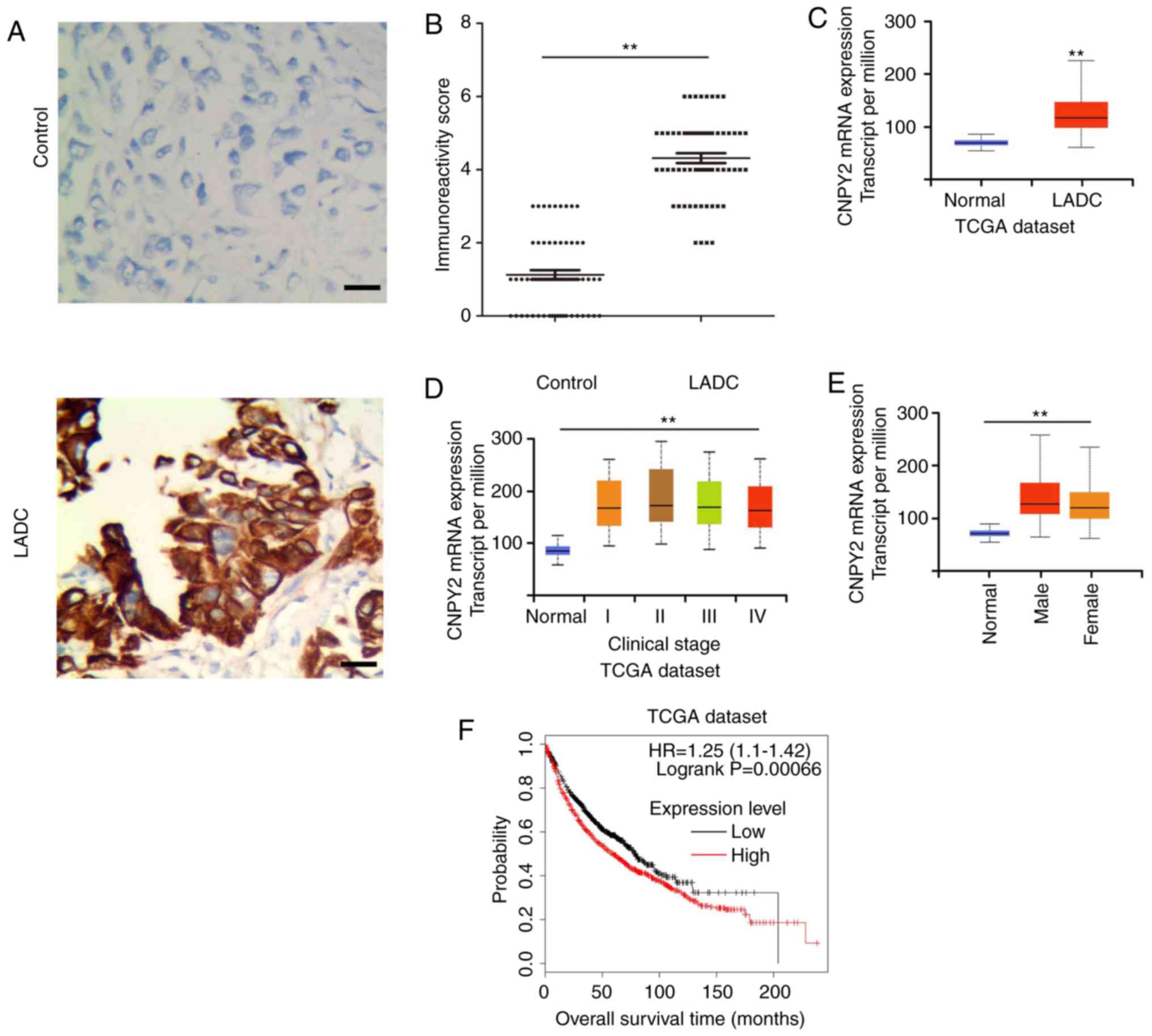
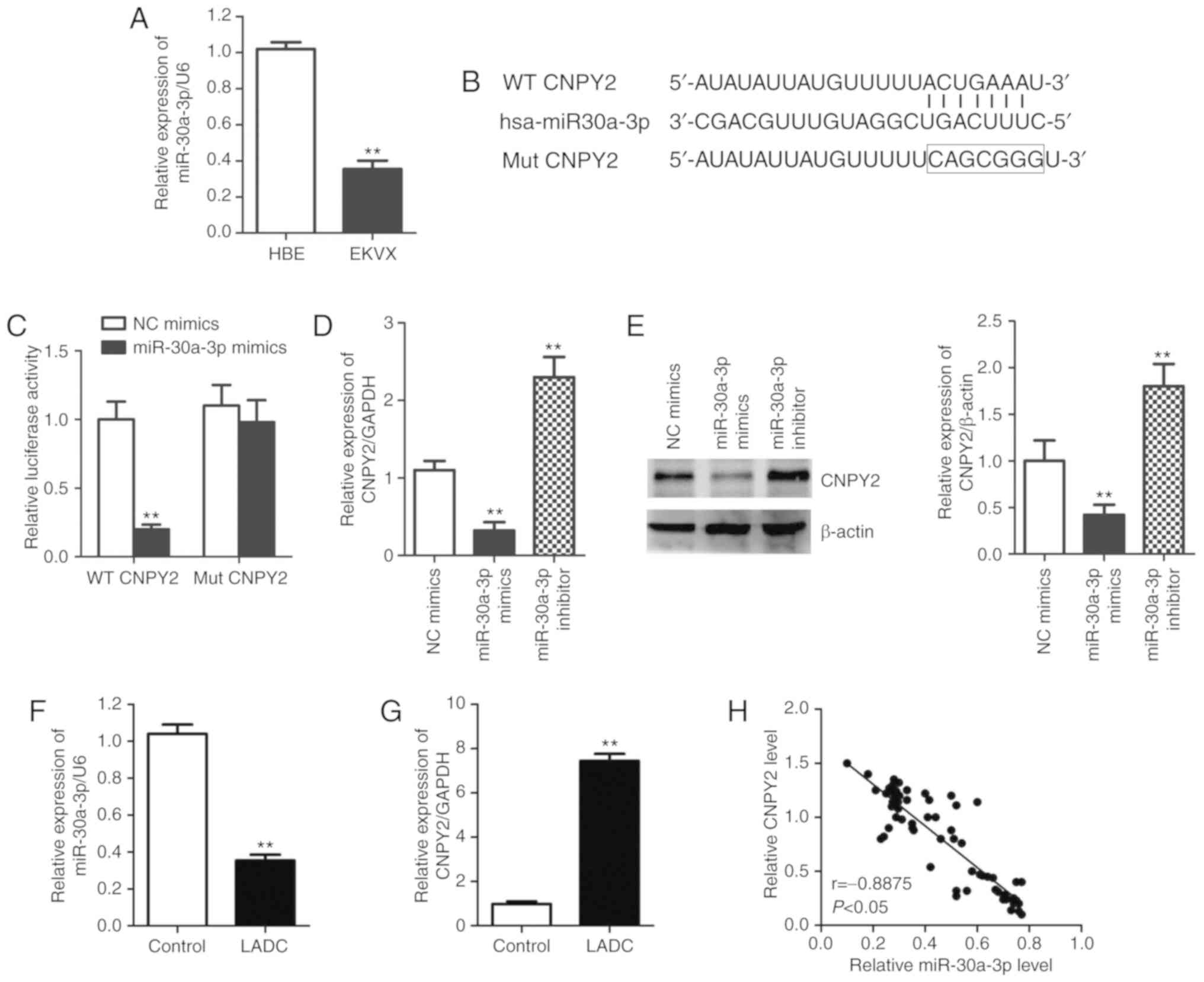
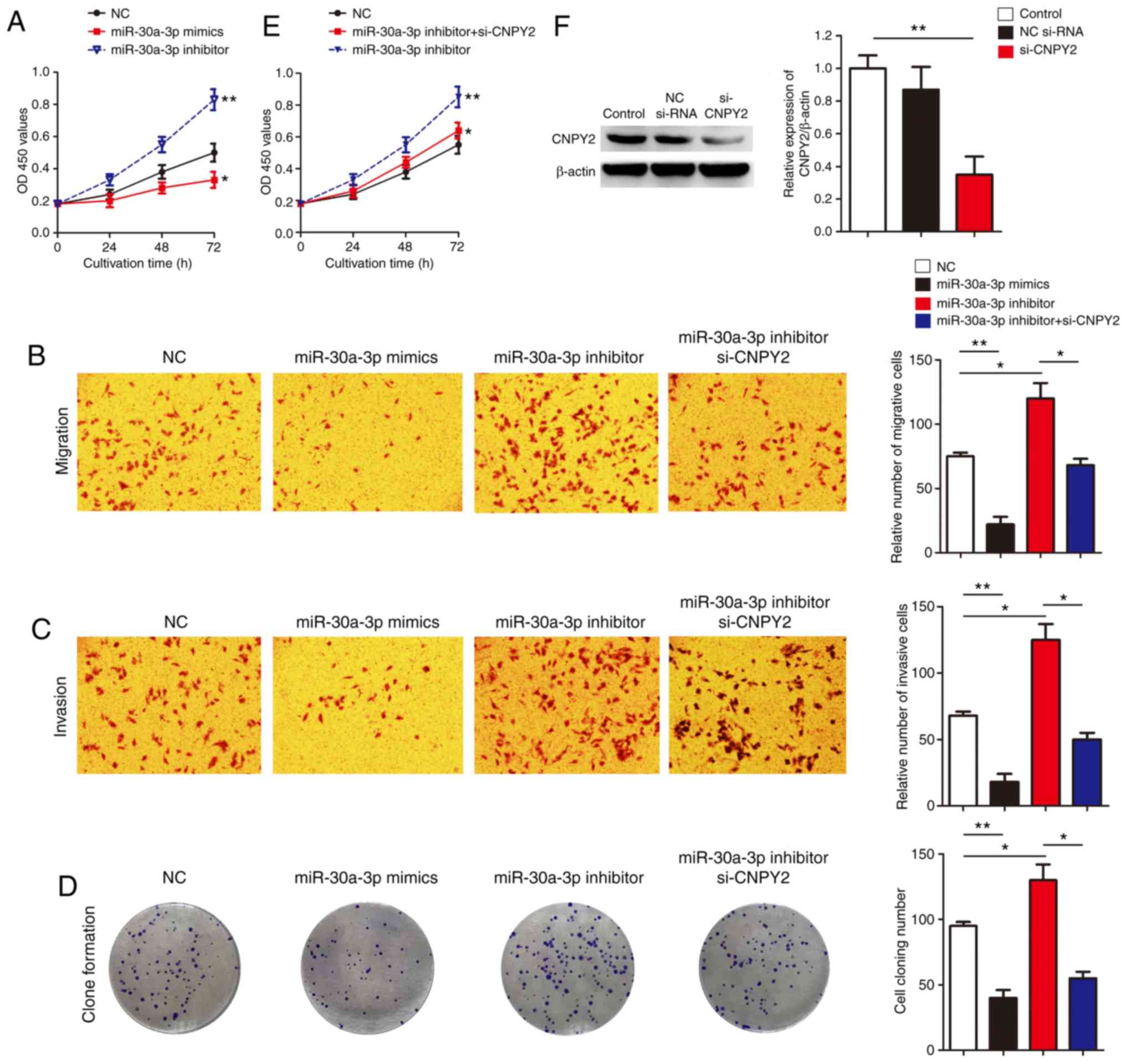
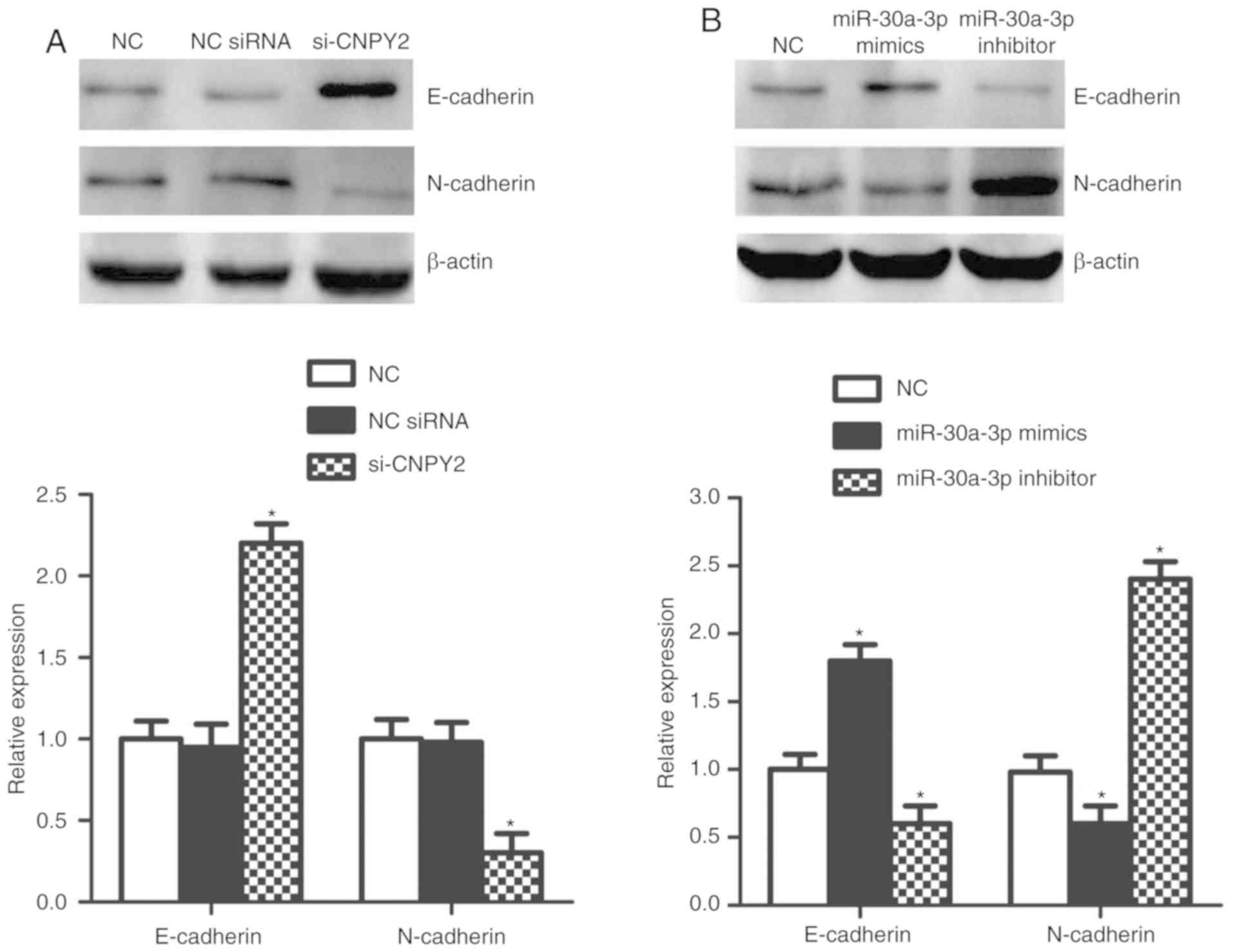
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara
S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, Gemma A, Harada M, Yoshizawa H, Kinoshita I,
et al: North-East japan study group: Gefitinib or chemotherapy for
non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med.
362:2380–2388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fukuoka M, Wu YL, Thongprasert S,
Sunpaweravong P, Leong SS, Sriuranpong V, Chao TY, Nakagawa K, Chu
DT, Saijo N, et al: Biomarker analyses and final overall survival
results from a phase III, randomized, open-label, first-line study
of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected
patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in asia (IPASS).
J Clin Oncol. 29:2866–2874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jänne PA, Yang JC, Kim DW, Planchard D,
Ohe Y, Ramalingam SS, Ahn MJ, Kim SW, Su WC, Horn L, et al: AZD9291
in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J
Med. 372:1689–1699. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bruhn H: A short guided tour through
functional and structural features of saposin-like proteins.
Biochem J. 389:249–257. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guo J, Zhang Y, Mihic A, Li SH, Sun Z,
Shao Z, Wu J, Weisel RD and Li RK: A secreted protein (Canopy 2,
CNPY2) enhances angiogenesis and promotes smooth muscle cell
migration and proliferation. Cardiovasc Res. 105:383–393. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guo J, Mihic A, Wu J, Zhang Y, Singh K,
Dhingra S, Weisel RD and Li RK: Canopy 2 attenuates the transition
from compensatory hypertrophy to dilated heart failure in
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J. 36:2530–2540. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ito S, Ueda T, Ueno A, Nakagawa H,
Taniguchi H, Kayukawa N and Miki T: A genetic screen in drosophila
for regulators of human prostate cancer progression. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 451:548–555. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yan P, Gong H, Zhai X, Feng Y, Wu J, He S,
Guo J, Wang X, Guo R, Xie J and Li RK: Decreasing CNPY2 expression
diminishes colorectal tumor growth and development through
activation of p53 pathway. Am J Pathol. 186:1015–1024. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Taniguchi H, Ito S, Ueda T, Morioka Y,
Kayukawa N, Ueno A, Nakagawa H, Fujihara A, Ushijima S, Kanazawa M,
et al: CNPY2 promoted the proliferation of renal cell carcinoma
cells and increased the expression of TP53. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 485:267–271. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shimura M, Mizuma M, Takadate T, Katoh Y,
Suzuki T, Iseki M, Hata T, Aoki S, Suzuki Y, Sakata N, et al: A
novel liver metastasis-correlated protein of pancreatic
neuroendocrine neoplasm (PanNEN) discovered by proteomic analysis.
Oncotarget. 9:24291–24303. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu D, Qin Y, Jun-Qiang L and Shun-Lin G:
CNPY2 enhances resistance to apoptosis induced by cisplatin via
activation of NF-kB pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer.
Biomed Pharmacother. 103:1658–1663. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fu J, Xu X, Kang L, Zhou L, Wang S, Lu J,
Cheng L, Fan Z, Yuan B, Tian P, et al: MiR-30a suppresses breast
cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting eya2. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 445:314–319. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang W, Lin H, Zhou L, Zhu Q, Gao S, Xie
H, Liu Z, Xu Z, Wei J, Huang X and Zheng S: MicroRNA-30a-3p
inhibits tumor proliferation, invasiveness and metastasis and is
downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol.
40:1586–1594. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu M, Huang F, Zhang D, Ju J, Wu XB, Wang
Y, Wang Y, Wu Y, Nie M, Li Z, et al: Heterochromatin protein HP1γ
promotes colorectal cancer progression and is regulated by miR-30a.
Cancer Res. 75:4593–4604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu Z, Chen L, Zhang X, Xu X, Xing H,
Zhang Y, Li W, Yu H, Zeng J and Jia J: RUNX3 regulates vimentin
expression via miR-30a during epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
gastric cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 18:610–623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao J, Li B, Shu C, Ma Y and Gong Y:
Downregulation of miR-30a is associated with proliferation and
invasion via targeting MEF2D in cervical cancer. Oncol Lett.
14:7437–7442. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Z, Dai X, Chen Y, Sun C, Zhu Q, Zhao
H, Liu G, Huang Q and Lan Q: MiR-30a-5p is induced by Wnt/β-catenin
pathway and promotes glioma cell invasion by repressing NCAM.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 465:374–380. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang HY, Li YY, Fu S, Wang XP, Huang MY,
Zhang X, Shao Q, Deng L, Zeng MS, Zeng YX and Shao JY: MicroRNA-30a
promotes invasiveness and metastasis in vitro and in vivo through
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and results in poor survival of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
239:891–898. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park D, Kim H, Kim Y and Jeoung D: MiR-30a
regulates the expression of CAGE and p53 and regulates the response
to anti-cancer drugs. Mol Cells. 39:299–309. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Feng Z, Gan H, Cai Z, Li N, Yang Z, Lu G
and Chen J: Aberrant expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α,
TWIST and E-cadherin is associated with aggressive tumor phenotypes
in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
43:396–403. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang H, Liu H, Min S, Shen Y, Li W and
Wang X: CDK16 overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and
regulates cancer cell growth and apoptosis via a p27-dependent
mechanism. Biomed Pharmacother. 103:399–405. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dou Y, Lei JQ, Guo SL, Zhao D, Yue HM and
Yu Q: The CNPY2 enhances epithelial-mesenchymal transition via
activating the AKT/GSK3β pathway in non-small cell lung cancer.
Cell Biol Int. 42:959–964. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhong B, Guo S, Zhang W and Zhang C, Wang
Y and Zhang C: Bioinformatics prediction of miR-30a targets and its
inhibition of cell proliferation of osteosarcoma by up-regulating
the expression of PTEN. BMC Med Genomics. 10:642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chaffer CL, San Juan BP, Lim E and
Weinberg RA: EMT, cell plasticity and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 35:645–654. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Santamaria PG, Moreno-Bueno G, Portillo F
and Cano A: EMT: Present and future in clinical oncology. Mol
Oncol. 11:718–738. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qi B, Wang Y, Chen ZJ, Li XN, Qi Y, Yang
Y, Cui GH, Guo HZ, Li WH and Zhao S: Down-regulation of
miR-30a-3p/5p promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell
proliferation by activating the Wnt signaling pathway. World J
Gastroenterol. 23:7965–7977. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Staton AA and Giraldez AJ: Use of target
protector morpholinos to analyze the physiological roles of
specific miRNA-mRNA pairs in vivo. Nat Protoc. 6:2035–2049. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Świtlik W, Karbownik MS, Suwalski M, Kozak
J and Szemraj J: MiR-30a-5p together with miR-210-3p as a promising
biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer: A preliminary study.
Cancer Biomark. 21:479–488. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu Q, Li H, Li Y and Jiang L:
MicroRNA-30a functions as tumor suppressor and inhibits the
proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer cells by
down-regulation of SIX1. Hum Cell. 30:290–299. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Han X, Zhen S, Ye Z, Lu J, Wang L, Li P,
Li J, Zheng X, Li H, Chen W and Zhao L: A feedback loop between
miR-30a/c-5p and DNMT1 mediates cisplatin resistance in ovarian
cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 41:973–986. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|