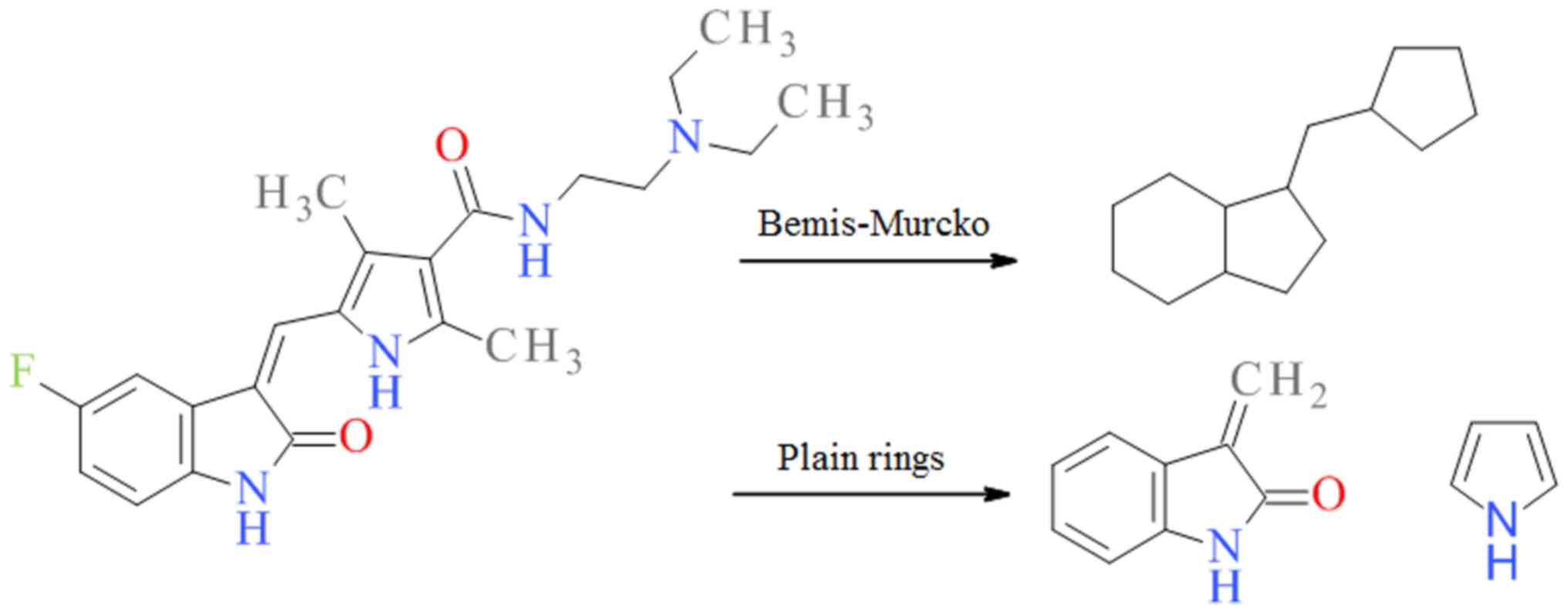
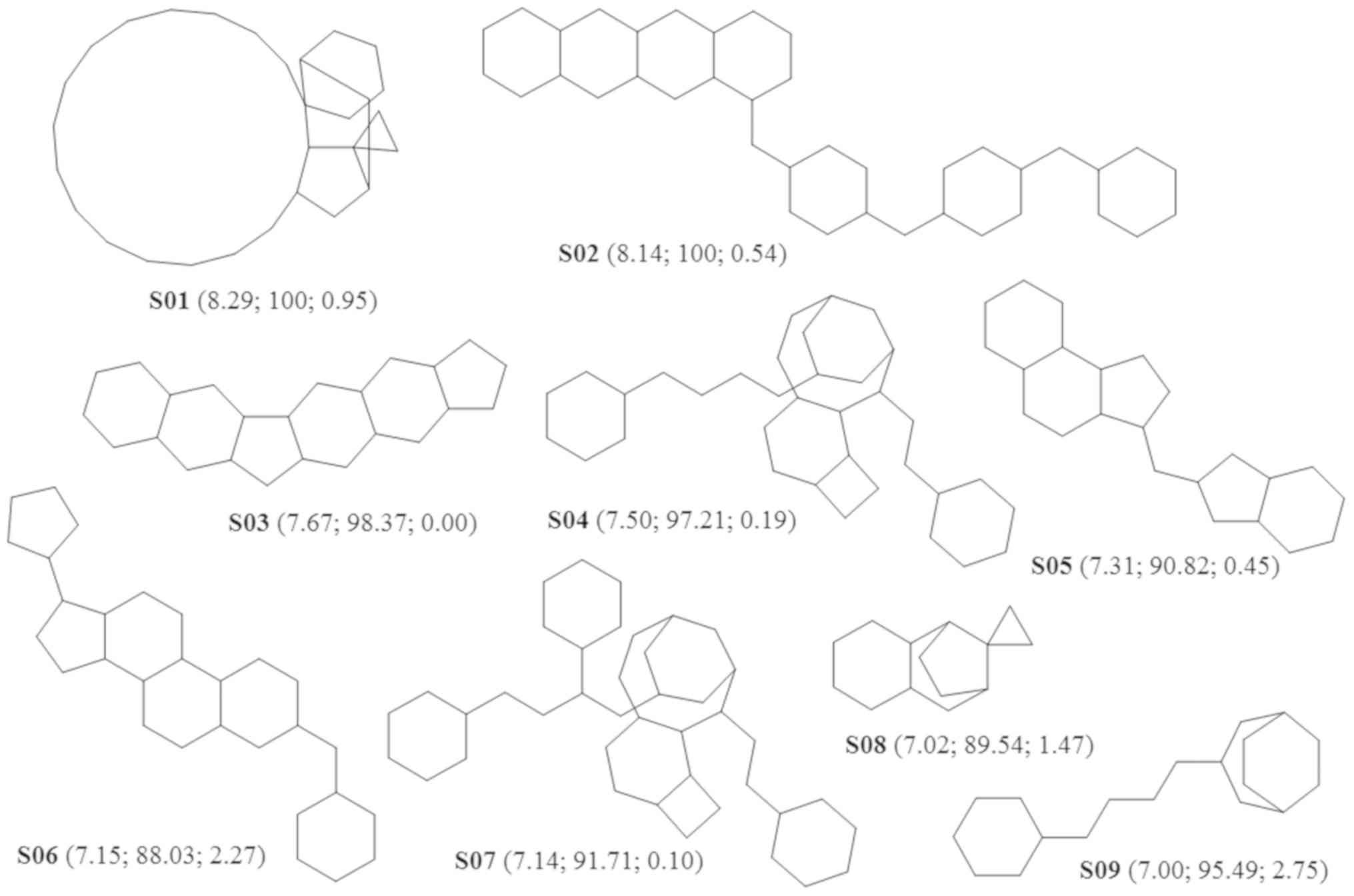
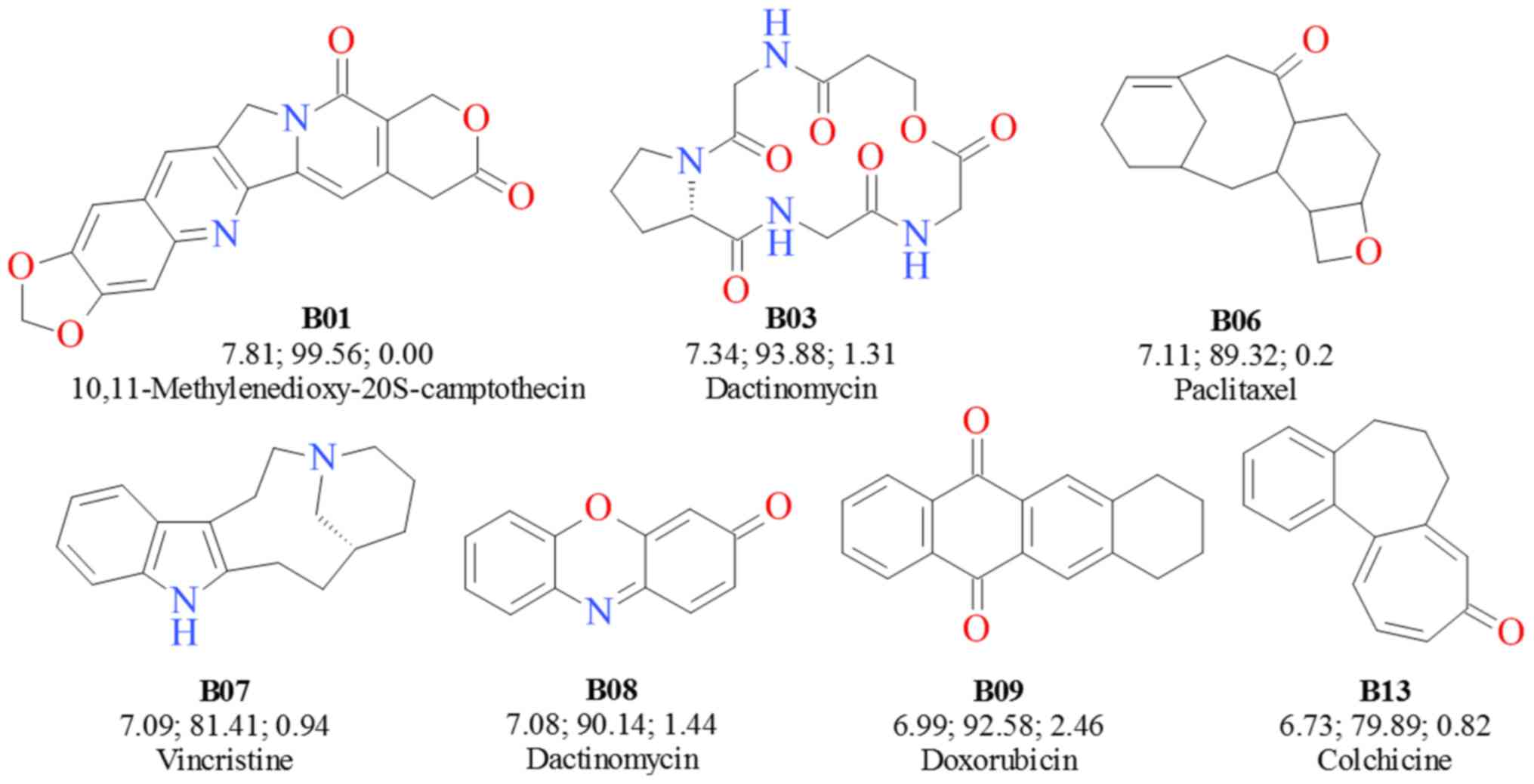
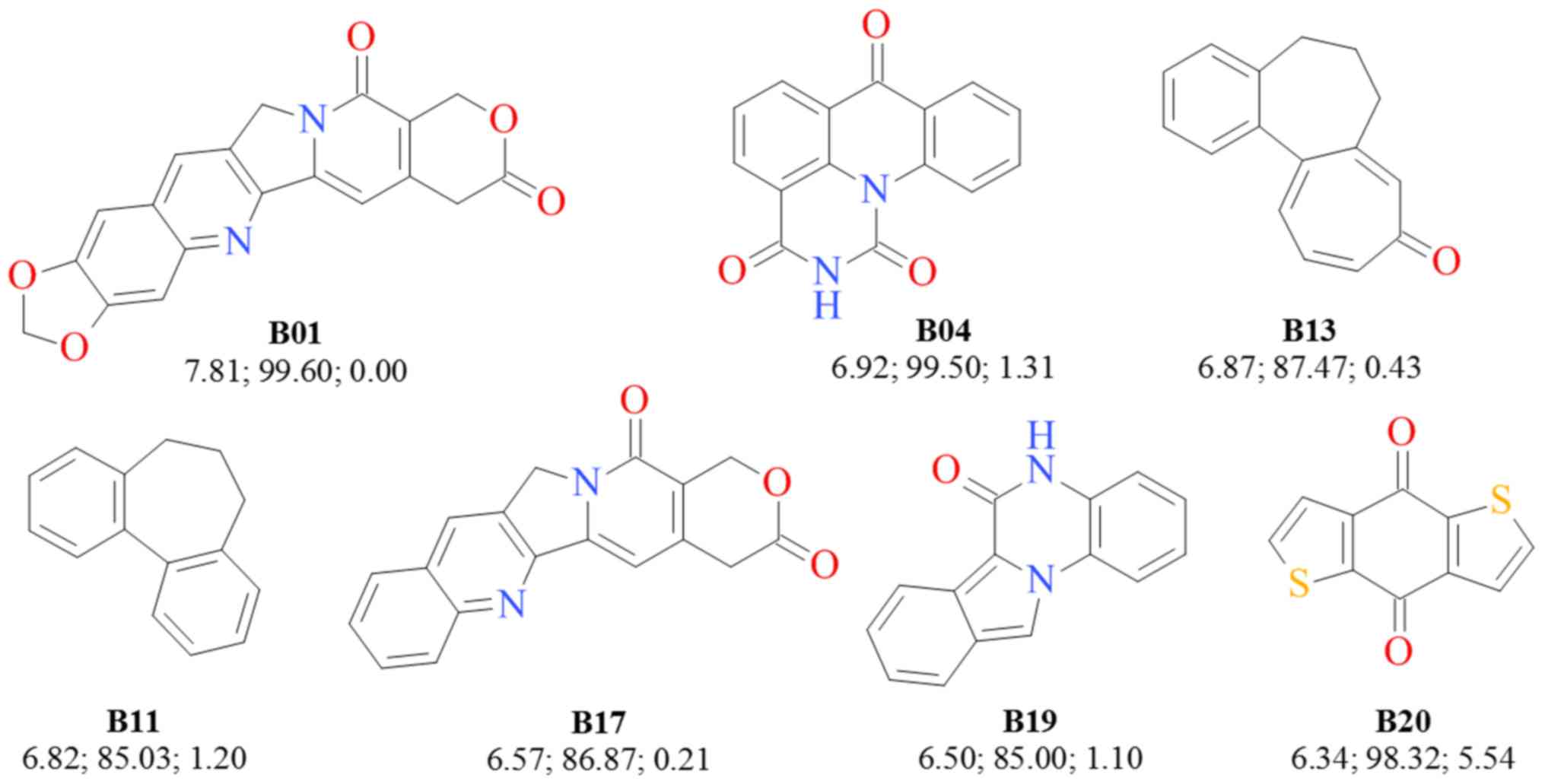
|
1
|
Schirrmacher V: From chemotherapy to
biological therapy: A review of novel concepts to reduce the side
effects of systemic cancer treatment (Review). Int J Oncol.
54:407–419. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferreira LG, Dos Santos RN, Oliva G and
Andricopulo AD: Molecular docking and structure-based drug design
strategies. Molecules. 20:13384–13421. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Śledź P and Caflisch A: Protein
structure-based drug design: From docking to molecular dynamics.
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 48:93–102. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lionta E, Spyrou G, Vassilatis DK and
Cournia Z: Structure-based virtual screening for drug discovery:
Principles, applications and recent advances. Curr Top Med Chem.
14:1923–1938. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen KC, Juang SH and Lien JC:
Identification of antiproliferative emodin analogues as inhibitors
of epidermal growth factor receptor in cancer. Int J Mol Med.
43:1281–1288. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Martin YC, Kofron JL and Traphagen LM: Do
structurally similar molecules have similar biological activity? J
Med Chem. 45:4350–4358. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun H, Tawa G and Wallqvist A:
Classification of scaffold-hopping approaches. Drug Discov Today.
17:310–324. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gomez L: Decision Making in Medicinal
Chemistry: The Power of Our Intuition. ACS Med Chem Lett.
9:956–958. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Segall M and Chadwick A: The risks of
subconscious biases in drug-discovery decision making. Future Med
Chem. 3:771–774. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sharma PC, Bansal KK, Sharma A, Sharma D
and Deep A: Thiazole-containing compounds as therapeutic targets
for cancer therapy. Eur J Med Chem. 188:1120162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dadashpour S and Emami S: Indole in the
target-based design of anticancer agents: A versatile scaffold with
diverse mechanisms. Eur J Med Chem. 150:9–29. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mazumder A, Cerella C and Diederich M:
Natural scaffolds in anticancer therapy and precision medicine.
Biotechnol Adv. 36:1563–1585. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Munteanu AC, Badea M, Olar R, Silvestro L,
Dulea C, Negut CD and Uivarosi V: Synthesis and Structural
Investigation of New Bio-Relevant Complexes of Lanthanides with
5-Hydroxyflavone: DNA Binding and Protein Interaction Studies.
Molecules. 21:17372016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ismail NSM, Ali EMH, Ibrahim DA, Serya RAT
and Abou El Ella DA: Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine based scaffold
derivatives targeting kinases as anticancer agents. Futur J Pharm
Sci. 2:20–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Nitulescu GM, Matei L, Aldea IM, Draghici
C, Olaru OT and Bleotu C: Ultrasound-assisted synthesis and
anticancer evaluation of new pyrazole derivatives as cell cycle
inhibitors. Arab J Chem. 12:816–824. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nitulescu GM, Draghici C, Olaru OT, Matei
L, Ioana A, Dragu LD and Bleotu C: Synthesis and apoptotic activity
of new pyrazole derivatives in cancer cell lines. Bioorg Med Chem.
23:5799–5808. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nitulescu GM, Draghici C and Olaru OT: New
potential antitumor pyrazole derivatives: Synthesis and cytotoxic
evaluation. Int J Mol Sci. 14:21805–21818. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nitulescu GM, Paunescu H, Draghici C,
Missir AV, Coman OA and Fulga I: Synthesis and pharmacological
evaluation of some new pyrazole derivatives. Farmacia. 58:190–197.
2010.
|
|
19
|
Takimoto CH: Anticancer drug development
at the US National Cancer Institute. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 52
(Suppl 1):S29–S33. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
DeVita VT Jr and Chu E: A history of
cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 68:8643–8653. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim HS, Sung YJ and Paik S: Cancer Cell
Line Panels Empower Genomics-Based Discovery of Precision Cancer
Medicine. Yonsei Med J. 56:1186–1198. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shoemaker RH: The NCI60 human tumour cell
line anticancer drug screen. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:813–823. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zaharevitz DW, Holbeck SL, Bowerman C and
Svetlik PA: COMPARE: A web accessible tool for investigating
mechanisms of cell growth inhibition. J Mol Graph Model.
20:297–303. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fang X, Shao L, Zhang H and Wang S:
Web-based tools for mining the NCI databases for anticancer drug
discovery. J Chem Inf Comput Sci. 44:249–257. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nitulescu GM, Soriga SG, Socea LI, Olaru
OT and Plesu V: Structure-activity relationships and
chemoinformatic analysis of the anticancer profile of an
aminopyrazole derivative. Rev Chim. 67:162–165. 2016.
|
|
26
|
Nitulescu GM, Iancu G, Nitulescu G, Iancu
RC, Bogdanici C and Vasile D: Brave new hope for breast cancer:
Aminopyrazole derivates between rational design and clinical
efficacy. Rev Chim. 68:754–757. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Herbowski L: Skeletal muscle metastases
from papillary and follicular thyroid carcinomas: An extensive
review of the literature. Oncol Lett. 15:7083–7089. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lipkus AH, Yuan Q, Lucas KA, Funk SA,
Bartelt WF III, Schenck RJ and Trippe AJ; CAS Registry, :
Structural diversity of organic chemistry. A scaffold analysis of
the CAS Registry. J Org Chem. 73:4443–4451. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Néda Z, Varga L and Biró TS: Science and
Facebook: The same popularity law! PLoS One. 12:e01796562017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ahmed K, Zaidi SF, Cui Z-G, Zhou D, Saeed
SA and Inadera H: Potential proapoptotic phytochemical agents for
the treatment and prevention of colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett.
18:487–498. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Paymode DJ and Ramana CV: Total Synthesis
of (±)-Allocolchicine and Its Analogues Using Co-Catalyzed Alkyne
[2 + 2 + 2]-Cyclotrimerization. ACS Omega. 2:5591–5600. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Armando RG, Mengual Gómez DL and Gomez DE:
New drugs are not enough drug repositioning in oncology: An update.
Int J Oncol. 56:651–684. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pushpakom S, Iorio F, Eyers PA, Escott KJ,
Hopper S, Wells A, Doig A, Guilliams T, Latimer J, McNamee C, et
al: Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 18:41–58. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ion GND, Mihai DP, Lupascu G and Nitulescu
GM: Application of molecular framework-based data-mining method in
the search for beta-secretase 1 inhibitors through drug
repurposing. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 37:3674–3685. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang X, Huang W-T, Wu H-Y, He R-Q, Ma J,
Liu A-G and Chen G: Novel drug candidate for the treatment of
several soft tissue sarcoma histologic subtypes: A computational
method using survival associated gene signatures for drug
repurposing. Oncol Rep. 41:2241–2253. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schneider P and Schneider G: Privileged
Structures Revisited. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 56:7971–7974. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Musiol R: An overview of quinoline as a
privileged scaffold in cancer drug discovery. Expert Opin Drug
Discov. 12:583–597. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Afzal O, Kumar S, Haider MR, Ali MR, Kumar
R, Jaggi M and Bawa S: A review on anticancer potential of
bioactive heterocycle quinoline. Eur J Med Chem. 97:871–910. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cui YJ, Tang LQ, Zhang CM and Liu ZP:
Synthesis of Novel Pyrazole Derivatives and Their Tumor Cell Growth
Inhibitory Activity. Molecules. 24:2792019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Nitulescu GM, Nedelcu G, Buzescu A and
Olaru OT: Aminopyrazoles as privileged structures in anticancer
drug design - an in silico study. Izv Him. 48:55–60. 2016.
|
|
41
|
Wang S, Dong G and Sheng C: Structural
simplification: An efficient strategy in lead optimization. Acta
Pharm Sin B. 9:880–901. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|