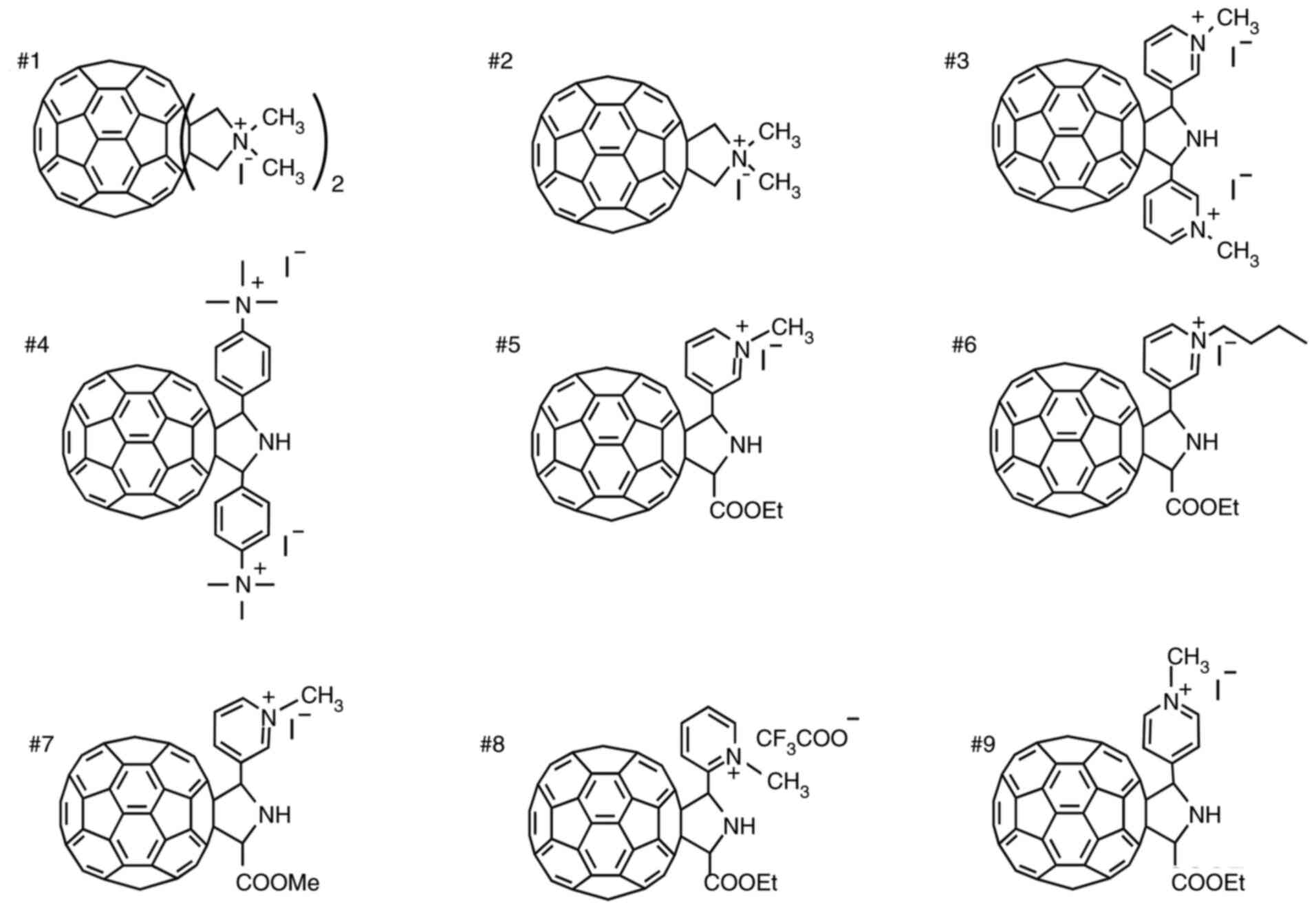
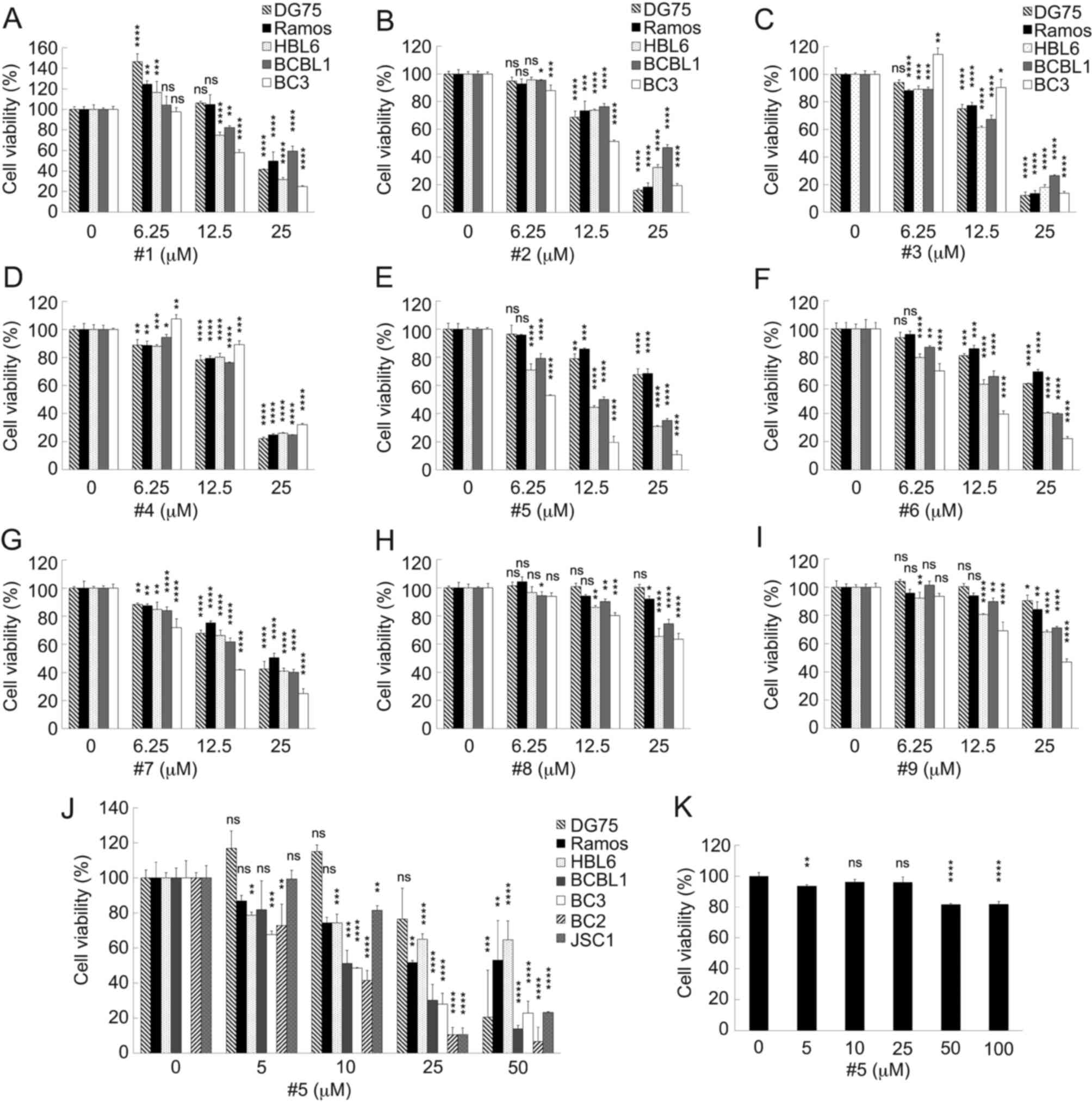
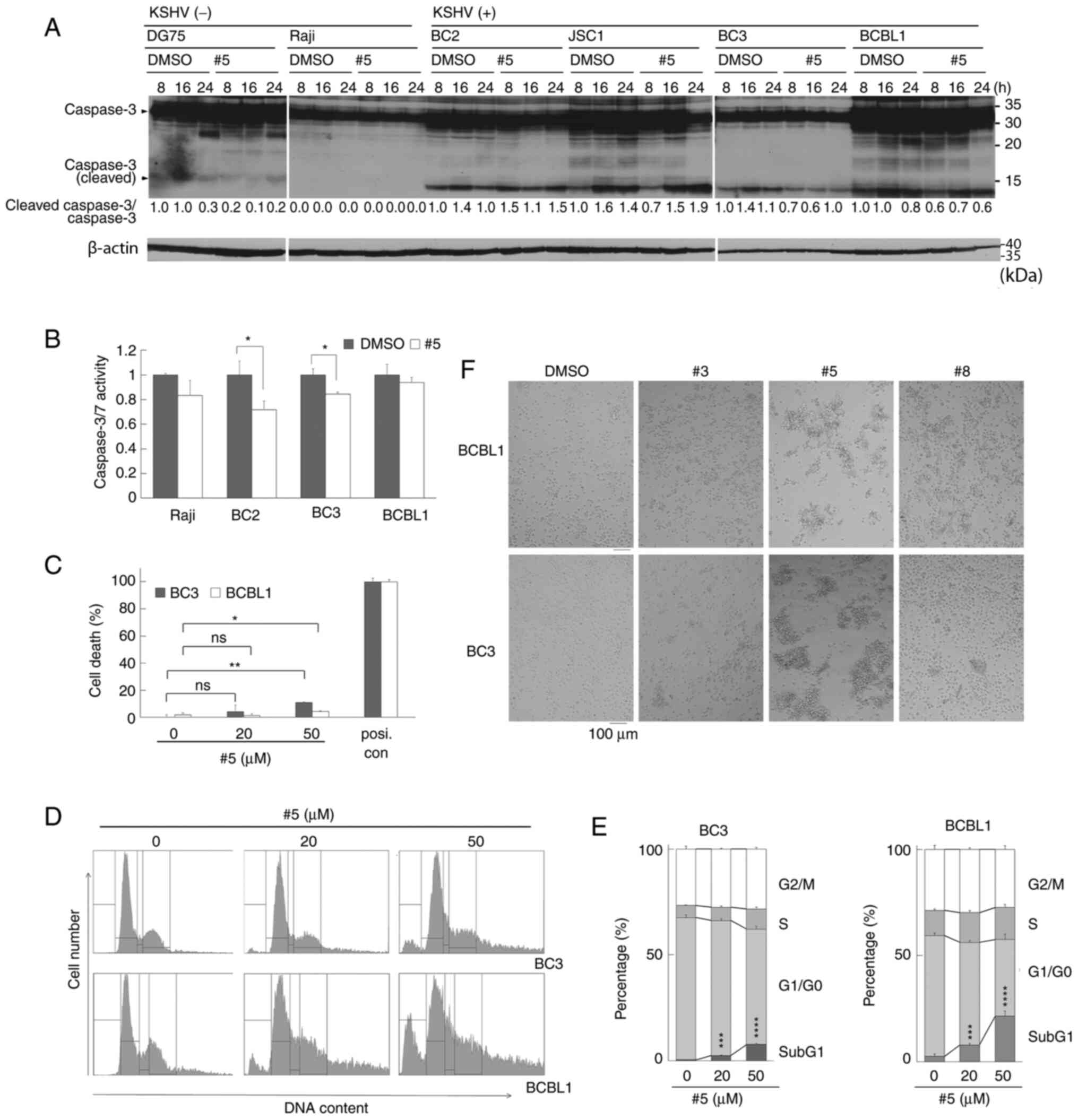
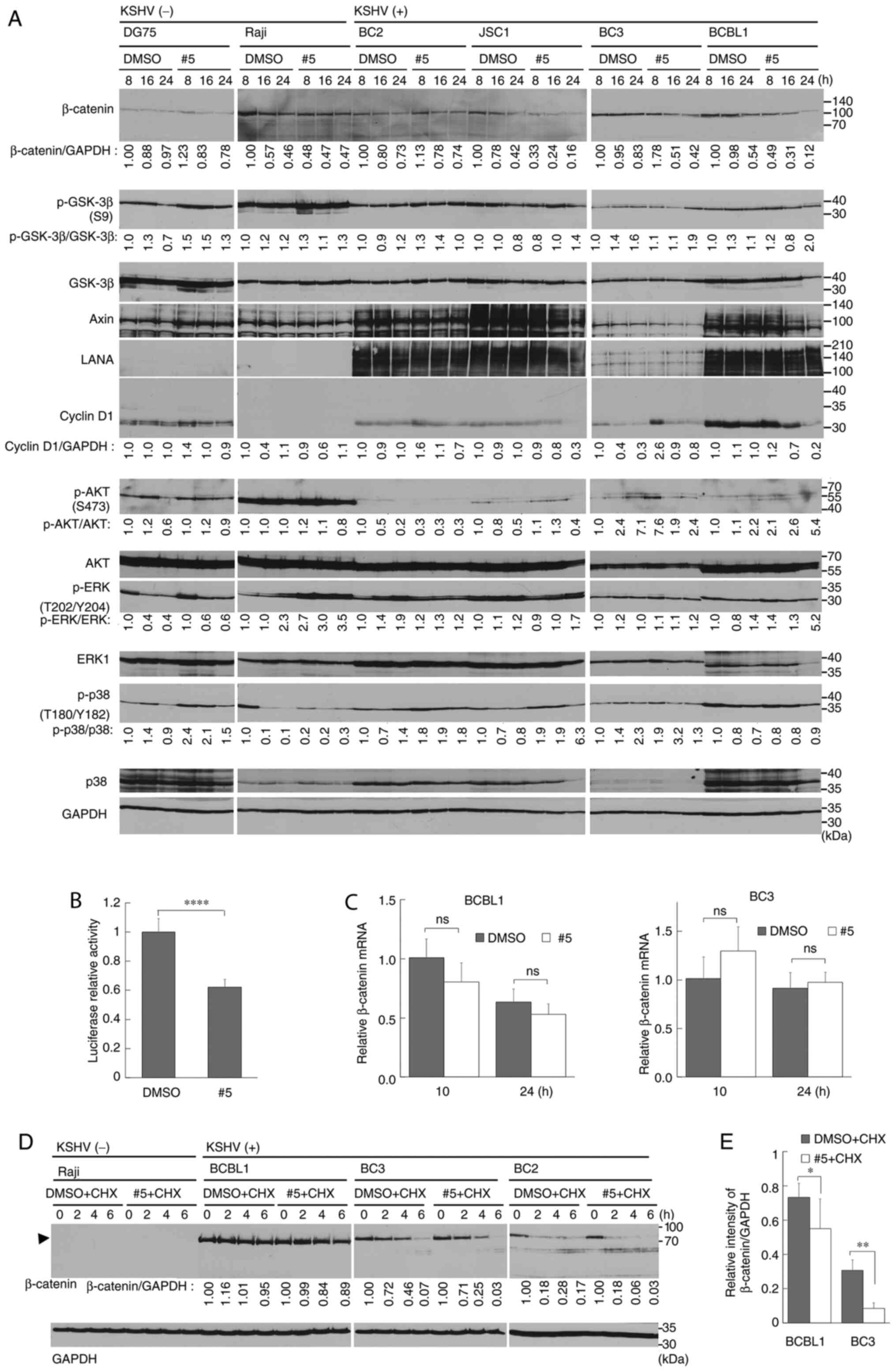
|
1
|
Russo JJ, Bohenzky RA, Chien MC, Chen J,
Yan M, Maddalena D, Parry JP, Peruzzi D, Edelman IS, Chang Y and
Moore PS: Nucleotide sequence of the Kaposi sarcoma-associated
herpesvirus (HHV8). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:14862–14867. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nador RG, Cesarman E, Chadburn A, Dawson
DB, Ansari MQ, Sald J and Knowles DM: Primary effusion lymphoma: A
distinct clinicopathologic entity associated with the Kaposi's
sarcoma-associated herpes virus. Blood. 88:645–656. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS, Lee F,
Culpepper J, Knowles DM and Moore PS: Identification of
herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma.
Science. 266:1865–1869. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Watanabe T, Sugimoto A, Hosokawa K and
Fujimuro M: Signal transduction pathways associated with
KSHV-related tumors. Human Herpesviruses. Kawaguchi Y, Mori Y and
Kimura H: Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg: pp. 321–355. 2018,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Damania B and Cesarman E: Kaposi's
sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Fields Virology. 6th edition. Knipe
DM and Howley PM: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; pp. 2080–2128.
2013
|
|
6
|
Fujimuro M, Wu FY, ApRhys C, Kajumbula H,
Young DB, Hayward GS and Hayward SD: A novel viral mechanism for
dysregulation of beta-catenin in Kaposis sarcoma-associated
herpesvirus latency. Nat Med. 9:300–306. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fujimuro M and Hayward SD: The
latency-associated nuclear antigen of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated
herpesvirus manipulates the activity of glycogen synthase
kinase-3beta. J Virol. 77:8019–8030. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fujimuro M, Liu J, Zhu J, Yokosawa H and
Hayward SD: Regulation of the interaction between glycogen synthase
kinase 3 and the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
latency-associated nuclear antigen. J Virol. 79:10429–10441. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hayward SD, Liu J and Fujimuro M: Notch
and Wnt signaling: Mimicry and manipulation by gamma herpesviruses.
Sci STKE. 2006:re42006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kroto HW, Heath JR, O'Brien SC, Curl RF
and Smalley RE: C60: Buckminsterfullerene. Nature.
318:162–163. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zakharian TY, Seryshev A, Sitharaman B,
Gilbert BE, Knight V and Wilson LJ: A fullerene-paclitaxel
chemotherapeutic: Synthesis, characterization, and study of
biological activity in tissue culture. J Am Chem Soc.
127:12508–12509. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chaudhuri P, Paraskar A, Soni S, Mashelkar
RA and Sengupta S: Fullerenol-cytotoxic conjugates for cancer
chemotherapy. ACS Nano. 3:2505–2514. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Isobe H, Nakanishi W, Tomita N, Jinno S,
Okayama H and Nakamura E: Nonviral gene delivery by tetraamino
fullerene. Mol Pharm. 3:124–134. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tokuyama H, Yamago S, Nakamura E, Shiraki
T and Sugiura Y: Photoinduced biochemical activity of fullerene
carboxylic acid. J Am Chem Soc. 115:7918–7919. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Okuda K, Mashino T and Hirobe M:
Superoxide radical quenching and cytochrome c peroxidase-like
activity of C60-dimalonic acid,
C64(COOH)4. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 6:539–542.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nishizawa C, Hashimoto N, Yokoo S,
Funakoshi-Tago M, Kasahara T, Takahashi K, Nakamura S and Mashino
T: Pyrrolidinium-type fullerene derivative-induced apoptosis by the
generation of reactive oxygen species in HL-60 cells. Free Radical
Res. 43:1240–1247. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mashino T, Nishikawa D, Takahashi K, Usui
N, Yamori T, Seki M, Endo T and Mochizuki M: Antibacterial and
antiproliferative activity of cationic fullerene derivatives.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 13:4395–4397. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Friedman SH, DeCamp DL, Sijbesma RP,
Srdanov G, Wudl F and Kenyon GL: Inhibition of the HIV-1 protease
by fullerene derivatives: Model building studies and experimental
verification. J Am Chem Soc. 115:6506–6509. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mashino T, Shimotohno K, Ikegami N,
Nishikawa D, Okuda K, Takahashi K, Nakamura S and Mochizuki M:
Human immunodeficiency virus-reverse transcriptase inhibition and
hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibition
activities of fullerene derivative. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
15:1107–1109. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shoji M, Takahashi E, Hatakeyama D, Iwai
Y, Morita Y, Shirayama R, Echigo N, Kido H, Nakamura S, Mashino T,
et al: Anti-influenza activity of C60 fullerene
derivatives. PLoS One. 8:e663372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Watanabe T, Nakamura S, Ono T, Ui S, Yagi
S, Kagawa H, Watanabe H, Ohe T, Mashino T and Fujimuro M:
Pyrrolidinium fullerene induces apoptosis by activation of
procaspase-9 via suppression of Akt in primary effusion lymphoma.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 451:93–100. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvasen
GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S and Reed JC: Regulation of
cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science.
282:1318–1321. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yasuno T, Ohe T, Ikeda H, Takahashi K,
Nakamura S and Mashino T: Synthesis and antitumor activity of novel
pyridinium fullerene derivatives. Int J Nanomedicine. 14:6325–6337.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yasuno T, Ohe T, Kataoka H, Hashimoto K,
Ishikawa Y, Furukawa K, Tateishi Y, Kobayashi T, Takahashi K,
Nakamura S and Mashino T: Fullerene derivatives as dual inhibitors
of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and protease. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
31:1276752021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yasuno T, Ohe T, Takahashi K, Nakamura S
and Mashino T: The human immunodeficiency virus-reverse
transcriptase inhibition activity of novel pyridine/pyridinium-type
fullerene derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 25:3226–3229. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shigemi Z, Furukawa Y, Hosokawa K, Minami
S, Matsuhiro J, Nakata S, Watanabe T, Kagawa H, Nakagawa K, Takeda
H and Fujimuro M: Diallyl trisulfide induces apoptosis by
suppressing NF-κB signaling through destabilization of TRAF6 in
primary effusion lymphoma. Int J Oncol. 48:293–304. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fujimuro M, Sawada H and Yokosawa H:
Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific
to multi-ubiquitin chains of polyubiquitinated proteins. FEBS Lett.
349:172–180. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen C and Okayama H: High-efficiency
transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol.
7:2745–2752. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Takahashi-Makise N, Suzu S, Hiyoshi M,
Ohsugi T, Katano H, Umezawa K and Okada S: Biscoclaurine alkaloid
cepharanthine inhibits the growth of primary effusion lymphoma in
vitro and in vivo and induces apoptosis via suppression of the
NF-kappaB pathway. Int J Cancer. 125:1464–1472. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim YJ, Kim Y, Kumar A, Kim CW, Toth Z,
Cho NH and Lee HR: Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
latency-associated nuclear antigen dysregulates expression of MCL-1
by targeting FBW7. PLoS Pathog. 17:e10091792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Saji C, Higashi C, Niinaka Y, Yamada K,
Noguchi K and Fujimuro M: Proteasome inhibitors induce apoptosis
and reduce viral replication in primary effusion lymphoma cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 415:573–578. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Higashi C, Saji C, Yamada K, Kagawa H,
Ohga R, Taira T and Fujimuro M: The effects of heat shock protein
90 inhibitors on apoptosis and viral replication in primary
effusion lymphoma cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 35:725–730. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ishiura Y, Ishimaru H, Watanabe T and
Fujimuro M: Sulforaphane exhibits cytotoxic effects against primary
effusion lymphoma cells by suppressing p38MAPK and AKT
phosphorylation. Bio Pharm Biol. 42:2109–2112. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Moriguchi M, Watanabe T, Kadota A and
Fujimuro M: Capsaicin induces apoptosis in KSHV-pisitive primary
effusion lymphoma by suppressing ERK and p38 MAPK signaling and
IL-6 expression. Front Oncol. 9:832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wakao K, Watanabe T, Takadama T, Ui S,
Shigemi Z, Kagawa H, Higashi C, Ohga R, Taira T and Fujimuro M:
Sangivamycin induces apoptosis by suppressing Erk signaling in
primary effusion lymphoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
444:135–140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Willert K and Jones KA: Wnt signaling: Is
the party in the nucleus? Genes Dev. 20:1394–1404. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kimelman D and Xu W: beta-catenin
destruction complex: Insights and questions from a structural
perspective. Oncogene. 25:7482–7491. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Albrecht LV, Tejeda-Muñoz N and De
Robertis EM: Cell biology of canonical Wnt signaling. Annu Rev Cell
Dev Biol. 37:369–389. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hoppler S and Kavanagh CL: Wnt signalling:
variety at the core. J Cell Sci. 120:385–393. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Segditsas S and Tomlinson I: Colorectal
cancer and genetic alterations in the Wnt pathway. Oncogene.
25:7531–7537. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Clements WM, Wang J, Sarnaik A, Kim OJ,
MacDonald J, Fenoglio-Preiser C, Groden J and Lowy AM: beta-Catenin
mutation is a frequent cause of Wnt pathway activation in gastric
cancer. Cancer Res. 62:3503–3506. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nakayama KI and Nakayama K: Ubiquitin
ligases: Cell-cycle control and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:369–381.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu C, Li Y, Semenov M, Han C, Baeg GH,
Tan Y, Zhang Z, Lin X and He X: Control of beta-catenin
phosphorylation/degradation by a dual-kinase mechanism. Cell.
108:837–847. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Amit S, Hatzubai A, Birman Y, Andersen JS,
Ben-Shushan E, Mann M, Ben-Neriah Y and Alkalay I: Axin-mediated
CKI phosphorylation of β-catenin at Ser 45: A molecular switch for
the Wnt pathway. Genes Dev. 16:1066–1076. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBIPubMed/NCBI
|