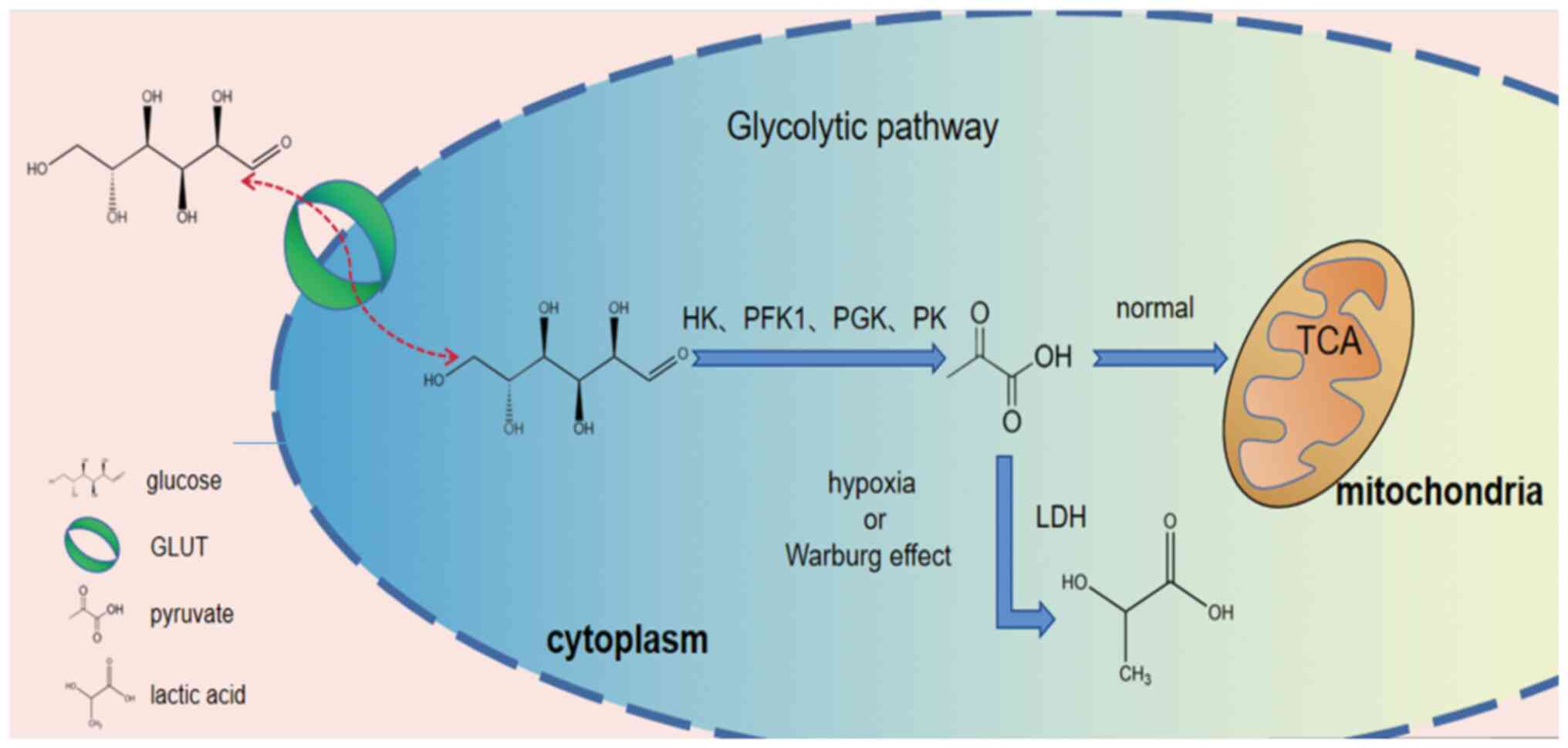
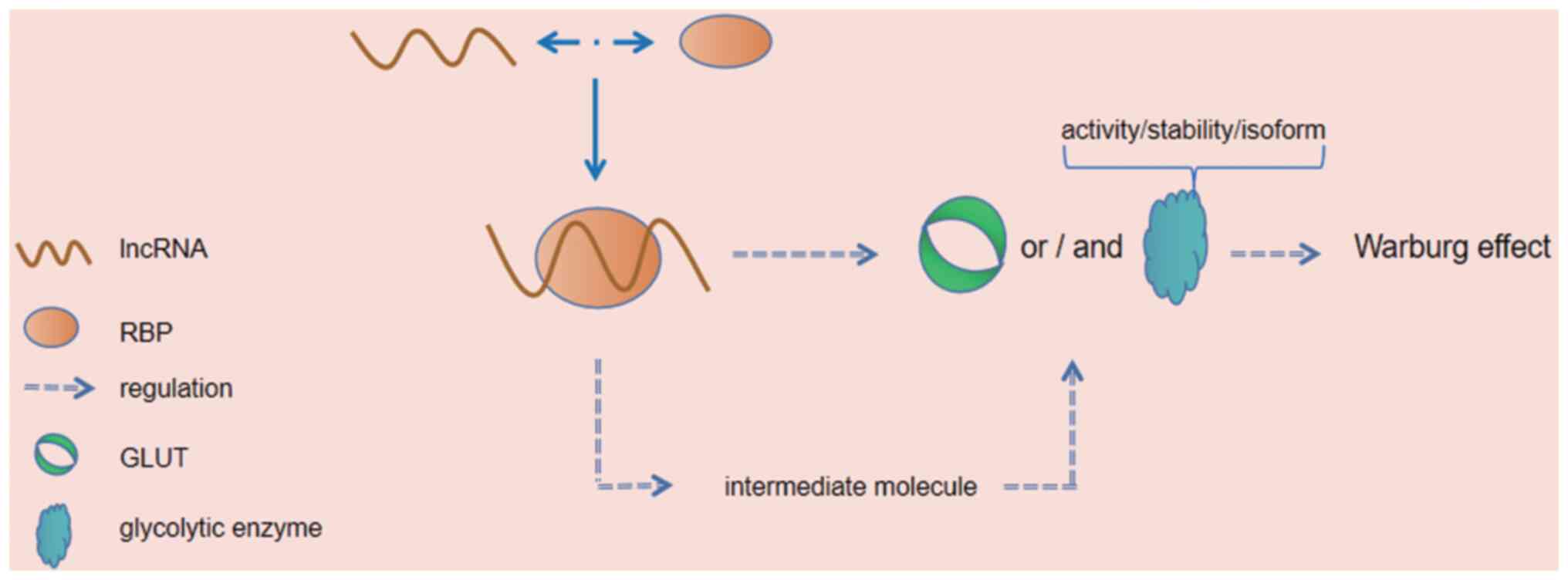
|
1
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hsu PP and Sabatini DM: Cancer cell
metabolism: Warburg and beyond. Cell. 134:703–707. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kroemer G and Pouyssegur J: Tumor cell
metabolism: Cancer's Achilles' heel. Cancer Cell. 13:472–482. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gatenby RA, Gawlinski ET, Gmitro AF,
Kaylor B and Gillies RJ: Acid-mediated tumor invasion: A
multidisciplinary study. Cancer Res. 66:5216–5223. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Koppenol WH, Bounds PL and Dang CV: Otto
Warburg's contributions to current concepts of cancer metabolism.
Nat Rev Cancer. 11:325–337. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mueckler M and Thorens B: The SLC2 (GLUT)
family of membrane transporters. Mol Aspects Med. 34:121–138. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ancey PB, Contat C and Meylan E: Glucose
transporters in cancer-from tumor cells to the tumor
microenvironment. FEBS J. 285:2926–2943. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li L, Liang Y, Kang L, Liu Y, Gao S, Chen
S, Li Y, You W, Dong Q, Hong T, et al: Transcriptional regulation
of the warburg effect in cancer by SIX1. Cancer Cell.
33:368–385.e7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Akins NS, Nielson TC and Le HV: Inhibition
of glycolysis and glutaminolysis: An emerging drug discovery
approach to combat cancer. Curr Top Med Chem. 18:494–504. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zheng Y, Liu P, Wang N, Wang S, Yang B, Li
M, Chen J, Situ H, Xie M, Lin Y and Wang Z: Betulinic acid
suppresses breast cancer metastasis by targeting GRP78-mediated
glycolysis and ER stress apoptotic pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019:87816902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Feng J, Li J, Wu L, Yu Q, Ji J, Wu J, Dai
W and Guo C: Emerging roles and the regulation of aerobic
glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
39:1262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu C, Li H, Chu F, Zhou X, Xie R, Wei Q,
Yang S, Li T, Liang S and Lü M: Long noncoding RNAs: Key regulators
involved in metabolic reprogramming in cancer (Review). Oncol Rep.
45:542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li Z and Sun X: Non-coding RNAs Operate in
the crosstalk between cancer metabolic reprogramming and
metastasis. Front Oncol. 10:8102020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Cabili MN, Trapnell C, Goff L, Koziol M,
Tazon-Vega B, Regev A and Rinn JL: Integrative annotation of human
large intergenic noncoding RNAs reveals global properties and
specific subclasses. Genes Dev. 25:1915–1927. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schmitt AM and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 29:452–463. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hentze MW, Castello A, Schwarzl T and
Preiss T: A brave new world of RNA-binding proteins. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 19:327–341. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ferre F, Colantoni A and Helmer-Citterich
M: Revealing protein-lncRNA interaction. Brief Bioinform.
17:106–116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wei S, Fan Q, Yang L, Zhang X, Ma Y, Zong
Z, Hua X, Su D, Sun H, Li H and Liu Z: Promotion of glycolysis by
HOTAIR through GLUT1 upregulation via mTOR signaling. Oncol Rep.
38:1902–1908. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Song H, Liu Y, Li X, Chen S, Xie R, Chen
D, Gao H, Wang G, Cai B and Yang X: Long noncoding RNA CASC11
promotes hepatocarcinogenesis and HCC progression through
EIF4A3-mediated E2F1 activation. Clin Transl Med. 10:e2202020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Luo J, Wang H, Wang L, Wang G, Yao Y, Xie
K, Li X, Xu L, Shen Y and Ren B: lncRNA GAS6-AS1 inhibits
progression and glucose metabolism reprogramming in LUAD via
repressing E2F1-mediated transcription of GLUT1. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 25:11–24. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu WT, Wilczynska A, Smith E and Bushell
M: The diverse roles of the eIF4A family: you are the company you
keep. Biochem Soc Trans. 42:166–172. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chan CC, Dostie J, Diem MD, Feng W, Mann
M, Rappsilber J and Dreyfuss G: eIF4A3 is a novel component of the
exon junction complex. RNA. 10:200–209. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu M, Seto E and Zhang J: E2F1 enhances
glycolysis through suppressing Sirt6 transcription in cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 6:11252–11263. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen HZ, Tsai SY and Leone G: Emerging
roles of E2Fs in cancer: An exit from cell cycle control. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:785–797. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Farra R, Grassi G, Tonon F, Abrami M,
Grassi M, Pozzato G, Fiotti N, Forte G and Dapas B: The role of the
transcription factor E2F1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Drug
Deliv. 14:272–281. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lis P, Dylag M, Niedzwiecka K, Ko YH,
Pedersen PL, Goffeau A and Ułaszewski S: The HK2 dependent ‘Warburg
Effect’ and mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in cancer:
Targets for effective therapy with 3-Bromopyruvate. Molecules.
21:17302016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gong L, Cui Z, Chen P, Han H, Peng J and
Leng X: Reduced survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
expressing hexokinase II. Med Oncol. 29:909–914. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wolf A, Agnihotri S, Micallef J, Mukherjee
J, Sabha N, Cairns R, Hawkins C and Guha A: Hexokinase 2 is a key
mediator of aerobic glycolysis and promotes tumor growth in human
glioblastoma multiforme. J Exp Med. 208:313–326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wolf A, Agnihotri S and Guha A: Targeting
metabolic remodeling in glioblastoma multiforme. Oncotarget.
1:552–562. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Patra KC, Wang Q, Bhaskar PT, Miller L,
Wang Z, Wheaton W, Chandel N, Laakso M, Muller WJ, Allen EL, et al:
Hexokinase 2 is required for tumor initiation and maintenance and
its systemic deletion is therapeutic in mouse models of cancer.
Cancer Cell. 24:213–228. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kanai S, Shimada T, Narita T and
Okabayashi K: Phosphofructokinase-1 subunit composition and
activity in the skeletal muscle, liver, and brain of dogs. J Vet
Med Sci. 81:712–716. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Al Hasawi N, Alkandari MF and Luqmani YA:
Phosphofructokinase: A mediator of glycolytic flux in cancer
progression. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 92:312–321. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Bartrons R, Rodríguez-García A,
Simon-Molas H, Castaño E, Manzano A and Navarro-Sabaté À: The
potential utility of PFKFB3 as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin
Ther Targets. 22:659–674. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
van Niekerk G and Engelbrecht AM: Role of
PKM2 in directing the metabolic fate of glucose in cancer: A
potential therapeutic target. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 41:343–351. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shang RZ, Qu SB and Wang DS: Reprogramming
of glucose metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma: Progress and
prospects. World J Gastroenterol. 22:9933–9943. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Anastasiou D, Yu Y, Israelsen WJ, Jiang
JK, Boxer MB, Hong BS, Tempel W, Dimov S, Shen M, Jha A, et al:
Pyruvate kinase M2 activators promote tetramer formation and
suppress tumorigenesis. Nat Chem Biol. 8:839–847. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Azoitei N, Becher A, Steinestel K, Rouhi
A, Diepold K, Genze F, Simmet T and Seufferlein T: PKM2 promotes
tumor angiogenesis by regulating HIF-1α through NF-κB activation.
Mol Cancer. 15:32016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
He Y, Luo Y, Zhang D, Wang X, Zhang P, Li
H, Ejaz S and Liang S: PGK1-mediated cancer progression and drug
resistance. Am J Cancer Res. 9:2280–2302. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Daly EB, Wind T, Jiang XM, Sun L and Hogg
PJ: Secretion of phosphoglycerate kinase from tumour cells is
controlled by oxygen-sensing hydroxylases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1691:17–22. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hu H, Zhu W, Qin J, Chen M, Gong L, Li L,
Liu X, Tao Y, Yin H, Zhou H, et al: Acetylation of PGK1 promotes
liver cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Hepatology.
65:515–528. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Feng Y, Xiong Y, Qiao T, Li X, Jia L and
Han Y: Lactate dehydrogenase A: A key player in carcinogenesis and
potential target in cancer therapy. Cancer Med. 7:6124–6136. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fan J, Hitosugi T, Chung TW, Xie J, Ge Q,
Gu TL, Polakiewicz RD, Chen GZ, Boggon TJ, Lonial S, et al:
Tyrosine phosphorylation of lactate dehydrogenase A is important
for NADH/NAD(+) redox homeostasis in cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol.
31:4938–4950. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Hitosugi T, Kang S, Vander Heiden MG,
Chung TW, Elf S, Lythgoe K, Dong S, Lonial S, Wang X, Chen GZ, et
al: Tyrosine phosphorylation inhibits PKM2 to promote the warburg
effect and tumor growth. Sci Signal. 2:ra732009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wang C, Li Y, Yan S, Wang H, Shao X, Xiao
M, Yang B, Qin G, Kong R, Chen R and Zhang N: Interactome analysis
reveals that lncRNA HULC promotes aerobic glycolysis through LDHA
and PKM2. Nat Commun. 11:31622020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hu R, Zhong P, Xiong L and Duan L: Long
Noncoding RNA cancer susceptibility candidate 8 suppresses the
proliferation of bladder cancer cells via regulating glycolysis.
DNA Cell Biol. 36:767–774. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Chen H, Pei H, Hu W, Ma J, Zhang J, Mao W,
Nie J, Xu C, Li B, Hei TK, et al: Long non-coding RNA CRYBG3
regulates glycolysis of lung cancer cells by interacting with
lactate dehydrogenase A. J Cancer. 9:2580–2588. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dai F, Wu Y, Lu Y, An C, Zheng X, Dai L,
Guo Y, Zhang L, Li H, Xu W and Gao W: Crosstalk between RNA
m6A Modification and Non-coding RNA Contributes to
Cancer Growth and Progression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 22:62–71.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yang J, Liu J, Zhao S and Tian F: NN
6-Methyladenosine METTL3 modulates the proliferation and apoptosis
of lens epithelial cells in diabetic cataract. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 20:111–116. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhong L, He X, Song H, Sun Y, Chen G, Si
X, Sun J, Chen X, Liao W, Liao Y and Bin J: METTL3 Induces AAA
development and progression by modulating
N6-methyladenosine-dependent primary miR34a processing. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 21:394–411. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang J, Chen L and Qiang P: The role of
IGF2BP2, an m6A reader gene, in human metabolic diseases and
cancers. Cancer Cell Int. 21:992021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Lu S, Han L, Hu X, Sun T, Xu D, Li Y, Chen
Q, Yao W, He M, Wang Z, et al: N6-methyladenosine reader IMP2
stabilizes the ZFAS1/OLA1 axis and activates the Warburg effect:
Implication in colorectal cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 14:1882021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Liu H, Qin S, Liu C, Jiang L, Li C, Yang
J, Zhang S, Yan Z, Liu X, Yang J and Sun X: m 6 A reader
IGF2BP2-stabilized CASC9 accelerates glioblastoma aerobic
glycolysis by enhancing HK2 mRNA stability. Cell Death Discov.
7:2922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang Y, Zhao L, Yang S, Cen Y, Zhu T,
Wang L, Xia L, Liu Y, Zou J, Xu J, et al: CircCDKN2B-AS1 interacts
with IMP3 to stabilize hexokinase 2 mRNA and facilitate cervical
squamous cell carcinoma aerobic glycolysis progression. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 39:2812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jiang D, Zhang Y, Yang L, Lu W, Mai L, Guo
H and Liu X: Long noncoding RNA HCG22 suppresses proliferation and
metastasis of bladder cancer cells by regulation of PTBP1. J Cell
Physiol. 235:1711–1722. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Minami K, Taniguchi K, Sugito N, Kuranaga
Y, Inamoto T, Takahara K, Takai T, Yoshikawa Y, Kiyama S, Akao Y
and Azuma H: MiR-145 negatively regulates Warburg effect by
silencing KLF4 and PTBP1 in bladder cancer cells. Oncotarget.
8:33064–33077. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Taniguchi K, Sakai M, Sugito N, Kumazaki
M, Shinohara H, Yamada N, Nakayama T, Ueda H, Nakagawa Y, Ito Y, et
al: PTBP1-associated microRNA-1 and −133b suppress the Warburg
effect in colorectal tumors. Oncotarget. 7:18940–18952. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Wang J and Maldonado MA: The
ubiquitin-proteasome system and its role in inflammatory and
autoimmune diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. 3:255–261. 2006.
|
|
58
|
Liu C, Zhang Y, She X, Fan L, Li P, Feng
J, Fu H, Liu Q, Liu Q, Zhao C, et al: A cytoplasmic long noncoding
RNA LINC00470 as a new AKT activator to mediate glioblastoma cell
autophagy. J Hematol Oncol. 11:772018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Wang RC, Wei Y, An Z, Zou Z, Xiao G,
Bhagat G, White M, Reichelt J and Levine B: Akt-mediated regulation
of autophagy and tumorigenesis through Beclin 1 phosphorylation.
Science. 338:956–959. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Le Grand M, Berges R, Pasquier E, Montero
MP, Borge L, Carrier A, Vasseur S, Bourgarel V, Buric D, André N,
et al: Akt targeting as a strategy to boost chemotherapy efficacy
in non-small cell lung cancer through metabolism suppression. Sci
Rep. 7:451362017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Polivka J Jr and Janku F: Molecular
targets for cancer therapy in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Pharmacol
Ther. 142:164–175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chen C, Wei M, Wang C, Sun D, Liu P, Zhong
X and Yu W: Long noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes colorectal
carcinogenesis by enhancing aerobic glycolysis via hexokinase-2.
Aging (Albany NY). 12:11685–11697. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hua Q, Mi B, Xu F, Wen J, Zhao L, Liu J
and Huang G: Hypoxia-induced lncRNA-AC020978 promotes proliferation
and glycolytic metabolism of non-small cell lung cancer by
regulating PKM2/HIF-1α axis. Theranostics. 10:4762–4778. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Bian Z, Zhang J, Li M, Feng Y, Wang X,
Zhang J, Yao S, Jin G, Du J, Han W, et al: LncRNA-FEZF1-AS1
promotes tumor proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer by
regulating PKM2 signaling. Clin Cancer Res. 24:4808–4819. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Jiang B, Chen Y, Xia F and Li X:
PTCSC3-mediated glycolysis suppresses thyroid cancer progression
via interfering with PGK1 degradation. J Cell Mol Med.
25:8454–8463. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ullah K, Chen S, Lu J, Wang X, Liu Q,
Zhang Y, Long Y, Hu Z and Xu G: The E3 ubiquitin ligase STUB1
attenuates cell senescence by promoting the ubiquitination and
degradation of the core circadian regulator BMAL1. J Biol Chem.
295:4696–4708. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Chu Z, Huo N, Zhu X, Liu H, Cong R, Ma L,
Kang X, Xue C, Li J, Li Q, et al: FOXO3A-induced LINC00926
suppresses breast tumor growth and metastasis through inhibition of
PGK1-mediated Warburg effect. Mol Ther. 29:2737–2753. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Chen M, Zhang J and Manley JL: Turning on
a fuel switch of cancer: HnRNP proteins regulate alternative
splicing of pyruvate kinase mRNA. Cancer Res. 70:8977–8980. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Christofk HR, Vander Heiden MG, Harris MH,
Ramanathan A, Gerszten RE, Wei R, Fleming MD, Schreiber SL and
Cantley LC: The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important
for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature. 452:230–233. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Lan Z, Yao X, Sun K, Li A, Liu S and Wang
X: The interaction between lncRNA SNHG6 and hnRNPA1 contributes to
the growth of colorectal cancer by enhancing aerobic glycolysis
through the regulation of alternative splicing of PKM. Front Oncol.
10:3632020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Zhou Z, Gong Q, Lin Z, Wang Y, Li M, Wang
L, Ding H and Li P: Emerging roles of SRSF3 as a therapeutic target
for cancer. Front Oncol. 10:5776362020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Jia G, Wang Y, Lin C, Lai S, Dai H, Wang
Z, Dai L, Su H, Song Y, Zhang N, et al: LNCAROD enhances
hepatocellular carcinoma malignancy by activating glycolysis
through induction of pyruvate kinase isoform PKM2. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 40:2992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lu J, Liu X, Zheng J, Song J, Liu Y, Ruan
X, Shen S, Shao L, Yang C, Wang D, et al: Lin28A promotes
IRF6-regulated aerobic glycolysis in glioma cells by stabilizing
SNHG14. Cell Death Dis. 11:4472020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ferretti E, Li B, Zewdu R, Wells V, Hebert
JM, Karner C, Anderson MJ, Williams T, Dixon J, Dixon MJ, et al: A
conserved Pbx-Wnt-p63-Irf6 regulatory module controls face
morphogenesis by promoting epithelial apoptosis. Dev Cell.
21:627–641. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Rotondo JC, Borghi A, Selvatici R, Magri
E, Bianchini E, Montinari E, Corazza M, Virgili A, Tognon M and
Martini F: Hypermethylation-Induced inactivation of the IRF6 gene
as a possible early event in progression of vulvar squamous cell
carcinoma associated with lichen sclerosus. JAMA Dermatol.
152:928–933. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Bailey CM, Abbott DE, Margaryan NV,
Khalkhali-Ellis Z and Hendrix MJ: Interferon regulatory factor 6
promotes cell cycle arrest and is regulated by the proteasome in a
cell cycle-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biol. 28:2235–2243. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Song H, Li D, Wang X, Fang E, Yang F, Hu
A, Wang J, Guo Y, Liu Y, Li H, et al: HNF4A-AS1/hnRNPU/CTCF axis as
a therapeutic target for aerobic glycolysis and neuroblastoma
progression. J Hematol Oncol. 13:242020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Ma F, Liu X, Zhou S, Li W, Liu C, Chadwick
M and Qian C: Long non-coding RNA FGF13-AS1 inhibits glycolysis and
stemness properties of breast cancer cells through
FGF13-AS1/IGF2BPs/Myc feedback loop. Cancer Lett. 450:63–75. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Ruan K, Song G and Ouyang G: Role of
hypoxia in the hallmarks of human cancer. J Cell Biochem.
107:1053–1062. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kaelin WG Jr and Ratcliffe PJ: Oxygen
sensing by metazoans: The central role of the HIF hydroxylase
pathway. Mol Cell. 30:393–402. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando
J, Ohh M, Salic A, Asara JM, Lane WS and Kaelin WG Jr: HIFalpha
targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation:
Implications for O2 sensing. Science. 292:464–468. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI,
Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ, von Kriegsheim A, Hebestreit HF, Mukherji
M, Schofield CJ, et al: Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von
Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl
hydroxylation. Science. 292:468–472. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW,
Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME, Wykoff CC, Pugh CW, Maher ER and
Ratcliffe PJ: The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets
hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature.
399:271–275. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Yao J, Man S, Dong H, Yang L, Ma L and Gao
W: Combinatorial treatment of Rhizoma Paridis saponins and
sorafenib overcomes the intolerance of sorafenib. J Steroid Biochem
Mol Biol. 183:159–166. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Marín-Hernández A, Gallardo-Pérez JC,
Ralph SJ, Rodríguez-Enríquez S and Moreno-Sánchez R: HIF-1alpha
modulates energy metabolism in cancer cells by inducing
over-expression of specific glycolytic isoforms. Mini Rev Med Chem.
9:1084–1101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Zheng F, Chen J, Zhang X, Wang Z, Chen J,
Lin X, Huang H, Fu W, Liang J, Wu W, et al: The HIF-1α antisense
long non-coding RNA drives a positive feedback loop of HIF-1α
mediated transactivation and glycolysis. Nat Commun. 12:13412021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Kim JW, Tchernyshyov I, Semenza GL and
Dang CV: HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase
kinase: A metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to
hypoxia. Cell Metab. 3:177–185. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Yeung SJ, Pan J and Lee MH: Roles of p53,
MYC and HIF-1 in regulating glycolysis-the seventh hallmark of
cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:3981–3999. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Su X, Li G and Liu W: The long noncoding
RNA cancer susceptibility candidate 9 promotes nasopharyngeal
carcinogenesis via stabilizing HIF1α. DNA Cell Biol. 36:394–400.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Lin A, Li C, Xing Z, Hu Q, Liang K, Han L,
Wang C, Hawke DH, Wang S, Zhang Y, et al: The LINK-A lncRNA
activates normoxic HIF1α signalling in triple-negative breast
cancer. Nat Cell Biol. 18:213–224. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Yang F, Zhang H, Mei Y and Wu M:
Reciprocal regulation of HIF-1α and lincRNA-p21 modulates the
Warburg effect. Mol Cell. 53:88–100. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Liu D and Li H: Long non-coding RNA GEHT1
promoted the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells via modulating
the protein stability of HIF1α. Biosci Rep. 39:2019.
|
|
93
|
Liao M, Liao W, Xu N, Li B, Liu F, Zhang
S, Wang Y, Wang S, Zhu Y, Chen D, et al: LncRNA EPB41L4A-AS1
regulates glycolysis and glutaminolysis by mediating nucleolar
translocation of HDAC2. EBioMedicine. 41:200–213. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Yoshida GJ: Emerging roles of Myc in stem
cell biology and novel tumor therapies. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
37:1732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Dang CV: Gene regulation: Fine-tuned
amplification in cells. Nature. 511:417–418. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Sabò A, Kress TR, Pelizzola M, de Pretis
S, Gorski MM, Tesi A, Morelli MJ, Bora P, Doni M, Verrecchia A, et
al: Selective transcriptional regulation by Myc in cellular growth
control and lymphomagenesis. Nature. 511:488–492. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Walz S, Lorenzin F, Morton J, Wiese KE,
von Eyss B, Herold S, Rycak L, Dumay-Odelot H, Karim S, Bartkuhn M,
et al: Activation and repression by oncogenic MYC shape
tumour-specific gene expression profiles. Nature. 511:483–487.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Dang CV, Kim JW, Gao P and Yustein J: The
interplay between MYC and HIF in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:51–56.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Grüning NM, Lehrach H and Ralser M:
Regulatory crosstalk of the metabolic network. Trends Biochem Sci.
35:220–227. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Kim JW, Gao P, Liu YC, Semenza GL and Dang
CV: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and dysregulated c-Myc cooperatively
induce vascular endothelial growth factor and metabolic switches
hexokinase 2 and pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1. Mol Cell Biol.
27:7381–7393. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Xiao ZD, Han L, Lee H, Zhuang L, Zhang Y,
Baddour J, Nagrath D, Wood CG, Gu J, Wu X, et al: Energy
stress-induced lncRNA FILNC1 represses c-Myc-mediated energy
metabolism and inhibits renal tumor development. Nat Commun.
8:7832017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Liao B, Hu Y and Brewer G: Competitive
binding of AUF1 and TIAR to MYC mRNA controls its translation. Nat
Struct Mol Biol. 14:511–518. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Huang H, Weng H, Sun W, Qin X, Shi H, Wu
H, Zhao BS, Mesquita A, Liu C, Yuan CL, et al: Recognition of RNA
N6-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA
stability and translation. Nat Cell Biol. 20:285–295. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Guo C, Shi H, Shang Y, Zhang Y, Cui J and
Yu H: LncRNA LINC00261 overexpression suppresses the growth and
metastasis of lung cancer via regulating miR-1269a/FOXO1 axis.
Cancer Cell Int. 20:2752020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Yu Y, Li L, Zheng Z, Chen S, Chen E and Hu
Y: Long non-coding RNA linc00261 suppresses gastric cancer
progression via promoting Slug degradation. J Cell Mol Med.
21:955–967. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Yan D, Liu W, Liu Y and Luo M: LINC00261
suppresses human colon cancer progression via sponging miR-324-3p
and inactivating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Cell Physiol.
234:22648–22656. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Zhai S, Xu Z, Xie J, Zhang J, Wang X, Peng
C, Li H, Chen H, Shen B and Deng X: Epigenetic silencing of LncRNA
LINC00261 promotes c-myc-mediated aerobic glycolysis by regulating
miR-222-3p/HIPK2/ERK axis and sequestering IGF2BP1. Oncogene.
40:277–291. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Wang Y, Lu JH, Wu QN, Jin Y, Wang DS, Chen
YX, Liu J, Luo XJ, Meng Q, Pu HY, et al: LncRNA LINRIS stabilizes
IGF2BP2 and promotes the aerobic glycolysis in colorectal cancer.
Mol Cancer. 18:1742019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Zhou Y, Li Y, Wang N, Li X, Zheng J and Ge
L: UPF1 inhibits the hepatocellular carcinoma progression by
targeting long non-coding RNA UCA1. Sci Rep. 9:66522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Koller-Eichhorn R, Marquardt T, Gail R,
Wittinghofer A, Kostrewa D, Kutay U and Kambach C: Human OLA1
defines an ATPase subfamily in the Obg family of GTP-binding
proteins. J Biol Chem. 282:19928–19937. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Whitaker-Menezes D, Martinez-Outschoorn
UE, Flomenberg N, Birbe RC, Witkiewicz AK, Howell A, Pavlides S,
Tsirigos A, Ertel A, Pestell RG, et al: Hyperactivation of
oxidative mitochondrial metabolism in epithelial cancer cells in
situ: Visualizing the therapeutic effects of metformin in tumor
tissue. Cell Cycle. 10:4047–4064. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|