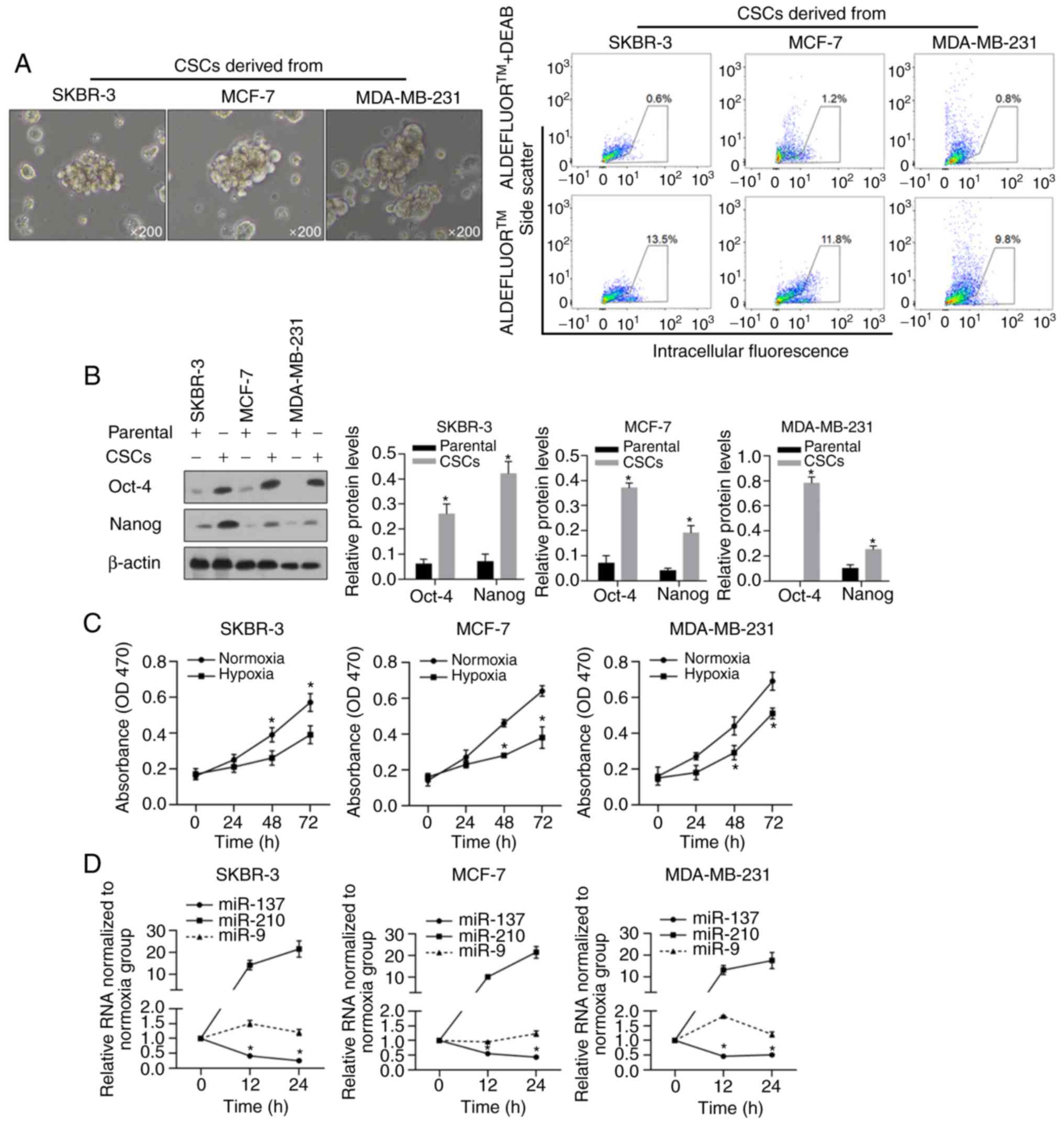
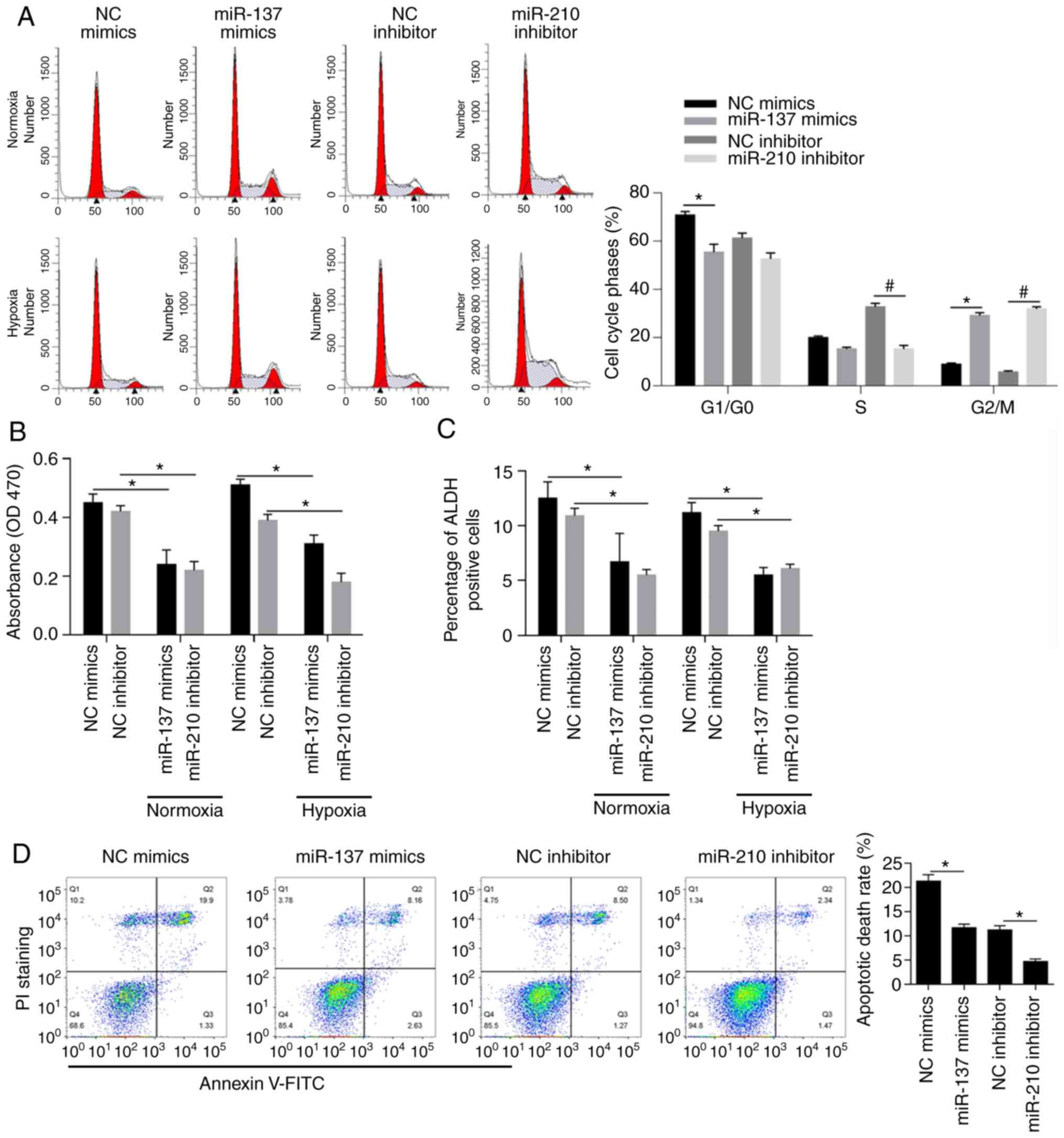
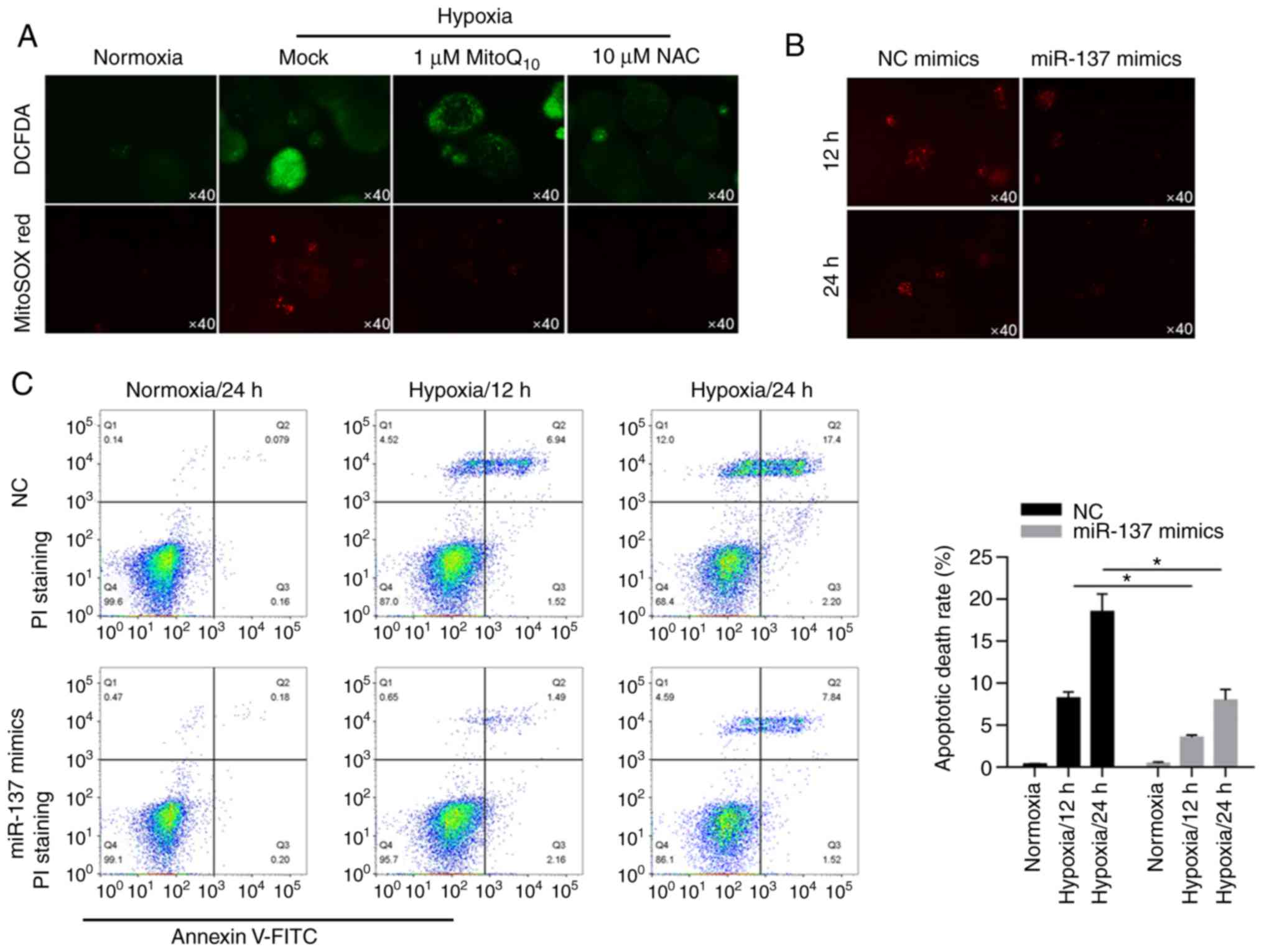
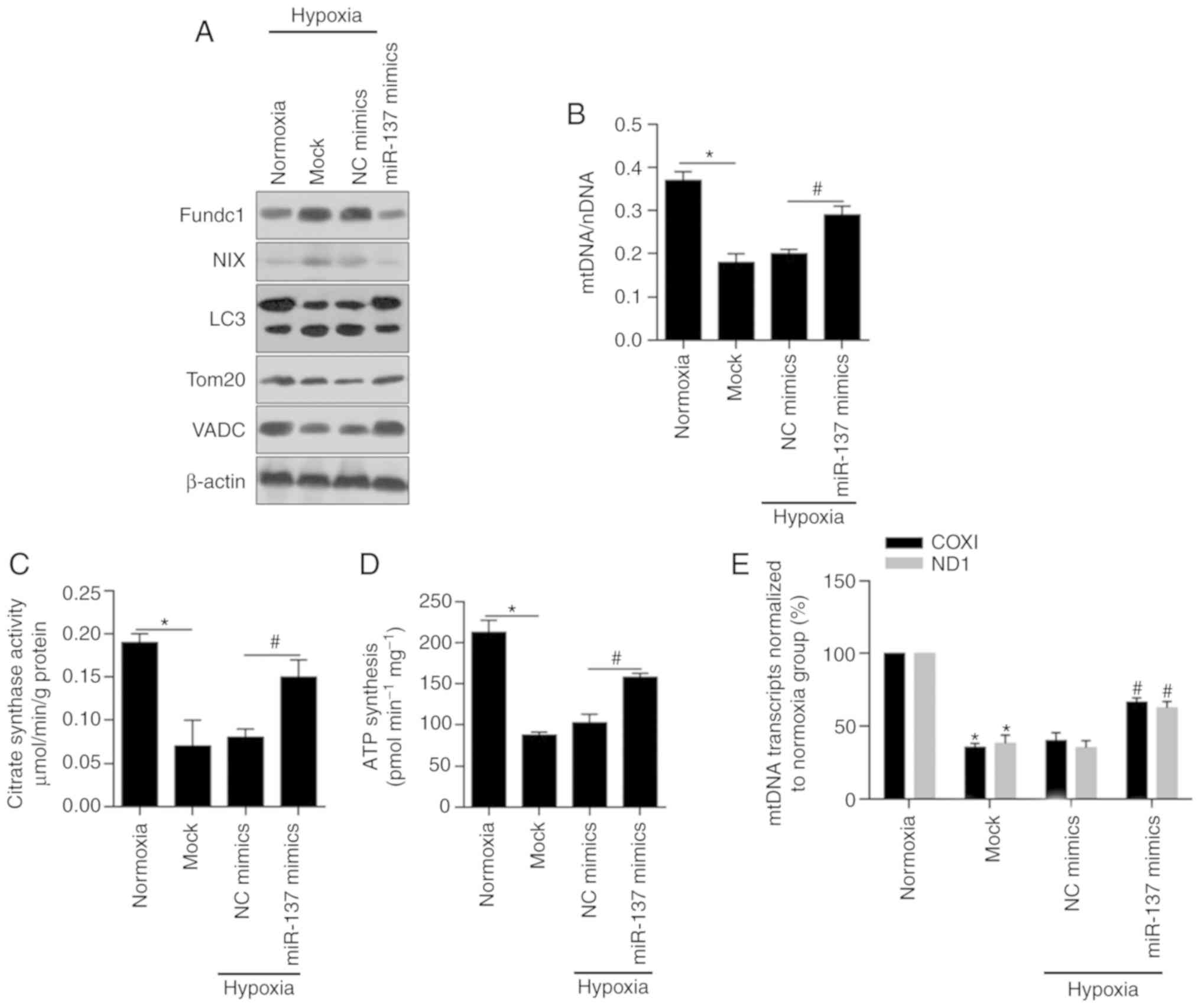
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Momenimovahed Z and Salehiniya H:
Epidemiological characteristics of and risk factors for breast
cancer in the world. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 11:151–164.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sousa B, Ribeiro AS and Paredes J:
Heterogeneity and plasticity of breast cancer stem cells. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 1139:83–103. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kong Y, Lyu N, Wu J, Tang H and Xie X,
Yang L, Li X, Wei W and Xie X: Breast cancer stem cell markers CD44
and ALDH1A1 in serum: Distribution and prognostic value in patients
with primary breast cancer. J Cancer. 9:3728–3735. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sjöström M, Hartman L, Honeth G, Grabau D,
Malmström P, Hegardt C, Fernö M and Niméus E: Stem cell biomarker
ALDH1A1 in breast cancer shows an association with prognosis and
clinicopathological variables that is highly cut-off dependent. J
Clin Pathol. 68:1012–1019. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang F, Cao L, Sun Z, Jin J, Fang H, Zhang
W and Guan X: Evaluation of breast cancer stem cells and intratumor
stemness heterogeneity in triple-negative breast cancer as
prognostic factors. Int J Biol Sci. 12:1568–1577. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Seo AN, Lee HJ, Kim EJ, Jang MH, Kim YJ,
Kim JH, Kim SW, Ryu HS, Park IA, Im SA, et al: Expression of breast
cancer stem cell markers as predictors of prognosis and response to
trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer. Br J Cancer.
114:1109–1116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sulaiman A, McGarry S, Li L, Jia D, Ooi S,
Addison C, Dimitroulakos J, Arnaout A, Nessim C, Yao Z, et al: Dual
inhibition of Wnt and Yes-associated protein signaling retards the
growth of triple-negative breast cancer in both mesenchymal and
epithelial states. Mol Oncol. 12:423–440. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yuan X, Wu H, Xu H, Xiong H, Chu Q, Yu S,
Wu GS and Wu K: Notch signaling: An emerging therapeutic target for
cancer treatment. Cancer Lett. 369:20–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
O'Toole SA, Machalek DA, Shearer RF,
Millar EK, Nair R, Schofield P, McLeod D, Cooper CL, McNeil CM,
McFarland A, et al: Hedgehog overexpression is associated with
stromal interactions and predicts for poor outcome in breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 71:4002–4014. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Palomeras S, Ruiz-Martínez S and Puig T:
Targeting breast cancer stem cells to overcome treatment
resistance. Molecules. 23:21932018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nwabo Kamdje AH, Seke Etet PF, Vecchio L,
Muller JM, Krampera M and Lukong KE: Signaling pathways in breast
cancer: Therapeutic targeting of the microenvironment. Cell Signal.
26:2843–2856. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Maruthanila VL, Elancheran R, Kunnumakkara
AB, Kabilan S and Kotoky J: Recent development of targeted
approaches for the treatment of breast cancer. Breast Cancer.
24:191–219. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nobre AR, Entenberg D, Wang Y, Condeelis J
and Aguirre-Ghiso JA: The different routes to metastasis via
hypoxia-regulated programs. Trends Cell Biol. 28:941–956. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Abe H, Semba H and Takeda N: The roles of
hypoxia signaling in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases. J
Atheroscler Thromb. 24:884–894. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fuhrmann DC and Brüne B: Mitochondrial
composition and function under the control of hypoxia. Redox Biol.
12:208–215. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tong WW, Tong GH and Liu Y: Cancer stem
cells and hypoxia-inducible factors (Review). Int J Oncol.
53:469–476. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Keith B and Simon MC: Hypoxia-inducible
factors, stem cells, and cancer. Cell. 129:465–472. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gonzalez FJ, Xie C and Jiang C: The role
of hypoxia-inducible factors in metabolic diseases. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 15:21–32. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mazumdar J, O'Brien WT, Johnson RS,
LaManna JC, Chavez JC, Klein PS and Simon MC: O2
regulates stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin signalling. Nat Cell
Biol. 12:1007–1013. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Z, Han H, Rong Y, Zhu K, Zhu Z, Tang
Z, Xiong C and Tao J: Hypoxia potentiates gemcitabine-induced
stemness in pancreatic cancer cells through AKT/Notch1 signaling. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:2912018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Catalano V, Turdo A, Di Franco S, Dieli F,
Todaro M and Stassi G: Tumor and its microenvironment: A
synergistic interplay. Semin Cancer Biol. 23:522–532. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mohr AM and Mott JL: Overview of microRNA
biology. Semin Liver Dis. 35:3–11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bandara KV, Michael MZ and Gleadle JM:
MicroRNA biogenesis in hypoxia. Microrna. 6:80–96. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li W, Zhang X, Zhuang H, Chen HG, Chen Y,
Tian W, Wu W, Li Y, Wang S, Zhang L, et al: MicroRNA-137 is a novel
hypoxia-responsive microRNA that inhibits mitophagy via regulation
of two mitophagy receptors FUNDC1 and NIX. J Biol Chem.
289:10691–10701. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li H, Zhu Z, Liu J, Wang J and Qu C:
MicroRNA-137 regulates hypoxia-induced retinal ganglion cell
apoptosis through Notch1. Int J Mol Med. 41:1774–1782.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chang J, Yan X and Zeng Y: Propofol
weakens hypoxia-aroused apoptosis and autophagy via elevating
microRNA-137 in neurocytes. Exp Mol Pathol. 112:1043272020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang H, Flach H, Onizawa M, Wei L, McManus
MT and Weiss A: Negative regulation of Hif1a expression and TH17
differentiation by the hypoxia-regulated microRNA miR-210. Nat
Immunol. 15:393–401. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
el Azzouzi H, Leptidis S, Dirkx E, Hoeks
J, van Bree B, Brand K, McClellan EA, Poels E, Sluimer JC, van den
Hoogenhof MM, et al: The hypoxia-inducible microRNA cluster
miR-199a-214 targets myocardial PPARδ and impairs mitochondrial
fatty acid oxidation. Cell Metab. 18:341–354. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chan SY, Zhang YY, Hemann C, Mahoney CE,
Zweier JL and Loscalzo J: MicroRNA-210 controls mitochondrial
metabolism during hypoxia by repressing the iron-sulfur cluster
assembly proteins ISCU1/2. Cell Metab. 10:273–284. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang X, Ji R, Liao X, Castillero E,
Kennel PJ, Brunjes DL, Franz M, Möbius-Winkler S, Drosatos K,
George I, et al: MicroRNA-195 regulates metabolism in failing
myocardium via alterations in sirtuin 3 expression and
mitochondrial protein acetylation. Circulation. 137:2052–2067.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li H, Zhang X, Wang F, Zhou L, Yin Z, Fan
J, Nie X, Wang P, Fu XD, Chen C and Wang DW: MicroRNA-21 lowers
blood pressure in spontaneous hypertensive rats by upregulating
mitochondrial translation. Circulation. 134:734–751. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ullmann P, Nurmik M, Begaj R, Haan S and
Letellier E: Hypoxia- and microRNA-induced metabolic reprogramming
of tumor-initiating cells. Cells. 8:5282019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Jafari N and Abediankenari S: MicroRNA-34
dysregulation in gastric cancer and gastric cancer stem cell.
Tumour Biol. 39:10104283177016522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Grosso S, Doyen J, Parks SK, Bertero T,
Paye A, Cardinaud B, Gounon P, Lacas-Gervais S, Noël A, Pouysségur
J, et al: miR-210 promotes a hypoxic phenotype and increases
radioresistance in human lung cancer cell lines. Cell Death Dis.
4:e5442013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gee HE, Ivan C, Calin GA and Ivan M:
HypoxamiRs and cancer: From biology to targeted therapy. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 21:1220–1238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qin Q, Furong W and Baosheng L: Multiple
functions of hypoxia-regulated miR-210 in cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 33:502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Almozyan S, Colak D, Mansour F, Alaiya A,
Al-Harazi O, Qattan A, Al-Mohanna F, Al-Alwan M and Ghebeh H: PD-L1
promotes OCT4 and Nanog expression in breast cancer stem cells by
sustaining PI3K/AKT pathway activation. Int J Cancer.
141:1402–1412. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yin X, Zhang BH, Zheng SS, Gao DM, Qiu SJ,
Wu WZ and Ren ZG: Coexpression of gene Oct4 and Nanog initiates
stem cell characteristics in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of Stat3/Snail
signaling. J Hematol Oncol. 8:232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang D, Lu P, Zhang H, Luo M, Zhang X, Wei
X, Gao J, Zhao Z and Liu C: Oct-4 and Nanog promote the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer stem cells and
are associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients.
Oncotarget. 5:10803–10815. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jeter CR, Yang T, Wang J, Chao HP and Tang
DG: Concise review: NANOG in cancer stem cells and tumor
development: An update and outstanding questions. Stem Cells.
33:2381–2390. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Charafe-Jauffret E, Ginestier C, Iovino F,
Tarpin C, Diebel M, Esterni B, Houvenaeghel G, Extra JM, Bertucci
F, Jacquemier J, et al: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1-positive cancer
stem cells mediate metastasis and poor clinical outcome in
inflammatory breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:45–55. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E,
Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG,
Liu S, et al: ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human
mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell
Stem Cell. 1:555–567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Balicki D: Moving forward in human mammary
stem cell biology and breast cancer prognostication using ALDH1.
Cell Stem Cell. 1:485–487. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wu H and Chen Q: Hypoxia activation of
mitophagy and its role in disease pathogenesis. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 22:1032–1046. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang H, Gao P, Fukuda R, Kumar G,
Krishnamachary B, Zeller KI, Dang CV and Semenza GL: HIF-1 inhibits
mitochondrial biogenesis and cellular respiration in VHL-deficient
renal cell carcinoma by repression of C-MYC activity. Cancer Cell.
11:407–420. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu L, Sakakibara K, Chen Q and Okamoto K:
Receptor-mediated mitophagy in yeast and mammalian systems. Cell
Res. 24:787–795. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wu X, Wu FH, Wu Q, Zhang S, Chen S and
Sima M: Phylogenetic and molecular evolutionary analysis of
mitophagy receptors under hypoxic conditions. Front Physiol.
8:5392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
van der Laan M, Rissler M and Rehling P:
Mitochondrial preprotein translocases as dynamic molecular
machines. FEMS Yeast Res. 6:849–861. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
DeHart DN, Fang D, Heslop K, Li L,
Lemasters JJ and Maldonado EN: Opening of voltage dependent anion
channels promotes reactive oxygen species generation, mitochondrial
dysfunction and cell death in cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol.
148:155–162. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chen Z, Siraj S, Liu L and Chen Q:
MARCH5-FUNDC1 axis fine-tunes hypoxia-induced mitophagy. Autophagy.
13:1244–1245. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hielscher A and Gerecht S: Hypoxia and
free radicals: Role in tumor progression and the use of
engineering-based platforms to address these relationships. Free
Radic Biol Med. 79:281–291. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Shadel GS and Horvath TL: Mitochondrial
ROS signaling in organismal homeostasis. Cell. 163:560–569. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Arakawa Y, Yokoyama K, Tasaki S, Kato J,
Nakashima K, Takeyama M, Nakatani A and Suzuki M: Transgenic mice
overexpressing miR-137 in the brain show schizophrenia-associated
behavioral deficits and transcriptome profiles. PLoS One.
14:e02203892019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Guella I, Sequeira A, Rollins B, Morgan L,
Torri F, van Erp TG, Myers RM, Barchas JD, Schatzberg AF, Watson
SJ, et al: Analysis of miR-137 expression and rs1625579 in
dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. J Psychiatr Res. 47:1215–1221.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Toiyama Y, Okugawa Y, Tanaka K, Araki T,
Uchida K, Hishida A, Uchino M, Ikeuchi H, Hirota S, Kusunoki M, et
al: A panel of methylated MicroRNA biomarkers for identifying
high-risk patients with ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal
cancer. Gastroenterology. 153:1634–1646.e8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cui S, Sun Y, Liu Y, Liu C, Wang J, Hao G
and Sun Q: MicroRNA-137 has a suppressive role in liver cancer via
targeting EZH2. Mol Med Rep. 16:9494–9502. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li KK, Yang L, Pang JC, Chan AK, Zhou L,
Mao Y, Wang Y, Lau KM, Poon WS, Shi Z and Ng HK: MIR-137 suppresses
growth and invasion, is downregulated in oligodendroglial tumors
and targets CSE1L. Brain Pathol. 23:426–439. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Guo J, He K, Zeng H, Shi Y, Ye P, Zhou Q,
Pan Z and Long X: Differential microRNA expression profiles
determined by next-generation sequencing in three
fulvestrant-resistant human breast cancer cell lines. Oncol Lett.
17:3765–3776. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cheng S, Huang Y, Lou C, He Y, Zhang Y and
Zhang Q: FSTL1 enhances chemoresistance and maintains stemness in
breast cancer cells via integrin β3/Wnt signaling under miR-137
regulation. Cancer Biol Ther. 20:328–337. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ying X, Sun Y and He P: MicroRNA-137
inhibits BMP7 to enhance the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of
breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:18348–18358. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Han Y, Bi Y, Bi H, Diao C, Zhang G, Cheng
K and Yang Z: miR-137 suppresses the invasion and procedure of EMT
of human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 through targeting CtBP1. Hum
Cell. 29:30–36. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
He Z, Guo X, Tian S, Zhu C, Chen S, Yu C,
Jiang J and Sun C: MicroRNA-137 reduces stemness features of
pancreatic cancer cells by targeting KLF12. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
38:1262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chen F, Luo N, Hu Y, Li X and Zhang K:
miR-137 suppresses triple-negative breast cancer stemness and
tumorigenesis by perturbing BCL11A-DNMT1 interaction. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 47:2147–2158. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Tang T, Yang Z, Zhu Q, Wu Y, Sun K,
Alahdal M, Zhang Y, Xing Y, Shen Y, Xia T, et al: Up-regulation of
miR-210 induced by a hypoxic microenvironment promotes breast
cancer stem cells metastasis, proliferation, and self-renewal by
targeting E-cadherin. FASEB J. Sep 6–2018.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|