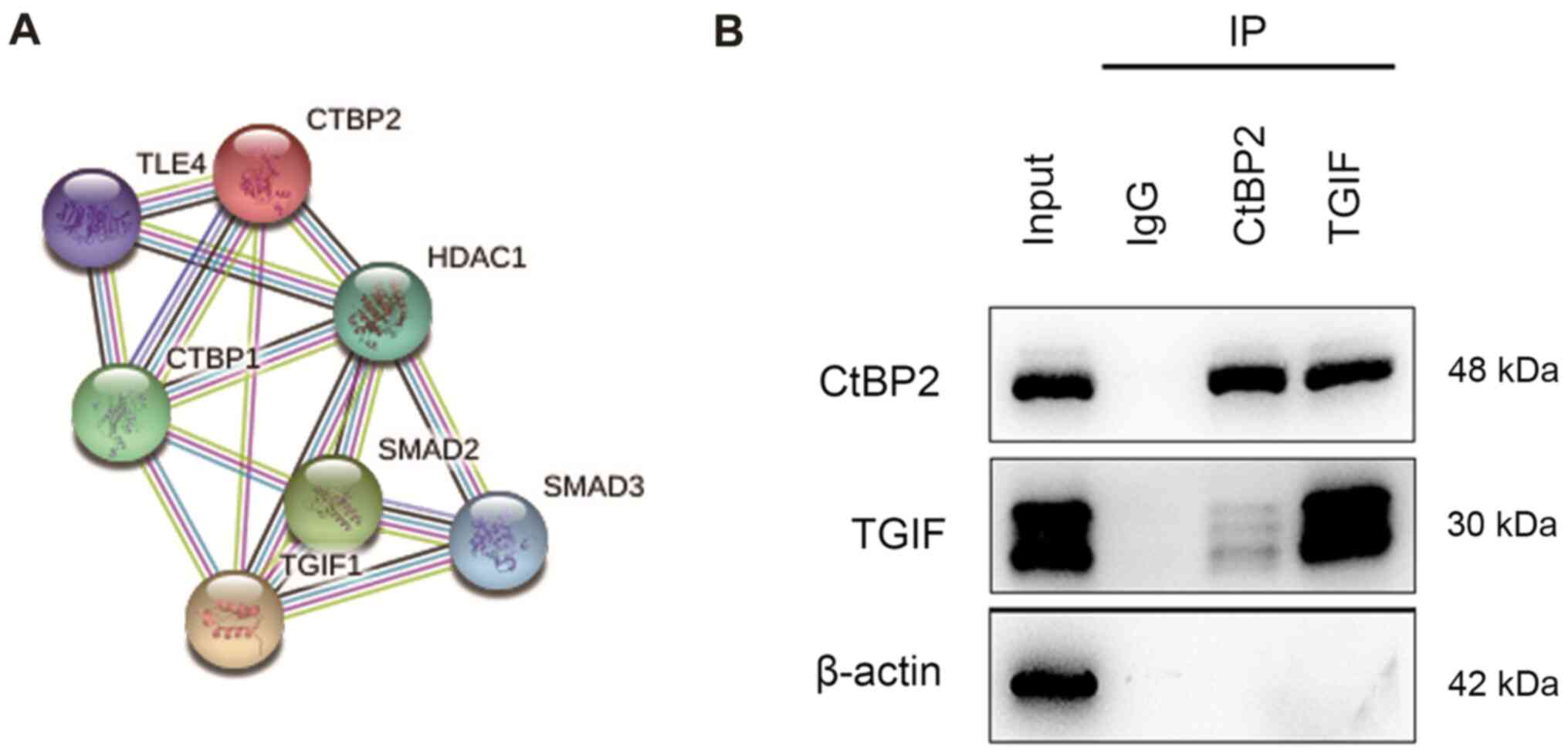
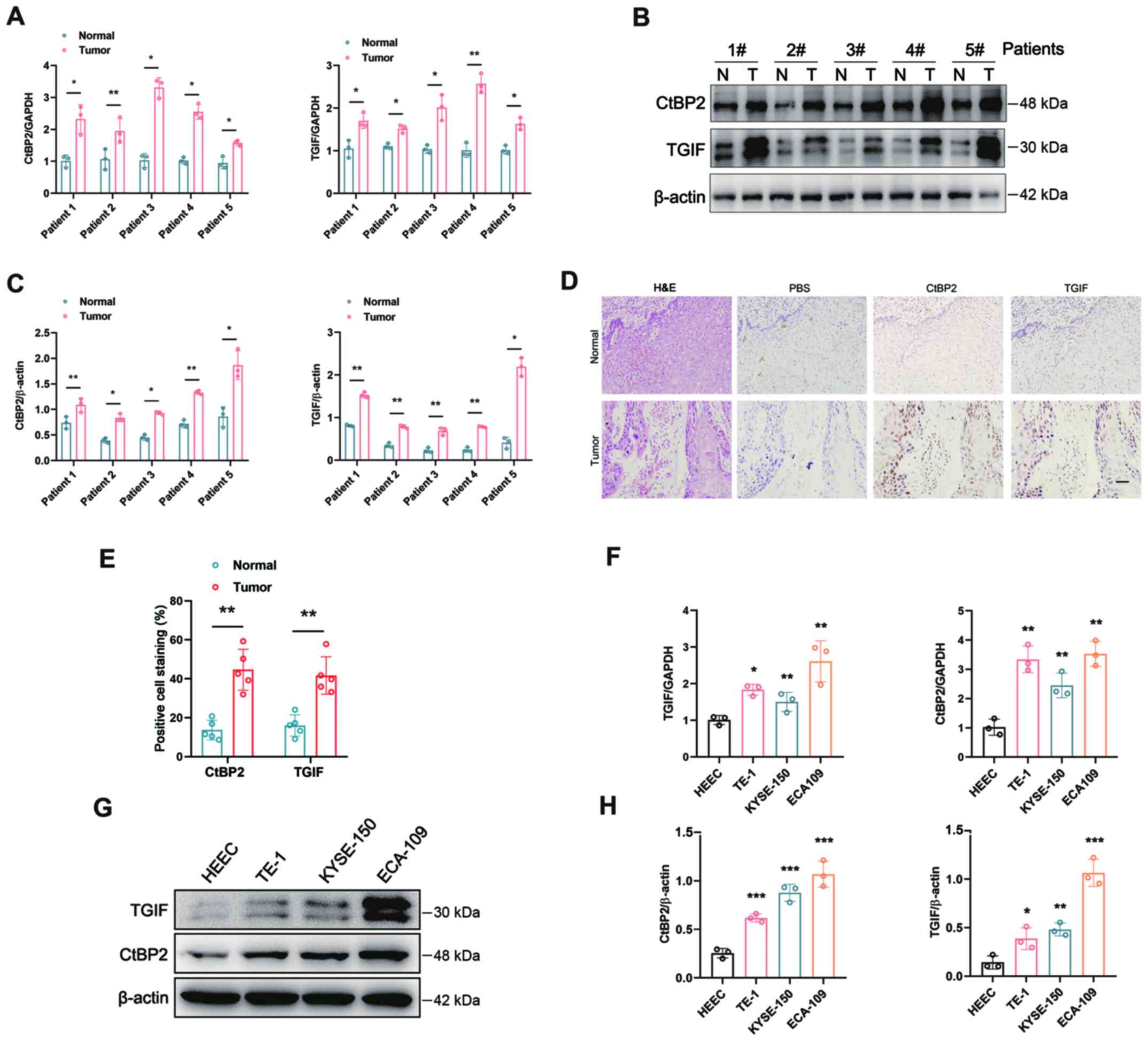
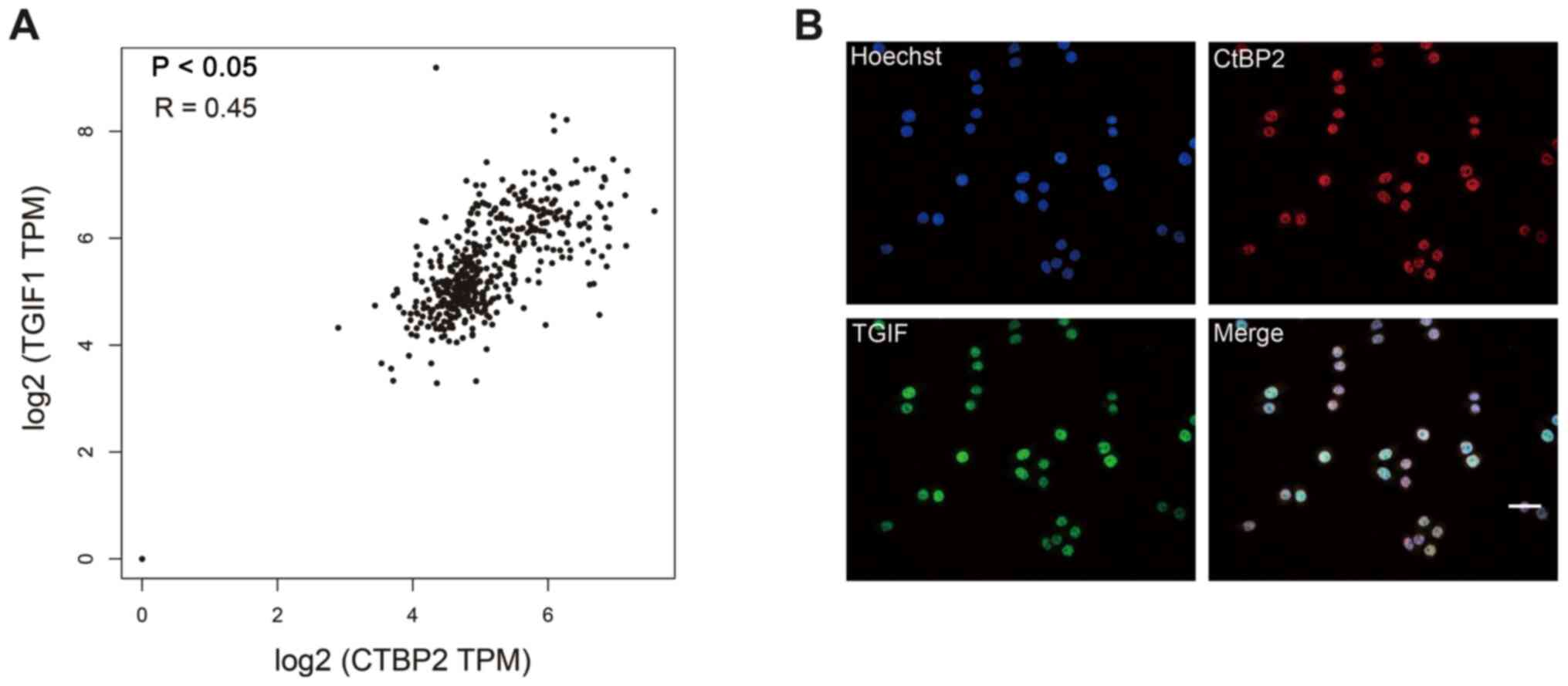
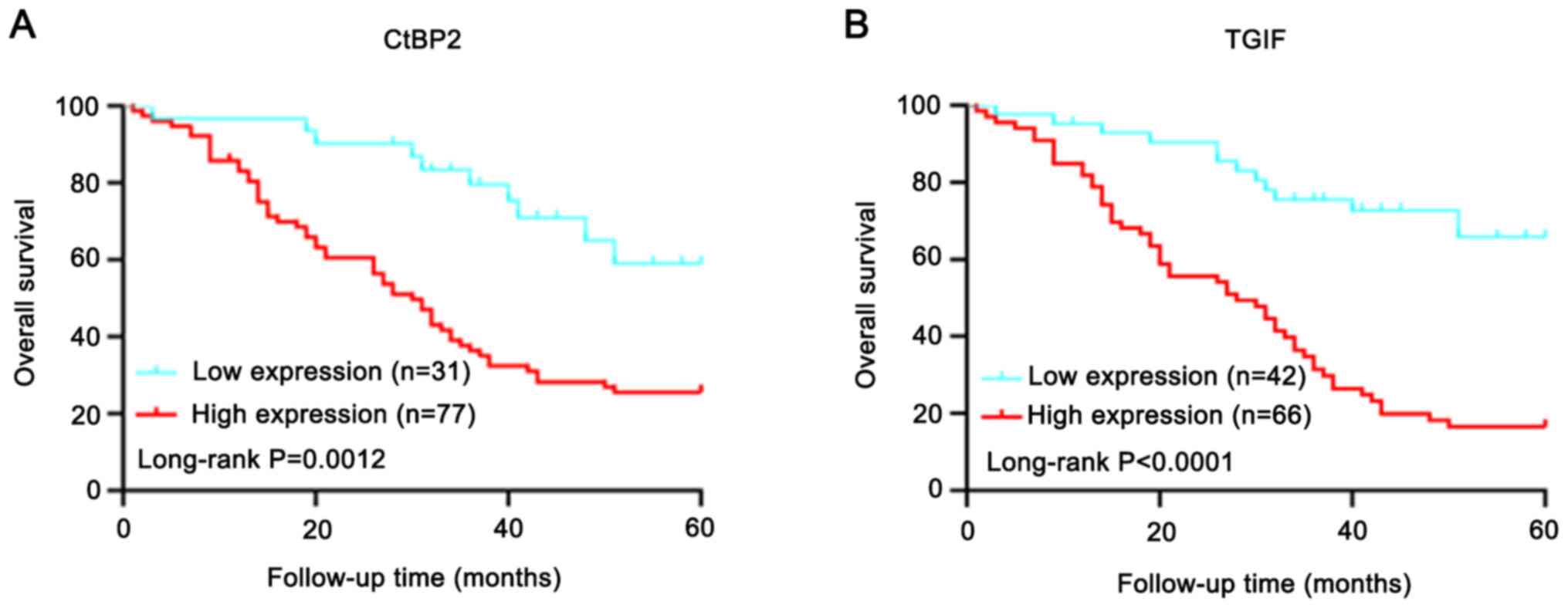
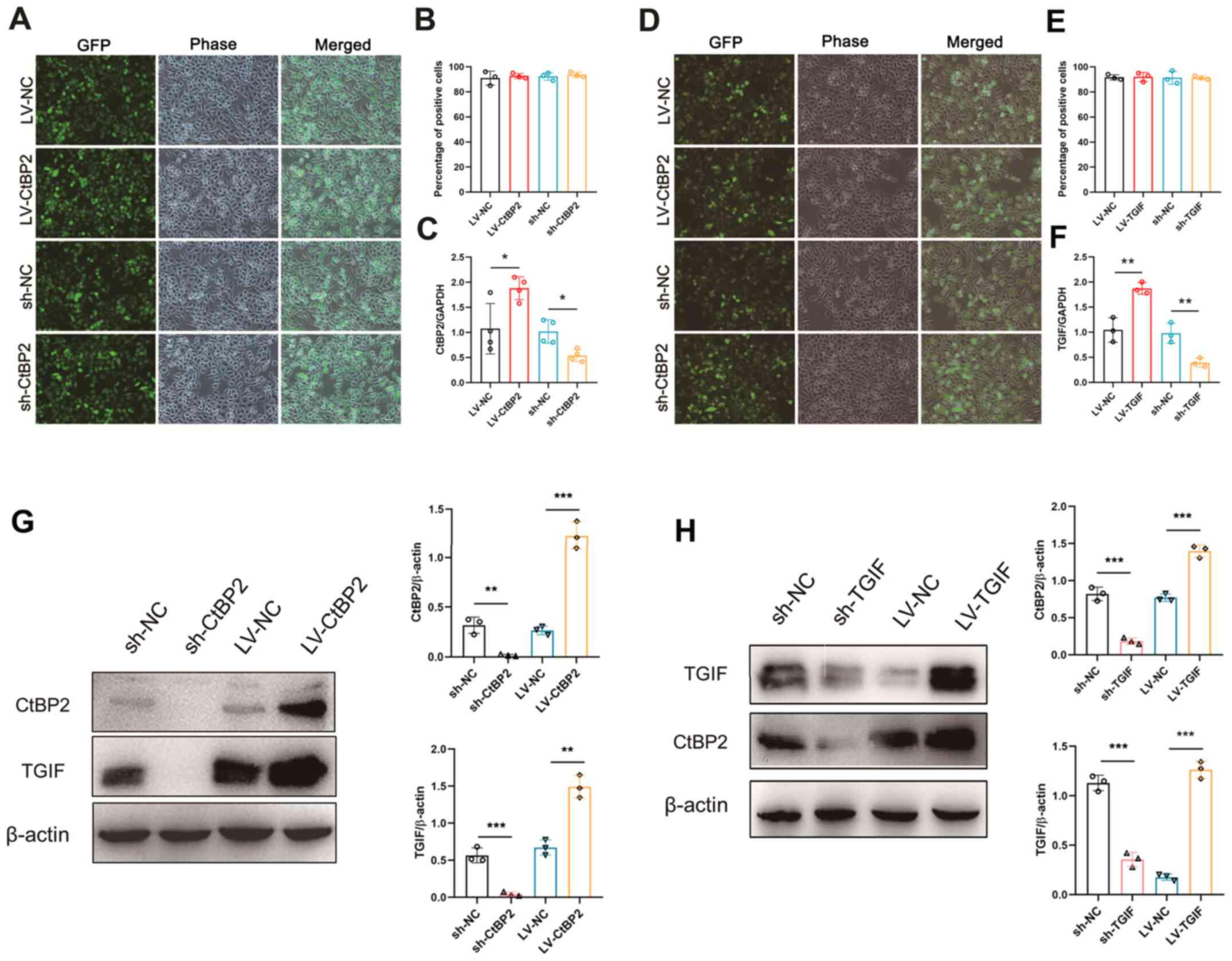
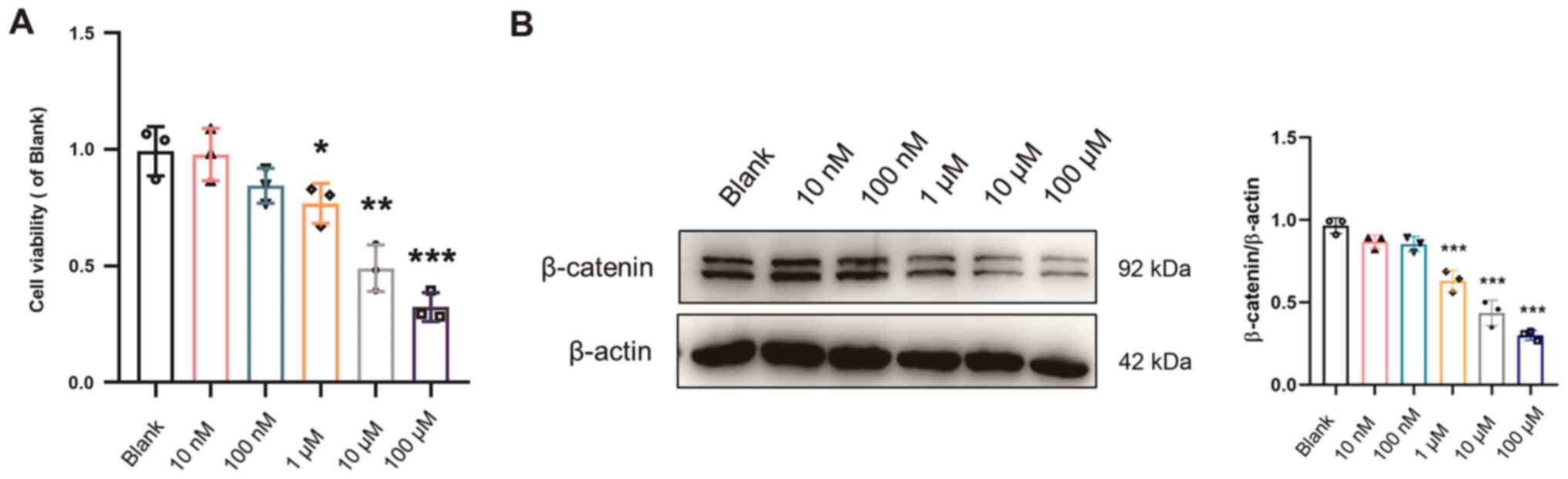
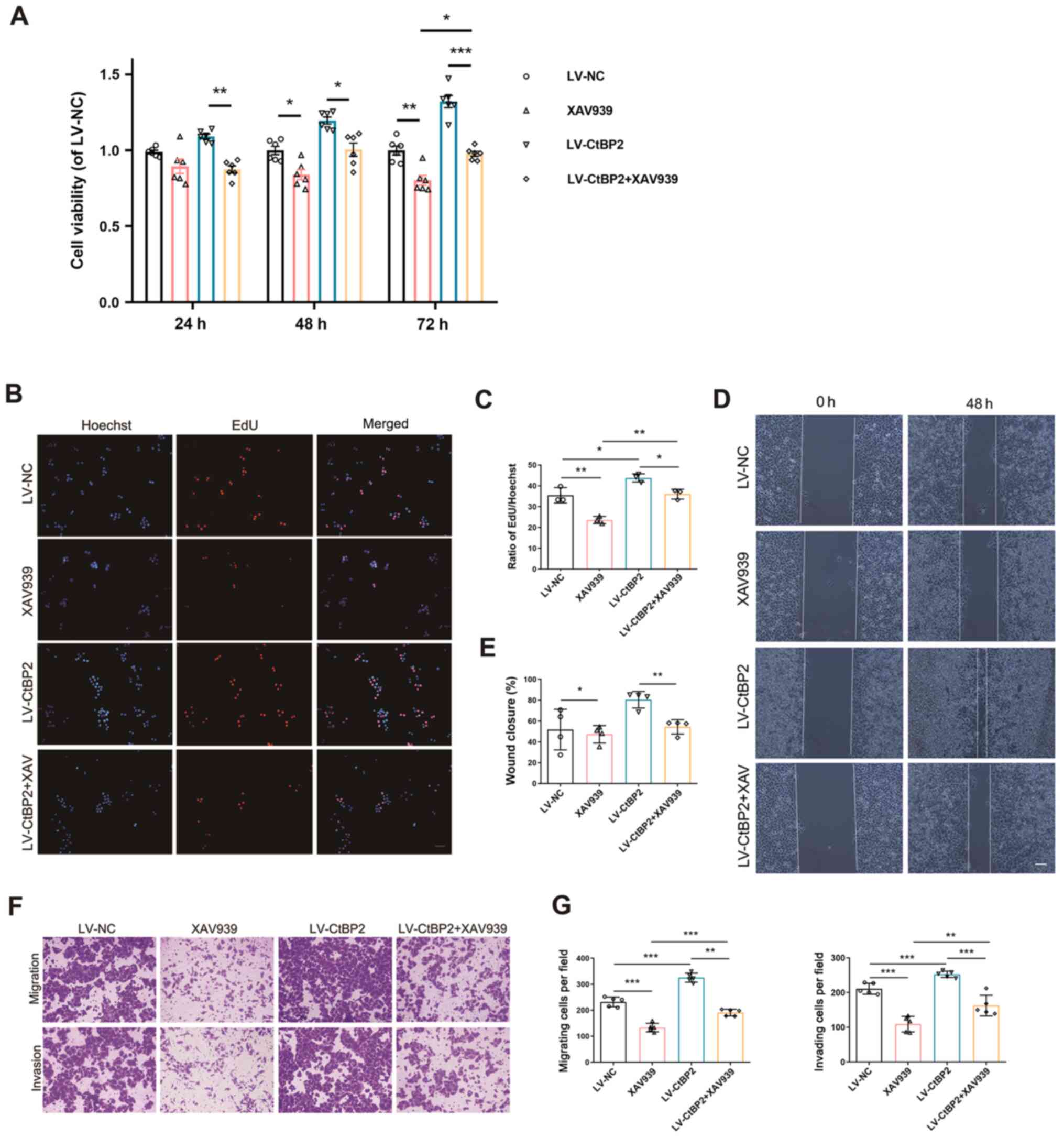
|
1
|
Lin Y, Totsuka Y, Shan B, Wang C, Wei W,
Qiao Y, Kikuchi S, Inoue M, Tanaka H and He Y: Esophageal cancer in
high-risk areas of China: Research progress and challenges. Ann
Epidemiol. 27:215–221. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yu C, Tang H, Guo Y, Bian Z, Yang L, Chen
Y, Tang A, Zhou X, Yang X, Chen J, et al China Kadoorie Biobank
Collaborative Group, : Hot tea consumption and its interactions
with alcohol and tobacco use on the risk for esophageal cancer: a
population-based cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 168:489–497. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin Y, Totsuka Y, He Y, Kikuchi S, Qiao Y,
Ueda J, Wei W, Inoue M and Tanaka H: Epidemiology of esophageal
cancer in Japan and China. J Epidemiol. 23:233–242. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang S, Lin S, Li N, Deng Y, Wang M, Xiang
D, Xiang G, Wang S, Ye X, Zheng Y, et al: Burden, trends, and risk
factors of esophageal cancer in China from 1990 to 2017: An
up-to-date overview and comparison with those in Japan and South
Korea. J Hematol Oncol. 13:1462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Anandavadivelan P and Lagergren P:
Cachexia in patients with oesophageal cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
13:185–198. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gao QY and Fang JY: Early esophageal
cancer screening in China. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
29:885–893. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen W, Li H, Zheng R, Ren J, Shi J, Cao
M, Sun D, Sun X, Cao X, Zhou J, et al: An initial screening
strategy based on epidemiologic information in esophageal cancer
screening: A prospective evaluation in a community-based cancer
screening cohort in rural China. Gastrointest Endosc.
93:110–118.e2. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen W, Li H, Ren J, Zheng R, Shi J, Li J,
Cao M, Sun D, He S, Sun X, et al: Selection of high-risk
individuals for esophageal cancer screening: A prediction model of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma based on a multicenter screening
cohort in rural China. Int J Cancer. 148:329–339. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu M, He Z, Guo C, Xu R, Li F, Ning T,
Pan Y, Li Y, Ding H, Zheng L, et al: Effectiveness of intensive
endoscopic screening for esophageal cancer in China: a
community-based study. Am J Epidemiol. 188:776–784. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kelly RJ: Emerging multimodality
approaches to treat localized esophageal cancer. J Natl Compr Canc
Netw. 17:1009–1014. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Borggreve AS, Kingma BF, Domrachev SA,
Koshkin MA, Ruurda JP, van Hillegersberg R, Takeda FR and Goense L:
Surgical treatment of esophageal cancer in the era of multimodality
management. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1434:192–209. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen L, Wang L, Qin J and Wei DS: CtBP2
interacts with ZBTB18 to promote malignancy of glioblastoma. Life
Sci. 262:1184772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang H, Xiao Z, Zheng J, Wu J, Hu XL, Yang
X and Shen Q: ZEB1 represses neural differentiation and cooperates
with CTBP2 to dynamically regulate cell migration during neocortex
development. Cell Rep. 27:2335–2353.e6. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao LJ, Subramanian T, Vijayalingam S and
Chinnadurai G: PLDLS-dependent interaction of E1A with CtBP:
Regulation of CtBP nuclear localization and transcriptional
functions. Oncogene. 26:7544–7551. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jecrois AM, Dcona MM, Deng X,
Bandyopadhyay D, Grossman SR, Schiffer CA and Royer WE Jr: Cryo-EM
structure of CtBP2 confirms tetrameric architecture. Structure.
29:310–319.e5. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma Y, Sekiya M, Kainoh K, Matsuda T,
Iwasaki H, Osaki Y, Sugano Y, Suzuki H, Takeuchi Y, Miyamoto T, et
al: Transcriptional co-repressor CtBP2 orchestrates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through a novel transcriptional
holocomplex with OCT1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 523:354–360.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang DP, Gu LL, Xue Q, Chen H and Mao GX:
CtBP2 promotes proliferation and reduces drug sensitivity in
non-small cell lung cancer via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Neoplasma. 65:888–897. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thio SS, Bonventre JV and Hsu SI: The
CtBP2 co-repressor is regulated by NADH-dependent dimerization and
possesses a novel N-terminal repression domain. Nucleic Acids Res.
32:1836–1847. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao Z, Hao D, Wang L, Li J, Meng Y, Li P,
Wang Y, Zhang C, Zhou H, Gardner K, et al: CtBP promotes metastasis
of breast cancer through repressing cholesterol and activating
TGF-β signaling. Oncogene. 38:2076–2091. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dcona MM, Damle PK, Zarate-Perez F, Morris
BL, Nawaz Z, Dennis MJ, Deng X, Korwar S, Singh SJ, Ellis KC, et
al: Active-site tryptophan, the target of antineoplastic C-terminal
binding protein inhibitors, mediates inhibitor disruption of CtBP
oligomerization and transcription coregulatory activities. Mol
Pharmacol. 96:99–108. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Thomas G, Jacobs KB, Yeager M, Kraft P,
Wacholder S, Orr N, Yu K, Chatterjee N, Welch R, Hutchinson A, et
al: Multiple loci identified in a genome-wide association study of
prostate cancer. Nat Genet. 40:310–315. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guan C, Shi H, Wang H, Zhang J, Ni W, Chen
B, Hou S, Yang X, Shen A and Ni R: CtBP2 contributes to malignant
development of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by
regulation of p16INK4A. J Cell Biochem. 114:1343–1354. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shi H, Mao Y, Ju Q, Wu Y, Bai W, Wang P,
Zhang Y and Jiang M: C-terminal binding protein-2 mediates
cisplatin chemoresistance in esophageal cancer cells via the
inhibition of apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 53:167–176. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Y, Liu F, Mao F, Hang Q, Huang X, He
S, Wang Y, Cheng C, Wang H, Xu G, et al: Interaction with cyclin
H/cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CCNH/CDK7) stabilizes C-terminal
binding protein 2 (CtBP2) and promotes cancer cell migration. J
Biol Chem. 288:9028–9034. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shi H, Xu J, Zhao R, Wu H, Gu L and Chen
Y: FGF2 regulates proliferation, migration, and invasion of ECA109
cells through PI3K/Akt signalling pathway in vitro. Cell Biol Int.
40:524–533. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shah A, Melhuish TA, Fox TE, Frierson HF
Jr and Wotton D: TGIF transcription factors repress acetyl CoA
metabolic gene expression and promote intestinal tumor growth.
Genes Dev. 33:388–402. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang Y, Shi L, Li J, Li L, Wang H and Yang
H: Long-term cadmium exposure promoted breast cancer cell migration
and invasion by up-regulating TGIF. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf.
175:110–117. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wotton D and Taniguchi K: Functions of
TGIF homeodomain proteins and their roles in normal brain
development and holoprosencephaly. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med
Genet. 178:128–139. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nakashima H, Tsujimura K, Irie K, Ishizu
M, Pan M, Kameda T and Nakashima K: Canonical TGF-β signaling
negatively regulates neuronal morphogenesis through TGIF/Smad
complex-mediated CRMP2 suppression. J Neurosci. 38:4791–4810. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sharma A, Sinha NR, Siddiqui S and Mohan
RR: Role of 5′TG3′-interacting factors (TGIFs) in Vorinostat (HDAC
inhibitor)-mediated Corneal Fibrosis Inhibition. Mol Vis.
21:974–984. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Du R, Shen W, Liu Y, Gao W, Zhou W, Li J,
Zhao S, Chen C, Chen Y, Liu Y, et al: TGIF2 promotes the
progression of lung adenocarcinoma by bridging EGFR/RAS/ERK
signaling to cancer cell stemness. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
4:602019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu ZM, Tseng HY, Tsai HW, Su FC and Huang
HS: Transforming growth factor β-interacting factor-induced
malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma cells depends on
superoxide production from Nox4. Free Radic Biol Med. 84:54–64.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang MZ, Ferrigno O, Wang Z, Ohnishi M,
Prunier C, Levy L, Razzaque M, Horne WC, Romero D, Tzivion G, et
al: TGIF governs a feed-forward network that empowers Wnt signaling
to drive mammary tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 27:547–560. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shi H, Shi J, Zhang Y, Guan C, Zhu J, Wang
F, Xu M, Ju Q, Fang S and Jiang M: Long non-coding RNA DANCR
promotes cell proliferation, migration, invasion and resistance to
apoptosis in esophageal cancer. J Thorac Dis. 10:2573–2582. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mo Y, Wang Y, Zhang S, Xiong F, Yan Q,
Jiang X, Deng X, Wang Y, Fan C, Tang L, et al: Circular RNA
circRNF13 inhibits proliferation and metastasis of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma via SUMO2. Mol Cancer. 20:1122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45((W1)):
W98–W102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shetti D, Zhang B, Fan C, Mo C, Lee BH and
Wei K: Low dose of paclitaxel combined with XAV939 attenuates
metastasis, angiogenesis and growth in breast cancer by suppressing
Wnt signaling. Cells. 8:82019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Huang X, Zhou X, Hu Q, Sun B, Deng M, Qi X
and Lü M: Advances in esophageal cancer: A new perspective on
pathogenesis associated with long non-coding RNAs. Cancer Lett.
413:94–101. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M,
Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein
association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res.
45(D1): D362–D368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang Y, Shi L, Li J, Wang H and Yang H:
The roles of TG-interacting factor in cadmium exposure-promoted
invasion and migration of lung cancer cells. Toxicol In Vitro.
61:1046302019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang LN, Zhao L, Yan XL and Huang YH:
Loss of G3BP1 suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion of
esophageal cancer cells via Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/AKT signaling
pathways. J Cell Physiol. 234:20469–20484. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yu F, Yu C, Li F, Zuo Y, Wang Y, Yao L, Wu
C, Wang C and Ye L: Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cancers and targeted
therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:3072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|