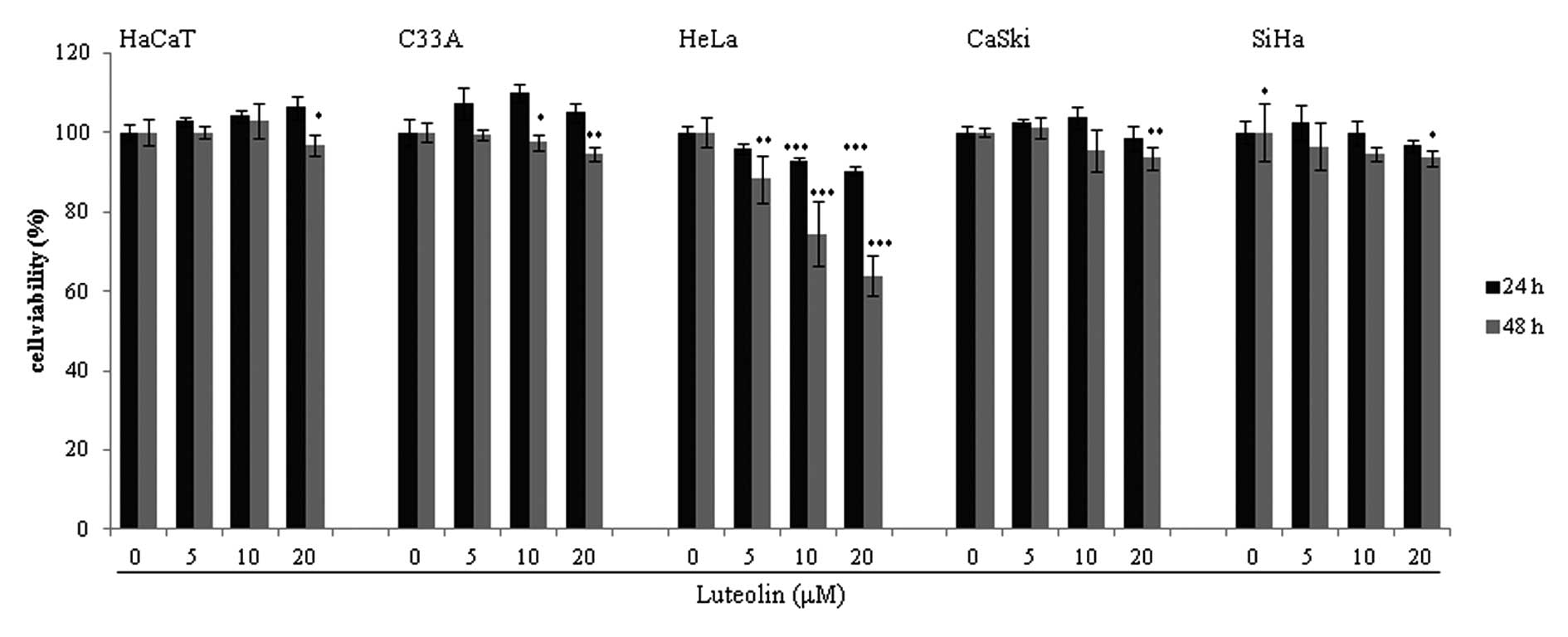
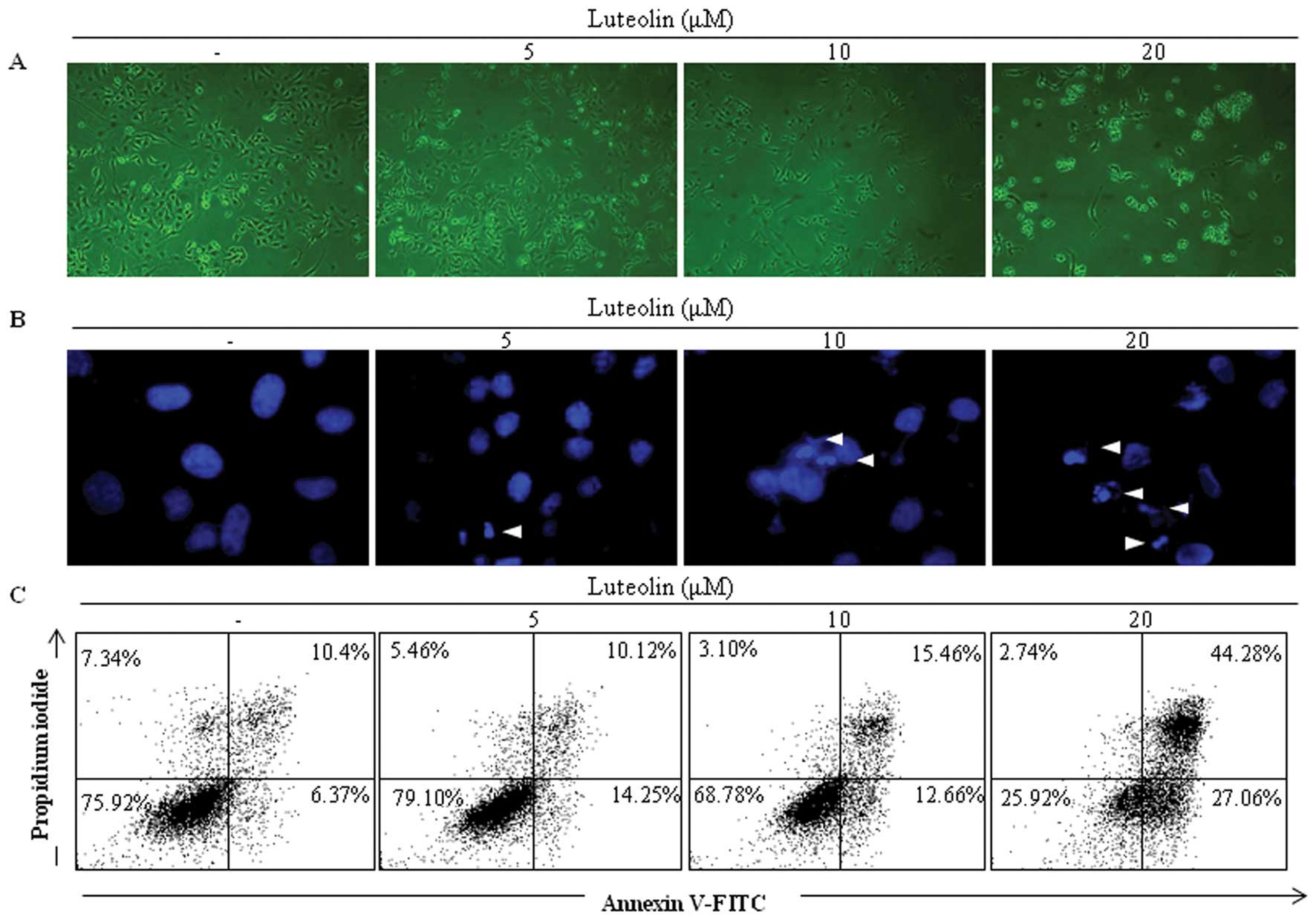
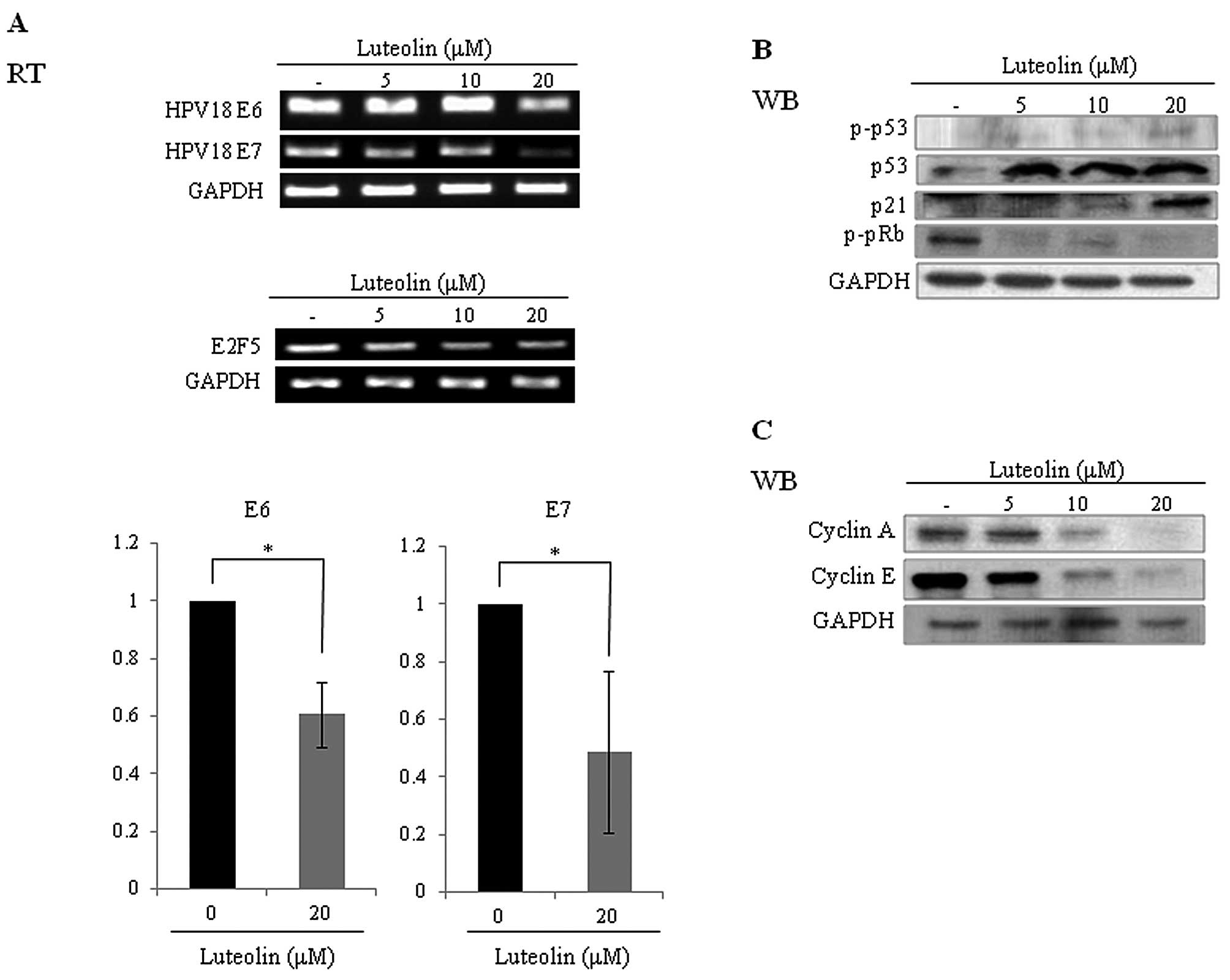
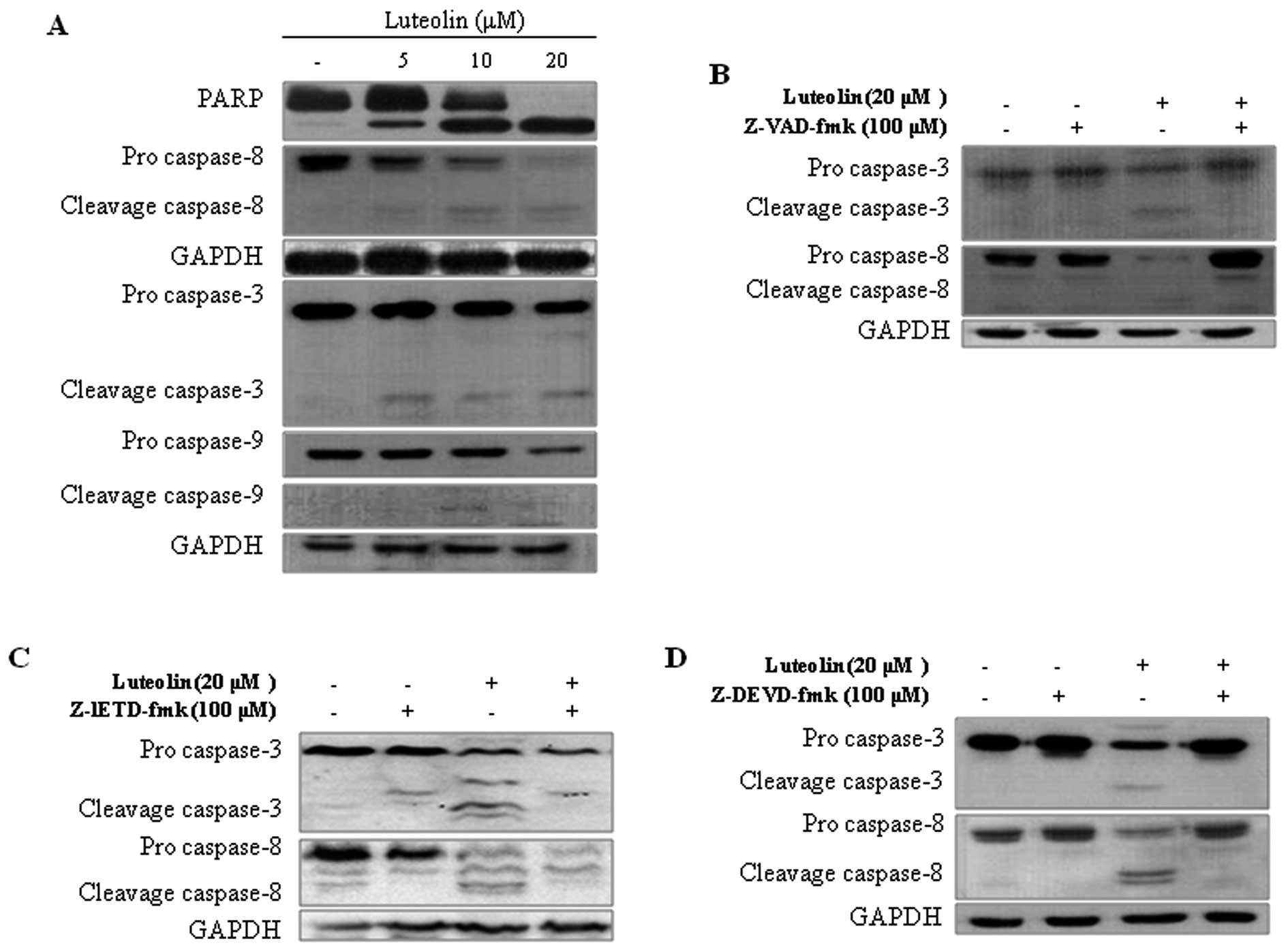
|
1
|
Seelinger G, Merfort I, Woelfle U and
Schempp CM: Anti-carcinogenic effects of the flavonoid luteolin.
Molecules. 13:2628–2651. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Birt DF, Hendrich S and Wang W: Dietary
agents in cancer prevention: flavonoids and isoflavonoids.
Pharmacol Ther. 90:157–177. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ren W, Qiao Z, Wang H, Zhu L and Zhang L:
Flavonoids: promising anticancer agents. Med Res Rev. 23:519–534.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hoensch H and Oertel R: Anti-inflammatory
effects of tea-flavonoids. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 137:2738–2740.
2012.(In German).
|
|
5
|
Ju HK, Lee HW, Chung KS, et al:
Standardized flavonoid-rich fraction of Artemisia princeps
Pampanini cv. Sajabal induces apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway
in human cervical cancer HeLa cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 141:460–468.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Munagala R, Kausar H, Munjal C and Gupta
RC: Withaferin A induces p53-dependent apoptosis by repression of
HPV oncogenes and upregulation of tumor suppressor proteins in
human cervical cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 32:1697–1705. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stern PL, van der Burg SH, Hampson IN, et
al: Therapy of human papillomavirus-related disease. Vaccine.
30(Suppl 5): F71–F82. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Grabowska AK and Riemer AB: The invisible
enemy - how human papillomaviruses avoid recognition and clearance
by the host immune system. Open Virol J. 6:249–256. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Teissier S, Pang CL and Thierry F: The
E2F5 repressor is an activator of E6/E7 transcription and of the
S-phase entry in HPV18-associated cells. Oncogene. 29:5061–5070.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Doorbar J, Quint W, Banks L, et al: The
biology and life-cycle of human papillomaviruses. Vaccine. 30(Suppl
5): F55–F70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Adhim Z, Otsuki N, Kitamoto J, et al: Gene
silencing with siRNA targeting E6/E7 as a therapeutic intervention
against head and neck cancer-containing HPV16 cell lines. Acta
Otolaryngol. 133:761–771. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jonson AL, Rogers LM, Ramakrishnan S and
Downs LS Jr: Gene silencing with siRNA targeting E6/E7 as a
therapeutic intervention in a mouse model of cervical cancer.
Gynecol Oncol. 111:356–364. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Manzo-Merino J, Thomas M, Fuentes-Gonzalez
AM, Lizano M and Banks L: HPV E6 oncoprotein as a potential
therapeutic target in HPV related cancers. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 17:1357–1368. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bosch FX, Broker TR, Forman D, et al:
Comprehensive control of human papillomavirus infections and
related diseases. Vaccine. 31(Suppl 7): H1–H31. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Walker NI, Harmon BV, Gobé GC and Kerr JF:
Patterns of cell death. Methods Achiev Exp Pathol. 13:18–54.
1988.
|
|
16
|
Bak YS, Kim HJ, Kang JW, et al: A
synthetic naringenin derivative,
5-hydroxy-7,4′-diacetyloxyflavanone-N-phenyl hydrazone (N101-43),
induces apoptosis through up-regulation of Fas/FasL expression and
inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling pathways in non-small-cell lung
cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem. 59:10286–10297. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
von Haefen C, Wieder T, Essmann F,
Schulze-Osthoff K, Dorken B and Daniel PT: Paclitaxel-induced
apoptosis in BJAB cells proceeds via a death receptor-independent,
caspases-3/-8-driven mitochondrial amplification loop. Oncogene.
22:2236–2247. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chung KS, Choi JH, Back NI, et al:
Eupafolin, a flavonoid isolated from Artemisia princeps,
induced apoptosis in human cervical adenocarcinoma HeLa cells. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 54:1318–1328. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Franklin JL: Redox regulation of the
intrinsic pathway in neuronal apoptosis. Antioxid Redox Signal.
14:1437–1448. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tan S, de Vries EG, van der Zee AG and de
Jong S: Anticancer drugs aimed at E6 and E7 activity in
HPV-positive cervical cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 12:170–184.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cory AH, Owen TC, Barltrop JA and Cory JG:
Use of an aqueous soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell
growth assays in culture. Cancer Commun. 3:207–212. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Daxhelet GA, Coene MM, Hoet PP and Cocito
CG: Spectrofluorometry of dyes with DNAs of different base
composition and conformation. Anal Biochem. 179:401–403. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H and
Reutelingsperger C: A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric
detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells
using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J Immunol Methods. 184:39–51.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Smiley ST, Reers M, Mottola-Hartshorn C,
et al: Intracellular heterogeneity in mitochondrial membrane
potentials revealed by a J-aggregate-forming lipophilic cation
JC-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 88:3671–3675. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Milde-Langosch K and Riethdorf S: Role of
cell-cycle regulatory proteins in gynecological cancer. J Cell
Physiol. 196:224–244. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yamamoto M, Yoshida M, Ono K, et al:
Effect of tumor suppressors on cell cycle-regulatory genes: RB
suppresses p34cdc2 expression and normal p53 suppresses cyclin A
expression. Exp Cell Res. 210:94–101. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jin CY, Moon DO, Lee JD, et al:
Sulforaphane sensitizes tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis through downregulation
of ERK and Akt in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Carcinogenesis.
28:1058–1066. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Moody CA and Laimins LA: Human
papillomavirus oncoproteins: pathways to transformation. Nat Rev
Cancer. 10:550–560. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bak Y, Ham S, Baatartsogt O, et al: A1E
inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in NCI-H460 lung
cancer cells via extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. Mol Biol Rep.
40:4507–4519. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Doorbar J: Molecular biology of human
papillomavirus infection and cervical cancer. Clin Sci.
110:525–541. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Horinaka M, Yoshida T, Shiraishi T, et al:
Luteolin induces apoptosis via death receptor 5 upregulation in
human malignant tumor cells. Oncogene. 24:7180–7189. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao J, Chen X, Lin W, et al: Total
alkaloids of Rubus aleaefolius Poir inhibit hepatocellular
carcinoma growth in vivo and in vitro via activation
of mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 42:971–978.
2013.
|