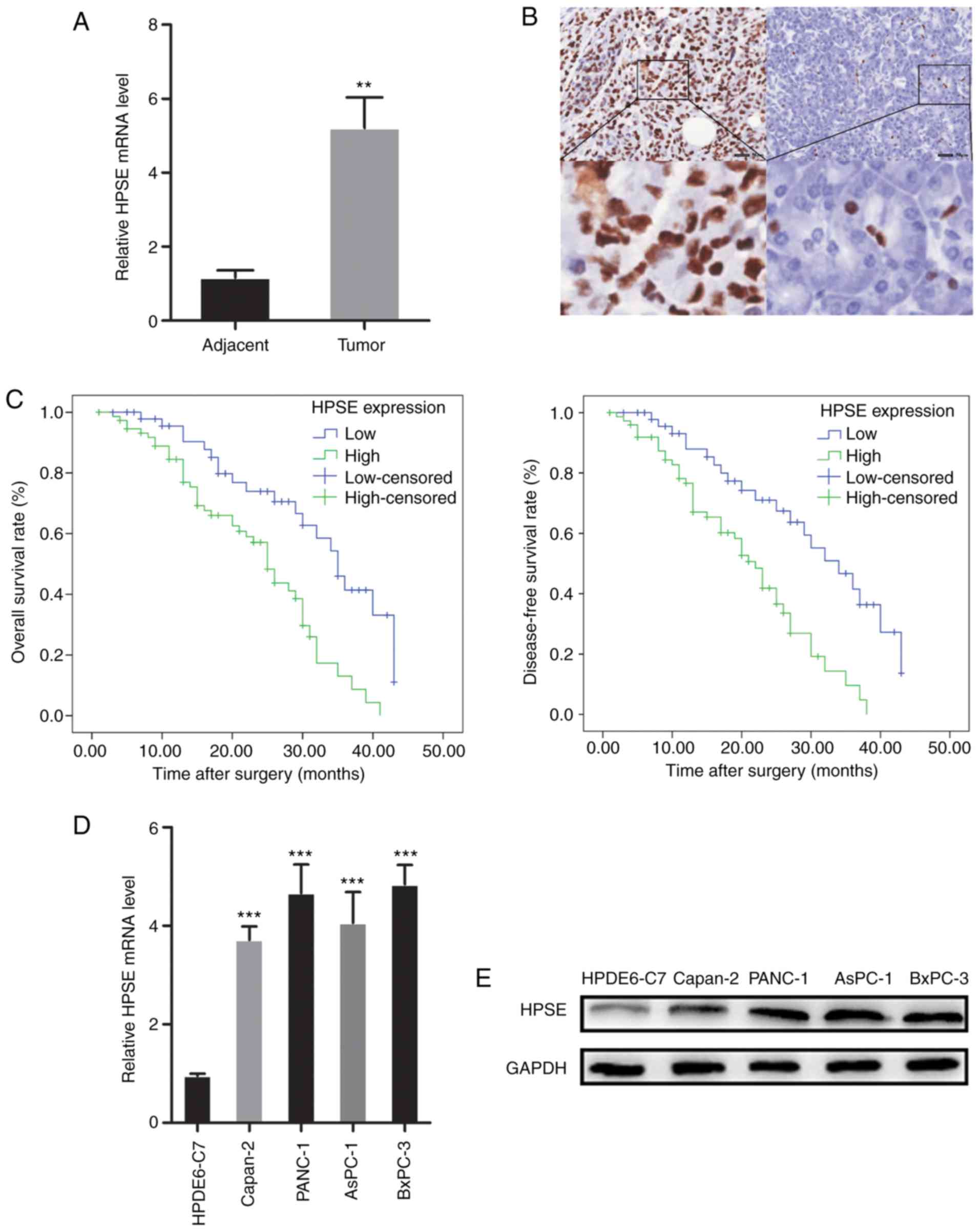
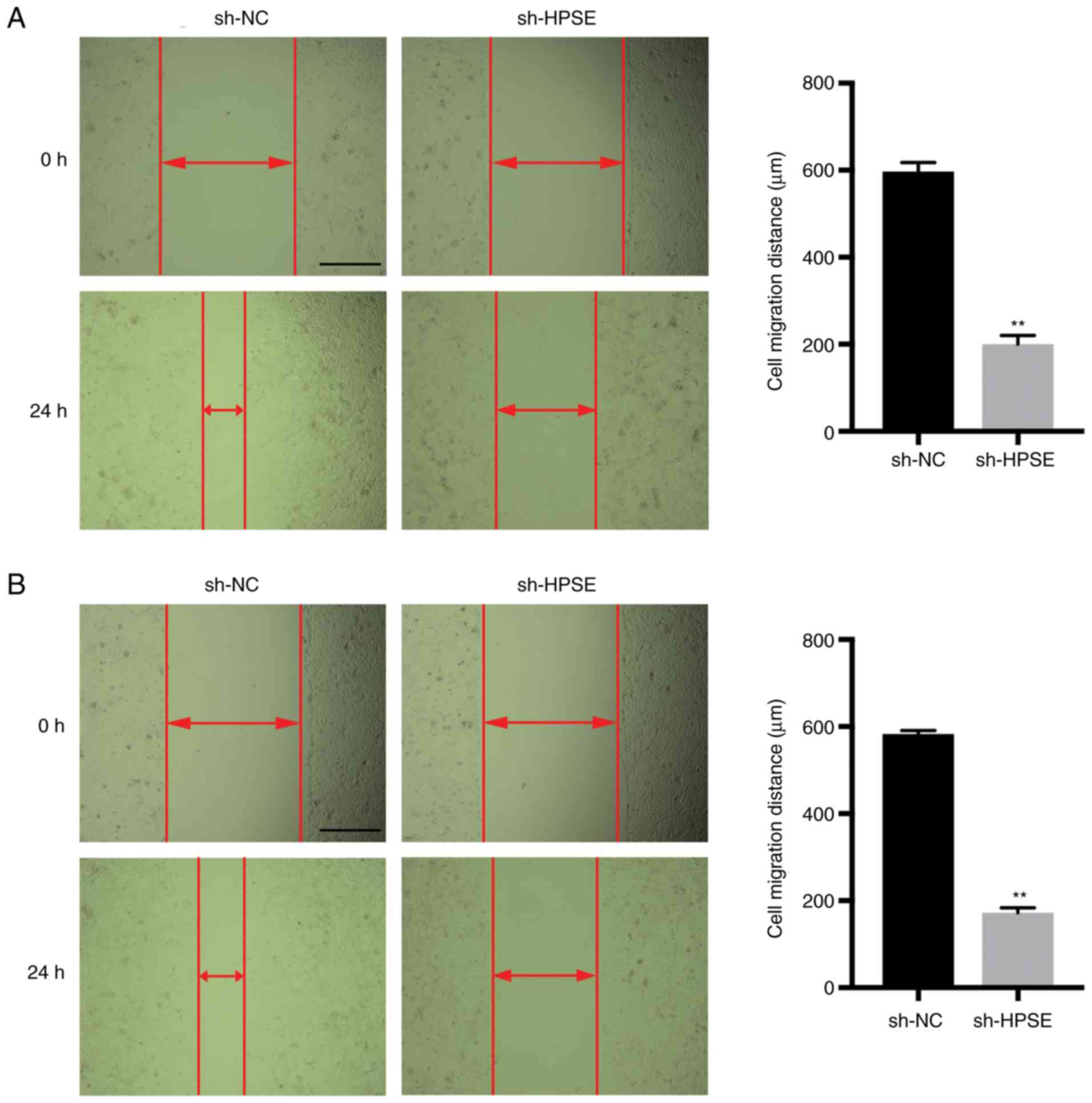
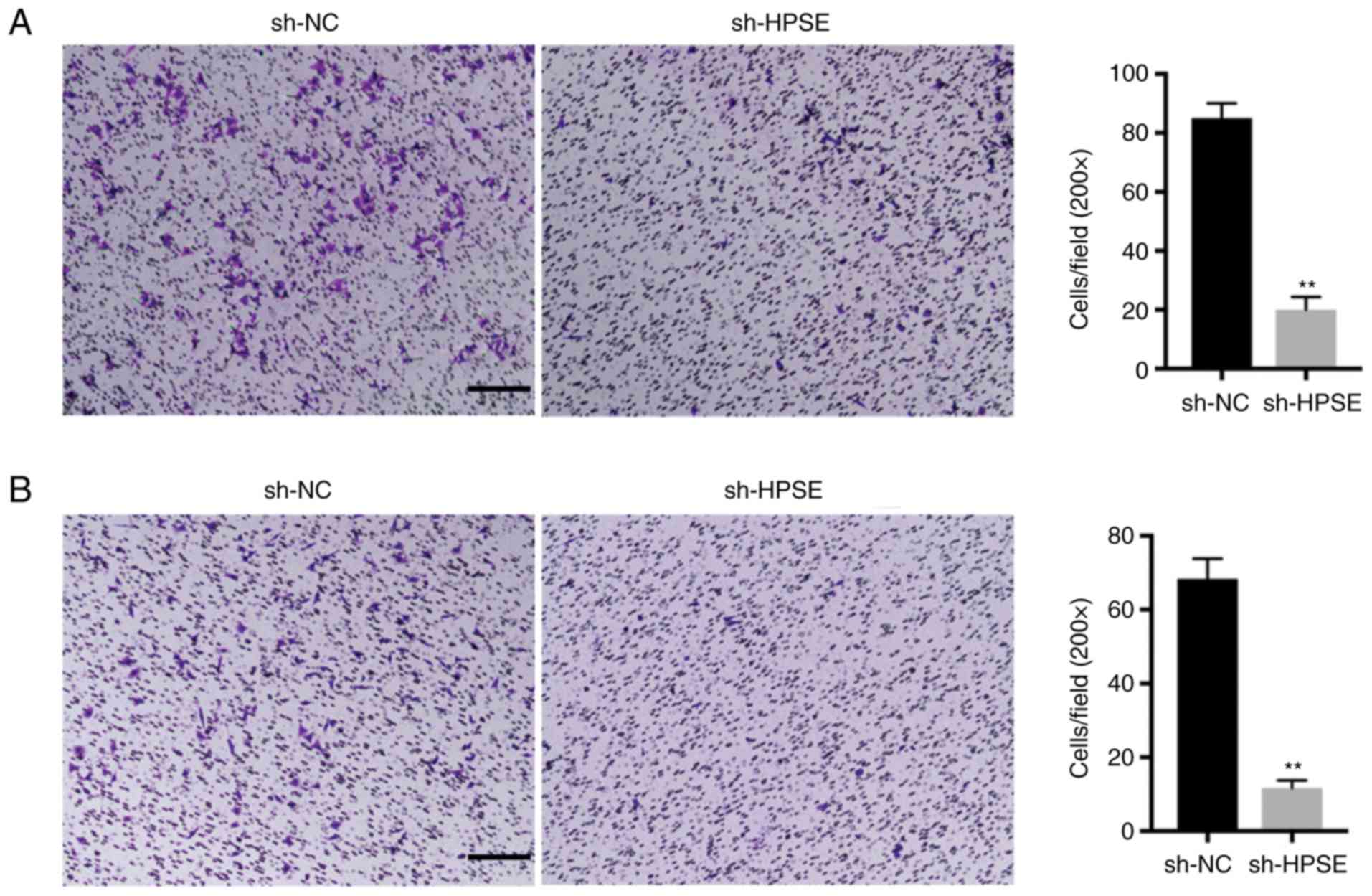
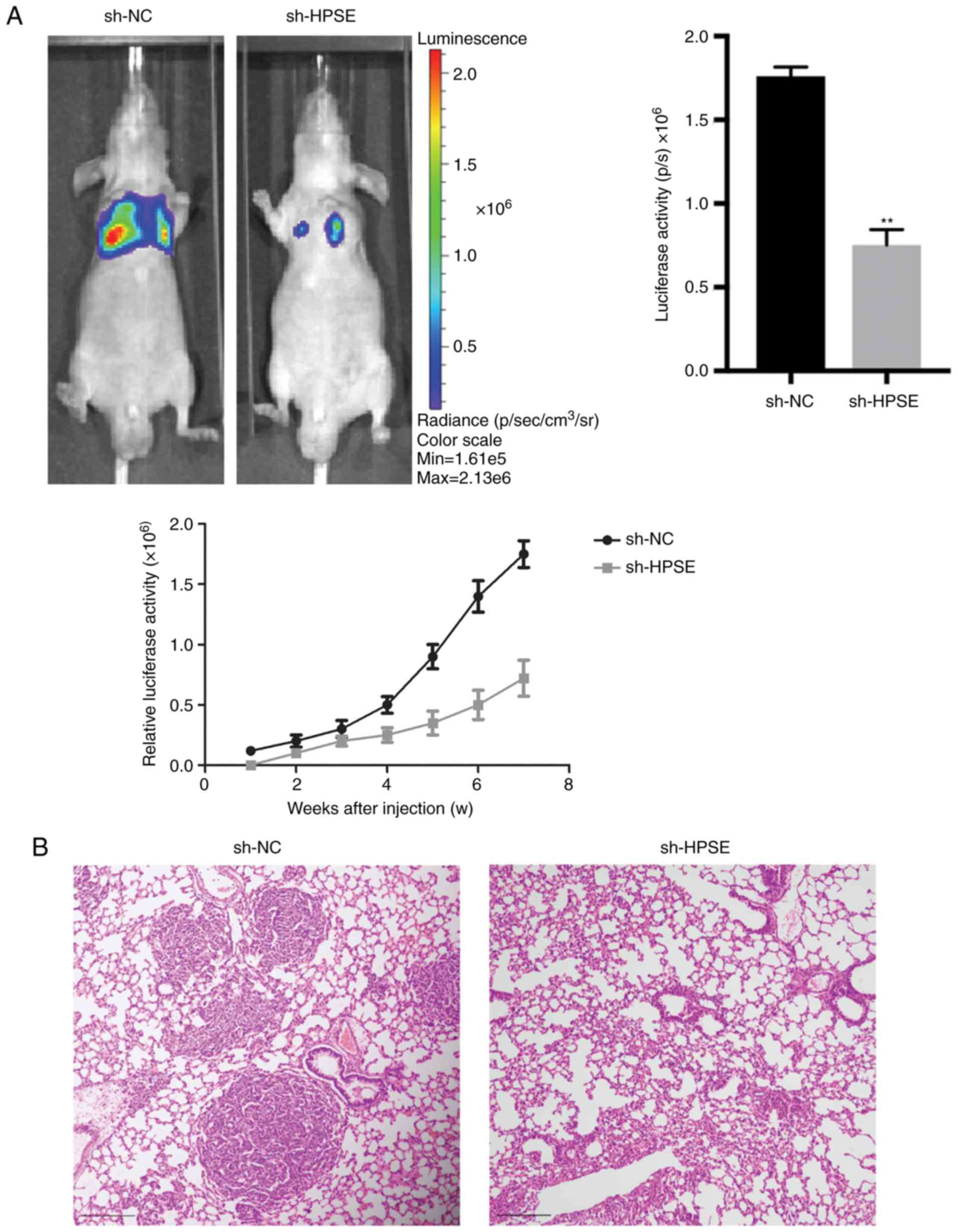
|
1
|
Kleeff J, Korc M, Apte M, La Vecchia C,
Johnson CD, Biankin AV, Neale RE, Tempero M, Tuveson DA, Hruban RH
and Neoptolemos JP: Pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
2:160222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Halbrook CJ and Lyssiotis CA: Employing
metabolism to improve the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic
cancer. Cancer Cell. 31:5–19. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hessmann E, Johnsen SA, Siveke JT and
Ellenrieder V: Epigenetic treatment of pancreatic cancer: Is there
a therapeutic perspective on the horizon? Gut. 66:168–179. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Masola V, Bellin G, Gambaro G and Onisto
M: Heparanase: A multitasking protein involved in extracellular
matrix (ECM) remodeling and intracellular events. Cells. 7:2362018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Masola V, Zaza G, Gambaro G, Franchi M and
Onisto M: Role of heparanase in tumor progression: Molecular
aspects and therapeutic options. Semin Cancer Biol. 62:86–98. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Caruana I, Savoldo B, Hoyos V, Weber G,
Liu H, Kim ES, Ittmann MM, Marchetti D and Dotti G: Heparanase
promotes tumor infiltration and antitumor activity of
CAR-redirected T lymphocytes. Nat Med. 21:524–529. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tran VM, Wade A, McKinney A, Chen K,
Lindberg OR, Engler JR, Persson AI and Phillips JJ: Heparan sulfate
glycosaminoglycans in glioblastoma promote tumor invasion. Mol
Cancer Res. 15:1623–1633. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brierley J, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: TNM Classification of Malignant tumours. John Wiley & Sons,
Inc.; Hoboken, New Jersey: 2017
|
|
9
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang G, Pan J, Zhang L, Wei Y and Wang C:
Long non-coding RNA CRNDE sponges miR-384 to promote proliferation
and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells through upregulating
IRS1. Cell Prolif. 50:e123892017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Vincent A, Herman J, Schulick R, Hruban RH
and Goggins M: Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 378:607–620. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vlodavsky I, Singh P, Boyango I,
Gutter-Kapon L, Elkin M, Sanderson RD and Ilan N: Heparanase: From
basic research to therapeutic applications in cancer and
inflammation. Drug Resist Updat. 29:54–75, 20165. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rabelink TJ, van den Berg BM, Garsen M,
Wang G, Elkin M and van der Vlag J: Heparanase: Roles in cell
survival, extracellular matrix remodelling and the development of
kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 13:201–212. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lv Q, Wu K, Liu F, Wu W, Chen Y and Zhang
W: Interleukin17A and heparanase promote angiogenesis and cell
proliferation and invasion in cervical cancer. Int J Oncol.
53:1809–1817. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lv B, Zhang B, Hu XY and Zeng QD:
Heparanase regulates in vitro VEGF-C expression and its clinical
significance to pancreatic ductal cell adenocarcinoma. Oncol Lett.
11:1327–1334. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu X, Zhou ZH, Li W, Zhang SK, Li J, Zhou
MJ and Song JW: Heparanase promotes tumor growth and liver
metastasis of colorectal cancer cells by activating the p38/MMP1
Axis. Front Oncol. 9:2162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen X, Jiang W, Yue C, Zhang W, Tong C,
Dai D, Cheng B, Huang C and Lu L: Heparanase contributes to
trans-endothelial migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J
Cancer. 8:3309–3317. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nieto MA, Huang RY, Jackson RA and Thiery
JP: Emt: 2016. Cell. 166:21–45. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen CL, Huang SS and Huang JS: Cellular
heparan sulfate negatively modulates transforming growth
factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) responsiveness in epithelial cells. J Biol
Chem. 281:11506–11514. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pearlman RL, Montes de Oca MK, Pal HC and
Afaq F: Potential therapeutic targets of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in melanoma. Cancer Lett. 391:125–140. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|