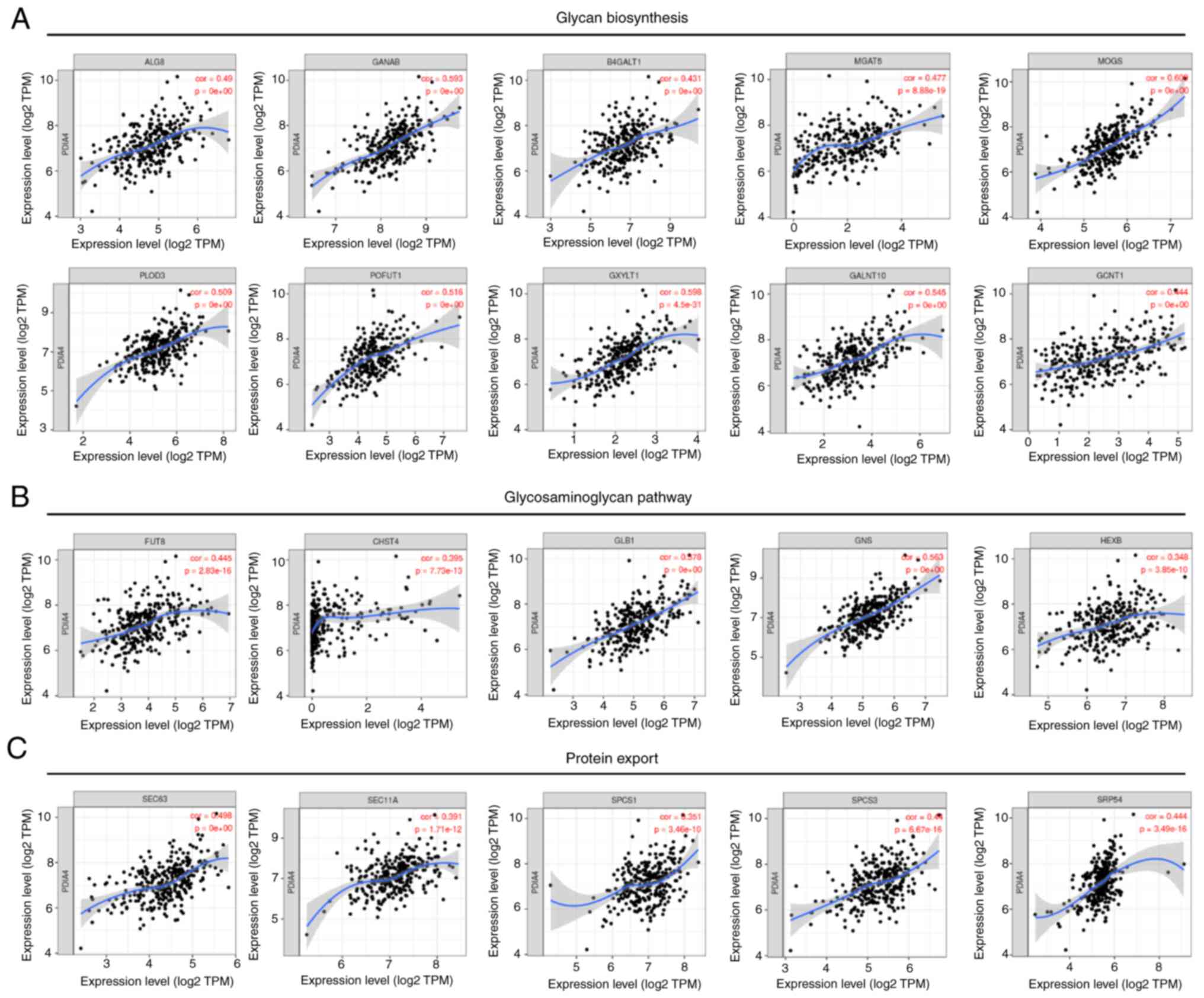
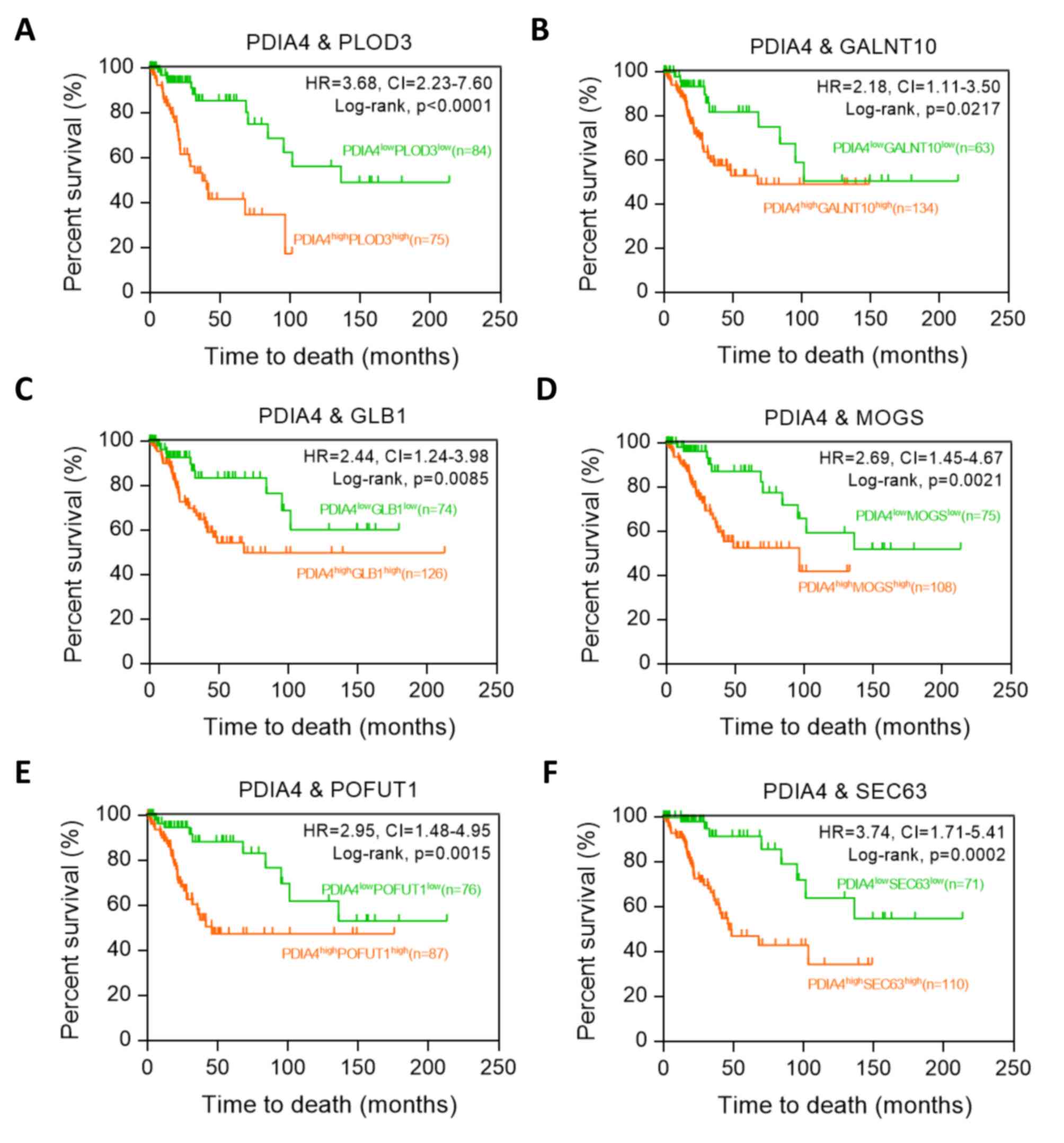
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer Statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Patrono MG, Calvo MF, Franco JV, Garrote V
and Vietto V: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the
prevalence of therapeutic targets in cervical cancer.
Ecancermedicalscience. 15:12002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Matsusaki M, Kanemura S, Kinoshita M, Lee
YH, Inaba K and Okumura M: The protein disulfide isomerase family:
From proteostasis to pathogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj.
1864:1293382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang Z, Zhang H and Cheng Q: PDIA4: The
basic characteristics, functions and its potential connection with
cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 122:1096882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Winship AL, Sorby K, Correia J, Rainczuk
A, Yap J and Dimitriadis E: Interleukin-11 up-regulates endoplasmic
reticulum stress induced target, PDIA4 in human first trimester
placenta and in vivo in mice. Placenta. 53:92–100. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pawar H, Kashyap MK, Sahasrabuddhe NA,
Renuse S, Harsha HC, Kumar P, Sharma J, Kandasamy K, Marimuthu A,
Nair B, et al: Quantitative tissue proteomics of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma for novel biomarker discovery. Cancer Biol
Ther. 12:510–522. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li H, Liu Q, Xiao K, He Z, Wu C, Sun J,
Chen X, Chen S, Yang J, Ma Q and Su J: PDIA4 Correlates with poor
prognosis and is a potential biomarker in glioma. Onco Targets
Ther. 14:125–138. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kuo TF, Chen TY, Jiang ST, Chen KW, Chiang
YM, Hsu YJ, Liu YJ, Chen HM, Yokoyama KK, Tsai KC, et al: Protein
disulfide isomerase a4 acts as a novel regulator of cancer growth
through the procaspase pathway. Oncogene. 36:5484–5496. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qian S, Zhang S, Wu Y, Ding Y, Shen and Li
X: Protein disulfide isomerase 4 drives docetaxel resistance in
prostate cancer. Chemotherapy. 65:125–133. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tufo G, Jones AW, Wang Z, Hamelin J,
Tajeddine N, Esposti DD, Martel C, Boursier C, Gallerne C, Migdal
C, et al: The protein disulfide isomerases PDIA4 and PDIA6 mediate
resistance to cisplatin-induced cell death in lung adenocarcinoma.
Cell Death Differ. 21:685–695. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chanjiao Y, Chunyan C, Xiaoxin Q and
Youjian H: MicroRNA-378a-3p contributes to ovarian cancer
progression through downregulating PDIA4. Immun Inflamm Dis.
9:108–119. 2021. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SA, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BV and Varambally
S: UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression
and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhai Y, Kuick R, Nan B, Ota I, Weiss SJ,
Trimble CL, Fearon ER and Cho KR: Gene expression analysis of
preinvasive and invasive cervical squamous cell carcinomas
identifies HOXC10 as a key mediator of invasion. Cancer Res.
67:10163–10172. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Scotto L, Narayan G, Nandula SV,
Arias-Pulido H, Subramaniyam S, Schneider A, Kaufmann AM, Wright
JD, Pothuri B, Mansukhani M and Murty VV: Identification of copy
number gain and overexpressed genes on chromosome arm 20q by an
integrative genomic approach in cervical cancer: Potential role in
progression. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 47:755–765. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Biewenga P, Buist MR, Moerland PD, Ver
Loren van Themaat E, van Kampen AH, ten Kate FJ and Baas F: Gene
expression in early stage cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
108:520–526. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nagy Á, Munkácsy G and Győrffy B:
Pancancer survival analysis of cancer hallmark genes. Sci Rep.
11:60472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vasaikar SV, Straub P, Wang J and Zhang B:
LinkedOmics: Analyzing multi-omics data within and across 32 cancer
types. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:D956–D963. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li T, Fan J, Wang B, Traugh N, Chen Q, Liu
JS, Li B and Liu XS: TIMER: A web server for comprehensive analysis
of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Cancer Res. 77:e108–e110. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Franz M, Rodriguez H, Lopes C, Zuberi K,
Montojo J, Bader GD and Morris Q: GeneMANIA update 2018. Nucleic
Acids Res. 46:W60–W64. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Oughtred R, Rust J, Chang C, Breitkreutz
BJ, Stark C, Willems A, Boucher L, Leung G, Kolas N, Zhang F, et
al: The BioGRID database: A comprehensive biomedical resource of
curated protein, genetic, and chemical interactions. Protein Sci.
30:187–200. 2021. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li C, Tang Z, Zhang W, Ye Z and Liu F:
GEPIA2021: Integrating multiple deconvolution-based analysis into
GEPIA. Nucleic Acids Res. 49:W242–W246. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Galligan JJ and Petersen DR: The human
protein disulfide isomerase gene family. Hum Genomics. 6:62012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hetz C: The unfolded protein response:
Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 13:89–102. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Powell LE and Foster PA: Protein
disulphide isomerase inhibition as a potential cancer therapeutic
strategy. Cancer Med. 10:2812–2825. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu S, Sankar S and Neamati N: Protein
disulfide isomerase: A promising target for cancer therapy. Drug
Discov Today. 19:222–240. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yamada R, Cao X, Butkevich AN, Millard M,
Odde S, Mordwinkin N, Gundla R, Zandi E, Louie SG, Petasis NA and
Neamati N: Discovery and preclinical evaluation of a novel class of
cytotoxic propynoic acid carbamoyl methyl amides (PACMAs). J Med
Chem. 54:2902–2914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu S, Butkevich AN, Yamada R, Zhou Y,
Debnath B, Duncan R, Zandi E, Petasis NA and Neamati N: Discovery
of an orally active small-molecule irreversible inhibitor of
protein disulfide isomerase for ovarian cancer treatment. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 109:16348–16353. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yin F, Yi S, Wei L, Zhao B, Li J, Cai X,
Dong C and Liu X: Microarray-based identification of genes
associated with prognosis and drug resistance in ovarian cancer. J
Cell Biochem. 120:6057–6070. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peng Z, Chen Y, Cao H, Zou H, Wan X, Zeng
W, Liu Y, Hu J, Zhang N, Xia Z, et al: Protein disulfide isomerases
are promising targets for predicting the survival and tumor
progression in glioma patients. Aging (Albany NY). 12:2347–2372.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang M, Zhang W, Liu Y, Ma Z, Xiang W, Wen
Y, Zhang D, Li Y, Li Y, Li T, et al: PDIA4 promotes glioblastoma
progression via the PI3K/AKT/m-TOR pathway. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 597:83–90. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|