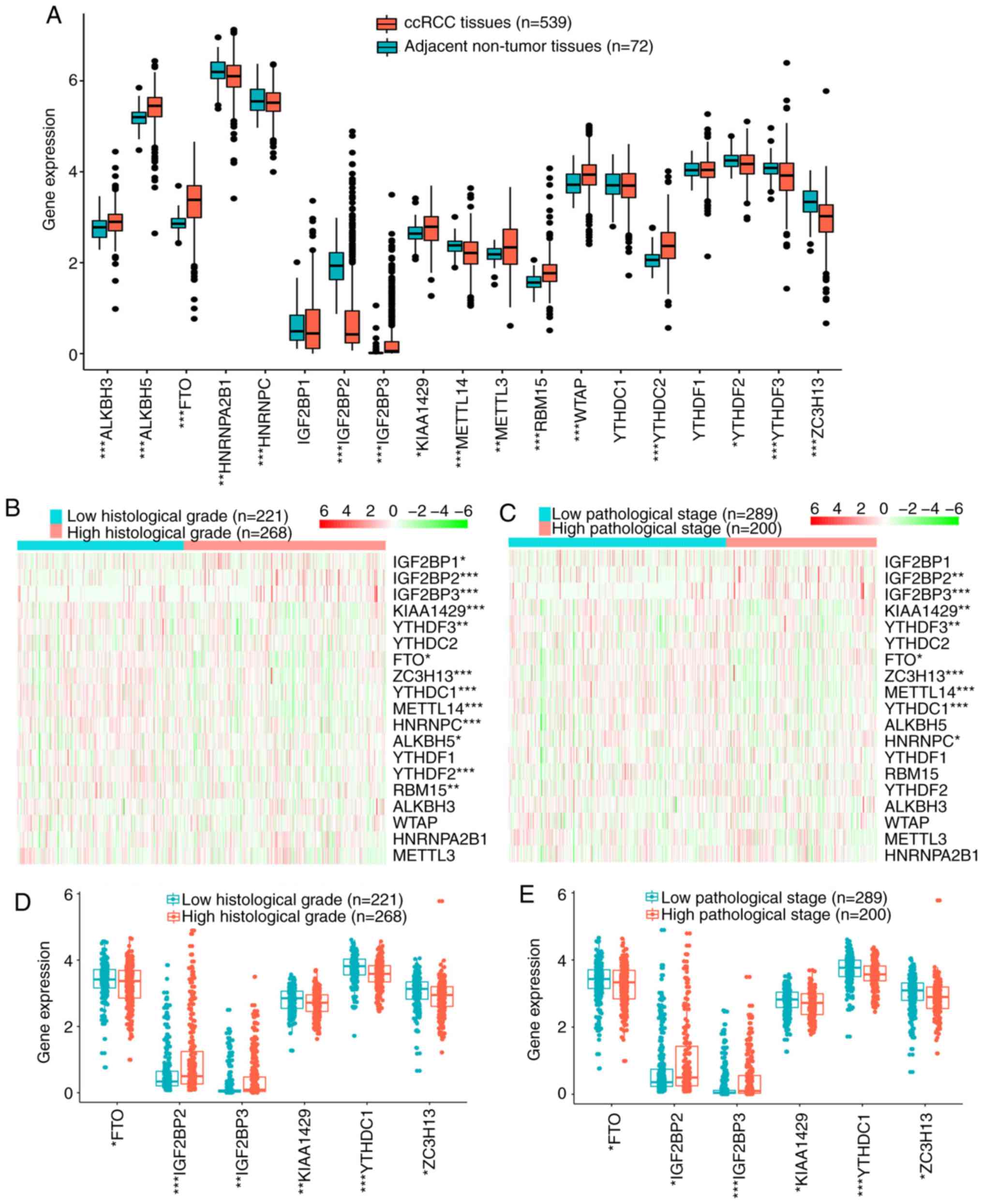
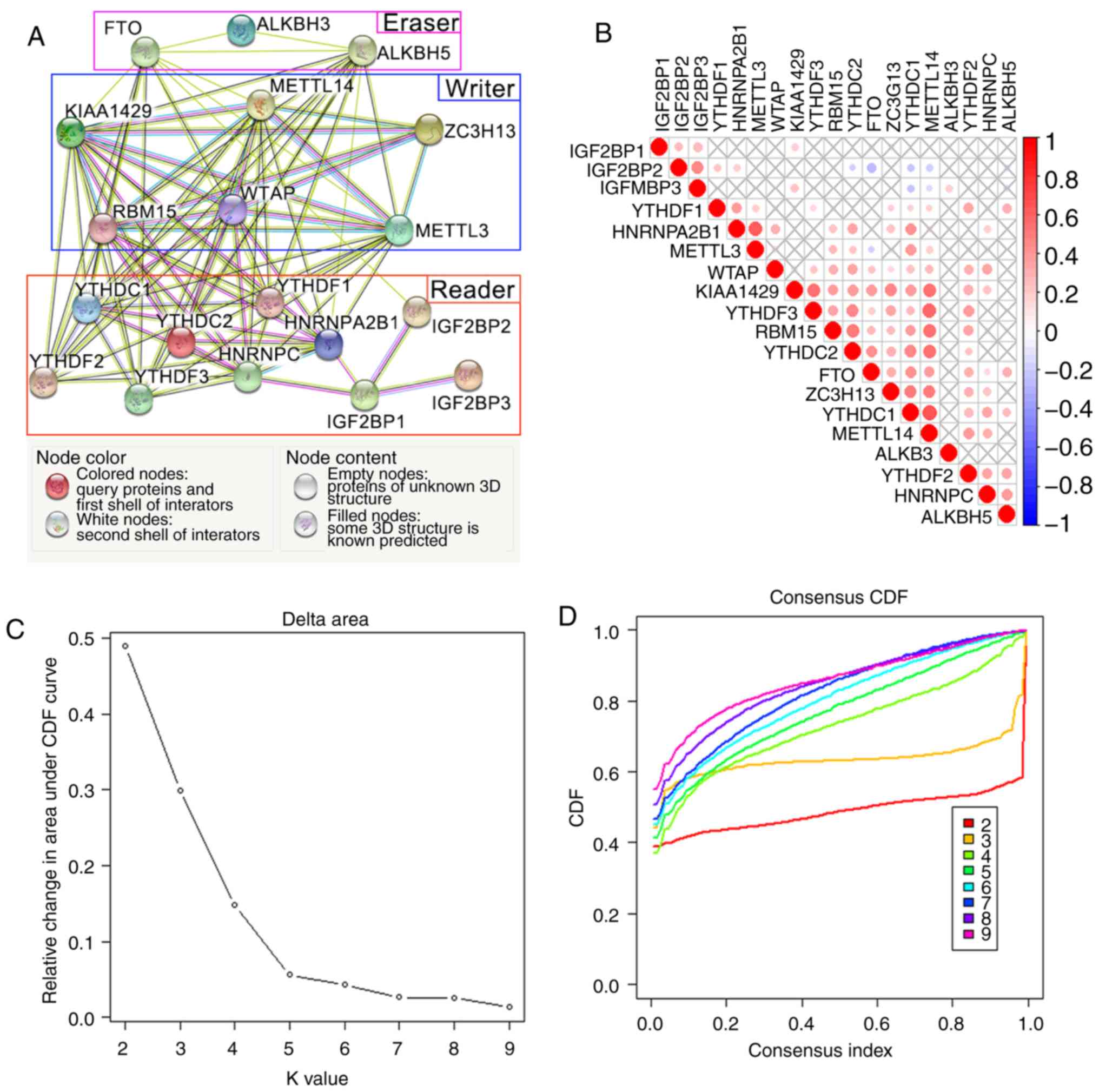
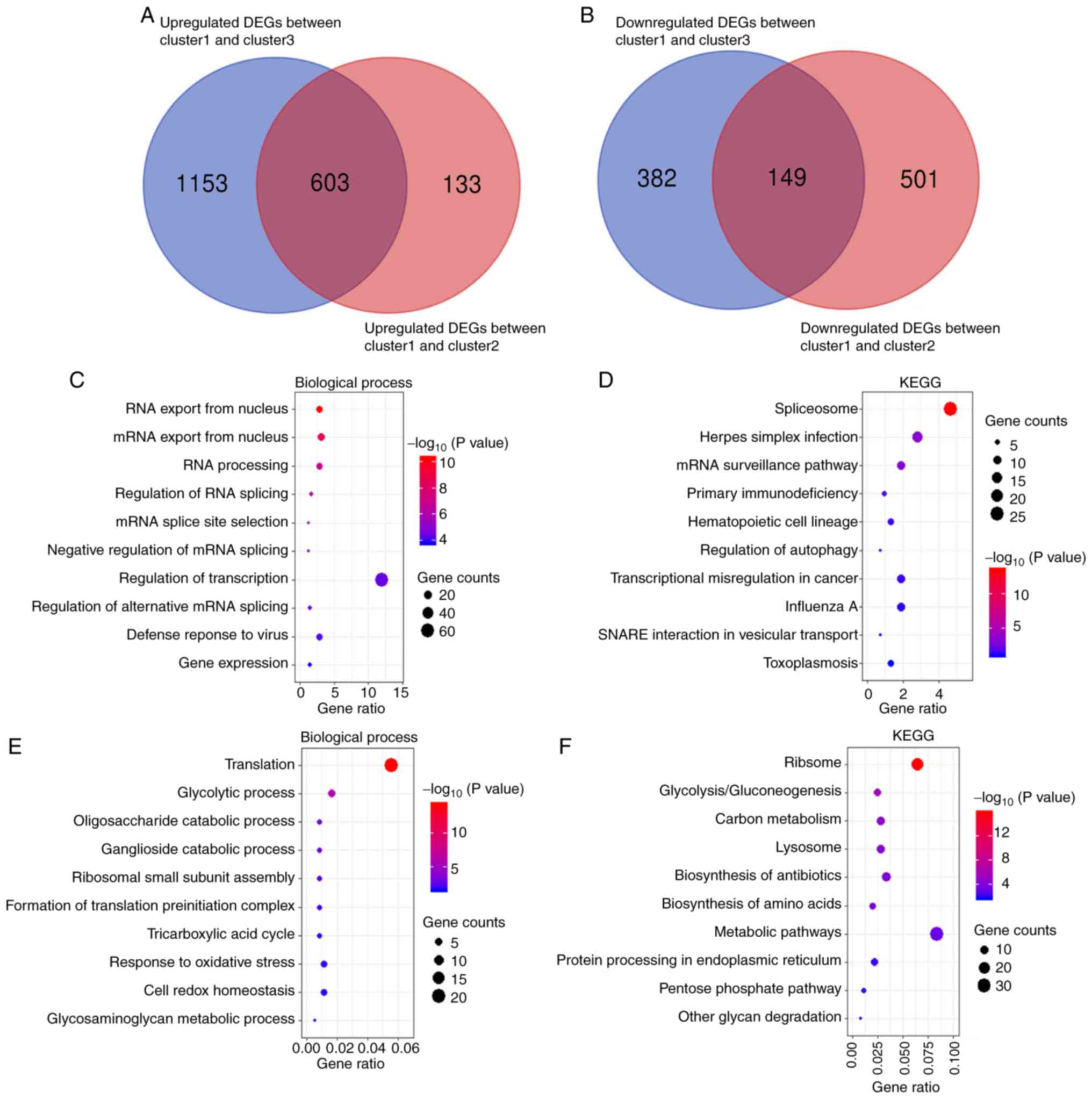
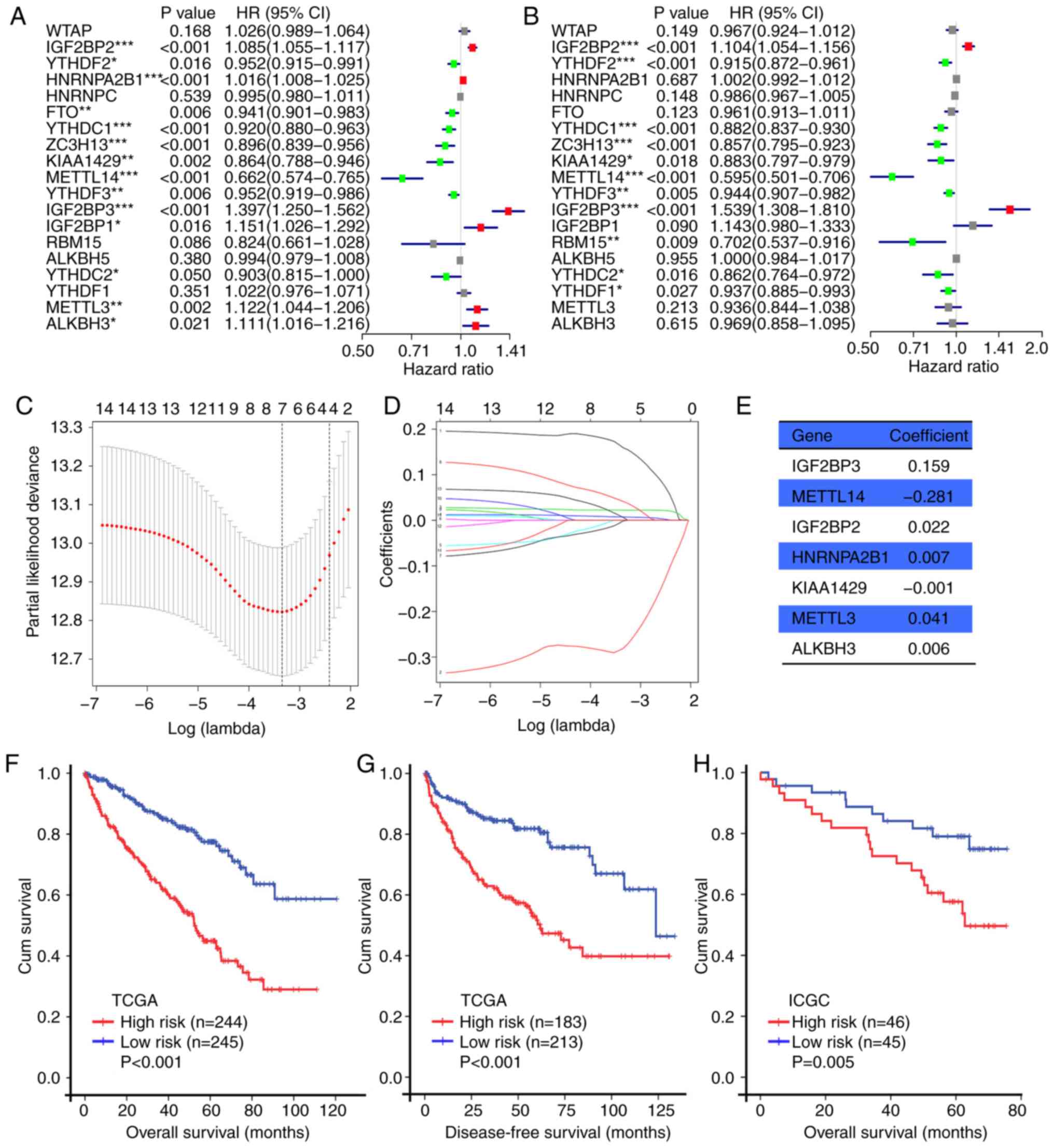
|
1
|
Boccaletto P, Machnicka MA, Purta E,
Piatkowski P, Baginski B, Wirecki TK, de Crecy-Lagard V, Ross R,
Limbach PA, Kotter A, et al: MODOMICS: A database of RNA
modification pathways. 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res.
46:D303–D307. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lewis CJ, Pan T and Kalsotra A: RNA
modifications and structures cooperate to guide RNA-protein
interactions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 18:202–210. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gilbert WV, Bell TA and Schaening C:
Messenger RNA modifications: Form, distribution, and function.
Science. 352:1408–1412. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Karijolich J, Kantartzis A and Yu YT: RNA
Modifications: A Mechanism that Modulates Gene Expression. Methods
Mol Biol. 629:1–19. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang S, Sun C, Li J, Zhang E, Ma Z, Xu W,
Li H, Qiu M, Xu Y, Xia W, et al: Roles of RNA methylation by means
of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in human cancers.
Cancer Lett. 408:112–120. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Desrosiers R, Friderici K and Rottman F:
Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from
Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 71:3971–3975.
1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S,
Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, Cesarkas K,
Jacob-Hirsch J, Amariglio N, Kupiec M, et al: Topology of the human
and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature.
485:201–206. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O,
Mason CE and Jaffrey SR: Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation
reveals enrichment in 3′ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell.
149:1635–1646. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun T, Wu R and Ming L: The role of m6A
RNA methylation in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 112:1086132019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Xiao J, Bai J, Tian Y, Qu Y, Chen X,
Wang Q, Li X, Zhang Y and Xu J: Molecular characterization and
clinical relevance of m6A regulators across 33 cancer
types. Mol Cancer. 18:1372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dai D, Wang H, Zhu L, Jin H and Wang X:
N6-methyladenosine links RNA metabolism to cancer progression. Cell
Death Dis. 9:1242018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Niu Y, Zhao X, Wu YS, Li MM, Wang XJ and
Yang YG: N6-methyl-adenosine (m6A) in RNA: An old modification with
a novel epigenetic function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics.
11:8–17. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fustin JM, Doi M, Yamaguchi Y, Hida H,
Nishimura S, Yoshida M, Isagawa T, Morioka MS, Kakeya H, Manabe I,
et al: RNA-methylation-dependent RNA processing controls the speed
of the circadian clock. Cell. 155:793–806. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Geula S, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S,
Dominissini D, Mansour AA, Kol N, Salmon-Divon M, Hershkovitz V,
Peer E, Mor N, Manor YS, et al: Stem cells. m6A mRNA methylation
facilitates resolution of naive pluripotency toward
differentiation. Science. 347:1002–1006. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiang Y, Laurent B, Hsu CH, Nachtergaele
S, Lu Z, Sheng W, Xu C, Chen H, Ouyang J, Wang S, et al: RNA
m6A methylation regulates the ultraviolet-induced DNA
damage response. Nature. 543:573–576. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cui Q, Shi H, Ye P, Li L, Qu Q, Sun G, Sun
G, Lu Z, Huang Y, Yang CG, et al: m6A RNA methylation
regulates the self-renewal and tumorigenesis of glioblastoma stem
cells. Cell Rep. 18:2622–2634. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chai RC, Wu F, Wang QX, Zhang S, Zhang KN,
Liu YQ, Zhao Z, Jiang T, Wang YZ and Kang CS: m6A RNA
methylation regulators contribute to malignant progression and have
clinical prognostic impact in gliomas. Aging. 11:1204–1225. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Z, Weng H, Su R, Weng X, Zuo Z, Li C,
Huang H, Nachtergaele S, Dong L, Hu C, et al: FTO plays an
oncogenic role in acute myeloid leukemia as a
N6-methyladenosine RNA demethylase. Cancer Cell.
31:127–141. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen M, Wei L, Law CT, Tsang FH, Shen J,
Cheng CL, Tsang LH, Ho DW, Chiu DK, Lee JM, et al: RNA
N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase-like 3 promotes liver cancer
progression through YTHDF2-dependent posttranscriptional silencing
of SOCS2. Hepatology. 67:2254–2270. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang C, Samanta D, Lu H, Bullen JW, Zhang
H, Chen I, He X and Semenza GL: Hypoxia induces the breast cancer
stem cell phenotype by HIF-dependent and ALKBH5-mediated
m6A-demethylation of NANOG mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:E2047–E2056. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lobo J, Barros-Silva D, Henrique R and
Jeronimo C: The emerging role of epitranscriptomics in cancer:
Focus on urological tumors. Genes (Basel). 9(pii): E5522018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou J, Wang J, Hong B, Ma K, Xie H, Li L,
Zhang K, Zhou B, Cai L and Gong K: Gene signatures and prognostic
values of m6A regulators in clear cell renal cell carcinoma-a
retrospective study using TCGA database. Aging (Albany NY).
11:1633–1647. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gong D, Zhang J, Chen Y, Xu Y, Ma J, Hu G,
Huang Y, Zheng J, Zhai W and Xue W: The m6A-suppressed
P2RX6 activation promotes renal cancer cells migration and invasion
through ATP-induced Ca2+ influx modulating ERK1/2
phosphorylation and MMP9 signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
38:2332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tang J, Wang F, Cheng G, Si S, Sun X, Han
J, Yu H, Zhang W, Lv Q, Wei JF and Yang H: Wilms' tumor
1-associating protein promotes renal cell carcinoma proliferation
by regulating CDK2 mRNA stability. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
37:402018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ghosh A and Barman S: Application of
Euclidean distance measurement and principal component analysis for
gene identification. Gene. 583:112–120. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Senbabaoglu Y, Michailidis G and Li JZ:
Critical limitations of consensus clustering in class discovery.
Sci Rep. 4:62072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Simon N, Friedman J, Hastie T and
Tibshirani R: Regularization paths for cox's proportional hazards
model via coordinate descent. J Stat Softw. 39:1–13. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Amin MB, Amin MB, Tamboli P, Javidan J,
Stricker H, de-Peralta Venturina M, Deshpande A and Menon M:
Prognostic impact of histologic subtyping of adult renal epithelial
neoplasms: An experience of 405 cases. Am J Surg Pathol.
26:281–291. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ricketts CJ, Morris MR, Gentle D, Brown M,
Wake N, Woodward ER, Clarke N, Latif F and Maher ER: Genome-wide
CpG island methylation analysis implicates novel genes in the
pathogenesis of renal cell carcinoma. Epigenetics. 7:278–290. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mosashvilli D, Kahl P, Mertens C,
Holzapfel S, Rogenhofer S, Hauser S, Buttner R, Von Ruecker A,
Muller SC and Ellinger J: Global histone acetylation levels:
Prognostic relevance in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Cancer
Sci. 101:2664–2669. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xing T and He H: Epigenomics of clear cell
renal cell carcinoma: Mechanisms and potential use in molecular
pathology. Chin J Cancer Res. 28:80–91. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yoshino H, Yonezawa T, Yonemori M,
Miyamoto K, Sakaguchi T, Sugita S, Osako Y, Tatarano S, Nakagawa M
and Enokida H: Downregulation of microRNA-1274a induces cell
apoptosis through regulation of BMPR1B in clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 39:173–181. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu J, Yue Y, Han D, Wang X, Fu Y, Zhang
L, Jia G, Yu M, Lu Z, Deng X, et al: A METTL3-METTL14 complex
mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat Chem
Biol. 10:93–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Weng H, Huang H, Wu H, Qin X, Zhao BS,
Dong L, Shi H, Skibbe J, Shen C, Hu C, et al: METTL14 inhibits
hematopoietic stem/progenitor differentiation and promotes
leukemogenesis via mRNA m6A Modification. Cell Stem
Cell. 22:191–205.e9. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ma JZ, Yang F, Zhou CC, Liu F, Yuan JH,
Wang F, Wang TT, Xu QG, Zhou WP and Sun SH: METTL14 suppresses the
metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating
N6-methyladenosine-dependent primary MicroRNA
processing. Hepatology. 65:529–543. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Harlander S, Schonenberger D, Toussaint
NC, Prummer M, Catalano A, Brandt L, Moch H, Wild PJ and Frew IJ:
Combined mutation in Vhl, Trp53 and Rb1 causes clear cell renal
cell carcinoma in mice. Nat Med. 23:869–877. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lan T, Li H, Zhang D, Xu L, Liu H, Hao X,
Yan X, Liao H, Chen X, Xie K, et al: KIAA1429 contributes to liver
cancer progression through N6-methyladenosine-dependent
post-transcriptional modification of GATA3. Mol Cancer. 18:1862019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cai J, Yang F, Zhan H, Situ J, Li W, Mao Y
and Luo Y: RNA m6A Methyltransferase METTL3 promotes the
growth of prostate cancer by regulating hedgehog pathway. Onco
Targets Ther. 12:9143–9152. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu T, Yang S, Sui J, Xu SY, Cheng YP,
Shen B, Zhang Y, Zhang XM, Yin LH, Pu YP and Liang GY: Dysregulated
N6-methyladenosine methylation writer METTL3 contributes to the
proliferation and migration of gastric cancer. J Cell Physiol.
235:548–562. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xia T, Wu X, Cao M, Zhang P, Shi G, Zhang
J, Lu Z, Wu P, Cai B, Miao Y and Jiang K: The RNA m6A
methyltransferase METTL3 promotes pancreatic cancer cell
proliferation and invasion. Pathol Res Pract. 215:1526662019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|