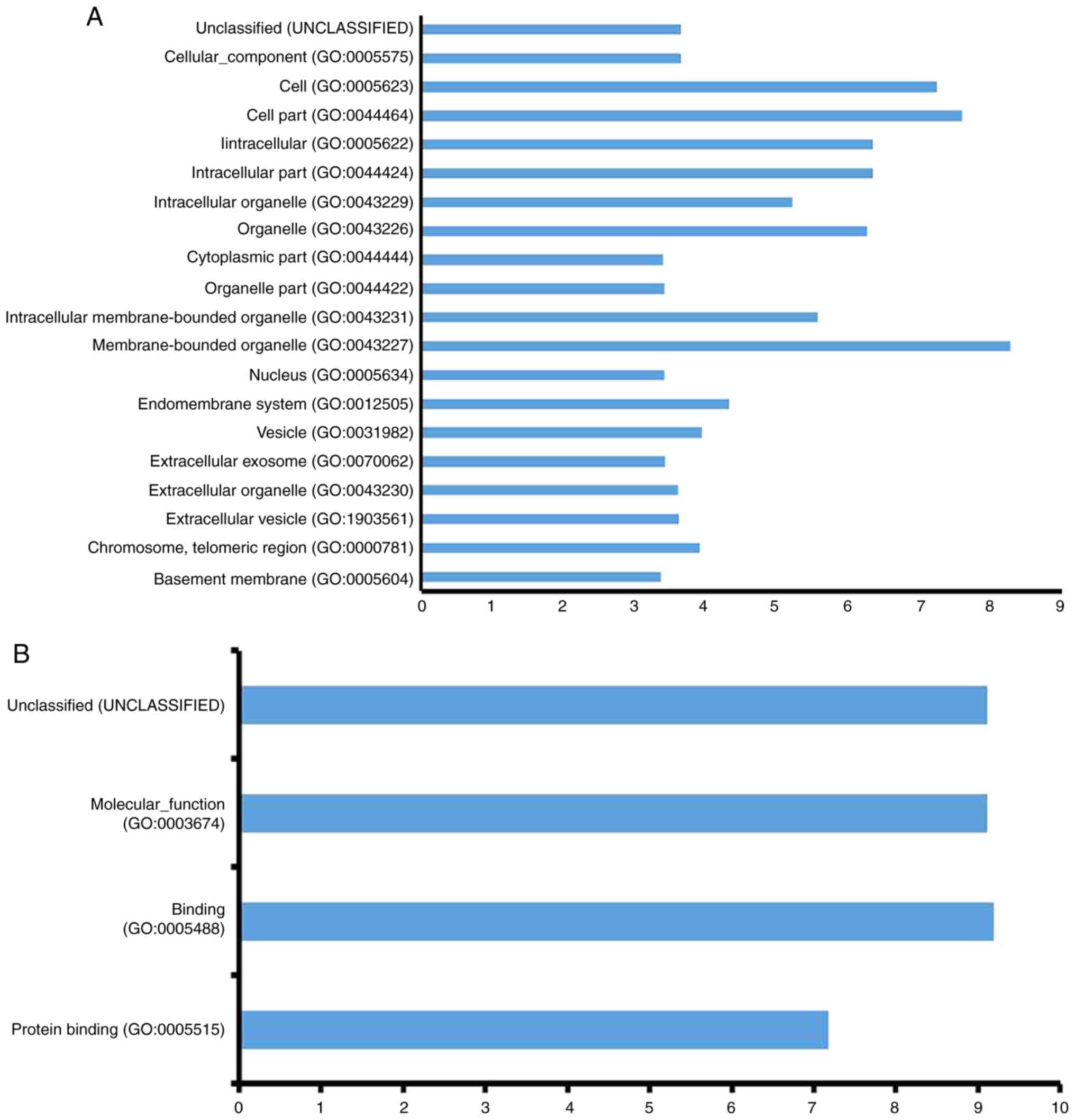
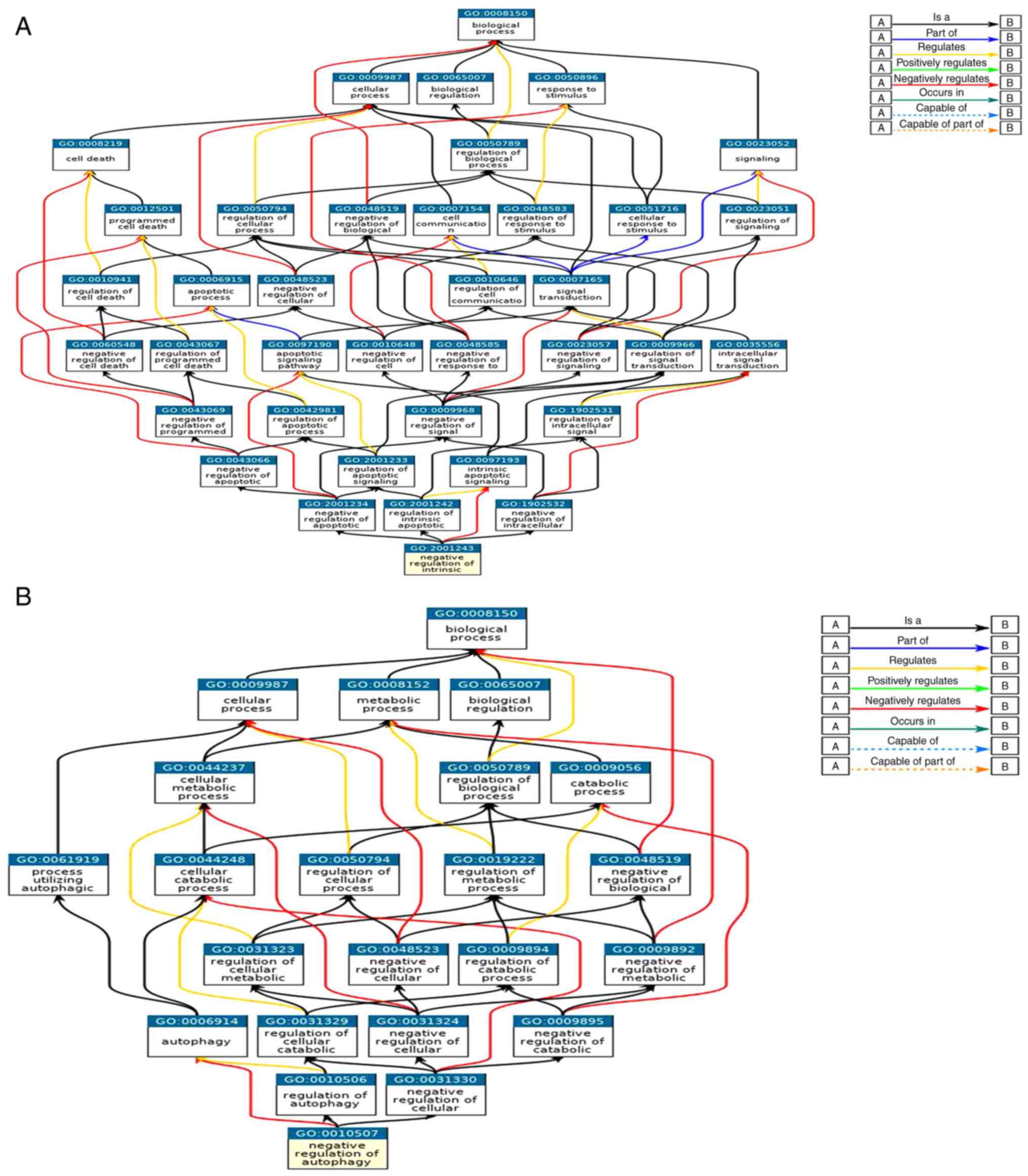
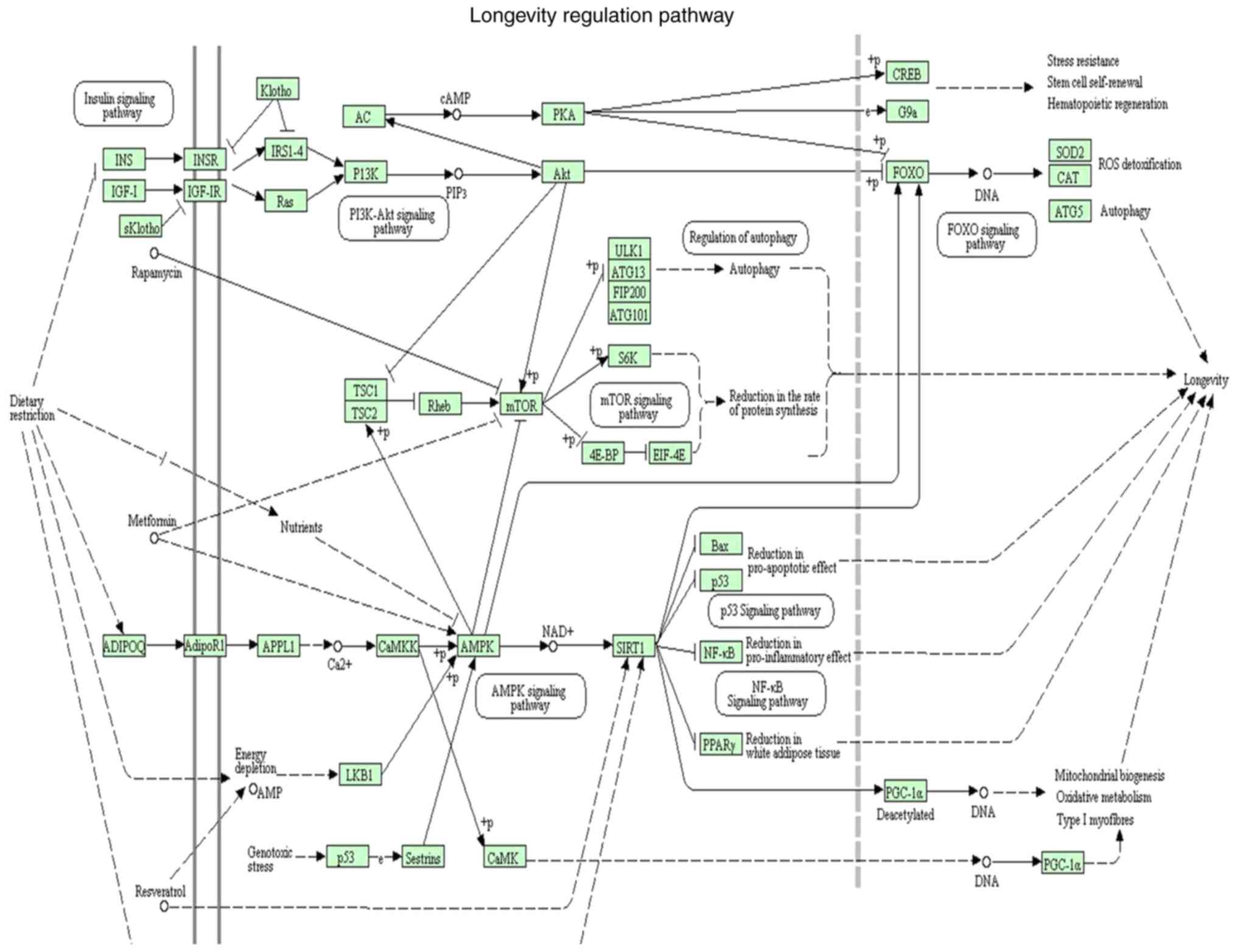
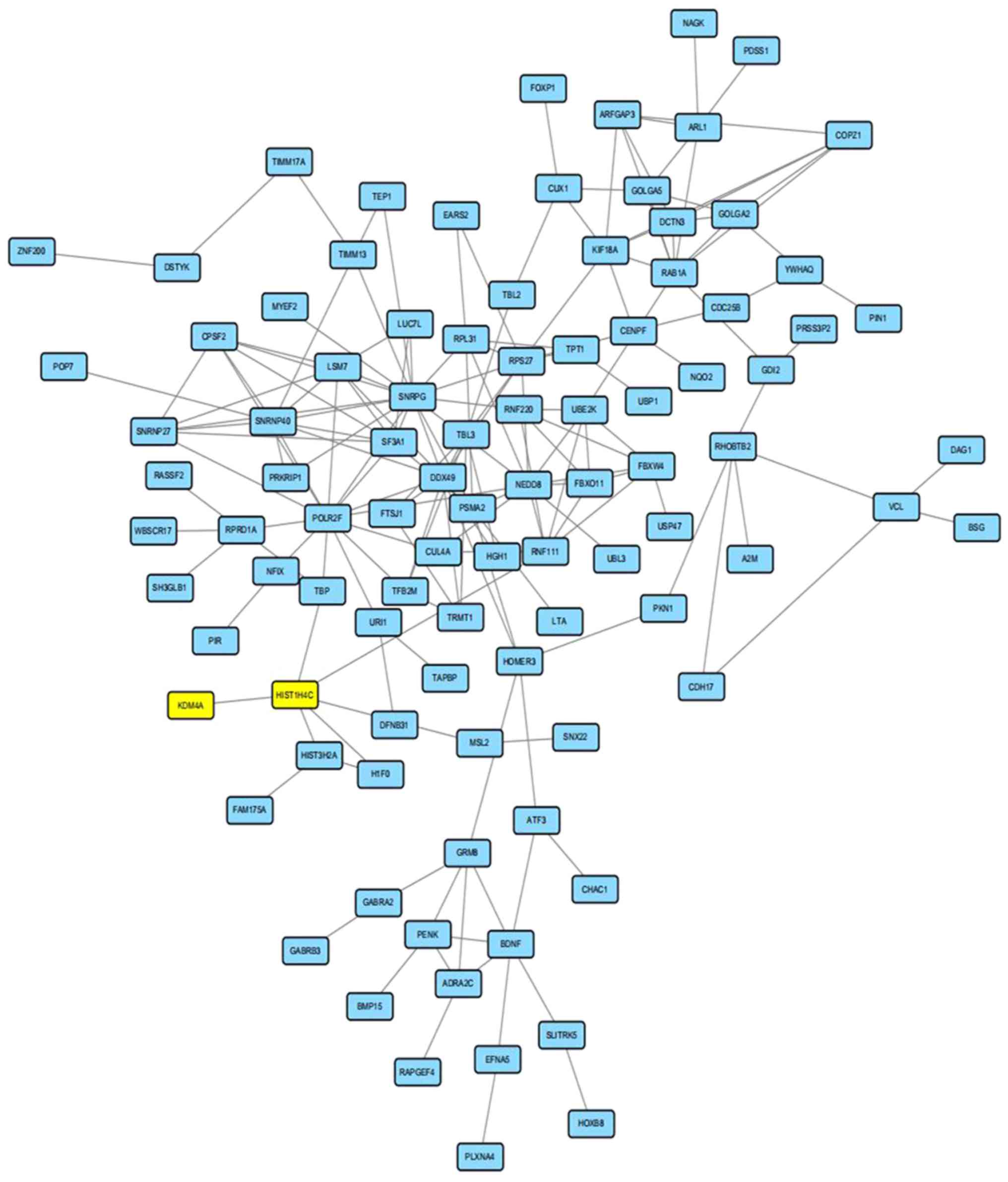
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goyama S and Kitamura T: Epigenetics in
normal and malignant hematopoiesis: An overview and update 2017.
Cancer Sci. 108:553–562. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cao R, Wang L, Wang H, Xia L,
Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Jones RS and Zhang Y: Role of
histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in Polycomb-group silencing.
Science. 298:1039–1043. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Morin RD, Johnson NA, Severson TM, Mungall
AJ, An J, Goya R, Paul JE, Boyle M, Woolcock BW, Kuchenbauer F, et
al: Somatic mutations altering EZH2 (Tyr641) in follicular and
diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of germinal-center origin. Nat
Genet. 42:181–185. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abd Al Kader L, Oka T, Takata K, Sun X,
Sato H, Murakami I, Toji T, Manabe A, Kimura H and Yoshino T: In
aggressive variants of non-Hodgkin lymphomas, Ezh2 is strongly
expressed and polycomb repressive complex PRC1.4 dominates over
PRC1.2. Virchows Arch. 463:697–711. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Asangani IA, Ateeq B, Cao Q, Dodson L,
Pandhi M, Kunju LP, Mehra R, Lonigro RJ, Siddiqui J, Palanisamy N,
et al: Characterization of the EZH2-MMSET histone methyltransferase
regulatory axis in cancer. Mol Cell. 49:80–93. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ernst T, Chase AJ, Score J, Hidalgo-Curtis
CE, Bryant C, Jones AV, Waghorn K, Zoi K, Ross FM, Reiter A, et al:
Inactivating mutations of the histone methyltransferase gene EZH2
in myeloid disorders. Nat Genet. 42:722–726. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nikoloski G, Langemeijer SM, Kuiper RP,
Knops R, Massop M, Tönnissen ER, van der Heijden A, Scheele TN,
Vandenberghe P, de Witte T, et al: Somatic mutations of the histone
methyltransferase gene EZH2 in myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat
Genet. 42:665–667. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ntziachristos P, Tsirigos A, Van
Vlierberghe P, Nedjic J, Trimarchi T, Flaherty MS, Ferres-Marco D,
da Ros V, Tang Z, Siegle J, et al: Genetic inactivation of the
polycomb repressive complex 2 in T cell acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Nat Med. 18:298–301. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Daigle SR, Olhava EJ, Therkelsen CA,
Basavapathruni A, Jin L, Boriack-Sjodin PA, Allain CJ, Klaus CR,
Raimondi A, Scott MP, et al: Potent inhibition of DOT1L as
treatment of MLL-fusion leukemia. Blood. 122:1017–1025. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Muntean AG and Hess JL: The pathogenesis
of mixed-lineage leukemia. Annu Rev Pathol. 7:283–301. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Müller-Tidow C, Klein HU, Hascher A, Isken
F, Tickenbrock L, Thoennissen N, Agrawal-Singh S, Tschanter P,
Disselhoff C, Wang Y, et al Study Alliance Leukemia, : Profiling of
histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation levels predicts transcription
factor activity and survival in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
116:3564–3571. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang H, Wenbing Y, Dong A, He Z, Yao R
and Guo W: Chidamide enhances the cytotoxicity of cytarabine and
sorafenib in acute myeloid leukemia cells by modulating H3K9me3 and
autophagy levels. Front Oncol. 9:12762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xie C, Mao X, Huang J, Ding Y, Wu J, Dong
S, Kong L, Gao G, Li CY and Wei L: KOBAS 3.0: A web server for
annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39:W316–W322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Furumichi M, Morishima
K and Tanabe M: New approach for understanding genome variations in
KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D590–D595. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kanehisa M: Toward understanding the
origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci.
28:1947–1951. 2019. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li X, Yan X, Guo W, Huang X, Huang J, Yu
M, Ma Z, Xu Y, Huang S, Li C, et al: Chidamide in FLT3-ITD positive
acute myeloid leukemia and the synergistic effect in combination
with cytarabine. Biomed Pharmacother. 90:699–704. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kleine-Kohlbrecher D, Christensen J,
Vandamme J, Abarrategui I, Bak M, Tommerup N, Shi X, Gozani O,
Rappsilber J, Salcini AE and Helin K: A functional link between the
histone demethylase PHF8 and the transcription factor ZNF711 in
X-linked mental retardation. Mol Cell. 38:165–178. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu G, Li F, Qin Y, Bo X, Wu Y and Wang S:
GOSemSim: an R package for measuring semantic similarity among GO
terms and gene products. Bioinformatics. 26:976–978. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guo W, Jin J, Pan J, Yao R, Li X, Huang X,
Ma Z, Huang S, Yan X, Jin J and Dong A: The change of nuclear LC3
distribution in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Exp Cell Res.
369:69–79. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mandrioli M and Borsatti F: Analysis of
heterochromatic epigenetic markers in the holocentric chromosomes
of the aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. Chromosome Res.
15:1015–1022. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Olcina MM, Leszczynska KB, Senra JM, Isa
NF, Harada H and Hammond EM: H3K9me3 facilitates hypoxia-induced
p53-dependent apoptosis through repression of APAK. Oncogene.
35:793–799. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu C, Yang D, Sabbatini ME, Colby AH,
Grinstaff MW, Oberlies NH, Pearce C and Liu K: Contrasting roles of
H3K4me3 and H3K9me3 in regulation of apoptosis and gemcitabine
resistance in human pancreatic cancer cells. BMC Cancer.
18:1492018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Biga PR, Latimer MN, Froehlich JM,
Gabillard JC and Seiliez I: Distribution of H3K27me3, H3K9me3, and
H3K4me3 along autophagy-related genes highly expressed in starved
zebrafish myotubes. Biol Open. 6:1720–1725. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fujiwara K, Fujita Y, Kasai A, Onaka Y,
Hashimoto H, Okada H and Yamashita T: Deletion of JMJD2B in neurons
leads to defective spine maturation, hyperactive behavior and
memory deficits in mouse. Transl Psychiatry. 6:e7662016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Magaraki A, van der Heijden G,
Sleddens-Linkels E, Magarakis L, van Cappellen WA, Peters AHFM,
Gribnau J, Baarends WM and Eijpe M: Silencing markers are retained
on pericentric heterochromatin during murine primordial germ cell
development. Epigenetics Chromatin. 10:112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun Y, Jiang X, Xu Y, Ayrapetov MK, Moreau
LA, Whetstine JR and Price BD: Histone H3 methylation links DNA
damage detection to activation of the tumour suppressor Tip60. Nat
Cell Biol. 11:1376–1382. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ayrapetov MK, Gursoy-Yuzugullu O, Xu C, Xu
Y and Price BD: DNA double-strand breaks promote methylation of
histone H3 on lysine 9 and transient formation of repressive
chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:9169–9174. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Khoury-Haddad H, Nadar-Ponniah PT, Awwad S
and Ayoub N: The emerging role of lysine demethylases in DNA damage
response: Dissecting the recruitment mode of KDM4D/JMJD2D to DNA
damage sites. Cell Cycle. 14:950–958. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu R, Wang Z, Zhang H, Gan H and Zhang Z:
H3K9me3 demethylase Kdm4d facilitates the formation of
pre-initiative complex and regulates DNA replication. Nucleic Acids
Res. 45:169–180. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hausmann M, Wagner E, Lee JH, Schrock G,
Schaufler W, Krufczik M, Papenfuß F, Port M, Bestvater F and
Scherthan H: Super-resolution localization microscopy of
radiation-induced histone H2AX-phosphorylation in relation to
H3K9-trimethylation in HeLa cells. Nanoscale. 10:4320–4331. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Saint-André V, Batsché E, Rachez C and
Muchardt C: Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation and HP1γ favor
inclusion of alternative exons. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 18:337–344.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bieberstein NI, Kozáková E, Huranová M,
Thakur PK, Krchňáková Z, Krausová M, Carrillo Oesterreich F and
Staněk D: TALE-directed local modulation of H3K9 methylation shapes
exon recognition. Sci Rep. 6:299612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Barrand S, Andersen IS and Collas P:
Promoter-exon relationship of H3 lysine 9, 27, 30 and 79
methylation on pluripotency-associated genes. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 401:611–617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pedersen MT, Kooistra SM, Radzisheuskaya
A, Laugesen A, Johansen JV, Hayward DG, Nilsson J, Agger K and
Helin K: Continual removal of H3K9 promoter methylation by Jmjd2
demethylases is vital for ESC self-renewal and early development.
EMBO J. 35:1550–1564. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Loh YH, Zhang W, Chen X, George J and Ng
HH: Jmjd1a and Jmjd2c histone H3 Lys 9 demethylases regulate
self-renewal in embryonic stem cells. Genes Dev. 21:2545–2557.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vakoc CR, Mandat SA, Olenchock BA and
Blobel GA: Histone H3 lysine 9 methylation and HP1gamma are
associated with transcription elongation through mammalian
chromatin. Mol Cell. 19:381–391. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Maksakova IA, Goyal P, Bullwinkel J, Brown
JP, Bilenky M, Mager DL, Singh PB and Lorincz MC: H3K9me3-binding
proteins are dispensable for SETDB1/H3K9me3-dependent retroviral
silencing. Epigenetics Chromatin. 4:122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Imai K, Kamio N, Cueno ME, Saito Y, Inoue
H, Saito I and Ochiai K: Role of the histone H3 lysine 9
methyltransferase Suv39 h1 in maintaining Epsteinn-Barr virus
latency in B95-8 cells. FEBS J. 281:2148–2158. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lang F, Li X, Vladimirova O, Hu B, Chen G,
Xiao Y, Singh V, Lu D, Li L, Han H, et al: CTCF interacts with the
lytic HSV-1 genome to promote viral transcription. Sci Rep.
7:398612017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fukuda A, Tomikawa J, Miura T, Hata K,
Nakabayashi K, Eggan K, Akutsu H and Umezawa A: The role of
maternal-specific H3K9me3 modification in establishing imprinted
X-chromosome inactivation and embryogenesis in mice. Nat Commun.
5:54642014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mendelsohn AR and Larrick JW: Stem cell
depletion by global disorganization of the H3K9me3 epigenetic
marker in aging. Rejuvenation Res. 18:371–375. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Koide S, Oshima M, Takubo K, Yamazaki S,
Nitta E, Saraya A, Aoyama K, Kato Y, Miyagi S, Nakajima-Takagi Y,
et al: Setdb1 maintains hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells by
restricting the ectopic activation of nonhematopoietic genes.
Blood. 128:638–649. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
McDonald OG, Li X, Saunders T,
Tryggvadottir R, Mentch SJ, Warmoes MO, Word AE, Carrer A, Salz TH,
Natsume S, et al: Epigenomic reprogramming during pancreatic cancer
progression links anabolic glucose metabolism to distant
metastasis. Nat Genet. 49:367–376. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chung YR, Schatoff E and Abdel-Wahab O:
Epigenetic alterations in hematopoietic malignancies. Int J
Hematol. 96:413–427. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lehmann U, Brakensiek K and Kreipe H: Role
of epigenetic changes in hematological malignancies. Ann Hematol.
83:137–152. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Becker JS, Nicetto D and Zaret KS:
H3K9me3-dependent heterochromatin: Barrier to cell fate changes.
Trends Genet. 32:29–41. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang C, Liu X, Gao Y, Yang L, Li C, Liu W,
Chen C, Kou X, Zhao Y, Chen J, et al: Reprogramming of
H3K9me3-dependent heterochromatin during mammalian embryo
development. Nat Cell Biol. 20:620–631. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nicetto D and Zaret KS: Role of H3K9me3
heterochromatin in cell identity establishment and maintenance.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 55:1–10. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Adamkova K, Yi YJ, Petr J, Zalmanova T,
Hoskova K, Jelinkova P, Moravec J, Kralickova M, Sutovsky M,
Sutovsky P and Nevoral J: SIRT1-dependent modulation of methylation
and acetylation of histone H3 on lysine 9 (H3K9) in the zygotic
pronuclei improves porcine embryo development. J Anim Sci
Biotechnol. 8:832017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lee MG, Norman J, Shilatifard A and
Shiekhattar R: Physical and functional association of a trimethyl
H3K4 demethylase and Ring6a/MBLR, a polycomb-like protein. Cell.
128:877–887. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Li L and Wang Y: Cross-talk between the
H3K36me3 and H4K16ac histone epigenetic marks in DNA double-strand
break repair. J Biol Chem. 292:11951–11959. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|