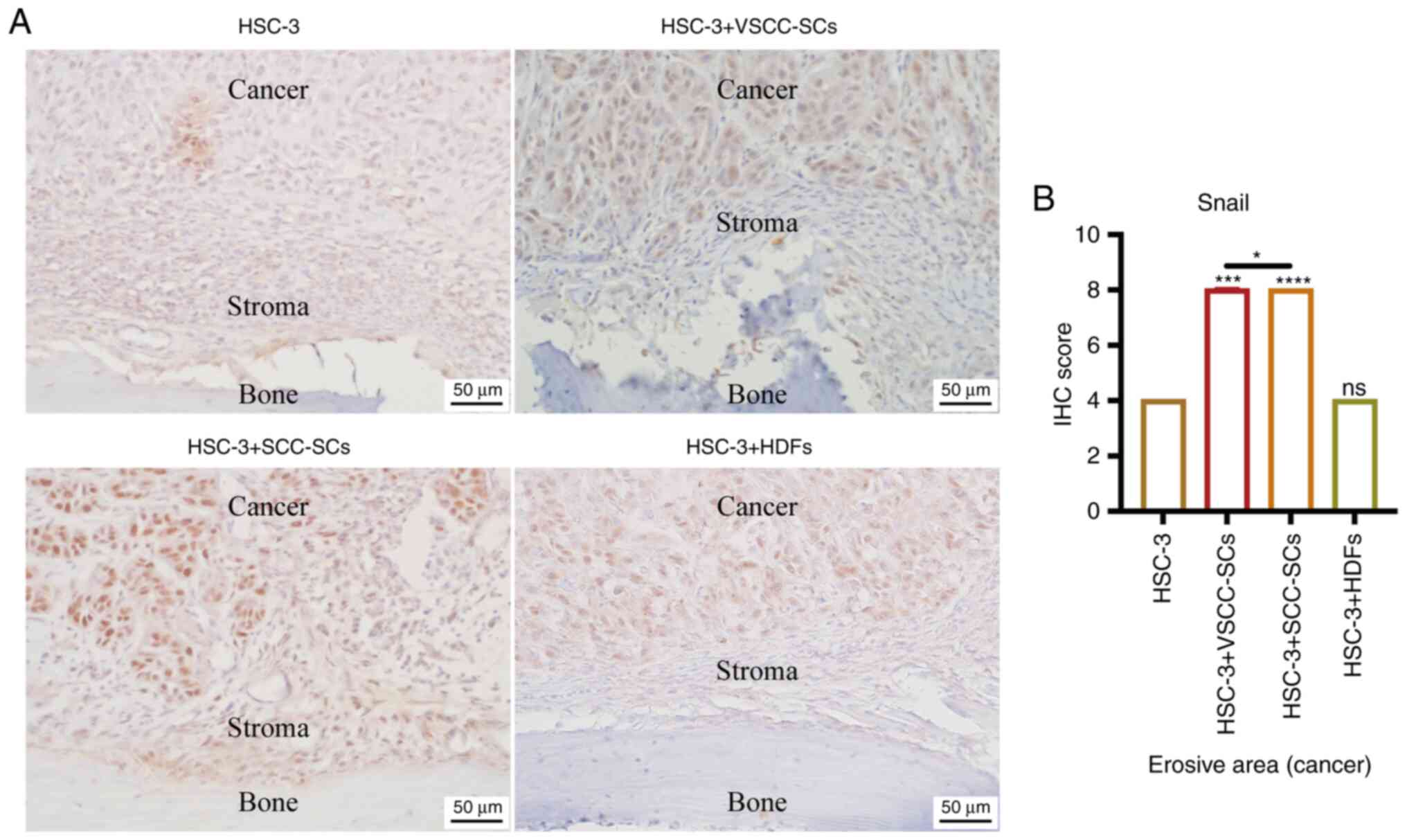
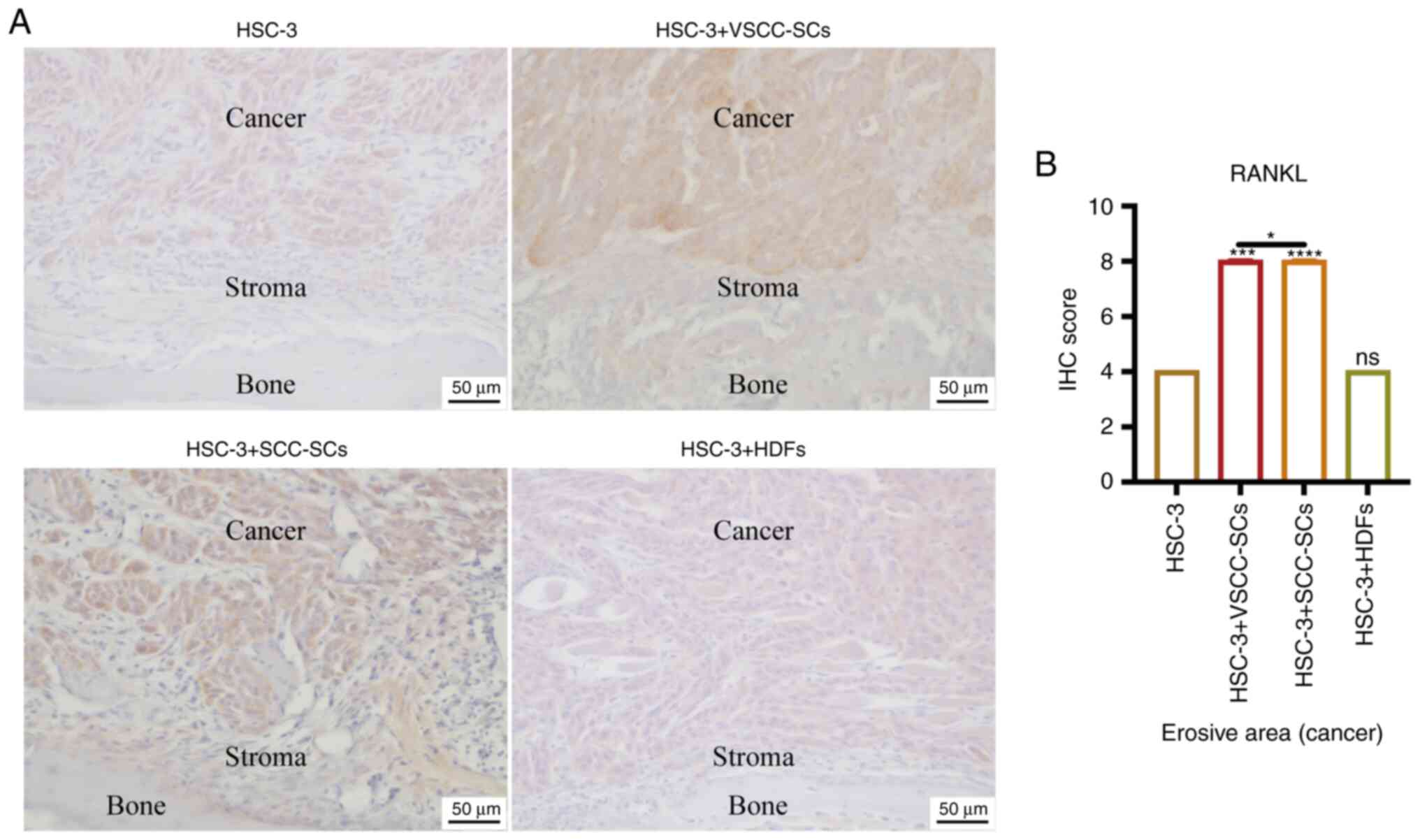
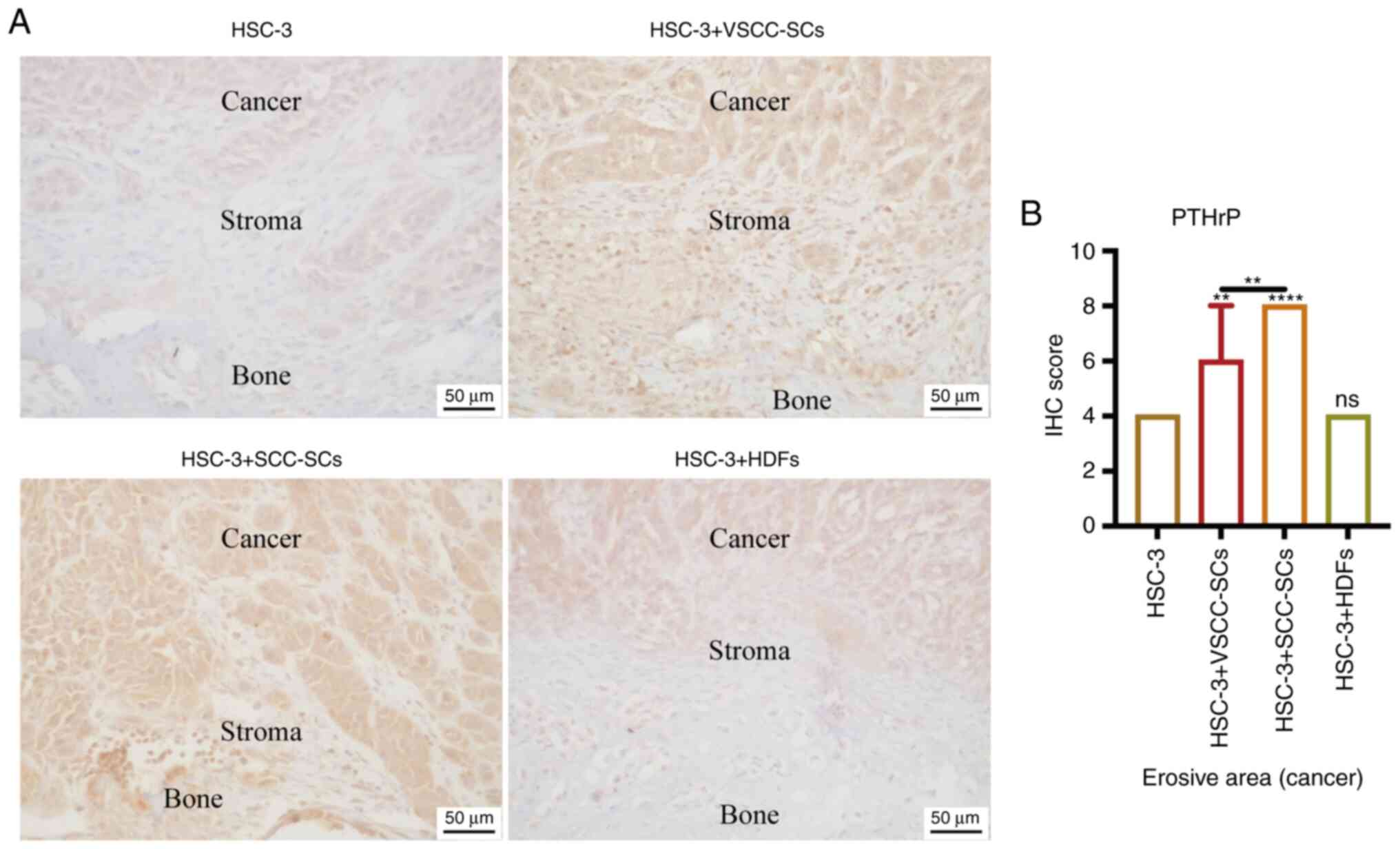
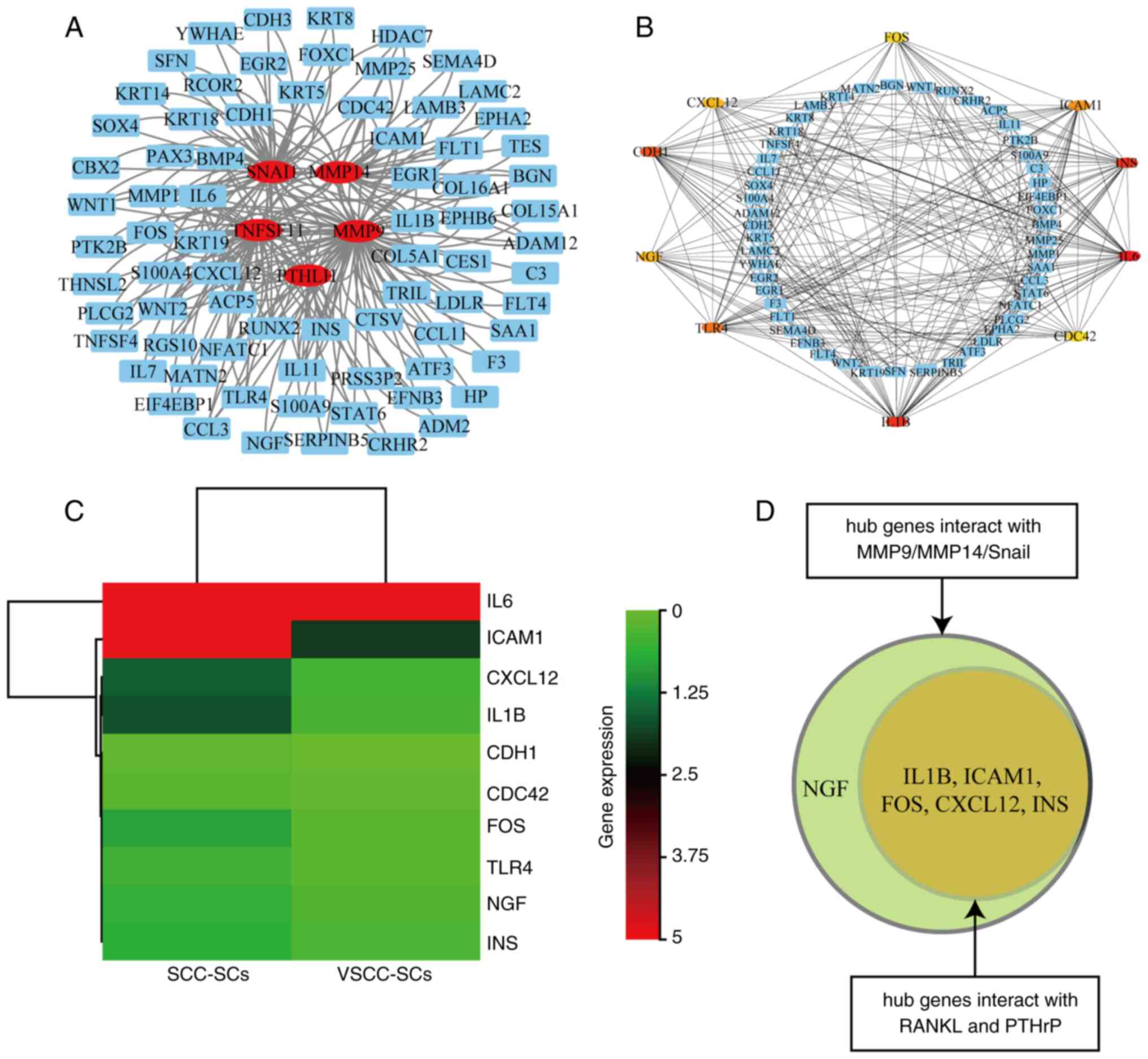
|
1
|
Warnakulasuriya S: Global epidemiology of
oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 45:309–316. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sacco AG and Cohen EE: Current treatment
options for recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 33:3305–3313. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nomura T, Shibahara T, Cui NH and Noma H:
Patterns of mandibular invasion by gingival squamous cell
carcinoma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 63:1489–1493. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen YL, Kuo SW, Fang KH and Hao SP:
Prognostic impact of marginal mandibulectomy in the presence of
superficial bone invasion and the nononcologic outcome. Head Neck.
33:708–713. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Teitelbaum SL and Ross FP: Genetic
regulation of osteoclast development and function. Nat Rev Genet.
4:638–649. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takayanagi H: Osteoimmunology: Shared
mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat
Rev Immunol. 7:292–304. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Teitelbaum SL: Osteoclasts: What do they
do and how do they do it? Am J Pathol. 170:427–435. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Okamoto M, Hiura K, Ohe G, Ohba Y, Terai
K, Oshikawa T, Furuichi S, Nishikawa H, Moriyama K, Yoshida H and
Sato M: Mechanism for bone invasion of oral cancer cells mediated
by interleukin-6 in vitro and in vivo. Cancer. 89:1966–1975. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tada T, Jimi E, Okamoto M, Ozeki S and
Okabe K: Oral squamous cell carcinoma cells induce osteoclast
differentiation by suppression of osteoprotegerin expression in
osteoblasts. Int J Cancer. 116:253–262. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ono K, Akatsu T, Kugai N, Pilbeam CC and
Raisz LG: The effect of deletion of cyclooxygenase-2, prostaglandin
receptor EP2, or EP4 in bone marrow cells on osteoclasts induced by
mouse mammary cancer cell lines. Bone. 33:798–804. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jimi E, Furuta H, Matsuo K, Tominaga K,
Takahashi T and Nakanishi O: The cellular and molecular mechanisms
of bone invasion by oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Dis.
17:462–468. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kayamori K, Sakamoto K, Nakashima T,
Takayanagi H, Morita K, Omura K, Nguyen ST, Miki Y, Iimura T,
Himeno A, et al: Roles of interleukin-6 and parathyroid
hormone-related peptide in osteoclast formation associated with
oral cancers: Significance of interleukin-6 synthesized by stromal
cells in response to cancer cells. Am J Pathol. 176:968–980. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Valkenburg KC, de Groot AE and Pienta KJ:
Targeting the tumour stroma to improve cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 15:366–381. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Quail DF and Joyce JA: Microenvironmental
regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med.
19:1423–1437. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wei LY, Lee JJ, Yeh CY, Yang CJ, Kok SH,
Ko JY, Tsai FC and Chia JS: Reciprocal activation of
cancer-associated fibroblasts and oral squamous carcinoma cells
through CXCL1. Oral Oncol. 88:115–123. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
An YZ, Cho E, Ling J and Zhang X: The
Axin2-snail axis promotes bone invasion by activating
cancer-associated fibroblasts in oral squamous cell carcinoma. BMC
Cancer. 20:9872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Elmusrati AA, Pilborough AE, Khurram SA
and Lambert DW: Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote bone invasion
in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 117:867–875. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Patel SG and Shah JP: TNM staging of
cancers of the head and neck: Striving for uniformity among
diversity. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:242–258. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Spiro RH, Guillamondegui O Jr, Paulino AF
and Huvos AG: Pattern of invasion and margin assessment in patients
with oral tongue cancer. Head Neck. 21:408–413. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hussein MR and Cullen K: Molecular
biomarkers in HNSCC: prognostic and therapeutic implications.
Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 1:116–124. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Takabatake K, Kawai H, Omori H, Qiusheng
S, Oo MW, Sukegawa S, Nakano K, Tsujigiwa H and Nagatsuka H: Impact
of the stroma on the biological characteristics of the parenchyma
in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 21:77142020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shan Q, Takabatake K, Omori H, Kawai H, Oo
MW, Nakano K, Ibaragi S, Sasaki A and Nagatsuka H: Stromal cells in
the tumor microenvironment promote the progression of oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 59:722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tohyama R, Kayamori K, Sato K, Hamagaki M,
Sakamoto K, Yasuda H and Yamaguchi A: Establishment of a xenograft
model to explore the mechanism of bone destruction by human oral
cancers and its application to analysis of role of RANKL. J Oral
Pathol Med. 45:356–364. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Flecknell PA: Laboratory Animal
Anesthesia. 3rd edition. Academic Press; San Diego, CA: 2009
|
|
25
|
Chuang FH, Hsue SS, Wu CW and Chen YK:
Immuno histochemical expression of RANKL, RANK, and OPG in human
oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 38:753–758. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shaw RJ, Brown JS, Woolgar JA, Lowe D,
Rogers SN and Vaughan ED: The influence of the pattern of
mandibular invasion on recurrence and survival in oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 26:861–869. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Brown JS, Lowe D, Kalavrezos N, D'Souza J,
Magennis P and Woolgar J: Patterns of invasion and routes of tumor
entry into the mandible by oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck.
24:370–383. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Uribe S, Rojas LA and Rosas CF: Accuracy
of imaging methods for detection of bone tissue invasion in
patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Dentomaxillofac Radiol.
42:201203462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gibo T, Yamada SI, Kawamoto M, Uehara T
and Kurita H: Immunohistochemical investigation of predictive
biomarkers for mandibular bone invasion in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 26:2381–2389. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Patel RS, Dirven R, Clark JR, Swinson BD,
Gao K and O'Brien CJ: The prognostic impact of extent of bone
invasion and extent of bone resection in oral carcinoma.
Laryngoscope. 118:780–785. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Quan J, Hou Y, Long W, Ye S and Wang Z:
Characterization of different osteoclast phenotypes in the
progression of bone invasion by oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol
Rep. 39:1043–1051. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Quan J, Johnson NW, Zhou G, Parsons PG,
Boyle GM and Gao J: Potential molecular targets for inhibiting bone
invasion by oral squamous cell carcinoma: A review of mechanisms.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 31:209–219. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Quan J, Zhou C, Johnson NW, Francis G,
Dahlstrom JE and Gao J: Molecular pathways involved in crosstalk
between cancer cells, osteoblasts and osteoclasts in the invasion
of bone by oral squamous cell carcinoma. Pathology. 44:221–227.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Woodward JK, Holen I, Coleman RE and
Buttle DJ: The roles of proteolytic enzymes in the development of
tumour-induced bone disease in breast and prostate cancer. Bone.
41:912–927. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
van der Pluijm G: Epithelial plasticity,
cancer stem cells and bone metastasis formation. Bone. 48:37–43.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yaginuma T, Gao J, Nagata K, Muroya R, Fei
H, Nagano H, Chishaki S, Matsubara T, Kokabu S, Matsuo K, et al:
p130Cas induces bone invasion by oral squamous cell carcinoma by
regulating tumor epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell
proliferation. Carcinogenesis. 41:1038–1048. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Quan J, Elhousiny M, Johnson NW and Gao J:
Transforming growth factor-β1 treatment of oral cancer induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes bone invasion via
enhanced activity of osteoclasts. Clin Exp Metastasis. 30:659–670.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Raggatt LJ and Partridge NC: Cellular and
molecular mechanisms of bone remodeling. J Biol Chem.
285:25103–25108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sambandam Y, Ethiraj P, Hathaway-Schrader
JD, Novince CM, Panneerselvam E, Sundaram K and Reddy SV:
Autoregulation of RANK ligand in oral squamous cell carcinoma tumor
cells. J Cell Physiol. 233:6125–6134. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shin M, Matsuo K, Tada T, Fukushima H,
Furuta H, Ozeki S, Kadowaki T, Yamamoto K, Okamoto M and Jimi E:
The inhibition of RANKL/RANK signaling by osteoprotegerin
suppresses bone invasion by oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.
Carcinogenesis. 32:1634–1640. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang X, Junior CR, Liu M, Li F, D'Silva
NJ and Kirkwood KL: Oral squamous carcinoma cells secrete RANKL
directly supporting osteolytic bone loss. Oral Oncol. 49:119–128.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Takayama Y, Mori T, Nomura T, Shibahara T
and Sakamoto M: Parathyroid-related protein plays a critical role
in bone invasion by oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
36:1387–1394. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Martin CK, Dirksen WP, Shu ST, Werbeck JL,
Thudi NK, Yamaguchi M, Wolfe TD, Heller KN and Rosol TJ:
Characterization of bone resorption in novel in vitro and in vivo
models of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 48:491–499.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang X, Wang B, Xie J, Hou D, Zhang H and
Huang H: Melatonin inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
gastric cancer cells via attenuation of IL-1β/NF-κB/MMP2/MMP9
signaling. Int J Mol Med. 42:2221–2228. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang Y, Galli M, Shade Silver A, Lee W,
Song Y, Mei Y, Bachus C, Glogauer M and McCulloch CA: IL1β and TNFα
promote RANKL-dependent adseverin expression and
osteoclastogenesis. J Cell Sci. 131:2139672018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Chung TW, Choi H, Lee JM, Ha SH, Kwak CH,
Abekura F, Park JY, Chang YC, Ha KT, Cho SH, et al: Oldenlandia
diffusa suppresses metastatic potential through inhibiting matrix
metalloproteinase-9 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1
expression via p38 and ERK1/2 MAPK pathways and induces apoptosis
in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 195:309–317.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Di D, Chen L, Wang L, Sun P, Liu Y, Xu Z
and Ju J: Downregulation of human intercellular adhesion molecule-1
attenuates the metastatic ability in human breast cancer cell
lines. Oncol Rep. 35:1541–1548. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Garcia-Palacios V, Chung HY, Choi SJ,
Sarmasik A, Kurihara N, Lee JW, Galson DL, Collins R and Roodman
GD: Eosinophil chemotactic factor-L (ECF-L) enhances osteoclast
formation by increasing in osteoclast precursors expression of
LFA-1 and ICAM-1. Bone. 40:316–322. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tsai CF, Chen JH, Wu CT, Chang PC, Wang SL
and Yeh WL: Induction of osteoclast-like cell formation by
leptin-induced soluble intercellular adhesion molecule secreted
from cancer cells. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 11:17588359198468062019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bhatia V, Cao Y, Ko TC and Falzon M:
Parathyroid hormone-related protein interacts with the transforming
growth factor-β/bone morphogenetic protein-2/gremlin signaling
pathway to regulate proinflammatory and profibrotic mediators in
pancreatic acinar and stellate cells. Pancreas. 45:659–670. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Milde-Langosch K, Röder H, Andritzky B,
Aslan B, Hemminger G, Brinkmann A, Bamberger CM, Löning T and
Bamberger AM: The role of the AP-1 transcription factors c-Fos,
FosB, Fra-1 and Fra-2 in the invasion process of mammary
carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 86:139–152. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chen SP, Liu BX, Xu J, Pei XF, Liao YJ,
Yuan F and Zheng F: MiR-449a suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by multiple
targets. BMC Cancer. 15:7062015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kwak SC, Baek JM, Lee CH, Yoon KH, Lee MS
and Kim JY: Umbelliferone prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced bone
loss and suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by attenuating
Akt-c-Fos-NFATc1 signaling. Int J Biol Sci. 15:2427–2437. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Berry JE, Ealba EL, Pettway GJ, Datta NS,
Swanson EC, Somerman MJ and McCauley LK: JunB as a downstream
mediator of PTHrP actions in cementoblasts. J Bone Miner Res.
21:246–57. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Rehman AO and Wang CY: CXCL12/SDF-1 alpha
activates NF-kappaB and promotes oral cancer invasion through the
Carma3/Bcl10/Malt1 complex. Int J Oral Sci. 1:105–118. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yang F, Takagaki Y, Yoshitomi Y, Ikeda T,
Li J, Kitada M, Kumagai A, Kawakita E, Shi S, Kanasaki K and Koya
D: Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 accelerates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and breast cancer metastasis via
the CXCL12/CXCR4/mTOR axis. Cancer Res. 79:735–746. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Shima K, Kimura K, Ishida M, Kishikawa A,
Ogawa S, Qi J, Shen WR, Ohori F, Noguchi T, Marahleh A and Kitaura
H: C-X-C motif chemokine 12 enhances lipopolysaccharide-induced
osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in vivo. Calcif Tissue Int.
103:431–442. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lei Y, He X, Huang H, He Y, Lan J, Yang J,
Liu W and Zhang T: Nerve growth factor orchestrates NGAL and matrix
metalloproteinases activity to promote colorectal cancer
metastasis. Clin Transl Oncol. 24:34–47. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lin C, Ren Z, Yang X, Yang R, Chen Y, Liu
Z, Dai Z, Zhang Y, He Y, Zhang C, et al: Nerve growth factor
(NGF)-TrkA axis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma triggers
EMT and confers resistance to the EGFR inhibitor erlotinib. Cancer
Lett. 472:81–96. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Gaspersic R, Kovacic U, Glisovic S, Cör A
and Skaleric U: Anti-NGF treatment reduces bone resorption in
periodontitis. J Dent Res. 89:515–520. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|