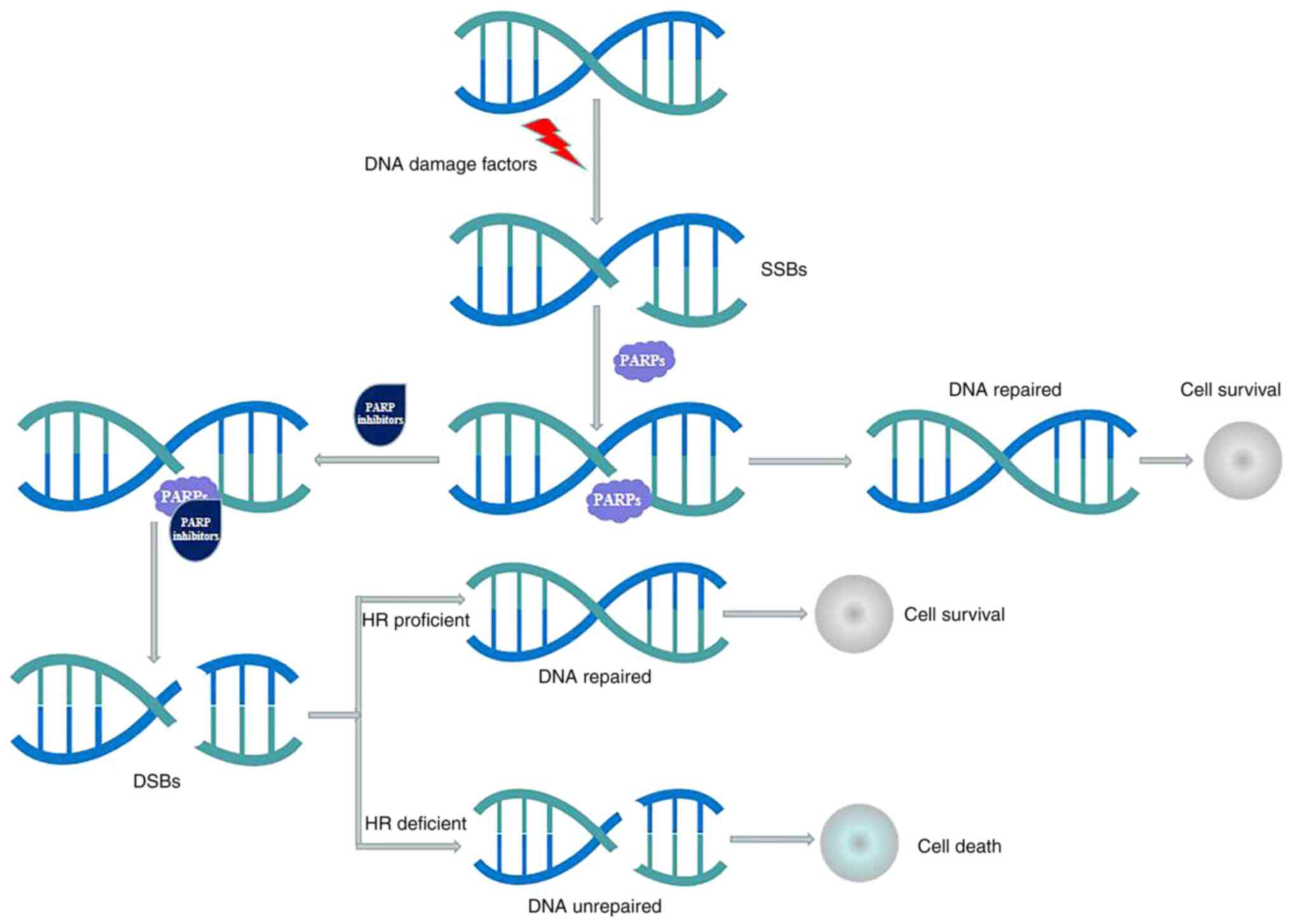
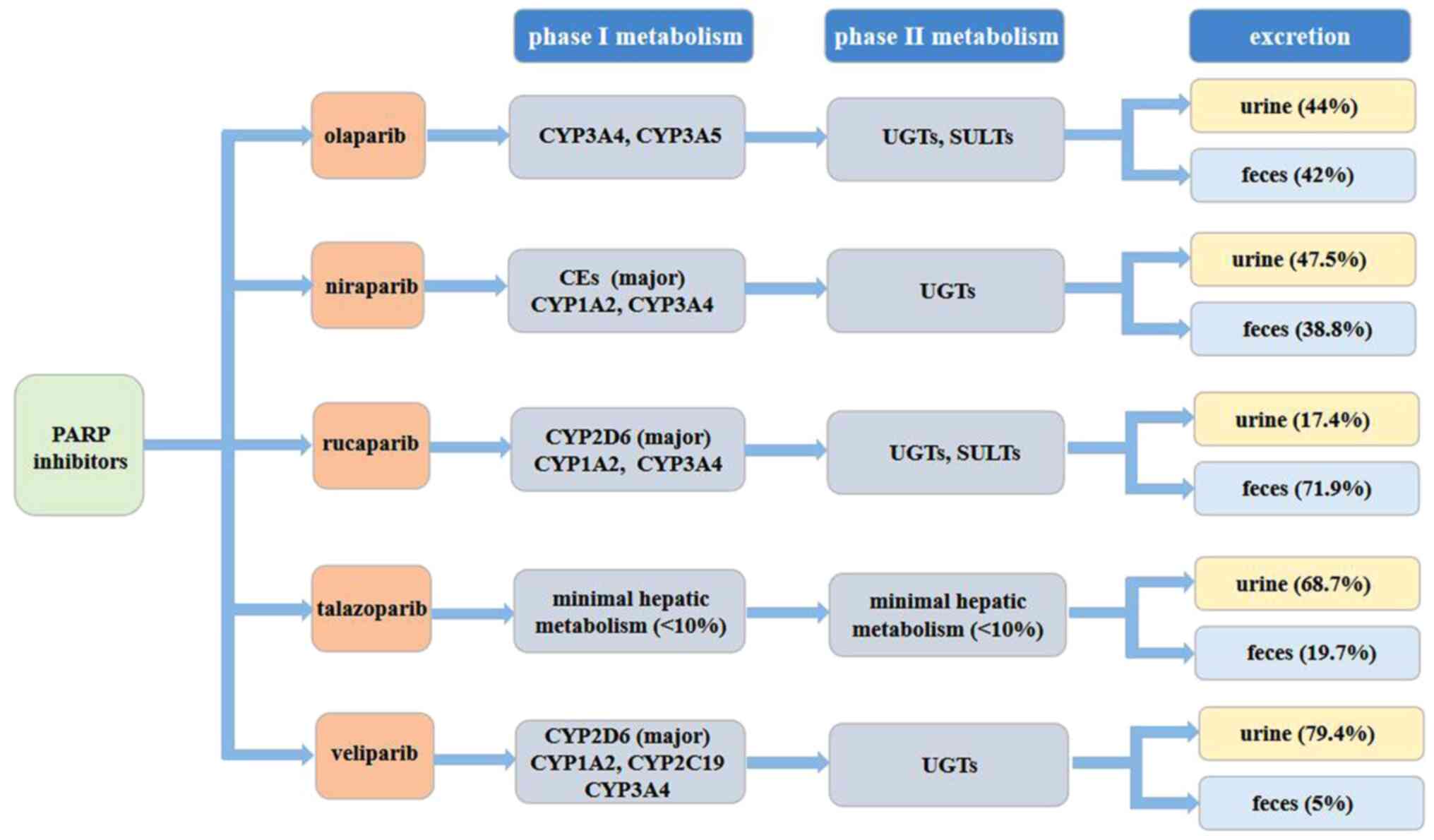
|
1
|
Liang X, Wu P, Yang Q, Xie Y, He C, Yin L,
Yin Z, Yue G, Zou Y, Li L, et al: An update of new small-molecule
anticancer drugs approved from 2015 to 2020. Eur J Med Chem.
220:1134732021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tew WP, Lacchetti C, Ellis A, Maxian K,
Banerjee S, Bookman M, Jones MB, Lee JM, Lheureux S, Liu JF, et al:
PARP inhibitors in the management of ovarian cancer: ASCO
guideline. J Clin Oncol. 38:3468–3493. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mirza MR, Coleman RL, González-Martín A,
Moore KN, Colombo N, Ray-Coquard I and Pignata S: The forefront of
ovarian cancer therapy: Update on PARP inhibitors. Ann Oncol.
31:1148–1159. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Valabrega G, Scotto G, Tuninetti V, Pani A
and Scaglione F: Differences in PARP inhibitors for the treatment
of ovarian cancer: Mechanisms of action, pharmacology, safety, and
efficacy. Int J Mol Sci. 22:42032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miller RE, Leary A, Scott CL, Serra V,
Lord CJ, Bowtell D, Chang DK, Garsed DW, Jonkers J, Ledermann JA,
et al: ESMO recommendations on predictive biomarker testing for
homologous recombination deficiency and PARP inhibitor benefit in
ovarian cancer. Ann Oncol. 31:1606–1622. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rolfo C, Swaisland H, Leunen K, Rutten A,
Soetekouw P, Slater S, Verheul HM, Fielding A, So K, Bannister W
and Dean E: Effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of olaparib
after oral dosing of the capsule formulation in patients with
advanced solid tumors. Adv Ther. 32:510–522. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dirix L, Swaisland H, Verheul HM, Rottey
S, Leunen K, Jerusalem G, Rolfo C, Nielsen D, Molife LR, Kristeleit
R, et al: Effect of itraconazole and rifampin on the
pharmacokinetics of olaparib in patients with advanced solid
tumors: Results of Two Phase I open-label studies. Clin Ther.
38:2286–2299. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiao JJ, Nowak D, Ramlau R,
Tomaszewska-Kiecana M, Wysocki PJ, Isaacson J, Beltman J, Nash E,
Kaczanowski R, Arold G and Watkins S: Evaluation of drug-drug
interactions of rucaparib and CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A, and
P-gp substrates in patients with an advanced solid tumor. Clin
Transl Sci. 12:58–65. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
van Leeuwen RW, van Gelder T, Mathijssen
RH and Jansman FG: Drug-drug interactions with tyrosine-kinase
inhibitors: A clinical perspective. Lancet Oncol. 15:e315–e326.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tannenbaum C and Sheehan NL: Understanding
and preventing drug-drug and drug-gene interactions. Expert Rev
Clin Pharmacol. 7:533–544. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
US Food and Drug Administration: Label.
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/206162s011lbl.pdfJune
25–2021
|
|
12
|
European Medicines Agency: Product
information. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/lynparza-epar-product-information_en.pdfJune
25–2021
|
|
13
|
US Food and Drug Administration Label.
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/208447s022s024lbl.pdfJune
25–2021
|
|
14
|
European Medicines Agency: Product
information. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/zejula-epar-product-information_en.pdfJune
25–2021
|
|
15
|
US Food and Drug Administration Label.
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/209115s008lbl.pdfJune
25–2021
|
|
16
|
European Medicines Agency: Product
information. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/rubraca-epar-product-information_en.pdfJune
25–2021
|
|
17
|
US Food and Drug Administration Label.
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/211651s006lbl.pdfJune
25–2021
|
|
18
|
European Medicines Agency: Product
information. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/talzenna-epar-product-information_en.pdfJune
25–2021
|
|
19
|
LoRusso PM, Li J, Burger A, Heilbrun LK,
Sausville EA, Boerner SA, Smith D, Pilat MJ, Zhang J, Tolaney SM,
et al: Phase I safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study
of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor veliparib
(ABT-888) in combination with Irinotecan in patients with advanced
solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 22:3227–3237. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mittica G, Ghisoni E, Giannone G, Genta S,
Aglietta M, Sapino A and Valabrega G: PARP inhibitors in ovarian
cancer. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 13:392–410. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li X, Delzer J, Voorman R, de Morais SM
and Lao Y: Disposition and drug-drug interaction potential of
veliparib (ABT-888), a novel and potent inhibitor of
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Drug Metab Dispos. 39:1161–1169. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Teo YL, Ho HK and Chan A:
Metabolism-related pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions with
tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Current understanding, challenges and
recommendations. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 79:241–253. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Paine MF, Hart HL, Ludington SS, Haining
RL, Rettie AE and Zeldin DC: The human intestinal cytochrome P450
‘pie’. Drug Metab Dispos. 34:880–886. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xie F, Ding X and Zhang QY: An update on
the role of intestinal cytochrome P450 enzymes in drug disposition.
Acta Pharm Sin B. 6:374–383. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Klomp F, Wenzel C, Drozdzik M and Oswald
S: Drug-drug interactions involving intestinal and Hepatic CYP1A
Enzymes. Pharmaceutics. 12:12012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
van Herwaarden AE, van Waterschoot RA and
Schinkel AH: How important is intestinal cytochrome P450 3A
metabolism? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 30:223–227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Scripture CD and Figg WD: Drug
interactions in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:546–558. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Manikandan P and Nagini S: Cytochrome P450
structure, function and clinical significance: A review. Curr Drug
Targets. 19:38–54. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Almazroo OA, Miah MK and Venkataramanan R:
Drug metabolism in the liver. Clin Liver Dis. 21:1–20. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
An S, Jeon M, Kennedy EL and Kyoung M:
Phase-separated condensates of metabolic complexes in living cells:
Purinosome and glucosome. Methods Enzymol. 628:1–17. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Roberts AG and Gibbs ME: Mechanisms and
the clinical relevance of complex drug-drug interactions. Clin
Pharmacol. 10:123–134. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hussaarts KGAM, Veerman GDM, Jansman FGA,
van Gelder T, Mathijssen RHJ and van Leeuwen RWF: Clinically
relevant drug interactions with multikinase inhibitors: A review.
Ther Adv Med Oncol. 11:17588359188183472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McCormick A, Swaisland H, Reddy VP,
Learoyd M and Scarfe G: In vitro evaluation of the inhibition and
induction potential of olaparib, a potent poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase inhibitor, on cytochrome P450. Xenobiotica. 48:555–564.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pilla Reddy V, Bui K, Scarfe G, Zhou D and
Learoyd M: Physiologically based Pharmacokinetic modeling for
olaparib dosing recommendations: Bridging formulations, drug
interactions, and patient populations. Clin Pharmacol Ther.
105:229–241. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Scott LJ: Niraparib: First global
approval. Drugs. 77:1029–1034. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
van Andel L, Zhang Z, Lu S, Kansra V,
Agarwal S, Hughes L, Tibben MM, Gebretensae A, Lucas L, Hillebrand
MJX, et al: Human mass balance study and metabolite profiling of
14C-niraparib, a novel poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase
(PARP)-1 and PARP-2 inhibitor, in patients with advanced cancer.
Invest New Drugs. 35:751–765. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liao M, Watkins S, Nash E, Isaacson J,
Etter J, Beltman J, Fan R, Shen L, Mutlib A, Kemeny V, et al:
Evaluation of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion
of [(14)C]-rucaparib, a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, in
patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs. 38:765–775.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liao M, Jaw-Tsai S, Beltman J, Simmons AD,
Harding TC and Xiao JJ: Evaluation of in vitro absorption,
distribution, metabolism, and excretion and assessment of drug-drug
interaction of rucaparib, an orally potent poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase inhibitor. Xenobiotica. 50:1032–1042. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Syed YY: Rucaparib: First global approval.
Drugs. 77:585–592. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hoy SM: Talazoparib: First global
approval. Drugs. 78:1939–1946. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Niu J, Scheuerell C, Mehrotra S, Karan S,
Puhalla S, Kiesel BF, Ji J, Chu E, Gopalakrishnan M, Ivaturi V, et
al: Parent-metabolite pharmacokinetic modeling and pharmacodynamics
of veliparib (ABT-888), a PARP inhibitor, in patients with BRCA
1/2-mutated cancer or PARP-sensitive tumor types. J Clin Pharmacol.
57:977–987. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yu J, Petrie ID, Levy RH and
Ragueneau-Majlessi I: Mechanisms and clinical significance of
pharmacokinetic-based drug-drug interactions with drugs approved by
the U.S. Food and drug administration in 2017. Drug Metab Dispos.
47:135–144. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Preskorn SH: Drug-drug interactions (DDIs)
in psychiatric practice, part 9: Interactions mediated by
drug-metabolizing cytochrome P450 enzymes. J Psychiatr Pract.
26:126–134. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mouly S, Lloret-Linares C, Sellier PO,
Sene D and Bergmann JF: Is the clinical relevance of drug-food and
drug-herb interactions limited to grapefruit juice and Saint-John's
Wort? Pharmacol Res. 118:82–92. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Thelen K and Dressman JB: Cytochrome
P450-mediated metabolism in the human gut wall. J Pharm Pharmacol.
61:541–558. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Rowland A, Miners JO and Mackenzie PI: The
UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: Their role in drug metabolism and
detoxification. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:1121–1132. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Miners JO, Chau N, Rowland A, Burns K,
McKinnon RA, Mackenzie PI, Tucker GT, Knights KM and Kichenadasse
G: Inhibition of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes by
lapatinib, pazopanib, regorafenib and sorafenib: Implications for
hyperbilirubinemia. Biochem Pharmacol. 129:85–95. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Miners JO, Rowland A, Novak JJ, Lapham K
and Goosen TC: Evidence-based strategies for the characterisation
of human drug and chemical glucuronidation in vitro and
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase reaction phenotyping. Pharmacol Ther.
218:1076892021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
US Food and Drug Administration: Guidance
for industry. drug interaction studies-study design, data analysis,
implications for dosing, and labelling recommendations. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformatiom/Guidances/default/htmJune
5–2021.
|
|
50
|
European Medicines Agency: Guideline on
the investigation of drug interactions. ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guideline/2012/07/WC500129606.pdfJune
5–2021
|
|
51
|
Cheng X, Lv X, Qu H, Li D, Hu M, Guo W, Ge
G and Dong R: Comparison of the inhibition potentials of icotinib
and erlotinib against human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1. Acta
Pharm Sin B. 7:657–664. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang Z, Wang X, Wang Z, Jia Y, Feng Y,
Jiang L, Xia Y, Cao J and Liu Y: In vitro inhibition of human
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A1 by osimertinib, and
prediction of in vivo drug-drug interactions. Toxicol Lett.
348:10–17. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Korprasertthaworn P, Chau N, Nair PC,
Rowland A and Miners JO: Inhibition of human
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes by kinase inhibitors:
Effects of dabrafenib, ibrutinib, nintedanib, trametinib and BIBF
1202. Biochem Pharmacol. 169:1136162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Min JS and Bae SK: Prediction of drug-drug
interaction potential using physiologically based pharmacokinetic
modeling. Arch Pharm Res. 40:1356–1379. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Falcão A, Fuseau E, Nunes T, Almeida L and
Soares-da-Silva P: Pharmacokinetics, drug interactions and
exposure-response relationship of eslicarbazepine acetate in adult
patients with partial-onset seizures: Population pharmacokinetic
and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analyses. CNS Drugs. 26:79–91.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zakrzewski-Jakubiak H, Doan J, Lamoureux
P, Singh D, Turgeon J and Tannenbaum C: Detection and prevention of
drug-drug interactions in the hospitalized elderly: Utility of new
cytochrome p450-based software. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother.
9:461–470. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Roblek T, Vaupotic T, Mrhar A and Lainscak
M: Drug-drug interaction software in clinical practice: A
systematic review. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 71:131–142. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Solassol I, Pinguet F and Quantin X: FDA-
and EMA-approved tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced
EGFR-Mutated Non-Small cell lung cancer: Safety, tolerability,
plasma concentration monitoring, and management. Biomolecules.
9:6682019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Janssen JM, Dorlo TPC, Steeghs N, Beijnen
JH, Hanff LM, van Eijkelenburg NKA, van der Lugt J, Zwaan CM and
Huitema ADR: Pharmacokinetic targets for therapeutic drug
monitoring of small molecule kinase inhibitors in pediatric
oncology. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 108:494–505. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Di Francia R, De Monaco A, Saggese M,
Iaccarino G, Crisci S, Frigeri F, De Filippi R, Berretta M and
Pinto A: Pharmacological profile and pharmacogenomics of
anti-cancer drugs used for targeted therapy. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 18:499–511. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cardoso E, Csajka C, Schneider MP and
Widmer N: Effect of adherence on pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic
relationships of oral targeted anticancer drugs. Clin
Pharmacokinet. 57:1–6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|