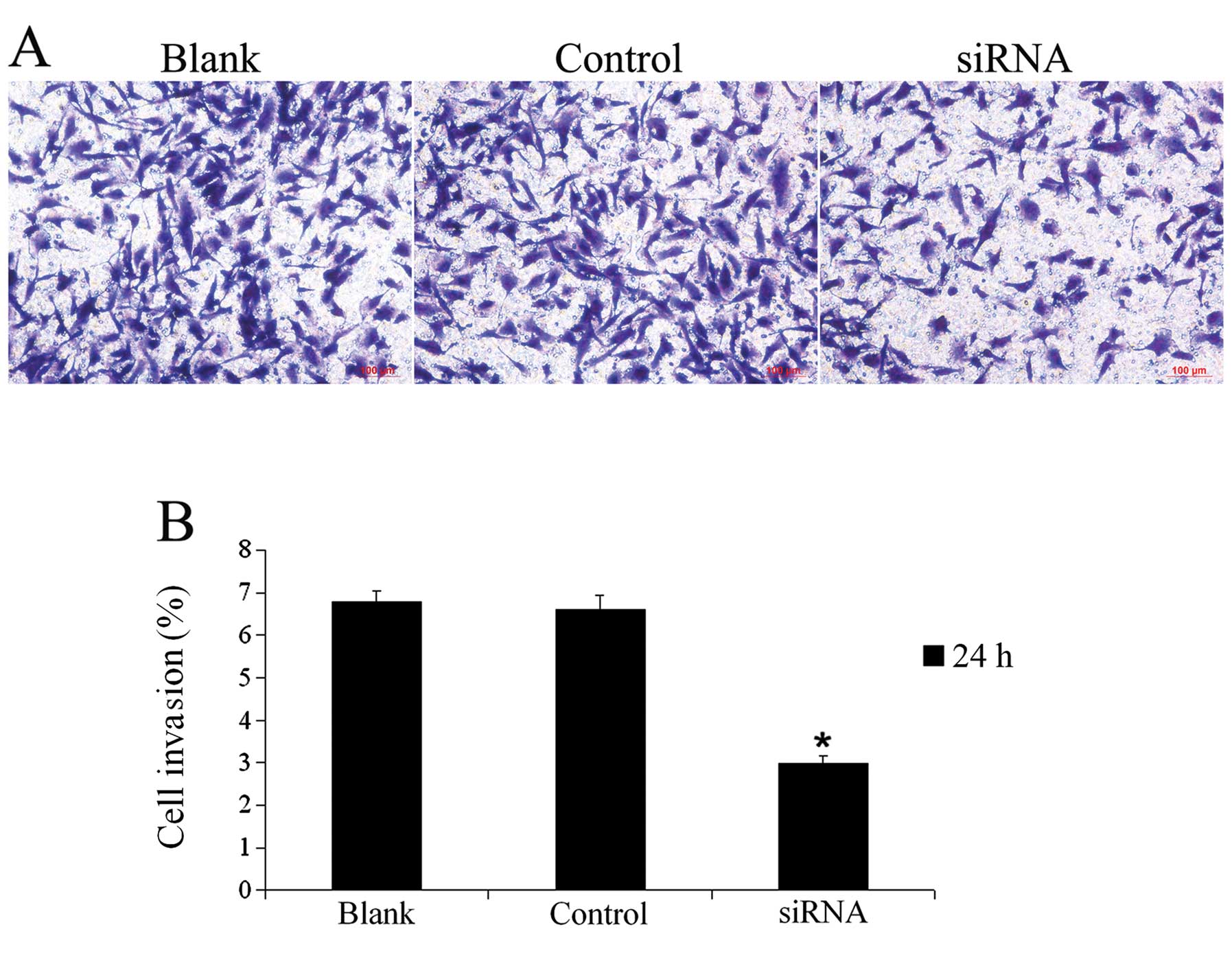
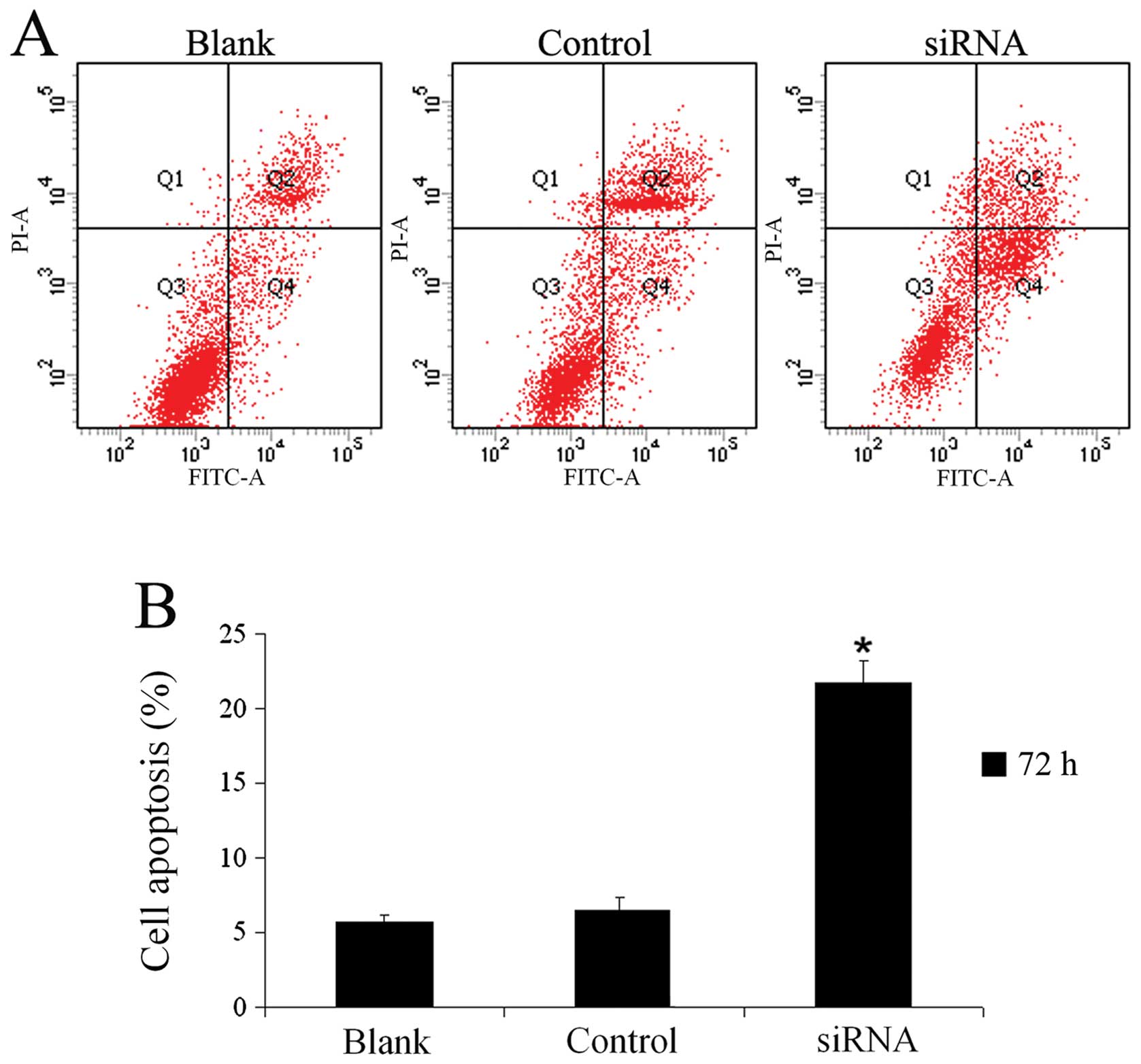
|
1
|
Binello E and Germano IM: Targeting glioma
stem cells: a novel framework for brain tumors. Cancer Sci.
102:1958–1966. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Diss JK, Fraser SP and Djamgoz MB:
Voltage-gated Na+ channels: multiplicity of expression,
plasticity, functional implications and pathophysiological aspects.
Eur Biophys J. 33:180–193. 2004.
|
|
3
|
Monk M and Holding C: Human embryonic
genes re-expressed in cancer cells. Oncogene. 20:8085–8091. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kunzelmann K: Ion channels and cancer. J
Membr Biol. 205:159–173. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
McFerrin MB and Sontheimer H: A role for
ion channels in glioma cell invasion. Neuron Glia Biol. 2:39–49.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brackenbury WJ, Djamgoz MB and Isom LL: An
emerging role for voltage-gated Na+ channels in cellular
migration: regulation of central nervous system development and
potentiation of invasive cancers. Neuroscientist. 14:571–583.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang J, Ou SW, Wang YJ, et al: New
variants of Nav1.5/SCN5A encode Na+ channels in the
brain. J Neurogenet. 22:57–75. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ou SW, Kameyama A, Hao LY, et al:
Tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ channels in human
neuroblastoma cells are encoded by new variants of Nav1.5/SCN5A.
Eur J Neurosci. 22:793–801. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang J, Ou SW, Wang YJ, Kameyama M,
Kameyama A and Zong ZH: Analysis of four novel variants of
Nav1.5/SCN5A cloned from the brain. Neurosci Res.
64:339–347. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fraser SP, Diss JK, Lloyd LJ, et al:
T-lymphocyte invasiveness: control by voltage-gated Na+
channel activity. FEBS Lett. 569:191–194. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fraser SP, Diss JK, Chioni AM, et al:
Voltage-gated sodium channel expression and potentiation of human
breast cancer metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 11:5381–5389. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Brackenbury WJ, Chioni AM, Diss JK and
Djamgoz MB: The neonatal splice variant of Nav1.5 potentiates in
vitro invasive behaviour of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 101:149–160. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qiu B, Sun X, Zhang D, Wang Y, Tao J and
Ou S: TRAIL and paclitaxel synergize to kill U87 cells and
U87-derived stem-like cells in vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 13:9142–9156.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yan X, Liang H, Deng T, et al: The
identification of novel targets of miR-16 and characterization of
their biological functions in cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 12:922013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Han G, Zhao W, Wang L, et al: Leptin
enhances the invasive ability of glioma stem-like cells depending
on leptin receptor expression. Brain Res. 1543:1–8. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Murphy KA, Erickson JR, Johnson CS, et al:
CD8+ T cell-independent tumor regression induced by
Fc-OX40L and therapeutic vaccination in a mouse model of glioma. J
Immunol. 192:224–233. 2014.
|
|
17
|
Ning J, Wakimoto H and Rabkin SD:
Immunovirotherapy for glioblastoma. Cell Cycle. 13:175–176. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
van Gool S: Immunotherapy for high-grade
glioma: how to go beyond Phase I/II clinical trials. Immunotherapy.
5:1043–1046. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kawaguchi A, Asano H, Matsushima K, Wada
T, Yoshida S and Ichida S: Enhancement of sodium current in
NG108-15 cells during neural differentiation is mainly due to an
increase in NaV1.7 expression. Neurochem Res.
32:1469–1475. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ross SB, Fuller CM, Bubien JK and Benos
DJ: Amiloride-sensitive Na+ channels contribute to
regulatory volume increases in human glioma cells. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 293:C1181–C1185. 2007.
|
|
21
|
Weiss RE and Sidell N: Sodium currents
during differentiation in a human neuroblastoma cell line. J Gen
Physiol. 97:521–539. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Olsen ML, Schade S, Lyons SA, Amaral MD
and Sontheimer H: Expression of voltage-gated chloride channels in
human glioma cells. J Neurosci. 23:5572–5582. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ducret T, Vacher AM and Vacher P:
Voltage-dependent ionic conductances in the human malignant
astrocytoma cell line U87-MG. Mol Membr Biol. 20:329–343. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vila-Carriles WH, Kovacs GG, Jovov B, et
al: Surface expression of ASIC2 inhibits the amiloride-sensitive
current and migration of glioma cells. J Biol Chem.
281:19220–19232. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang WX and Ji YH: Scorpion venom induces
glioma cell apoptosis in vivo and inhibits glioma tumor growth in
vitro. J Neurooncol. 73:1–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Onganer PU and Djamgoz MB: Small-cell lung
cancer (human): potentiation of endocytic membrane activity by
voltage-gated Na+ channel expression in vitro. J Membr
Biol. 204:67–75. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mycielska ME, Fraser SP, Szatkowski M and
Djamgoz MB: Contribution of functional voltage-gated Na+
channel expression to cell behaviors involved in the metastatic
cascade in rat prostate cancer: II. Secretory membrane activity. J
Cell Physiol. 195:461–469. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ren CT, Li DM, Ou SW, et al: Cloning and
expression of the two new variants of Nav1.5/SCN5A in rat brain.
Mol Cell Biochem. 365:139–148. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Catterall WA: From ionic currents to
molecular mechanisms: the structure and function of voltage-gated
sodium channels. Neuron. 26:13–25. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Roger S, Besson P and Le Guennec JY:
Involvement of a novel fast inward sodium current in the invasion
capacity of a breast cancer cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1616:107–111. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Roger S, Rollin J, Barascu A, et al:
Voltage-gated sodium channels potentiate the invasive capacities of
human non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 39:774–786. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
House CD, Vaske CJ, Schwartz AM, et al:
Voltage-gated Na+ channel SCN5A is a key regulator of a
gene transcriptional network that controls colon cancer invasion.
Cancer Res. 70:6957–6967. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gao R, Shen Y, Cai J, Lei M and Wang Z:
Expression of voltage-gated sodium channel α subunit in human
ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 23:1293–1299. 2010.
|
|
34
|
Diaz D, Delgadillo DM, Hernández-Gallegos
E, et al: Functional expression of voltage-gated sodium channels in
primary cultures of human cervical cancer. J Cell Physiol.
210:469–478. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Diss JK, Stewart D, Pani F, et al: A
potential novel marker for human prostate cancer: voltage-gated
sodium channel expression in vivo. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
8:266–273. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang M, Kozminski DJ, Wold LA, et al:
Therapeutic potential for phenytoin: targeting Nav1.5
sodium channels to reduce migration and invasion in metastatic
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 134:603–615.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Onkal R, Mattis JH, Fraser SP, et al:
Alternative splicing of Nav1.5: an electrophysiological comparison
of ‘neonatal’ and ‘adult’ isoforms and critical involvement of a
lysine residue. J Cell Physiol. 216:716–726. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Aman TK, Grieco-Calub TM, Chen C, et al:
Regulation of persistent Na current by interactions between β
subunits of voltage-gated Na channels. J Neurosci. 29:2027–2042.
2009.
|
|
39
|
Leterrier C, Brachet A, Fache MP and
Dargent B: Voltage-gated sodium channel organization in neurons:
protein interactions and trafficking pathways. Neurosci Lett.
486:92–100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Corry B and Thomas M: Mechanism of ion
permeation and selectivity in a voltage gated sodium channel. J Am
Chem Soc. 134:1840–1846. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chioni AM, Shao D, Grose R and Djamgoz MB:
Protein kinase A and regulation of neonatal Nav1.5 expression in
human breast cancer cells: activity-dependent positive feedback and
cellular migration. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 42:346–358. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Brackenbury WJ: Voltage-gated sodium
channels and metastatic disease. Channels. 6:352–361. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Abdul M and Hoosein N: Voltage-gated
potassium ion channels in colon cancer. Oncol Rep. 9:961–964.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Andrikopoulos P, Fraser SP, Patterson L,
et al: Angiogenic functions of voltage-gated Na+
channels in human endothelial cells: modulation of vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling. J Biol Chem.
286:16846–16860. 2011.
|
|
45
|
Fraser SP, Grimes JA and Djamgoz MB:
Effects of voltage-gated ion channel modulators on rat prostatic
cancer cell proliferation: comparison of strongly and weakly
metastatic cell lines. Prostate. 44:61–76. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|