|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yu LX and Schwabe RF: The gut microbiome
and liver cancer: Mechanisms and clinical translation. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14:527–539. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lau WY and Lai EC: Hepatocellular
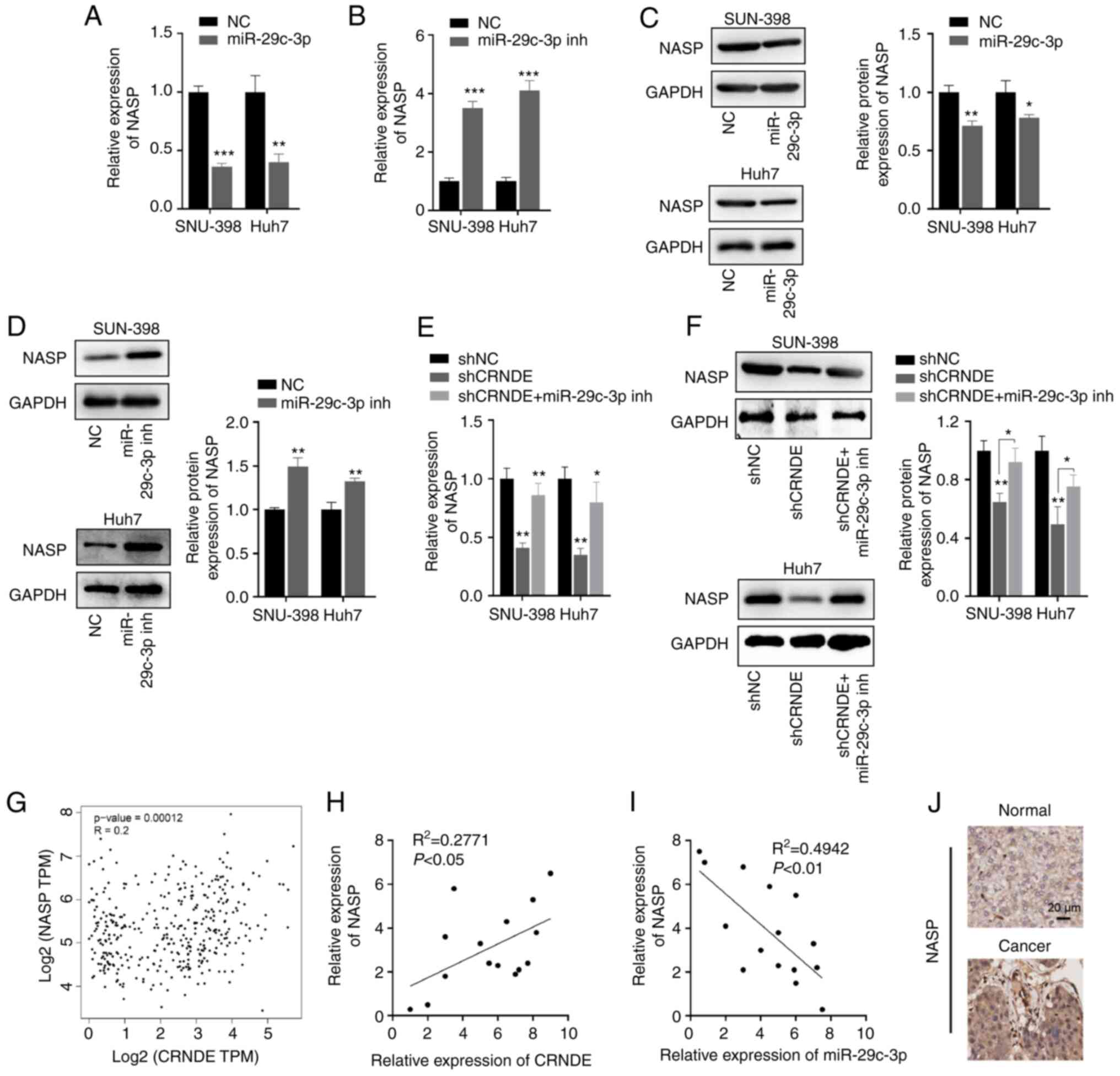
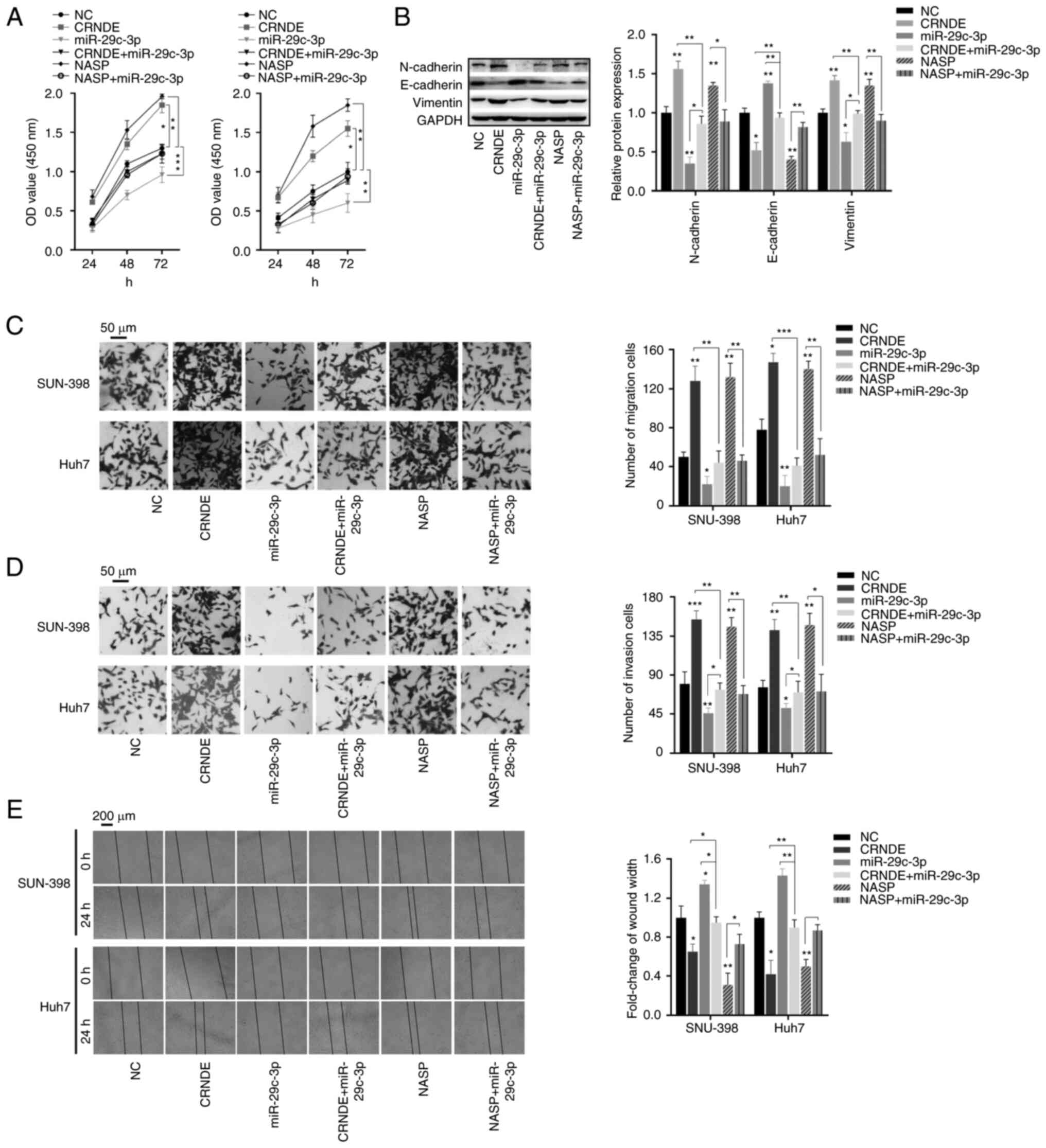
carcinoma: Current management and recent advances. Hepatobiliary
Pancreat Dis Int. 7:237–257. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Portolani N, Coniglio A, Ghidoni S,
Giovanelli M, Benetti A, Tiberio GA and Giulini SM: Early and late
recurrence after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma:
Prognostic and therapeutic implications. Ann Surg. 243:229–235.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kulik L and El-Serag HB: Epidemiology and
management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
156:477–491.e1. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Long
non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet.
10:155–159. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zeng Z, Dong J, Li Y, Dong Z, Liu Z, Huang
J, Wang Y, Zhen Y and Lu Y: The expression level and clinical
significance of lncRNA X91348 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Artif
Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47:3067–3071. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang MH, Zhao L, Wang L, Ou-Yang W, Hu SS,
Li WL, Ai ML, Wang YQ, Han Y, Li TT, et al: Nuclear lncRNA HOXD-AS1
suppresses colorectal carcinoma growth and metastasis via
inhibiting HOXD3-induced integrin β3 transcriptional activating and
MAPK/AKT signalling. Mol Cancer. 18:312019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mu M, Niu W, Zhang X, Hu S and Niu C:
LncRNA BCYRN1 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis by competitively
binding with miR-619-5p to regulate CUEDC2 expression and the
PTEN/AKT/p21 pathway. Oncogene. 39:6879–6892. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li H, Jia J, Yang L, Chu J, Sheng J, Wang
C, Meng W, Jia Z, Yin H, Wan J and He F: LncRNA MIR205HG drives
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by regulating
miR-214/SOX4 axis. Onco Targets Ther. 13:13097–13109. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Z, Zhou W, Lin C, Wang X, Zhang X,
Zhang Y, Yang R, Chen W and Cao W: Dysregulation of FOXD2-AS1
promotes cell proliferation and migration and predicts poor
prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma: A study based on TCGA
data. Aging (Albany NY). 13:2379–2396. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kan Z, Zheng H, Liu X, Li S, Barber TD,
Gong Z, Gao H, Hao K, Willard MD, Xu J, et al: Whole-genome
sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Genome Res. 23:1422–1433. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Lu JH, Wu QN, Jin Y, Wang DS, Chen
YX, Liu J, Luo XJ, Meng Q, Pu HY, et al: LncRNA LINRIS stabilizes
IGF2BP2 and promotes the aerobic glycolysis in colorectal cancer.
Mol Cancer. 18:1742019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Z, Hou P, Fan D, Dong M, Ma M, Li H,
Yao R, Li Y, Wang G, Geng P, et al: The degradation of EZH2
mediated by lncRNA ANCR attenuated the invasion and metastasis of
breast cancer. Cell Death Differ. 24:59–71. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Han P, Li JW, Zhang BM, Lv JC, Li YM, Gu
XY, Yu ZW, Jia YH, Bai XF, Li L, et al: The lncRNA CRNDE promotes
colorectal cancer cell proliferation and chemoresistance via
miR-181a-5p-mediated regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol
Cancer. 16:92017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang F, Wang H, Yu J, Yao X, Yang S, Li
W, Xu L and Zhao L: LncRNA CRNDE attenuates chemoresistance in
gastric cancer via SRSF6-regulated alternative splicing of PICALM.
Mol Cancer. 20:62021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen C, Huang Z, Mo X, Song Y, Li X, Li X
and Zhang M: The circular RNA 001971/miR-29c-3p axis modulates
colorectal cancer growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis through
VEGFA. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:912020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu H, Zhang W, Wu Z, Liu Y, Shi Y, Gong J,
Shen W and Liu C: miR-29c-3p regulates DNMT3B and LATS1 methylation
to inhibit tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell
Death Dis. 10:482019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu B, Chen X, Li J, Gu Q, Zhu Z, Li C, Su
L and Liu B: microRNA-29c inhibits cell proliferation by targeting
NASP in human gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 17:1092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ali-Fehmi R, Chatterjee M, Ionan A, Levin
NK, Arabi H, Bandyopadhyay S, Shah JP, Bryant CS, Hewitt SM, O'Rand
MG, et al: Analysis of the expression of human tumor antigens in
ovarian cancer tissues. Cancer Biomark. 6:33–48. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kang X, Feng Y, Gan Z, Zeng S, Guo X, Chen
X, Zhang Y, Wang C, Liu K, Chen X, et al: NASP antagonize chromatin
accessibility through maintaining histone H3K9me1 in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1864:3438–3448.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang L, Cho KB, Li Y, Tao G, Xie Z and Guo
B: Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-mediated competing endogenous RNA
networks provide novel potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets
for colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 20:57582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chan JJ and Tay Y: Noncoding RNA:RNA
regulatory networks in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 19:13102018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
He Y, Meng XM, Huang C, Wu BM, Zhang L, Lv
XW and Li J: Long noncoding RNAs: Novel insights into hepatocelluar
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 344:20–27. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hu M, Fu Q, Jing C, Zhang X, Qin T and Pan
Y: LncRNA HOTAIR knockdown inhibits glycolysis by regulating
miR-130a-3p/HIF1A in hepatocellular carcinoma under hypoxia. Biomed
Pharmacother. 125:1097032020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kang CL, Qi B, Cai QQ, Fu LS, Yang Y, Tang
C, Zhu P, Chen QW, Pan J, Chen MH and Wu XZ: LncRNA AY promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by stimulating ITGAV
transcription. Theranostics. 9:4421–4436. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhong JH, Xiang X, Wang YY, Liu X, Qi LN,
Luo CP, Wei WE, You XM, Ma L, Xiang BD and Li LQ: The lncRNA SNHG16
affects prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating p62
expression. J Cell Physiol. 235:1090–1102. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Y, He L, Du Y, Zhu P, Huang G, Luo J,
Yan X, Ye B, Li C, Xia P, et al: The long noncoding RNA lncTCF7
promotes self-renewal of human liver cancer stem cells through
activation of Wnt signaling. Cell Stem Cell. 16:413–425. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang G, Pan J, Zhang L, Wei Y and Wang C:
Long non-coding RNA CRNDE sponges miR-384 to promote proliferation
and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells through upregulating
IRS1. Cell Prolif. 50:e123892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ji D, Jiang C, Zhang L, Liang N, Jiang T,
Yang B and Liang H: LncRNA CRNDE promotes hepatocellular carcinoma
cell proliferation, invasion, and migration through regulating
miR-203/BCAT1 axis. J Cell Physiol. 234:6548–6560. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zheng J, Liu X, Wang P, Xue Y, Ma J, Qu C
and Liu Y: CRNDE promotes malignant progression of Glioma by
attenuating miR-384/PIWIL4/STAT3 axis. Mol Ther. 24:1199–1215.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lou W, Ding B, Zhong G, Yao J, Fan W and
Fu P: RP11-480I12.5-004 promotes growth and tumorigenesis of breast
cancer by relieving miR-29c-3p-mediated AKT3 and CDK6 degradation.
Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 21:916–931. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Han Y, Wu N, Jiang M, Chu Y, Wang Z, Liu
H, Cao J, Liu H, Xu B and Xie X: Long non-coding RNA MYOSLID
functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate MCL-1
expression by sponging miR-29c-3p in gastric cancer. Cell Prolif.
52:e126782019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kong F, Li L, Wang C, Zhang Q and He S:
MiR-381-3p suppresses biological characteristics of cancer in
head-neck squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting nuclear
autoantigenic sperm protein (NASP). Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
84:703–713. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|