Introduction
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) accounts for
approximately 80% of acute leukemia cases with a median age of 67
years (1). Its incidence is
expected to increase with the improvement in life expectancy. In
AML patients younger than 60 years, the clinical management is
based on high-dose chemotherapy. However, in the majority of AML
patients older than 60 years, such chemotherapy is associated with
high mortality. Thus, the development of novel and effective
anti-AML therapies is urgently required.
Differentiation therapy, which is associated with
relatively less severe side effects, may be an alternative to
chemotherapy in this circumstance. All-trans retinoic acid
(ATRA), a prominent example of differentiation therapy, has been
successfully applied in the treatment of acute promyelocytic
leukemia (APL) for decades (2). The
degradation of promyelocytic leukemia (PML)-retinoic acid receptor
(RAR) α fusion protein, the key player in APL leukemogenesis, is
widely accepted as one of the important mechanisms of ATRA
treatment in APL patients (2).
Unfortunately, ATRA-induced differentiation of AML cells has only
been observed in APL patients. Since the RA signaling pathway is
involved in the regulation of myeloid differentiation and all other
AML subtypes express RARs, research approaches that further
sensitize cells to ATRA and extend the efficacy of ATRA-based
therapy to non-APL AML are being sought. Molecules involved in the
epigenetic modulation of the RA signaling pathway have become
therapeutic targets of AML. For example, valproic acid (VPA), an
inhibitor of histone deacetylase, was found to exhibit a
synergistic differentiation-inducing effect with ATRA in an AML
cell line and primary AML cells (3). However, clinical trials of VPA
combined with ATRA in AML patients did not demonstrate improvement
in complete remission (4–6). Inhibition of lysine-specific
demethylase 1 by tranylcypromine was shown to unlock the
ATRA-triggered differentiation in non-APL AML, suggesting that such
epigenetic therapy with ATRA may yield clinical benefit in AML
(7). Other approaches which
prevented the degradation of RARα were also demonstrated to
increase sensitivity to ATRA in ATRA-responsive cell lines, HL-60
and NB4 (8,9).
Staurosporine is a highly potent but non-specific
inhibitor of protein kinase C (PKC), which has demonstrated
antitumor activity in a variety of cell lines by inducing apoptosis
or differentiation (10–14). Staurosporine was found to synergize
with ATRA to trigger granulocytic differentiation in the
ATRA-sensitive HL-60 cell line, an AML-M2 cell line with morphology
similar to APL cells but without the APL symbol, PML-RARα fusion
protein (15). Moreover, such
synergism was also observed in ATRA-resistant APL cell lines
(16). Since the differentiation
induced by the combined treatment was independent of the PML-RARα
fusion protein in ATRA-resistant APL cell lines (16) and such a combination was also
effective in one non-APL AML cell line HL-60, we were encouraged to
investigate the effect of the combined treatment on other AML cell
lines. The AML-M2b cell line Kasumi, erythroleukemia cell line K562
and monocytic leukemia cell line U937 were studied. Staurosporine
could not restore ATRA sensitivity in ATRA unresponsive cell lines,
K562 and Kasumi. However, it significantly enhanced ATRA-induced
granulocytic differentiation and upregulation of
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β (C/EBPβ) and C/EBPε in U937 cells.
Both enhanced effects of staurosporine were dependent on
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK)/extracellular
signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation.
Materials and methods
Reagents
ATRA was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis,
MO, USA). UCN-1, Go6976, rottlerin, staurosporine and U0126 were
obtained from EMD Chemicals, Inc. (San Diego, CA, USA). They were
all dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as a stock solution at 1
mM, 100 µM, 100 µM, 2 mM, 2 µM and 10 mM,
respectively.
Cell culture, cell viability and cell
proliferation
U937, K562 and Kasumi cell lines were cultured in
RPMI-1640 medium, supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (Thermo
Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) in a humidified
atmosphere of 95% air/5% CO2 at 37°C. To avoid possible
effects of cell density on cell growth and survival, the cells were
maintained at less than 5×105 cells/ml. Cell viability
was assessed by trypan-blue exclusion assay. Actual viable cell
numbers were calculated by multiplying diluted times with the
counted viable cell numbers.
Cell differentiation assays
Cell maturation was evaluated by cellular morphology
and the content of cell surface differentiation-related antigen
CD11b. Morphology was determined using May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining
of cells centrifuged onto slides by cytospin (500 rpm, 5 min;
Shandon, Runcorn, UK) and viewed at ×1,000 magnification. The
expression of cell surface differentiation-related antigen CD11b
was determined by flow cytometry (EPICS XL; Beckman Coulter,
Hialeah, FL, USA). Fluorochrome-labeled anti-human CD11b/FITC
antibodies were purchased from Immunotech (Marseilles, France).
PKC activity assay by ELISA
Detection of PKC activity was performed by ELISA
using PKC kinase activity kit (Enzo Life Sciences, Inc.,
Farmingdale, NY, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Briefly, the cells were lysed with lysis buffer (20 mM MOPS, 1%
NP-40, 5 mM EGTA, 2 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT) and cell lysates were
centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 20 min at 4°C. Supernatants were
collected and quantified by Bio-Rad DC protein assay (Bio-Rad
Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). Five micrograms of protein
extracts together with 10 µg ATP were added to PKC substrate
microtiter plate and incubated at 30°C for 90 min. After washing
four times, samples were incubated with phospho-specific substrate
antibody followed by horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated
anti-rabbit IgG. Protein binding was quantified by adding TMB
substrate and measuring absorbance at 450 nm in a microplate reader
(BioTek Instruments, Inc., Winooski, VT, USA).
Western blot analysis
Cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline
(PBS) twice and lysed with RIPA buffer (Sigma-Aldrich). Cell
lysates were centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C.
Supernatants were collected and quantified by Bio-Rad DC protein
assay. Protein extracts were loaded on 8% SDS-polyacrylamide gel,
subjected to electrophoresis, and transferred to polyvinylidene
difluoride membranes (GE Healthcare UK Ltd., Buckinghamshire, UK).
After blocking with 5% nonfat milk in PBS, the membranes were
probed with antibodies against C/EBPε, C/EBPβ, anti-β-actin (all
from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Dallas, TX, USA),
phospho-MEK1/2 (Ser217/Try 221) and phospho-p44/42 Erk1/2
(Thr202/Try 204) (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Beverly, MA,
USA). Then, the membranes were incubated with HRP-conjugated
secondary antibody (GE Healthcare UK Ltd.). Immunocomplexes were
visualized by a chemiluminescence kit (GE Healthcare UK Ltd.)
according to the manufacturer's instructions. To detect Erk1/2 and
MEK1/2, the same membrane incubated with the phosphorylated MEK1/2
or Erk1/2 was stripped with stripping buffer (2% SDS, 100 mM
β-mercaptoethanol, 50 mM Tris, pH 6.8) followed by blocking and
probing with anti-MEK1/2 or anti-Erk1/2 (both from Cell Signaling
Technology, Inc.). The density of the protein band was quantitated
using ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD,
USA) and expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of the
relative levels of the objective protein and β-actin from three
independent experiments.
Statistical analysis
For the PKC kinase assay and quantitated analysis of
the proteins, a two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test was used. The
flow cytometric analysis of CD11b was analyzed by Chi-square test
(χ2).
Results
Staurosporine enhances ATRA-induced
granulocytic differentiation in U937 cells
To investigate the effect of the combined treatment
of staurosporine and ATRA on K562, Kasumi and U937 cells, we first
tested the concentration of staurosporine studied in these cell
lines. Five nanomoles of staurosporine was used to treat the K562
cells while 2 nM was applied to treat the Kasumi and U937 cells
since they were the maximum concentrations with no obvious effects
on cell proliferation and survival in these cell lines for 72 h
(data not shown). The corresponding DMSO concentrations were
regarded as solvent controls since both ATRA and staurosporine were
dissolved in it.
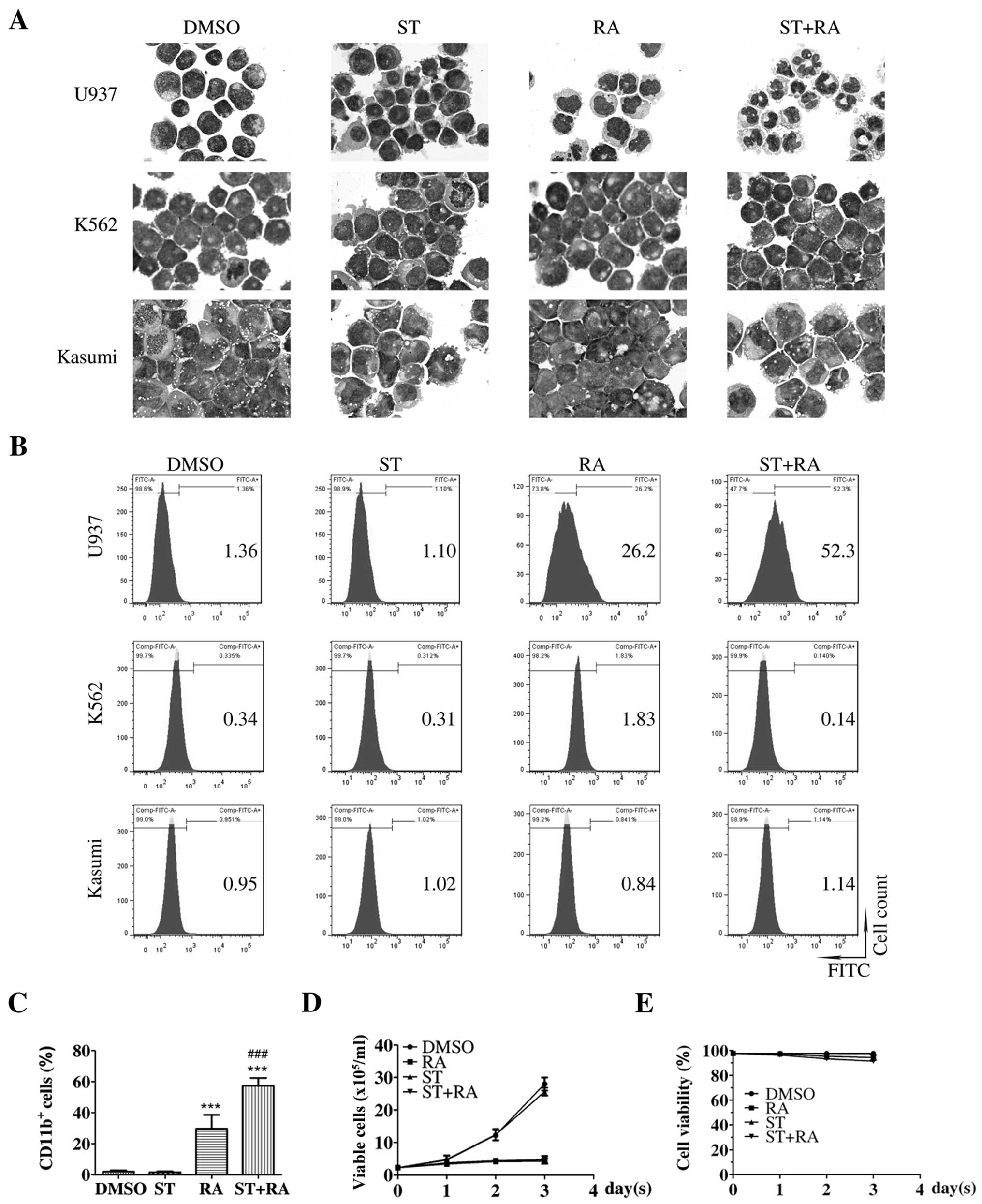
The cells were treated with 1 µM ATRA and the
corresponding concentration of staurosporine for 72 h. Parental
U937 cells presented irregular nuclei and a high nuclear/cytoplasm
ratio, which was almost retained in the cells treated with 2 nM
staurosporine (Fig. 1A, upper
panel). After 1 µM ATRA treatment for 72 h, cells with
decreased nuclear/cytoplasm ratio and kidney-shaped nuclei were
observed. Following the combined treatment of 2 nM staurosporine
and 1 µM ATRA for 72 h, cells displayed the appearance of
matured granulocytes, such as lobed nuclei accompanied by markedly
decreased nuclear/cytoplasm ratio (Fig.
1A, upper panel). However, no significant morphological change
was presented in the K562 or Kasumi cells with either ATRA
treatment or the combined treatment for 72 h (Fig. 1A, middle and lower panels). There
was also no marked alteration in the population of
CD11b+ cells in these two cell lines following these
treatments (Fig. 1B, middle and
lower panels). As shown in Fig. 1B and
C, consistent with the morphological change, the percentage of
CD11b+ cells was enhanced following ATRA treatment in
the U937 cells (RA compared with DMSO, 29.6±3.2 vs. 2.0±0.5%,
χ2=2877.1, P<0.001). Although staurosporine treatment
alone did not elevate the percentage of CD11b+ U937
cells, following the combination of staurosporine and ATRA, a more
than additive effect was observed. The percentage of
CD11b+ U937 cells was significantly increased following
the combined treatment (ST+RA compared with DMSO, 57.3±2.9 vs.
2.0±0.5%, χ2=7347.3, P<0.001; ST+RA compared with RA,
57.3±2.9 vs. 29.6±3.2%, χ2=1561.4, P<0.001; Fig. 1B and C). However, the percentage of
CD14+ U937 cells was not altered with either ATRA or the
combined treatment (data not shown). Thus, it was demonstrated that
staurosporine enhanced ATRA-induced granulocytic differentiation in
the U937 cells but not in the ATRA-unresponsive K562 and Kasumi
cells. Meanwhile, staurosporine neither suppressed cell
proliferation nor affected ATRA-inhibited cell growth in the U937
cells (Fig. 1D). The cell viability
was maintained above 90% with any treatment for 72 h (Fig. 1E).
Staurosporine-enhanced ATRA-induced
granulocytic differentiation in U937 cells is independent of
PKC
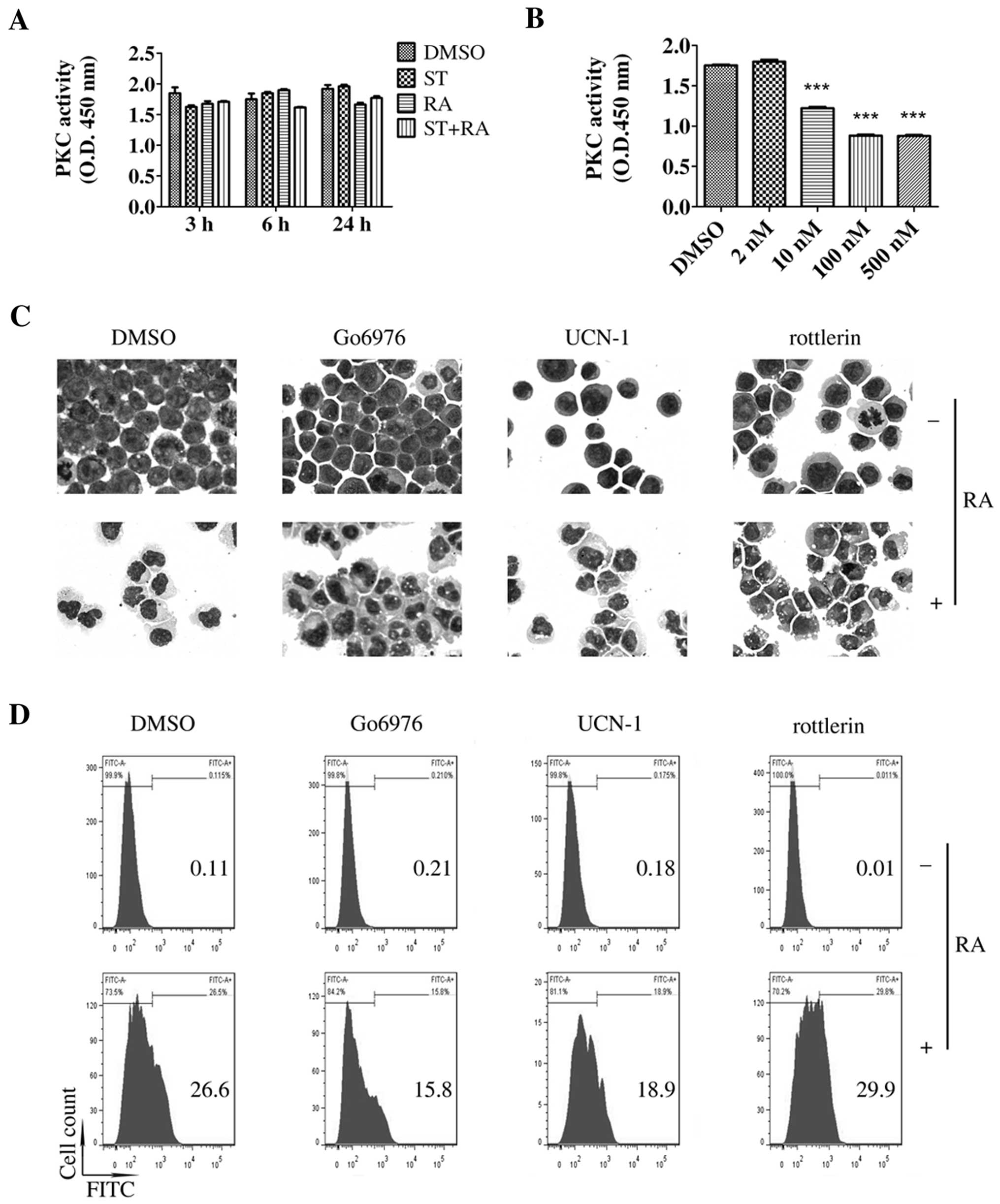
To explore the mechanisms of the enhanced effect of
staurosporine on ATRA-induced differentiation in U937 cells, we
first examined the role of PKC since staurosporine is a potent PKC
inhibitor with IC50 value of 2.7 nM in an isolated
enzyme assay (10), a slightly
higher concentration than we used in this study. As shown in
Fig. 2A, compared with the PKC
activity noted in the DMSO-treated cells, a similar level of PKC
activity was detected following treatment with 2 nM staurosporine
or the combined treatment. Staurosporine did inhibit PKC activity
in the U937 cells only at concentrations of 10 nM or higher after a
6-h incubation (Fig. 2B). However,
as mentioned above, 2 nM was the maximum concentration of
staurosporine that could be applied in this study. Therefore, 2 nM
staurosporine or the combined treatment had no effect on PKC
activity.
U937 cells express PKC-βI, -βII, -δ, -ε and -ζ
isoforms (17). To further confirm
the role of PKC, we evaluated whether the combination of ATRA with
several selective PKC inhibitors could mimic the effect of
staurosporine on ATRA-induced differentiation in U937 cells. Go6976
(an inhibitor of PKC-α, -βI and -µ isoforms), UCN-01 (an
inhibitor of PKC-α, -β, -γ, -δ, and -ε isoforms) and rottlerin (an
inhibitor of PKC-δ, -α, -β, -γ, -ε and -ζ isoforms) were used in
the following experiment. Compared with ATRA treatment alone, no
more matured cells were observed following the combined treatment
of ATRA and any of the above selective PKC inhibitors (Fig. 2C). CD11b+ cells were
slightly increased by the combined treatment of rottlerin and ATRA
while Go6976 or UCN-01 decreased the ATRA-enhanced population of
CD11b+ cells (Fig. 2D).
Thus, these selective PKC inhibitors did not enhance ATRA-induced
differentiation in the U937 cells. Therefore, it was suggested that
staurosporine-enhanced ATRA-induced granulocytic differentiation in
U937 cells may be independent of PKC.
Staurosporine activates MEK/ERK and
enhances ATRA-promoted upregulation of C/EBPs
To further investigate the molecular mechanisms of
the enhanced effect of staurosporine on ATRA-induced
differentiation in U937 cells, we focused on certain proteins or
signaling pathways involving in granulocytic differentiation.
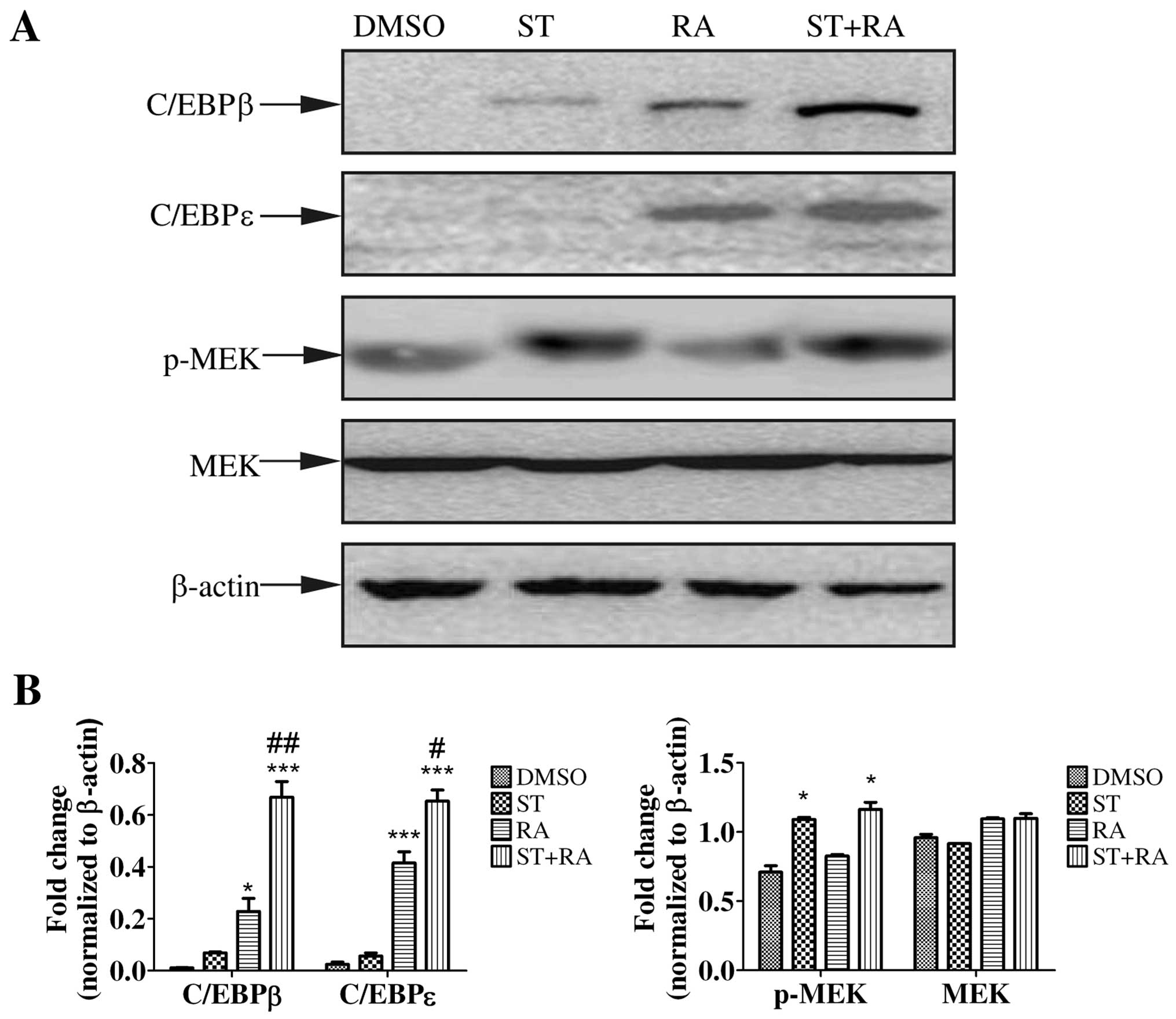
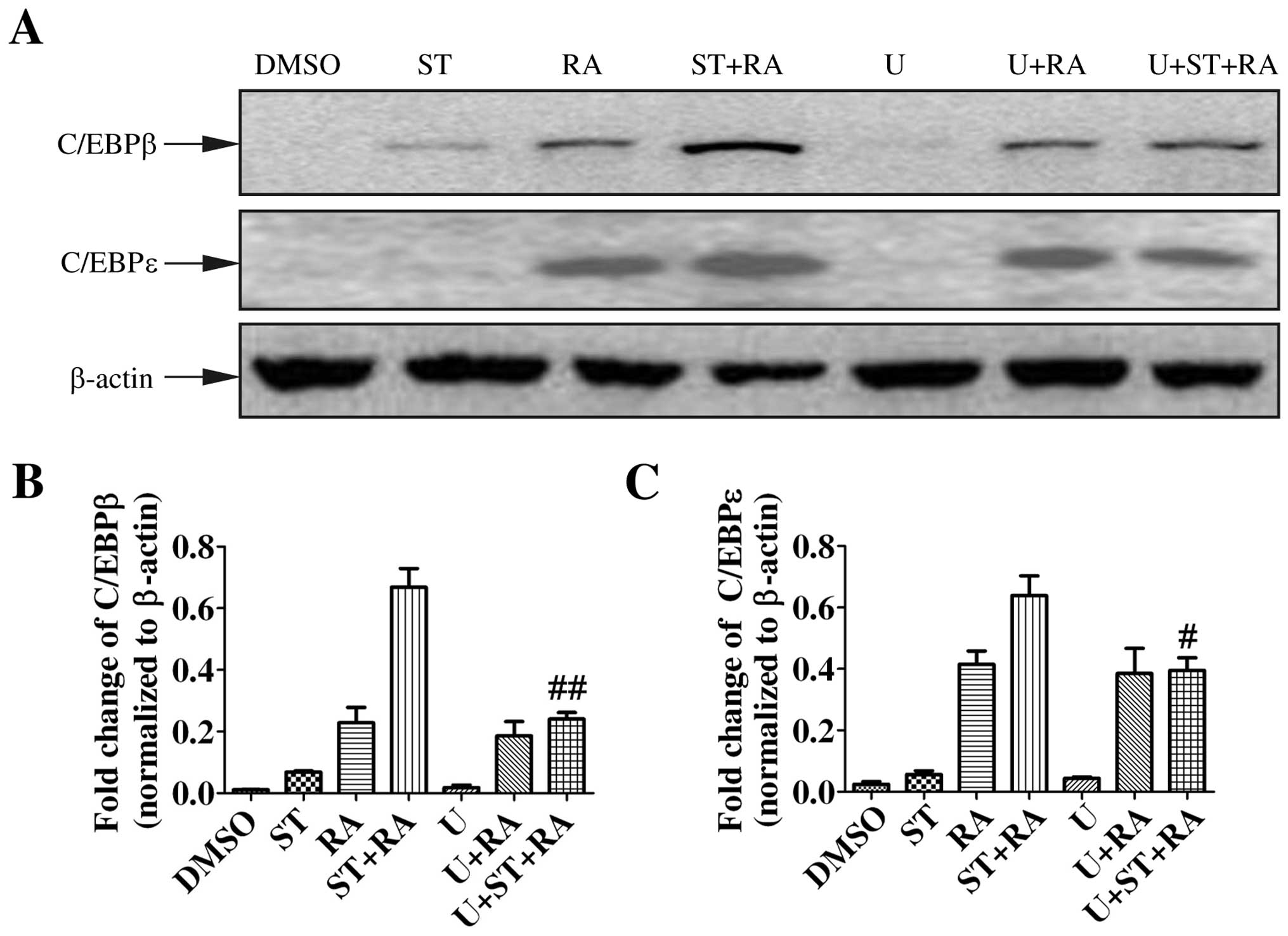
First, we examined the protein level of C/EBPβ and C/EBPε by
immunoblotting. The induction of C/EBPβ and C/EBPε expression is
implicated in the later stage of granulocytic differentiation
(18,19). Moreover, C/EBPβ and C/EBPε were
demonstrated to be required for ATRA-mediated differentiation in
APL cells (20,21). Therefore, U937 cells were treated
with 2 nM staurosporine, 1 µM ATRA, or the combined
treatment for 24 h. As shown in Fig.
3, ATRA enhanced the protein levels of both C/EBPβ and C/EBPε
while staurosporine only slightly elevated the C/EBPβ protein level
but not C/EBPε. However, with the addition of staurosporine to ATRA
treatment, the upregulation of C/EBPβ and C/EBPε was more marked
(Fig. 3).
Activation of MEK/ERK was demonstrated to be
required for some cytokine-induced myeloid differentiation as well
as ATRA-triggered granulocytic differentiation in APL cells
(22–26). To explore whether the MEK/ERK
signaling pathway was activated, phosphorylated MEK and ERK1/2 were
assessed by western blot analysis in cells treated with 1 µM
ATRA or/and 2 nM staurosporine for 24 h. As shown in Figs. 3 and 4A, staurosporine but not ATRA increased
the amount of phosphorylation of MEK and ERK1/2. Similar levels of
phosphorylated MEK and ERK1/2 were detected following the combined
treatment. The total amount of MEK and ERK1/2 in both cell lines
remained almost unaltered. Therefore, only staurosporine could
activate the MEK/ERK signaling pathway.
MEK/ERK activation is required for the
enhanced effect of staurosporine on ATRA-induced granulocytic
differentiation and the upregulation of C/EBPs
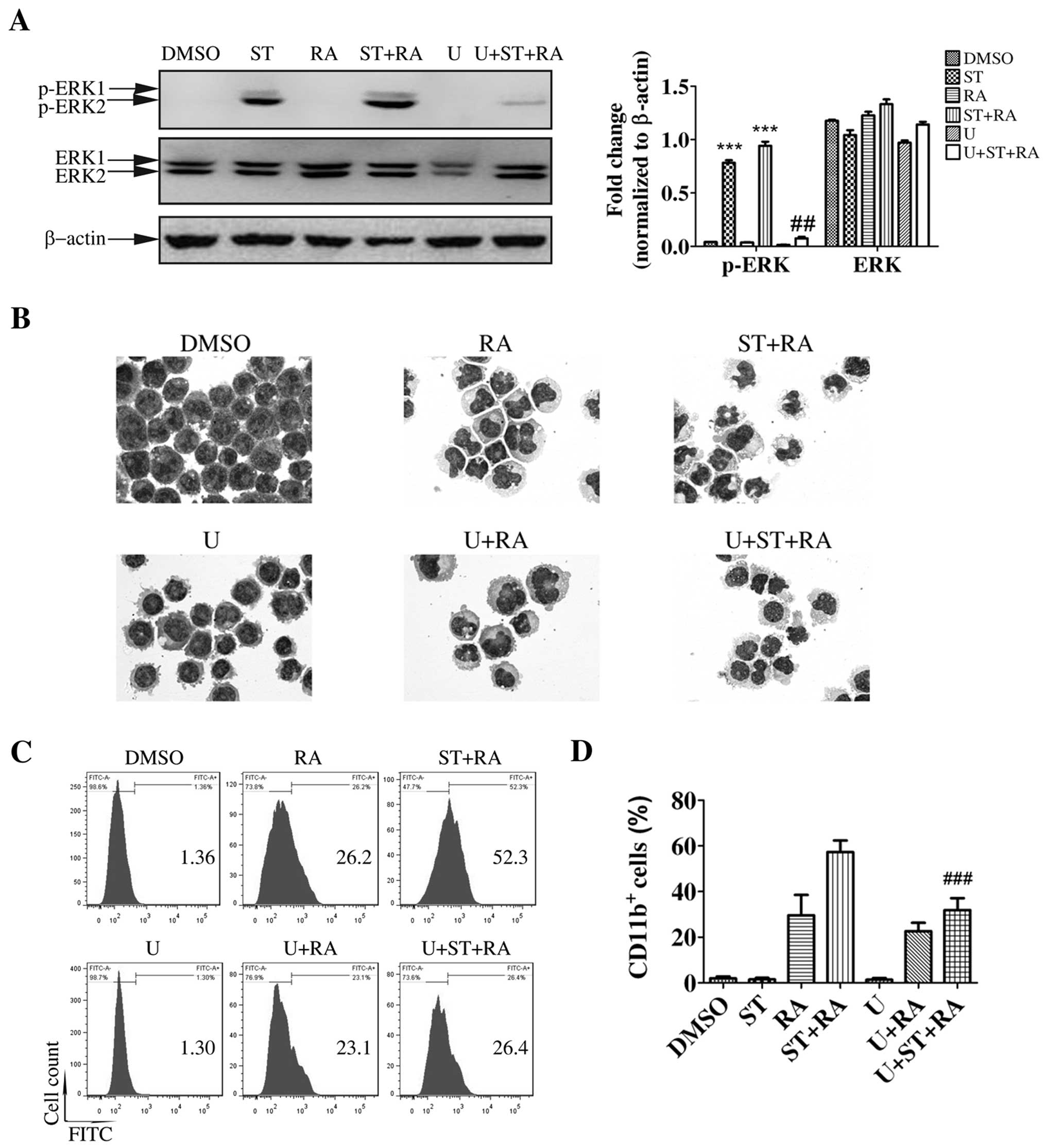
Having validated the activation of MEK/ERK by
staurosporine, we next ascertained whether the MEK/ERK signaling
pathway was required for staurosporine-enhanced ATRA-induced
granulocytic differentiation in U937 cells. Cells were treated with
10 µM U0126, a specific inhibitor of MEK for 1 h prior to
the other treatments. The effectiveness of U0126 was assessed by
ERK1/2 phosphorylation. U0126 did suppress ERK1/2 activation in the
U937 cells following the combined treatment (Fig. 4A). Meanwhile, U0126 partially
inhibited differentiation induced by the combination of
staurosporine and ATRA. Following U0126 pretreatment, typical
granulocytic differentiated cells with lobed nuclei observed
following the combined treatment were displaced by cells with
kidney-shaped or round nuclei, which were also presented following
ATRA treatment (Fig. 4B). However,
U0126 pretreatment barely affected the morphological change with
ATRA treatment (Fig. 4B). In
addition, following U0126 pretreatment, the increased percentage of
CD11b+ cells following the combined treatment was
significantly decreased to a similar level as that following ATRA
treatment (U+ST+RA compared with ST+RA, 31.9±3.1 vs. 57.3±2.9%,
χ2=1312.8, P<0.001; Fig.
4C and D). Whereas, U0126 only slightly suppressed the
population of CD11b+ cells with ATRA treatment (Fig. 4C and D). These results excluded the
effect of the MEK/ERK signaling pathway on ATRA-triggered
differentiation but highlighted its major role in the enhanced
effect of staurosporine on ATRA-induced granulocytic
differentiation in U937 cells.
Consistent with cell differentiation, U0126
pretreatment attenuated the combined treatment-enhanced C/EBPβ and
C/EBPε protein levels to a similar level of that following ATRA
treatment. However, the increased protein levels of C/EBPβ and
C/EBPε following ATRA treatment were not altered in the presence of
U0126 (Fig. 5). Therefore,
staurosporine-enhanced upregulation of C/EBPβ and C/EBPε following
ATRA treatment was mediated by the MEK/ERK signaling pathway.
Discussion
In the present study, we first demonstrated that
staurosporine enhanced ATRA-induced granulocytic differentiation in
U937 cells. A high concentration of staurosporine (1 µM) was
reported to induce necroptotic cell death while a relatively lower
concentration (100 nM staurosporine) was found to activate rapid
homotypic intercellular adhesion of U937 cells (27,28).
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to show that
very low concentrations of staurosporine exhibit synergism with
ATRA to promote granulocytic differentiation in U937 cells.
However, the combination of staurosporine and ATRA did not induce
differentiation in ATRA-unresponsive cell lines K562 and Kasumi. It
was also previously shown that the same combined treatment
synergized to trigger differentiation in ATRA-resistant APL cell
lines NB4-R1 and NB4-R2 (16).
Although NB4-R1 and NB4-R2 cell lines were regarded as
ATRA-resistant cell lines, they are not completely unresponsive to
ATRA. They are just poorly sensitive to ATRA, that is, ATRA
slightly increased the content of CD11b+ cells
accompanied by some morphologically partial differentiation cells
in these two cell lines (16).
Meanwhile, 5 nM staurosporine also achieved the similar enhanced
effect in ATRA-sensitive HL-60 cells (15). Therefore, it was suggested that
staurosporine may only be able to enhance ATRA-promoted
differentiation but not to restore ATRA sensitivity.
Staurosporine is a potent but non-selective PKC
inhibitor. Some PKC isoforms regulate granulocytic differentiation,
that is, PKC-α was suggested to negatively modulate terminal
neutrophil differentiation while activated PKC-δ resulted in ATRA
resistance in APL cells (29,30).
Thus, we first determined the role of PKC in the combination of
staurosporine and ATRA in U937 cells. Two nanomoles of
staurosporine, which was used in this study, did not suppress PKC
activity. However, being a PKC inhibitor, in concentrations of 10
nM or higher, staurosporine did inhibit PKC activity in the U937
cells. Since the IC50 value of staurosporine, which was
2.7 nM, was tested in isolated enzyme, it was possible that much
higher concentrations of staurosporine were required to suppress
PKC activity in the whole cell system. In further study, we used
other selective PKC inhibitors, whose inhibition spectrum covered
all the PKC isoforms expressed in U937 cells. However, it was
confirmed that they all failed to enhance ATRA-induced granulocytic
differentiation in U937 cells. Therefore, staurosporine-enhanced
ATRA-induced granulocytic differentiation in U937 cells may be
independent of PKC. Some other biological effects of staurosporine
were also reported to be PKC-independent (31–35).
To further survey the possible mechanisms of the
enhanced effect of staurosporine on ATRA-induced differentiation in
U937 cells, due to sparse information regarding the mechanisms of
ATRA-triggered differentiation in U937 cells, we focused on certain
proteins or signaling pathways involved in granulocytic
differentiation. Although an abundance of literature has
highlighted the important role of the MEK/ERK signaling pathway in
promoting the proliferation and survival of myeloid leukemia cells,
rapid and sustained activation of MEK/ERK is also required for
myeloid differentiation (22–26).
In addition, 100 nM staurosporine was demonstrated to activate ERK
in U937 cells (28). In the present
study, staurosporine but not ATRA activated the MEK/ERK signaling
pathway and the blockade of MEK activation inhibited
staurosporine-enhanced differentiation in the U937 cells.
Meanwhile, consistent with the fact that no MEK/ERK activation was
detected following ATRA treatment, inhibition of MEK activation
barely affected ATRA-induced differentiation. Therefore, it was
concluded that MEK/ERK activation was required for the enhanced
effect of staurosporine on ATRA-induced granulocytic
differentiation in U937 cells.
The protein levels of C/EBPβ and C/EBPε were shown
to be increased following ATRA treatment in U937 cells. Accompanied
by the enhanced effect of staurosporine on ATRA-induced
granulocytic differentiation, the upregulation of these two
proteins was also elevated by the addition of staurosporine to the
ATRA treatment. Meanwhile, although staurosporine activated
MEK/ERK, it did not significantly promote the expression of C/EBPβ
and C/EBPε as well as the differentiation in U937 cells. Hence, it
was suggested that the increased protein levels of C/EBPβ and
C/EBPε are associated with differentiation in this system.
Interestingly, further study confirmed that the inhibition of MEK
activation suppressed the enhanced effect of staurosporine not only
on ATRA-induced differentiation but also on the upregulation of
protein levels of C/EBPβ and C/EBPε. Thus, the enhanced effect of
staurosporine on ATRA-induced granulocytic differentiation was
modulated by MEK/ERK-mediated upregulation of C/EBPβ and C/EBPε.
Being the downstream target of the MEK/ERK signaling pathway, the
expression as well as the transcription activity of C/EBPβ was
modulated by MEK/ERK (36–40). Moreover, in ATRA-treated APL cells,
C/EBPβ was demonstrated to promote the expression of C/EBPε
(20). Hence, there may exist an
MEK-C/EBPβ-C/EBPε cascade in the enhanced effect of staurosporine
on ATRA-induced granulocytic differentiation in U937 cells.
In conclusion, staurosporine synergized with ATRA to
promote granulocytic differentiation in poorly ATRA-sensitive U937
cells but not in ATRA unresponsive K562 and Kasumi cells. It was
implicated that such a combination may be a potential therapeutic
strategy for various subtypes of AML with poor sensitivity to ATRA.
Staurosporine enhanced ATRA-induced granulocytic differentiation in
U937 cells via MEK/ERK-mediated modulation of the protein level of
C/EBPs. Hence, stimulation of the MEK/ERK signaling pathway or
upregulation of C/EBPs may be an alternative therapeutic approach
for certain subtypes of AML.
Abbreviations:
|
ATRA
|
all-trans retinoic acid
|
|
PKC
|
protein kinase C
|
|
MEK
|
mitogen-activated protein kinase
kinase
|
|
ERK
|
extracellular signal-regulated
kinase
|
|
C/EBP
|
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein
|
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by the Natural
Science Foundation of Shanghai (13ZR1425400).
References
|
1
|
Wang ES: Treating acute myeloid leukemia
in older adults. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program.
2014:14–20. 2014.
|
|
2
|
Ablain J and de Thé H: Retinoic acid
signaling in cancer: The parable of acute promyelocytic leukemia.
Int J Cancer. 135:2262–2272. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Göttlicher M, Minucci S, Zhu P, Krämer OH,
Schimpf A, Giavara S, Sleeman JP, Lo Coco F, Nervi C, Pelicci PG,
et al: Valproic acid defines a novel class of HDAC inhibitors
inducing differentiation of transformed cells. EMBO J.
20:6969–6978. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tassara M, Döhner K, Brossart P, Held G,
Götze K, Horst HA, Ringhoffer M, Köhne CH, Kremers S, Raghavachar
A, et al: Valproic acid in combination with all-trans retinoic acid
and intensive therapy for acute myeloid leukemia in older patients.
Blood. 123:4027–4036. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bug G, Ritter M, Wassmann B, Schoch C,
Heinzel T, Schwarz K, Romanski A, Kramer OH, Kampfmann M, Hoelzer
D, et al: Clinical trial of valproic acid and all-trans retinoic
acid in patients with poor-risk acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer.
104:2717–2725. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kuendgen A, Schmid M, Schlenk R, Knipp S,
Hildebrandt B, Steidl C, Germing U, Haas R, Dohner H and Gattermann
N: The histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor valproic acid as
monotherapy or in combination with all-trans retinoic acid in
patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer. 106:112–119. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Schenk T, Chen WC, Göllner S, Howell L,
Jin L, Hebestreit K, Klein HU, Popescu AC, Burnett A, Mills K, et
al: Inhibition of the LSD1 (KDM1A) demethylase reactivates the
all-trans-retinoic acid differentiation pathway in acute myeloid
leukemia. Nat Med. 18:605–611. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ying M, Zhou X, Zhong L, Lin N, Jing H,
Luo P, Yang X, Song H, Yang B and He Q: Bortezomib sensitizes human
acute myeloid leukemia cells to all-trans-retinoic acid-induced
differentiation by modifying the RARα/STAT1 axis. Mol Cancer Ther.
12:195–206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Gianni' M, Boldetti A, Guarnaccia V,
Rambaldi A, Parrella E, Raska I Jr, Rochette-Egly C, Del Sal G,
Rustighi A, Terao M, et al: Inhibition of the
peptidyl-prolyl-isomerase Pin1 enhances the responses of acute
myeloid leukemia cells to retinoic acid via stabilization of
RARalpha and PML-RARalpha. Cancer Res. 69:1016–1026. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Omura S, Sasaki Y, Iwai Y and Takeshima H:
Staurosporine, a potentially important gift from a microorganism. J
Antibiot (Tokyo). 48:535–548. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yoo CB, Yun SM, Jo C and Koh YH:
γ-Secretase-dependent cleavage of E-cadherin by staurosporine in
breast cancer cells. Cell Commun Adhes. 19:11–16. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mollereau C, Zajac JM and Roumy M:
Staurosporine differentiation of NPFF2
receptor-transfected SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells induces
selectivity of NPFF activity towards opioid receptors. Peptides.
28:1125–1128. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao C, Yin P, Mei C, Li N, Yao W, Li X,
Qi J, Fan K, Li Z, Wang L, et al: Down-regulation of DNA
methyltransferase 3B in staurosporine-induced apoptosis and its
mechanism in human hepatocarcinoma cell lines. Mol Cell Biochem.
376:111–119. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shimizu T, Okayama A, Inoue T and Takeda
K: Analysis of gene expression during staurosporine-induced
neuronal differentiation of human prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
14:441–448. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Okazaki T, Kato Y, Mochizuki T, Tashima M,
Sawada H and Uchino H: Staurosporine, a novel protein kinase
inhibitor, enhances HL-60-cell differentiation induced by various
compounds. Exp Hematol. 16:42–48. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ge DZ, Sheng Y and Cai X: Combined
staurosporine and retinoic acid induces differentiation in retinoic
acid resistant acute promyelocytic leukemia cell lines. Sci Rep.
4:48212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kiley SC and Parker PJ: Differential
localization of protein kinase C isozymes in U937 cells: Evidence
for distinct isozyme functions during monocyte differentiation. J
Cell Sci. 108:1003–1016. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Scott LM, Civin CI, Rorth P and Friedman
AD: A novel temporal expression pattern of three C/EBP family
members in differentiating myelomonocytic cells. Blood.
80:1725–1735. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lekstrom-Himes JA: The role of
C/EBP(epsilon) in the terminal stages of granulocyte
differentiation. Stem Cells. 19:125–133. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Duprez E, Wagner K, Koch H and Tenen DG:
C/EBPbeta: A major PML-RARA-responsive gene in retinoic
acid-induced differentiation of APL cells. EMBO J. 22:5806–5816.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Truong BT, Lee YJ, Lodie TA, Park DJ,
Perrotti D, Watanabe N, Koeffler HP, Nakajima H, Tenen DG and Kogan
SC: CCAAT/Enhancer binding proteins repress the leukemic phenotype
of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 101:1141–1148. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Miranda MB, McGuire TF and Johnson DE:
Importance of MEK-1/-2 signaling in monocytic and granulocytic
differentiation of myeloid cell lines. Leukemia. 16:683–692. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gobert Gosse S, Bourgin C, Liu WQ, Garbay
C and Mouchiroud G: M-CSF stimulated differentiation requires
persistent MEK activity and MAPK phosphorylation independent of
Grb2-Sos association and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity.
Cell Signal. 17:1352–1362. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Miranda MB, Xu H, Torchia JA and Johnson
DE: Cytokine-induced myeloid differentiation is dependent on
activation of the MEK/ERK pathway. Leuk Res. 29:1293–1306. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Barbarroja N, Siendones E, Torres LA,
Luque MJ, Martinez JM, Dorado G, Velasco F, Torres A and
López-Pedrera C: MEK inhibition induces caspases activation,
differentiation blockade and PML/RARalpha degradation in acute
promyelocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 142:27–35. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Milella M, Konopleva M, Precupanu CM, Tabe
Y, Ricciardi MR, Gregorj C, Collins SJ, Carter BZ, D'Angelo C,
Petrucci MT, et al: MEK blockade converts AML differentiating
response to retinoids into extensive apoptosis. Blood.
109:2121–2129. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Dunai ZA, Imre G, Barna G, Korcsmaros T,
Petak I, Bauer PI and Mihalik R: Staurosporine induces necroptotic
cell death under caspase-compromised conditions in U937 cells. PLoS
One. 7:e419452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cho JY, Katz DR and Chain BM:
Staurosporine induces rapid homotypic intercellular adhesion of
U937 cells via multiple kinase activation. Br J Pharmacol.
140:269–276. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Devalia V, Thomas NS, Roberts PJ, Jones HM
and Linch DC: Down-regulation of human protein kinase C alpha is
associated with terminal neutrophil differentiation. Blood.
80:68–76. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
McNamara S, Nichol JN, Wang H and Miller
WH Jr: Targeting PKC delta-mediated topoisomerase II beta
overexpression subverts the differentiation block in a retinoic
acid-resistant APL cell line. Leukemia. 24:729–739. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ko JH, Park WS and Earm YE: The protein
kinase inhibitor, staurosporine, inhibits L-type Ca2+
current in rabbit atrial myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
329:531–537. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Park WS, Son YK, Han J, Kim N, Ko JH, Bae
YM and Earm YE: Staurosporine inhibits voltage-dependent
K+ current through a PKC-independent mechanism in
isolated coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. J Cardiovasc
Pharmacol. 45:260–269. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yagi Y, Sotani T, Nagao T, Horio T,
Yamamoto I and Gohda E: Induction by staurosporine of hepatocyte
growth factor production in human skin fibroblasts independent of
protein kinase inhibition. Biochem Pharmacol. 66:1797–1808. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tabakman R, Lazarovici P, Matsuda Y,
Brodie C and Ovadia H: Protein kinase C-independent selective
induction of nitric oxide synthase activity in rat alveolar
macrophages by staurosporine. Nitric Oxide. 2:250–258. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sowa G and Przewłocki R: Enhancing effect
of staurosporine on NO production in rat peritoneal macrophages via
a protein kinase C-independent mechanism. Br J Pharmacol.
116:1711–1712. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Davis RJ: Transcriptional regulation by
MAP kinases. Mol Reprod Dev. 42:459–467. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lu J, Wu DM, Zheng YL, Hu B, Cheng W,
Zhang ZF and Li MQ: Troxerutin counteracts domoic acid-induced
memory deficits in mice by inhibiting CCAAT/enhancer binding
protein β-mediated inflammatory response and oxidative stress. J
Immunol. 190:3466–3479. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Alam M, Ahmad R, Rajabi H, Kharbanda A and
Kufe D: MUC1-C oncoprotein activates ERK→C/EBPβ signaling and
induction of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1 in breast cancer cells. J
Biol Chem. 288:30892–30903. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Piwien Pilipuk G, Galigniana MD and
Schwartz J: Subnuclear localization of C/EBP beta is regulated by
growth hormone and dependent on MAPK. J Biol Chem. 278:35668–35677.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Park BH, Qiang L and Farmer SR:
Phosphorylation of C/EBPbeta at a consensus extracellular
signal-regulated kinase/glycogen synthase kinase 3 site is required
for the induction of adiponectin gene expression during the
differentiation of mouse fibroblasts into adipocytes. Mol Cell
Biol. 24:8671–8680. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|