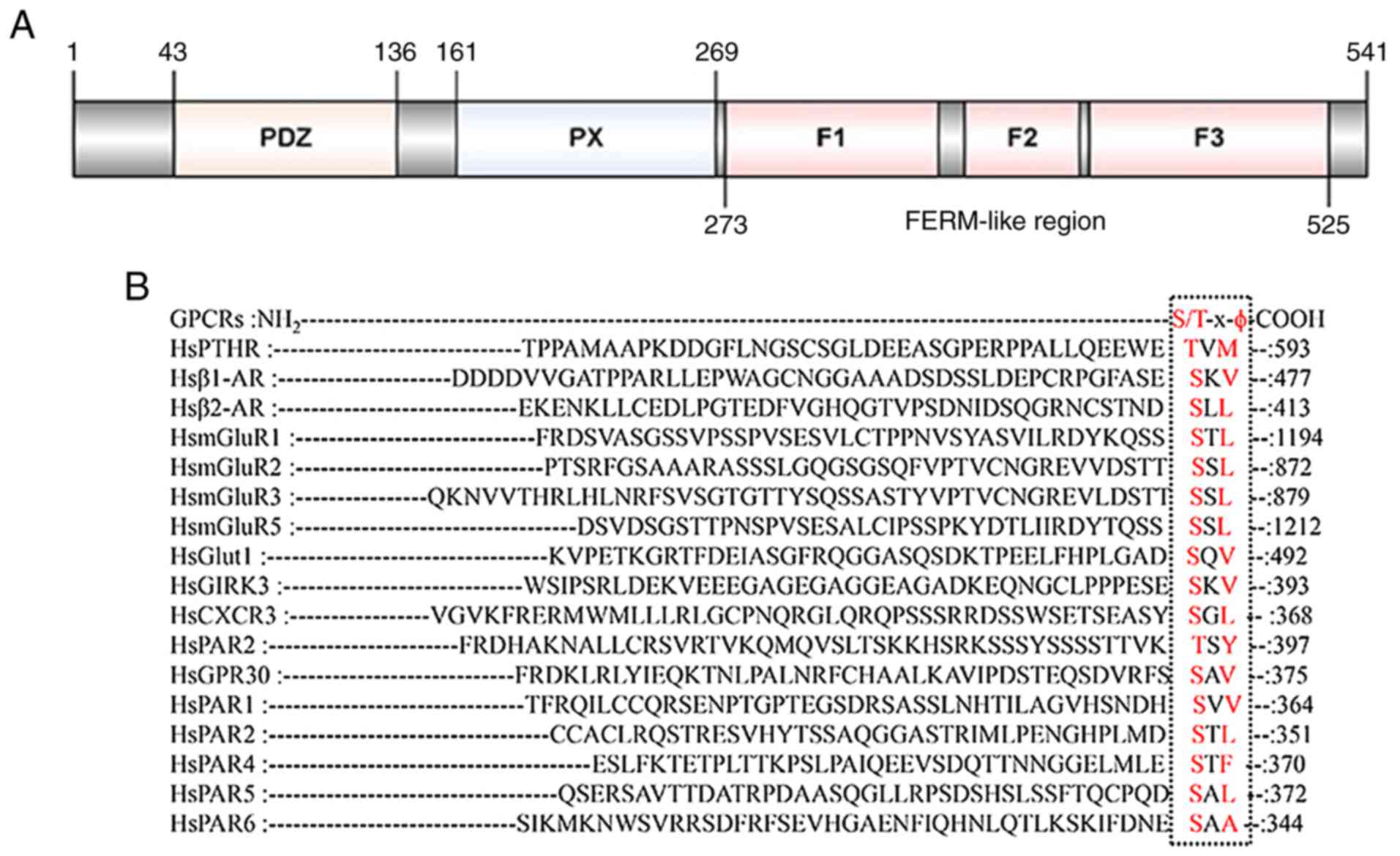
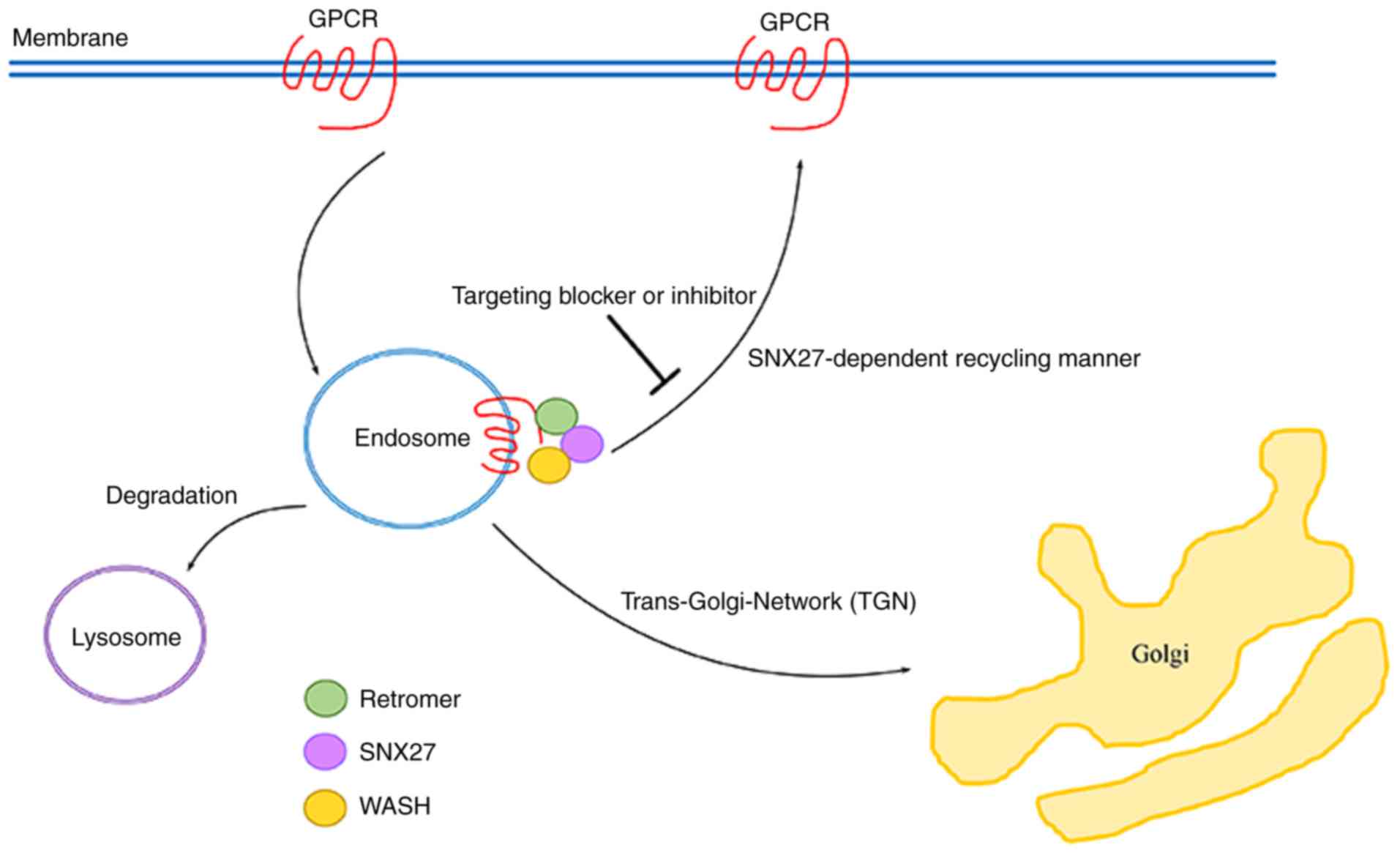
|
1
|
Gallon M and Cullen PJ: Retromer and
sorting nexins in endosomal sorting. Biochem Soc Trans. 43:33–47.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Temkin P, Lauffer B, Jäger S, Cimermancic
P, Krogan NJ and von Zastrow M: SNX27 mediates retromer tubule
entry and endosome-to-plasma membrane trafficking of signalling
receptors. Nat Cell Biol. 13:715–721. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Clairfeuille T, Mas C, Chan AS, Yang Z,
Tello-Lafoz M, Chandra M, Widagdo J, Kerr MC, Paul B, Mérida I, et
al: A molecular code for endosomal recycling of phosphorylated
cargos by the SNX27-retromer complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
23:921–932. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pavlos NJ and Friedman PA: GPCR signaling
and trafficking: The long and short of it. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
28:213–226. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang J, Li K, Zhang Y, Lu R, Wu S, Tang
J, Xia Y and Sun J: Deletion of sorting nexin 27 suppresses
proliferation in highly aggressive breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells
in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer. 19:5552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sharma P, Parveen S, Shah LV, Mukherjee M,
Kalaidzidis Y, Kozielski AJ, Rosato R, Chang JC and Datta S:
SNX27-retromer assembly recycles MT1-MMP to invadopodia and
promotes breast cancer metastasis. J Cell Biol. 219:e2018120982020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bjarnadóttir TK, Gloriam DE, Hellstrand
SH, Kristiansson H, Fredriksson R and Schiöth HB: Comprehensive
repertoire and phylogenetic analysis of the G protein-coupled
receptors in human and mouse. Genomics. 88:263–273. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lefkowitz RJ: A brief history of G-protein
coupled receptors (Nobel Lecture). Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.
52:6366–6378. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luttrell LM, Ferguson SS, Daaka Y, Miller
WE, Maudsley S, Della Rocca GJ, Lin F, Kawakatsu H, Owada K,
Luttrell DK, et al: Beta-arrestin-dependent formation of beta2
adrenergic receptor-Src protein kinase complexes. Science.
283:655–661. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
DeFea KA, Zalevsky J, Thoma MS, Déry O,
Mullins RD and Bunnett NW: Beta-arrestin-dependent endocytosis of
proteinase-activated receptor 2 is required for intracellular
targeting of activated ERK1/2. J Cell Biol. 148:1267–1281. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McDonald PH, Chow CW, Miller WE, Laporte
SA, Field ME, Lin FT, Davis RJ and Lefkowitz RJ: Beta-arrestin 2: A
receptor-regulated MAPK scaffold for the activation of JNK3.
Science. 290:1574–1577. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eichel K, Jullié D and von Zastrow M:
β-Arrestin drives MAP kinase signalling from clathrin-coated
structures after GPCR dissociation. Nat Cell Biol. 18:303–310.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Oakley RH, Laporte SA, Holt JA, Caron MG
and Barak LS: Differential affinities of visual arrestin, beta
arrestin1, and beta arrestin2 for G protein-coupled receptors
delineate two major classes of receptors. J Biol Chem.
275:17201–17210. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Thomsen ARB, Plouffe B, Cahill TJ III,
Shukla AK, Tarrasch JT, Dosey AM, Kahsai AW, Strachan RT, Pani B,
Mahoney JP, et al: GPCR-G protein-β-arrestin super-complex mediates
sustained G protein signaling. Cell. 166:907–919. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang W, Qiao Y and Li Z: New insights into
modes of GPCR activation. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 39:367–386. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thomsen ARB, Jensen DD, Hicks GA and
Bunnett NW: Therapeutic targeting of endosomal G-protein-coupled
receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 39:879–891. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nieto Gutierrez A and McDonald PH: GPCRs:
Emerging anti-cancer drug targets. Cell Signal. 41:65–74. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bar-Shavit R, Maoz M, Kancharla A, Nag JK,
Agranovich D, Grisaru-Granovsky S and Uziely B: G protein-coupled
receptors in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 17:13202016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Young D, Waitches G, Birchmeier C, Fasano
O and Wigler M: Isolation and characterization of a new cellular
oncogene encoding a protein with multiple potential transmembrane
domains. Cell. 45:711–719. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chan AS, Clairfeuille T, Landao-Bassonga
E, Kinna G, Ng PY, Loo LS, Cheng TS, Zheng M, Hong W, Teasdale RD,
et al: Sorting nexin 27 couples PTHR trafficking to retromer for
signal regulation in osteoblasts during bone growth. Mol Biol Cell.
27:1367–1382. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nakagawa T and Asahi M: β1-adrenergic
receptor recycles via a membranous organelle, recycling endosome,
by binding with sorting nexin27. J Membr Biol. 246:571–579. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nooh MM, Mancarella S and Bahouth SW:
Identification of novel transplantable GPCR recycling motif for
drug discovery. Biochem Pharmacol. 120:22–32. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin TB, Lai CY, Hsieh MC, Wang HH, Cheng
JK, Chau YP, Chen GD and Peng HY: VPS26A-SNX27
interaction-dependent mGluR5 recycling in dorsal horn neurons
mediates neuropathic pain in rats. J Neurosci. 35:14943–14955.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Balana B, Maslennikov I, Kwiatkowski W,
Stern KM, Bahima L, Choe S and Slesinger PA: Mechanism underlying
selective regulation of G protein-gated inwardly rectifying
potassium channels by the psychostimulant-sensitive sorting nexin
27. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:5831–5836. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nassirpour R and Slesinger PA:
Subunit-specific regulation of Kir3 channels by sorting nexin 27.
Channels (Austin). 1:331–333. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zeng CM, Chen Z and Fu L: Frizzled
receptors as potential therapeutic targets in human cancers. Int J
Mol Sci. 19:15432018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lupp A, Klenk C, Röcken C, Evert M, Mawrin
C and Schulz S: Immunohistochemical identification of the PTHR1
parathyroid hormone receptor in normal and neoplastic human
tissues. Eur J Endocrinol. 162:979–986. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Calvo N, Martin MJ, de Boland AR and
Gentili C: Involvement of ERK1/2, p38 MAPK, and PI3K/Akt signaling
pathways in the regulation of cell cycle progression by PTHrP in
colon adenocarcinoma cells. Biochem Cell Biol. 92:305–315. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Boras-Granic K and Wysolmerski JJ: PTHrP
and breast cancer: More than hypercalcemia and bone metastases.
Breast Cancer Res. 14:3072012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ongkeko WM, Burton D, Kiang A, Abhold E,
Kuo SZ, Rahimy E, Yang M, Hoffman RM, Wang-Rodriguez J and Deftos
LJ: Parathyroid hormone related-protein promotes
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer. PLoS One.
9:e858032014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Coelho M, Soares-Silva C, Brandão D,
Marino F, Cosentino M and Ribeiro L: β-adrenergic modulation of
cancer cell proliferation: Available evidence and clinical
perspectives. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 143:275–291. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu HC, Wang C, Xie N, Zhuang Z, Liu X,
Hou J and Huang H: Activation of adrenergic receptor β2 promotes
tumor progression and epithelial mesenchymal transition in tongue
squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 41:147–154. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pu J, Zhang X, Luo H, Xu L, Lu X and Lu J:
Adrenaline promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via
HuR-TGFβ regulatory axis in pancreatic cancer cells and the
implication in cancer prognosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
493:1273–1279. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cole SW and Sood AK: Molecular pathways:
Beta-adrenergic signaling in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:1201–1206.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang D, Ma QY, Hu HT and Zhang M:
β2-adrenergic antagonists suppress pancreatic cancer cell invasion
by inhibiting CREB, NFκB and AP-1. Cancer Biol Ther. 10:19–29.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Du J, Li XH and Li YJ: Glutamate in
peripheral organs: Biology and pharmacology. Eur J Pharmacol.
784:42–48. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Skerry TM and Genever PG: Glutamate
signalling in non-neuronal tissues. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
22:174–181. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Robert SM and Sontheimer H: Glutamate
transporters in the biology of malignant gliomas. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 71:1839–1854. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Prickett TD and Samuels Y: Molecular
pathways: Dysregulated glutamatergic signaling pathways in cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 18:4240–4246. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Iacovelli L, Bruno V, Salvatore L,
Melchiorri D, Gradini R, Caricasole A, Barletta E, De Blasi A and
Nicoletti F: Native group-III metabotropic glutamate receptors are
coupled to the mitogen-activated protein
kinase/phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathways. J Neurochem.
82:216–223. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu B, Zhao S, Qi C, Zhao X, Liu B, Hao F
and Zhao Z: Inhibition of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5
facilitates hypoxia-induced glioma cell death. Brain Res.
1704:241–248. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Touhara KK and MacKinnon R: Molecular
basis of signaling specificity between GIRK channels and GPCRs.
Elife. 7:e429082018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Takanami I, Inoue Y and Gika M: G-protein
inwardly rectifying potassium channel 1 (GIRK 1) gene expression
correlates with tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer.
BMC Cancer. 4:792004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rezania S, Kammerer S, Li C,
Steinecker-Frohnwieser B, Gorischek A, DeVaney TT, Verheyen S,
Passegger CA, Tabrizi-Wizsy NG, Hackl H, et al: Overexpression of
KCNJ3 gene splice variants affects vital parameters of the
malignant breast cancer cell line MCF-7 in an opposing manner. BMC
Cancer. 16:6282016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Plummer HK III, Dhar MS, Cekanova M and
Schuller HM: Expression of G-protein inwardly rectifying potassium
channels (GIRKs) in lung cancer cell lines. BMC Cancer. 5:1042005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Munoz MB and Slesinger PA: Sorting nexin
27 regulation of G protein-gated inwardly rectifying K(+) channels
attenuates in vivo cocaine response. Neuron. 82:659–669. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Katanaev VL: The Wnt/Frizzled GPCR
signaling pathway. Biochemistry (Mosc). 75:1428–1434. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chakravarthi BVSK, Chandrashekar DS,
Hodigere Balasubramanya SA, Robinson AD, Carskadon S, Rao U,
Gordetsky J, Manne U, Netto GJ, Sudarshan S, et al: Wnt receptor
Frizzled 8 is a target of ERG in prostate cancer. Prostate.
78:1311–1320. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sun L, Hu X, Chen W, He W, Zhang Z and
Wang T: Sorting nexin 27 interacts with Fzd7 and mediates Wnt
signalling. Biosci Rep. 36:e002962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wu J, Li L, Liu J, Wang Y, Wang Z, Wang Y,
Liu W, Zhou Z, Chen C, Liu R and Yang R: CC chemokine receptor 7
promotes triple-negative breast cancer growth and metastasis. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 50:835–842. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lin HY, Sun SM, Lu XF, Chen PY, Chen CF,
Liang WQ and Peng CY: CCR10 activation stimulates the invasion and
migration of breast cancer cells through the ERK1/2/MMP-7 signaling
pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 51:124–130. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bai M, Chen X and Ba YI: CXCL10/CXCR3
overexpression as a biomarker of poor prognosis in patients with
stage II colorectal cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 4:23–30. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wojtukiewicz MZ, Hempel D, Sierko E,
Tucker SC and Honn KV: Protease-activated receptors (PARs)-biology
and role in cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
34:775–796. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Arakaki AKS, Pan WA and Trejo J: GPCRs in
cancer: Protease-activated receptors, endocytic adaptors and
signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 19:18862018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Wang J, Sun Y, Qu JK, Yan Y, Yang Y and
Cai H: Roles of LPA receptor signaling in breast cancer. Expert Rev
Mol Diagn. 16:1103–1111. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lopane C, Agosti P, Gigante I, Sabbà C and
Mazzocca A: Implications of the lysophosphatidic acid signaling
axis in liver cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1868:277–282. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ren Z, Zhang C, Ma L, Zhang X, Shi S, Tang
D, Xu J, Hu Y, Wang B, Zhang F, et al: Lysophosphatidic acid
induces the migration and invasion of SGC-7901 gastric cancer cells
through the LPA2 and Notch signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med.
44:67–78. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yu X, Zhang Y and Chen H: LPA receptor 1
mediates LPA-induced ovarian cancer metastasis: An in vitro and in
vivo study. BMC Cancer. 16:8462016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Feldman RD and Limbird LE: GPER (GPR30): A
nongenomic receptor (GPCR) for steroid hormones with implications
for cardiovascular disease and cancer. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
57:567–584. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Noll B, Benz D, Frey Y, Meyer F, Lauinger
M, Eisler SA, Schmid S, Hordijk PL and Olayioye MA: DLC3 suppresses
MT1-MMP-dependent matrix degradation by controlling RhoB and actin
remodeling at endosomal membranes. J Cell Sci. 132:jcs2231722019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yang Z, Follett J, Kerr MC, Clairfeuille
T, Chandra M, Collins BM and Teasdale RD: Sorting nexin 27 (SNX27)
regulates the trafficking and activity of the glutamine transporter
ASCT2. J Biol Chem. 293:6802–6811. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Steinberg F, Gallon M, Winfield M, Thomas
EC, Bell AJ, Heesom KJ, Tavaré JM and Cullen PJ: A global analysis
of SNX27-retromer assembly and cargo specificity reveals a function
in glucose and metal ion transport. Nat Cell Biol. 15:461–471.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Feinstein TN, Wehbi VL, Ardura JA, Wheeler
DS, Ferrandon S, Gardella TJ and Vilardaga JP: Retromer terminates
the generation of cAMP by internalized PTH receptors. Nat Chem
Biol. 7:278–284. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Irannejad R and von Zastrow M: GPCR
signaling along the endocytic pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
27:109–116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Eichel K and von Zastrow M: Subcellular
organization of GPCR signaling. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 39:200–208.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Gupta MK, Mohan ML and Naga Prasad SV: G
protein-coupled receptor resensitization paradigms. Int Rev Cell
Mol Biol. 339:63–91. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Vardarajan BN, Breusegem SY, Harbour ME,
Inzelberg R, Friedland R, St George-Hyslop P, Seaman MN and Farrer
LA: Identification of Alzheimer disease-associated variants in
genes that regulate retromer function. Neurobiol Aging.
34:2231.e15–2231.e30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Tsika E, Glauser L, Moser R, Fiser A,
Daniel G, Sheerin UM, Lees A, Troncoso JC, Lewis PA, Bandopadhyay
R, et al: Parkinson's disease-linked mutations in VPS35 induce
dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Hum Mol Genet. 23:4621–4638. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wang X, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Badie H, Zhou Y,
Mu Y, Loo LS, Cai L, Thompson RC, Yang B, et al: Loss of sorting
nexin 27 contributes to excitatory synaptic dysfunction by
modulating glutamate receptor recycling in Down's syndrome. Nat
Med. 19:473–480. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Damseh N, Danson CM, Al-Ashhab M,
Abu-Libdeh B, Gallon M, Sharma K, Yaacov B, Coulthard E, Caldwell
MA, Edvardson S, et al: A defect in the retromer accessory protein,
SNX27, manifests by infantile myoclonic epilepsy and
neurodegeneration. Neurogenetics. 16:215–221. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Hussain NK, Diering GH, Sole J, Anggono V
and Huganir RL: Sorting Nexin 27 regulates basal and
activity-dependent trafficking of AMPARs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:11840–11845. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Choy RW, Park M, Temkin P, Herring BE,
Marley A, Nicoll RA and von Zastrow M: Retromer mediates a discrete
route of local membrane delivery to dendrites. Neuron. 82:55–62.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
McGarvey JC, Xiao K, Bowman SL, Mamonova
T, Zhang Q, Bisello A, Sneddon WB, Ardura JA, Jean-Alphonse F,
Vilardaga JP, et al: Actin-sorting nexin 27 (SNX27)-retromer
complex mediates rapid parathyroid hormone receptor recycling. J
Biol Chem. 291:10986–11002. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Lauffer BE, Melero C, Temkin P, Lei C,
Hong W, Kortemme T and von Zastrow M: SNX27 mediates PDZ-directed
sorting from endosomes to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol.
190:565–574. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Rincón E, Santos T, Avila-Flores A, Albar
JP, Lalioti V, Lei C, Hong W and Mérida I: Proteomics
identification of sorting nexin 27 as a diacylglycerol kinase
zeta-associated protein: New diacylglycerol kinase roles in
endocytic recycling. Mol Cell Proteomics. 6:1073–1087. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Seaman MN, Gautreau A and Billadeau DD:
Retromer-mediated endosomal protein sorting: All WASHed up! Trends
Cell Biol. 23:522–528. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Dev KK: Making protein interactions
druggable: Targeting PDZ domains. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 3:1047–1056.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Grandy D, Shan J, Zhang X, Rao S, Akunuru
S, Li H, Zhang Y, Alpatov I, Zhang XA, Lang RA, et al: Discovery
and characterization of a small molecule inhibitor of the PDZ
domain of dishevelled. J Biol Chem. 284:16256–16263. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Patra CR, Rupasinghe CN, Dutta SK,
Bhattacharya S, Wang E, Spaller MR and Mukhopadhyay D: Chemically
modified peptides targeting the PDZ domain of GIPC as a therapeutic
approach for cancer. ACS Chem Biol. 7:770–779. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Liu J, Qu J, Zhou W, Huang Y, Jia L, Huang
X, Qian Z, Xia J and Yu Y: Syntenin-targeted peptide blocker
inhibits progression of cancer cells. Eur J Med Chem. 154:354–366.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Das SK, Kegelman TP, Pradhan AK, Shen XN,
Bhoopathi P, Talukdar S, Maji S, Sarkar D, Emdad L and Fisher PB:
Suppression of prostate cancer pathogenesis using an MDA-9/Syntenin
(SDCBP) PDZ1 small-molecule inhibitor. Mol Cancer Ther.
18:1997–2007. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Shinde SR and Maddika S: PTEN regulates
glucose transporter recycling by impairing SNX27 retromer assembly.
Cell Rep. 21:1655–1666. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|