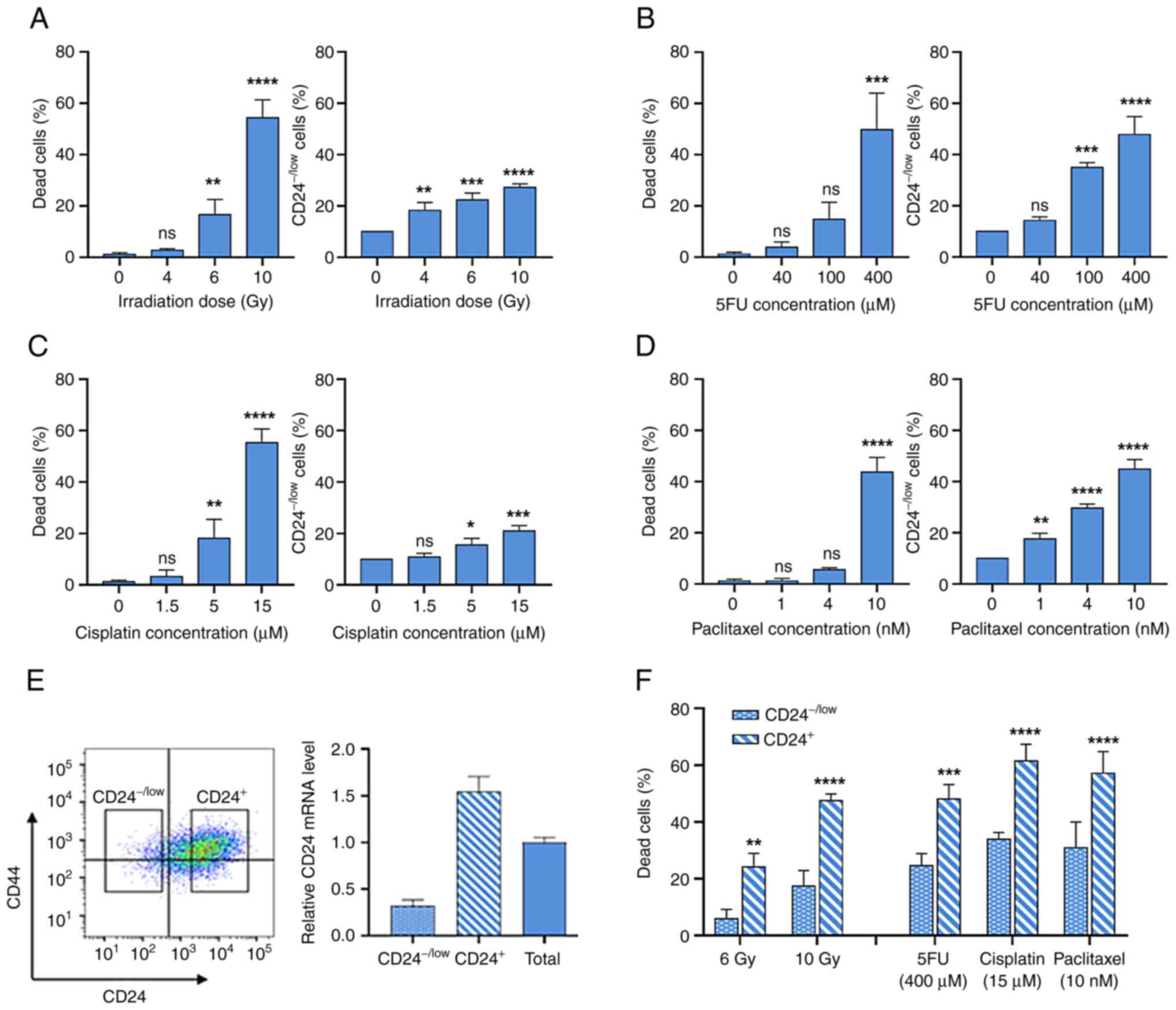
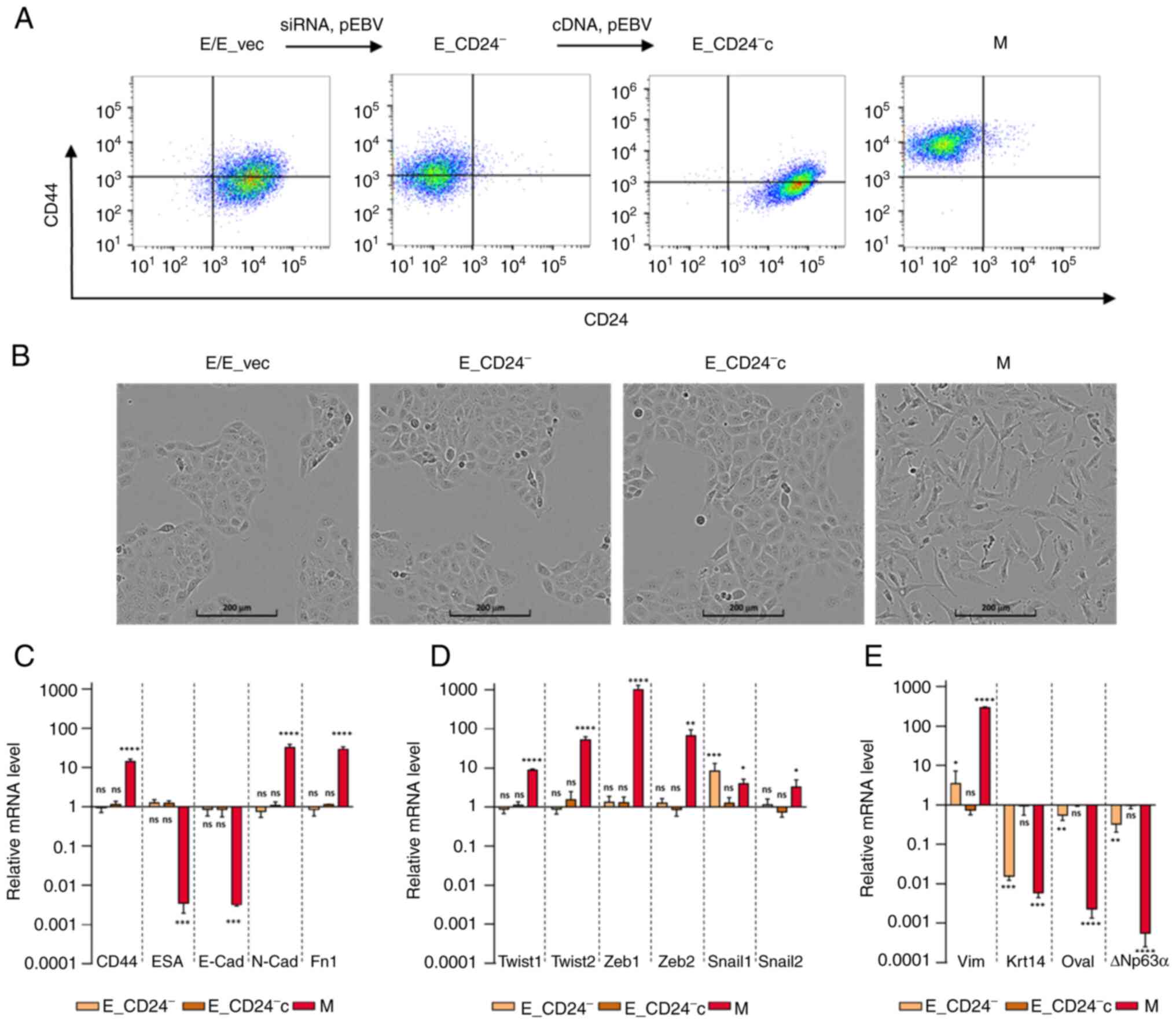
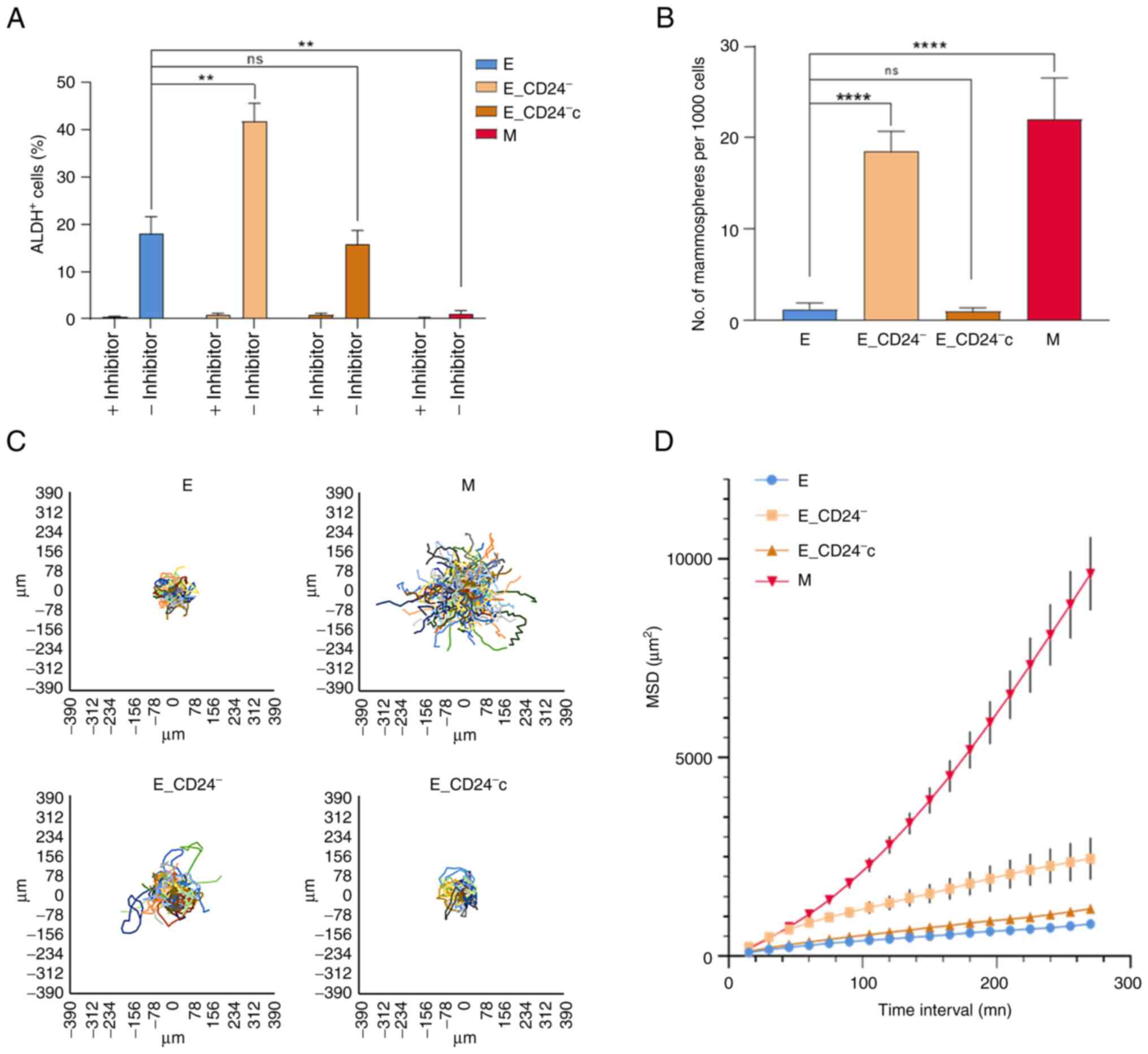
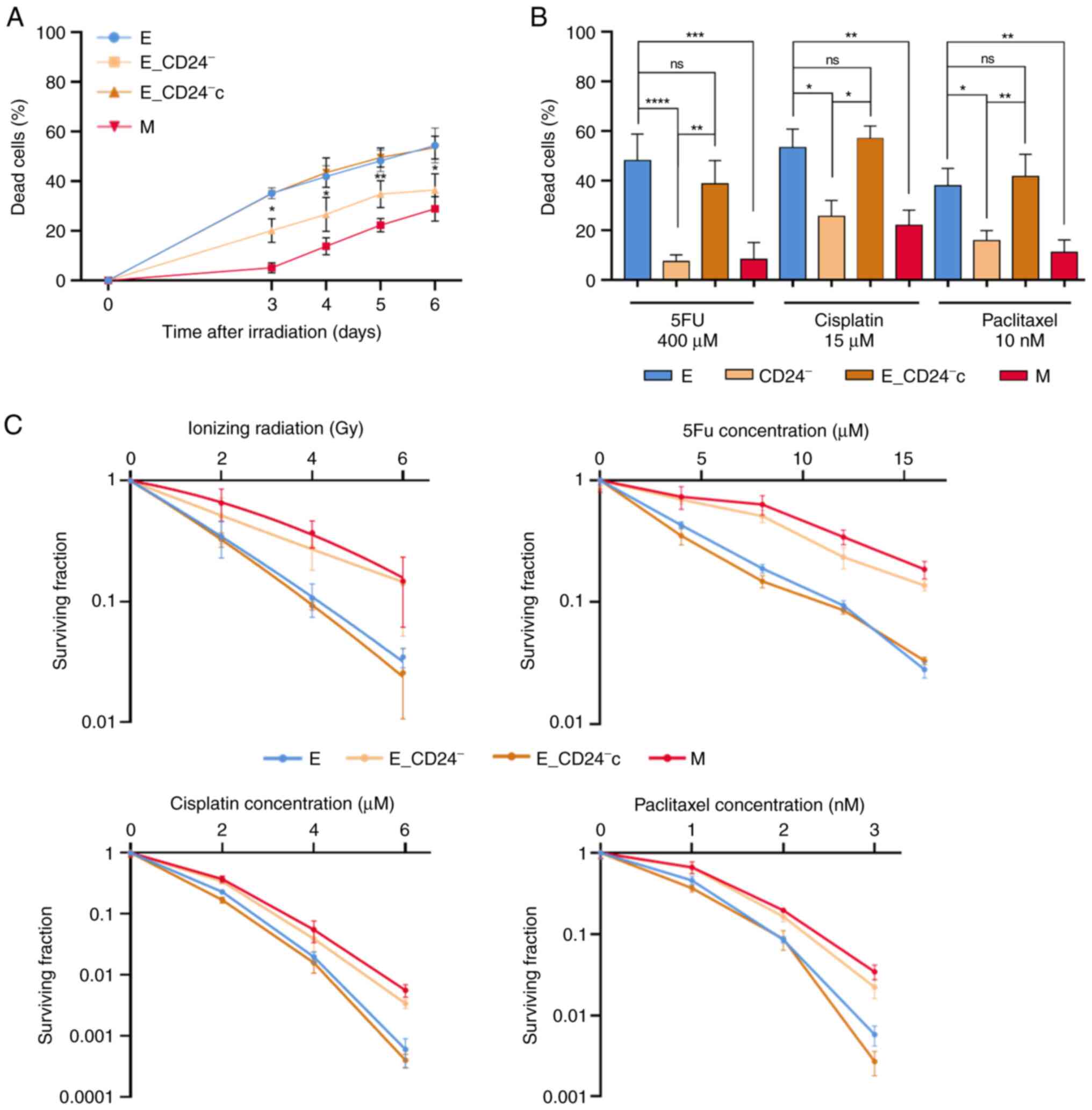
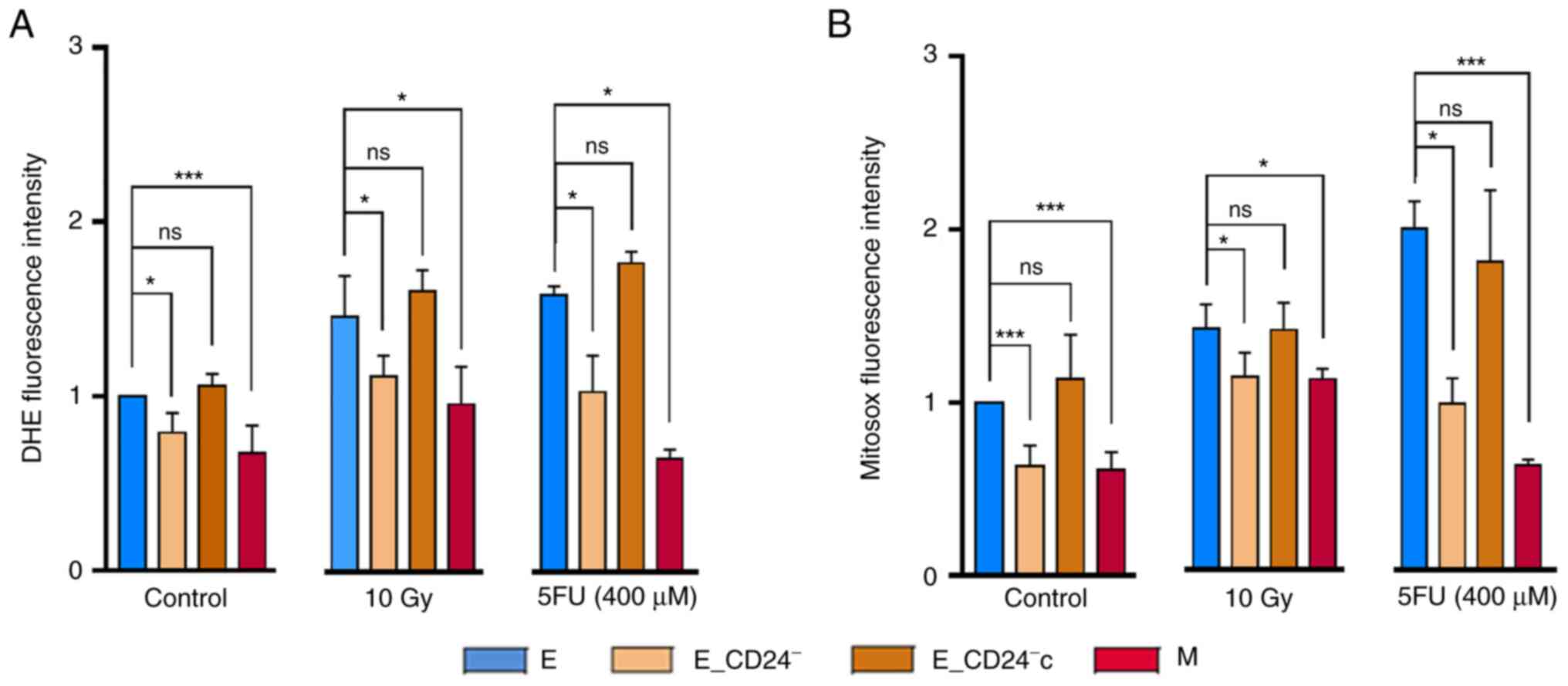
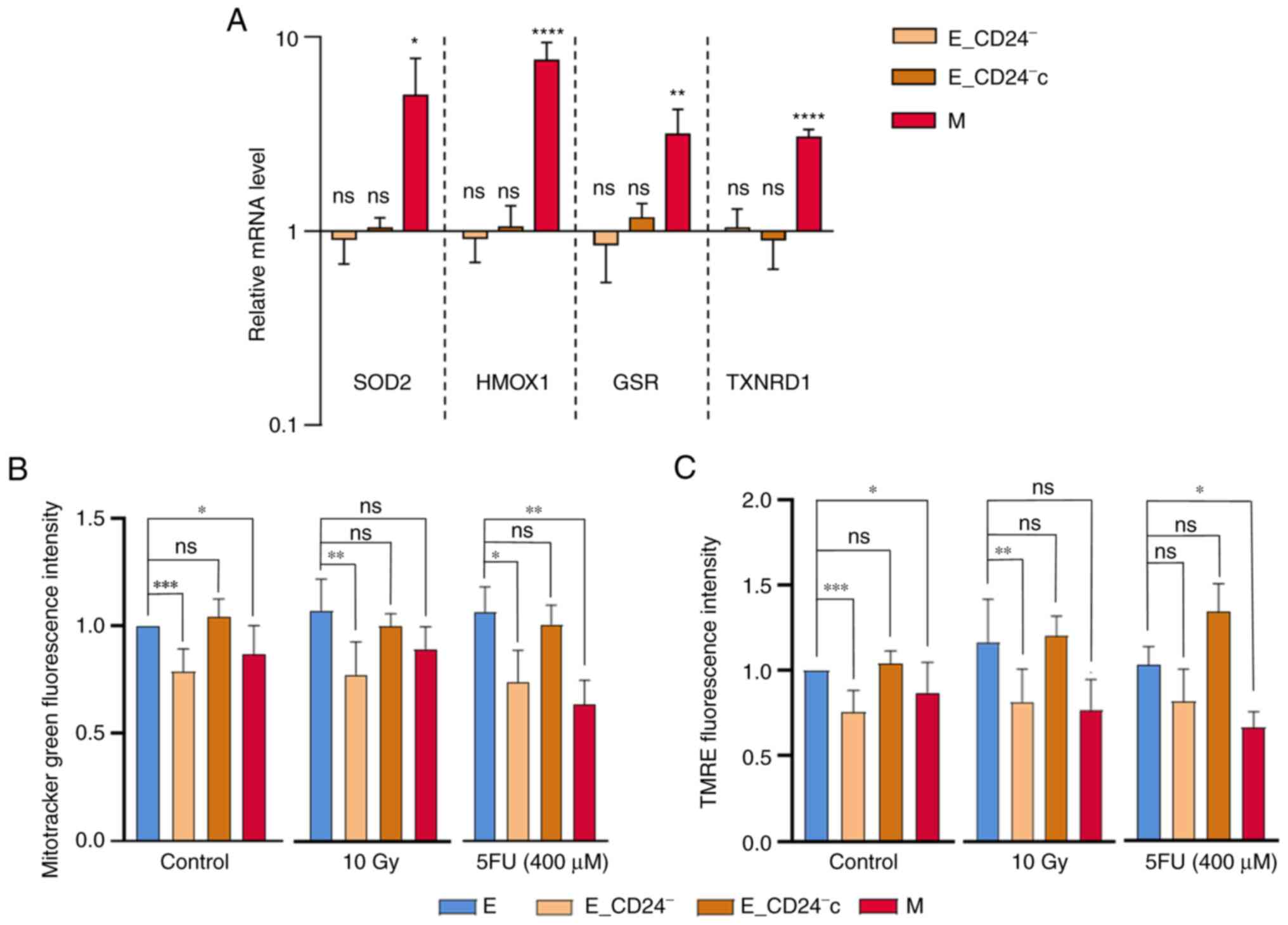
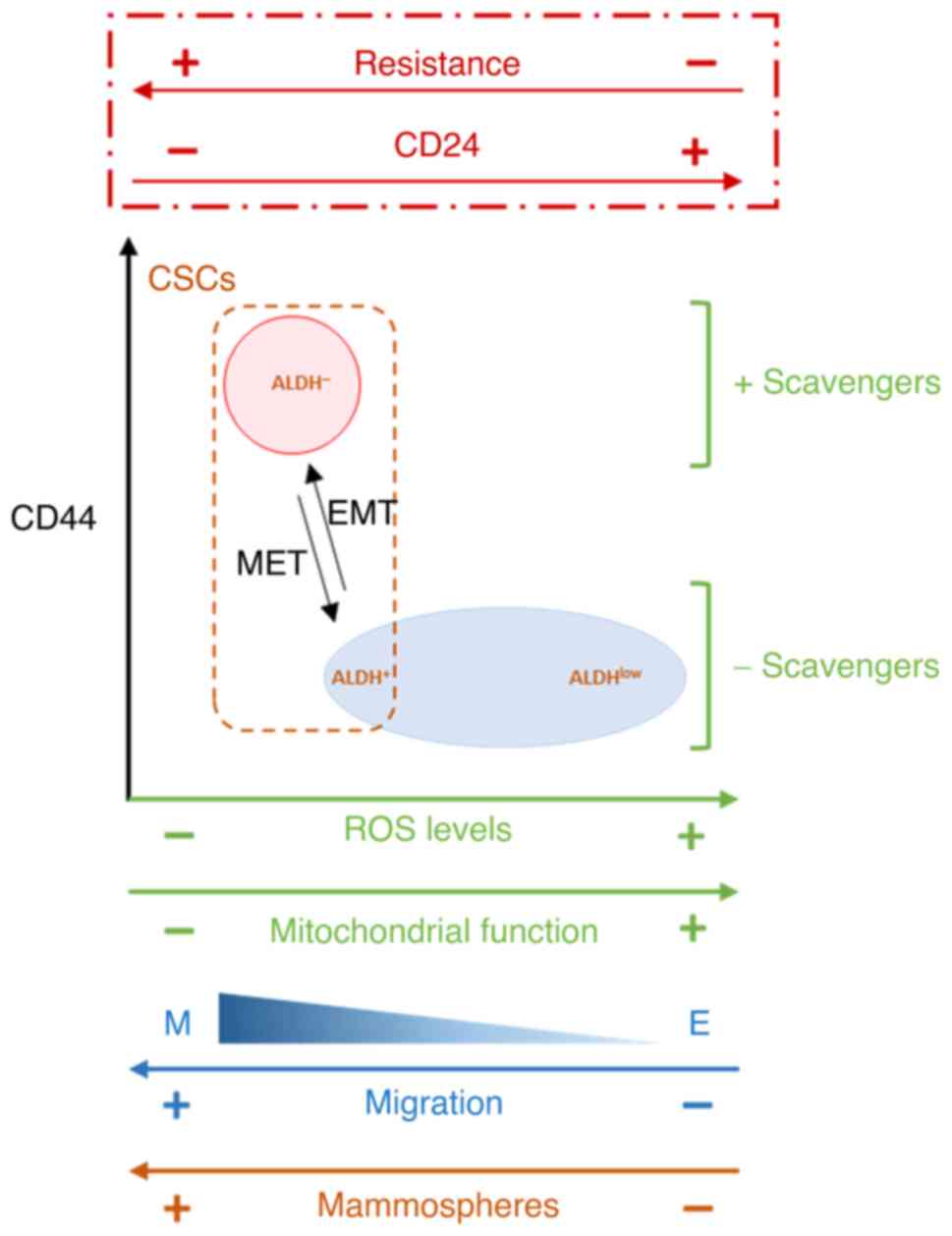
|
1
|
Marusyk A, Almendro V and Polyak K:
Intra-tumour heterogeneity: A looking glass for cancer? Nat Rev
Cancer. 12:323–334. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pece S, Tosoni D, Confalonieri S, Mazzarol
G, Vecchi M, Ronzoni S, Bernard L, Viale G, Pelicci PG and Di Fiore
PP: Biological and molecular heterogeneity of breast cancers
correlates with their cancer stem cell content. Cell. 140:62–73.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Batlle E and Clevers H: Cancer stem cells
revisited. Nat Med. 23:1124–1134. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E,
Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG,
Liu S, et al: ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human
mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell
Stem Cell. 1:555–567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hwang-Verslues WW, Kuo WH, Chang PH, Pan
CC, Wang HH, Tsai ST, Jeng YM, Shew JY, Kung JT, Chen CH, et al:
Multiple lineages of human breast cancer stem/progenitor cells
identified by profiling with stem cell markers. PLoS One.
4:e83772009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang R, Tu J and Liu S: Novel molecular
regulators of breast cancer stem cell plasticity and heterogeneity.
Semin Cancer Biol. 82:11–25. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Morel AP, Lièvre M, Thomas C, Hinkal G,
Ansieau S and Puisieux A: Generation of breast cancer stem cells
through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 3:e28882008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Konge J, Leteurtre F, Goislard M, Biard D,
Morel-Altmeyer S, Vaurijoux A, Gruel G, Chevillard S and Lebeau J:
Breast cancer stem cell-like cells generated during TGFβ-induced
EMT are radioresistant. Oncotarget. 9:23519–23531. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu S, Cong Y, Wang D, Sun Y, Deng L, Liu
Y, Martin-Trevino R, Shang L, McDermott SP, Landis MD, et al:
Breast cancer stem cells transition between epithelial and
mesenchymal states reflective of their normal counterparts. Stem
Cell Reports. 2:78–91. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pastushenko I and Blanpain C: EMT
transition states during tumor progression and metastasis. Trends
Cell Biol. 29:212–226. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pasani S, Sahoo S and Jolly MK: Hybrid E/M
phenotype(s) and stemness: A mechanistic connection embedded in
network topology. J Clin Med. 10:602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kröger C, Afeyan A, Mraz J, Eaton EN,
Reinhardt F, Khodor YL, Thiru P, Bierie B, Ye X, Burge CB and
Weinberg RA: Acquisition of a hybrid E/M state is essential for
tumorigenicity of basal breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 116:7353–7362. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Luo M, Brooks M and Wicha MS:
Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity of breast cancer stem cells:
Implications for metastasis and therapeutic resistance. Curr Pharm
Des. 21:1301–1310. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Phillips TM, McBride WH and Pajonk F: The
response of CD24(−/low)/CD44+ breast cancer-initiating cells to
radiation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 98:1777–1785. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li X, Lewis MT, Huang J, Gutierrez C,
Osborne CK, Wu MF, Hilsenbeck SG, Pavlick A, Zhang X, Chamness GC,
et al: Intrinsic resistance of tumorigenic breast cancer cells to
chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 100:672–679. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kamble D, Mahajan M, Dhat R and Sitasawad
S: Keap1-Nrf2 pathway regulates ALDH and contributes to
radioresistance in breast cancer stem cells. Cells. 10:832021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tanei T, Morimoto K, Shimazu K, Kim SJ,
Tanji Y, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y and Noguchi S: Association of breast
cancer stem cells identified by aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 expression
with resistance to sequential Paclitaxel and epirubicin-base
chemotherapy for breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 15:4234–4241.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Palomeras S, Ruiz-Martínez S and Puig T:
Targeting breast cancer stem cells to overcome treatment
resistance. Molecules. 23:21932018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
García-Heredia JM and Carnero A: Role of
mitochondria in cancer stem cell resistance. Cells. 9:16932020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bensimon J, Altmeyer-Morel S, Benjelloun
H, Chevillard S and Lebeau J: CD24(−/low) stem-like breast cancer
marker defines the radiation-resistant cells involved in
memorization and transmission of radiation-induced genomic
instability. Oncogene. 32:251–258. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bensimon J, Biard D, Paget V, Goislard M,
Morel-Altmeyer S, Konge J, Chevillard S and Lebeau J: Forced
extinction of CD24 stem-like breast cancer marker alone promotes
radiation resistance through the control of oxidative stress. Mol
Carcinog. 55:245–254. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Diehn M, Cho RW, Lobo NA, Kalisky T, Dorie
MJ, Kulp AN, Qian D, Lam JS, Ailles LE, Wong M, et al: Association
of reactive oxygen species levels and radioresistance in cancer
stem cells. Nature. 458:780–783. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee JH, Kim SH, Lee ES and Kim YS: CD24
overexpression in cancer development and progression: A
meta-analysis. Oncol Rep. 22:1149–1156. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Altevogt P, Sammar M, Hüser L and
Kristiansen G: Novel insights into the function of CD24: A driving
force in cancer. Int J Cancer. 148:546–559. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kristiansen G, Machado E, Bretz N, Rupp C,
Winzer KJ, König AK, Moldenhauer G, Marmé F, Costa J and Altevogt
P: Molecular and clinical dissection of CD24 antibody specificity
by a comprehensive comparative analysis. Lab Invest. 90:1102–1116.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Weber E, Lehmann HP, Beck-Sickinger AG,
Wawrzynczak EJ, Waibel R, Folkers G and Stahel RA: Antibodies to
the protein core of the small cell lung cancer workshop antigen
cluster-w4 and to the leucocyte workshop antigen CD24 recognize the
same short protein sequence leucine-alanine-proline. Clin Exp
Immunol. 93:279–285. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Riley PA: Free radicals in biology:
Oxidative stress and the effects of ionizing radiation. Int J
Radiat Biol. 65:27–33. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mohiuddin M and Kasahara K: Cisplatin
activates the growth inhibitory signaling pathways by enhancing the
production of reactive oxygen species in non-small cell lung cancer
carrying an EGFR exon 19 deletion. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 18
(3 Suppl):S471–S486. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mosca L, Ilari A, Fazi F, Assaraf YG and
Colotti G: Taxanes in cancer treatment: Activity, chemoresistance
and its overcoming. Drug Resist Updat. 54:1007422021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pan X, Zhang X, Sun H, Zhang J, Yan M and
Zhang H: Autophagy inhibition promotes 5-fluorouraci-induced
apoptosis by stimulating ROS formation in human non-small cell lung
cancer A549 cells. PLoS One. 8:e566792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Elenbaas B, Spirio L, Koerner F, Fleming
MD, Zimonjic DB, Donaher JL, Popescu NC, Hahn WC and Weinberg RA:
Human breast cancer cells generated by oncogenic transformation of
primary mammary epithelial cells. Genes Dev. 15:50–65. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lombardo Y, de Giorgio A, Coombes CR,
Stebbing J and Castellano L: Mammosphere formation assay from human
breast cancer tissues and cell lines. J Vis Exp.
526712015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Biard DS, Despras E, Sarasin A and Angulo
JF: Development of new EBV-based vectors for stable expression of
small interfering RNA to mimick human syndromes: Application to NER
gene silencing. Mol Cancer Res. 3:519–529. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vert JP, Foveau N, Lajaunie C and
Vandenbrouck Y: An accurate and interpretable model for siRNA
efficacy prediction. BMC Bioinformatics. 7:5202006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Meijering E, Dzyubachyk O and Smal I:
Methods for cell and particle tracking. Methods Enzymol.
504:183–200. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gorelik R and Gautreau A: Quantitative and
unbiased analysis of directional persistence in cell migration. Nat
Protoc. 9:1931–1943. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pastushenko I, Brisebarre A, Sifrim A,
Fioramonti M, Revenco T, Boumahdi S, Van Keymeulen A, Brown D,
Moers V, Lemaire S, et al: Identification of the tumour transition
states occurring during EMT. Nature. 556:463–468. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yoh KE, Regunath K, Guzman A, Lee SM,
Pfister NT, Akanni O, Kaufman LJ, Prives C and Prywes R: Repression
of p63 and induction of EMT by mutant Ras in mammary epithelial
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:E6107–E6116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bocci F, Tripathi SC, Vilchez Mercedes SA,
George JT, Casabar JP, Wong PK, Hanash SM, Levine H, Onuchic JN and
Jolly MK: NRF2 activates a partial epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and is maximally present in a hybrid
epithelial/mesenchymal phenotype. Integr Biol (Camb). 11:251–263.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim D, Choi B, Ryoo I and Kwak MK: High
NRF2 level mediates cancer stem cell-like properties of aldehyde
dehydrogenase (ALDH)-high ovarian cancer cells: Inhibitory role of
all-trans retinoic acid in ALDH/NRF2 signaling. Cell Death Dis.
9:8962018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tang JY, Ou-Yang F, Hou MF, Huang HW, Wang
HR, Li KT, Fayyaz S, Shu CW and Chang HW: Oxidative
stress-modulating drugs have preferential anticancer
effects-involving the regulation of apoptosis, DNA damage,
endoplasmic reticulum stress, autophagy, metabolism, and migration.
Semin Cancer Biol. 58:109–117. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Peiris-Pagès M, Martinez-Outschoorn UE,
Pestell RG, Sotgia F and Lisanti MP: Cancer stem cell metabolism.
Breast Cancer Res. 18:552016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bhatia S, Monkman J, Blick T, Pinto C,
Waltham M, Nagaraj SH and Thompson EW: Interrogation of phenotypic
plasticity between epithelial and mesenchymal states in breast
cancer. J Clin Med. 8:8932019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gupta PB, Fillmore CM, Jiang G, Shapira
SD, Tao K, Kuperwasser C and Lander ES: Stochastic state
transitions give rise to phenotypic equilibrium in populations of
cancer cells. Cell. 146:633–644. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ruscetti M, Dadashian EL, Guo W,
Mulholland DJ, Park JW, Tran LM, Kobayashi N, Bianchi-Frias D, Xing
Y, Nelson PS and Wu H: HDAC inhibition impedes
epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity and suppresses metastatic,
castration-resistant prostate cancer. Oncogene. 35:3781–3795. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Meyer MJ, Fleming JM, Ali MA, Pesesky MW,
Ginsburg E and Vonderhaar BK: Dynamic regulation of CD24 and the
invasive, CD44posCD24neg phenotype in breast cancer cell lines.
Breast Cancer Res. 11:R822009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ricardo S, Vieira AF, Gerhard R, Leitão D,
Pinto R, Cameselle-Teijeiro JF, Milanezi F, Schmitt F and Paredes
J: Breast cancer stem cell markers CD44, CD24 and ALDH1: Expression
distribution within intrinsic molecular subtype. J Clin Pathol.
64:937–946. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xia F and Powell SN: The molecular basis
of radiosensitivity and chemosensitivity in the treatment of breast
cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 12:296–304. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Luce A, Courtin A, Levalois C,
Altmeyer-Morel S, Romeo PH, Chevillard S and Lebeau J: Death
receptor pathways mediate targeted and non-targeted effects of
ionizing radiations in breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis.
30:432–439. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Longley DB, Harkin DP and Johnston PG:
5-fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat
Rev Cancer. 3:330–338. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tchounwou PB, Dasari S, Noubissi FK, Ray P
and Kumar S: Advances in our understanding of the molecular
mechanisms of action of cisplatin in cancer therapy. J Exp
Pharmacol. 13:303–328. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Abu Samaan TM, Samec M, Liskova A, Kubatka
P and Büsselberg D: Paclitaxel's mechanistic and clinical effects
on breast cancer. Biomolecules. 9:7892019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Pinto CA, Widodo E, Waltham M and Thompson
EW: Breast cancer stem cells and epithelial mesenchymal
plasticity-implications for chemoresistance. Cancer Lett.
341:56–62. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bierie B, Pierce SE, Kroeger C, Stover DG,
Pattabiraman DR, Thiru P, Liu Donaher J, Reinhardt F, Chaffer CL,
Keckesova Z and Weinberg RA: Integrin-β4 identifies cancer stem
cell-enriched populations of partially mesenchymal carcinoma cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:E2337–E2346. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Unternaehrer JJ, Zhao R, Kim K, Cesana M,
Powers JT, Ratanasirintrawoot S, Onder T, Shibue T, Weinberg RA and
Daley GQ: The epithelial-mesenchymal transition factor SNAIL
paradoxically enhances reprogramming. Stem Cell Reports. 3:691–698.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gingold JA, Fidalgo M, Guallar D, Lau Z,
Sun Z, Zhou H, Faiola F, Huang X, Lee DF, Waghray A, et al: A
genome-wide RNAi screen identifies opposing functions of Snai1 and
Snai2 on the Nanog dependency in reprogramming. Mol Cell.
56:140–152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ma SY, Park JH, Jung H, Ha SM, Kim Y, Park
DH, Lee DH, Lee S, Chu IH, Jung SY, et al: Snail maintains
metastatic potential, cancer stem-like properties, and
chemoresistance in mesenchymal mouse breast cancer TUBO-P2J cells.
Oncol Rep. 38:1867–1876. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Roca H, Hernandez J, Weidner S, McEachin
RC, Fuller D, Sud S, Schumann T, Wilkinson JE, Zaslavsky A, Li H,
et al: Transcription factors OVOL1 and OVOL2 induce the mesenchymal
to epithelial transition in human cancer. PLoS One. 8:e767732013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wu RS, Hong JJ, Wu JF, Yan S, Wu D, Liu N,
Liu QF, Wu QW, Xie YY, Liu YJ, et al: OVOL2 antagonizes TGF-β
signaling to regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition during
mammary tumor metastasis. Oncotarget. 8:39401–39416. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hong T, Watanabe K, Ta CH,
Villarreal-Ponce A, Nie Q and Dai X: An Ovol2-Zeb1 mutual
inhibitory circuit governs bidirectional and multi-step transition
between epithelial and mesenchymal states. PLoS Comput Biol.
11:e10045692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Westcott JM, Camacho S, Nasir A, Huysman
ME, Rahhal R, Dang TT, Riegel AT, Brekken RA and Pearson GW:
ΔNp63-regulated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition state
heterogeneity confers a leader-follower relationship that drives
collective invasion. Cancer Res. 80:3933–3944. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Jolly MK, Boareto M, Debeb BG, Aceto N,
Farach-Carson MC, Woodward WA and Levine H: Inflammatory breast
cancer: A model for investigating cluster-based dissemination. NPJ
Breast Cancer. 3:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ryoo I, Lee S and Kwak MK: Redox
modulating NRF2: A potential mediator of cancer stem cell
resistance. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:24281532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Jia D, Tan Y, Liu H, Ooi S, Li L, Wright
K, Bennett S, Addison CL and Wang L: Cardamonin reduces
chemotherapy-enriched breast cancer stem-like cells in vitro and in
vivo. Oncotarget. 7:771–785. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Vipparthi K, Hari K, Chakraborty P, Ghosh
S, Patel AK, Ghosh A, Biswas NK, Sharan R, Arun P, Jolly MK and
Singh S: Emergence of hybrid states of stem-like cancer cells
correlates with poor prognosis in oral cancer. iScience.
25:1043172022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Grosse-Wilde A, Kuestner RE, Skelton SM,
MacIntosh E, d'Hérouël AF, Ertaylan G, Del Sol A, Skupin A and
Huang S: Loss of inter-cellular cooperation by complete
epithelial-mesenchymal transition supports favorable outcomes in
basal breast cancer patients. Oncotarget. 9:20018–20033. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Gammon L, Biddle A, Heywood HK,
Johannessen AC and Mackenzie IC: Sub-sets of cancer stem cells
differ intrinsically in their patterns of oxygen metabolism. PLoS
One. 8:e624932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Sciacovelli M and Frezza C: Metabolic
reprogramming and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer.
FEBS J. 284:3132–3144. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lee SY, Ju MK, Jeon HM, Lee YJ, Kim CH,
Park HG, Han SI and Kang HS: Reactive oxygen species induce
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, glycolytic switch, and
mitochondrial repression through the Dlx-2/Snail signaling pathways
in MCF-7 cells. Mol Med Rep. 20:2339–2346. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Jia D, Park JH, Kaur H, Jung KH, Yang S,
Tripathi S, Galbraith M, Deng Y, Jolly MK, Kaipparettu BA, et al:
Towards decoding the coupled decision-making of metabolism and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Br J Cancer.
124:1902–1911. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Fang X, Zheng P, Tang J and Liu Y: CD24:
From A to Z. Cell Mol Immunol. 7:100–103. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Deng X, Apple S, Zhao H, Song J, Lee M,
Luo W, Wu X, Chung D, Pietras RJ and Chang HR: CD24 expression and
differential resistance to chemotherapy in triple-negative breast
cancer. Oncotarget. 8:38294–38308. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Shen Y, Schmidt BUS, Kubitschke H,
Morawetz EW, Wolf B, Käs JA and Losert W: Detecting heterogeneity
in and between breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Converg. 4:12020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Li W, Ma H, Zhang J, Zhu L, Wang C and
Yang Y: Unraveling the roles of CD44/CD24 and ALDH1 as cancer stem
cell markers in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Sci Rep. 7:138562017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Gupta PB, Pastushenko I, Skibinski A,
Blanpain C and Kuperwasser C: Phenotypic plasticity: Driver of
cancer initiation, progression, and therapy resistance. Cell Stem
Cell. 24:65–78. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|