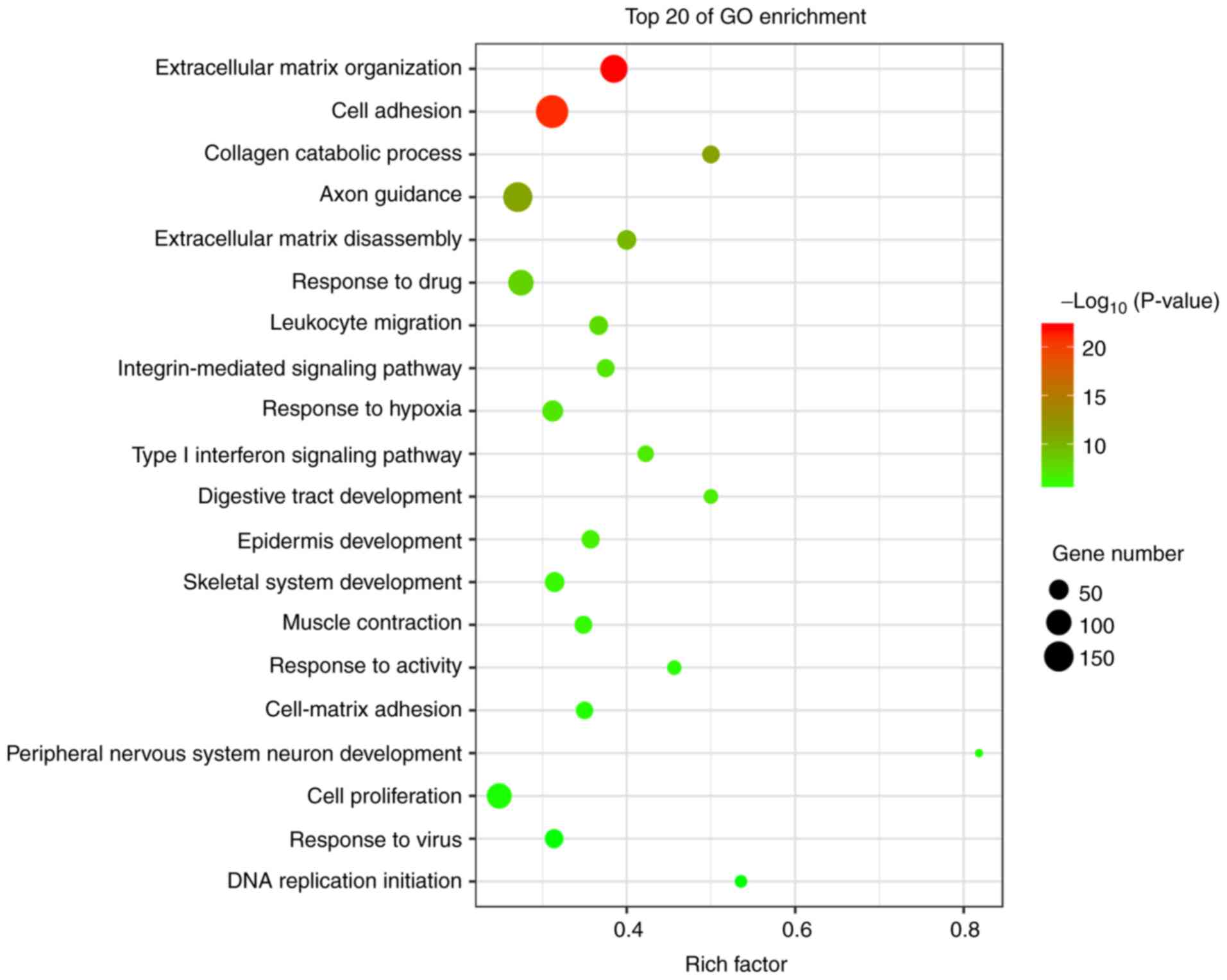
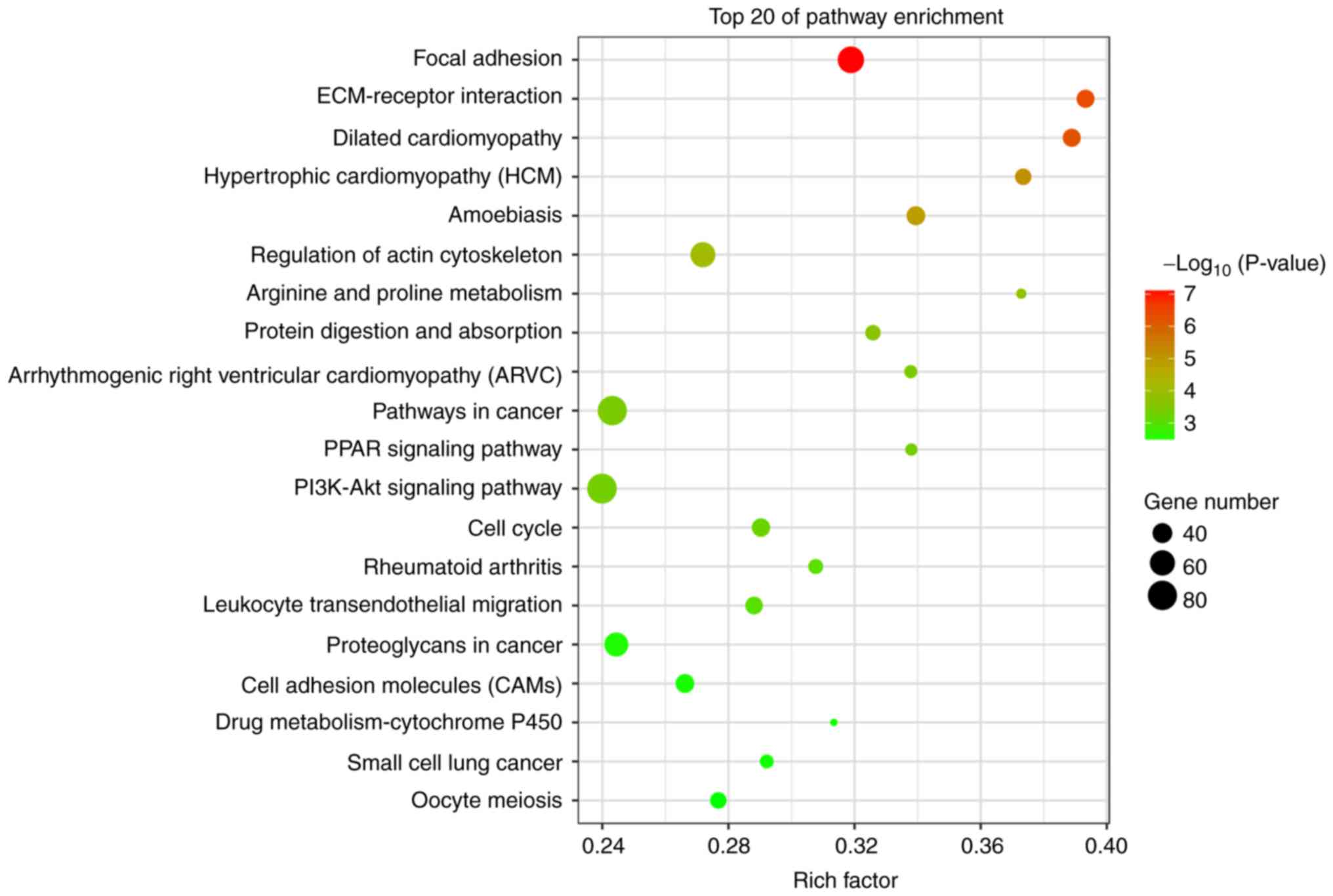
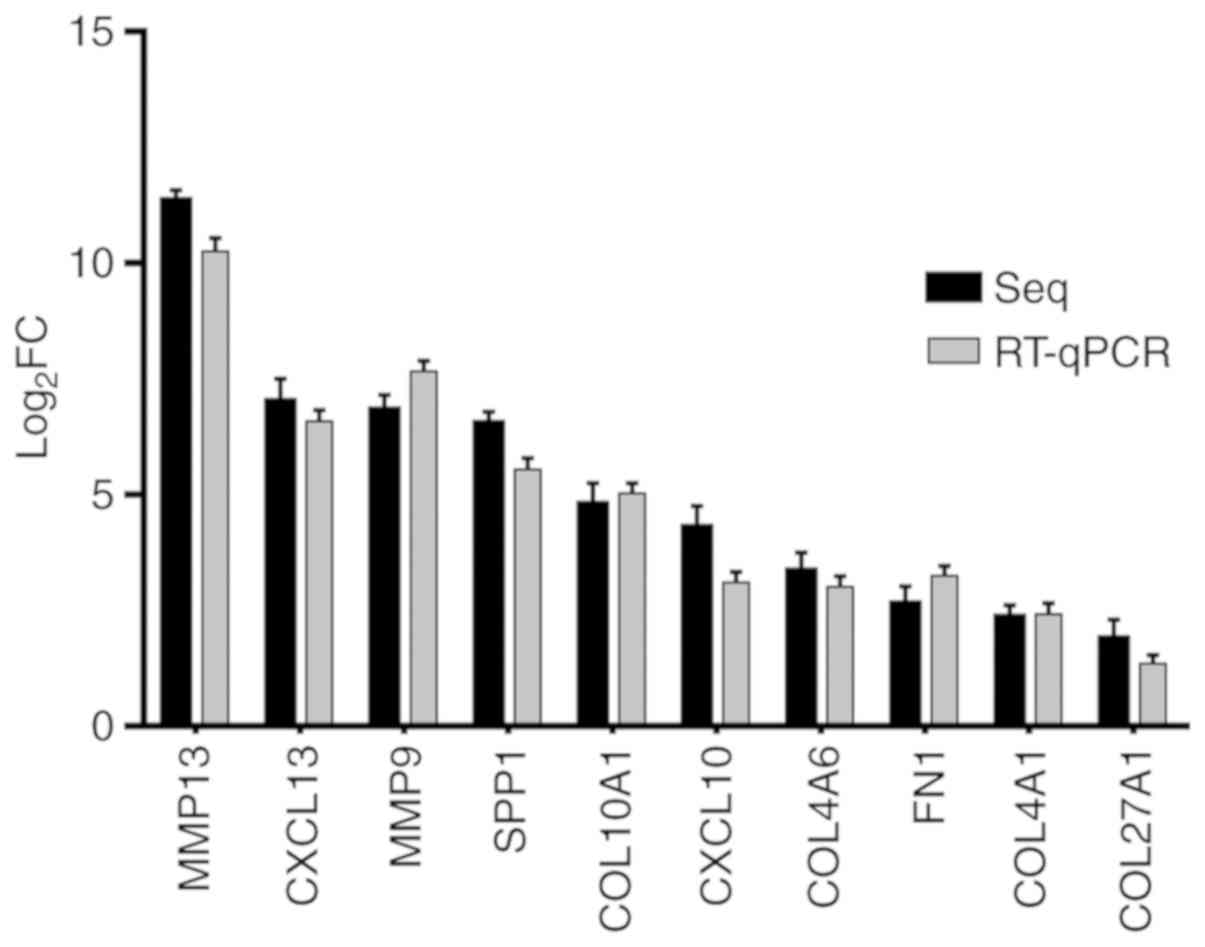
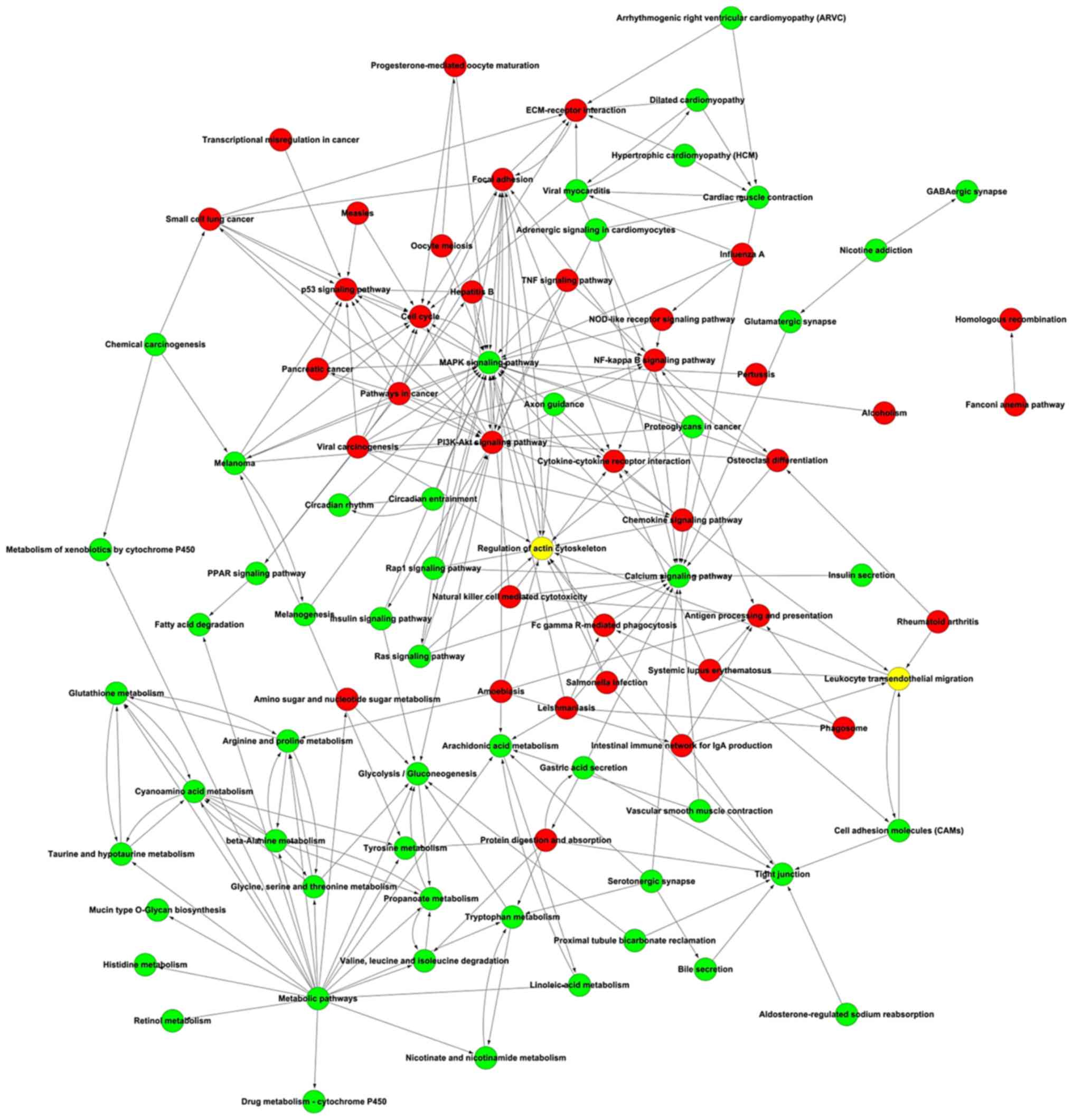
|
1
|
Wade J, Smith H, Hankins M and Llewellyn
C: Conducting oral examinations for cancer in general practice:
What are the barriers? Fam Pract. 27:77–84. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Nemeth Z, Somogyi A, Takacsi-Nagy Z,
Barabas J, Nemeth G and Szabo G: Possibilities of preventing
osteoradionecrosis during complex therapy of tumors of the oral
cavity. Pathol Oncol Res. 6:53–58. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mann J, Julie D, Mahase SS, D'Angelo D,
Potters L, Wernicke AG and Parashar B: Elective neck dissection,
but not adjuvant radiation therapy, improves survival in stage I
and II oral tongue cancer with depth of invasion >4 mm. Cureus.
11:e62882019.
|
|
4
|
Warnakulasuriya S: Global epidemiology of
oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 45:309–316. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hao SP and Tsang NM: The role of
supraomohyoid neck dissection in patients of oral cavity carcinoma.
Oral Οncol. 38:309–312. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
St John MA, Abemayor E and Wong DT: Recent
new approaches to the treatment of head and neck cancer.
Anti-cancer Drugs. 17:365–375. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Calabrese L, Bruschini R, Giugliano G,
Ostuni A, Maffini F, Massaro MA, Santoro L, Navach V, Preda L,
Alterio D, et al: Compartmental tongue surgery: Long term oncologic
results in the treatment of tongue cancer. Oral Oncol. 47:174–179.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Uma RS, Naresh KN, D'Cruz AK, Mulherkar R
and Borges AM: Metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma of the oral
tongue is associated with down-regulation of epidermal fatty acid
binding protein (E-FABP). Oral Oncol. 43:27–32. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Sun QL, Zhao CP, Wang TY, Hao XB, Wang XY,
Zhang X and Li YC: Expression profile analysis of long non-coding
RNA associated with vincristine resistance in colon cancer cells by
next-generation sequencing. Gene. 572:79–86. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: Causes and
consequences of microRNA dysregulation. Cancer J. 18:215–222. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Wang F, Ren X and Zhang X: Role of
microRNA-150 in solid tumors. Oncol Lett. 10:11–16. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Zhang HL, Yu LX, Yang W, Tang L, Lin Y, Wu
H, Zhai B, Tan YX, Shan L, Liu Q, et al: Profound impact of gut
homeostasis on chemically-induced pro-tumorigenic inflammation and
hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. J Hepatol. 57:803–812. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, Singhal U,
Sahu A, Hosono Y, Barrette TR, Prensner JR, Evans JR, Zhao S, et
al: The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human
transcriptome. Nat Genet. 47:199–208. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Rucklidge GJ, Dean V, Robins SP, Mella O
and Bjerkvig R: Immunolocalization of extracellular matrix proteins
during brain tumor invasion in BD IX rats. Cancer Res.
49:5419–5423. 1989.
|
|
15
|
Ohlund D, Elyada E and Tuveson D:
Fibroblast heterogeneity in the cancer wound. J Exp Med.
211:1503–1523. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Schafer M and Werner S: Cancer as an
overhealing wound: An old hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 9:628–638. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bergamaschi A, Tagliabue E, Sorlie T,
Naume B, Triulzi T, Orlandi R, Russnes HG, Nesland JM, Tammi R,
Auvinen P, et al: Extracellular matrix signature identifies breast
cancer subgroups with different clinical outcome. J Pathol.
214:357–367. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Emery LA, Tripathi A, King C, Kavanah M,
Mendez J, Stone MD, de las Morenas A, Sebastiani P and Rosenberg
CL: Early dysregulation of cell adhesion and extracellular matrix
pathways in breast cancer progression. Am J Pathol. 175:1292–1302.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Lai KK, Shang S, Lohia N, Booth GC, Masse
DJ, Fausto N, Campbell JS and Beretta L: Extracellular matrix
dynamics in hepatocarcinogenesis: A comparative proteomics study of
PDGFC transgenic and pten null mouse models. PLoS Genet.
7:e10021472011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Rasmussen BB, Pedersen BV, Thorpe SM and
Rose C: Elastosis in relation to prognosis in primary breast
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 45:1428–1430. 1985.
|
|
21
|
Frantz C, Stewart KM and Weaver VM: The
extracellular matrix at a glance. J Cell Sci. 123:4195–4200. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Liu Y, Carson-Walter EB, Cooper A, Winans
BN, Johnson MD and Walter KA: Vascular gene expression patterns are
conserved in primary and metastatic brain tumors. J NeuroOncol.
99:13–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Ameur N, Lacroix L, Roucan S, Roux V,
Broutin S, Talbot M, Dupuy C, Caillou B, Schlumberger M and Bidart
JM: Aggressive inherited and sporadic medullary thyroid carcinomas
display similar oncogenic pathways. Endocr Relat Cancer.
16:1261–1272. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bianchini G, Qi Y, Alvarez RH, Iwamoto T,
Coutant C, Ibrahim NK, Valero V, Cristofanilli M, Green MC,
Radvanyi L, et al: Molecular anatomy of breast cancer stroma and
its prognostic value in estrogen receptor-positive and -negative
cancers. J Clin Oncol. 28:4316–4323. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lahmann C, Young AR, Wittern KP and
Bergemann J: Induction of mRNA for matrix metalloproteinase 1 and
tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 in human skin in vivo by
solar simulated radiation. Photochem Photobiol. 73:657–663. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gomes JR, Omar NF, dos Santos Neves J,
Narvaes EA and Novaes PD: Immunolocalization and activity of the
MMP-9 and MMP-2 in odontogenic region of the rat incisor tooth
after post shortening procedure. J Mol Histol. 42:153–159. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Brummer O, Bohmer G, Hollwitz B, Flemming
P, Petry KU and Kuhnle H: MMP-1 and MMP-2 in the cervix uteri in
different steps of malignant transformation-an immunohistochemical
study. Gynecol Oncol. 84:222–227. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hynes RO and Naba A: Overview of the
matrisome-an inventory of extracellular matrix constituents and
functions. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4:a0049032012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Fang T, Hou J, He M, Wang L, Zheng M, Wang
X and Xia J: Actinidia chinensis planch root extract (acRoots)
inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inhibiting EP3
expression. Cell Biol Toxicol. 32:499–511. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kashiwagi E, Shiota M, Yokomizo A, Itsumi
M, Inokuchi J, Uchiumi T and Naito S: Prostaglandin receptor EP3
mediates growth inhibitory effect of aspirin through androgen
receptor and contributes to castration resistance in prostate
cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer. 20:431–441. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kawada K, Hosogi H, Sonoshita M, Sakashita
H, Manabe T, Shimahara Y, Sakai Y, Takabayashi A, Oshima M and
Taketo MM: Chemokine receptor CXCR3 promotes colon cancer
metastasis to lymph nodes. Oncogene. 26:4679–4688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zipin-Roitman A, Meshel T, Sagi-Assif O,
Shalmon B, Avivi C, Pfeffer RM, Witz IP and Ben-Baruch A: CXCL10
promotes invasion-related properties in human colorectal carcinoma
cells. Cancer Res. 67:3396–3405. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Osaki M, Oshimura M and Ito H: PI3K-Akt
pathway: Its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis.
9:667–676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Juric D, Krop I, Ramanathan RK, Wilson TR,
Ware JA, Sanabria Bohorquez SM, Savage HM, Sampath D, Salphati L,
Lin RS, et al: Phase I dose-escalation study of taselisib, an oral
PI3K inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer
Discov. 7:704–715. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Shultz JC, Goehe RW, Wijesinghe DS,
Murudkar C, Hawkins AJ, Shay JW, Minna JD and Chalfant CE:
Alternative splicing of caspase 9 is modulated by the
phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway via phosphorylation of
SRp30a. Cancer Res. 70:9185–9196. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Jin G, Kim MJ, Jeon HS, Choi JE, Kim DS,
Lee EB, Cha SI, Yoon GS, Kim CH, Jung TH and Park JY: PTEN
mutations and relationship to EGFR, ERBB2, KRAS, and TP53 mutations
in non-small cell lung cancers. Lung Cancer. 69:279–283. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yoon MK, Mitrea DM, Ou L and Kriwacki RW:
Cell cycle regulation by the intrinsically disordered proteins p21
and p27. Biochem Soc Trans. 40:981–988. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Cheng JC and Leung PC: Type I collagen
down-regulates E-cadherin expression by increasing PI3KCA in cancer
cells. Cancer Lett. 304:107–116. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Nieto MA, Huang RY, Jackson RA and Thiery
JP: Emt: 2016. Cell. 166:21–45. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Cavallaro U and Christofori G: Cell
adhesion and signalling by cadherins and Ig-CAMs in cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 4:118–132. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Min A, Zhu C, Wang J, Peng S, Shuai C, Gao
S, Tang Z and Su T: Focal adhesion kinase knockdown in
carcinoma-associated fibroblasts inhibits oral squamous cell
carcinoma metastasis via downregulating MCP-1/CCL2 expression. J
Biochem Mol Toxicol. 29:70–76. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
McLean GW, Komiyama NH, Serrels B, Asano
H, Reynolds L, Conti F, Hodivala-Dilke K, Metzger D, Chambon P,
Grant SG and Frame MC: Specific deletion of focal adhesion kinase
suppresses tumor formation and blocks malignant progression. Genes
Dev. 18:2998–3003. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Canel M, Secades P, Garzon-Arango M,
Allonca E, Suarez C, Serrels A, Frame M, Brunton V and Chiara MD:
Involvement of focal adhesion kinase in cellular invasion of head
and neck squamous cell carcinomas via regulation of MMP-2
expression. Br J Cancer. 98:1274–1284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
Gabriel B, zur Hausen A, Stickeler E,
Dietz C, Gitsch G, Fischer DC, Bouda J, Tempfer C and Hasenburg A:
Weak expression of focal adhesion kinase (pp125FAK) in patients
with cervical cancer is associated with poor disease outcome. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:2476–2483. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yuan Z, Zheng Q, Fan J, Ai KX, Chen J and
Huang XY: Expression and prognostic significance of focal adhesion
kinase in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
136:1489–1496. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ramaiah SK and Rittling S:
Pathophysiological role of osteopontin in hepatic inflammation,
toxicity, and cancer. Toxicol Sci. 103:4–13. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wai PY and Kuo PC: Osteopontin: Regulation
in tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27:103–118. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|