|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hashibe M, Brennan P, Chuang SC, Boccia S,
Castellsague X, Chen C, Curado MP, Dal Maso L, Daudt AW, Fabianova
E, et al: Interaction between tobacco and alcohol use and the risk
of head and neck cancer: Pooled analysis in the international head
and neck cancer epidemiology consortium. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 18:541–550. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tota JE, Anderson WF, Coffey C, Califano
J, Cozen W, Ferris RL, St John M, Cohen EE and Chaturvedi AK:
Rising incidence of oral tongue cancer among white men and women in
the United States, 1973–2012. Oral Oncol. 67:146–152. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hussein AA, Helder MN, de Visscher JG,
Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ, de Vet HCW and Forouzanfar T: Global
incidence of oral and oropharynx cancer in patients younger than 45
years versus older patients: A systematic review. Eur J Cancer.
82:115–127. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sherman L, Sleeman J, Herrlich P and Ponta
H: Hyaluronate receptors: Key players in growth, differentiation,
migration and tumor progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 6:726–733.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Slevin M, Krupinski J, Gaffney J, Matou S,
West D, Delisser H, Savani RC and Kumar S: Hyaluronan-mediated
angiogenesis in vascular disease: Uncovering RHAMM and CD44
receptor signaling pathways. Matrix Biol. 26:58–68. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rodrigo JP, Dominguez F, Alvarez C,
Gonzalez MV, Herrero A and Suárez C: Clinicopathologic significance
of expression of CD44s and CD44v6 isoforms in squamous cell
carcinoma of the supraglottic larynx. Am J Clin Pathol. 118:67–72.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zöller M: CD44: Can a cancer-initiating
cell profit from an abundantly expressed molecule? Nat Rev Cancer.
11:254–267. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Greenfield B, Wang WC, Marquardt H,
Piepkorn M, Wolff EA, Aruffo A and Bennett KL: Characterization of
the heparan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate assembly sites in CD44.
J Biol Chem. 274:2511–2517. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Skelton TP, Zeng C, Nocks A and
Stamenkovic I: Glycosylation provides both stimulatory and
inhibitory effects on cell surface and soluble CD44 binding to
hyaluronan. J Cell Biol. 140:431–446. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hofmann M, Rudy W, Zöller M, Tölg C, Ponta
H, Herrlich P and Günthert U: CD44 splice variants confer
metastatic behavior in rats: Homologous sequences are expressed in
human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 51:5292–5297. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Günthert U, Hofmann M, Rudy W, Reber S,
Zöller M, Haussmann I, Matzku S, Wenzel A, Ponta H and Herrlich P:
A new variant of glycoprotein CD44 confers metastatic potential to
rat carcinoma cells. Cell. 65:13–24. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tremmel M, Matzke A, Albrecht I, Laib AM,
Olaku V, Ballmer-Hofer K, Christofori G, Héroult M, Augustin HG,
Ponta H and Orian-Rousseau V: A CD44v6 peptide reveals a role of
CD44 in VEGFR-2 signaling and angiogenesis. Blood. 114:5236–5244.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Orian-Rousseau V, Morrison H, Matzke A,
Kastilan T, Pace G, Herrlich P and Ponta H: Hepatocyte growth
factor-induced Ras activation requires ERM proteins linked to both
CD44v6 and F-actin. Mol Biol Cell. 18:76–83. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Orian-Rousseau V, Chen L, Sleeman JP,
Herrlich P and Ponta H: CD44 is required for two consecutive steps
in HGF/c-Met signaling. Genes Dev. 16:3074–3086. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rudy W, Hofmann M, Schwartz-Albiez R,
Zöller M, Heider KH, Ponta H and Herrlich P: The two major CD44
proteins expressed on a metastatic rat tumor cell line are derived
from different splice variants: Each one individually suffices to
confer metastatic behavior. Cancer Res. 53:1262–1268.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jackson DG, Bell JI, Dickinson R, Timans
J, Shields J and Whittle N: Proteoglycan forms of the lymphocyte
homing receptor CD44 are alternatively spliced variants containing
the v3 exon. J Cell Biol. 128:673–685. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bennett KL, Jackson DG, Simon JC, Tanczos
E, Peach R, Modrell B, Stamenkovic I, Plowman G and Aruffo A: CD44
isoforms containing exon V3 are responsible for the presentation of
heparin-binding growth factor. J Cell Biol. 128:687–698. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hu S, Wu X, Zhou B, Xu Z, Qin J, Lu H, Lv
L, Gao Y, Deng L, Yin J and Li G: IMP3 combined with CD44s, a novel
predictor for prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 140:883–893. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Auvinen P, Tammi R, Kosma VM, Sironen R,
Soini Y, Mannermaa A, Tumelius R, Uljas E and Tammi M: Increased
hyaluronan content and stromal cell CD44 associate with HER2
positivity and poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer.
132:531–539. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fang YJ, Zhang L, Wu XJ, Lu ZH, Li JB, Ou
QJ, Zhang MF, Ding PR, Pan ZZ and Wan DS: Impact of ERβ and CD44
expression on the prognosis of patients with stage II colon cancer.
Tumour Biol. 33:1907–1914. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kokko LL, Hurme S, Maula SM, Alanen K,
Grénman R, Kinnunen I and Ventelä S: Significance of site-specific
prognosis of cancer stem cell marker CD44 in head and neck
squamous-cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 47:510–516. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nguyen VN, Mirejovský T, Melinová L and
Mandys V: CD44 and its v6 spliced variant in lung carcinomas:
Relation to NCAM, CEA, EMA and UP1 and prognostic significance.
Neoplasma. 47:400–408. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ghatak S, Misra S and Toole BP: Hyaluronan
oligosaccharides inhibit anchorage-independent growth of tumor
cells by suppressing the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt cell
survival pathway. J Biol Chem. 277:38013–38020. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Marangoni E, Lecomte N, Durand L, de
Pinieux G, Decaudin D, Chomienne C, Smadja-Joffe F and Poupon MF:
CD44 targeting reduces tumour growth and prevents post-chemotherapy
relapse of human breast cancers xenografts. Br J Cancer.
100:918–922. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jin L, Hope KJ, Zhai Q, Smadja-Joffe F and
Dick JE: Targeting of CD44 eradicates human acute myeloid leukemic
stem cells. Nat Med. 12:1167–1174. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
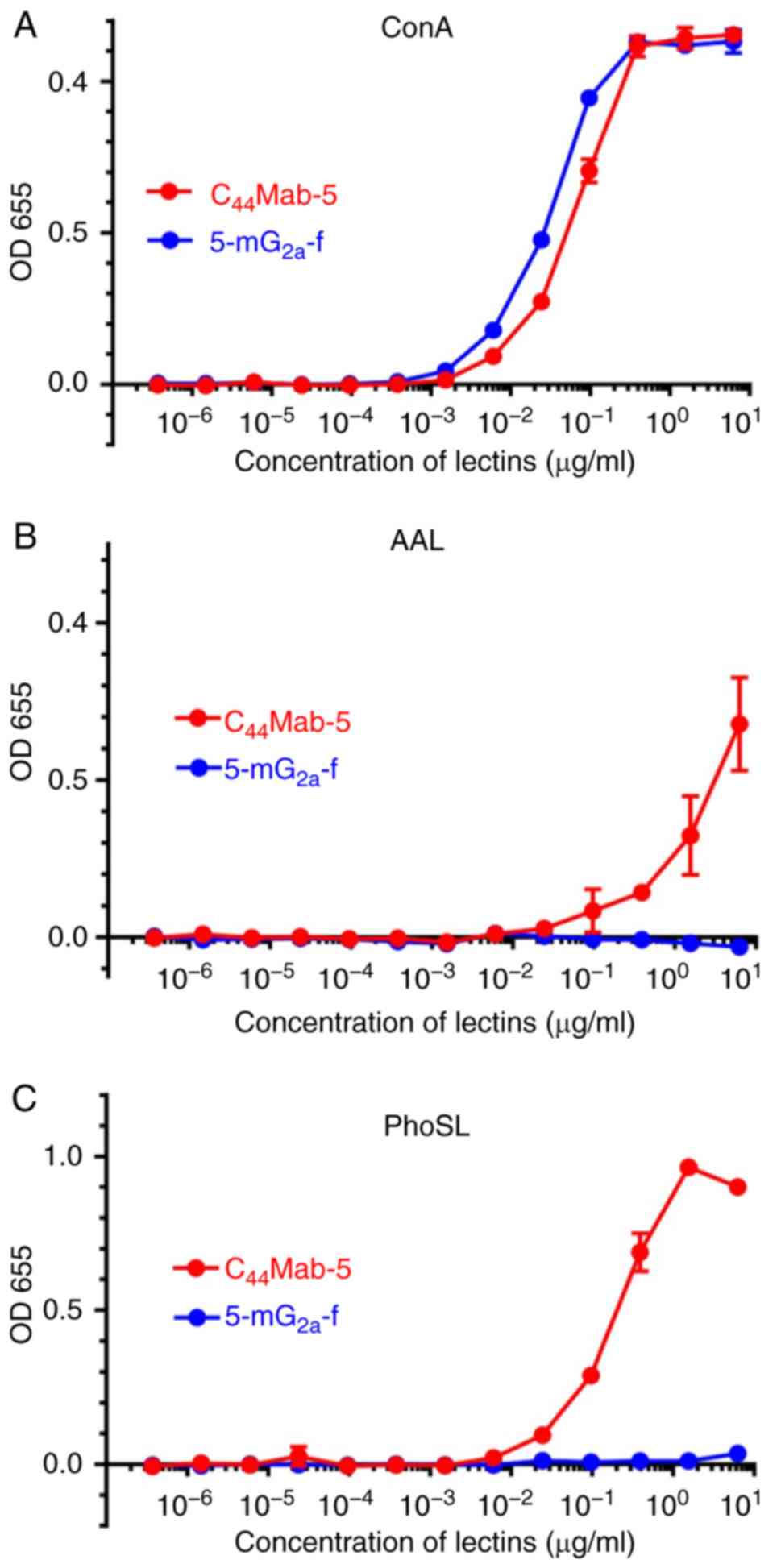
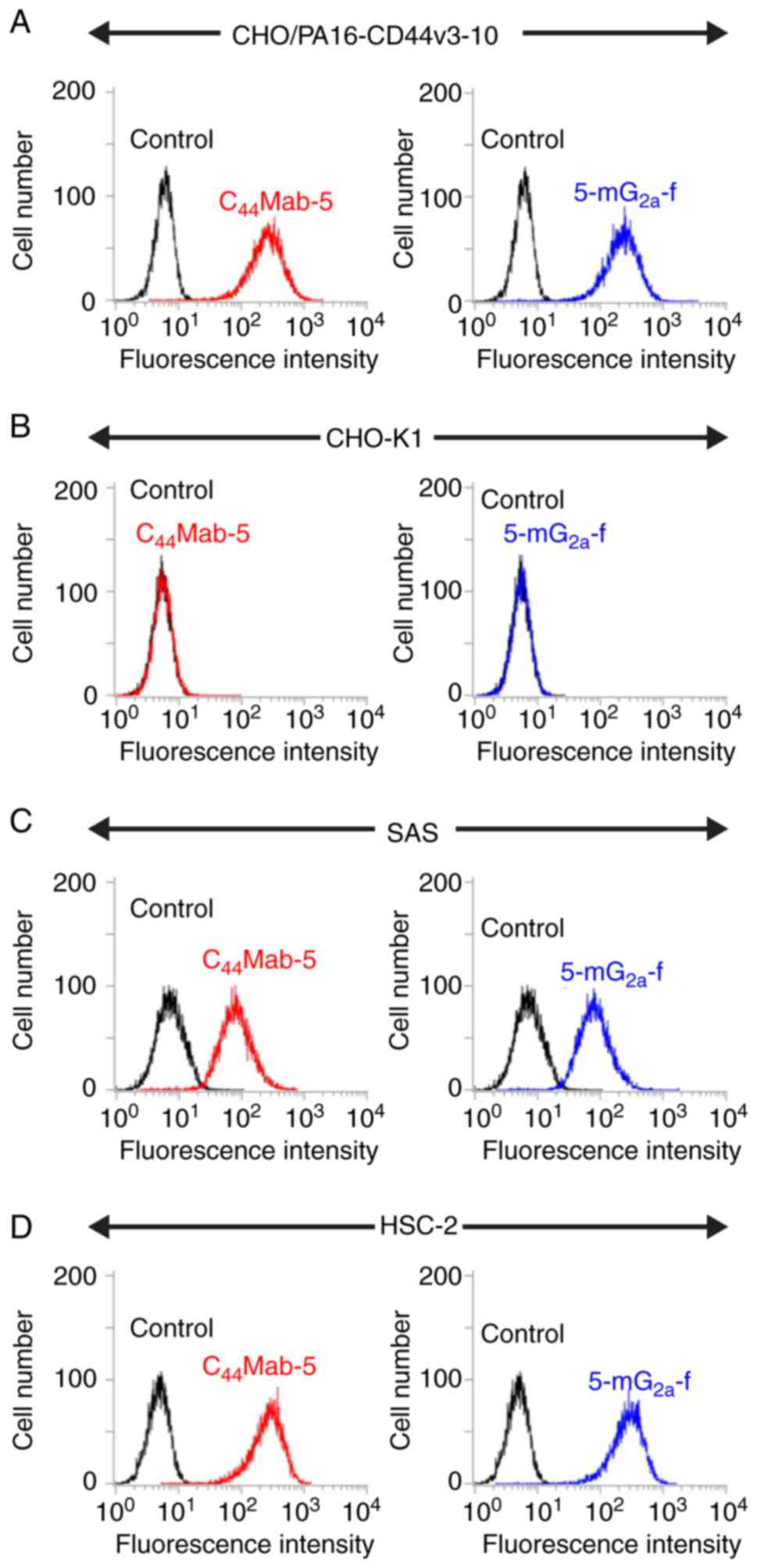
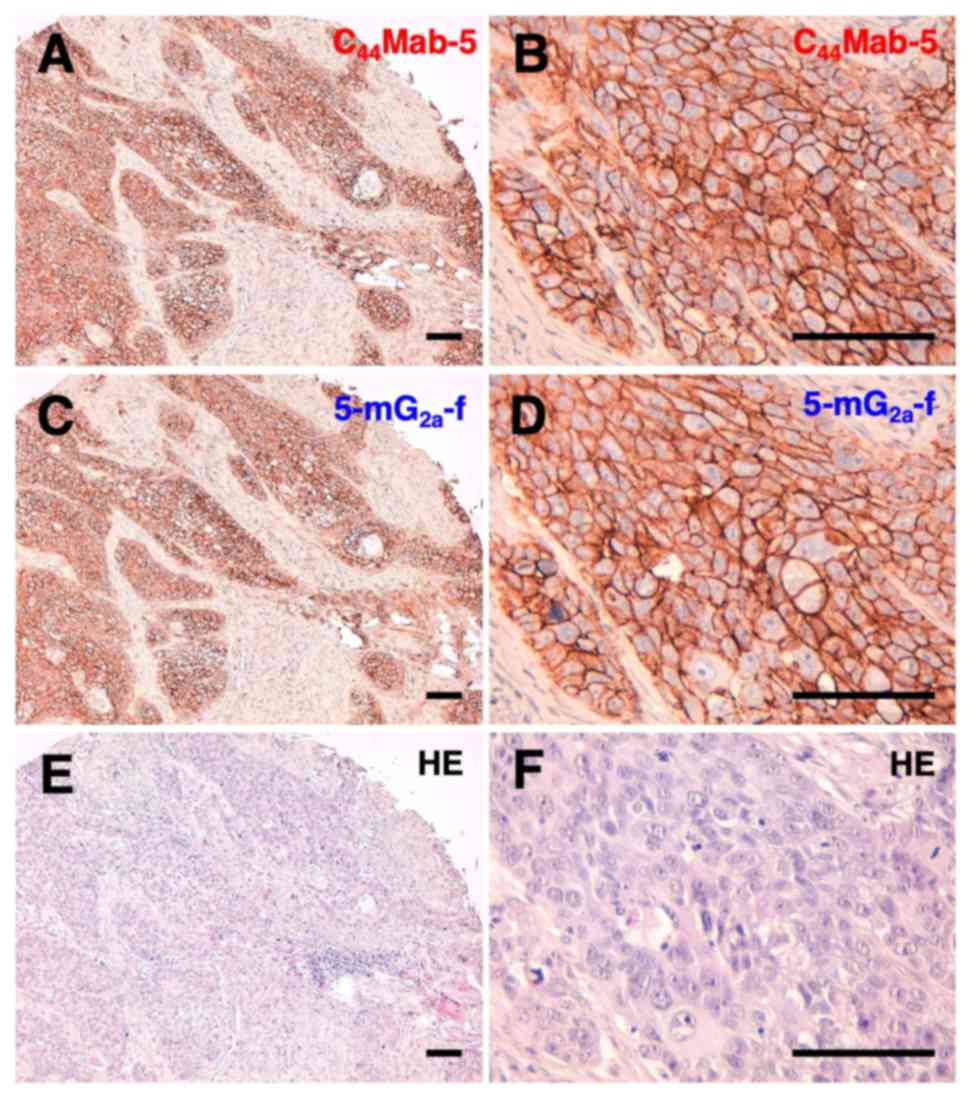
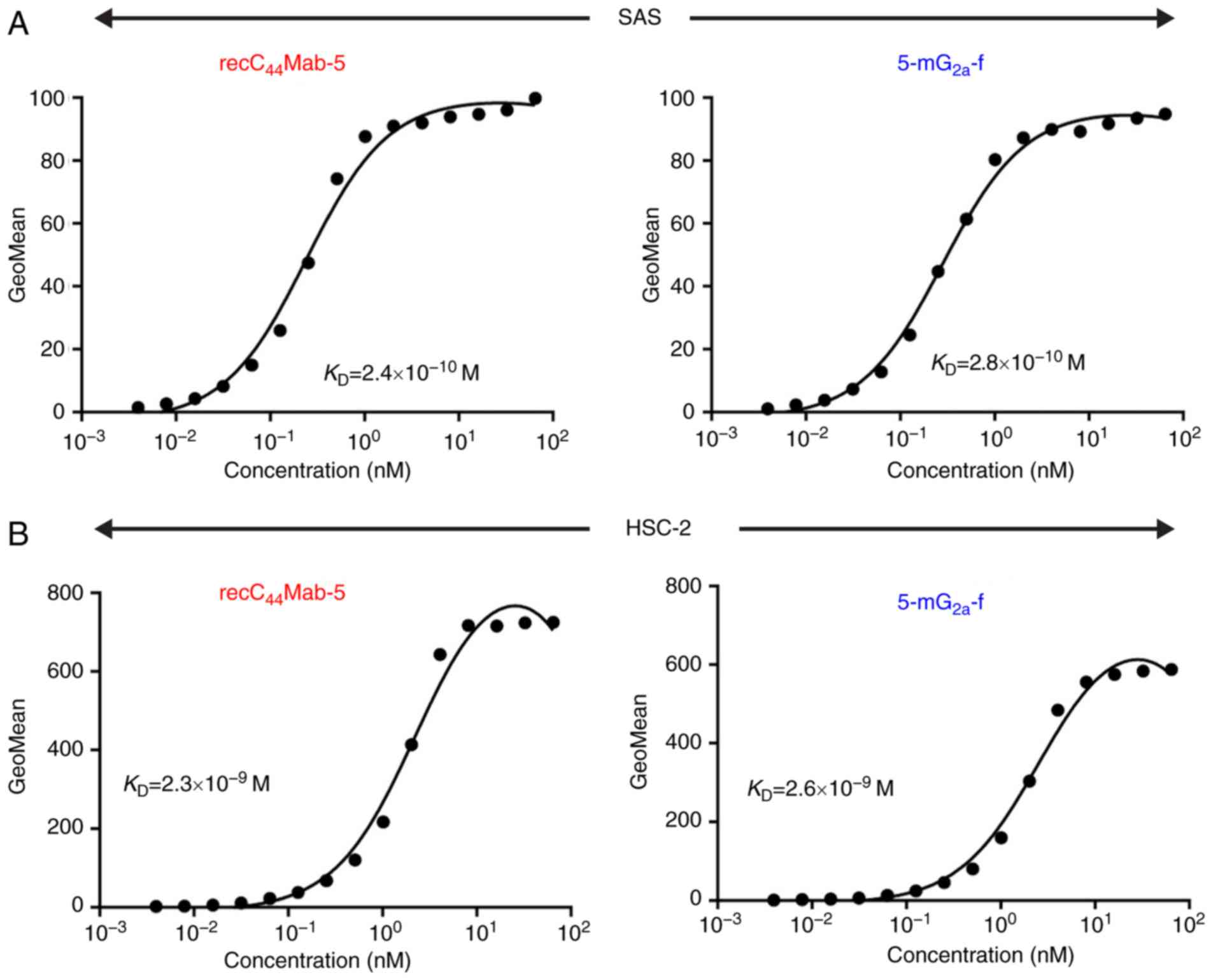
Yamada S, Itai S, Nakamura T, Yanaka M,
Kaneko MK and Kato Y: Detection of high CD44 expression in oral
cancers using the novel monoclonal antibody, C44Mab-5.
Biochem Biophys Rep. 14:64–68. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kato Y, Mizuno T, Yamada S, Nakamura T,
Itai S, Yanaka M, Sano M and Kaneko MK: Establishment of P38Bf, a
core-fucose-deficient mouse-canine chimeric antibody against dog
podoplanin. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 37:218–223.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson
M and Altman DG: Improving bioscience research reporting: The
ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol.
8:e10004122010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Aske KC and Waugh CA: Expanding the 3R
principles: More rigour and transparency in research using animals.
EMBO Rep. 18:1490–1492. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kobayashi Y, Tateno H, Dohra H, Moriwaki
K, Miyoshi E, Hirabayashi J and Kawagishi H: A novel core
fucose-specific lectin from the mushroom Pholiota squarrosa.
J Biol Chem. 287:33973–33982. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Takei J, Kaneko MK, Ohishi T, Kawada M,
Harada H and Kato Y: A novel anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody
(EMab-17) exerts antitumor activity against oral squamous cell
carcinomas via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and
complement-dependent cytotoxicity. Oncol Lett. 19:2809–2816.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kato Y, Kunita A, Fukayama M, Abe S,
Nishioka Y, Uchida H, Tahara H, Yamada S, Yanaka M, Nakamura T, et
al: Antiglycopeptide mouse monoclonal antibody LpMab-21 exerts
antitumor activity against human podoplanin through
antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and complement-dependent
cytotoxicity. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 36:20–24.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wimmerova M, Mitchell E, Sanchez JF,
Gautier C and Imberty A: Crystal structure of fungal lectin:
Six-bladed beta-propeller fold and novel fucose recognition mode
for Aleuria aurantia lectin. J Biol Chem. 278:27059–27067.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sumner JB, Howell SF and Zeissig A:
Concanavalin a and Hemagglutination. Science. 82:65–66. 1935.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rivera C: Essentials of oral cancer. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:11884–11894. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Güneri P and Epstein JB: Late stage
diagnosis of oral cancer: Components and possible solutions. Oral
Oncol. 50:1131–1136. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Vokes EE: Induction chemotherapy for head
and neck cancer: Recent data. Oncologist. 15 (Suppl 3):S3–S7. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Marcazzan S, Varoni EM, Blanco E, Lodi G
and Ferrari M: Nanomedicine, an emerging therapeutic strategy for
oral cancer therapy. Oral Oncol. 76:1–7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Furness S, Glenny AM, Worthington HV,
Pavitt S, Oliver R, Clarkson JE, Macluskey M, Chan KK and Conway
DI: Interventions for the treatment of oral cavity and
oropharyngeal cancer: Chemotherapy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
2011:CD0063862011.
|
|
41
|
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N,
Shin DM, Cohen RB, Jones CU, Sur R, Raben D, Jassem J, et al:
Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head
and neck. N Engl J Med. 354:567–578. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vermorken JB, Mesia R, Rivera F, Remenar
E, Kawecki A, Rottey S, Erfan J, Zabolotnyy D, Kienzer HR, Cupissol
D, et al: Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and
neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 359:1116–1127. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Naruse T, Yanamoto S, Matsushita Y,
Sakamoto Y, Morishita K, Ohba S, Shiraishi T, Yamada SI, Asahina I
and Umeda M: Cetuximab for the treatment of locally advanced and
recurrent/metastatic oral cancer: An investigation of distant
metastasis. Mol Clin Oncol. 5:246–252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Amit M, Yen TC, Liao CT, Chaturvedi P,
Agarwal JP, Kowalski LP, Ebrahimi A, Clark JR, Kreppel M, Zöller J,
et al: Improvement in survival of patients with oral cavity
squamous cell carcinoma: An international collaborative study.
Cancer. 119:4242–4248. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Takei J, Kaneko MK, Ohishi T, Kawada M,
Harada H and Kato Y: H2Mab-19, an anti-human epidermal
growth factor receptor 2 monoclonal antibody exerts antitumor
activity in mouse oral cancer xenografts. Exp Ther Med. 20:846–853.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hanken H, Gaudin R, Gröbe A, Fraederich M,
Eichhorn W, Smeets R, Simon R, Sauter G, Grupp K, Izbicki JR, et
al: Her2 expression and gene amplification is rarely detectable in
patients with oral squamous cell carcinomas. J Oral Pathol Med.
43:304–308. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yan M, Schwaederle M, Arguello D, Millis
SZ, Gatalica Z and Kurzrock R: HER2 expression status in diverse
cancers: Review of results from 37,992 patients. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 34:157–164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kondo N, Ishiguro Y, Kimura M, Sano D,
Fujita K, Sakakibara A, Taguchi T, Toth G, Matsuda H and Tsukuda M:
Antitumor effect of gefitinib on head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma enhanced by trastuzumab. Oncol Rep. 20:373–378.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kondo N, Tsukuda M, Sakakibara A,
Takahashi H, Hyakusoku H, Komatsu M, Niho T, Nakazaki K and Toth G:
Combined molecular targeted drug therapy for EGFR and HER-2 in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Int J Oncol.
40:1805–1812. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Itai S, Ohishi T, Kaneko MK, Yamada S, Abe
S, Nakamura T, Yanaka M, Chang YW, Ohba SI, Nishioka Y, et al:
Anti-podocalyxin antibody exerts antitumor effects via
antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in mouse xenograft models
of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 9:22480–22497. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kato Y and Kaneko MK: A cancer-specific
monoclonal antibody recognizes the aberrantly glycosylated
podoplanin. Sci Rep. 4:59242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yamada S, Ogasawara S, Kaneko MK and Kato
Y: LpMab-23: A cancer-specific monoclonal antibody against human
podoplanin. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 36:72–76. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kaneko MK, Yamada S, Nakamura T, Abe S,
Nishioka Y, Kunita A, Fukayama M, Fujii Y, Ogasawara S and Kato Y:
Antitumor activity of chLpMab-2, a human-mouse chimeric
cancer-specific antihuman podoplanin antibody, via
antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Cancer Med. 6:768–777.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kaneko MK, Nakamura T, Kunita A, Fukayama
M, Abe S, Nishioka Y, Yamada S, Yanaka M, Saidoh N, Yoshida K, et
al: ChLpMab-23: Cancer-specific human-mouse chimeric
anti-podoplanin antibody exhibits antitumor activity via
antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Monoclon Antib
Immunodiagn Immunother. 36:104–112. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|