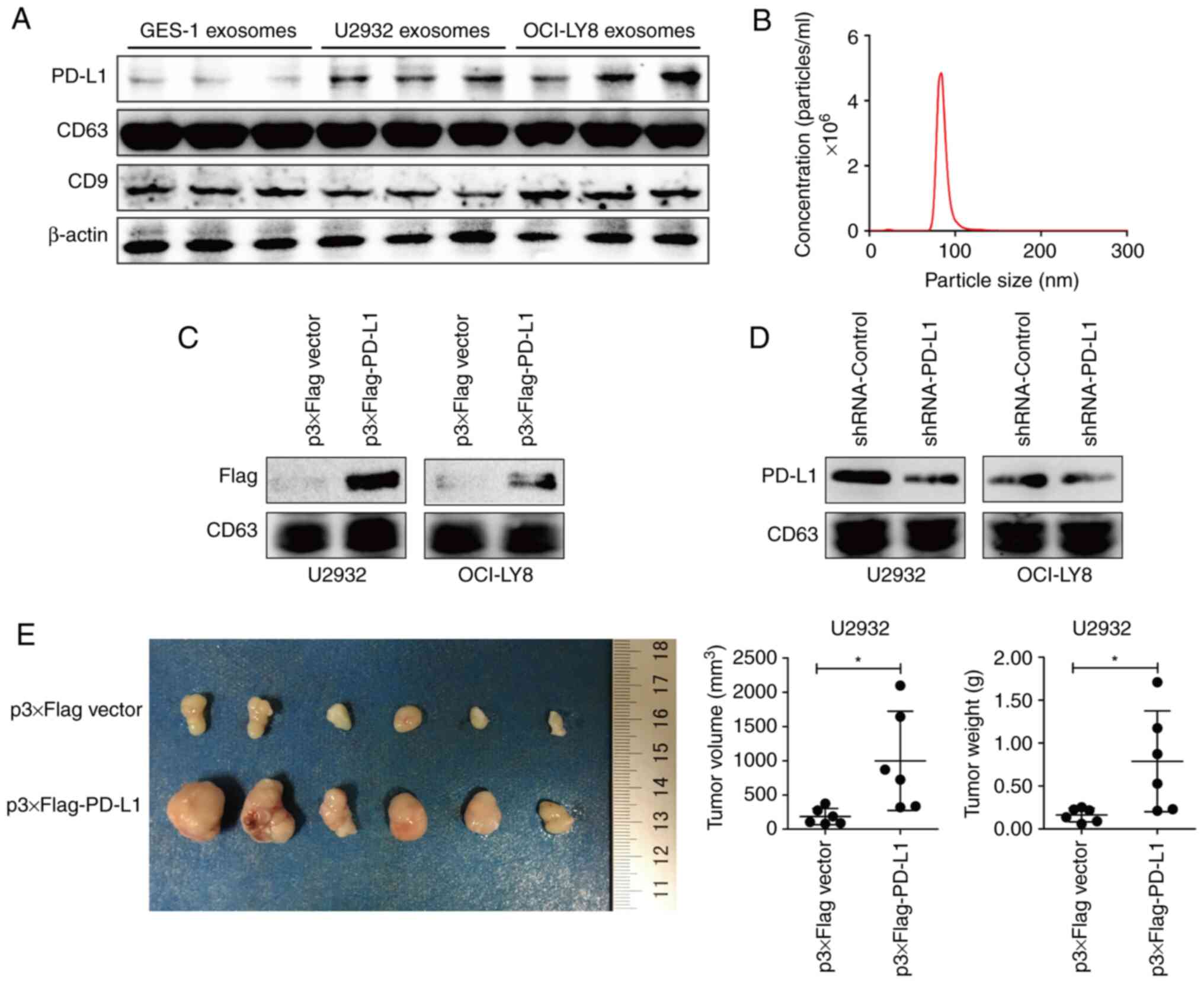
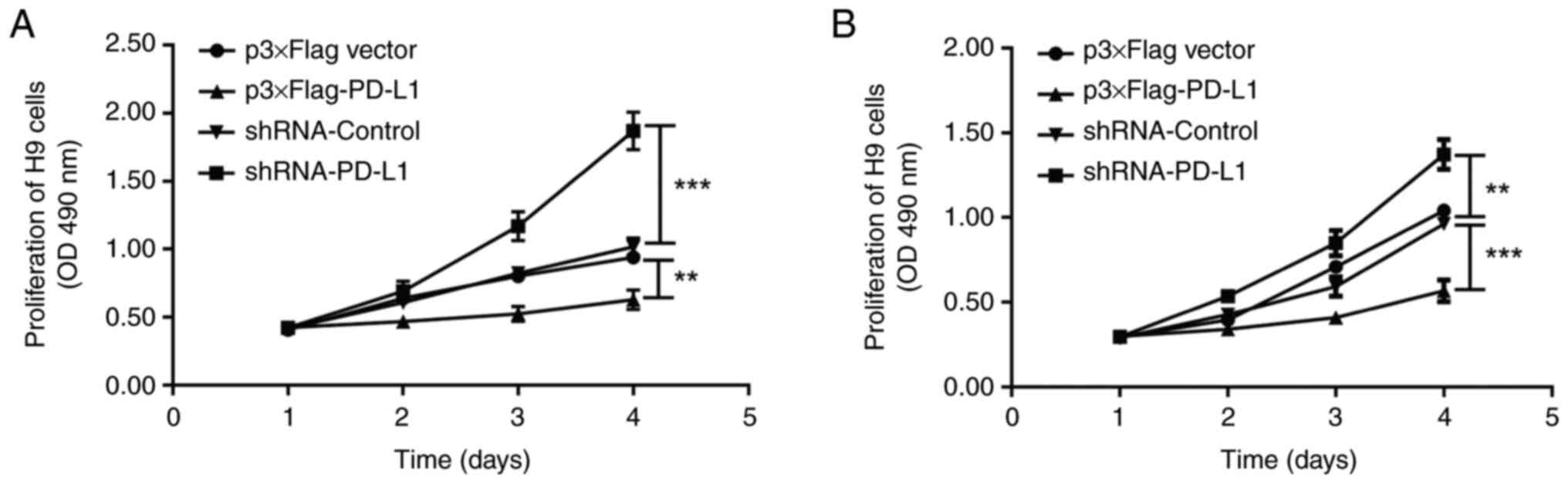
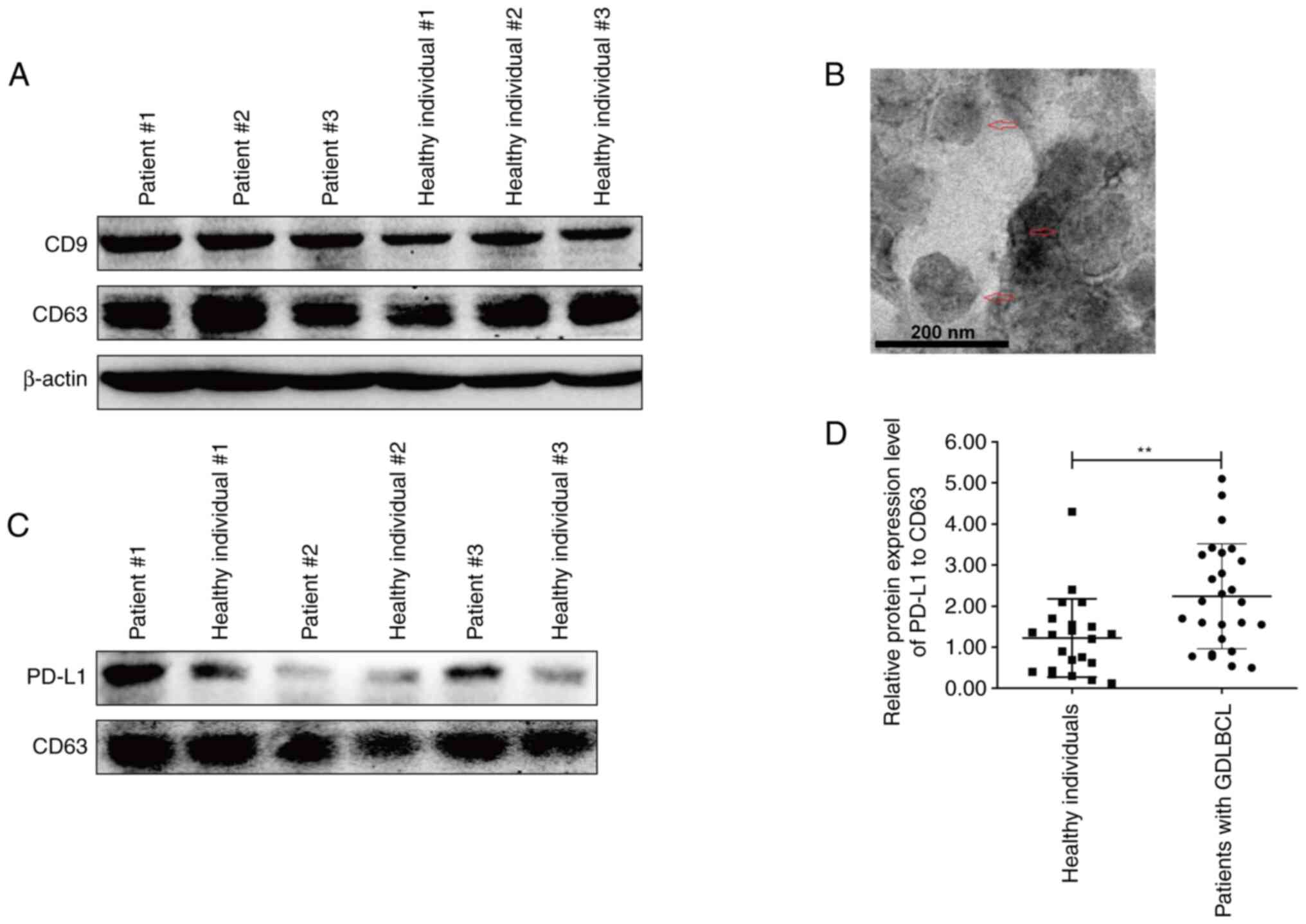
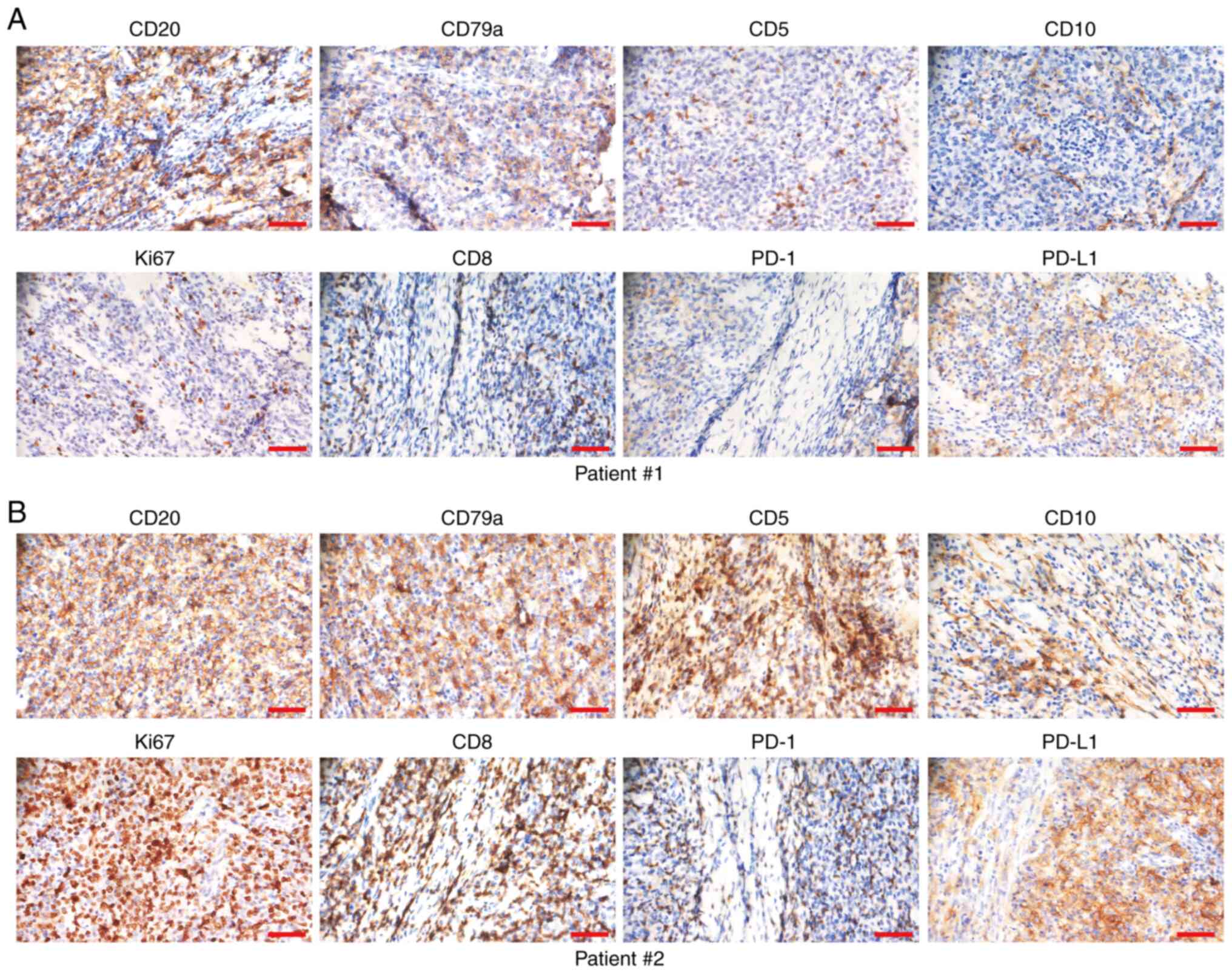
|
1
|
Juarez-Salcedo LM, Sokol L, Chavez JC and
Dalia S: Primary gastric lymphoma, epidemiology, clinical
diagnosis, and treatment. Cancer Control. 25:10732748187782562018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fujishima F, Katsushima H, Fukuhara N,
Konosu-Fukaya S, Nakamura Y, Sasano H and Ichinohasama R: Incidence
rate, subtype frequency, and occurrence site of malignant lymphoma
in the gastrointestinal tract: Population-based analysis in miyagi,
Japan. Tohoku J Exp Med. 245:159–165. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rotaru I, Găman GD, Stănescu C and Găman
AM: Evaluation of parameters with potential prognosis impact in
patients with primary gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
(PG-DLBCL). Rom J Morphol Embryol. 55:15–21. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Deng Y, Su W, Zhu J, Ji H, Zhou X, Geng J,
Zhu J and Zhang Q: Helicobacter pylori infection disturbs the tumor
immune microenvironment and is associated with a discrepant
prognosis in gastric de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J
Immunother Cancer. 9:e0029472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zepeda-Gomez S, Camacho J, Oviedo-Cardenas
E and Lome-Maldonado C: Gastric infiltration of diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma: endoscopic diagnosis and improvement of lesions
after chemotherapy. World J Gastroenterol. 14:4407–4409. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Topalian SL, Drake CG and Pardoll DM:
Immune checkpoint blockade: A common denominator approach to cancer
therapy. Cancer Cell. 27:450–461. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ansell SM, Lesokhin AM, Borrello I,
Halwani A, Scott EC, Gutierrez M, Schuster SJ, Millenson MM, Cattry
D, Freeman GJ, et al: PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed or
refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 372:311–319. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schumacher TN, Kesmir C and van Buuren MM:
Biomarkers in cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Cell. 27:12–14. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sia D, Jiao Y, Martinez-Quetglas I, Kuchuk
O, Villacorta-Martin C, Castro de Moura M, Putra J, Camprecios G,
Bassaganyas L, Akers N, et al: Identification of an Immune-specific
Class of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Based on Molecular Features.
Gastroenterology. 153:812–826. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li CJ, Lin LT, Hou MF and Chu PY: PDL1/PD1
blockade in breast cancer: The immunotherapy era (Review). Oncol
Rep. 45:5–12. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sohn BS, Kim SM, Yoon DH, Kim S, Lee DH,
Kim JH, Lee SW, Huh J and Suh C: The comparison between CHOP and
R-CHOP in primary gastric diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Ann
Hematol. 91:1731–1739. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Deng R, Zuo C, Li Y, Xue B, Xun Z, Guo Y,
Wang X, Xu Y, Tian R, Chen S, et al: The innate immune effector
ISG12a promotes cancer immunity by suppressing the canonical
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Mol Immunol. 17:1163–1179.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang J, Shang S, Li J, Deng H, Ouyang L,
Xie H, Zhu H, Li Y and Zuo C: PD-L1 and miR-34a are prognostic
factors for primary gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients
treated with R-CHOP. Cancer Manag Res. 12:4999–5008. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
van Niel G, D'Angelo G and Raposo G:
Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 19:213–228. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shao H, Im H, Castro CM, Breakefield X,
Weissleder R and Lee H: New technologies for analysis of
extracellular vesicles. Chem Rev. 118:1917–1950. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lobb RJ, Hastie ML, Norris EL, van
Amerongen R, Gorman JJ and Moller A: Oncogenic transformation of
lung cells results in distinct exosome protein profile similar to
the cell of origin. Proteomics. 17:16004322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Meehan K and Vella LJ: The contribution of
tumour-derived exosomes to the hallmarks of cancer. Crit Rev Clin
Lab Sci. 53:121–131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moller A and Lobb RJ: The evolving
translational potential of small extracellular vesicles in cancer.
Nat Rev Cancer. 20:697–709. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nakaoka A, Nakahana M, Inubushi S, Akasaka
H, Salah M, Fujita Y, Kubota H, Hassan M, Nishikawa R, Mukumoto N,
et al: Exosome-mediated radiosensitizing effect on neighboring
cancer cells via increase in intracellular levels of reactive
oxygen species. Oncol Rep. 45:132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Theodoraki MN, Yerneni SS, Hoffmann TK,
Gooding WE and Whiteside TL: Clinical significance of
PD-L1+ exosomes in plasma of head and neck cancer
patients. Clin Cancer Res. 24:896–905. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen G, Huang AC, Zhang W, Zhang G, Wu M,
Xu W, Yu Z, Yang J, Wang B, Sun H, et al: Exosomal PD-L1
contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1
response. Nature. 560:382–386. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun Y, Guo J, Yu L, Guo T, Wang J, Wang X
and Chen Y: PD-L1+ exosomes from bone marrow-derived
cells of tumor-bearing mice inhibit antitumor immunity. Cell Mol
Immunol. 18:2402–2409. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen Z, You L, Wang L, Huang X, Liu H, Wei
JY, Zhu L and Qian W: Dual effect of DLBCL-derived EXOs in lymphoma
to improve DC vaccine efficacy in vitro while favor tumorgenesis in
vivo. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:1902018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Saibil SD and Ohashi PS: Targeting T cell
activation in immuno-oncology. Curr Oncol. 27 (Suppl 2):S98–S105.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen DS and Mellman I: Elements of cancer
immunity and the cancer-immune set point. Nature. 541:321–330.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
El-Galaly TC, Cheah CY, Kristensen D,
Hutchison A, Hay K, Callreus T and Villa D: Potentials, challenges
and future of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in
non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Acta Oncol. 59:766–774. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang T, Xu L, Gao L, Tang G, Chen L, Chen
J, Wang Y, Fu W, Yue W, Ye M, et al: Chimeric antigen receptor
T-cell therapy combined with autologous stem cell transplantation
improved progression-free survival of relapsed or refractory
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients: A single-center,
retrospective, cohort study. Hematol Oncol. 40:637–644. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Thery C, Amigorena S, Raposo G and Clayton
A: Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture
supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. Chapter
3:Unit 3.22. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shang S, Wang J, Chen S, Tian R, Zeng H,
Wang L, Xia M, Zhu H and Zuo C: Exosomal miRNA-1231 derived from
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibits the activity of
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Med. 8:7728–7740. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cheson BD, Ansell S, Schwartz L, Gordon
LI, Advani R, Jacene HA, Hoos A, Barrington SF and Armand P:
Refinement of the lugano classification lymphoma response criteria
in the era of immunomodulatory therapy. Blood. 128:2489–2496. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald
C, Gill K, Hoskins P, Klasa R, Savage KJ, Shenkier T, Sutherland J,
et al: The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a
better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood.
109:1857–1861. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Malipatel R, Patil M, Pritilata Rout P,
Correa M and Devarbhavi H: Primary Gastric Lymphoma:
Clinicopathological Profile. Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol.
8:6–10. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ,
Topalian SL, Hwu P, Drake CG, Camacho LH, Kauh J, Odunsi K, et al:
Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with
advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:2455–2465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Postow MA, Callahan MK and Wolchok JD:
Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy. J Clin Oncol.
33:1974–1982. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Page DB, Postow MA, Callahan MK, Allison
JP and Wolchok JD: Immune modulation in cancer with antibodies.
Annu Rev Med. 65:185–202. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wei Y, Zhao Q, Gao Z, Lao XM, Lin WM, Chen
DP, Mu M, Huang CX, Liu ZY, Li B, et al: The local immune landscape
determines tumor PD-L1 heterogeneity and sensitivity to therapy. J
Clin Invest. 129:3347–3360. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
You W, Shang B, Sun J, Liu X, Su L and
Jiang S: Mechanistic insight of predictive biomarkers for antitumor
PD1/PDL1 blockade: A paradigm shift towards immunome evaluation
(Review). Oncol Rep. 44:424–437. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Juneja VR, McGuire KA, Manguso RT, LaFleur
MW, Collins N, Haining WN, Freeman GJ and Sharpe AH: PD-L1 on tumor
cells is sufficient for immune evasion in immunogenic tumors and
inhibits CD8 T cell cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 214:895–904. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen BJ, Chapuy B, Ouyang J, Sun HH,
Roemer MG, Xu ML, Yu H, Fletcher CD, Freeman GJ, Shipp MA and Rodig
SJ: PD-L1 expression is characteristic of a subset of aggressive
B-cell lymphomas and virus-associated malignancies. Clin Cancer
Res. 19:3462–3473. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tanaka A and Sakaguchi S: Regulatory T
cells in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 27:109–118. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Groth C, Hu X, Weber R, Fleming V,
Altevogt P, Utikal J and Umansky V: Immunosuppression mediated by
myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) during tumour progression.
Br J Cancer. 120:16–25. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Boussiotis VA: Molecular and biochemical
aspects of the PD-1 checkpoint pathway. N Engl J Med.
375:1767–1778. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bunggulawa EJ, Wang W, Yin T, Wang N,
Durkan C, Wang Y and Wang G: Recent advancements in the use of
exosomes as drug delivery systems. J Nanobiotechnology. 16:812018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Poggio M, Hu T, Pai CC, Chu B, Belair CD,
Chang A, Montabana E, Lang UE, Fu Q, Fong L and Blelloch R:
Suppression of exosomal PD-L1 induces systemic anti-tumor immunity
and memory. Cell. 177:414–427.e13. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Daassi D, Mahoney KM and Freeman GJ: The
importance of exosomal PDL1 in tumour immune evasion. Nat Rev
Immunol. 20:209–215. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wen SW, Sceneay J, Lima LG, Wong CS,
Becker M, Krumeich S, Lobb RJ, Castillo V, Wong KN, Ellis S, et al:
The biodistribution and immune suppressive effects of breast
cancer-derived exosomes. Cancer Res. 76:6816–6827. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Morrissey SM and Yan J: Exosomal PD-L1:
Roles in tumor progression and immunotherapy. Trends Cancer.
6:550–558. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sharma P, Diergaarde B, Ferrone S,
Kirkwood JM and Whiteside TL: Melanoma cell-derived exosomes in
plasma of melanoma patients suppress functions of immune effector
cells. Sci Rep. 10:922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wu L, Zhang X, Zhang B, Shi H, Yuan X, Sun
Y, Pan Z, Qian H and Xu W: Exosomes derived from gastric cancer
cells activate NF-κB pathway in macrophages to promote cancer
progression. Tumour Biol. 37:12169–12180. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gabrusiewicz K, Li X, Wei J, Hashimoto Y,
Marisetty AL, Ott M, Wang F, Hawke D, Yu J, Healy LM, et al:
Glioblastoma stem cell-derived exosomes induce M2 macrophages and
PD-L1 expression on human monocytes. Oncoimmunology.
7:e14129092018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Andorsky DJ, Yamada RE, Said J, Pinkus GS,
Betting DJ and Timmerman JM: Programmed death ligand 1 is expressed
by non-hodgkin lymphomas and inhibits the activity of
tumor-associated T cells. Clin Cancer Res. 17:4232–4244. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Rossille D, Gressier M, Damotte D,
Maucort-Boulch D, Pangault C, Semana G, Le Gouill S, Haioun C,
Tarte K, Lamy T, et al: High level of soluble programmed cell death
ligand 1 in blood impacts overall survival in aggressive diffuse
large B-Cell lymphoma: Results from a French multicenter clinical
trial. Leukemia. 28:2367–2375. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sinha D, Roy S, Saha P, Chatterjee N and
Bishayee A: Trends in research on exosomes in cancer progression
and anticancer therapy. Cancers (Basel). 13:3262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|