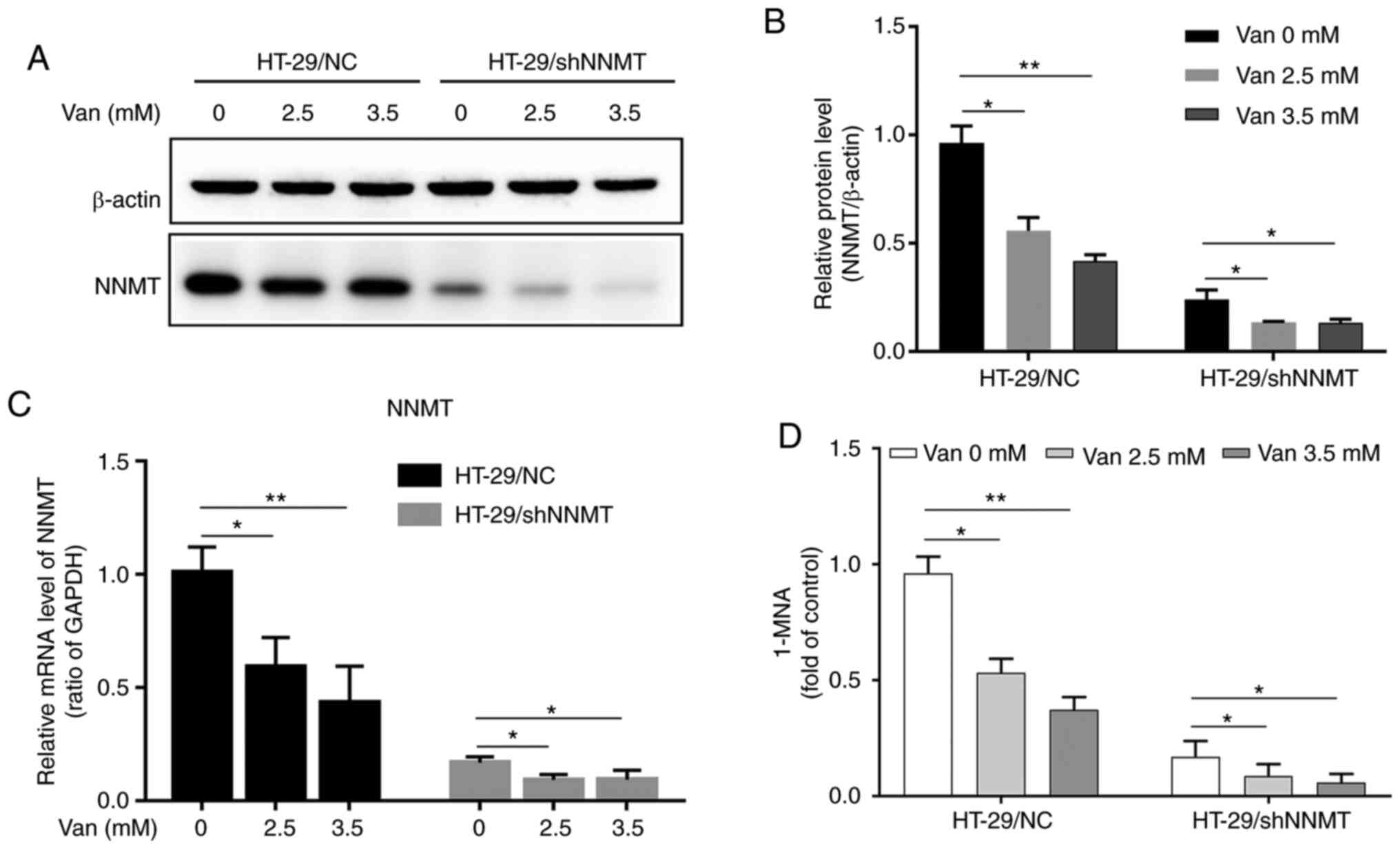
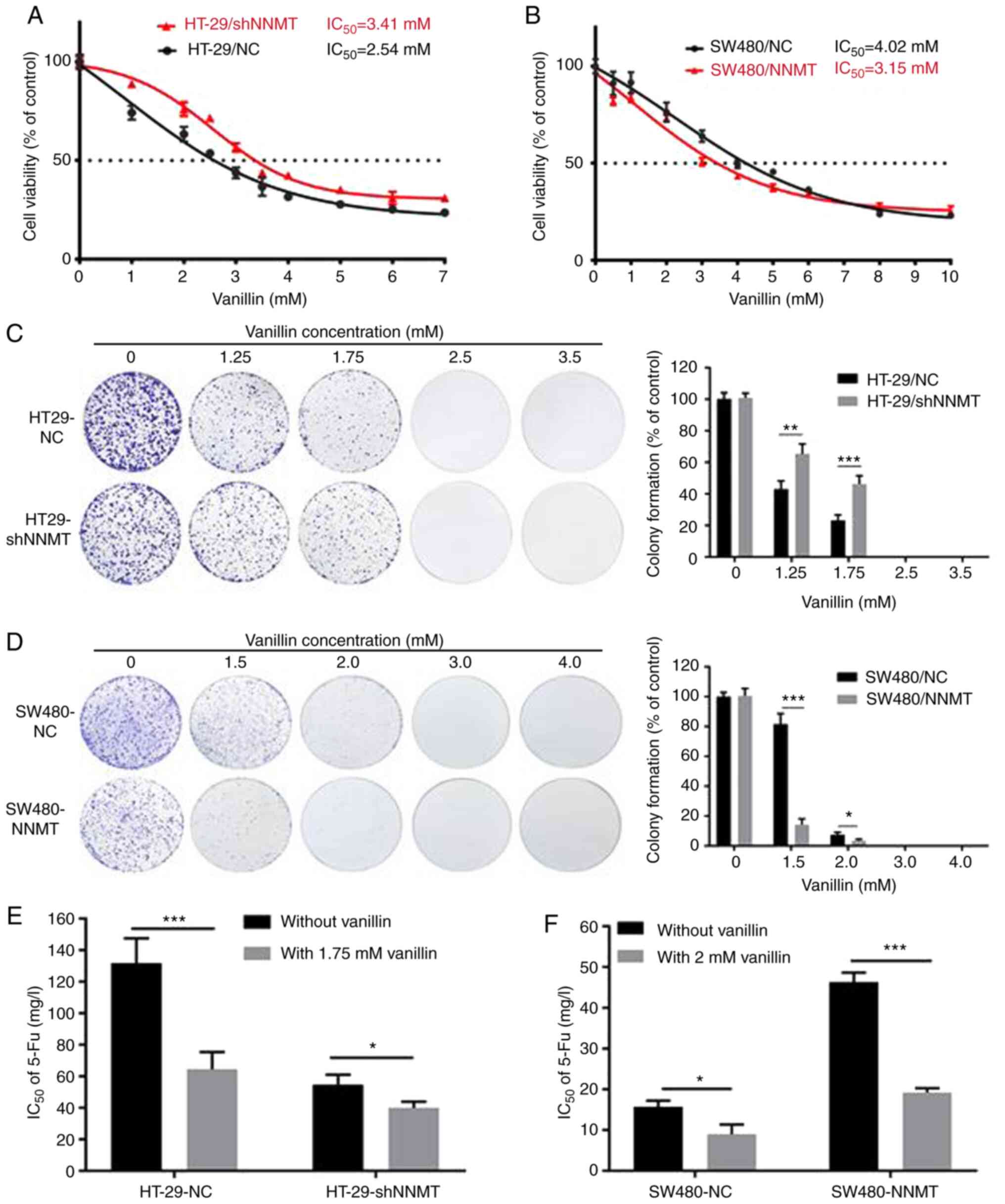
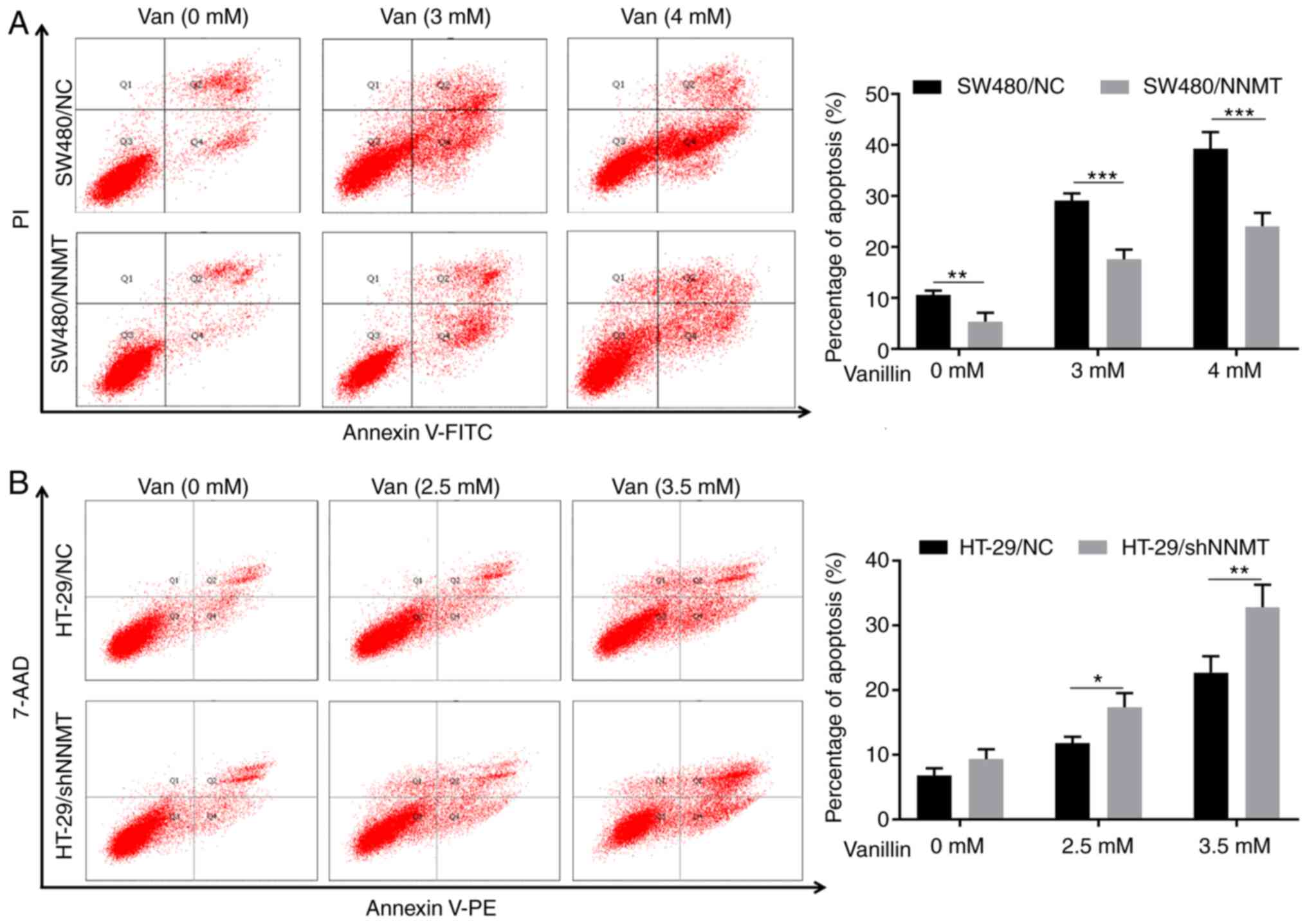
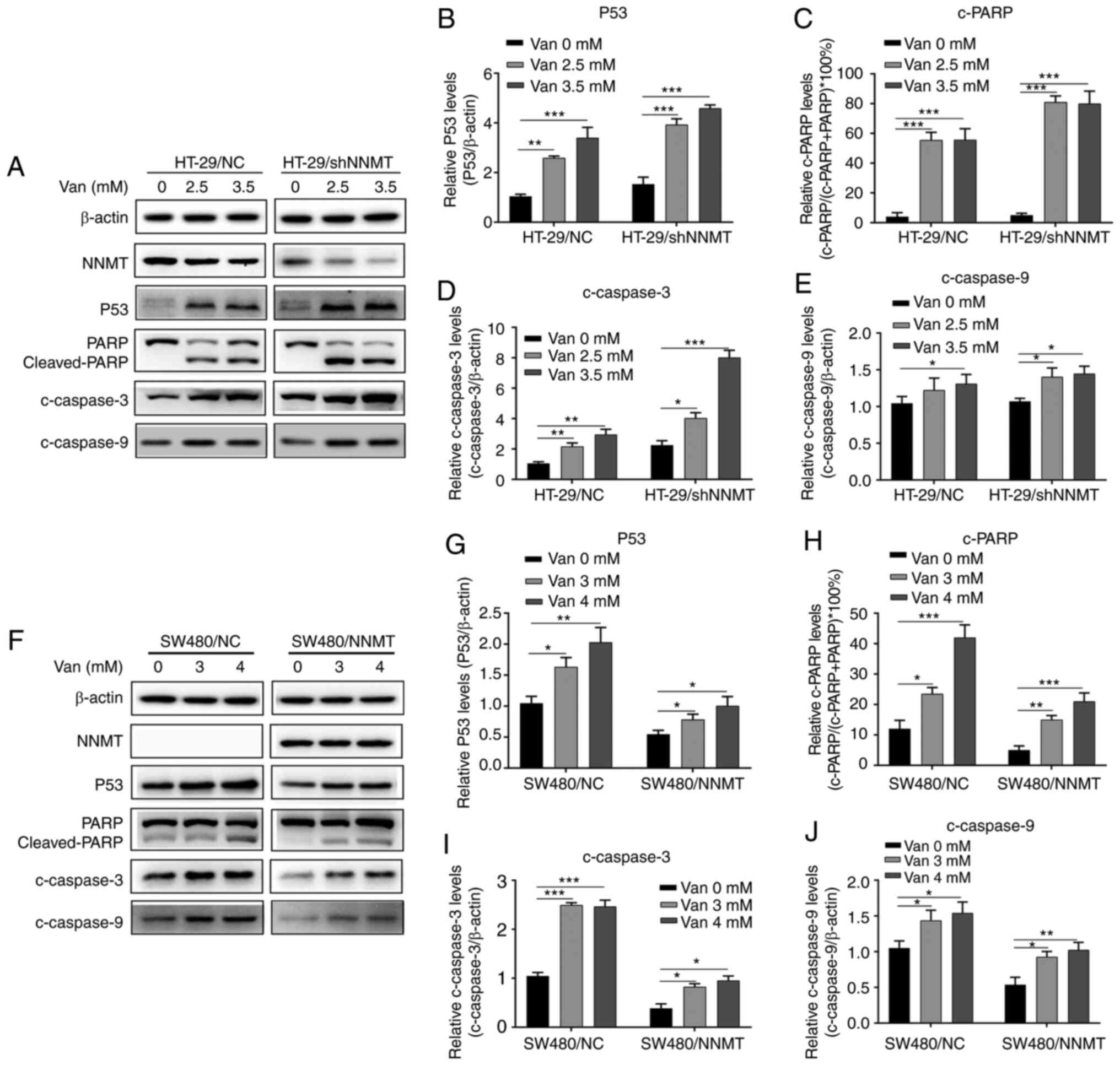
|
1
|
Testa U, Pelosi E and Castelli G:
Colorectal cancer: Genetic abnormalities, tumor progression, tumor
heterogeneity, clonal evolution and tumor-initiating cells. Med Sci
(Basel). 6:312018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wong CS, Wong VW, Chan CM, Ma BB, Hui EP,
Wong MC, Lam MY, Au TC, Chan WH, Cheuk W and Chan AT:
Identification of 5-fluorouracil response proteins in colorectal
carcinoma cell line SW480 by two-dimensional electrophoresis and
MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Oncol Rep. 20:89–98. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Roessler M, Rollinger W, Palme S, Hagmann
ML, Berndt P, Engel AM, Schneidinger B, Pfeffer M, Andres H, Karl
J, et al: Identification of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase as a
novel serum tumor marker for colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
11:6550–6557. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jung J, Kim LJ, Wang X, Wu Q, Sanvoranart
T, Hubert CG, Prager BC, Wallace LC, Jin X, Mack SC and Rich JN:
Nicotinamide metabolism regulates glioblastoma stem cell
maintenance. JCI Insight. 2:e900192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xie X, Yu H, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Li G, Ruan Z,
Li F, Wang X, Liu H and Zhang J: Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase
enhances the capacity of tumorigenesis associated with the
promotion of cell cycle progression in human colorectal cancer
cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 564:52–66. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xie X, Liu H, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Yu H, Li G,
Ruan Z, Li F, Wang X and Zhang J: Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase
enhances resistance to 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer cells
through inhibition of the ASK1-p38 MAPK pathway. Oncotarget.
7:45837–45848. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Akaberi M, Mehri S and Iranshahi M:
Multiple pro-apoptotic targets of abietane diterpenoids from Salvia
species. Fitoterapia. 100:118–132. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Priefert H, Rabenhorst J and Steinbuchel
A: Biotechnological production of vanillin. Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 56:296–314. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ho K, Yazan LS, Ismail N and Ismail M:
Apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of human colorectal cancer cell
line HT-29 induced by vanillin. Cancer Epidemiol. 33:155–160. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ramadoss DP and Sivalingam N: Vanillin
extracted from Proso and Barnyard millets induce apoptotic cell
death in HT-29 human colon cancer cell line. Nutr Cancer.
72:1422–1437. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Naz H, Tarique M, Khan P, Luqman S, Ahamad
S, Islam A, Ahmad F and Hassan MI: Evidence of vanillin binding to
CAMKIV explains the anti-cancer mechanism in human hepatic
carcinoma and neuroblastoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 438:35–45.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Khan P, Rahman S, Queen A, Manzoor S, Naz
F, Hasan GM, Luqman S, Kim J, Islam A, Ahmad F and Hassan MI:
Elucidation of dietary polyphenolics as potential inhibitor of
microtubule affinity regulating Kinase 4: In silico and in vitro
studies. Sci Rep. 7:94702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liang JA, Wu SL, Lo HY, Hsiang CY and Ho
TY: Vanillin inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression through
down-regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 75:151–157. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lirdprapamongkol K, Kramb JP,
Suthiphongchai T, Surarit R, Srisomsap C, Dannhardt G and Svasti J:
Vanillin suppresses metastatic potential of human cancer cells
through PI3K inhibition and decreases angiogenesis in vivo. J Agric
Food Chem. 57:3055–3063. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lirdprapamongkol K, Sakurai H, Kawasaki N,
Choo MK, Saitoh Y, Aozuka Y, Singhirunnusorn P, Ruchirawat S,
Svasti J and Saiki I: Vanillin suppresses in vitro invasion and in
vivo metastasis of mouse breast cancer cells. Eur J Pharm Sci.
25:57–65. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park EJ, Lee YM, Oh TI, Kim BM, Lim BO and
Lim JH: Vanillin suppresses cell motility by inhibiting
STAT3-Mediated HIF-1α mRNA expression in malignant melanoma cells.
Int J Mol Sci. 18:5322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Durant S and Karran P: Vanillins-a novel
family of DNA-PK inhibitors. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:5501–5512. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Elsherbiny NM, Younis NN, Shaheen MA and
Elseweidy MM: The synergistic effect between vanillin and
doxorubicin in ehrlich ascites carcinoma solid tumor and MCF-7
human breast cancer cell line. Pathol Res Pract. 212:767–777. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang J, Wang Y, Li G, Yu H and Xie X:
Down-regulation of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase induces
apoptosis in human breast cancer cells via the
mitochondria-mediated pathway. PLoS One. 9:e892022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tomida M, Ohtake H, Yokota T, Kobayashi Y
and Kurosumi M: Stat3 up-regulates expression of nicotinamide
N-methyltransferase in human cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
134:551–559. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ji Y, Dai F, Yan S, Shi JY and Zhou B:
Identification of catechol-type diphenylbutadiene as a
tyrosinase-activated pro-oxidative chemosensitizer against melanoma
A375 cells via glutathione S-transferase inhibition. J Agric Food
Chem. 67:9060–9069. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Starkov AA: The role of mitochondria in
reactive oxygen species metabolism and signaling. Ann NY Acad Sci.
1147:37–52. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu T, Guo F, Yu Y, Sun T, Ma D, Han J,
Qian Y, Kryczek I, Sun D, Nagarsheth N, et al: Fusobacterium
nucleatum promotes chemoresistance to colorectal cancer by
modulating autophagy. Cell. 170:548–563.e16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Horning BD, Suciu RM, Ghadiri DA,
Ulanovskaya OA, Matthews ML, Lum KM, Backus KM, Brown SJ, Rosen H
and Cravatt BF: Chemical proteomic profiling of human
methyltransferases. J Am Chem Soc. 138:13335–13343. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ruf S, Hallur MS, Anchan NK, Swamy IN,
Murugesan KR, Sarkar S, Narasimhulu LK, Putta VP, Shaik S,
Chandrasekar DV, et al: Novel nicotinamide analog as inhibitor of
nicotinamide N-methyltransferase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 28:922–925.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kannt A, Rajagopal S, Kadnur SV, Suresh J,
Bhamidipati RK, Swaminathan S, Hallur MS, Kristam R, Elvert R,
Czech J, et al: A small molecule inhibitor of nicotinamide
N-methyltransferase for the treatment of metabolic disorders. Sci
Rep. 8:36602018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Neelakantan H, Wang HY, Vance V, Hommel
JD, McHardy SF and Watowich SJ: Structure-activity relationship for
small molecule inhibitors of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase. J
Med Chem. 60:5015–5028. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
van Haren MJ, Taig R, Kuppens J, Sastre
Toraño J, Moret EE, Parsons RB, Sartini D, Emanuelli M and Martin
NI: Inhibitors of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase designed to
mimic the methylation reaction transition state. Org Biomol Chem.
15:6656–6667. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Babault N, Allali-Hassani A, Li F, Fan J,
Yue A, Ju K, Liu F, Vedadi M, Liu J and Jin J: Discovery of
bisubstrate inhibitors of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT).
J Med Chem. 61:1541–1551. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gao Y, van Haren MJ, Moret EE, Rood JJ,
Sartini D, Salvucci A, Emanuelli M, Craveur P, Babault N, Jin J and
Martin NI: Bisubstrate inhibitors of nicotinamide
N-methyltransferase (NNMT) with enhanced activity. J Med Chem.
62:6597–6614. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sulaiman S, Arafat K, Iratni R and Attoub
S: PTC-209 anti-cancer effects involved the inhibition of STAT3
Phosphorylation. Front Pharmacol. 10:11992019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mojzeš A, Tomljanović M, Milković L,
Kujundžić RN, Gašparović AČ and Trošelj KG: Cell-type specific
metabolic response of cancer cells to curcumin. Int J Mol Sci.
21:16612020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xue H, Li T, Wang P, Mo X, Zhang H, Ding
S, Ma D, Lv W, Zhang J and Han W: CMTM4 inhibits cell proliferation
and migration via AKT, ERK1/2, and STAT3 pathway in colorectal
cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 51:915–924. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Laudisi F, Cherubini F, Di Grazia A,
Dinallo V, Di Fusco D, Franzè E, Ortenzi A, Salvatori I,
Scaricamazza S, Monteleone I, et al: Progranulin sustains STAT3
hyper-activation and oncogenic function in colorectal cancer cells.
Mol Oncol. 13:2142–2159. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao S, Guan X, Hou R, Zhang X, Guo F,
Zhang Z and Hua C: Vitexin attenuates epithelial ovarian cancer
cell viability and motility in vitro and carcinogenesis in vivo via
p38 and ERK1/2 pathways related VEGFA. Ann Transl Med. 8:11392020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lin S, Pan Y and Xu C: Effects of aspirin
on pancreatic cancer cells PANC-1 and its potential molecular
mechanism. J BUON. 25:2449–2455. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|