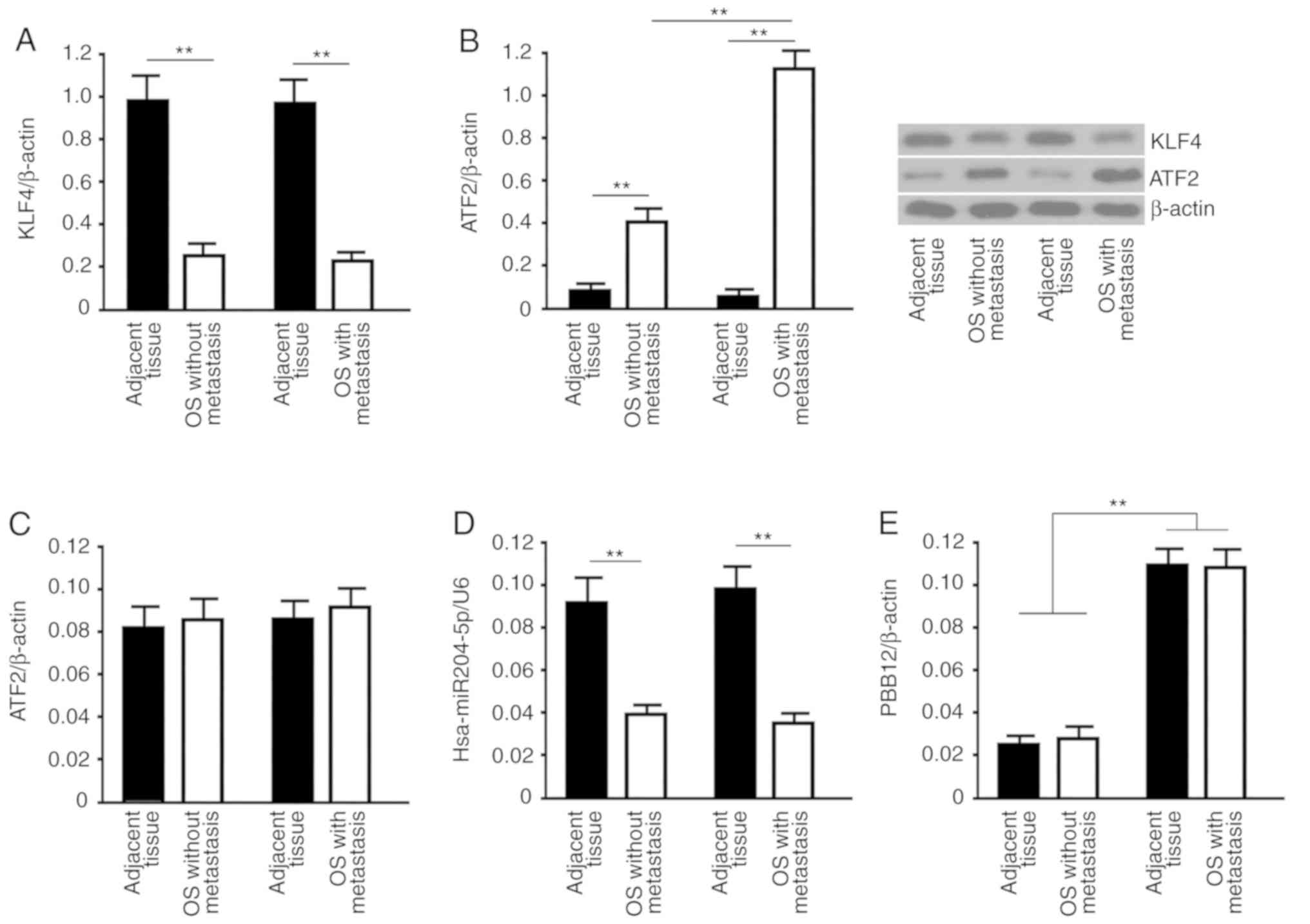
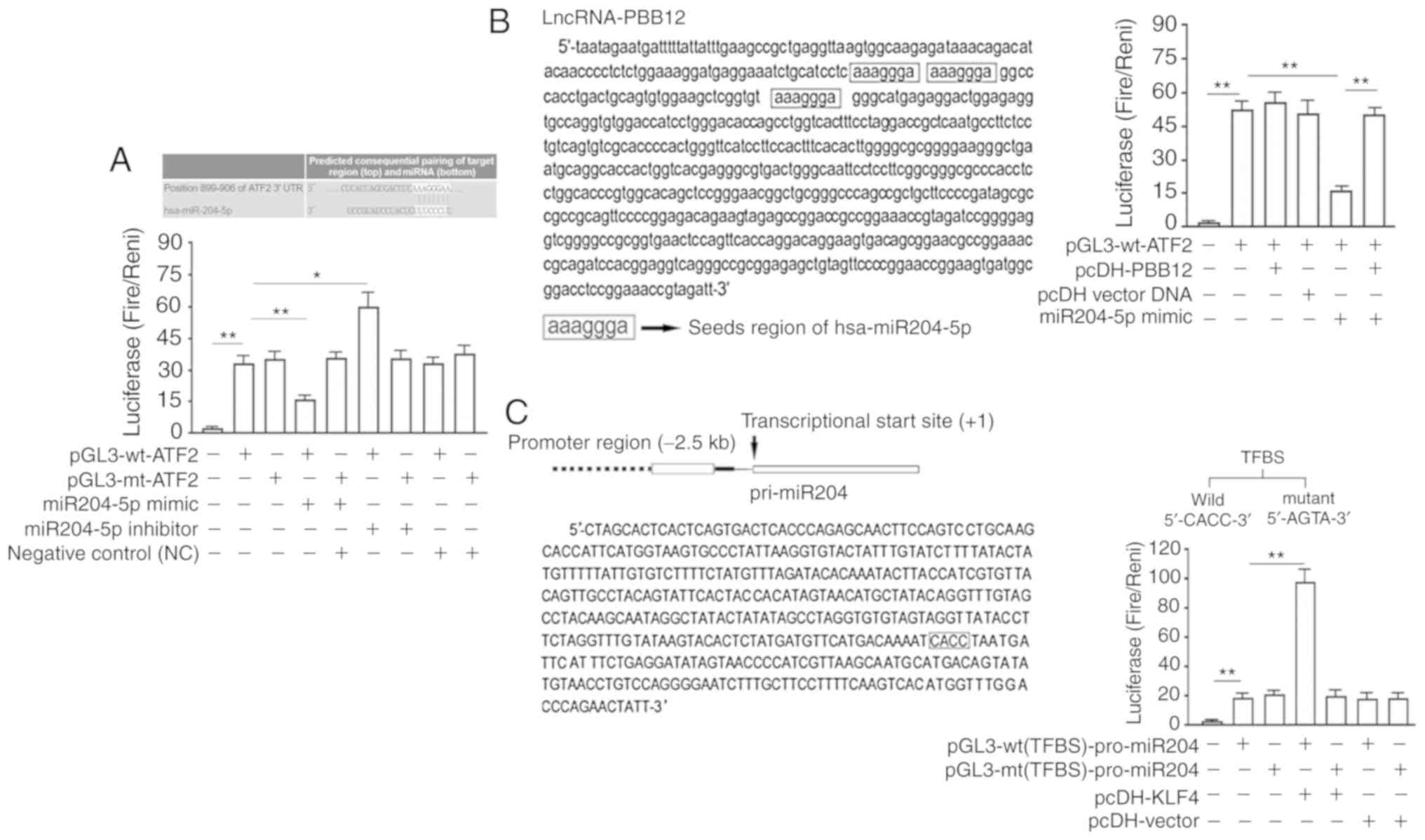
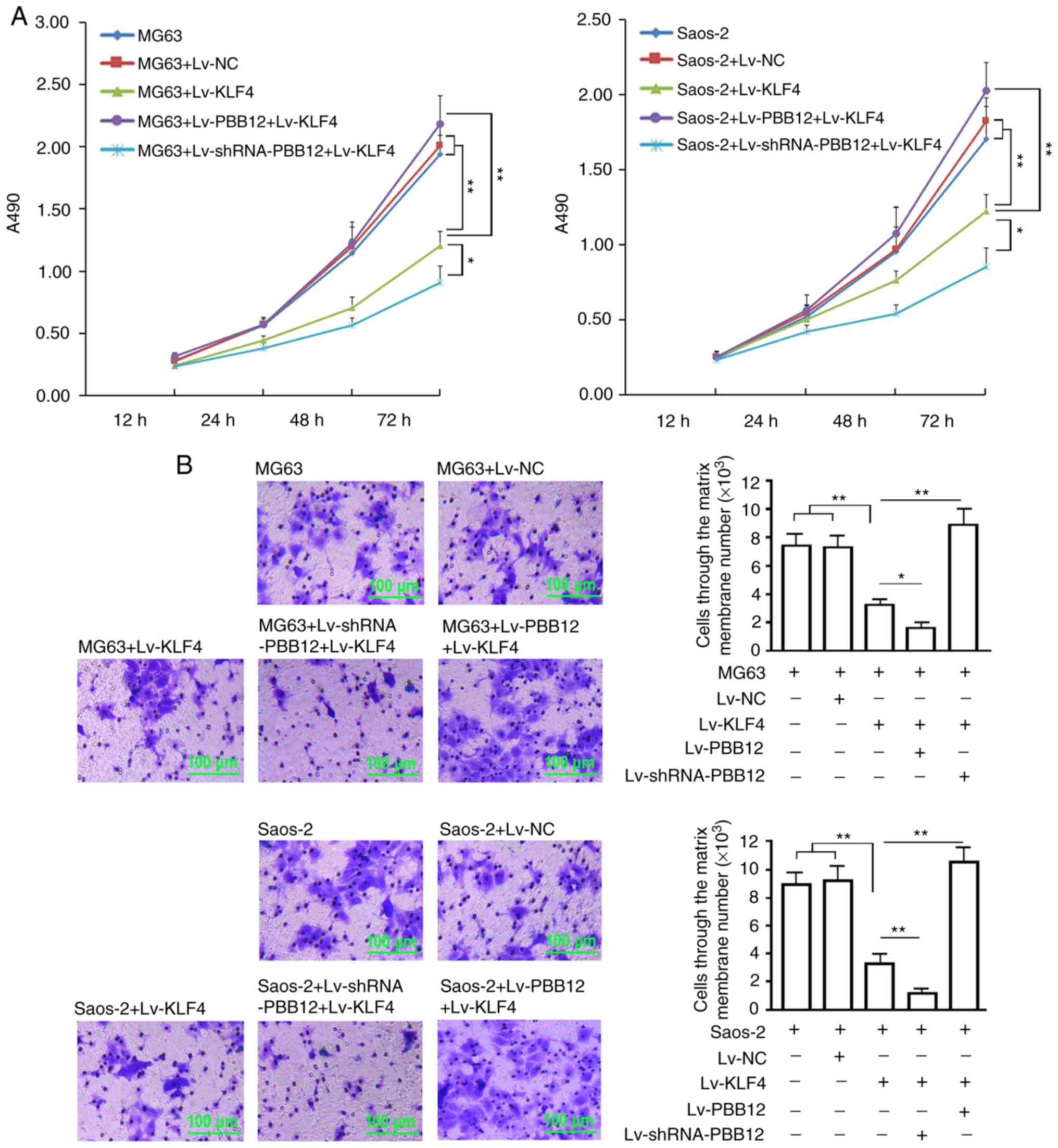
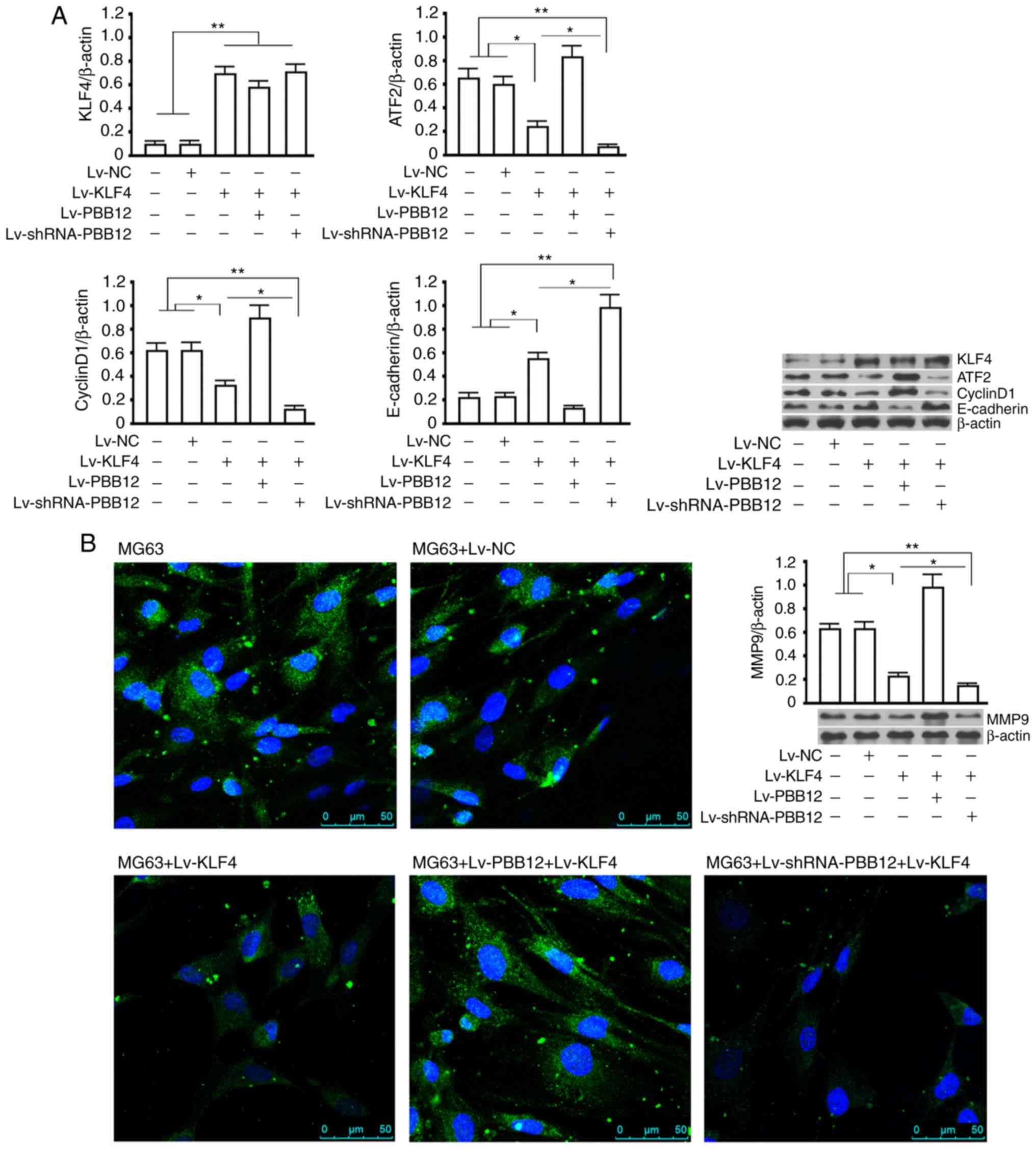
|
1
|
Kasinski AL and Slack FJ: Epigenetics and
genetics. MicroRNAs en route to the clinic: Progress in validating
and targeting microRNAs for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:849–864. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liang W, Gao B, Fu P, Xu S, Qian Y and Fu
Q: The miRNAs in the pathgenesis of osteosarcoma. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 18:788–794. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hauptman N and Glavač D: Long non-coding
RNA in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 14:4655–4669. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Abdelmohsen K and Gorospe M: Noncoding RNA
control of cellular senescence. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA.
6:615–629. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alaei-Mahabadi B and Larsson E: Limited
evidence for evolutionarily conserved targeting of long non-coding
RNAs by microRNAs. Silence. 4:42013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou DK, Yang XW, Li H, Yang Y, Zhu ZJ and
Wu N: Up-regulation of long noncoding RNA CCAL predicts poor
patient prognosis and promotes tumor metastasis in osteosarcoma.
Int J Biol Markers. 32:e108–e112. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li W, Xie P and Ruan WH: Overexpression of
lncRNA UCA1 promotes osteosarcoma progression and correlates with
poor prognosis. J Bone Oncol. 5:80–85. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fan H, Liu G, Zhao C, Li X and Yang X:
Transcription factor Oct4 promotes osteosarcoma by regulating
lncRNA AK055347. Oncol Lett. 13:396–402. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fornes O, Castro-Mondragon JA, Khan A, van
der Lee R, Zhang X, Richmond PA, Modi BP, Correard S, Gheorghe M,
Baranašić D, et al: JASPAR 2020: Update of the open-access database
of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. Nov
8–2019.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ponting CP, Oliver PL and Reik W:
Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 136:629–641.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bergmann JH and Spector DL: Long
non-coding RNAs: Modulators of nuclear structure and function. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 26:10–18. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Deng G and Sui G: Noncoding RNA in
oncogenesis: A new era of identifying key players. Int J Mol Sci.
14:18319–18349. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pickard MR and Williams GT: Molecular and
cellular mechanisms of action of tumour suppressor GAS5 lncRNA.
Genes (Basel). 6:484–499. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pang M, Xing C, Adams N, Rodriguez-Uribe
L, Hughs SE, Hanson SF and Zhang J: Comparative expression of miRNA
genes and miRNA-based AFLP marker analysis in cultivated tetraploid
cottons. J Plant Physiol. 168:824–830. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brodersen P, Sakvarelidze-Achard L,
Schaller H, Khafif M, Schott G, Bendahmane A and Voinnet O:
Isoprenoid biosynthesis is required for miRNA function and affects
membrane association of ARGONAUTE 1 in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 109:1778–1783. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sampson VB, Yoo S, Kumar A, Vetter NS and
Kolb EA: MicroRNAs and potential targets in osteosarcoma: Review.
Front Pediatr. 3:692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng CJ, Bahal R, Babar IA, Pincus Z,
Barrera F, Liu C, Svoronos A, Braddock DT, Glazer PM, Engelman DM,
et al: MicroRNA silencing for cancer therapy targeted to the tumour
microenvironment. Nature. 518:107–110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ziyan W, Shuhua Y, Xiufang W and Xiaoyun
L: MicroRNA-21 is involved in osteosarcoma cell invasion and
migration. Med Oncol. 28:1469–1474. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ren X, Shen Y, Zheng S, Liu J and Jiang X:
miR-21 predicts poor prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma. Br J
Biomed Sci. 73:158–162. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tian R, Xie X, Han J, Luo C, Yong B, Peng
H, Shen J and Peng T: miR-199a-3p negatively regulates the
progression of osteosarcoma through targeting AXL. Am J Cancer Res.
4:738–750. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang F, Yu D, Liu Z, Wang R, Xu Y, Cui H
and Zhao T: MiR-125b Functions as a tumor suppressor and enhances
chemosensitivity to cisplatin in osteosarcoma. Technol Cancer Res
Treat. 15:NP105–NP112. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Thayanithy V, Sarver AL, Kartha RV, Li L,
Angstadt AY, Breen M, Steer CJ, Modiano JF and Subramanian S:
Perturbation of 14q32 miRNAs-cMYC gene network in osteosarcoma.
Bone. 50:171–181. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu JJ, Pi WS, Cao Y, Peng AF, Cao ZY, Liu
JM, Huang SH, Liu ZL and Zhang W: Let-7a inhibits osteosarcoma cell
growth and lung metastasis by targeting Aurora-B. Cancer Manag Res.
10:6305–6315. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang RJ, Shi KR, Zhang J, Zhang J, Gao RR
and Zhu SC: Effects of miR-93 on proliferation and apoptosis of
osteosarcoma cells. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 45:866–870.
2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aftab MN, Dinger ME and Perera RJ: The
role of microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in the pathology,
diagnosis, and management of melanoma. Arch Biochem Biophys.
563:60–70. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xie CH, Cao YM, Huang Y, Shi QW, Guo JH,
Fan ZW, Li JG, Chen BW and Wu BY: Long non-coding RNA TUG1
contributes to tumorigenesis of human osteosarcoma by sponging
miR-9-5p and regulating POU2F1 expression. Tumour Biol.
37:15031–15041. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang Q, Geng PL, Yin P, Wang XL, Jia JP
and Yao J: Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA TUG1 inhibits
osteosarcoma cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 14:2311–2315. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Y, Yang T, Zhang Z, Lu M, Zhao W,
Zeng X and Zhang W: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes migration and
invasion by acting as a ceRNA of miR-335-5p in osteosarcoma cells.
Cancer Sci. 108:859–867. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou Q, Chen F, Zhao J, Li B, Liang Y, Pan
W, Zhang S, Wang X and Zheng D: Long non-coding RNA PVT1 promotes
osteosarcoma development by acting as a molecular sponge to
regulate miR-195. Oncotarget. 7:82620–82633. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chan LH, Wang W, Yeung W, Deng Y, Yuan P
and Mak KK: Hedgehog signaling induces osteosarcoma development
through Yap1 and H19 overexpression. Oncogene. 33:4857–4866. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li M, Chen H, Zhao Y, Gao S and Cheng C:
H19 functions as a ceRNA in promoting metastasis through decreasing
miR-200s activity in osteosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol. 35:235–240. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Taniguchi M, Fujiwara K, Nakai Y, Ozaki T,
Koshikawa N, Toshio K, Kataba M, Oguni A, Matsuda H, Yoshida Y, et
al: Inhibition of malignant phenotypes of human osteosarcoma cells
by a gene silencer, a pyrrole-imidazole polyamide, which targets an
E-box motif. FEBS Open Bio. 4:328–334. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Luan W, Qian Y, Ni X, Bu X, Xia Y, Wang J,
Ruan H, Ma S and Xu B: miR-204-5p acts as a tumor suppressor by
targeting matrix metalloproteinases-9 and B-cell lymphoma-2 in
malignant melanoma. Onco Targets Ther. 10:1237–1246. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sümbül AT, Göğebakan B, Ergün S, Yengil E,
Batmacı CY, Tonyalı Ö and Yaldız M: miR-204-5p expression in
colorectal cancer: An autophagy-associated gene. Tumour Biol.
35:12713–12719. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zeng J, Wei M, Shi R, Cai C, Liu X, Li T
and Ma W: MiR-204-5p/Six1 feedback loop promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Tumour Biol.
37:2729–2735. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vlahopoulos SA, Logotheti S, Mikas D,
Giarika A, Gorgoulis V and Zoumpourlis V: The role of ATF-2 in
oncogenesis. Bioessays. 30:314–327. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hsu CC and Hu CD: Critical role of
N-terminal end-localized nuclear export signal in regulation of
activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2) subcellular localization
and transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem. 287:8621–8632. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lewis JS, Vijayanathan V, Thomas TJ,
Pestell RG, Albanese C, Gallo MA and Thomas T: Activation of cyclin
D1 by estradiol and spermine in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: A
mechanism involving the p38 MAP kinase and phosphorylation of
ATF-2. Oncol Res. 15:113–128. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fan Z, Duan X, Cai H, Wang L, Li M, Qu J,
Li W, Wang Y and Wang J: Curcumin inhibits the invasion of lung
cancer cells by modulating the PKCα/Nox-2/ROS/ATF-2/MMP-9 signaling
pathway. Oncol Rep. 34:691–698. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xu Y, Liu Z and Guo K: The effect of JDP2
and ATF2 on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human
pancreatic cancer cell lines. Pathol Oncol Res. 18:571–577. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tang J, Liao Y, He S, Shi J, Peng L, Xu X,
Xie F, Diao N, Huang J, Xie Q, et al: Autocrine parathyroid
hormone-like hormone promotes intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell
proliferation via increased ERK/JNK-ATF2-cyclinD1 signaling. J
Transl Med. 15:2382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pu M, Li C, Qi X, Chen J, Wang Y, Gao L,
Miao L and Ren J: MiR-1254 suppresses HO-1 expression through seed
region-dependent silencing and non-seed interaction with TFAP2A
transcript to attenuate NSCLC growth. PLoS Genet. 13:e10068962017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhao Y, Qi X, Chen J, Wei W, Yu C, Yan H,
Pu M, Li Y, Miao L, Li C and Ren J: The miR-491-3p/Sp3/ABCB1 axis
attenuates multidrug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer
Lett. 408:102–111. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|