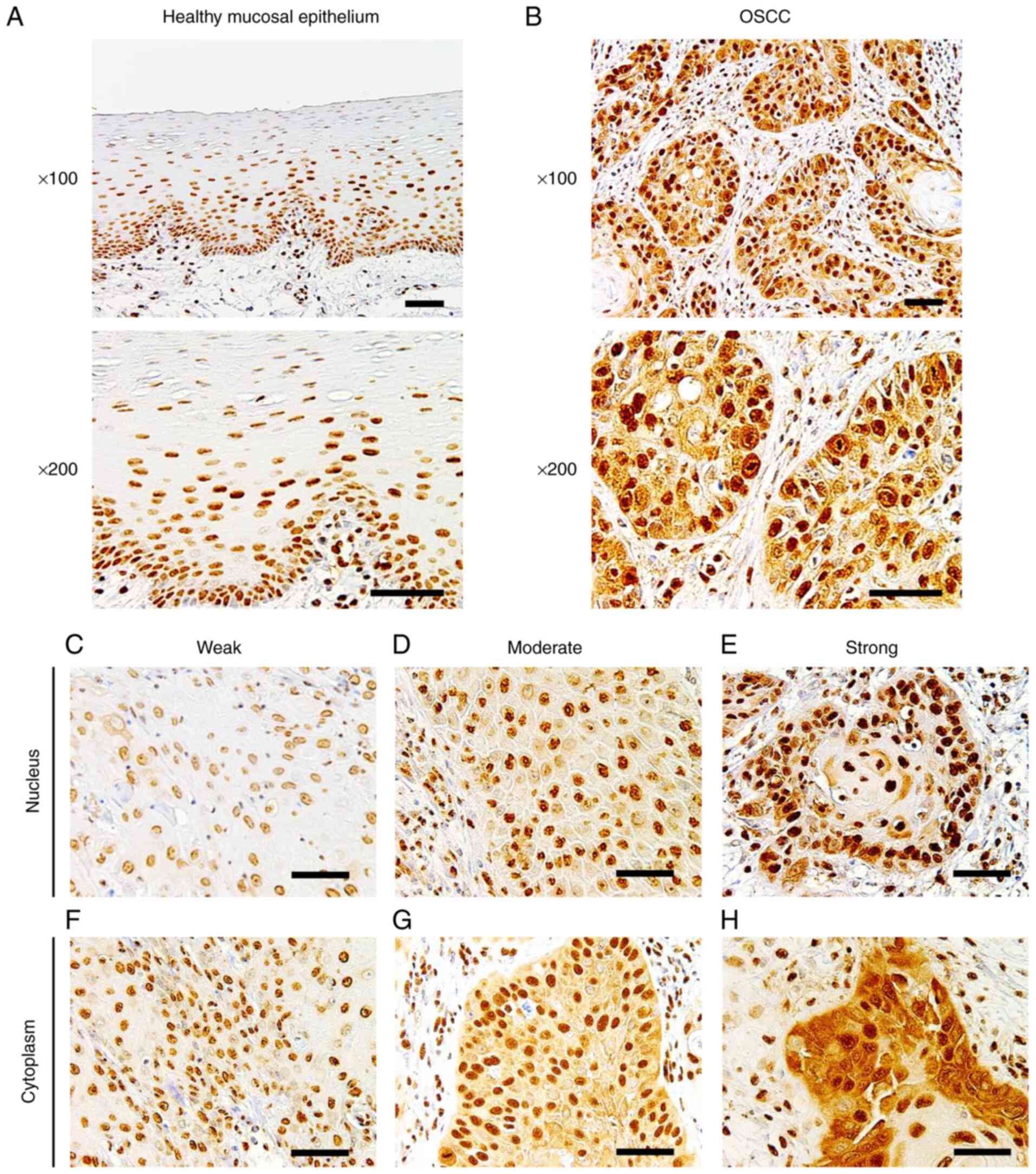
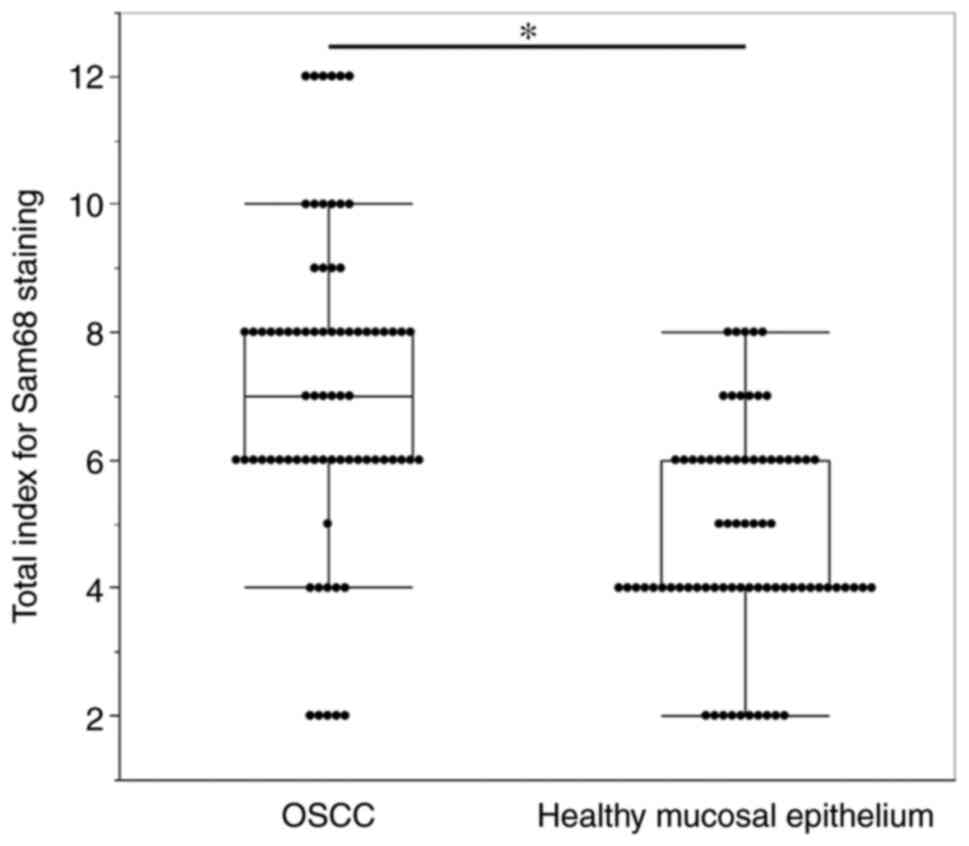
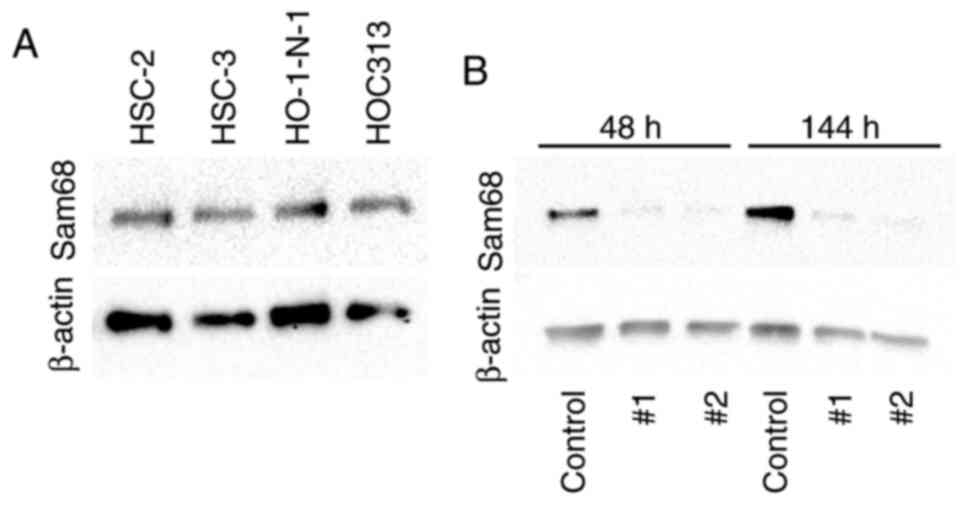
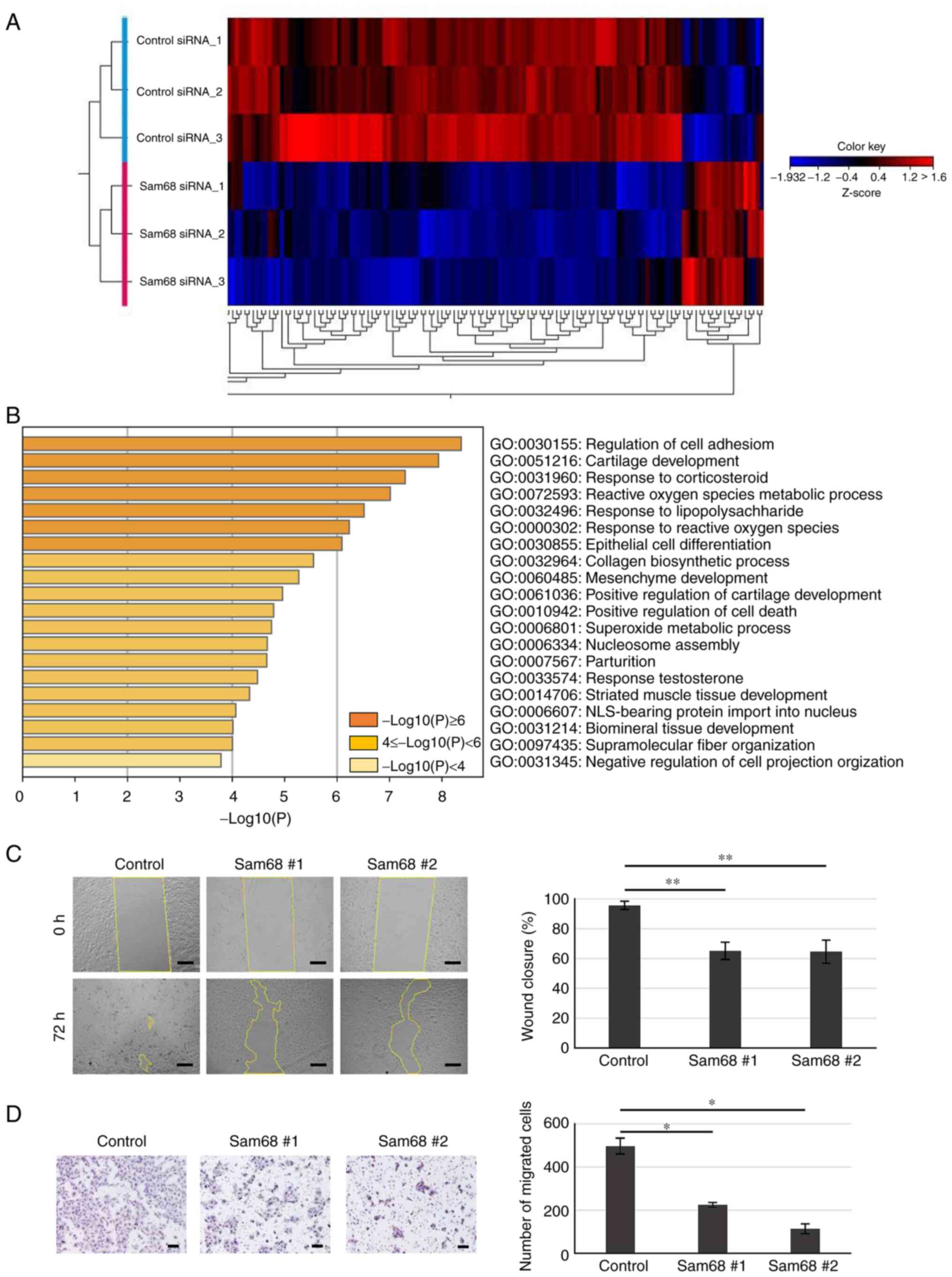
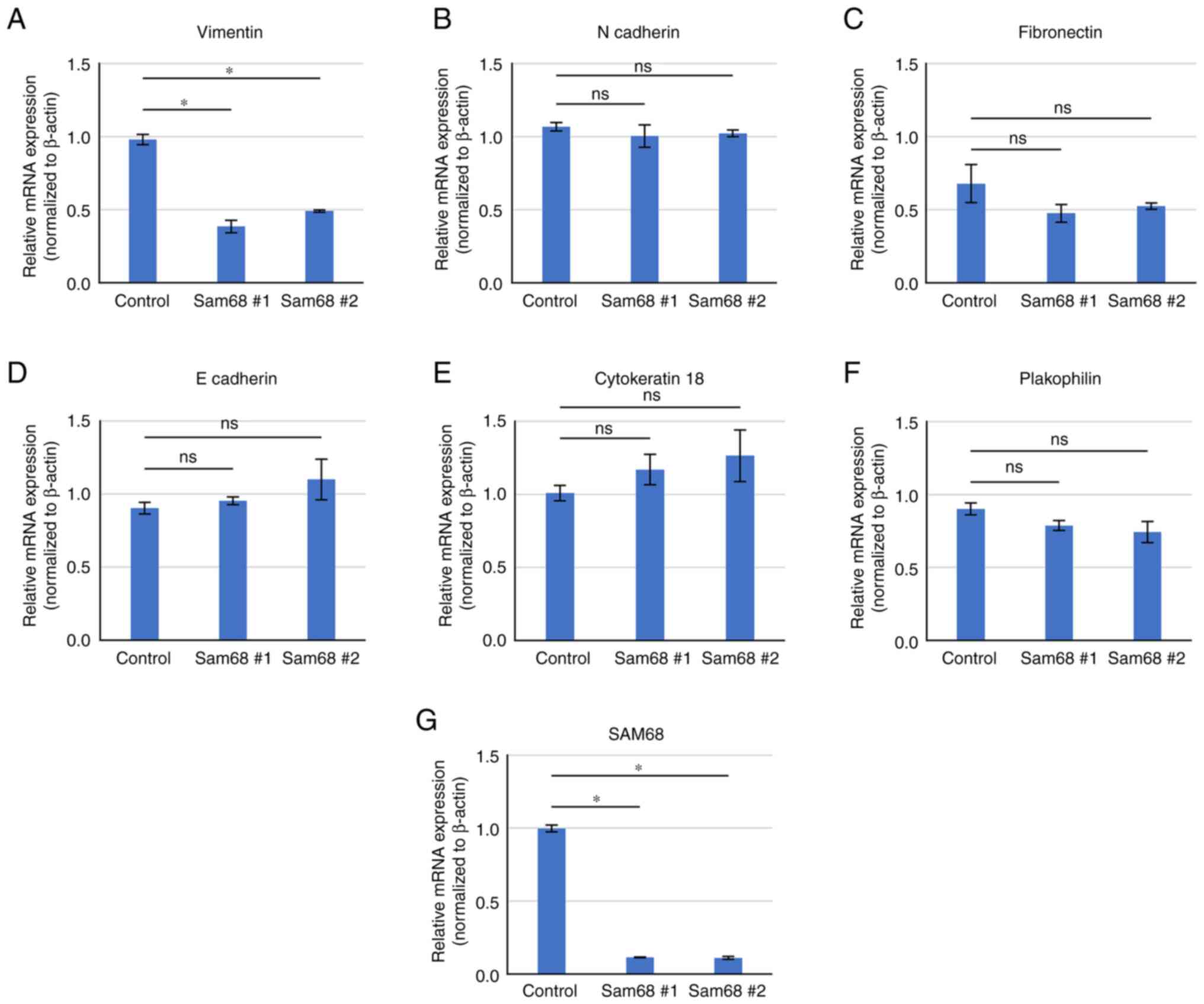
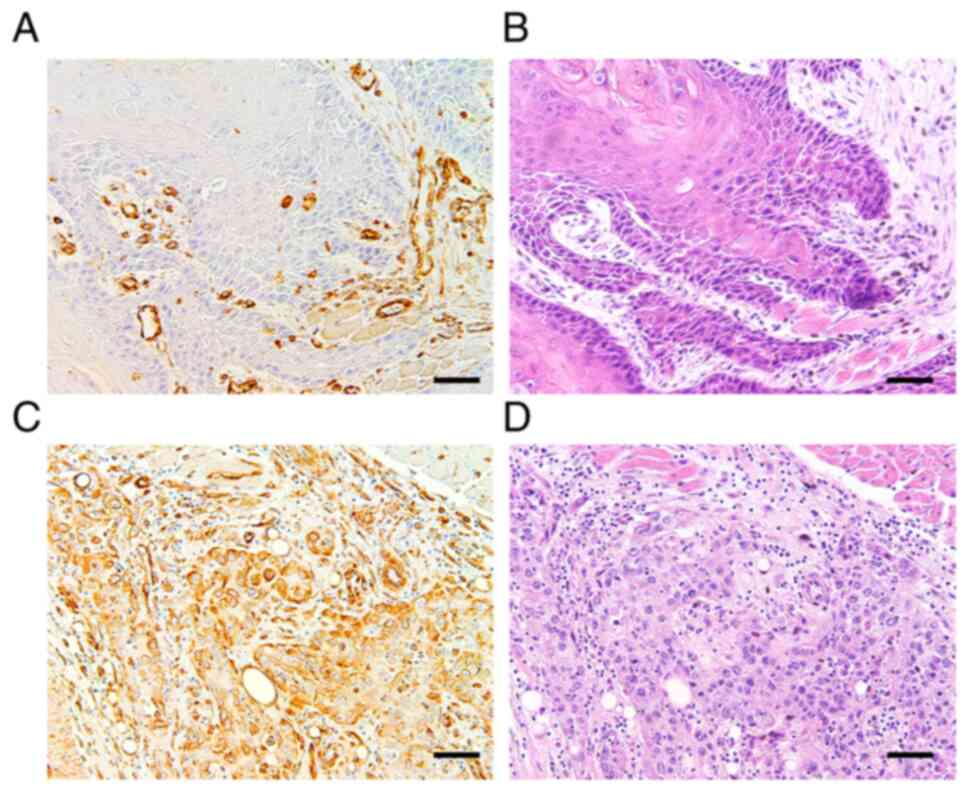
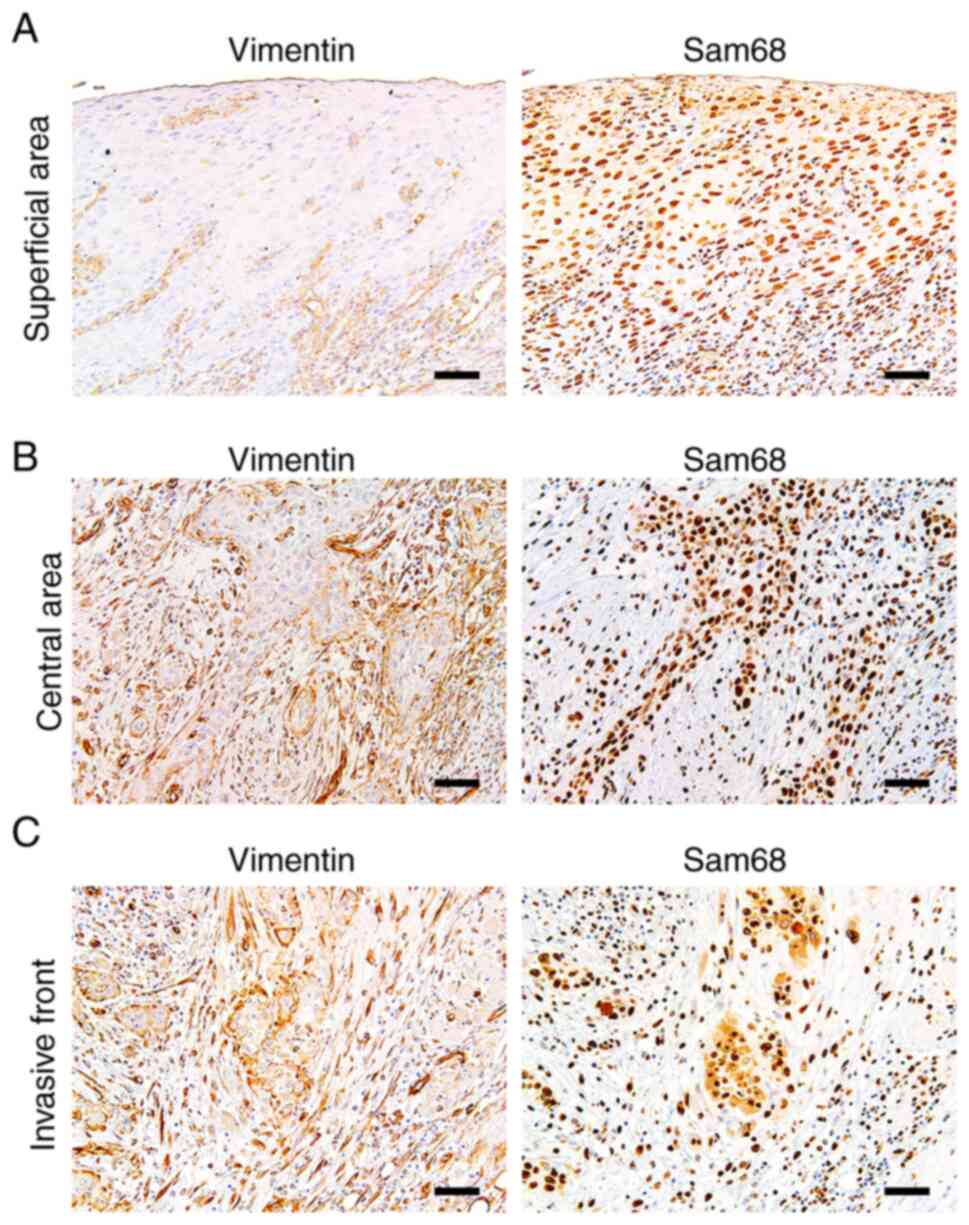
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
El-Naggar AK, Chan JKC, Grandis JR, Takata
T and Slootweg PJ: WHO classification of head and neck tumours. 4th
edition. IARC Press; Lyon: 2017
|
|
3
|
Sato J, Kitagawa Y, Watanabe S, Asaka T,
Ohga N, Hirata K, Shiga T, Satoh A and Tamaki N: Hypoxic volume
evaluated by 18F-fluoromisonidazole positron emission
tomography (FMISO-PET) may be a prognostic factor in patients with
oral squamous cell carcinoma: Preliminary analyses. Int J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 47:553–560. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Larsen SR, Johansen J, Sørensen JA and
Krogdahl A: The prognostic significance of histological features in
oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 38:657–662. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oikawa Y, Kugimoto T, Kashima Y, Okuyama
K, Ohsako T, Kuroshima T, Hirai H, Tomioka H, Shimamoto H, Michi Y
and Harada H: Surgical treatment for oral tongue squamous cell
carcinoma: A retrospective study of 432 patients. Glob Health Med.
3:157–162. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tomioka H, Yamagata Y, Oikawa Y, Ohsako T,
Kugimoto T, Kuroshima T, Hirai H, Shimamoto H and Harada H: Risk
factors for distant metastasis in locoregionally controlled oral
squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective study. Sci Rep.
11:52132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kuroshima T, Onozato Y, Oikawa Y, Ohsako
T, Kugimoto T, Hirai H, Tomioka H, Michi Y, Miura M, Yoshimura R
and Harada H: Prognostic impact of lingual lymph node metastasis in
patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: A
retrospective study. Sci Rep. 11:205352021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vernet C and Artzt K: STAR, a gene family
involved in signal transduction and activation of RNA. Trends
Genet. 13:479–484. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bielli P, Busà R, Paronetto MP and Sette
C: The RNA-binding protein Sam68 is a multifunctional player in
human cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 18:R91–R102. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Henao-Mejia J and He JJ: Sam68
relocalization into stress granules in response to oxidative stress
through complexing with TIA-1. Exp Cell Res. 315:3381–3395. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu J, Zhou L, Tonissen K, Tee R and Artzt
K: The quaking I-5 protein (QKI-5) has a novel nuclear localization
signal and shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. J Biol
Chem. 274:29202–29210. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li J, Liu Y, Kim BO and He JJ: Direct
participation of Sam68, the 68-kilodalton Src-associated protein in
mitosis, in the CRM1-mediated Rev nuclear export pathway. J Virol.
76:8374–8382. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Babic I, Cherry E and Fujita DJ: SUMO
modification of Sam68 enhances its ability to repress cyclin D1
expression and inhibits its ability to induce apoptosis. Oncogene.
25:4955–4964. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Paronetto MP, Achsel T, Massiello A,
Chalfant CE and Sette C: The RNA-binding protein Sam68 modulates
the alternative splicing of Bcl-x. J Cell Biol. 176:929–939. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hong W, Resnick RJ, Rakowski C, Shalloway
D, Taylor SJ and Blobel GA: Physical and functional interaction
between the transcriptional cofactor CBP and the KH domain protein
Sam68. Mol Cancer Res. 1:48–55. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Richard S, Torabi N, Franco GV, Tremblay
GA, Chen T, Vogel G, Morel M, Cléroux P, Forget-Richard A, Komarova
S, et al: Ablation of the Sam68 RNA binding protein protects mice
from age-related bone loss. PLoS Genet. 1:e742005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Iijima T, Wu K, Witte H, Hanno-Iijima Y,
Glatter T, Richard S and Scheiffele P: SAM68 regulates neuronal
activity-dependent alternative splicing of neurexin-1. Cell.
147:1601–1614. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Frisone P, Pradella D, Di Matteo A,
Belloni E, Ghigna C and Paronetto MP: SAM68: Signal transduction
and RNA metabolism in human cancer. Biomed Res Int.
2015:5289542015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Valacca C, Bonomi S, Buratti E, Pedrotti
S, Baralle FE, Sette C, Ghigna C and Biamonti G: Sam68 regulates
EMT through alternative splicing-activated nonsense-mediated mRNA
decay of the SF2/ASF proto-oncogene. J Cell Biol. 191:87–99. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen S, Li H, Zhuang S, Zhang J, Gao F,
Wang X, Chen W and Song M: Sam68 reduces cisplatin-induced
apoptosis in tongue carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:1232016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xiao J, Wang Q, Yang Q, Wang H, Qiang F,
He S, Cai J, Yang L and Wang Y: Clinical significance and effect of
Sam68 expression in gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 15:4745–4752.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li X, Zhou X, Hua F, Fan Y, Zu L, Wang Y,
Shen W, Pan H and Zhou Q: The RNA-binding protein Sam68 is critical
for non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation by regulating
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 10:8281–8291.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li Z, Yu CP, Zhong Y, Liu TJ, Huang QD,
Zhao XH, Huang H, Tu H, Jiang S, Zhang Y, et al: Sam68 expression
and cytoplasmic localization is correlated with lymph node
metastasis as well as prognosis in patients with early-stage
cervical cancer. Ann Oncol. 23:638–646. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Z, Li J, Zheng H, Yu C, Chen J, Liu
Z, Li M, Zeng M, Zhou F and Song L: Expression and cytoplasmic
localization of SAM68 is a significant and independent prognostic
marker for renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
18:2685–2693. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sumithra B, Saxena U and Das AB: A
comprehensive study on genome-wide coexpression network of
KHDRBS1/Sam68 reveals its cancer and patient-specific association.
Sci Rep. 9:110832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Song L, Wang L, Li Y, Xiong H, Wu J, Li J
and Li M: Sam68 up-regulation correlates with, and its
down-regulation inhibits, proliferation and tumourigenicity of
breast cancer cells. J Pathol. 222:227–237. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yamamoto E, Kohama G, Sunakawa H, Iwai M
and Hiratsuka H: Mode of invasion, bleomycin sensitivity, and
clinical course in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity.
Cancer. 51:2175–2180. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene FL and Trotti AA: American Joint Committee on Cancer: AJCC
cancer staging manual. 7th edition. Springer-Verlag; New York:
2009
|
|
29
|
Costa LC, Leite CF, Cardoso SV, Loyola AM,
Faria PR, Souza PE and Horta MC: Expression of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers at the invasive front of
oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Appl Oral Sci. 23:169–178. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tran CM, Kuroshima T, Oikawa Y, Michi Y,
Kayamori K and Harada H: Clinicopathological and
immunohistochemical characteristics of pigmented oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 21:3392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Momose F, Araida T, Negishi A, Ichijo H,
Shioda S and Sasaki S: Variant sublines with different metastatic
potentials selected in nude mice from human oral squamous cell
carcinomas. J Oral Pathol Med. 18:391–395. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tadokoro K, Ueda M, Ohshima T, Fujita K,
Rikimaru K, Takahashi N, Enomoto S and Tsuchida N: Activation of
oncogenes in human oral cancer cells: A novel codon 13 mutation of
c-H-ras-1 and concurrent amplifications of c-erbB-1 and c-myc.
Oncogene. 4:499–505. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tamai S, Fujita SI, Komine R, Kanki Y,
Aoki K, Watanabe K, Takekoshi K and Sugasawa T: Acute cold stress
induces transient MuRF1 upregulation in the skeletal muscle of
zebrafish. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 608:59–65. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M,
Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C and Chanda SK: Metascape
provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of
systems-level datasets. Nat Commun. 10:15232019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Le Bras GF, Taubenslag KJ and Andl CD: The
regulation of cell-cell adhesion during epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, motility and tumor progression. Cell Adh Migr.
6:365–373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sun BO, Fang Y, Li Z, Chen Z and Xiang J:
Role of cellular cytoskeleton in epithelial-mesenchymal transition
process during cancer progression. Biomed Rep. 3:603–610. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kurihara K, Isobe T, Yamamoto G, Tanaka Y,
Katakura A and Tachikawa T: Expression of BMI1 and ZEB1 in
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tongue squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 34:771–778. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xu B, Salama AM, Valero C, Yuan A, Khimraj
A, Saliba M, Zanoni DK, Ganly I, Patel SG, Katabi N and Ghossein R:
The prognostic role of histologic grade, worst pattern of invasion,
and tumor budding in early oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma: A
comparative study. Virchows Arch. 479:597–606. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kane SV, Gupta M, Kakade AC and D' Cruz A:
Depth of invasion is the most significant histological predictor of
subclinical cervical lymph node metastasis in early squamous
carcinomas of the oral cavity. Eur J Surg Oncol. 32:795–803. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kolokythas A, Park S, Schlieve T, Pytynia
K and Cox D: Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue:
Histopathological parameters associated with outcome. Int J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 44:1069–1074. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Guan Y, Xu F, Wang Y, Tian J, Wan Z, Wang
Z and Chong T: Identification of key genes and functions of
circulating tumor cells in multiple cancers through bioinformatic
analysis. BMC Med Genomics. 13:1402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Han Y, Yamada SI, Kawamoto M, Gibo T,
Hashidume M, Otagiri H, Tanaka H, Takizawa A, Kondo E, Sakai H, et
al: Immunohistochemical investigation of biomarkers for predicting
adipose tissue invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral
Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol. 34:507–513. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Saito D, Kyakumoto S, Chosa N, Ibi M,
Takahashi N, Okubo N, Sawada S, Ishisaki A and Kamo M: Transforming
growth factor-β1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
integrin α3β1-mediated cell migration of HSC-4 human squamous cell
carcinoma cells through Slug. J Biochem. 153:303–315. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zeisberg M and Neilson EG: Biomarkers for
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest. 119:1429–1437.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jolly MK, Somarelli JA, Sheth M, Biddle A,
Tripathi SC, Armstrong AJ, Hanash SM, Bapat SA, Rangarajan A and
Levine H: Hybrid epithelial/mesenchymal phenotypes promote
metastasis and therapy resistance across carcinomas. Pharmacol
Ther. 194:161–184. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Saitoh M: Involvement of partial EMT in
cancer progression. J Biochem. 164:257–264. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sakakitani S, Podyma-Inoue KA, Takayama R,
Takahashi K, Ishigami-Yuasa M, Kagechika H, Harada H and Watabe T:
Activation of β2-adrenergic receptor signals suppresses mesenchymal
phenotypes of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci.
112:155–167. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lin CH, Liao CC, Wang SY, Peng CY, Yeh YC,
Chen MY and Chou TY: Comparative O-GlcNAc proteomic analysis
reveals a role of O-GlcNAcylated SAM68 in lung cancer
aggressiveness. Cancers (Basel). 14:2432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lucena MC, Carvalho-Cruz P, Donadio JL,
Oliveira IA, de Queiroz RM, Marinho-Carvalho MM, Sola-Penna M, de
Paula IF, Gondim KC, McComb ME, et al: Epithelial mesenchymal
transition induces aberrant glycosylation through hexosamine
biosynthetic pathway activation. J Biol Chem. 291:12917–12929.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|