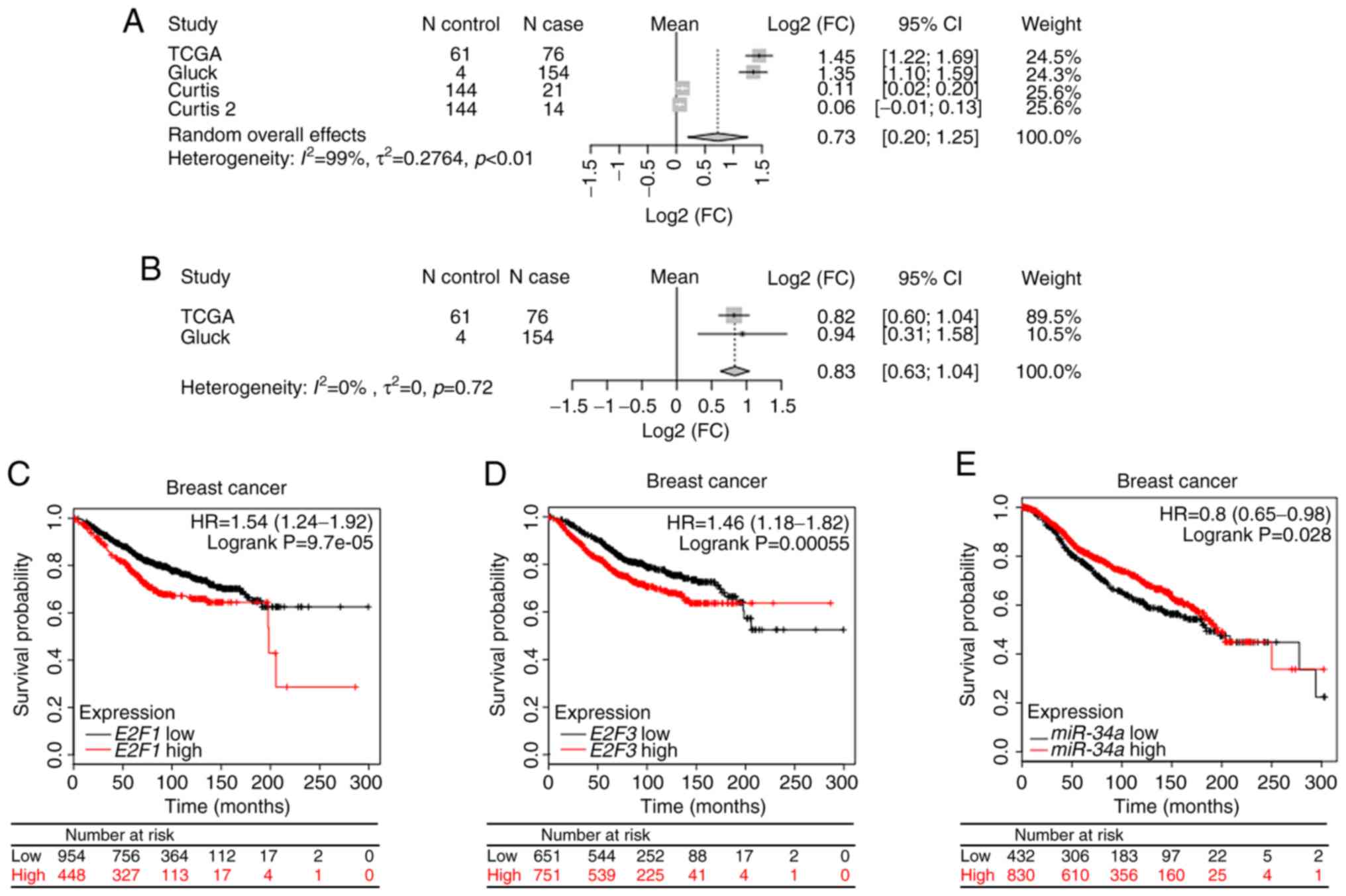
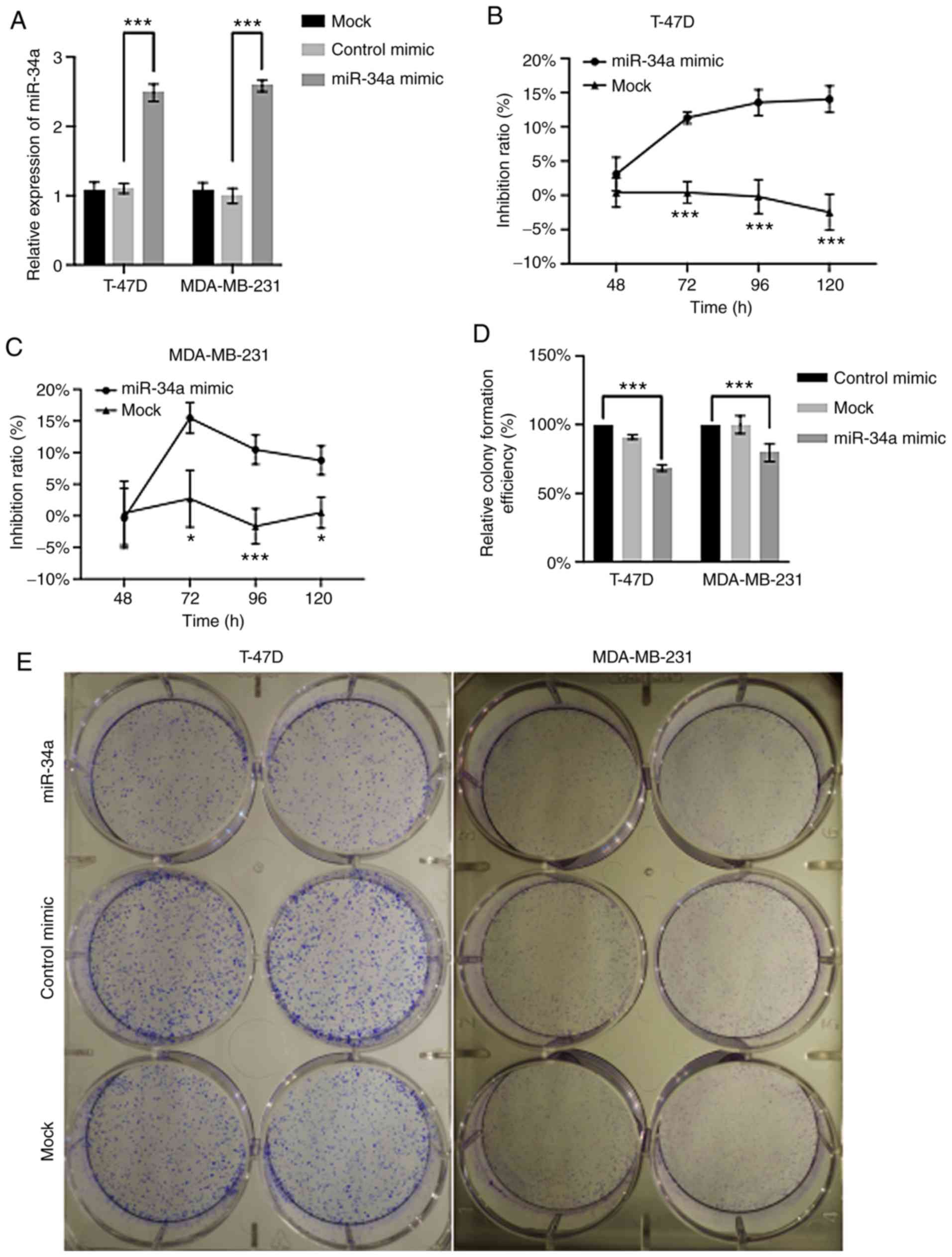
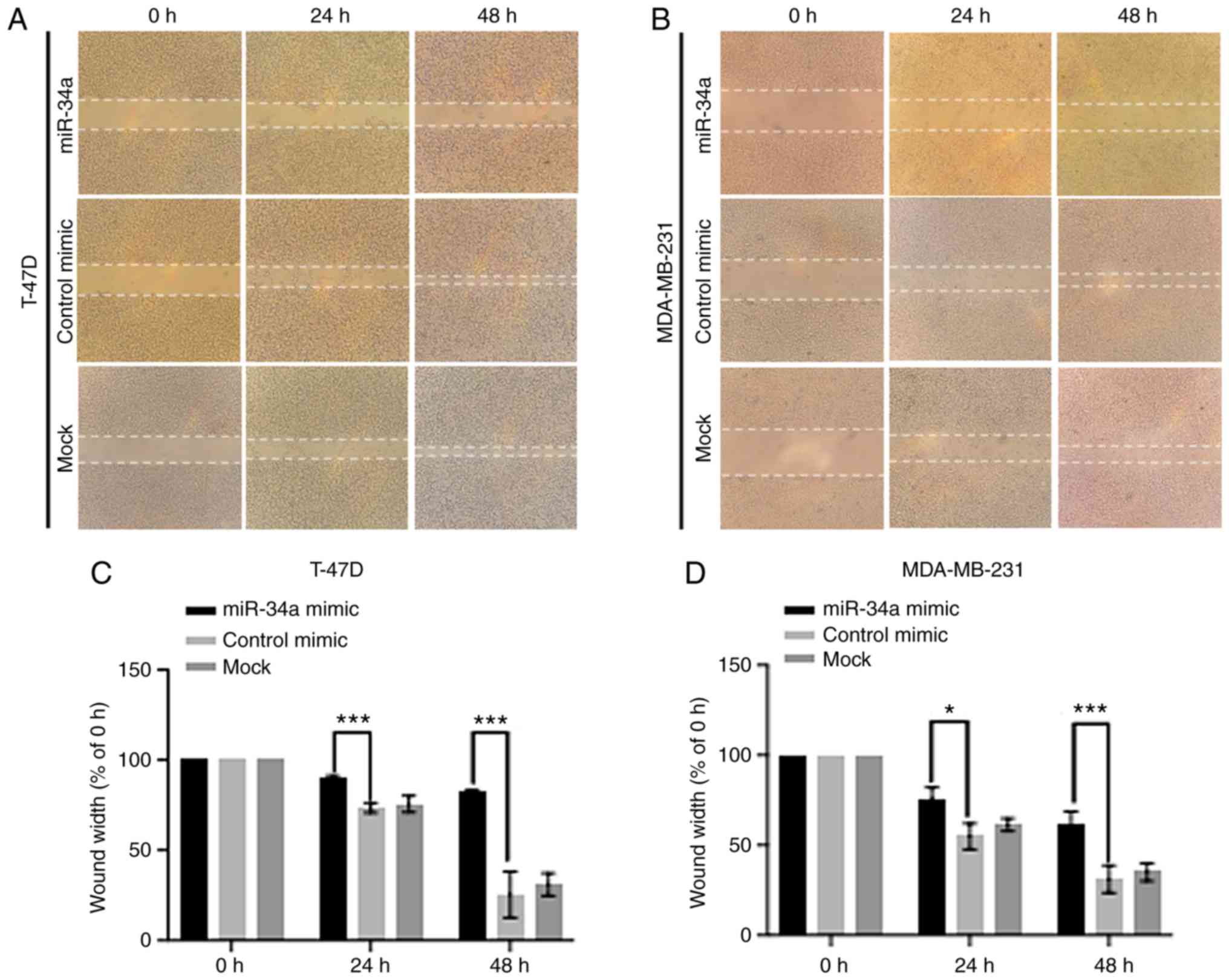
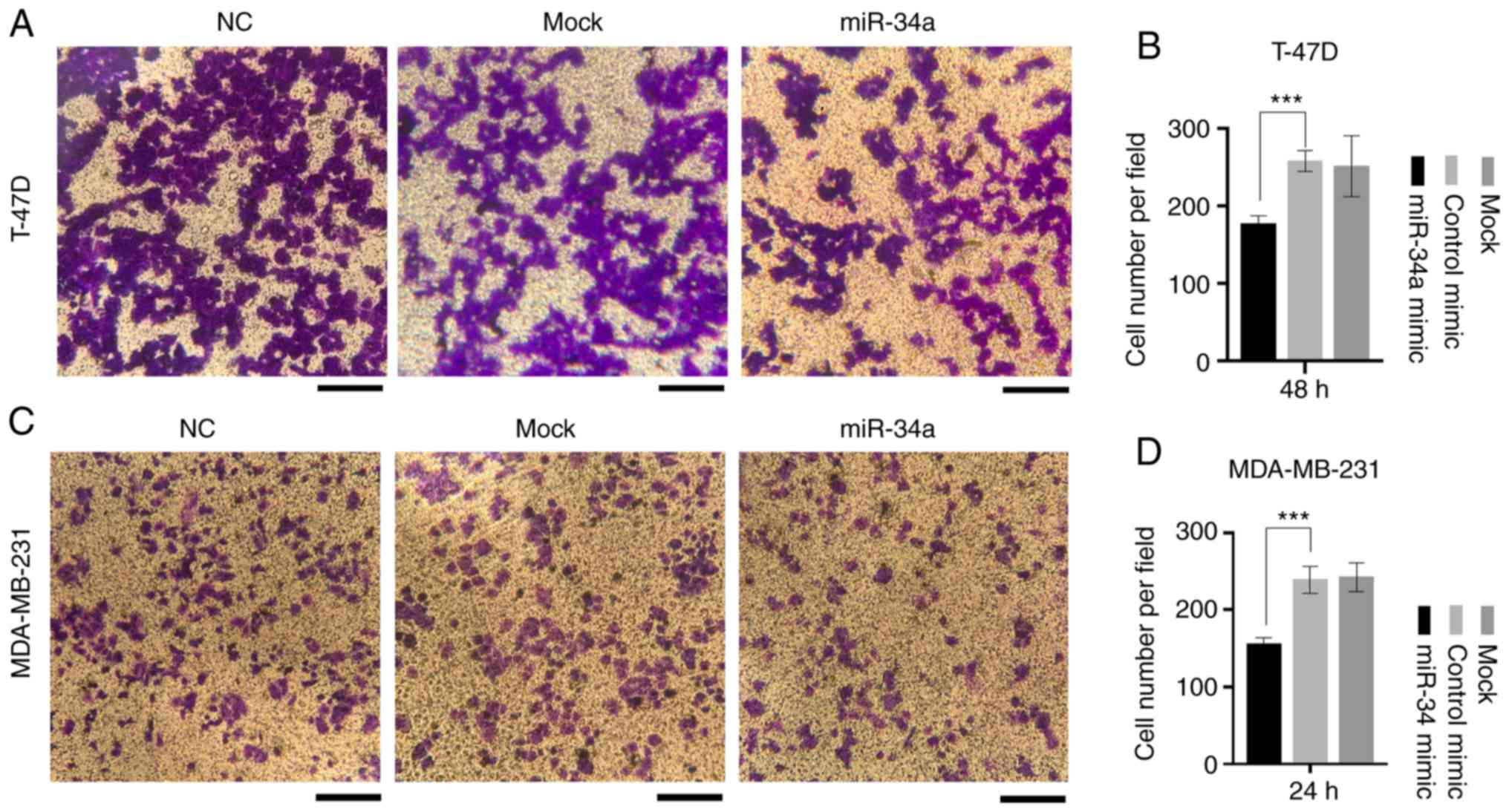
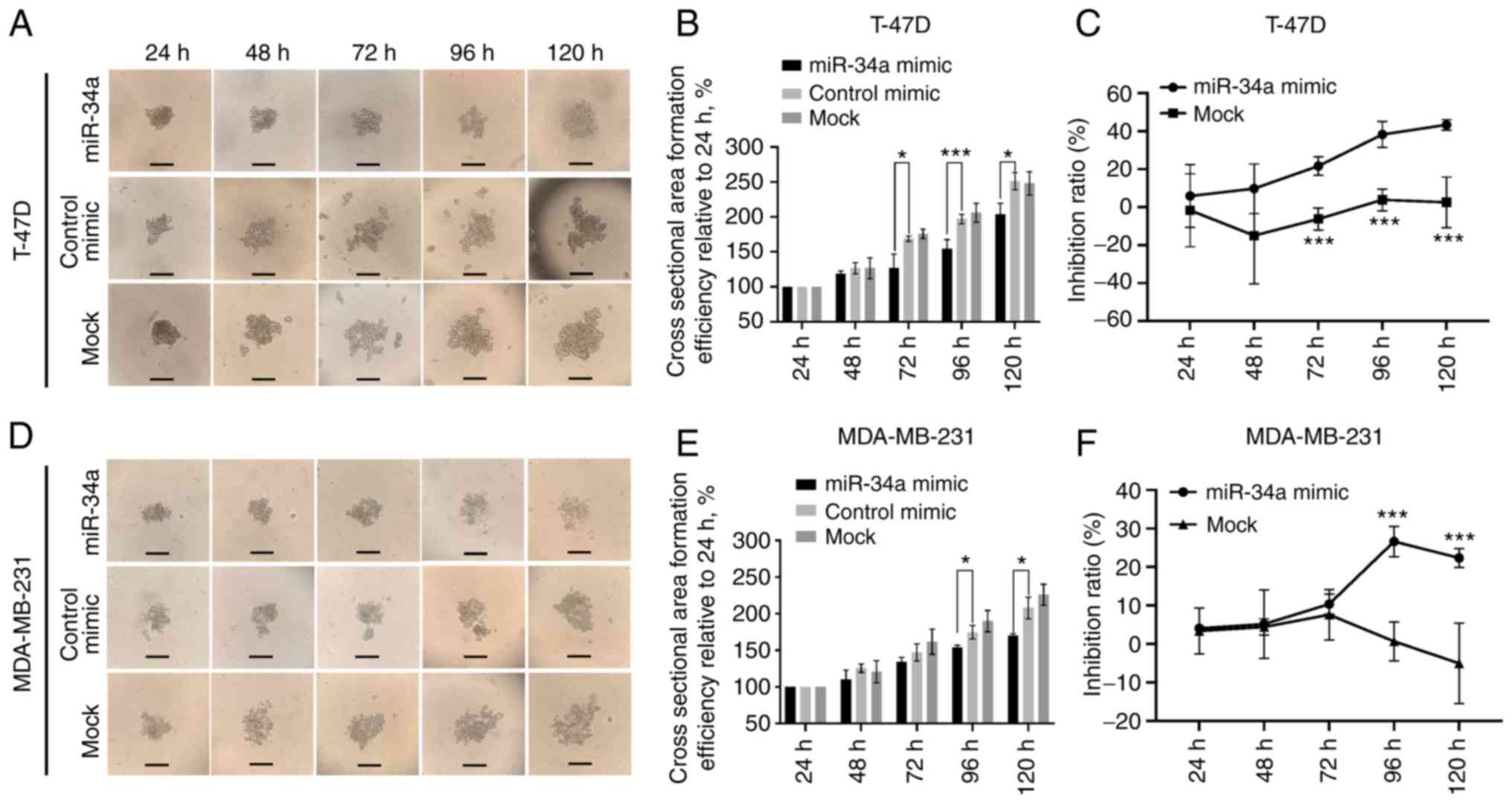
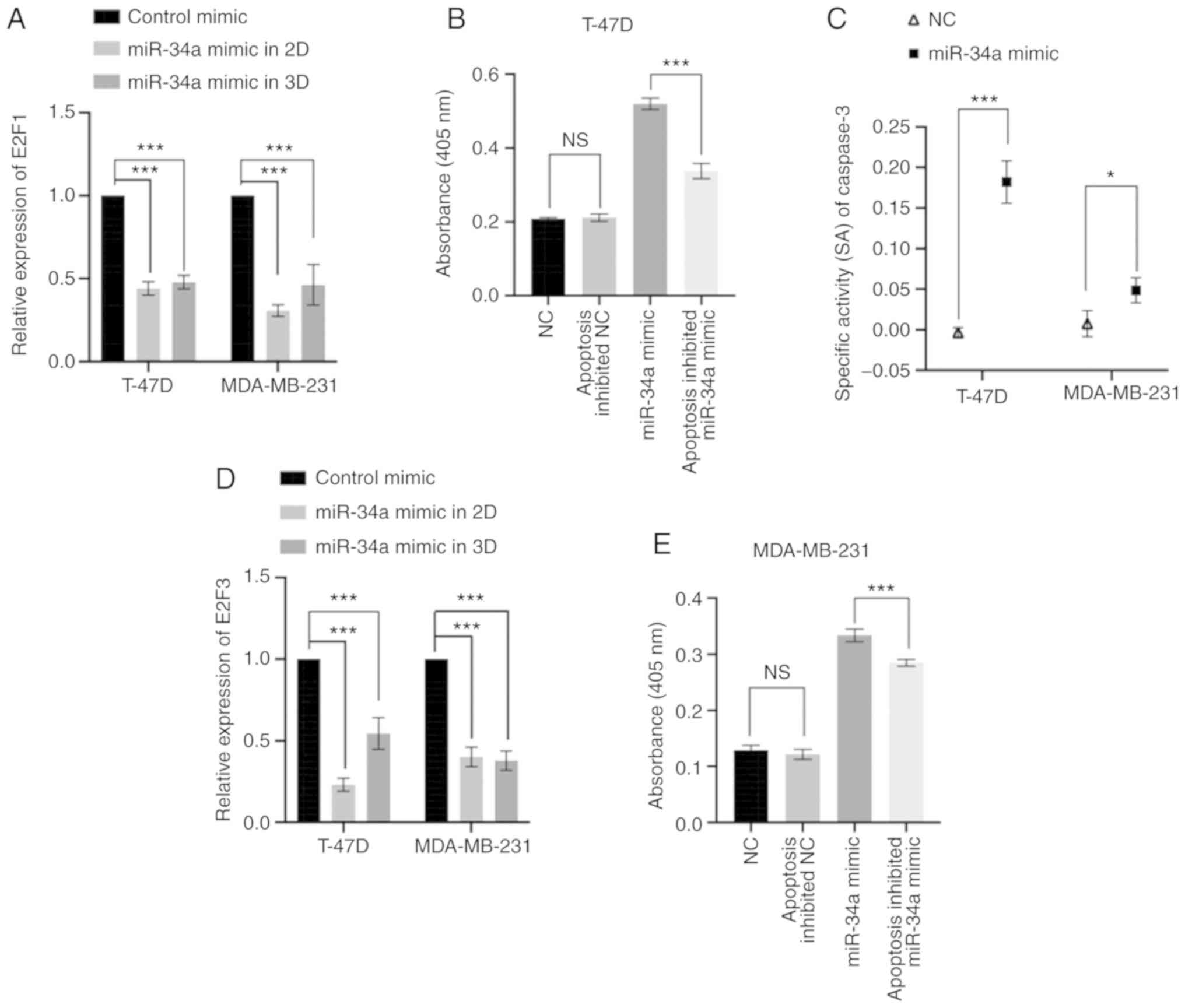
|
1
|
Malvezzi M, Carioli G, Bertuccio P,
Boffetta P, Levi F, La Vecchia C and Negri E: European cancer
mortality predictions for the year 2019 with focus on breast
cancer. Ann Oncol. 30:781–787. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hartkopf AD, Müller V, Wöckel A, Lux MP,
Janni W, Nabieva N, Taran FA, Ettl J, Lüftner D, Belleville E, et
al: Update breast cancer 2019 Part 1-implementation of study
results of novel study designs in clinical practice in patients
with early breast cancer. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 79:256–267.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Janni W, Schneeweiss A, Müller V, Wöckel
A, Lux MP, Hartkopf AD, Nabieva N, Taran FA, Tesch H, Overkamp F,
et al: Update breast cancer 2019 Part 2-implementation of novel
diagnostics and therapeutics in advanced breast cancer patients in
clinical practice. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 79:268–280. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Li N, Long B, Han W, Yuan S and Wang K:
microRNAs: Important regulators of stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther.
8:1102017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Zhao K, Cheng J, Chen B, Liu Q, Xu D and
Zhang Y: Circulating microRNA-34 family low expression correlates
with poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J
Thorac Dis. 9:3735–3746. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Tao ZQ, Shi AM, Li R, Wang YQ, Wang X and
Zhao J: Role of microRNA in prostate cancer stem/progenitor cells
regulation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:3040–3044. 2016.
|
|
7
|
Gangopadhyay S, Nandy A, Hor P and
Mukhopadhyay A: Breast cancer stem cells: A novel therapeutic
target. Clin Breast Cancer. 13:7–15. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Alizadeh S, Ghader Azizi S, Soleimani M,
Farshi Y and Kashani Khatib Z: The role of MicroRNAs in
myeloproliferative neoplasia. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res.
10:172–185. 2016.
|
|
9
|
Guessous F, Zhang Y, Kofman A, Catania A,
Li Y, Schiff D, Purow B and Abounader R: microRNA-34a is tumor
suppressive in brain tumors and glioma stem cells. Cell Cycle.
9:1031–1036. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Li J, Lam M, Iorns E, Gunn W, Tan FE,
Lomax J, Errington TM and Massagué J: Registered report: The
microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis
by directly repressing CD44. Elife. 4:e064342015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Craig V, Tzankov A, Flori M, Schmid CA,
Bader AG and Müller A: Systemic microRNA-34a delivery induces
apoptosis and abrogates growth of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in
vivo. Leukemia. 26:2421–2424. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tammali R, Saxena A, Srivastava SK and
Ramana KV: Aldose reductase regulates vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation by modulating G1/S phase transition of cell cycle.
Endocrinology. 151:2140–2150. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Lee M, Oprea-Ilies G and Saavedra HI:
Silencing of E2F3 suppresses tumor growth of Her2+ breast cancer
cells by restricting mitosis. Oncotarget. 6:37316–37334. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Hollern DP, Honeysett J, Cardiff RD and
Andrechek ER: The E2F transcription factors regulate tumor
development and metastasis in a mouse model of metastatic breast
cancer. Mol Cell Biol. 34:3229–3243. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Knoll S, Emmrich S and Pützer BM: The
E2F1-miRNA cancer progression network. Adv Exp Med Biol.
774:135–147. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Julian LM and Blais A: Transcriptional
control of stem cell fate by E2Fs and pocket proteins. Front Genet.
6:1612015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Bellmunt J: Stem-like signature predicting
disease progression in early stage bladder cancer. The role of E2F3
and SOX4. Biomedicines. 6(pii): E852018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Farra R, Dapas B, Grassi M, Benedetti F
and Grassi G: E2F1 as a molecular drug target in ovarian cancer.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 23:161–164. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fang Y, Gu X, Li Z, Xiang J and Chen Z:
miR-449b inhibits the proliferation of SW1116 colon cancer stem
cells through downregulation of CCND1 and E2F3 expression. Oncol
Rep. 30:399–406. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ren J, Ding L, Xu Q, Shi G, Li X, Li X, Ji
J, Zhang D, Wang Y, Wang T and Hou Y: LF-MF inhibits iron
metabolism and suppresses lung cancer through activation of
P53-miR-34a-E2F1/E2F3 pathway. Sci Rep. 7:7492017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Han R, Chen X, Li Y, Zhang S, Li R and Lu
L: MicroRNA-34a suppresses aggressiveness of hepatocellular
carcinoma by modulating E2F1, E2F3, and Caspase-3. Cancer Manag
Res. 11:2963–2976. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Santos M, Martínez-Fernández M, Dueñas M,
García-Escudero R, Alfaya B, Villacampa F, Saiz-Ladera C, Costa C,
Oteo M, Duarte J, et al: In vivo disruption of an Rb-E2F-Ezh2
signaling loop causes bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 74:6565–6577.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Suzuki T, Yasui W, Yokozaki H, Naka K,
Ishikawa T and Tahara E: Expression of the E2F family in human
gastrointestinal carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 81:535–538. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gao Y, Feng B, Lu L, Han S, Chu X, Chen L
and Wang R: MiRNAs and E2F3: A complex network of reciprocal
regulations in human cancers. Oncotarget. 8:60624–60639. 2017.
|
|
25
|
Liu X and Wu X: Utilizing matrigel
transwell invasion assay to detect and enumerate circulating tumor
cells. Methods Mol Biol. 634:277–282. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Brown MF, Leibowitz BJ, Chen D, He K, Zou
F, Sobol RW, Beer-Stolz D, Zhang L and Yu J: Loss of caspase-3
sensitizes colon cancer cells to genotoxic stress via
RIP1-dependent necrosis. Cell Death Dis. 6:e17292015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Holliday DL and Speirs V: Choosing the
right cell line for breast cancer research. Breast Cancer Res.
13:2152011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Li Y, Sturgis EM, Zhu L, Cao X, Wei Q,
Zhang H and Li G: E2F transcription factor 2 variants as predictive
biomarkers for recurrence risk in patients with squamous cell
carcinoma of the oropharynx. Mol Carcinog. 56:1335–1343. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Curtis C, Shah SP, Chin SF, Turashvili G,
Rueda OM, Dunning MJ, Speed D, Lynch AG, Samarajiwa S, Yuan Y, et
al: The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast
tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature. 486:346–352. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Altundag K: Patients with invasive lobular
and ductal carcinoma or pleomorphic lobular carcinoma might
increase pathologic complete response rate and lower mastectomy
rates compared to classical lobular type. J Surg Oncol. 20:5652019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liu YY, Yu TJ and Liu GY: The predictive
value of the prognostic staging system in the 8th edition of the
American Joint Committee on Cancer for triple-negative breast
cancer: A SEER population-based analysis. Future Oncol. 15:391–400.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Adams BD, Parsons C and Slack FJ: The
tumor-suppressive and potential therapeutic functions of miR-34a in
epithelial carcinomas. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 20:737–753. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ren FH, Yang H, He RQ, Lu JN, Lin XG,
Liang HW, Dang YW, Feng ZB, Chen G and Luo DZ: Analysis of
microarrays of miR-34a and its identification of prospective target
gene signature in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 18:122018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Sun TY, Xie HJ, Li Z, Kong LF, Gou XN, Li
DJ, Shi YJ and Ding YZ: miR-34a regulates HDAC1 expression to
affect the proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Am J Transl Res. 9:103–114. 2017.
|
|
36
|
Fang Z, Gong C, Liu H, Zhang X, Mei L,
Song M, Qiu L, Luo S, Zhu Z, Zhang R, et al: E2F1 promote the
aggressiveness of human colorectal cancer by activating the
ribonucleotide reductase small subunit M2. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 464:407–415. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Pulikkan JA, Peramangalam PS, Dengler V,
Ho PA, Preudhomme C, Meshinchi S, Christopeit M, Nibourel O,
Müller-Tidow C, Bohlander SK, et al: C/EBPα regulated microRNA-34a
targets E2F3 during granulopoiesis and is down-regulated in AML
with CEBPA mutations. Blood. 116:5638–5649. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Cao Q, Xia Y, Azadniv M and Crispe IN: The
E2F-1 transcription factor promotes caspase-8 and bid expression,
and enhances Fas signaling in T cells. J Immunol. 173:1111–1117.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Li ZH, Weng X, Xiong QY, Tu JH, Xiao A,
Qiu W, Gong Y, Hu EW, Huang S and Cao YL: miR-34a expression in
human breast cancer is associated with drug resistance. Oncotarget.
8:106270–106282. 2017.
|
|
40
|
Rokavec M, Li H, Jiang L and Hermeking H:
The p53/miR-34 axis in development and disease. J Mol Cell Biol.
6:214–230. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Bader AG: miR-34-a microRNA replacement
therapy is headed to the clinic. Front Genet. 3:1202012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Bu P, Wang L, Chen KY, Srinivasan T,
Murthy PK, Tung KL, Varanko AK, Chen HJ, Ai Y, King S, et al: A
miR-34a-Numb Feedforward loop triggered by inflammation regulates
asymmetric stem cell division in intestine and colon cancer. Cell
Stem Cell. 18:189–202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Tazawa H, Tsuchiya N, Izumiya M and
Nakagama H: Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like
growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon
cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:15472–15477. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Raver-Shapira N, Marciano E, Meiri E,
Spector Y, Rosenfeld N, Moskovits N, Bentwich Z and Oren M:
Transcriptional activation of miR-34a contributes to p53-mediated
apoptosis. Mol Cell. 26:731–743. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zauli G, Voltan R, di Iasio MG, Bosco R,
Melloni E, Sana ME and Secchiero P: miR-34a induces the
downregulation of both E2F1 and B-Myb oncogenes in leukemic cells.
Clin Cancer Res. 17:2712–2724. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yamamura S, Saini S, Majid S, Hirata H,
Ueno K, Chang I, Tanaka Y, Gupta A and Dahiya R: MicroRNA-34a
suppresses malignant transformation by targeting c-Myc
transcriptional complexes in human renal cell carcinoma.
Carcinogenesis. 33:294–300. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Hao Q, Lu X, Liu N, Xue X, Li M, Zhang C,
Qin X, Li W, Shu Z, Song B, et al: Posttranscriptional deregulation
of Src due to aberrant miR34a and miR203 contributes to gastric
cancer development. BMB Rep. 46:316–321. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Wei WY, Yan LH, Wang XT, Li L, Cao WL,
Zhang XS, Zhan ZX, Yu H, Xie YB and Xiao Q: E2F-1 overexpression
inhibits human gastric cancer MGC-803 cell growth in vivo. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:491–501. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
Atkinson EA, Barry M, Darmon AJ, Shostak
I, Turner PC, Moyer RW and Bleackley RC: Cytotoxic T
lymphocyte-assisted suicide. Caspase 3 activation is primarily the
result of the direct action of granzyme B. J Biol Chem.
273:21261–21266. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Huang Q, Zheng Y, Ou Y, Xiong H, Yang H,
Zhang Z, Chen S and Ye Y: miR-34a/Bcl-2 signaling pathway
contributes to age-related hearing loss by modulating hair cell
apoptosis. Neurosci Lett. 661:51–56. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Noble P, Vyas M, Al-Attar A, Durrant S,
Scholefield J and Durrant L: High levels of cleaved caspase-3 in
colorectal tumour stroma predict good survival. Br J Cancer.
108:2097–2105. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
52
|
Jakubowska K, Guzińska-Ustymowicz K,
Famulski W, Cepowicz D, Jagodzińska D and Pryczynicz A: Reduced
expression of caspase-8 and cleaved caspase-3 in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 11:1879–1884. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
53
|
Sheldon LA: Inhibition of E2F1 activity
and cell cycle progression by arsenic via retinoblastoma protein.
Cell Cycle. 16:2058–2072. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
54
|
Kent LN, Bae S, Tsai SY, Tang X,
Srivastava A, Koivisto C, Martin CK, Ridolfi E, Miller GC, Zorko
SM, et al: Dosage-dependent copy number gains in E2f1 and E2f3
drive hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 127:830–842. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
55
|
Zhou Y, Xiong M, Niu J, Sun Q, Su W, Zen
K, Dai C and Yang J: Secreted fibroblast-derived miR-34a induces
tubular cell apoptosis in fibrotic kidney. J Cell Sci.
127:4494–4506. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Ding N, Wu H, Tao T and Peng E: NEAT1
regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of ovarian cancer by
miR-34a-5p/BCL2. Onco Targets Ther. 10:4905–4915. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
57
|
Li LH, Tu QY, Deng XH, Xia J, Hou DR, Guo
K and Zi XH: Mutant presenilin2 promotes apoptosis through the
p53/miR-34a axis in neuronal cells. Brain Res. 1662:57–64. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Chen YC and Yoon E: High-throughput cancer
cell sphere formation for 3D cell culture. Methods Mol Biol.
1612:281–291. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|