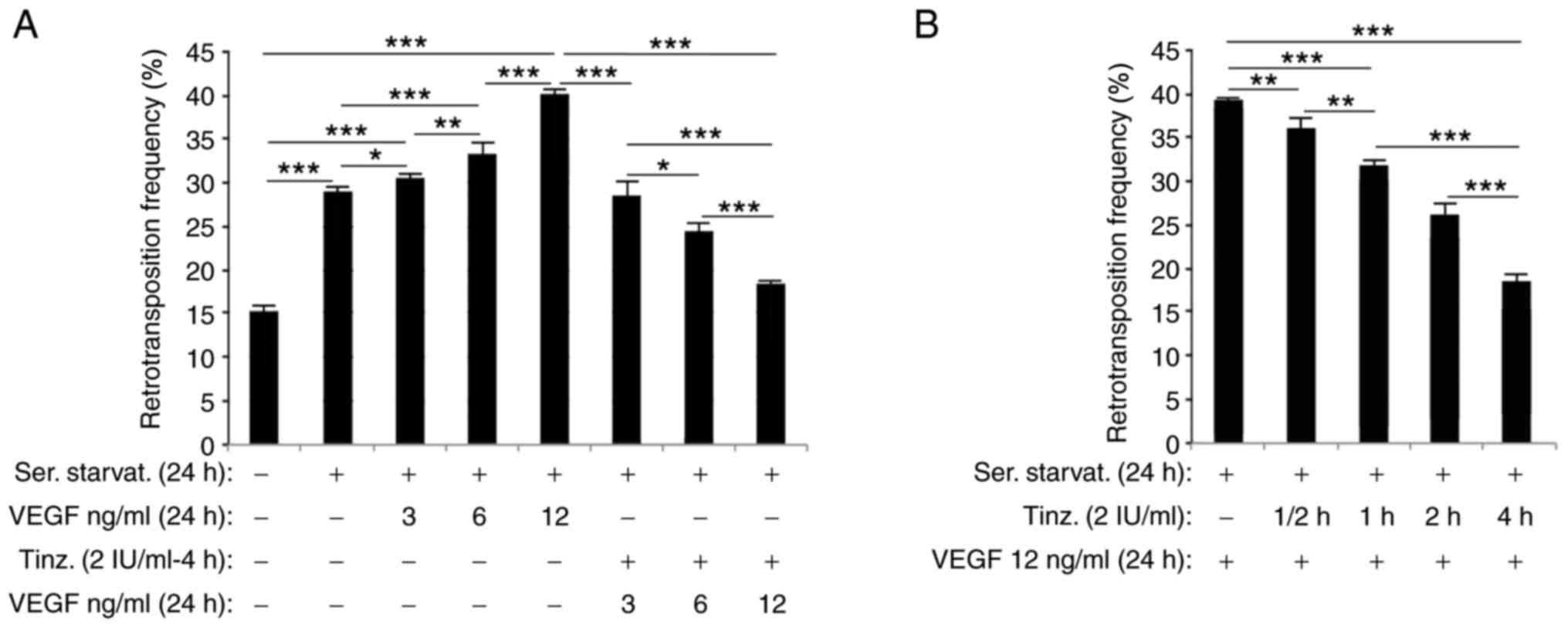
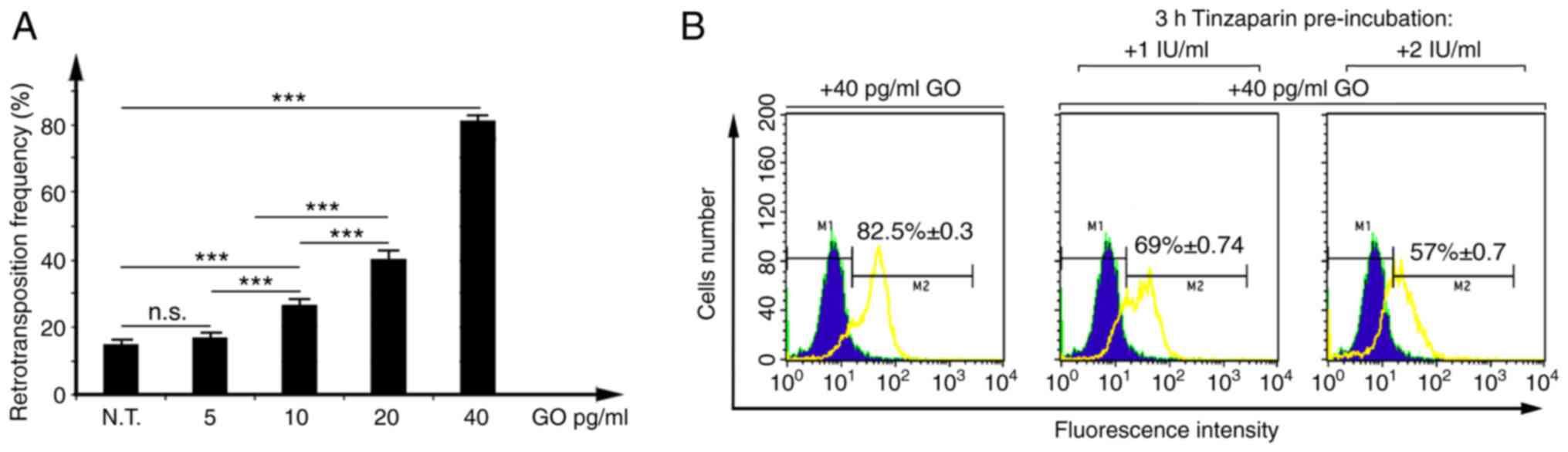
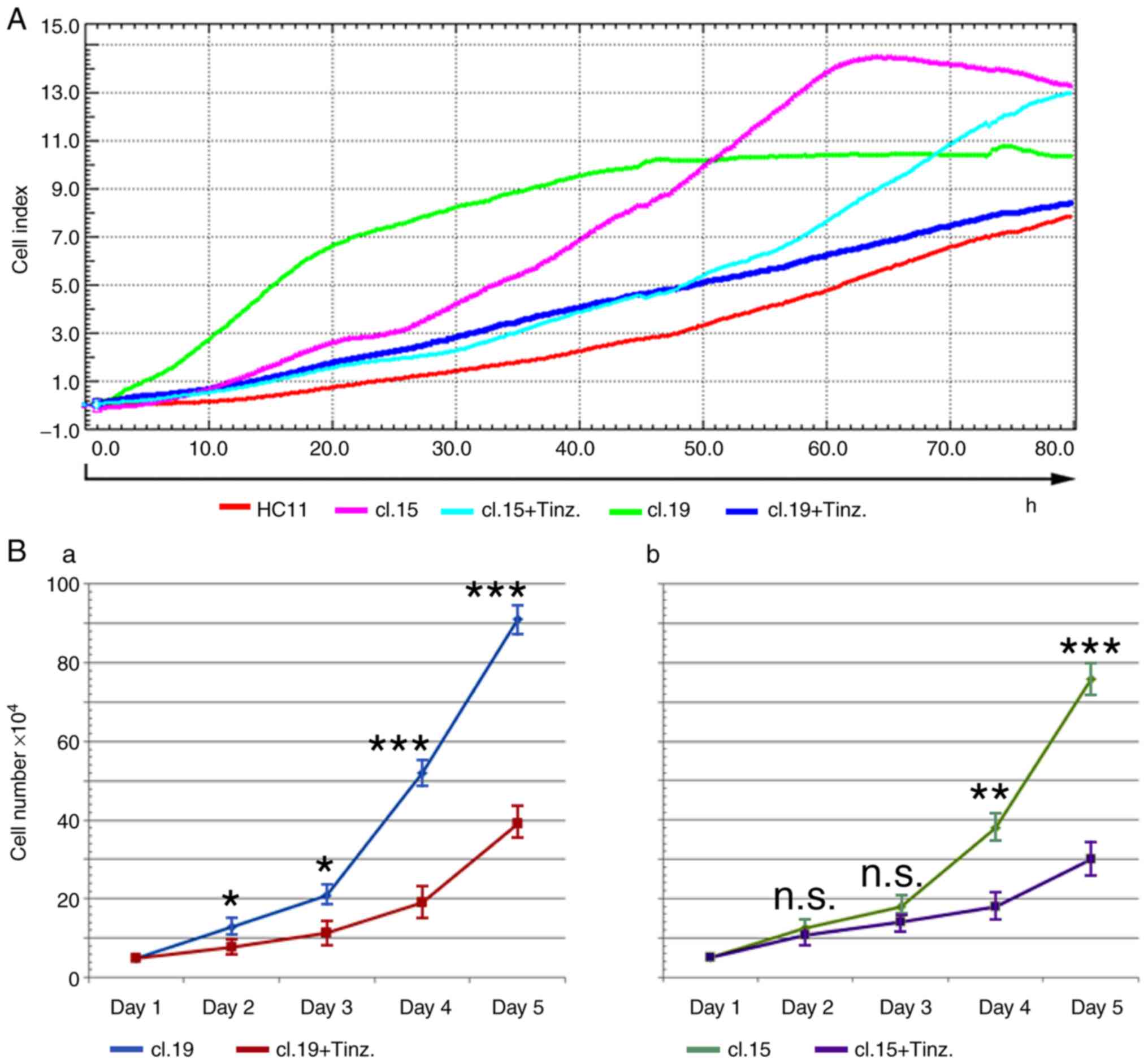
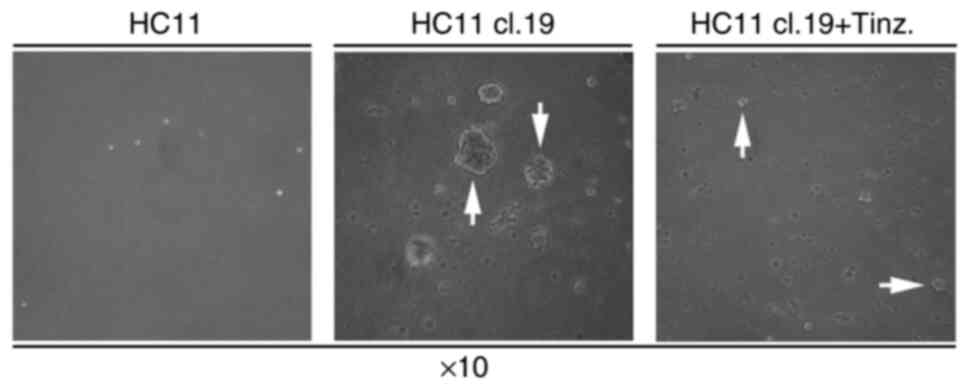
|
1
|
Khorana AA and Connolly GC: Assessing risk
of venous thromboembolism in the patient with cancer. J Clin Oncol.
27:4839–4847. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mandalà M, Falanga A and Roila F; ESMO
Guidelines Working Group, : Management of venous thromboembolism
(VTE) in cancer patients: ESMO clinical practice guidelines. Ann
Oncol. 22 (Supp 6):vi85–vi92. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lyman GH, Bohlke K, Khorana AA, Kuderer
NM, Lee AY, Arcelus JI, Balaban EP, Clarke JM, Flowers CR, Francis
CW, et al: Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis and treatment in
patients with cancer: American society of clinical oncology
clinical practice guideline update 2014. J Clin Oncol. 33:654–656.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dahlbäck B: Blood coagulation. Lancet.
355:1627–1632. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wong NN: Tinzaparin. Heart Dis. 4:331–340.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Horton J: Venous thrombotic events in
cancer: The bottom line. Cancer Control. 12 (Suppl 1):S31–S37.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Scotté F, Rey JB and Launay-Vacher V:
Thrombosis, cancer and renal insufficiency: Low molecular weight
heparin at the crossroads. Support Care Cancer. 20:3033–3042. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Perry SL, Bohlin C, Reardon DA, Desjardins
A, Friedman AH, Friedman HS and Vredenburgh JJ: Tinzaparin
prophylaxis against venous thromboembolic complications in brain
tumor patients. J Neurooncol. 95:129–134. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stevenson JL, Choi SH and Varki A:
Differential metastasis inhibition by clinically relevant levels of
heparins-correlation with selectin inhibition, not antithrombotic
activity. Clin Cancer Res. 11:7003–7011. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schlesinger M, Roblek M, Ortmann K, Naggi
A, Torri G, Borsig L and Bendas G: The role of VLA-4 binding for
experimental melanoma metastasis and its inhibition by heparin.
Thromb Res. 133:855–862. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Harvey JR, Mellor P, Eldaly H, Lennard TW,
Kirby JA and Ali S: Inhibition of CXCR4-mediated breast cancer
metastasis: A potential role for heparinoids? Clin Cancer Res.
13:1562–1570. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Alyahya R, Sudha T, Racz M, Stain SC and
Mousa SA: Anti-metastasis efficacy and safety of non-anticoagulant
heparin derivative versus low molecular weight heparin in surgical
pancreatic cancer models. Int J Oncol. 46:1225–1231. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bauer AT, Suckau J, Frank K, Desch A,
Goertz L, Wagner AH, Hecker M, Goerge T, Umansky L, Beckhove P, et
al: von Willebrand factor fibers promote cancer-associated platelet
aggregation in malignant melanoma of mice and humans. Blood.
125:3153–3163. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Amirkhosravi A, Mousa SA, Amaya M and
Francis JL: Antimetastatic effect of tinzaparin, a
low-molecular-weight heparin. J Thromb Haemost. 1:1972–1976. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mousa SA and Mohamed S: Anti-angiogenic
mechanisms and efficacy of the low molecular weight heparin,
tinzaparin: Anti-cancer efficacy. Oncol Rep. 12:683–688.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mousa SA and Mohamed S: Inhibition of
endothelial cell tube formation by the low molecular weight
heparin, tinzaparin, is mediated by tissue factor pathway
inhibitor. Thromb Haemost. 92:627–633. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pfankuchen DB, Stölting DP, Schlesinger M,
Royer HD and Bendas G: Low molecular weight heparin tinzaparin
antagonizes cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 97:147–157. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dimakakos EP, Vathiotis I and Syrigos K:
The role of tinzaparin in oncology. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost.
24:697–707. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kragh M, Binderup L, Vig Hjarnaa PJ, Bramm
E, Johansen KB and Frimundt Petersen C: Non-anti-coagulant heparin
inhibits metastasis but not primary tumor growth. Oncol Rep.
14:99–104. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis in cancer,
vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1:27–31. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gamperl H, Plattfaut C, Freund A, Quecke
T, Theophil F and Gieseler F: Extracellular vesicles from malignant
effusions induce tumor cell migration: Inhibitory effect of LMWH
tinzaparin. Cell Biol Int. 40:1050–1061. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sudha T, Yalcin M, Lin HY, Elmetwally AM,
Nazeer T, Arumugam T, Phillips P and Mousa SA: Suppression of
pancreatic cancer by sulfated non-anticoagulant low molecular
weight heparin. Cancer Lett. 350:25–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guarino M, Rubino B and Ballabio G: The
role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology.
Pathology. 39:305–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hugo H, Ackland ML, Blick T, Lawrence MG,
Clements JA, Williams ED and Thompson EW: Epithelial-mesenchymal
and mesenchymal-epithelial transitions in carcinoma progression. J
Cell Physiol. 213:374–383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang AD, Camp ER, Fan F, Shen L, Gray MJ,
Liu W, Somcio R, Bauer TW, Wu Y, Hicklin DJ and Ellis LM: Vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor-1 activation mediates epithelial
to mesenchymal transition in human pancreatic carcinoma cells.
Cancer Res. 66:46–51. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hayashida T, Jinno H, Kitagawa Y and
Kitajima M: Cooperation of cancer stem cell properties and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the establishment of breast
cancer metastasis. J Oncol. 2011:5914272011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cordaux R and Batzer MA: The impact of
retrotransposons on human genome evolution. Nat Rev Genet.
10:691–703. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Boeke JD, Garfinkel DJ, Styles CA and Fink
GR: Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell.
40:491–500. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hancks DC and Kazazian HH Jr: Roles for
retrotransposon insertions in human disease. Mob DNA. 7:92016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Heidmann T, Heidmann O and Nicolas JF: An
indicator gene to demonstrate intracellular transposition of
defective retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 85:2219–2223. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Georgiou I, Noutsopoulos D, Dimitriadou E,
Markopoulos G, Apergi A, Lazaros L, Vaxevanoglou T, Pantos K,
Syrrou M and Tzavaras T: Retrotransposon RNA expression and
evidence for retrotransposition events in human oocytes. Hum Mol
Genet. 18:1221–1228. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Goodier JL and Kazazian HH Jr:
Retrotransposons revisited: The restraint and rehabilitation of
parasites. Cell. 135:23–35. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
French NS and Norton JD: Structure and
functional properties of mouse VL30 retrotransposons. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1352:33–47. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Garen A and Song X: Regulatory roles of
tumor-suppressor proteins and noncoding RNA in cancer and normal
cell functions. Int J Cancer. 122:1687–1689. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Markopoulos G, Noutsopoulos D, Mantziou S,
Gerogiannis D, Thrasyvoulou S, Vartholomatos G, Kolettas E and
Tzavaras T: Genomic analysis of mouse VL30 retrotransposons. Mob
DNA. 7:102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Brunmeir R, Lagger S, Simboeck E, Sawicka
A, Egger G, Hagelkruys A, Zhang Y, Matthias P, Miller WJ and Seiser
C: Epigenetic regulation of a murine retrotransposon by a dual
histone modification mark. PLoS Genet. 6:e10009272010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Noutsopoulos D, Vartholomatos G, Kolaitis
N and Tzavaras T: SV40 large T antigen up-regulates the
retrotransposition frequency of viral-like 30 elements. J Mol Biol.
361:450–461. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Noutsopoulos D, Markopoulos G, Koliou M,
Dova L, Vartholomatos G, Kolettas E and Tzavaras T: Vanadium
induces VL30 retrotransposition at an unusually high level: A
possible carcinogenesis mechanism. J Mol Biol. 374:80–90. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Markopoulos G, Noutsopoulos D, Mantziou S,
Vartholomatos G, Monokrousos N, Angelidis C and Tzavaras T: Arsenic
induces VL30 retrotransposition: The involvement of oxidative
stress and heat-shock protein 70. Toxicol Sci. 134:312–322. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tzavaras T, Eftaxia S, Tavoulari S, Hatzi
P and Angelidis C: Factors influencing the expression of endogenous
reverse transcriptases and viral-like 30 elements in mouse NIH3T3
cells. Int J Oncol. 23:1237–1243. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Konisti S, Mantziou S, Markopoulos G,
Thrasyvoulou S, Vartholomatos G, Sainis I, Kolettas E, Noutsopoulos
D and Tzavaras T: H2O2 signals via iron induction of VL30
retrotransposition correlated with cytotoxicity. Free Radic Biol
Med. 52:2072–2081. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Noutsopoulos D, Markopoulos G,
Vartholomatos G, Kolettas E, Kolaitis N and Tzavaras T: VL30
retrotransposition signals activation of a caspase-independent and
p53-dependent death pathway associated with mitochondrial and
lysosomal damage. Cell Res. 20:553–562. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Thrasyvoulou S, Vartholomatos G,
Markopoulos G, Noutsopoulos D, Mantziou S, Gkartziou F, Papageorgis
P, Charchanti A, Kouklis P, Constantinou AI and Tzavaras T: VL30
retrotransposition is associated with induced EMT, CSC generation
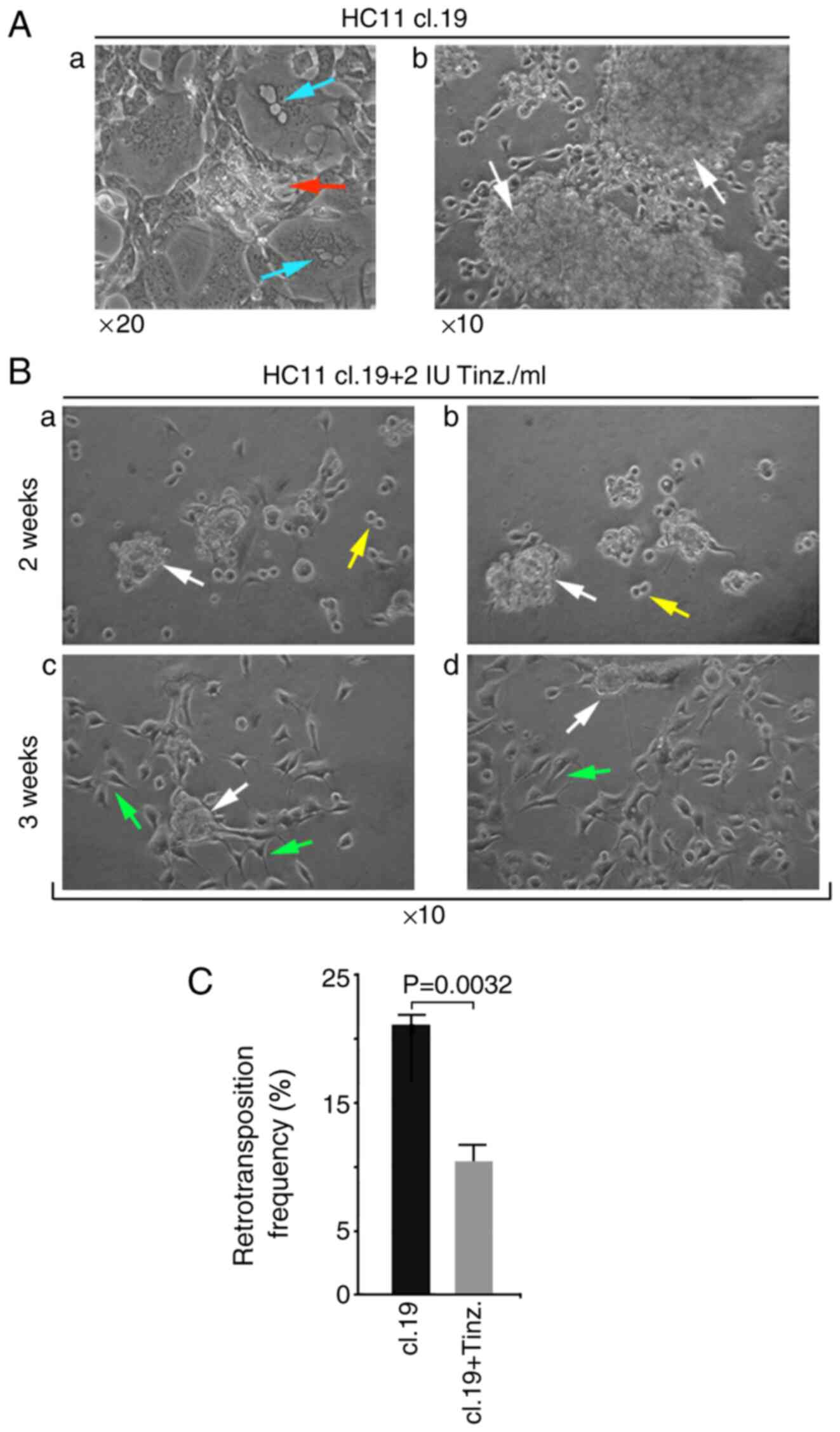
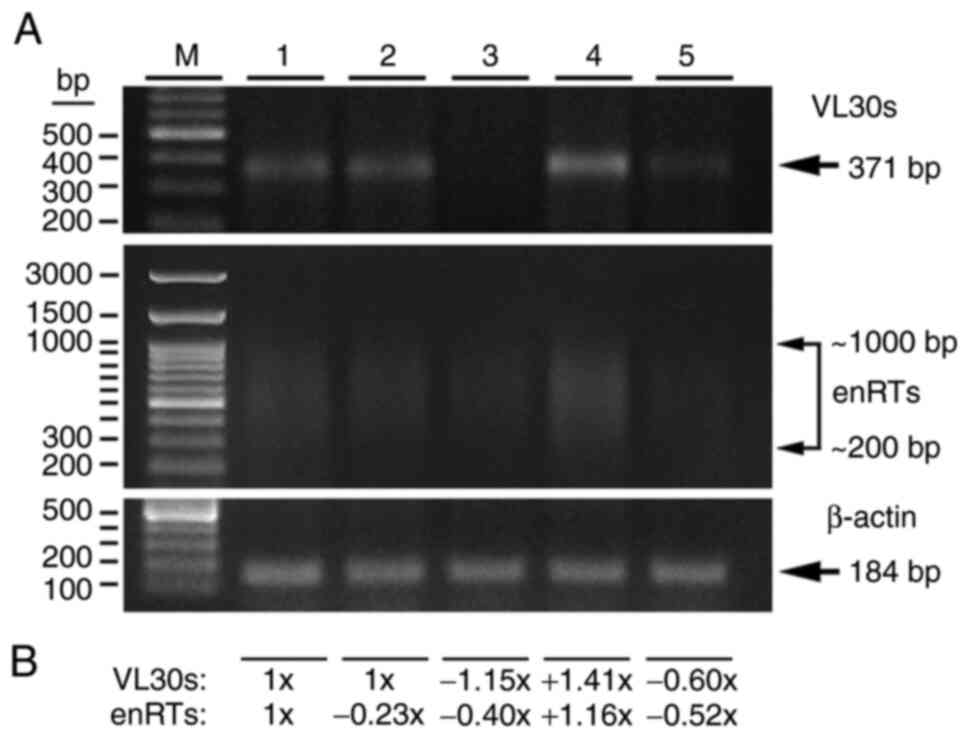
and tumorigenesis in HC11 mouse mammary stem-ike epithelial cells.
Oncol Rep. 44:126–138. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ball RK, Friis RR, Schoenenberger CA,
Doppler W and Groner B: Prolactin regulation of beta-casein gene
expression and of a cytosolic 120-kd protein in a cloned mouse
mammary epithelial cell line. EMBO J. 7:2089–2095. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Williams C, Helguero L, Edvardsson K,
Haldosén LA and Gustafsson JA: Gene expression in murine mammary
epithelial stem cell-like cells shows similarities to human breast
cancer gene expression. Breast Cancer Res. 11:R262009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Borowicz S, Van Scoyk M, Avasarala S,
Karuppusamy Rathinam MK, Tauler J, Bikkavilli RK and Winn RA: The
soft agar colony formation assay. J Vis Exp. e519982014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ostertag EM, Prak ET, DeBerardinis RJ,
Moran JV and Kazazian HH Jr: Determination of L1 retrotransposition
kinetics in cultured cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:1418–1423. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Xiong Y and Eickbush TH: Origin and
evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase
sequences. EMBO J. 9:3353–3362. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Puschendorf M, Stein P, Oakeley EJ,
Schultz RM, Peters AH and Svoboda P: Abundant transcripts from
retrotransposons are unstable in fully grown mouse oocytes. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 347:36–43. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bloushtain-Qimron N, Yao J, Snyder EL,
Shipitsin M, Campbell LL, Mani SA, Hu M, Chen H, Ustyansky V,
Antosiewicz JE, et al: Cell type-specific DNA methylation patterns
in the human breast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:14076–14081. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
White EZ, Pennant NM, Carter JR, Hawsawi
O, Odero-Marah V and Hinton CV: Serum deprivation initiates
adaptation and survival to oxidative stress in prostate cancer
cells. Sci Rep. 10:125052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Merlo GR, Venesio T, Taverna D, Marte BM,
Callahan R and Hynes NE: Growth suppression of normal mammary
epithelial cells by wild-type p53. Oncogene. 9:443–453.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ferrara N and Davis-Smyth T: The biology
of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr Rev. 18:4–25. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Grugel S, Finkenzeller G, Weindel K,
Barleon B and Marmé D: Both v-Ha-Ras and v-Raf stimulate expression
of the vascular endothelial growth factor in NIH 3T3 cells. J Biol
Chem. 270:25915–25919. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Scherz-Shouval R, Shvets E, Fass E, Shorer
H, Gil L and Elazar Z: Reactive oxygen species are essential for
autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4. EMBO J.
26:1749–1760. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wu Y, Meitzler JL, Antony S, Juhasz A, Lu
J, Jiang G, Liu H, Hollingshead M, Haines DC, Butcher D, et al:
Dual oxidase 2 and pancreatic adenocarcinoma: IFN-γ-mediated dual
oxidase 2 overexpression results in H2O2-induced, ERK-associated
up-regulation of HIF-1α and VEGF-A. Oncotarget. 7:68412–68433.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Szatrowski TP and Nathan CF: Production of
large amounts of hydrogen peroxide by human tumor cells. Cancer
Res. 51:794–798. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Gloire G, Legrand-Poels S and Piette J:
NF-kappaB activation by reactive oxygen species: Fifteen years
later. Biochem Pharmacol. 72:1493–1505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Jia J, Ye T, Cui P, Hua Q, Zeng H and Zhao
D: AP-1 transcription factor mediates VEGF-induced endothelial cell
migration and proliferation. Microvasc Res. 105:103–108. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Liu JP: Studies of the molecular
mechanisms in the regulation of telomerase activity. FASEB J.
13:2091–2104. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Reth M: Hydrogen peroxide as second
messenger in lymphocyte activation. Nat Immunol. 3:1129–1134. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kobayashi CI and Suda T: Regulation of
reactive oxygen species in stem cells and cancer stem cells. J Cell
Physiol. 227:421–430. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Spadafora C: Endogenous reverse
transcriptase: A mediator of cell proliferation and
differentiation. Cytogenet Genome Res. 105:346–350. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bernfield M, Götte M, Park PW, Reizes O,
Fitzgerald ML, Lincecum J and Zako M: Functions of cell surface
heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu Rev Biochem. 68:729–777. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Bendas G and Borsig L: Cancer cell
adhesion and metastasis: Selectins, integrins, and the inhibitory
potential of heparins. Int J Cell Biol. 2012:6767312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Knelson EH, Nee JC and Blobe GC: Heparan
sulfate signaling in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. 39:277–288. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Knelson EH, Gaviglio AL, Nee JC, Starr MD,
Nixon AB, Marcus SG and Blobe GC: Stromal heparan sulfate
differentiates neuroblasts to suppress neuroblastoma growth. J Clin
Invest. 124:3016–3031. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Creighton CJ, Li X, Landis M, Dixon JM,
Neumeister VM, Sjolund A, Rimm DL, Wong H, Rodriguez A,
Herschkowitz JI, et al: Residual breast cancers after conventional
therapy display mesenchymal as well as tumor-initiating features.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:13820–13825. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ji P, Zhang Y, Wang SJ, Ge HL, Zhao GP, Xu
YC and Wang Y: CD44hiCD24lo mammosphere-forming cells from primary
breast cancer display resistance to multiple chemotherapeutic
drugs. Oncol Rep. 35:3293–3302. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|