Introduction
Reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as the
superoxide and hydrogen peroxide, damage DNA and enzymes,
eventually leading to cell and tissue injury and dysfunction
(1). Antioxidants, scavenging these
free radicals and favored as prophylactic treatment, are used to
prevent cardiovascular diseases and cancers to prolong longevity
(2,3). However, many studies have shown that
antioxidants may induce the proliferation of cancer cells. Serafini
et al (4) found that
antioxidants displayed an increased risk of distal gastric cancer
in a clinical trial of 1.3 million people. A previous study
reported that application of antioxidant inhibitors is a useful
strategy for the treatment of solid tumors (5). Sayin et al (6) found that antioxidants markedly
increased tumor progression and reduced the survival rate via
decreasing p53 protein expression in mouse lung cancer. p53 was
recognized as a key tumor-suppressor gene, and induced tumor cell
apoptosis via the Bcl-2 family (7,8).
Propofol (2,6-diisopropylphenol), one of the most
common anesthetic agents widely used in the clinic, contains a
hydroxyl to develop its antioxidative property via activating the
nuclear factor E2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) pathway (9,10). As
a type of antioxidant, the effects of propofol on cancer cells has
not been demonstrated (10,11). Additionally, it is still unclear
whether the effects of propofol on cancer cells are related to the
p53 protein. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate
the effects of p53 and Nrf2 on human breast cancer cell line
MDA-MB-231 after treatment with propofol.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
Human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 that
carries a wild-type p53 gene was obtained from the American Type
Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA), and cultured in
complete medium containing RPMI-1640 medium (HyClone, Logan, UT,
USA), 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco Life Technologies,
Paisley, UK), and 1% penicillin/streptomycin mixture (Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology, Shanghai, China). The MDA-MB-231 cells
were cultured in a humidified incubator containing 5% carbon
dioxide (CO2)/95% air at 37°C.
Groups and drug application
The MDA-MB-231 cells were stimulated with propofol
(≥97.0%; Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO, USA) dissolved
in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology)
and in complete medium at 2, 5 and 10 µg/ml for 1, 4 and 12 h. The
DMSO and complete medium without propofol were also tested at an
equal concentration and volume as the vehicle-control group (VC
group) and normal control group (NC group), respectively. The final
concentration of DMSO was less than 0.1%.
Cell proliferation assay
The MDA-MB-231 cells at a density of
2×104 cells/ml were seeded in 96-well plates at 100
µl/well, and incubated for 12 h. After treatment with propofol for
the indicated time, the cells were cultivated for an additional 24
h in the same incubator. Then, 10 µl MTT (Wuhan Boster Biological
Engineering Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China) was added to each well for
another 4 h of incubation. A 100 µl formazan solution was added to
each well and shaken for 15 min in the dark. The absorbance (A) was
measured at 562 nm with a microplate reader (ELX800; BioTek
Instruments, Inc., Winooski, VT, USA). The proliferation rate was
determined according to the following formula: (A562 of test well -
A562 of NC group well)/(A562 of NC group well - A562 of zero set
well) × 100%.
Wound healing assay
The MDA-MB-231 cells were seeded in a 30-mm culture
dish at a density of 1×106 cells. When the cells reached
100% confluence, the complete medium was replaced by fresh
serum-free medium, and incubated for 4 h. Then the cells were
wounded across the center of the well into a clean straight edge
with a 200-µl micropipette tip, and treated with propofol according
to the study design. The cell migration ability was assessed by
microscopic examination in three fields that were randomly selected
along each edge, and the remaining scratch area was evaluated by
ImageJ (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA), and the
result of wound closure was expressed as the percentage of the
initial scratch area.
Apoptosis detection
After treatment of propofol, terminal
deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL)
staining was used to evaluate cell apoptosis using the Colorimetric
TUNEL apoptosis assay kit (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology)
according to the manufacturer's instructions. Apoptosis index, the
number of TUNEL-positive cells in every 100 cells, was calculated
in three randomly selected fields per section. Additionally, the
activity of caspase-3 was detected by the caspase-3 activity assay
kit (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) following the
manufacturer's instructions. The protein concentration was detected
by a bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay (Beyotime Institute of
Biotechnology). One unit of caspase-3 enzyme activity is the amount
of enzyme that will cleave 1.0 nmol of the colorimetric substrate
Ac-DEVD-pNA per hour at 37°C under saturated substrate
concentrations. The result was expressed as units per milligram of
protein (U/mg protein).
Western blot analysis
The MDA-MB-231 cells were seeded in 6-well plates at
a density of 2×106 cells and treated with propofol. The
cells were homogenized with lysis buffer (Beyotime Institute of
Biotechnology) for 30 min to extract the total protein, and the
protein concentration was detected by a BCA assay. The lysates were
centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 30 min and the supernatant was
separated by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel
electrophoresis and, then electroblotted onto polyvinyl difluoride
membranes. After 2 h of blocking, the primary antibody of p53
(1:2,000) and Nrf2 (1:2,000) (both from ABclonal Biotech Co., Ltd.,
Cambridge, MA, USA) was used overnight. Then the membrane was
incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated antibody (1:5,000;
ABclonal Biotech Co., Ltd.) for 1 h. The membranes were developed
with diaminobenzidine staining and exposed to film. All gels were
repeated three times and the data are expressed as a ratio of
targeted protein to β-actin protein by the integrated density
values.
Nrf2 inhibitor treatment
To investigate the effect of Nrf2, the Nrf2
inhibitor (12) at 0.1, 0.3 and 1.0
µM (PIK-75; Selleck Chemicals, Houston, TX, USA) was added to the
MDA-MB-231 cells for 4 h before the treatment of propofol (10
µg/ml). The proliferation and wound healing assays were evaluated
after the treatment of propofol for 12 h, and the apoptosis index,
caspase-3 activity, and the expression of p53 and Nrf2 were
detected by western blot analysis.
Statistical analysis
All of the experiments in this study were performed
for three repetitions independently, and the data are expressed as
mean values ± standard deviations. Differences between groups were
assessed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), and differences
between each two groups were analyzed by the Student-Newman-Keuls
test. A P-value <0.05 was considered statistically
significant.
Results
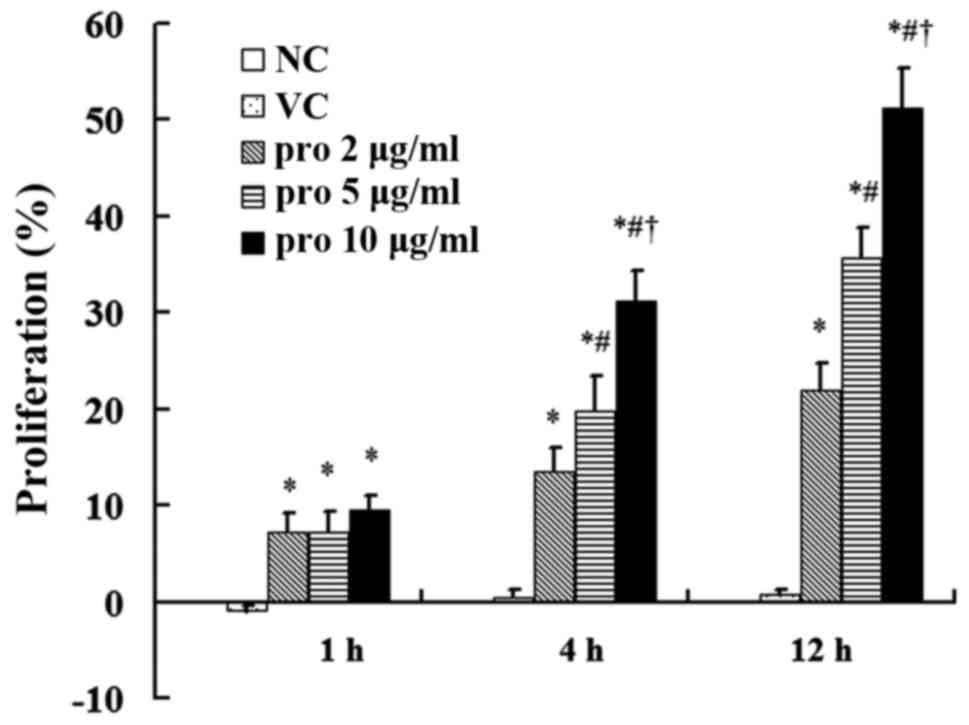
Effect of propofol on the
proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells
The cell proliferation in the VC group was not
significantly different compared with that noted in the NC group.
The proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells treated with propofol was
significantly increased compared with that noted in the NC group
(P<0.05). However, cell proliferation had no significant
difference after the treatment with different concentrations of
propofol for 1 h. After a 12-h treatment with propofol at the
concentrations of 2, 5, and 10 µg/ml, the proliferation was
increased by 22.0±2.7, 35.7±3.0, and 51.3±4.1% compared to the NC
group, respectively, and the proliferation following treatment with
10 µg/ml was higher than the proliferation following treatment with
2 and 5 µg/ml (P<0.05; Fig.
1).
Effect of propofol on the migration of
MDA-MB-231 cells
The scratch area in the NC and VC groups showed
similar changes with no statistical difference. After treatment
with propofol for 1 h, the scratches in the MDA-MB-231 cells
treated with 5 and 10 µg/ml were narrower than the NC group and the
cells treated with 2 µg/ml (P<0.05). However, the scratch in the
cells treated with 5 and 10 µg/ml did not differ (Fig. 2A). After treatment with propofol for
12 h, the percentage of the initial scratch area in the cells
treated with 2, 5 and 10 µg/ml propofol (40.1±3.1, 25.3±2.8 and
17.0±3.8%, respectively) were lower than the NC group (57.5±2.5%)
at 24 h (P<0.05), and the percentage of the scratch area in the
cells treated with 10 µg/ml was lower than the 2 and 5 µg/ml groups
(P<0.05; Fig. 2B and C).
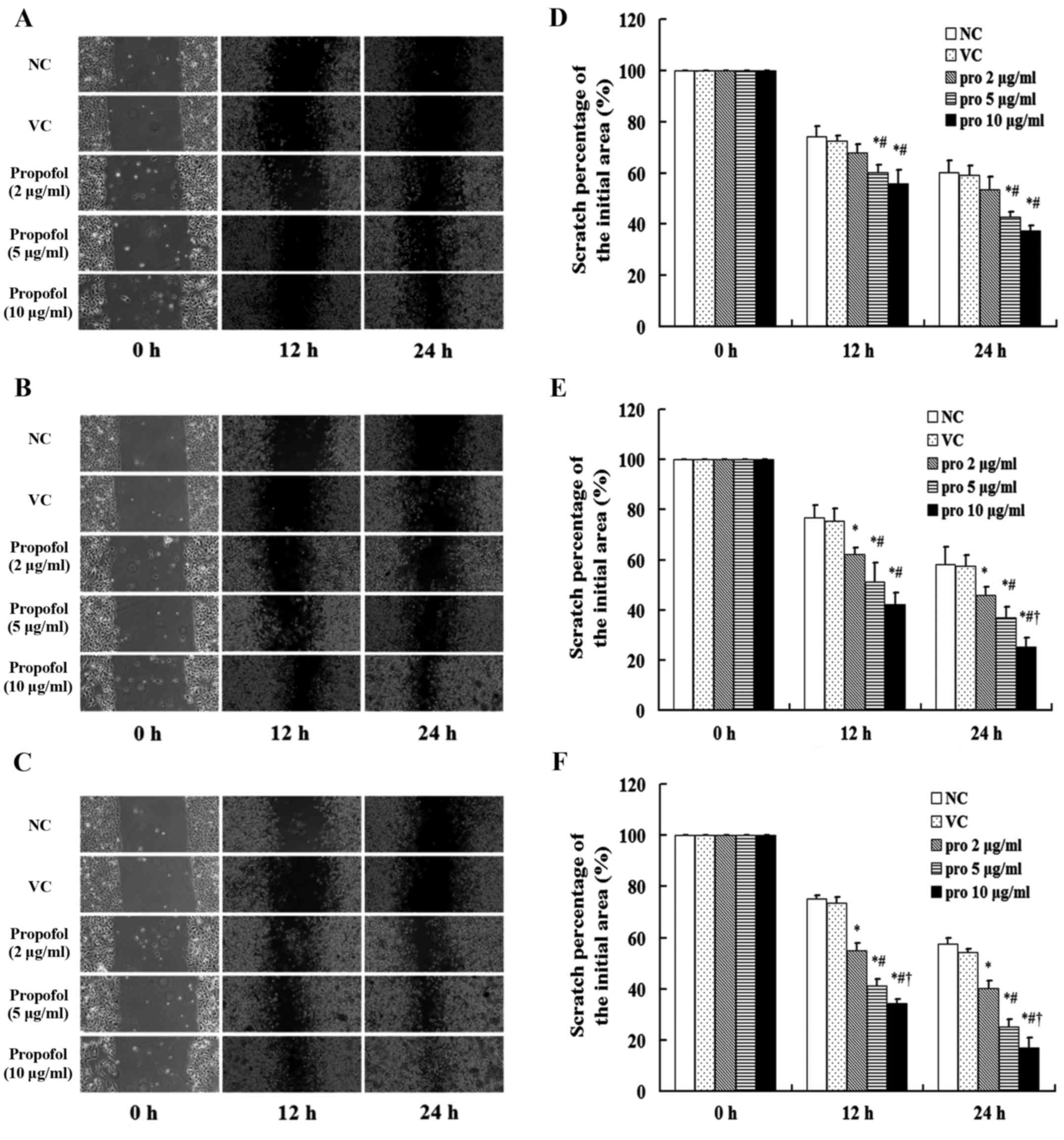 | Figure 2.Effect of propofol on cell migration.
After the treatment with propofol at the concentrations of 2, 5 and
10 µg/ml for (A) 1, (B) 4 and (C) 12 h, the migration of the human
breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 was analyzed via scratch area
detection at 12 and 24 h (magnification, ×200). (D-F) The result of
the wound closure assay is expressed as the percentage of the
initial scratch area. Treatment with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO,
<0.1%) was used as the VC group, and without propofol as the NC
group. The migration was significantly increased after the
treatment of propofol compared with the NC group, and the
percentage of the initial scratch area in the propofol (pro) 10
µg/ml group was lower than that in the pro 2 and 5 µg/ml groups
(P<0.05). Data are shown as the mean values ± standard
deviations (n=3). VC, vehicle-control group; NC, normal control
group; pro, propofol. *P<0.05 vs. NC group;
#P<0.05 vs. pro 2 µg/ml group; †P<0.05
vs. pro 5 µg/ml group. |
Effects of propofol on the expression
of Nrf2 and p53 protein in MDA-MB-231 cells
The expression of p53 and Nrf2 protein in the NC and
VC groups had no significant difference. Yet, the expression of p53
protein in the 2, 5 and 10 µg/ml propofol groups was significantly
lower than that in the NC group after treatment with propofol for 1
h (P<0.05), but no significant differences were found among the
2, 5 and 10 µg/ml groups. After treatment with propofol for 12 h,
the expression of p53 protein in the 10 µg/ml group was obviously
lower than that noted in the 2 and 5 µg/ml groups (P<0.05).
Expression of p53 protein was inhibited in a dose- and
time-dependent manner after treatment with propofol for 4 and 12 h.
However, the Nrf2 protein expression showed a contrary trend when
compared with p53. The expression of Nrf2 protein in the 10 µg/ml
group was significantly higher than that in the 2 and 5 µg/ml
groups after treatment with propofol for 12 h (P<0.05; Fig. 3).
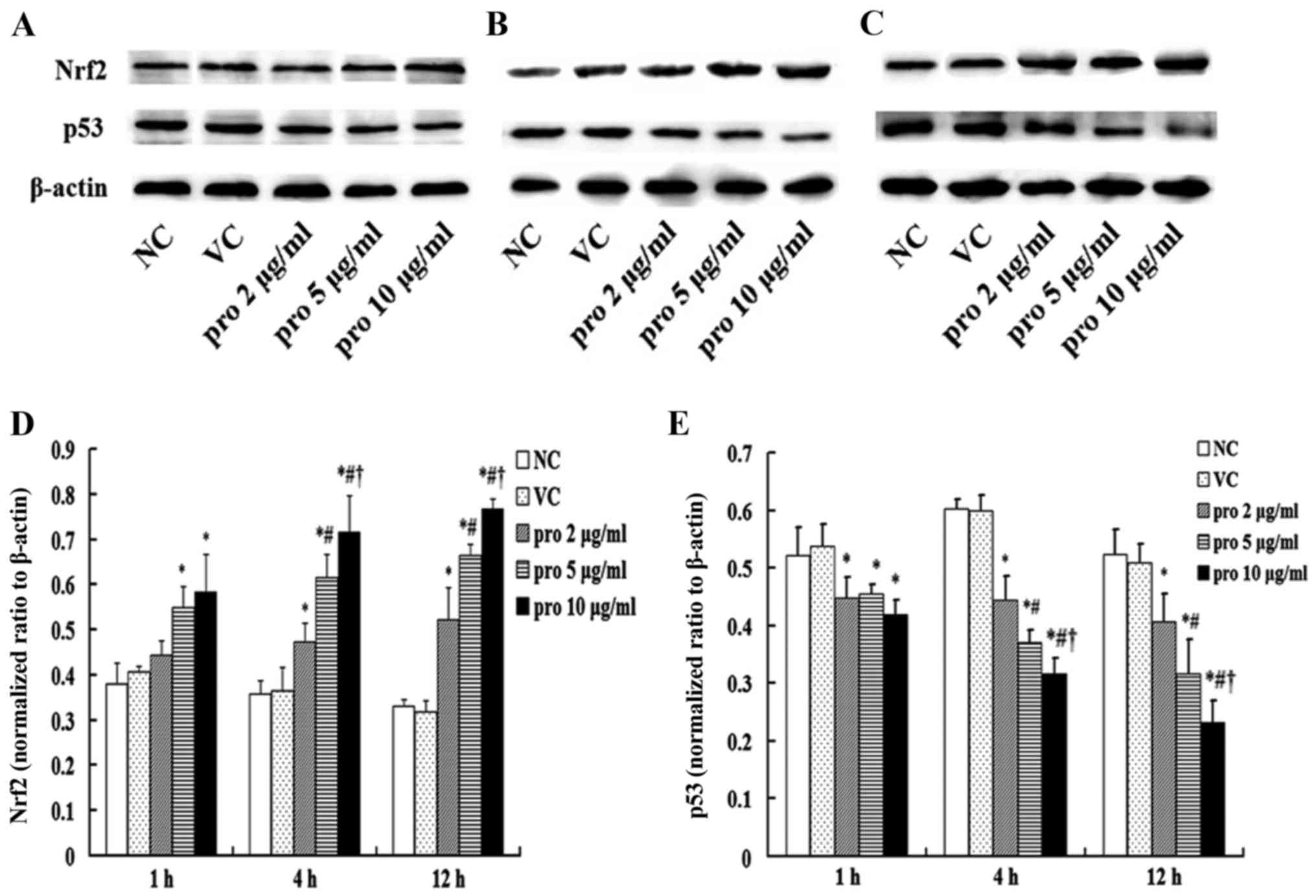 | Figure 3.Effects of propofol on the expression
of p53 and Nrf2 protein. The expression levels of p53 and Nrf2
protein were detected by western blot analysis after the treatment
with propofol at the concentrations of 2, 5 and 10 µg/ml for (A) 1,
(B) 4 and (C) 12 h. (D and E) Bar charts of the p53 and Nrf2
protein. The treatment with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, <0.1%) was
used as the VC group, and without propofol as the NC group. After
treatment with propofol for 12 h, the expression of p53 protein was
decreased compared with the NC group, and that in the pro 10 µg/ml
group was lower than that in the pro 2 and 5 µg/ml groups
(P<0.05). On the contrary, Nrf2 was activated by propofol, and
the expression in the pro 10 µg/ml group was higher than that in
the pro 2 and 5 µg/ml groups (P<0.05). Data are shown as the
mean values ± standard deviations (n=3). VC, vehicle-control group;
NC, normal control group; pro, propofol. *P<0.05 vs. NC group;
#P<0.05 vs. pro 2 µg/ml group; †P<0.05
vs. pro 5 µg/ml group. |
Effects of the Nrf2 inhibitor on the
proliferation, migration, and p53 protein in the MDA-MB-231
cells
The proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells in the 10
µg/ml group was increased significantly compared with that in the
NC group. But the proliferation was decreased significantly in a
dose-dependent manner after the treatment with the inhibitor of
Nrf2, PIK-75 at 0.1, 0.3 and 1.0 µM (P<0.05). Although the
proliferation was decreased after treatment with the inhibitor, it
was still higher than that in the NC group (P<0.05; Fig. 4A). After treatment with the
inhibitor, the expression of Nrf2 protein was inhibited in a
dose-dependent manner, while the expression of p53 protein was not
significantly changed (Fig. 4B).
Additionally, the scratch area was narrowed dramatically after
exposure to propofol, which was significantly attenuated following
treatment with the Nrf2 inhibitor at 1.0 µM which did not differ
compared with the NC group (Figs. 4C
and D).
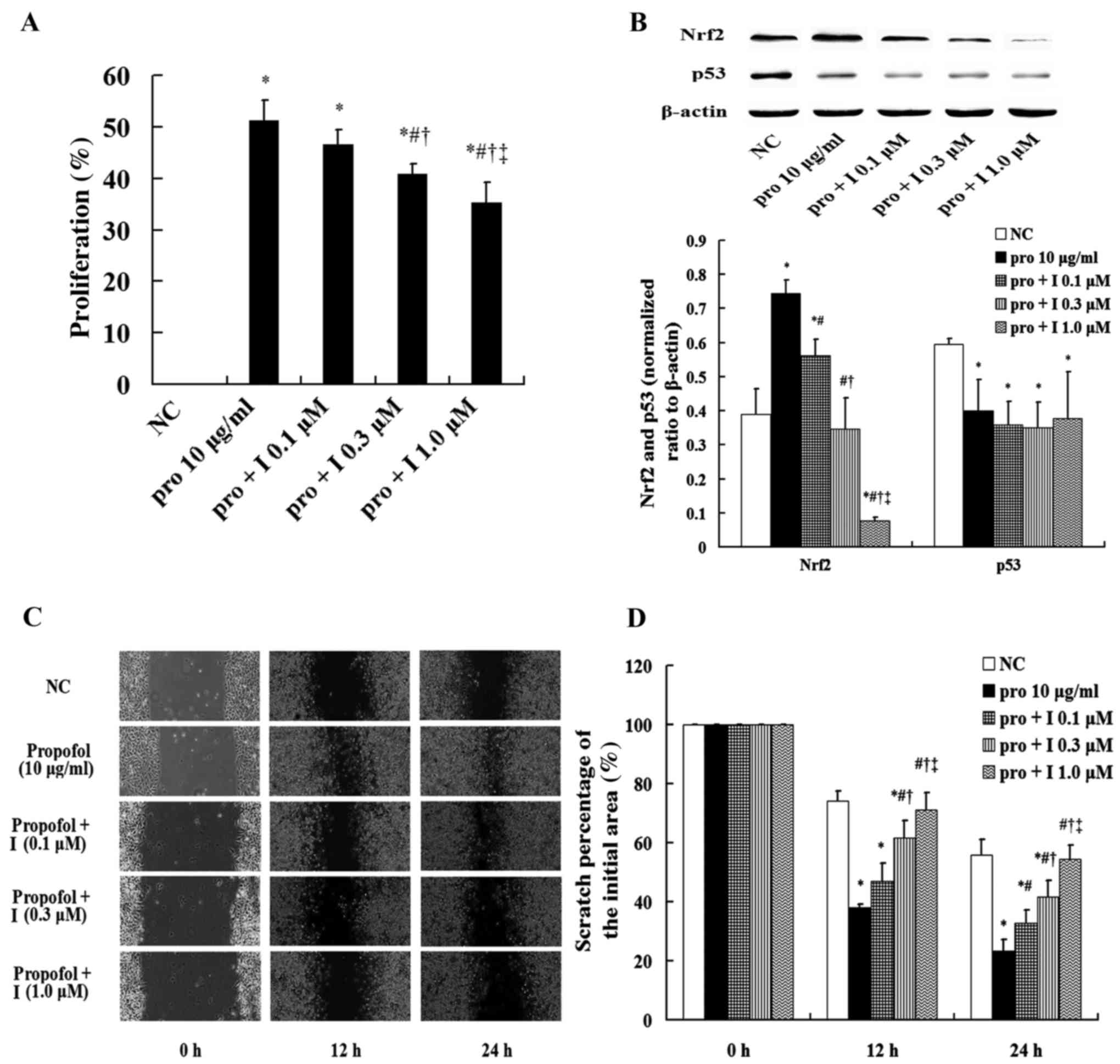 | Figure 4.Effects of Nrf2 inhibitor on
proliferation, migration, and p53 protein in MDA-MB-231 cells.
After treatment with PIK-75, a potent Nrf2 inhibitor, at 0.1, 0.3
and 1.0 µM for 4 h, the MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with propofol
at 10 µg/ml for 12 h. Then, the relative indices were detected. (A)
The proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells. (B) The expression levels of
p53 and Nrf2 protein, and the bar charts of the p53 and Nrf2
proteins. (C) Image of the migration assay in the MDA-MB-231 cells
(magnification, ×200). (D) The percentage of the initial scratch
area. Compared with the NC group, the proliferation and migration
in the pro 10 µg/ml group was increased significantly, and that in
the pro + I 0.1, 0.3 and 1.0 µM groups was decreased markedly
compared with the pro 10 µg/ml group (P<0.05). After the
treatment with propofol, the expression of p53 protein was
decreased and the Nrf2 was increased compared with the NC group
(P<0.05), and the expression of Nrf2 protein in the pro + I 1.0
µM group was almost completely inhibited. However, the expression
of p53 protein in the pro 10 µg/ml group was not different with the
pro + I 0.1, 0.3 and 1.0 µM groups. Data are shown as the mean
values ± standard deviations (n=3). NC, normal control group; pro,
propofol; I, Nrf2 inhibitor. *P<0.05 vs. NC group;
#P<0.05 vs. pro 10 µg/ml group; †P<0.05
vs. pro + I 0.1 µM group; ‡P<0.05 vs. pro + I 0.3 µM
group. |
Effects of propofol and the Nrf2
inhibitor on cell apoptosis
Compared with the NC group, the caspase-3 activity
and apoptosis index showed no significant difference in the VC
group, which was significantly decreased after the treatment with
propofol at 2, 5 and 10 µg/ml for 12 h (P<0.05). After the
treatment with propofol at 10 µg/ml for 12 h, the caspase-3
activity and apoptosis index of the MDA-MB-231 cell were lower than
these values in the 2 and 5 µg/ml groups (P<0.05; Fig. 5). However, this trend was inhibited
by the Nrf2 inhibitor in a dose-dependent manner. After the
treatment with the inhibitor at 1.0 µM, the caspase-3 activity and
apoptosis index were increased markedly compared with these values
in the 10 µg/ml group (P<0.05; Fig.
5).
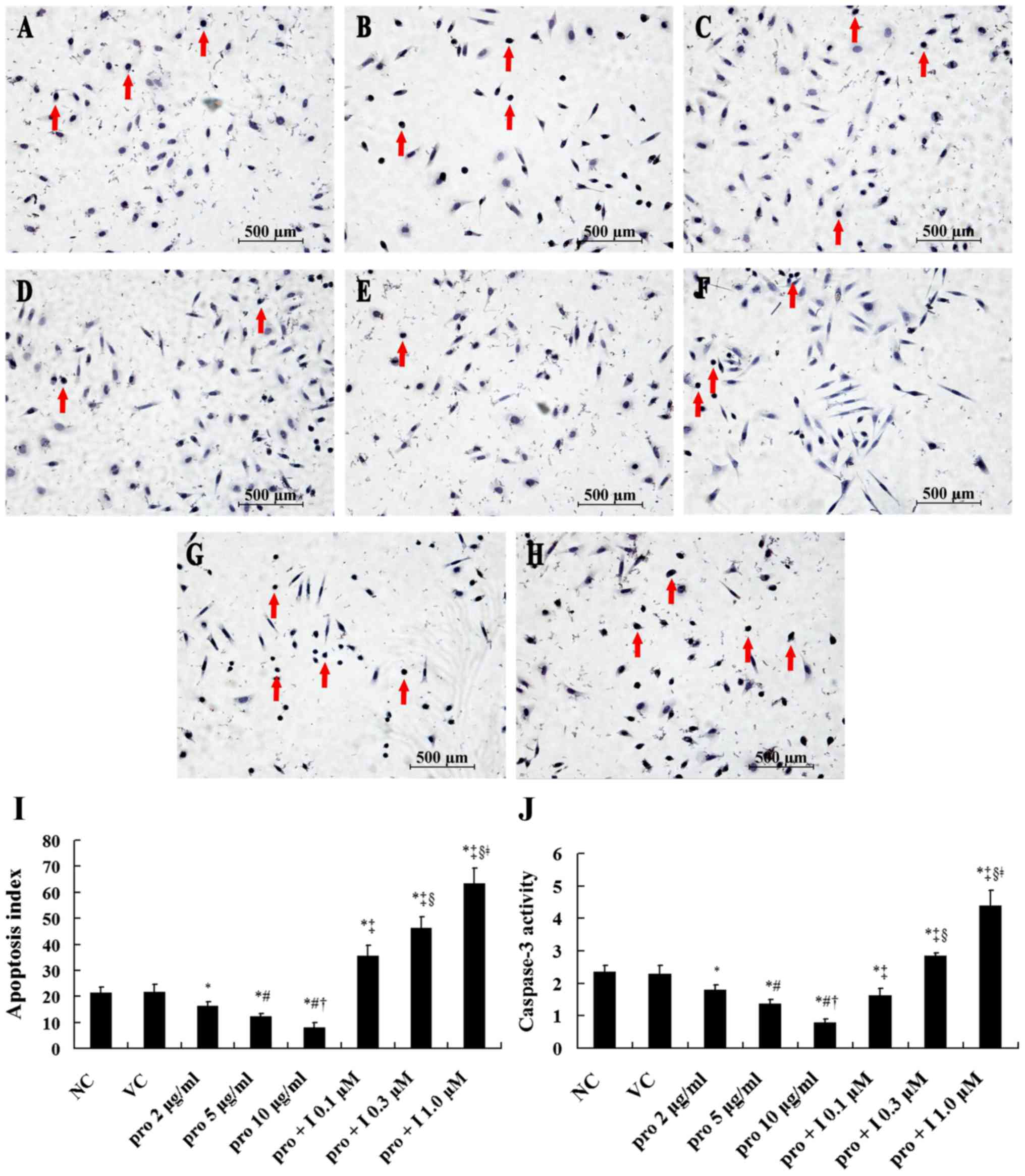 | Figure 5.Cell apoptosis in the MDA-MB-231 cells
after treatment with propofol and the Nrf2 inhibitor PIK-75. After
treatment with propofol at concentrations of 2, 5 and 10 µg/ml for
12 h, the cell apoptosis was detected via terminal deoxynucleotidyl
transferase dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) staining and caspase-3
activity. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, <0.1%) and complete medium
without propofol were used as the VC and NC groups. Then, following
the treatment with the Nrf2 inhibitor at 0.1, 0.3 and 1.0 µM for 4
h, the MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with propofol at 10 µg/ml for
12 h. The TUNEL-positive cells and caspase-3 activity were
detected. Positive cells are represented by brown-yellow nuclear
staining (red arrows). Figures are represented as ×200 of the
original magnification. Data are shown as the mean values ±
standard deviations (n=3). (A) NC group; (B) VC group; (C) pro 2
µg/ml group; (D) pro 5 µg/ml group; (E) pro 10 µg/ml group; (F) pro
+ I 0.1 µM group; (G) pro + I 0.3 µM group; (H) pro + I 1.0 µM
group; (I) apoptosis index; (J) caspase-3 activity. VC,
vehicle-control group; NC, normal control group; pro, propofol; I,
Nrf2 inhibitor. *P<0.05 vs. NC group; #P<0.05 vs.
pro 2 µg/ml group; †P<0.05 vs. pro 5 µg/ml group;
‡P<0.05 vs. pro 10 µg/ml group; §P<0.05
vs. pro + I 0.1 µM group; ǂP<0.05 vs. pro + I 0.3 µM
group. |
Discussion
In this study, propofol induced proliferation as
indicated by the MTT assay and migration as indicated by the wound
healing assay in the human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. Our
results also showed that propofol inhibited the expression of p53,
activated the Nrf2 pathway, and decreased cell apoptosis indicated
by the number of TUNEL-positive cells and caspase-3 activity. After
treatment with the Nrf2 inhibitor, the TUNEL-positive cells and
caspase-3 activity increased, and the migration decreased. However,
the proliferation was inhibited slightly and the expression of p53
protein was not affected.
p53 is recognized as a key tumor-suppressor gene and
a major regulator of cell apoptosis, and p53 inhibits the
proliferation of tumor cells mainly via inducing cell apoptosis
(7). p53 translocates into the
mitochondria and activates the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway,
which is closely linked with the Bcl-2 family (7–8,13).
Additionally, p53-induced cell apoptosis may be related to many
other pro-apoptotic genes such as Bax, Puma, Noxa, and Bid
(14). In this study, propofol
inhibited the expression of p53 in MDA-MB-231 cells, and the number
of apoptotic cells was decreased along with increased cell
viability and proliferation. Similar results have been shown in
previous studies. Antioxidants increased lung cancer cell
proliferation by reducing the expression of p53 and DNA damage in
mice (6). Sayin et al
(15) reported that activation of
p53 reduced lesional macrophage proliferation by the loss of one
copy Zfp148. Zhang et al (10) found that propofol decreased the cell
apoptosis and induced the proliferation of gallbladder cancer
cells. Therefore, propofol induced proliferation of MDA-MB-231
cells via a decrease in the percentage of apoptotic cells, which
may be through inhibition of the expression of p53.
Nrf2, an important redox-sensitive transcription
factor for inducing antioxidant defense system, belongs to the
cap'n'collar (CNC) family of basic region-leucine zipper
(bZip)-type transcription factors (16,17).
When Nrf2 was activated, the oxidative stress injury in cells and
tissues was ameliorated, and the cell apoptosis was attenuated.
Additionally, the Nrf2 pathway was also found to contribute to
cancer initiation and progression (18). In this study, propofol activated the
Nrf2 pathway in MDA-MB-231 cells, and decreased oxidative stress
injury and the apoptotic index, and increased proliferation and
migration. Several studies have demonstrated that propofol
activates the Nrf2 pathway in gallbladder cancer cells, human
alveolar epithelial cells, and lung cancer cells (11,19,20).
Zhang et al (21) found that
Nrf2 promoted proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma by
decreasing cell apoptosis and upregulation of the expression of
anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-xL. Pan et al (22) also showed that Nrf2 is involved in
the migration and invasion of human glioma cell line U251. A number
of studies with similar results have been reported previously
(23–26). Therefore, propofol induced the
proliferation and migration of MDA-MB-231 cells, which may be
related to activation of the Nrf2 pathway.
In order to confirm the possible effects of p53 and
Nrf2, the Nrf2 inhibitor was used in this study. siRNA is also a
potential technique for silencing a specific gene, but it may cause
other genes to be overexpressed (27). Therefore, the Nrf2 PIK-75 inhibitor
was used in this study. Our results showed that the Nrf2 inhibitor
increased the percentage of apoptotic cells, and slightly decreased
the degree of proliferation. However, the expression of p53 protein
was not affected. Thus, both p53 and Nrf2 were involved in the cell
apoptosis and proliferation after treatment with propofol, and
propofol induced the proliferation mainly via decreased expression
of p53 in the MDA-MB-231 cells. Additionally, our results also
showed that the Nrf2 inhibitor completely decreased the migration
induced by propofol. Therefore, Nrf2, not p53, was involved in the
migration of MDA-MB-231 cells after propofol treatment.
In similar studies, Garib et al (28,29)
found that propofol caused cell migration via activation of the
GABA-A receptor and mediating L-type calcium channels in human
breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-468. In contrast to our results, Li
et al (30) found that
propofol inhibited the migration and invasion of human breast
cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. However, in a study by Li et
al, MDA-MB-231 cells were treated for 24 h which was longer
than that used in the clinic, and whether the MDA-MB-231 cells
expressed functional p53 protein was not clear. Several studies
have also focused on the above issues (31,32).
Additionally, Deegan et al (33) revealed that proliferation of
MDA-MB-231 cells treated with serum from patients who received
propofol anesthesia was decreased. Because the effects of propofol
were closely related to the content of extracellular albumin
(34), the composition of serum
from patients was too complex to assess the role of propofol
itself. In this study, clinically relevant doses of propofol were
selected and administered for appropriate times as in surgery
(30–31,35).
Therefore, our study clearly showed the effects of propofol itself
on the MDA-MB-231 cells.
In conclusion, propofol increased the cell
proliferation at least partially via the inhibition of p53, and
induced the migration via the activation of Nrf2 in the human
breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. However, whether these effects
can be applied to other cancer cells or normal tissue cells, and
different cancer cell types will be investigated in future
research. Additionally, further in vivo studies, including
animal trials and prospective clinical studies, are warranted.
References
|
1
|
Choi YK, Por ED, Kwon YG and Kim YM:
Regulation of ROS production and vascular function by carbon
monoxide. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012:7942372012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Clarke MW, Burnett JR and Croft KD:
Vitamin E in human health and disease. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci.
45:417–450. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rayman MP: Selenium and human health.
Lancet. 379:1256–1268. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Serafini M, Bellocco R, Wolk A and Ekström
AM: Total antioxidant potential of fruit and vegetables and risk of
gastric cancer. Gastroenterology. 123:985–991. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kong Q and Lillehei KO: Antioxidant
inhibitors for cancer therapy. Med Hypotheses. 51:405–409. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sayin VI, Ibrahim MX, Larsson E, Nilsson
JA, Lindahl P and Bergo MO: Antioxidants accelerate lung cancer
progression in mice. Sci Transl Med. 6:221ra15. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wolff S, Erster S, Palacios G and Moll UM:
p53's mitochondrial translocation and MOMP action is independent of
Puma and Bax and severely disrupts mitochondrial membrane
integrity. Cell Res. 18:733–744. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Leu JI, Dumont P, Hafey M, Murphy ME and
George DL: Mitochondrial p53 activates Bak and causes disruption of
a Bak-Mcl1 complex. Nat Cell Biol. 6:443–450. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Marik PE: Propofol: Therapeutic
indications and side-effects. Curr Pharm Des. 10:3639–3649. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang L, Wang N, Zhou S, Ye W, Jing G and
Zhang M: Propofol induces proliferation and invasion of gallbladder
cancer cells through activation of Nrf2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
31:662012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu YB, Du QH, Zhang MY, Yun P and He CY:
Propofol suppresses proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis by
down-regulating ERK-VEGF/MMP-9 signaling in Eca-109 esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
17:2486–2494. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Duong HQ, Yi YW, Kang HJ, Hong YB, Tang W,
Wang A, Seong YS and Bae I: Inhibition of NRF2 by PIK-75 augments
sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine. Int J Oncol.
44:959–969. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chakraborty S, Mazumdar M, Mukherjee S,
Bhattacharjee P, Adhikary A, Manna A, Chakraborty S, Khan P, Sen A
and Das T: Restoration of p53/miR-34a regulatory axis decreases
survival advantage and ensures Bax-dependent apoptosis of non-small
cell lung carcinoma cells. FEBS Lett. 588:549–559. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Moll UM, Marchenko N and Zhang XK: p53 and
Nur77/TR3-transcription factors that directly target mitochondria
for cell death induction. Oncogene. 25:4725–4743. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sayin VI, Khan OM, Pehlivanoglu LE,
Staffas A, Ibrahim MX, Asplund A, Agren P, Nilton A, Bergström G,
Bergo MO, et al: Loss of one copy of Zfp148 reduces lesional
macrophage proliferation and atherosclerosis in mice by activating
p53. Circ Res. 115:781–789. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Moi P, Chan K, Asunis I, Cao A and Kan YW:
Isolation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a NF-E2-like basic
leucine zipper transcriptional activator that binds to the tandem
NF-E2/AP1 repeat of the beta-globin locus control region. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 91:9926–9930. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maher J and Yamamoto M: The rise of
antioxidant signaling - the evolution and hormetic actions of Nrf2.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 244:4–15. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jaramillo MC and Zhang DD: The emerging
role of the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway in cancer. Genes Dev.
27:2179–2191. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hsu HT, Tseng YT, Hsu YY, Cheng KI, Chou
SH and Lo YC: Propofol attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced
reactive oxygen species production through activation of Nrf2/GSH
and suppression of NADPH oxidase in human alveolar epithelial
cells. Inflammation. 38:415–423. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen J, Zhao WH, Song ZJ, Chen HG, Xie KL,
Zhao XX and Lei GY: Effects of propofol on proliferation and
apoptosis of HCC827 cells. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University
(Medical Sciences). 3:361–363, 384. 2014.[(In Chinese)].
|
|
21
|
Zhang M, Zhang C, Zhang L, Yang Q, Zhou S,
Wen Q and Wang J: Nrf2 is a potential prognostic marker and
promotes proliferation and invasion in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 15:5312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pan H, Wang H, Zhu L, Mao L, Qiao L and Su
X: The role of Nrf2 in migration and invasion of human glioma cell
U251. World Neurosurg. 80:363–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang J, Zhang M, Zhang L, Cai H, Zhou S,
Zhang J and Wang Y: Correlation of Nrf2, HO-1, and MRP3 in
gallbladder cancer and their relationships to clinicopathologic
features and survival. J Surg Res. 164:e99–e105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma RQ, Zhang MX, Wang JS, Cai H, Yeer MK
and Duan XY: Expression and distribution of Nrf2 in several
hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue
Za Zhi. 27:608–610. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mao JT, Tangsakar E, Shen H, Wang ZQ,
Zhang MX, Chen JX, Zhang G and Wang JS: Expression and clinical
significance of Nrf2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Xi Bao
Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 27:1231–1233. 2011.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou S, Ye W, Shao Q, Zhang M and Liang J:
Nrf2 is a potential therapeutic target in radioresistance in human
cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 88:706–715. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kesharwani P, Gajbhiye V and Jain NK: A
review of nanocarriers for the delivery of small interfering RNA.
Biomaterials. 33:7138–7150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Garib V, Niggemann B, Zänker KS, Brandt L
and Kubens BS: Influence of non-volatile anesthetics on the
migration behavior of the human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-468.
Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 46:836–844. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Garib V, Lang K, Niggemann B, Zänker KS,
Brandt L and Dittmar T: Propofol-induced calcium signalling and
actin reorganization within breast carcinoma cells. Eur J
Anaesthesiol. 22:609–615. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li Q, Zhang L, Han Y, Jiang Z and Wang Q:
Propofol reduces MMPs expression by inhibiting NF-κB activity in
human MDA-MB-231 cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 66:52–56. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ecimovic P, Murray D, Doran P and Buggy
DJ: Propofol and bupivacaine in breast cancer cell function in
vitro - role of the NET1 gene. Anticancer Res. 34:1321–1331.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Siddiqui RA, Zerouga M, Wu M, Castillo A,
Harvey K, Zaloga GP and Stillwell W: Anticancer properties of
propofol-docosahexaenoate and propofol-eicosapentaenoate on breast
cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 7:R645–R654. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Deegan CA, Murray D, Doran P, Ecimovic P,
Moriarty DC and Buggy DJ: Effect of anaesthetic technique on
oestrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cell function in vitro.
Br J Anaesth. 103:685–690. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Belouchi NE, Roux E, Savineau JP and
Marthan R: Interaction of extracellular albumin and intravenous
anaesthetics, etomidate and propofol, on calcium signalling in rat
airway smooth muscle cells. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 14:395–400.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cui WY, Liu Y, Zhu YQ, Song T and Wang QS:
Propofol induces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and apoptosis in
lung cancer cell H460. Tumour Biol. 35:5213–5217. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|