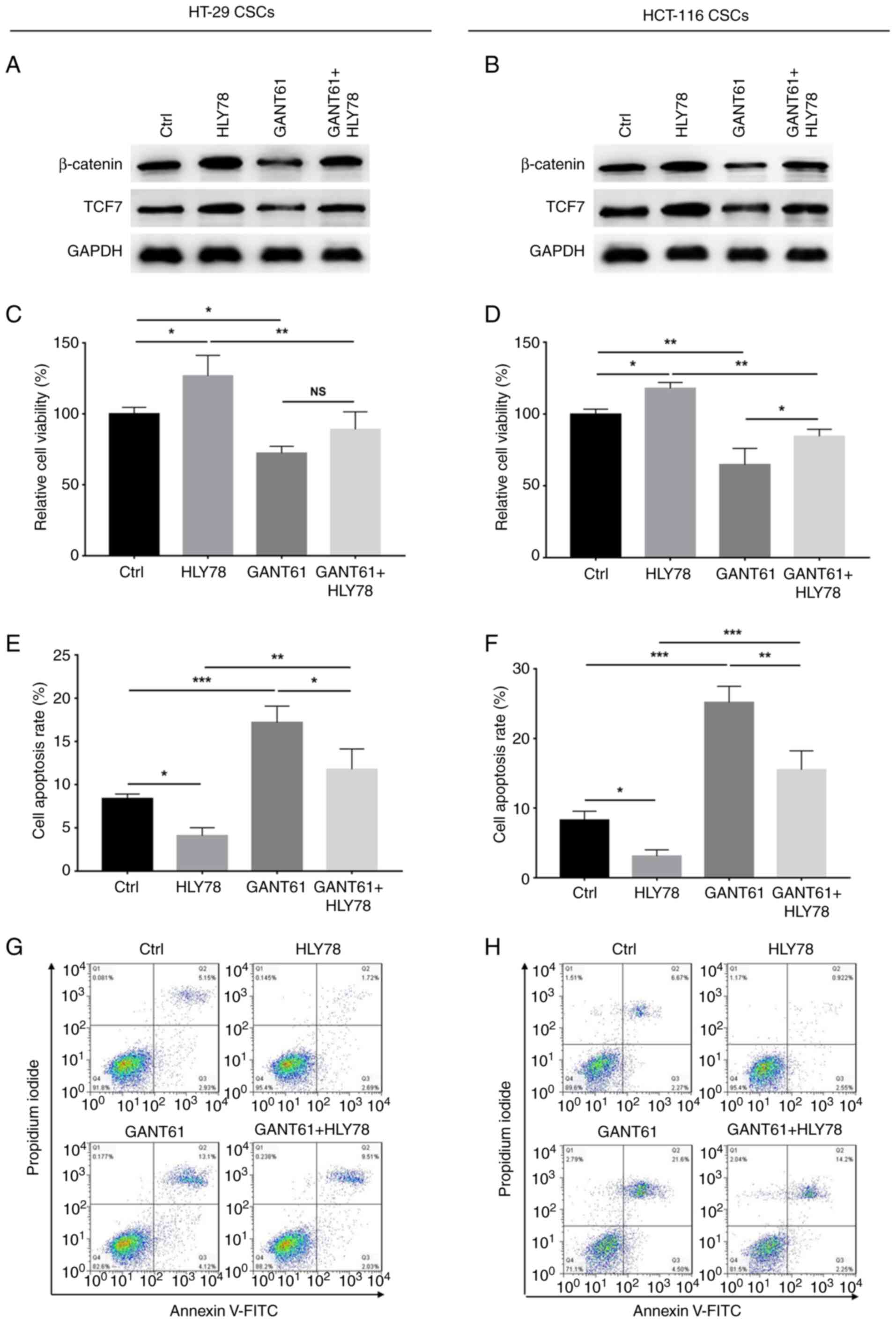
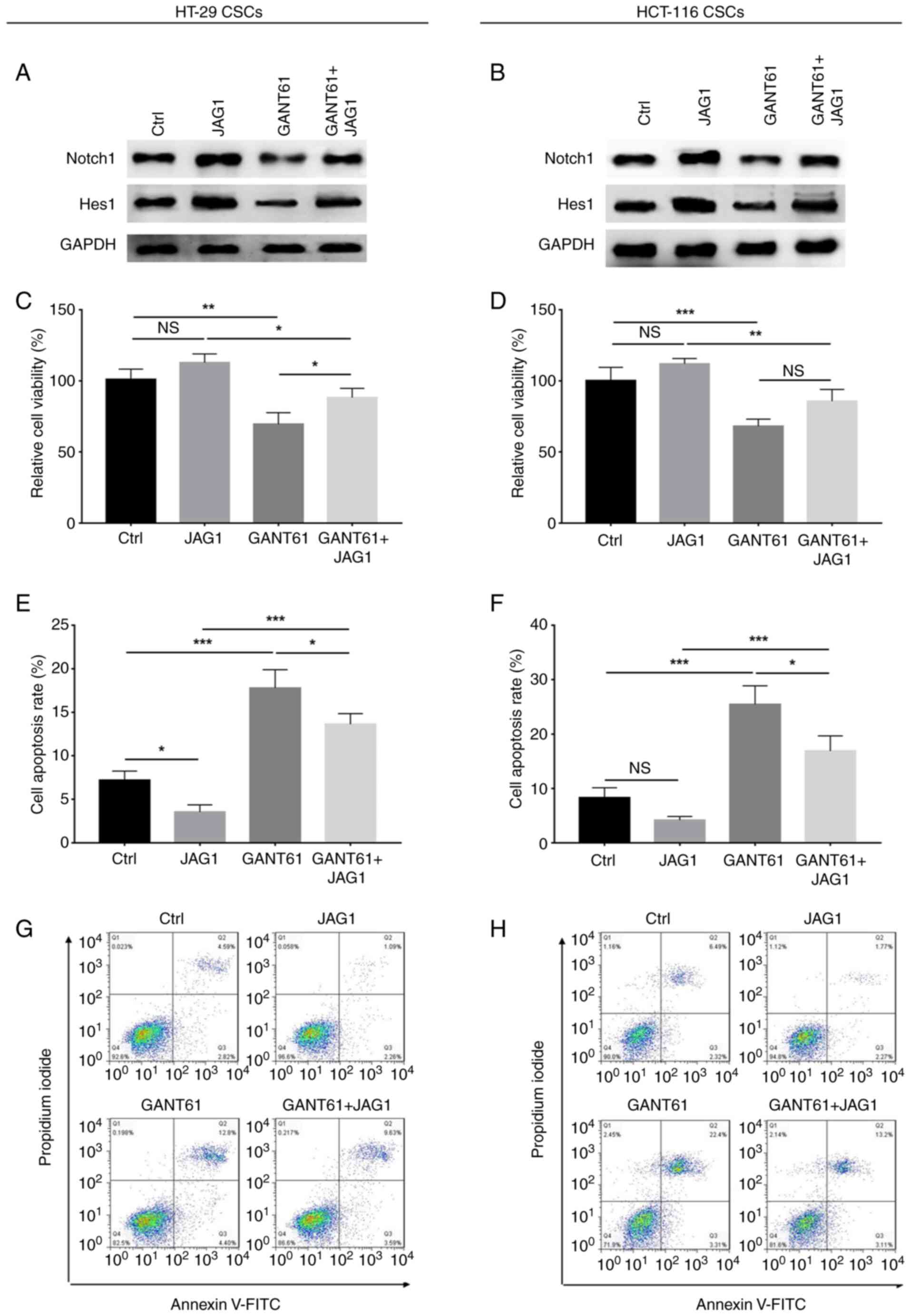
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global patterns and trends in
colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. 66:683–691. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
World Cancer Research Fund
International/American Institute for Cancer Research, . Continuous
update project report: Diet, nutrition, physical activity, and
colorectal cancer. American Institute for Cancer Research.
https://www.aicr.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/colorectal-cancer-2017-report.pdf
|
|
4
|
Marmol I, Sanchez-de-Diego C, Pradilla
Dieste A, Cerrada E and Rodriguez Yoldi MJ: Colorectal Carcinoma: A
general overview and future perspectives in colorectal cancer. Int
J Mol Sci. 18:1972017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brody H: Colorectal cancer. Nature.
521:S12015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nassar D and Blanpain C: Cancer stem
cells: Basic concepts and therapeutic implications. Annu Rev
Pathol. 11:47–76. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Quarni W, Dutta R, Green R, Katiri S,
Patel B, Mohapatra SS and Mohapatra S: Mithramycin a inhibits
colorectal cancer growth by targeting cancer stem cells. Sci Rep.
9:152022019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park SY, Lee CJ, Choi JH, Kim JH, Kim JW,
Kim JY and Nam JS: The JAK2/STAT3/CCND2 Axis promotes colorectal
Cancer stem cell persistence and radioresistance. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 38:3992019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou Y, Xia L, Wang H, Oyang L, Su M, Liu
Q, Lin J, Tan S, Tian Y, Liao Q and Cao D: Cancer stem cells in
progression of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 9:33403–33415. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Elbadawy M, Usui T, Yamawaki H and Sasaki
K: Emerging Roles of C-Myc in cancer stem cell-related signaling
and resistance to cancer chemotherapy: A potential therapeutic
target against colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 20:23402019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dimou A, Bamias A, Gogas H and Syrigos K:
Inhibition of the Hedgehog pathway in lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
133:56–61. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kotulak-Chrzaszcz A, Klacz J, Matuszewski
M, Kmiec Z and Wierzbicki PM: Expression of the Sonic Hedgehog
pathway components in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
18:5801–5810. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Carpenter RL and Ray H: Safety and
tolerability of sonic hedgehog pathway inhibitors in cancer. Drug
Saf. 42:263–279. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Usui T, Sakurai M, Umata K, Elbadawy M,
Ohama T, Yamawaki H, Hazama S, Takenouchi H, Nakajima M, Tsunedomi
R, et al: Hedgehog signals mediate anti-cancer drug resistance in
three-dimensional primary colorectal cancer organoid culture. Int J
Mol Sci. 19:10982018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim BR, Na YJ, Kim JL, Jeong YA, Park SH,
Jo MJ, Jeong S, Kang S, Oh SC and Lee DH: RUNX3 suppresses
metastasis and stemness by inhibiting Hedgehog signaling in
colorectal cancer. Cell Death Differ. 27:676–694. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Papadopoulos V, Tsapakidis K, Riobo Del
Galdo NA, Papandreou CN, Del Galdo F, Anthoney A, Sakellaridis N,
Dimas K and Kamposioras K: The prognostic significance of the
Hedgehog signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal
Cancer. 15:116–127. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lu J, Liu L, Zheng M, Li X, Wu A, Wu Q,
Liao C, Zou J and Song H: MEKK2 and MEKK3 suppress Hedgehog
pathway-dependent medulloblastoma by inhibiting GLI1 function.
Oncogene. 37:3864–3878. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu L, Wu M, Zhao F, Fu W, Li W, Li X and
Liu T: Prognostic and clinicopathological value of Gli-1 expression
in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 7:69087–69096.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lauth M, Bergstrom A, Shimokawa T and
Toftgard R: Inhibition of GLI-mediated transcription and tumor cell
growth by small-molecule antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:8455–8460. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Calcaterra A, Iovine V, Botta B, Quaglio
D, D'Acquarica I, Ciogli A, Iazzetti A, Alfonsi R, Lospinoso
Severini L, Infante P, et al: Chemical, computational and
functional insights into the chemical stability of the Hedgehog
pathway inhibitor GANT61. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 33:349–358.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gonnissen A, Isebaert S, McKee CM, Dok R,
Haustermans K and Muschel RJ: The hedgehog inhibitor GANT61
sensitizes prostate cancer cells to ionizing radiation both in
vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 7:84286–84298. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Koike Y, Ohta Y, Saitoh W, Yamashita T,
Kanomata N, Moriya T and Kurebayashi J: Anti-cell growth and
anti-cancer stem cell activities of the non-canonical hedgehog
inhibitor GANT61 in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Breast
Cancer. 24:683–693. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zlobin A, Jang M and Miele L: Toward the
rational design of cell fate modifiers: Notch signaling as a target
for novel biopharmaceuticals. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 1:83–106.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nickoloff BJ, Qin JZ, Chaturvedi V,
Denning MF, Bonish B and Miele L: Jagged-1 mediated activation of
notch signaling induces complete maturation of human keratinocytes
through NF-kappaB and PPARgamma. Cell Death Differ. 9:842–855.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wen F, Wong HK, Tay CY, Yu H, Li H, Yu T,
Tijore A, Boey FY, Venkatraman SS and Tan LP: Induction of myogenic
differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells cultured on Notch
agonist (Jagged-1) modified biodegradable scaffold surface. ACS
Appl Mater Interfaces. 6:1652–1661. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yakisich JS, Azad N, Kaushik V, O'Doherty
GA and Iyer AK: Nigericin decreases the viability of
multidrug-resistant cancer cells and lung tumorspheres and
potentiates the effects of cardiac glycosides. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283176943102017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guo X, Zhang L, Fan Y, Zhang D, Qin L,
Dong S and Li G: Oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 8
inhibits gastric cancer growth through induction of ER stress,
inhibition of wnt signaling, and activation of apoptosis. Oncol
Res. 25:799–808. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou Y, An Q, Guo RX, Qiao YH, Li LX,
Zhang XY and Zhao XL: MiR424-5p functions as an anti-oncogene in
cervical cancer cell growth by targeting KDM5B via the Notch
signaling pathway. Life Sci. 171:9–15. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Karimzadeh F, Modarres Mousavi SM, Alipour
F, Hosseini Ravandi H, Kovac S and Gorji A: Developmental changes
in Notch1 and NLE1 expression in a genetic model of absence
epilepsy. Brain Struct Funct. 222:2773–2785. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hemmati HD, Nakano I, Lazareff JA,
Masterman-Smith M, Geschwind DH, Bronner-Fraser M and Kornblum HI:
Cancerous stem cells can arise from pediatric brain tumors. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:15178–15183. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang L, Hirohashi Y, Ogawa T, Shen M,
Takeda R, Murai A, Yamamoto E, Kubo T and Nakatsugawa M: LY6/PLAUR
domain containing 3 has a role in the maintenance of colorectal
cancer stem-like cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 486:232–238.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Roth AD, Tejpar S, Delorenzi M, Yan P,
Fiocca R, Klingbiel D, Dietrich D, Biesmans B, Bodoky G, Barone C,
et al: Prognostic role of KRAS and BRAF in stage II and III
resected colon cancer: Results of the translational study on the
PETACC-3, EORTC 40993, SAKK 60–00 trial. J Clin Oncol. 28:466–474.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rahbari NN, Kedrin D, Incio J, Liu H, Ho
WW, Nia HT, Edrich CM, Jung K, Daubriac J, Chen I, et al: Anti-VEGF
therapy induces ECM remodeling and mechanical barriers to therapy
in colorectal cancer liver metastases. Sci Transl Med.
8:360ra1352016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tiwari A, Saraf S, Verma A, Panda PK and
Jain SK: Novel targeting approaches and signaling pathways of
colorectal cancer: An insight. World J Gastroenterol. 24:4428–4435.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Park SH, Jo MJ, Kim BR, Jeong YA, Na YJ,
Kim JL, Jeong S, Yun HK, Kim DY, Kim BG, et al: Sonic hedgehog
pathway activation is associated with cetuximab resistance and
EPHB3 receptor induction in colorectal cancer. Theranostics.
9:2235–2251. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chang Y, Chen H, Duan J, Wu W, Le F and
Mou F: The inhibitory effect and safety of GANT61 on HeLa cells in
nude mice. Exp Mol Pathol. 113:1043522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Matsumoto T, Tabata K and Suzuki T: The
GANT61, a GLI inhibitor, induces caspase-independent apoptosis of
SK-N-LO cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 37:633–641. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Geng L, Lu K, Li P, Li X, Zhou X, Li Y and
Wang X: GLI1 inhibitor GANT61 exhibits antitumor efficacy in T-cell
lymphoma cells through down-regulation of p-STAT3 and SOCS3.
Oncotarget. 8:48701–48710. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sun W, Li L, Du Z, Quan Z, Yuan M, Cheng
H, Gao Y, Luo C and Wu X: Combination of phospholipase Cε knockdown
with GANT61 sensitizes castrationresistant prostate cancer cells to
enzalutamide by suppressing the androgen receptor signaling
pathway. Oncol Rep. 41:2689–2702. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kurebayashi J, Koike Y, Ohta Y, Saitoh W,
Yamashita T, Kanomata N and Moriya T: Anti-cancer stem cell
activity of a hedgehog inhibitor GANT61 in estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 108:918–930.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Vlckova K, Reda J, Ondrusova L, Krayem M,
Ghanem G and Vachtenheim J: GLI inhibitor GANT61 kills melanoma
cells and acts in synergy with obatoclax. Int J Oncol. 49:953–960.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tong W, Qiu L, Qi M, Liu J, Hu K, Lin W,
Huang Y and Fu J: GANT-61 and GDC-0449 induce apoptosis of prostate
cancer stem cells through a GLI-dependent mechanism. J Cell
Biochem. 119:3641–3652. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rubinstein MR, Baik JE, Lagana SM, Han RP,
Raab WJ, Sahoo D, Dalerba P, Wang TC and Han YW: Fusobacterium
nucleatum promotes colorectal cancer by inducing Wnt/β-catenin
modulator Annexin A1. EMBO Rep. 20:e476382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhan T, Ambrosi G, Wandmacher AM, Rauscher
B, Betge J, Rindtorff N, Häussler RS, Hinsenkamp I, Bamberg L,
Hessling B, et al: MEK inhibitors activate Wnt signalling and
induce stem cell plasticity in colorectal cancer. Nat Commun.
10:21972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jackstadt R, van Hooff SR, Leach JD,
Cortes-Lavaud X, Lohuis JO, Ridgway RA, Wouters VM, Roper J,
Kendall TJ, Roxburgh CS, et al: Epithelial NOTCH signaling rewires
the tumor microenvironment of colorectal cancer to drive
poor-prognosis subtypes and metastasis. Cancer Cell. 36:319–336.e7.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Miyazaki Y, Matsubara S, Ding Q, Tsukasa
K, Yoshimitsu M, Kosai K and Takao S: Efficient elimination of
pancreatic cancer stem cells by hedgehog/GLI inhibitor GANT61 in
combination with mTOR inhibition. Mol Cancer. 15:492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hua F, Shang S, Yang YW, Zhang HZ, Xu TL,
Yu JJ, Zhou DD, Cui B, Li K, Lv XX, et al: TRIB3 interacts With
β-Catenin and TCF4 to increase stem cell features of colorectal
cancer stem cells and tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology.
156:708–721.e15. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Huang R, Wang G, Song Y, Tang Q, You Q,
Liu Z, Chen Y, Zhang Q, Li J, Muhammand S and Wang X: Colorectal
cancer stem cell and chemoresistant colorectal cancer cell
phenotypes and increased sensitivity to Notch pathway inhibitor.
Mol Med Rep. 12:2417–2424. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|