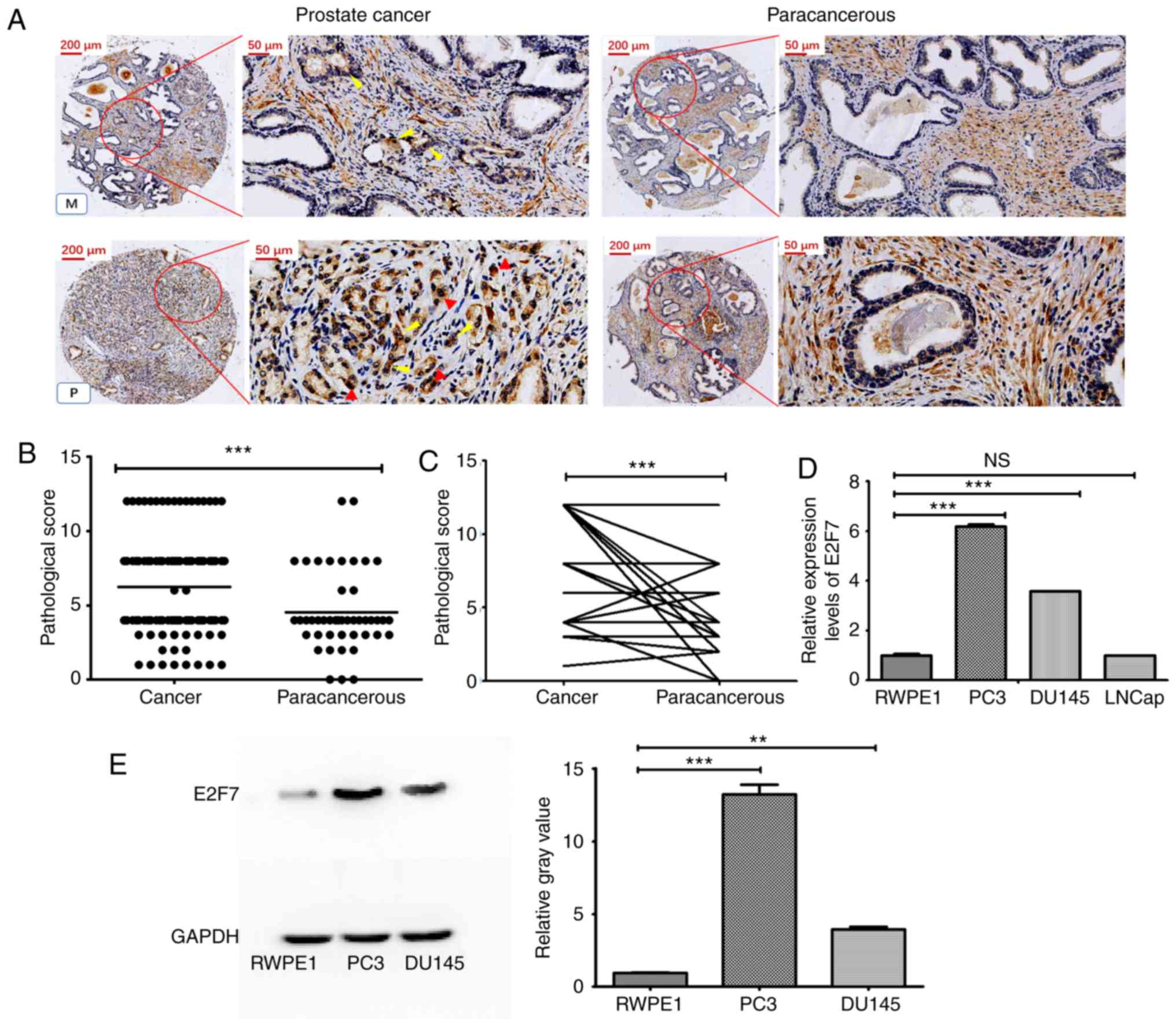
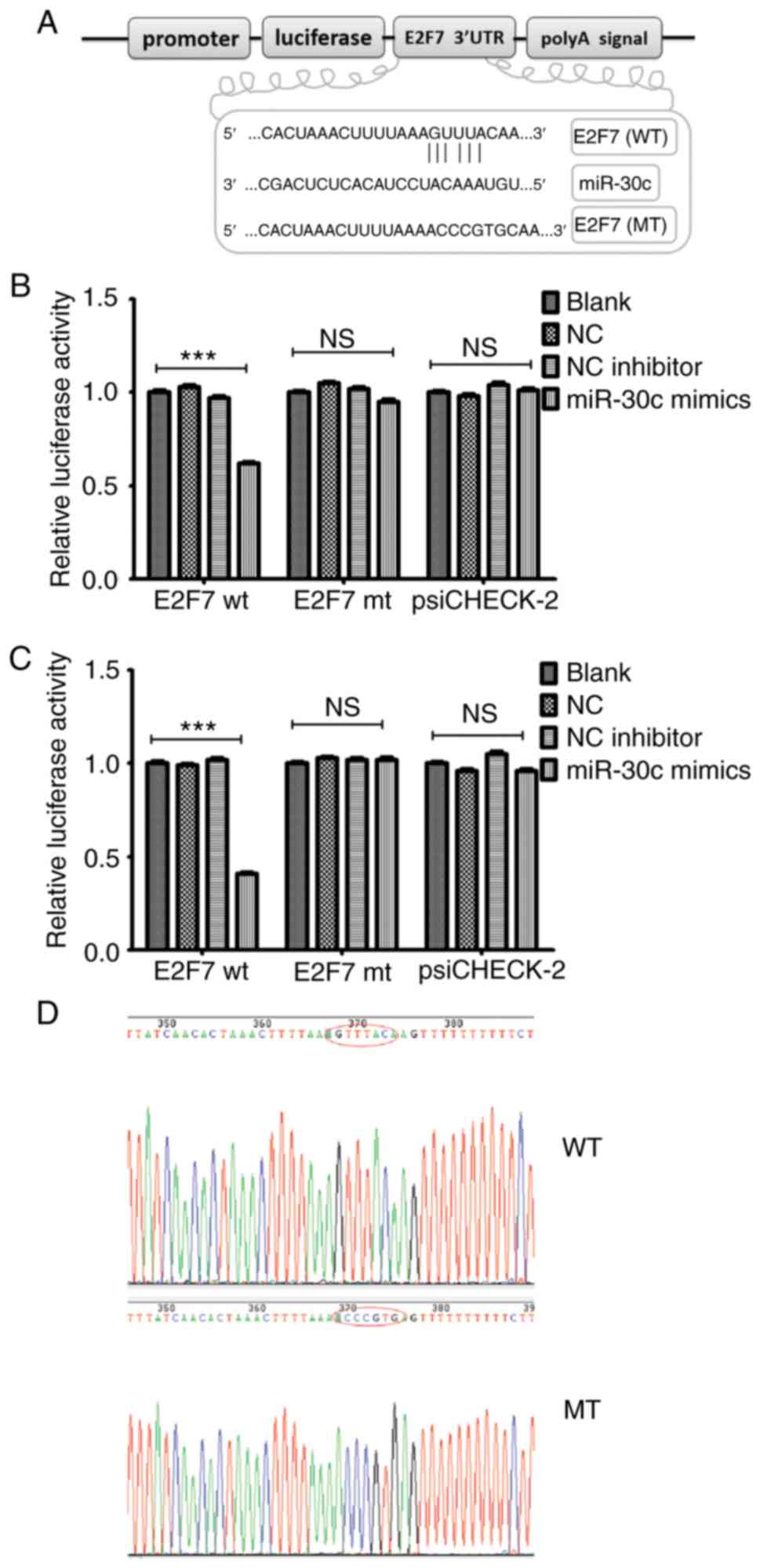
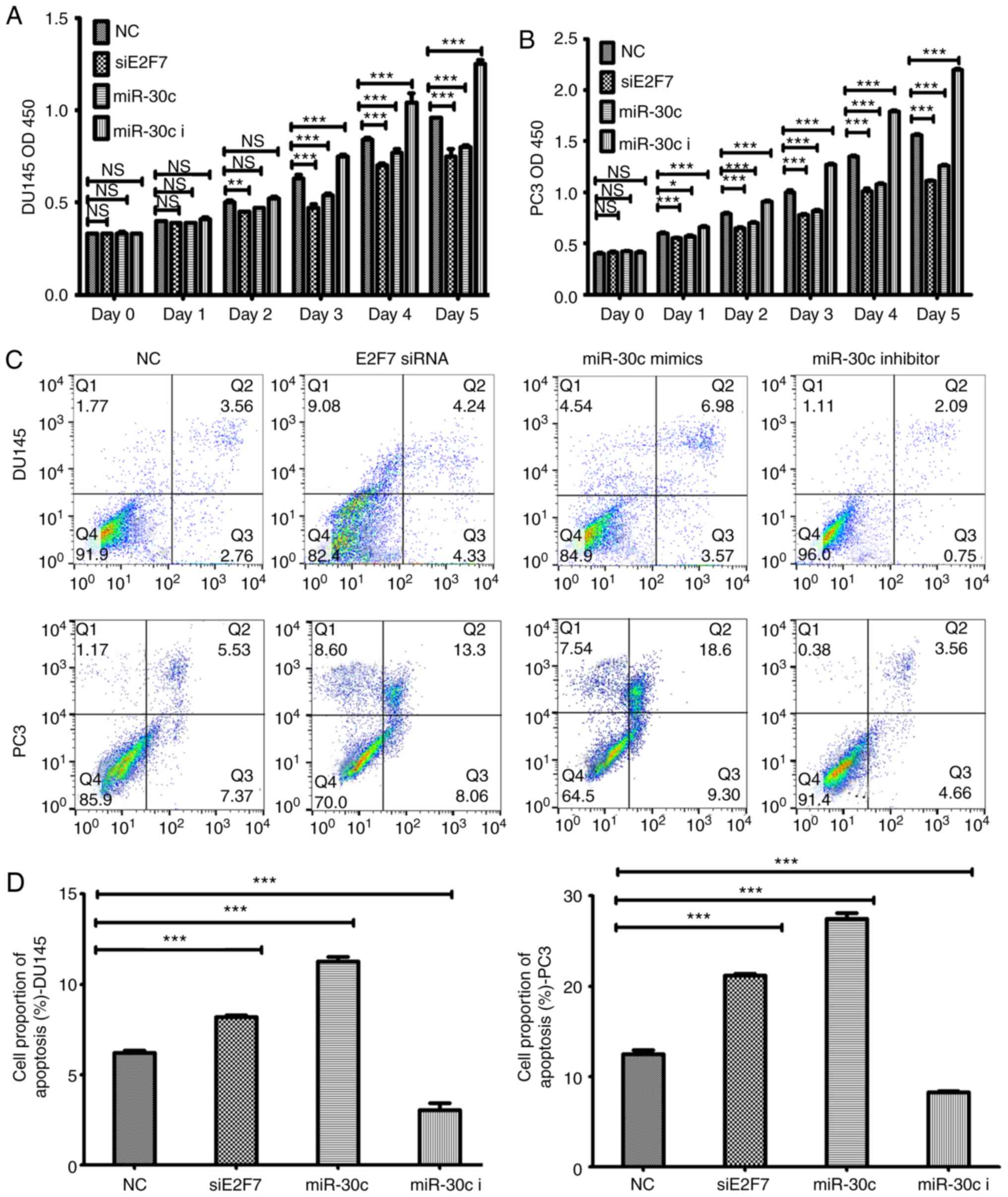
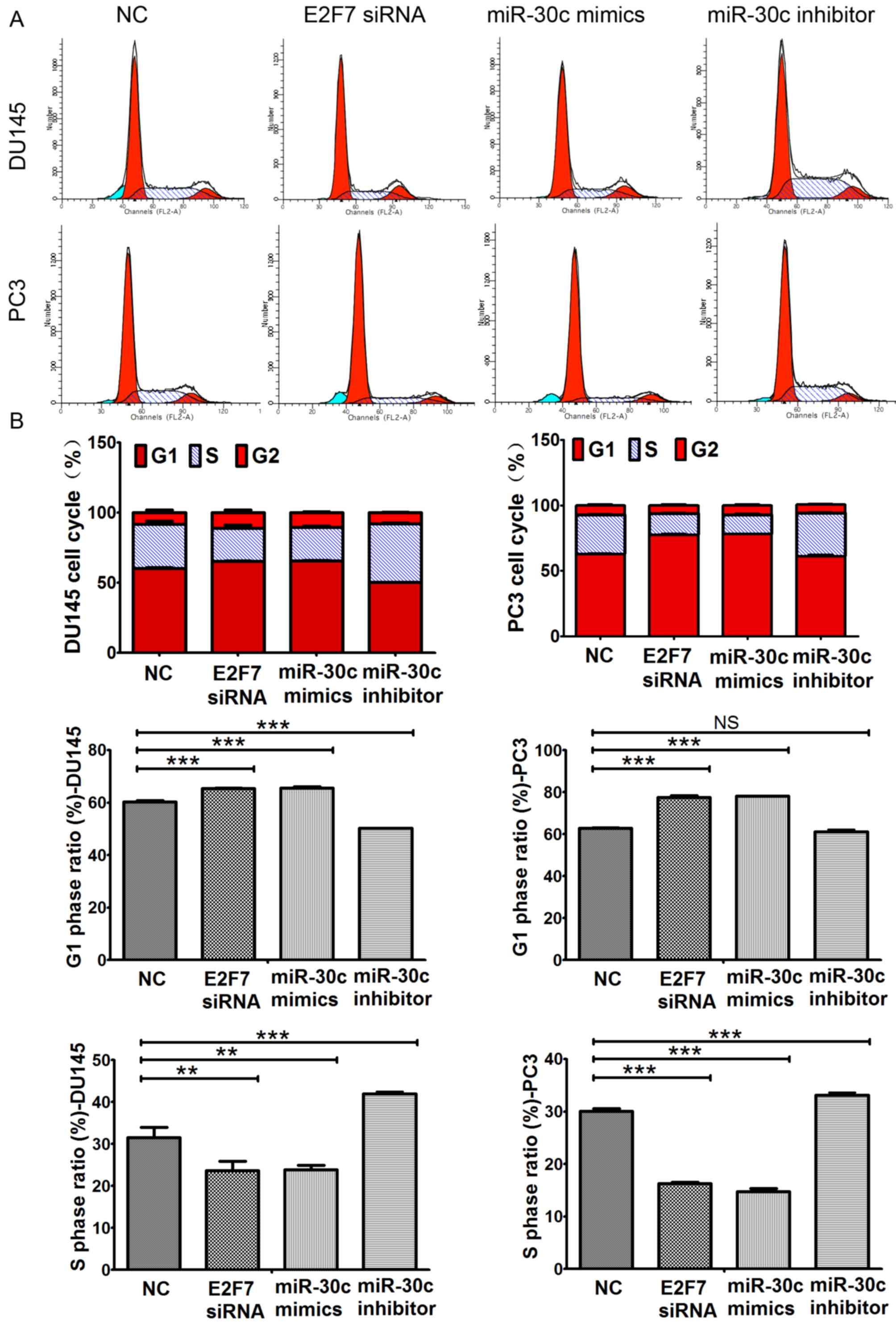
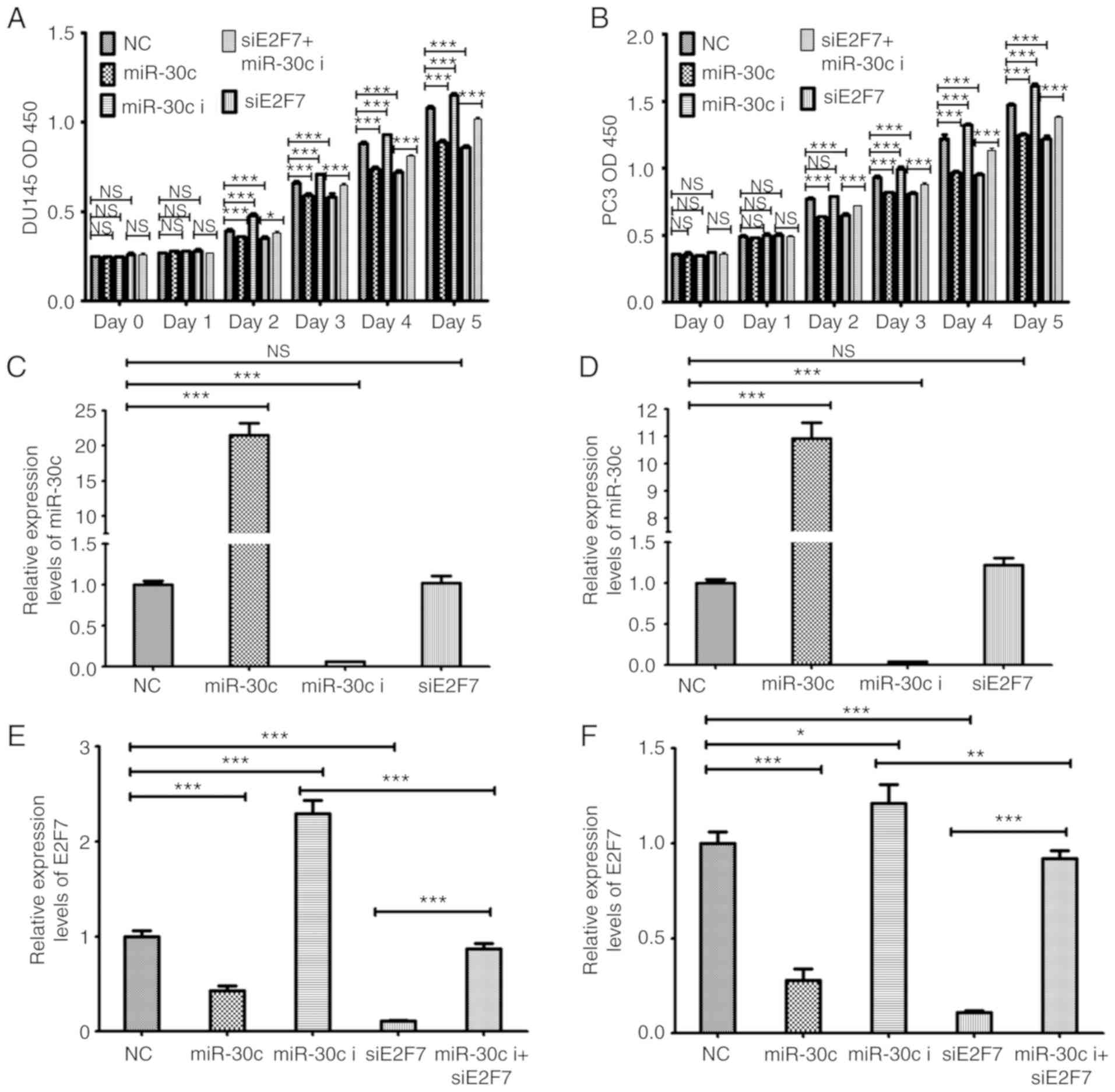
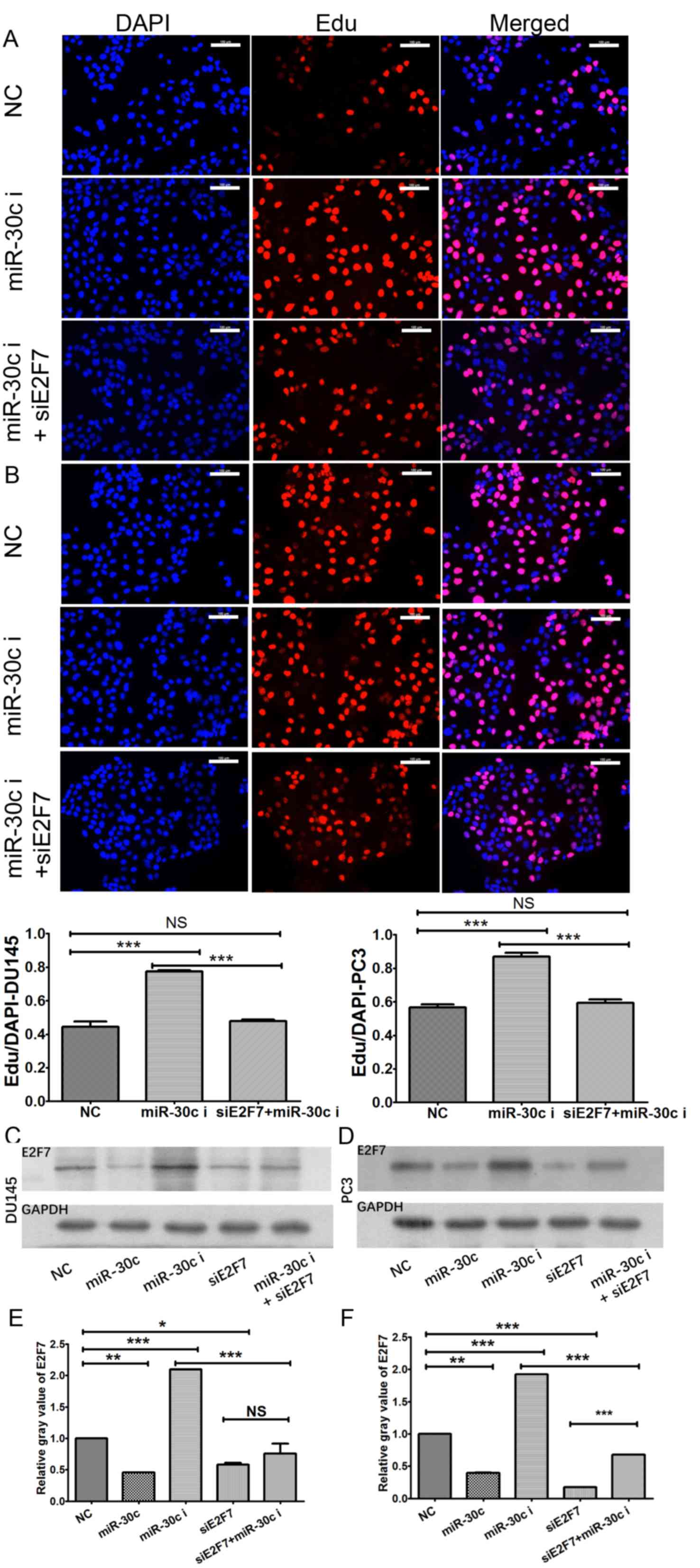
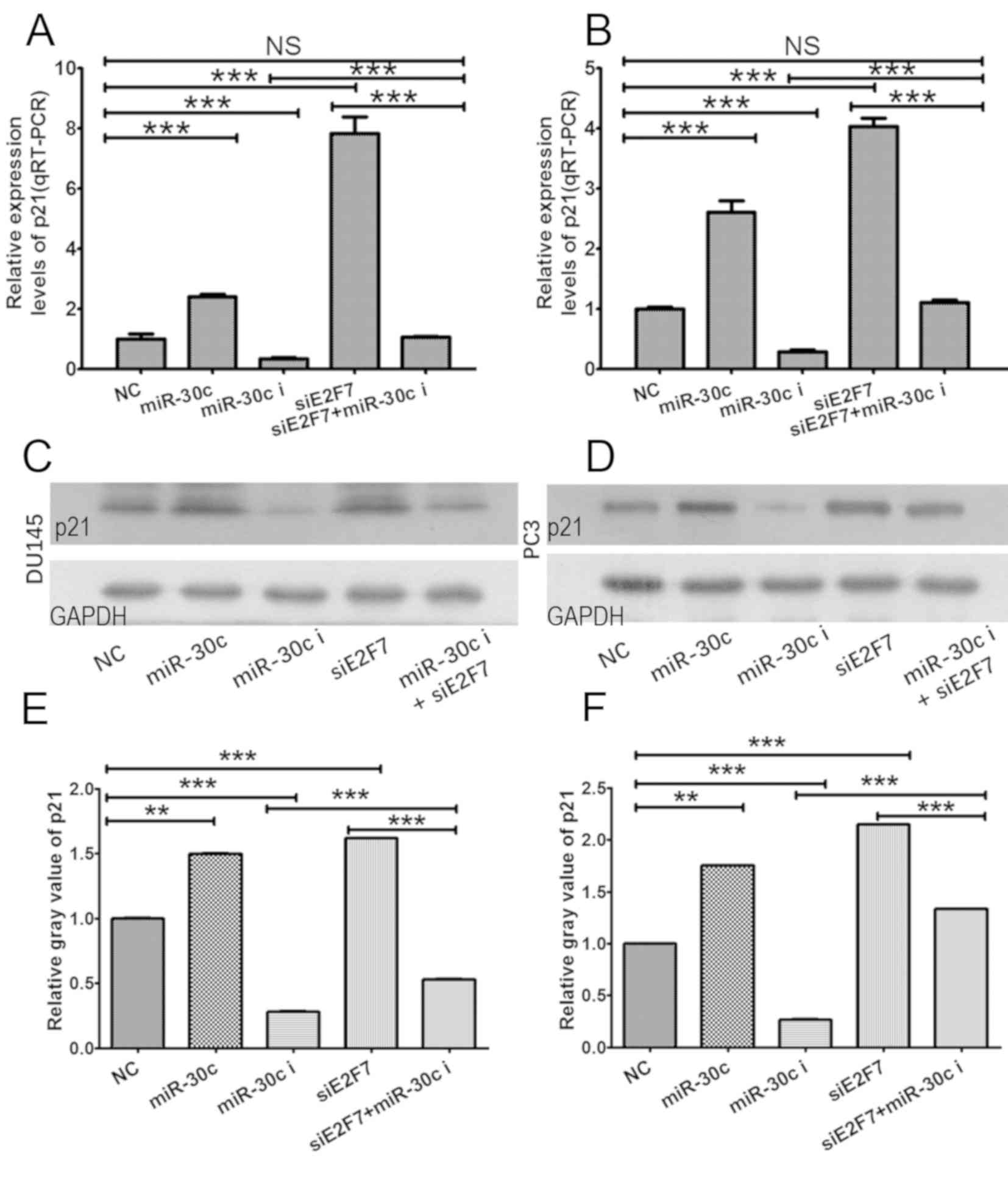
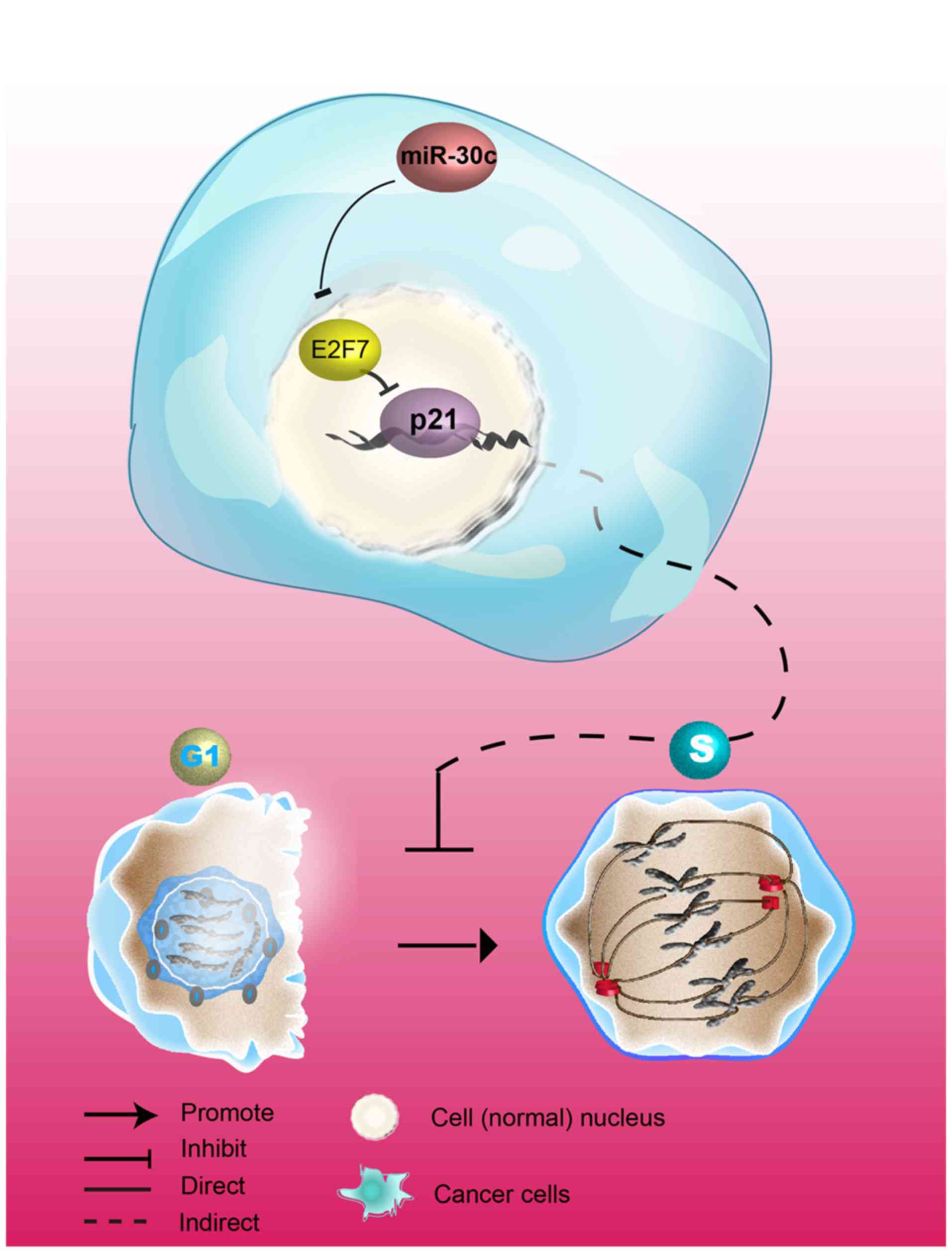
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2018.
|
|
2
|
Nelson WG, De Marzo AM and Isaacs WB:
Prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 349:366–681. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nevins JR: The Rb/E2F pathway and cancer.
Human Mol Genet. 10:699–703. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dyson N: The regulation of E2F by
pRB-family proteins. Genes Dev. 12:2245–2262. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thwaites MJ, Cecchini MJ and Dick FA:
Analyzing RB and E2F during the G1-S transition. Methods
Mol Biol. 1170:449–461. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Subtil-Rodríguez A, Vázquez-Chávez E,
Ceballos-Chávez M, Rodríguez-Paredes M, Martín-Subero JI, Esteller
M and Reyes JC: The chromatin remodeller CHD8 is required for
E2F-dependent transcription activation of S-phase genes. Nucleic
Acids Res. 42:2185–2196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
De AB, Maiti B, Jakoi L, Timmers C, Buerki
R and Leone G: Identification and characterization of E2F7, a novel
mammalian E2F family member capable of blocking cellular
proliferation. J Biol Chem. 278:42041–42049. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zong S, Liu X, Zhou N and Yue Y: E2F7,
EREG, miR-451a and miR-106b-5p are associated with the cervical
cancer development. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 299:1089–1098. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma YS, Lv ZW, Yu F, Chang ZY, Cong XL,
Zhong XM, Lu GX, Zhu J and Fu D: MicroRNA-302a/d inhibits the
self-renewal capability and cell cycle entry of liver cancer stem
cells by targeting the E2F7/AKT axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
37:2522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Salvatori B, Iosue I, Mangiavacchi A,
Loddo G, Padula F, Chiaretti S, Peragine N, Bozzoni I, Fazi F and
Fatica A: The microRNA-26a target E2F7 sustains cell proliferation
and inhibits monocytic differentiation of acute myeloid leukemia
cells. Cell Death & Disease. 3:e4132012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jian L, Xiang L, Meng W, Xiao G, Yang G,
Wang H, Li Y, Sun X, Qin S, Du N, et al: A miR-26a/E2F7 feedback
loop contributes to tamoxifen resistance in ER-positive breast
cancer. Int J Oncol. 53:1601–1612. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Endo-Munoz L, Dahler A, Teakle N, Rickwood
D, Hazar-Rethinam M, Abdul-Jabbar I, Sommerville S, Dickinson I,
Kaur P, Paquet-Fifield S and Saunders N: E2F7 can regulate
proliferation, differentiation, and apoptotic responses in human
keratinocytes: Implications for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
formation. Cancer Res. 69:1800–1808. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Quan L, Qiu XM, Li QH, Wang XY, Li L, Xu
M, Dong M and Xiao YB: MicroRNA-424 may function as a tumor
suppressor in endometrial carcinoma cells by targeting E2F7.
Oncology Rep. 33:2354–2360. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ye YY, Mei JW, Xiang SS, Li HF, Ma Q, Song
XL, Wang Z, Zhang YC, Liu YC, Jin YP, et al: MicroRNA-30a-5p
inhibits gallbladder cancer cell proliferation, migration and
metastasis by targeting E2F7. Cell Death Dis. 9:4102018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Karimian A, Ahmadi Y and Yousefi B:
Multiple functions of p21 in cell cycle, apoptosis and
transcriptional regulation after DNA damage. DNA Repair (Amst.).
42:63–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jun L, Gad G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Behmansmant I, Rehwinkel J, Doerks T,
Stark A, Bork P and Izaurralde E: mRNA degradation by miRNAs and
GW182 requires both CCR4:NOT deadenylase and DCP1:DCP2 decapping
complexes. Genes Dev. 20:1885–1898. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lytle JR, Yario TA and Steitz JA: Target
mRNAs are repressed as efficiently by microRNA-binding sites in the
5′ UTR as in the 3′ UTR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:9667–9672.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cao JM, Li GZ, Han M, Xu HL and Huang KM:
MiR-30c-5p suppresses migration, invasion and epithelial to
mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer via targeting MTA1. Biomed
Pharmacother. 93:554–560. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang J, Yao X, Zhang J, Dong B, Chen Q,
Xue W, Liu D and Huang Y: Hypoxia-induced downregulation of miR-30c
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human renal cell
carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 104:1609–1617. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang YQ, Ling XH, Yuan RQ, Chen ZY, Yang
SB, Huang HX, Zhong WD and Qiu SP: miR-30c suppresses prostate
cancer survival by targeting the ASF/SF2 splicing factor
oncoprotein. Mol Med Rep. 16:2431–2438. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tanic M, Yanowsky K, Rodriguez-Antona C,
Andrés R, Márquez-Rodas I, Osorio A, Benitez J and Martinez-Delgado
B: Deregulated miRNAs in hereditary breast cancer revealed a role
for miR-30c in regulating KRAS oncogene. PLoS One. 7:e388472012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
GJ L: ETHICS. The Pelople's publishing
house. 1989.
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kurien BT and Scofield RH: Western
blotting. Methods. 38:283–293. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Madamanchi NR and Runge MS: Western
blotting. Methods Mol Med. 51:245–256. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Miyake M, Goodison S, Lawton A,
Gomes-Giacoia E and Rosser CJ: Angiogenin promotes tumoral growth
and angiogenesis by regulating matrix metallopeptidase-2 expression
via the ERK1/2 pathway. Oncogene. 34:890–901. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Giacoia EG, Miyake M, Lawton A, Goodison S
and Rosser CJ: PAI-1 leads to G1-phase cell-cycle
progression through cyclin D3/cdk4/6 upregulation. Mol Cancer Res.
12:322–334. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
La Thangue NB: DRTF1/E2F: An expanding
family of heterodimeric transcription factors implicated in
cell-cycle control. Trends Biochem Sci. 19:108–114. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao LJ, Subramanian T, Vijayalingam S and
Chinnadurai G: CtBP2 proteome: Role of CtBP in E2F7-mediated
repression and cell proliferation. Genes Cancer. 5:31–40.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Weijts BGMW, Westendorp B, Hien BT,
Martínez-López LM, Zijp M, Thurlings I, Thomas RE, Schulte-Merker
S, Bakker WJ and de Bruin A: Atypical E2Fs inhibit tumor
angiogenesis. Oncogene. 37:271–276. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li J, Ran C, Li E, Gordon F, Comstock G,
Siddiqui H, Cleghorn W, Chen HZ, Kornacker K, Liu CG, et al:
Synergistic function of E2F7 and E2F8 is essential for cell
survival and embryonic development. Dev Cell. 14:62–75. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zalmas LP, Zhao X, Graham AL, Fisher R,
Reilly C, Coutts AS and La Thangue NB: DNA-damage response control
of E2F7 and E2F8. EMBO Rep. 9:252–259. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zalmas LP, Coutts A, Helleday T and La
Thangue NB: E2F-7 couples DNA damage-dependent transcription with
the DNA repair process. Cell Cycle. 12:3037–3051. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Carvajal LA, Hamard PJ, Tonnessen C and
Manfredi JJ: E2F7, a novel target, is up-regulated by p53 and
mediates DNA damage-dependent transcriptional repression. Genes
Dev. 26:1533–1545. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yin WW, Wang B, Ding M, Huo Y, Hu H, Cai
R, Zhou T, Gao Z, Wang Z and Chen D: Elevated E2F7 expression
predicts poor prognosis in human patients with gliomas. J Clin
Neurosci. 33:187–193. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Weijts BG, Bakker WJ, Cornelissen PW,
Liang KH, Schaftenaar FH, Westendorp B, de Wolf CA, Paciejewska M,
Scheele CL, Kent L, et al: E2F7 and E2F8 promote angiogenesis
through transcriptional activation of VEGFA in cooperation with
HIF1. EMBO J. 31:3871–3884. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chu J, Zhu Y, Liu Y, Sun L, Lv X, Wu Y, Hu
P, Su F, Gong C, Song E, et al: E2F7 overexpression leads to
tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells by competing with E2F1
at miR-15a/16 promoter. Oncotarget. 6:31944–31957. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Batra A and Winquist E: Emerging cell
cycle inhibitors for treating metastatic castration-resistant
prostate cancer. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 23:271–282. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu R, Poland B, Wada R, Liu Q, Musib L,
Maslyar D, Cho E, Yu W, Ma H, Jin JY and Budha N:
Exposure-response-based product profile-driven clinical utility
index for ipatasertib dose selection in prostate cancer. CPT
Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 8:240–248. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Beltran H, Danila D, Montgomery B,
Szmulewitz R, Vaishampayan U, Armstrong A, Stein M, Hoimes C,
Pinski J, Scher H, et al: A phase 2 study of the aurora kinase A
inhibitor alisertib for patients with neuroendocrine prostate
cancer (NEPC). Ann Oncol. 27 (Suppl 6):V15652016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kang SY, Kim HI, Hong SH, Ku JM, Lee K,
Kim MS, Choi YJ, Cheon C, Ko Y, Huang CW, et al: Abstract 300:
Taeumjowi-tang (TJ001) induces G2/M cell cycle arrest
but not apoptosis in p53-mutant prostate cancer via up-regulation
of p21 WAF/CIP1. Cancer Res. 77 (Suppl 13):3002017.
|
|
43
|
Mitxelena J, Apraiz A, Vallejo-Rodríguez
J, García-Santisteban I, Fullaondo A, Alvarez-Fernández M,
Malumbres M and Zubiaga AM: An E2F7-dependent transcriptional
program modulates DNA damage repair and genomic stability. Nucleic
Acids Res. 46:4546–4559. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Bockhorn J, Yee K, Chang YF, Prat A, Huo
D, Nwachukwu C, Dalton R, Huang S, Swanson KE, Perou CM, et al:
MicroRNA-30c targets cytoskeleton genes involved in breast cancer
cell invasion. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 137:373–382. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu X, Li M, Peng Y, Hu X, Xu J, Zhu S, Yu
Z and Han S: miR-30c regulates proliferation, apoptosis and
differentiation via the Shh signaling pathway in P19 cells. Exp Mol
Med. 48:e2482016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ling XH, Han ZD, Xia D, He HC, Jiang FN,
Lin ZY, Fu X, Deng YH, Dai QS, Cai C, et al: MicroRNA-30c serves as
an independent biochemical recurrence predictor and potential tumor
suppressor for prostate cancer. Mol Biol Rep. 41:2779–2788. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|