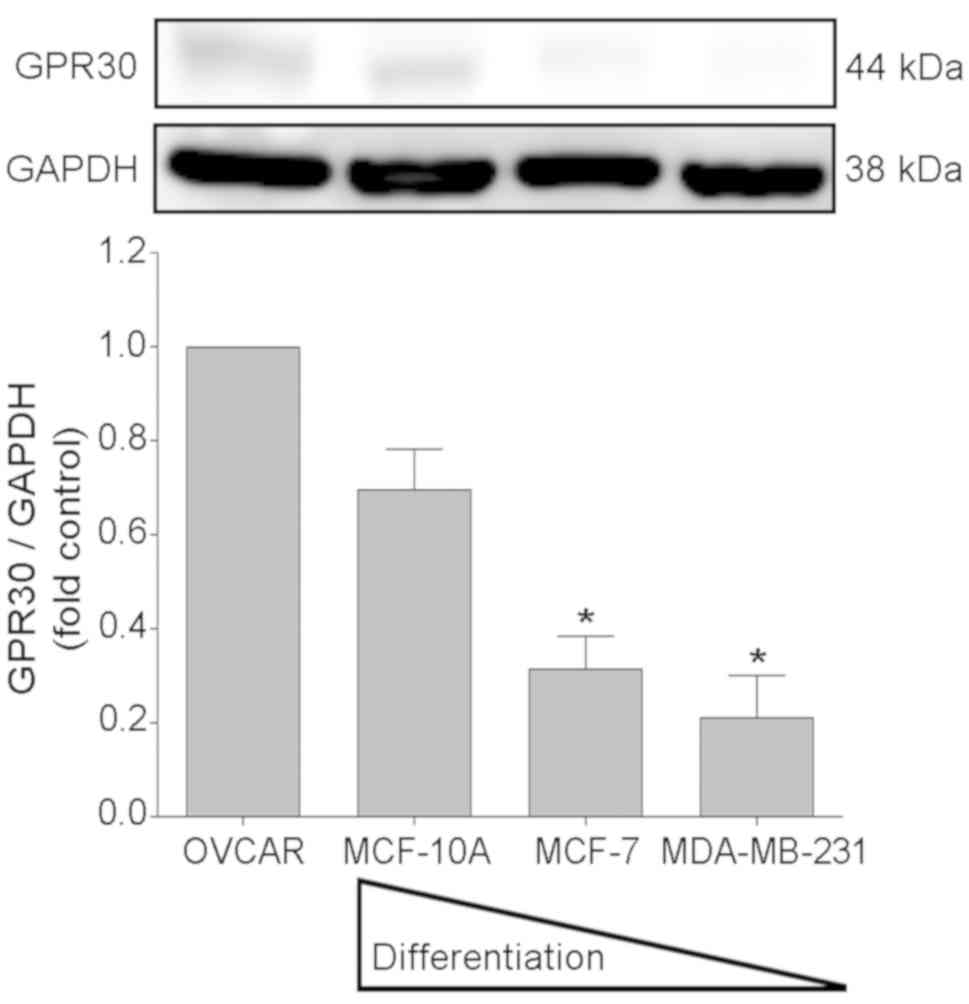
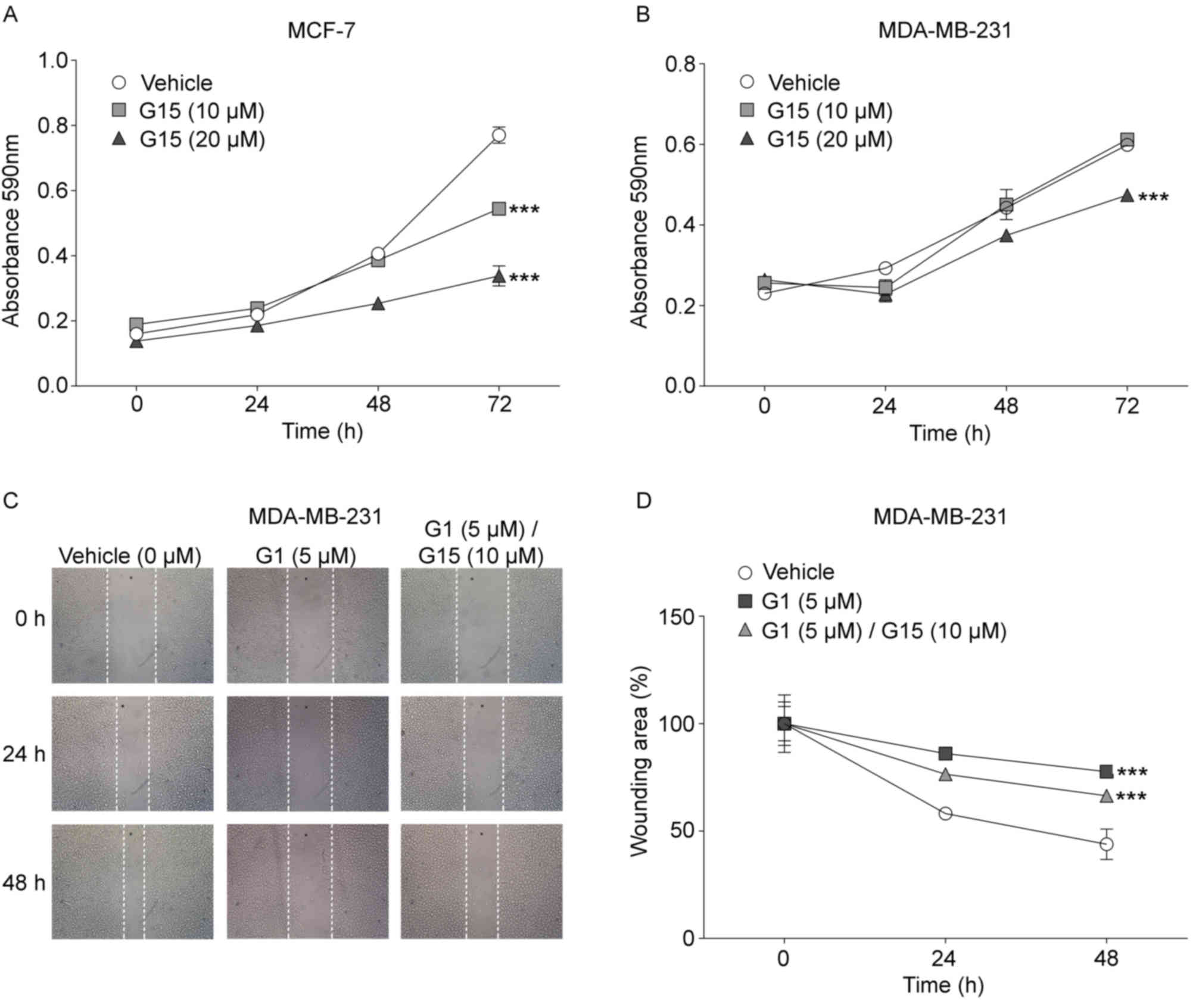
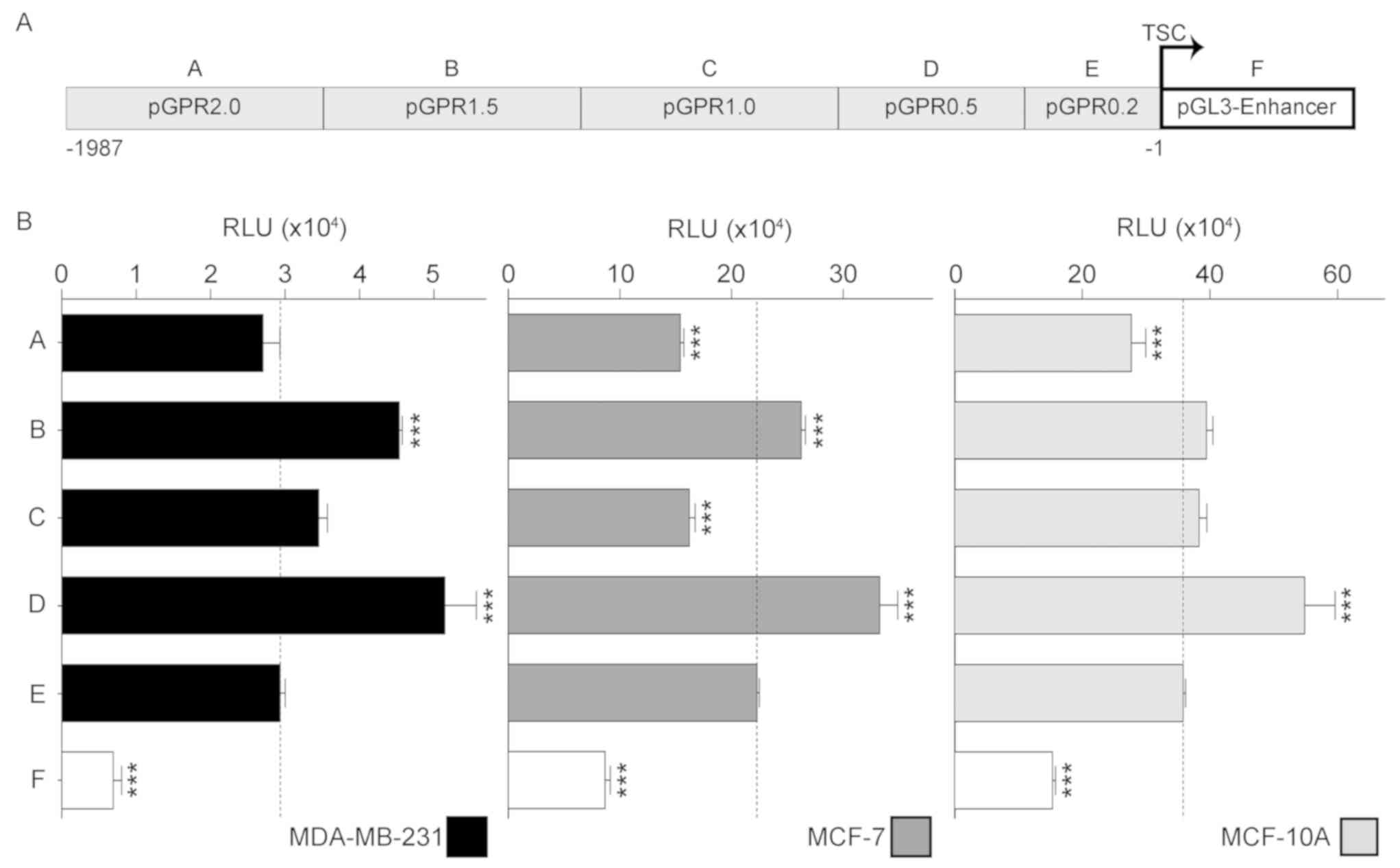
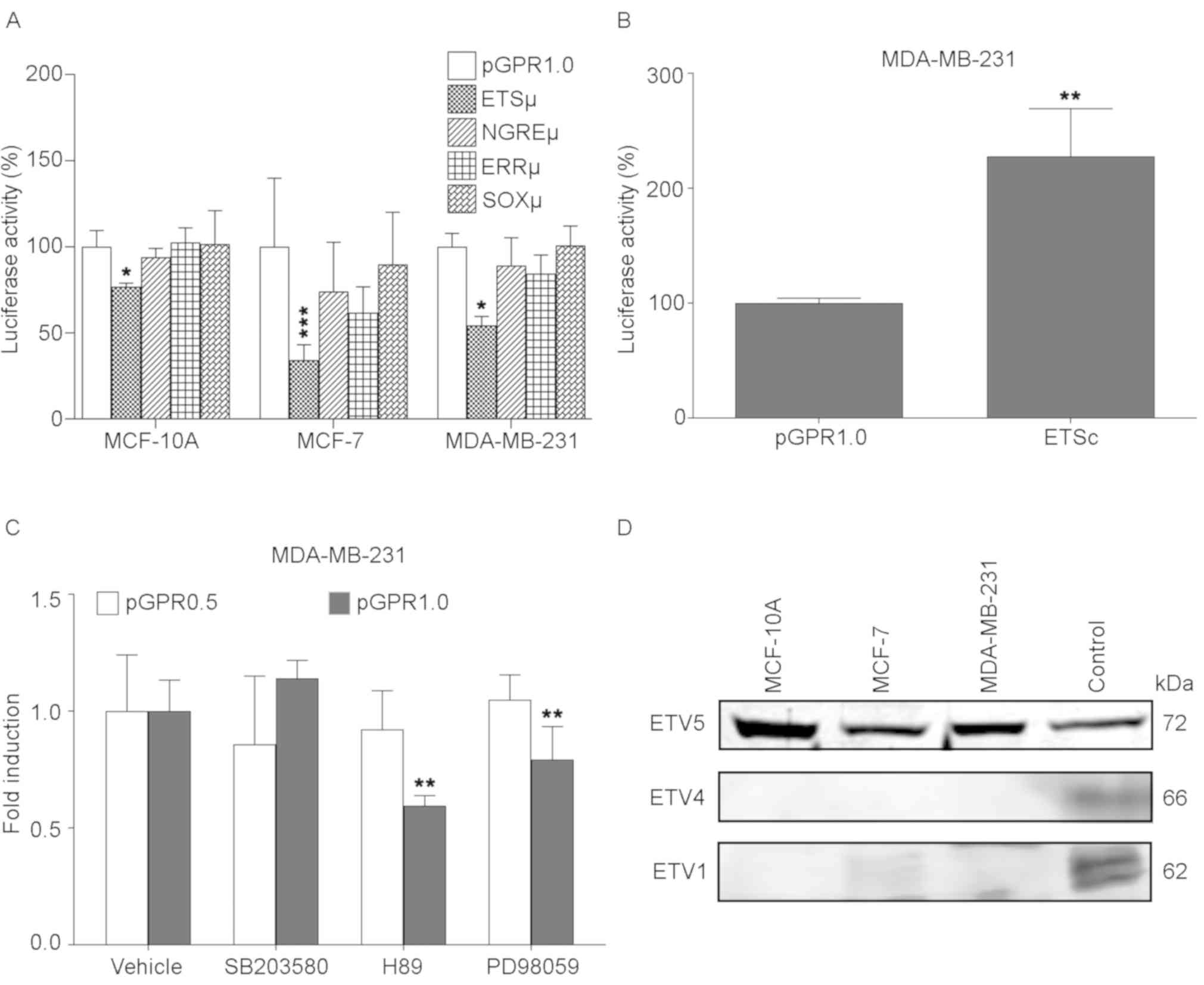
|
1
|
Vergote I, Amant F, Leunen K, Van Gorp T,
Berteloot P and Neven P: Metastatic breast cancer: Sequencing
hormonal therapy and positioning of fulvestrant. Int J Gynecol
Cancer. 16 (Suppl 2):S524–S526. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
DeSantis CE, Ma J, Gaudet MM, Newman LA,
Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, Jemal A and Siegel RL: Breast cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:438–451. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fan W, Chang J and Fu P: Endocrine therapy
resistance in breast cancer: Current status, possible mechanisms
and overcoming strategies. Future Med Chem. 7:1511–1519. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barton M, Filardo EJ, Lolait SJ, Thomas P,
Maggiolini M and Prossnitz ER: Twenty years of the G
protein-coupled estrogen receptor GPER: Historical and personal
perspectives. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 176:4–15. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ruan SQ, Wang SW, Wang ZH and Zhang SZ:
Regulation of HRG-β1-induced proliferation, migration and invasion
of MCF-7 cells by upregulation of GPR30 expression. Mol Med Rep.
6:131–138. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Girgert R, Emons G and Gründker C:
17β-estradiol-induced growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells
is prevented by the reduction of GPER expression after treatment
with gefitinib. Oncol Rep. 37:1212–1218. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Molina L, Figueroa CD, Bhoola KD and
Ehrenfeld P: GPER-1/GPR30 a novel estrogen receptor sited in the
cell membrane: Therapeutic coupling to breast cancer. Expert Opin
Ther Targets. 21:755–766. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Thomas P and Dong J: Binding and
activation of the seven-transmembrane estrogen receptor GPR30 by
environmental estrogens: A potential novel mechanism of endocrine
disruption. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 102:175–179. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Long N, Long B, Mana A, Le D, Nguyen L,
Chokr S and Sinchak K: Tamoxifen and ICI 182,780 activate
hypothalamic G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 to rapidly
facilitate lordosis in female rats. Horm Behav. 89:98–103. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bologa CG, Revankar CM, Young SM, Edwards
BS, Arterburn JB, Kiselyov AS, Parker MA, Tkachenko SE, Savchuck
NP, Sklar LA, et al: Virtual and biomolecular screening converge on
a selective agonist for GPR30. Nat Chem Biol. 2:207–212. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dennis MK, Burai R, Ramesh C, Petrie WK,
Alcon SN, Nayak TK, Bologa CG, Leitao A, Brailoiu E, Deliu E, et
al: In vivo effects of a GPR30 antagonist. Nat Chem Biol.
5:4212009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dennis MK, Field AS, Burai R, Ramesh C,
Petrie WK, Bologa CG, Oprea TI, Yamaguchi Y, Hayashi S, Sklar LA,
et al: Identification of a GPER/GPR30 antagonist with improved
estrogen receptor counterselectivity. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
127:358–366. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mo Z, Liu M, Yang F, Luo H, Li Z, Tu G and
Yang G: GPR30 as an initiator of tamoxifen resistance in
hormone-dependent breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 15:R1142013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pandey DP, Lappano R, Albanito L, Madeo A,
Maggiolini M and Picard D: Estrogenic GPR30 signalling induces
proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells through CTGF.
EMBO J. 28:523–532. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lucki NC and Sewer MB: Genistein
stimulates MCF-7 breast cancer cell growth by inducing acid
ceramidase (ASAH1) gene expression. J Biol Chem. 86:19399–19409.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Recchia AG, De Francesco EM, Vivacqua A,
Sisci D, Panno ML, Andò S and Maggiolini M: The G protein-coupled
receptor 30 is up-regulated by hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha
(HIF-1alpha) in breast cancer cells and cardiomyocytes. J Biol
Chem. 286:10773–10782. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
De Francesco EM, Maggiolini M and Musti
AM: Crosstalk between Notch, HIF-1α and GPER in Breast Cancer EMT.
Int J Mol Sci. 19(pii): E20112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ariazi EA, Brailoiu E, Yerrum S, Shupp HA,
Slifker MJ, Cunliffe HE, Black MA, Donato AL, Arterburn JB, Oprea
TI, et al: The G protein-coupled receptor GPR30 inhibits
proliferation of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 70:1184–1194. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen ZJ, Wei W, Jiang GM, Liu H, Wei WD,
Yang X, Wu YM, Liu H, Wong CK, Du J and Wang HS: Activation of GPER
suppresses epithelial mesenchymal transition of triple negative
breast cancer cells via NF-κB signals. Mol Oncol. 10:775–788. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Filardo EJ, Quinn JA, Frackelton AR Jr and
Bland KI: Estrogen action via the G protein-coupled receptor,
GPR30: Stimulation of adenylyl cyclase and cAMP-mediated
attenuation of the epidermal growth factor receptor-to-MAPK
signaling axis. Mol Endocrinol. 16:70–84. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Filigheddu N, Sampietro S, Chianale F,
Porporato PE, Gaggianesi M, Gregnanin I, Rainero E, Ferrara M,
Perego B, Riboni F, et al: Diacylglycerol kinase α mediates
17-β-estradiol-induced proliferation, motility, and
anchorage-independent growth of Hec-1A endometrial cancer cell line
through the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor GPR30. Cell Signal.
23:1988–1996. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ge C, Yu M and Zhang C: G protein-coupled
receptor 30 mediates estrogen-induced proliferation of primordial
germ cells via EGFR/Akt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Endocrinology.
153:3504–3516. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hsu LH, Chu NM, Lin YF and Kao SH:
G-protein coupled estrogen receptor in breast cancer. Int J Mol
Sci. 20(pii): E3062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Poola I, Abraham J, Liu A, Marshalleck JJ
and DeWitty RL: The cell surface estrogen receptor, G
protein-coupled receptor 30 (GPR30), is markedly down regulated
during breast tumorigenesis. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 1:65–78.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wei W, Chen ZJ, Zhang KS, Yang XL, Wu YM,
Chen XH, Huang HB, Liu HL, Cai SH, Du J and Wang HS: The activation
of G protein-coupled receptor 30 (GPR30) inhibits proliferation of
estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells in vitro and in
vivo. Cell Death Dis. 5:e14282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu T, Liu M, Luo H, Wu C, Tang X, Tang S,
Hu P, Yan Y, Wang Z and Tu G: GPER mediates enhanced cell viability
and motility via non-genomic signaling induced by 17β-estradiol in
triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
143:392–403. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schreiber E, Matthias P, Müller MM and
Schaffner W: Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with
‘mini-extracts’, prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic
Acids Res. 17:64191989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF and Maniatis T:
Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor
Laboratory Press; pp. 1–3. 1989
|
|
29
|
Filardo EJ and Thomas P: Minireview: G
protein-coupled estrogen receptor-1, GPER-1: Its mechanism of
action and role in female reproductive cancer, renal and vascular
physiology. Endocrinology. 153:2953–2962. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Janknecht R, Monté D, Baert JL and de
Launoit Y: The ETS-related transcription factor ERM is a nuclear
target of signaling cascades involving MAPK and PKA. Oncogene.
13:1745–1754. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu J and Janknecht R: Regulation of the
ETS transcription factor ER81 by the 90-kDa ribosomal S6 kinase 1
and protein kinase A. J Biol Chem. 277:42669–42679. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang JW, Kim MR, Kim HG, Kim SK, Jeong HG
and Kang KW: Differential regulation of ErbB2 expression by
cAMP-dependent protein kinase in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer
cells. Arch Pharm Res. 31:350–356. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Barrett JM, Puglia MA, Singh G and Tozer
RG: Expression of Ets-related transcription factors and matrix
metalloproteinase genes in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 72:227–232. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chotteau-Lelièvre A, Révillion F,
Lhotellier V, Hornez L, Desbiens X, Cabaret V, de Launoit Y and
Peyrat JP: Prognostic value of ERM gene expression in human primary
breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 10:7297–7303. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Goueli BS and Janknecht R: Upregulation of
the catalytic telomerase subunit by the transcription factor ER81
and oncogenic HER2/Neu, Ras, or Raf. Mol Cell Biol. 24:25–35. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jiang J, Wei Y, Liu D, Zhou J, Shen J,
Chen X, Zhang S, Kong X and Gu J: E1AF promotes breast cancer cell
cycle progression via upregulation of Cyclin D3 transcription.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 358:53–58. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shepherd TG, Kockeritz L, Szrajber MR,
Muller WJ and Hassell JA: The pea3 subfamily ETS genes are required
for HER2/Neu-mediated mammary oncogenesis. Curr Biol. 11:1739–1748.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wu X and Sukumar S: ETS genes in breast
cancer: A step in the right direction. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:83–84.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hong H, Yu H, Yuan J, Guo C, Cao H, Li W
and Xiao C: MicroRNA-200b impacts breast cancer cell migration and
invasion by regulating Ezrin-Radixin-Moesin. Med Sci Monit.
22:1946–1952. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Baert JL, Monté D, Musgrove EA, Albagli O,
Sutherland RL and Launoit Y: Expression of the PEA3 group of
ETS-related transcription factors in human breast-cancer cells. Int
J Cancer. 70:590–597. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Müller P, Kietz S, Gustafsson JA and Ström
A: The anti-estrogenic effect of all-trans-retinoic acid on the
breast cancer cell line MCF-7 is dependent on HES-1 expression. J
Biol Chem. 277:28376–28379. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Müller P, Crofts JD, Newman BS,
Bridgewater LC, Lin CY, Gustafsson JA and Ström A: SOX9 mediates
the retinoic acid-induced HES-1 gene expression in human breast
cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 120:317–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Park S-W, Do H-J, Ha WT, Han MH, Song H,
Uhm SJ, Chung HJ and Kim JH: Differential expression of ETS family
transcription factors in NCCIT human embryonic carcinoma cells upon
retinoic acid-induced differentiation. Biol Pharm Bull. 37:659–665.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Owman C, Blay P, Nilsson C and Lolait SJ:
Cloning of human cDNA encoding a novel heptahelix receptor
expressed in Burkitt's lymphoma and widely distributed in brain and
peripheral tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 228:285–292. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Olde B and Leeb-Lundberg LM: GPR30/GPER1:
Searching for a role in estrogen physiology. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 20:409–416. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhou X, Wang S, Wang Z, Feng X, Liu P, Lv
XB, Li F, Yu FX, Sun Y, Yuan H, et al: Estrogen regulates Hippo
signaling via GPER in breast cancer. J Clin Invest. 125:2123–2135.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Scaling AL, Prossnitz ER and Hathaway HJ:
GPER mediates estrogen-induced signaling and proliferation in human
breast epithelial cells and normal and malignant breast. Horm
Cancer. 5:146–160. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lappano R, Pisano A and Maggiolini M: GPER
function in breast cancer: An overview. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 5:662014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Weißenborn C, Ignatov T, Poehlmann A, Wege
AK, Costa SD, Zenclussen AC and Ignatov A: GPER functions as a
tumor suppressor in MCF-7 and SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 140:663–671. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Martin SG, Lebot MN, Sukkarn B, Ball G,
Green AR, Rakha EA, Ellis IO and Storr SJ: Low expression of G
protein-coupled oestrogen receptor 1 (GPER) is associated with
adverse survival of breast cancer patients. Oncotarget.
9:25946–25956. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Manjegowda MC, Gupta PS and Limaye AM:
Hyper-methylation of the upstream CpG island shore is a likely
mechanism of GPER1 silencing in breast cancer cells. Gene.
614:65–73. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ignatov T, Weißenborn C, Poehlmann A,
Lemke A, Semczuk A, Roessner A, Costa SD, Kalinski T and Ignatov A:
GPER-1 expression decreases during breast cancer tumorigenesis.
Cancer Invest. 31:309–315. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Steiman J, Peralta EA, Louis S and Kamel
O: Biology of the estrogen receptor, GPR30, in triple negative
breast cancer. Am J Surg. 206:698–703. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lv X, He C, Huang C, Hua G, Wang Z,
Remmenga SW, Rodabough KJ, Karpf AR, Dong J, Davis JS and Wang C:
G-1 inhibits breast cancer cell growth via targeting
colchicine-binding site of tubulin to interfere with microtubule
assembly. Mol Cancer Ther. 16:1080–1091. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Weissenborn C, Ignatov T, Nass N, Kalinski
T, Dan Costa S, Zenclussen AC and Ignatov A: GPER promoter
methylation controls GPER expression in breast cancer patients.
Cancer Invest. 35:100–107. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kohrman AQ and Matus DQ: Divide or
conquer: Cell cycle regulation of invasive behavior. Trends Cell
Biol. 27:12–25. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kamath L, Meydani A, Foss F and Kuliopulos
A: Signaling from protease-activated receptor-1 inhibits migration
and invasion of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 61:5933–5940.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ignatov A, Ignatov T, Roessner A, Costa SD
and Kalinski T: Role of GPR30 in the mechanisms of tamoxifen
resistance in breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
123:87–96. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Broselid S, Cheng B, Sjöström M, Lövgren
K, Klug-De Santiago HL, Belting M, Jirström K, Malmström P, Olde B,
Bendahl PO, et al: G protein-coupled estrogen receptor is apoptotic
and correlates with increased distant disease-free survival of
estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res.
19:1681–1692. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Vivacqua A, Lappano R, De Marco P, Sisci
D, Aquila S, De Amicis F, Fuqua SA, Andò S and Maggiolini M: G
protein-coupled receptor 30 expression is up-regulated by EGF and
TGF alpha in estrogen receptor alpha-positive cancer cells. Mol
Endocrinol. 23:1815–1826. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Manjegowda MC and Limaye AM: DNA
methylation dependent suppression of GPER1 in colorectal cancer.
Med Res Arch. 6:2018.
|
|
62
|
Lelièvre E, Lionneton F, Soncin F and
Vandenbunder B: The Ets family contains transcriptional activators
and repressors involved in angiogenesis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
33:391–407. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Mavrothalassitis G and Ghysdael J:
Proteins of the ETS family with transcriptional repressor activity.
Oncogene. 19:6524–6532. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kim GC, Kwon HK, Lee CG, Verma R, Rudra D,
Kim T, Kang K, Nam JH, Kim Y and Im SH: Upregulation of Ets1
expression by NFATc2 and NFKB1/RELA promotes breast cancer cell
invasiveness. Oncogenesis. 7:912018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wallace JA, Li F, Balakrishnan S,
Cantemir-Stone CZ, Pecot T, Martin C, Kladney RD, Sharma SM,
Trimboli AJ, Fernandez SA, et al: Ets2 in tumor fibroblasts
promotes angiogenesis in breast cancer. PLoS One. 8:e715332013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
de Launoit Y, Chotteau-Lelievre A,
Beaudoin C, Coutte L, Netzer S, Brenner C, Huvent I and Baert JL:
The PEA3 group of ETS-related transcription factors: Role in breast
cancer metastasis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 480:107–116. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
De Luca A, Maiello MR, D'Alessio A,
Pergameno M and Normanno N: The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and the PI3K/AKT
signalling pathways: Role in cancer pathogenesis and implications
for therapeutic approaches. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16 (Suppl
2):S17–S27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Jiang P, Enomoto A and Takahashi M: Cell
biology of the movement of breast cancer cells: Intracellular
signalling and the actin cytoskeleton. Cancer Lett. 284:122–130.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Nguyen DH, Hussaini IM and Gonias SL:
Binding of urokinase-type plasminogen activator to its receptor in
MCF-7 cells activates extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2
which is required for increased cellular motility. J Biol Chem.
273:8502–8507. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Palorini R, Votta G, Pirola Y, De Vitto H,
De Palma S, Airoldi C, Vasso M, Ricciardiello F, Lombardi PP,
Cirulli C, et al: Protein kinase A activation promotes cancer cell
resistance to glucose starvation and anoikis. PLoS Genet.
12:e10059312016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Svensson S, Jirström K, Rydén L, Roos G,
Emdin S, Ostrowski MC and Landberg G: ERK phosphorylation is linked
to VEGFR2 expression and Ets-2 phosphorylation in breast cancer and
is associated with tamoxifen treatment resistance and small tumours
with good prognosis. Oncogene. 24:4370–4379. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Switzer CH, Cheng RY, Ridnour LA, Glynn
SA, Ambs S and Wink DA: Ets-1 is a transcriptional mediator of
oncogenic nitric oxide signaling in estrogen receptor-negative
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 14:R1252012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Baert J-L, Beaudoin C, Coutte L and De
Launoit Y: ERM transactivation is up-regulated by the repression of
DNA binding after the PKA phosphorylation of a consensus site at
the edge of the ETS domain. J Biol Chem. 277:1002–1012. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Keld R, Guo B, Downey P, Cummins R,
Gulmann C, Ang YS and Sharrocks AD: PEA3/ETV4-related transcription
factors coupled with active ERK signalling are associated with poor
prognosis in gastric adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 105:124–130.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|