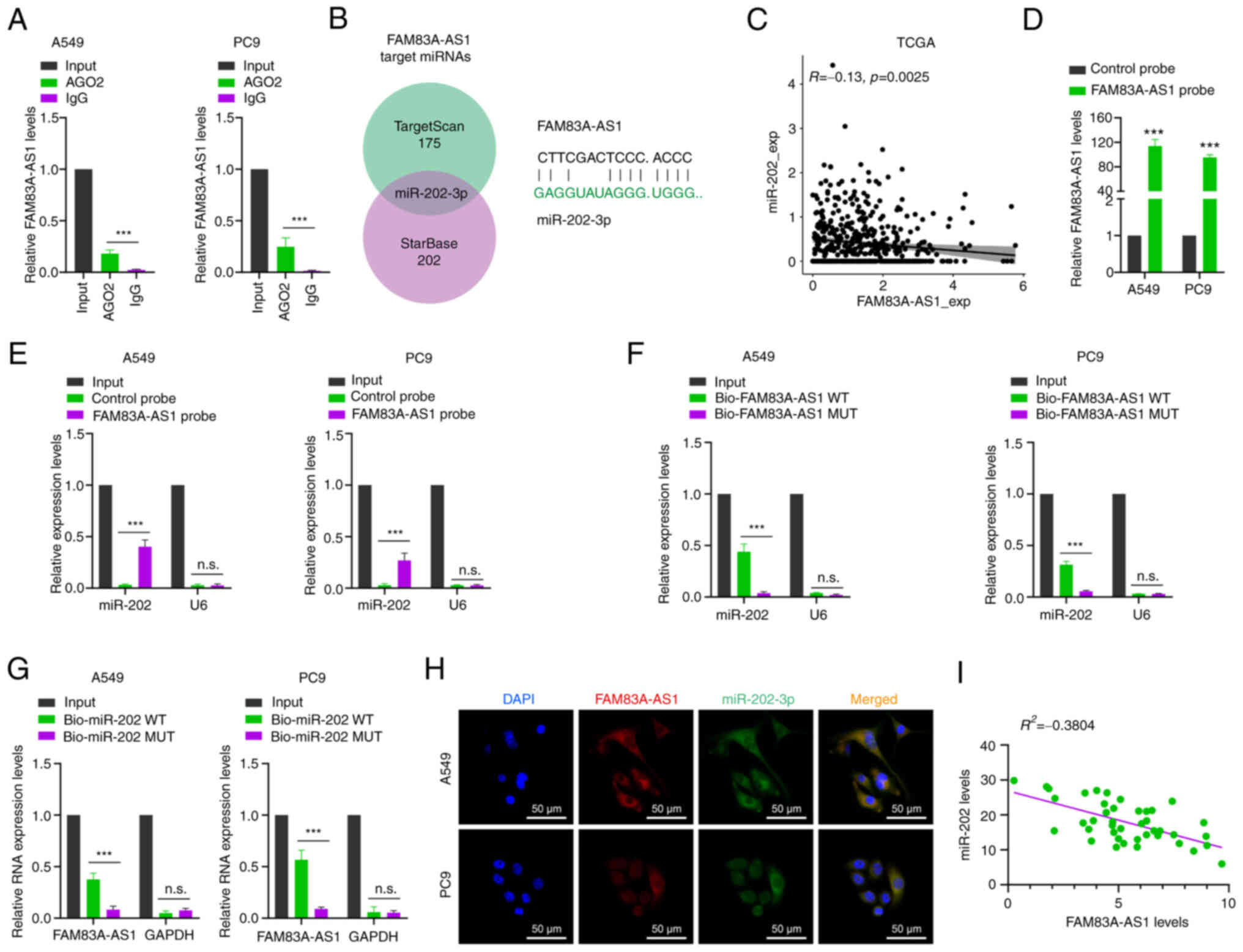
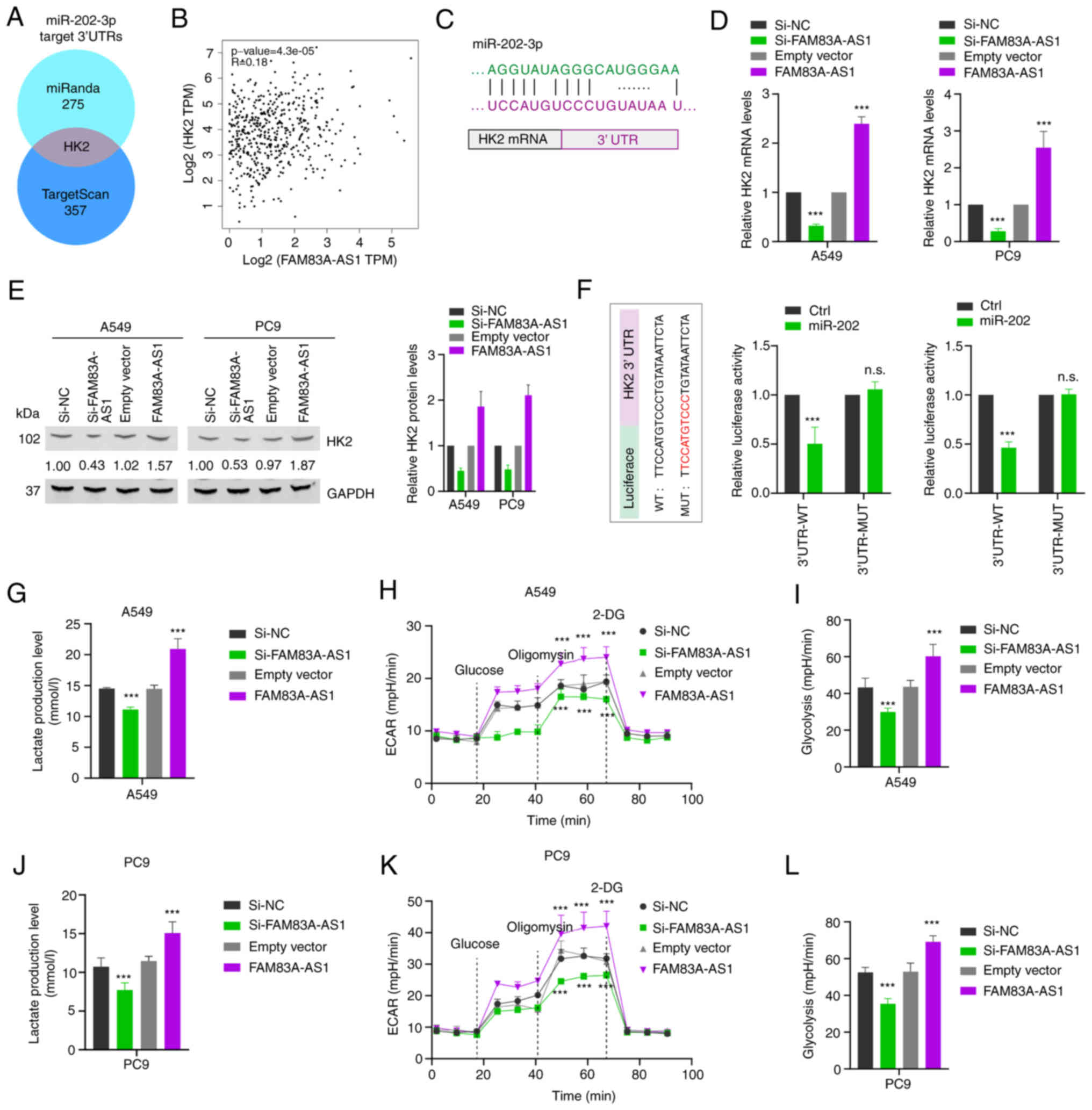
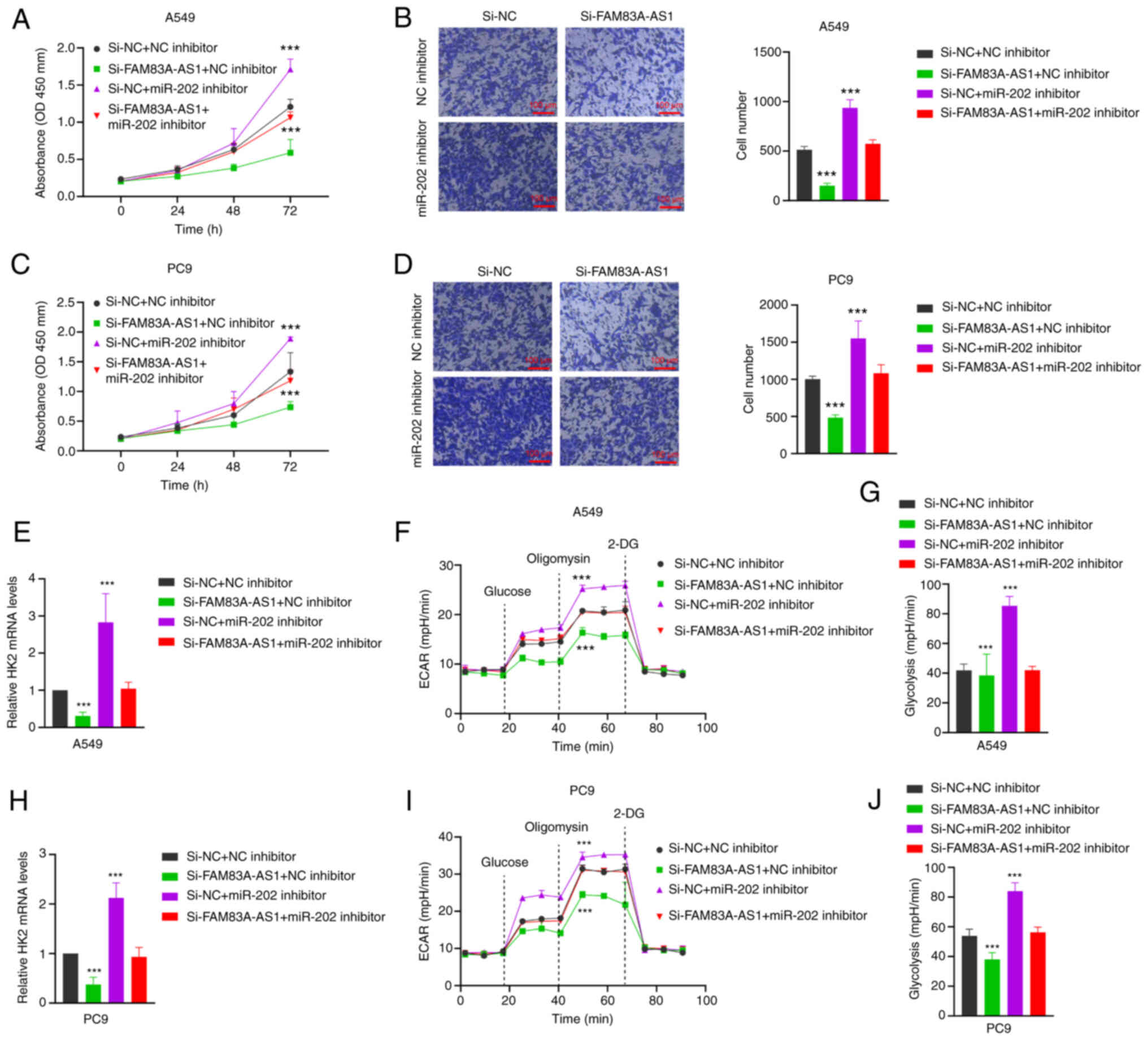
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 72:7–33. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
He D, Wang D, Lu P, Yang N, Xue Z, Zhu X,
Zhang P and Fan G: Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals heterogeneous
tumor and immune cell populations in early-stage lung
adenocarcinomas harboring EGFR mutations. Oncogene. 40:355–368.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dong ZY, Zhang C, Li YF, Su J, Xie Z, Liu
SY, Yan LX, Chen ZH, Yang XN, Lin JT, et al: Genetic and immune
profiles of solid predominant lung adenocarcinoma reveal potential
immunotherapeutic strategies. J Thorac Oncol. 13:85–96. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schneider F and Dacic S: Histopathologic
and molecular approach to staging of multiple lung nodules. Transl
Lung Cancer Res. 6:540–549. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bhan A, Soleimani M and Mandal SS: Long
noncoding RNA and cancer: A new paradigm. Cancer Res. 77:3965–3981.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yousefi H, Maheronnaghsh M, Molaei F,
Mashouri L, Reza Aref A, Momeny M and Alahari SK: Long noncoding
RNAs and exosomal lncRNAs: Classification, and mechanisms in breast
cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Oncogene. 39:953–974. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li SY, Zhu Y, Li RN, Huang JH, You K, Yuan
YF and Zhuang SM: LncRNA Lnc-APUE is repressed by HNF4α and
promotes G1/S phase transition and tumor growth by regulating
MiR-20b/E2F1 axis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 8:20030942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Parasramka MA, Maji S, Matsuda A, Yan IK
and Patel T: Long non-coding RNAs as novel targets for therapy in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Pharmacol Ther. 161:67–78. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen HY, Chan SJ, Liu X, Wei AC, Jian RI,
Huang KW, Lang YD, Shih JH, Liao CC, Luan CL, et al: Long noncoding
RNA Smyca coactivates TGF-β/Smad and Myc pathways to drive tumor
progression. J Hematol Oncol. 15:852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma F, Liu X, Zhou S, Li W, Liu C, Chadwick
M and Qian C: Long non-coding RNA FGF13-AS1 inhibits glycolysis and
stemness properties of breast cancer cells through
FGF13-AS1/IGF2BPs/Myc feedback loop. Cancer Lett. 450:63–75. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Venkatesh J, Wasson MD, Brown JM, Fernando
W and Marcato P: LncRNA-miRNA axes in breast cancer: Novel points
of interaction for strategic attack. Cancer Lett. 509:81–88. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang H, Yang C, Zhang Q, Zhuo T, Li X, Li
N, Zhu L, Luo C, Gan J and Wu Y: Long non-coding RNA FAM83A
antisense RNA 1 (lncRNA FAM83A-AS1) targets microRNA-141-3p to
regulate lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, migration,
invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression.
Bioengineered. 13:4964–4977. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang J, Bi Y, Liu XP, Yu D, Yan X, Yao J,
Liu T and Li S: To construct a ceRNA regulatory network as
prognostic biomarkers for bladder cancer. J Cell Mol Med.
24:5375–5386. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Su L, Li R, Zhang Z, Liu J, Du J and Wei
H: Identification of altered exosomal microRNAs and mRNAs in
Alzheimer's disease. Ageing Res Rev. 73:1014972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi T, Ma Y, Cao L, Zhan S, Xu Y, Fu F,
Liu C, Zhang G, Wang Z, Wang R, et al: B7-H3 promotes aerobic
glycolysis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer cells by
regulating HK2. Cell Death Dis. 10:3082019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Caso R, Sanchez-Vega F, Tan KS,
Mastrogiacomo B, Zhou J, Jones GD, Nguyen B, Schultz N, Connolly
JG, Brandt WS, et al: The underlying tumor genomics of predominant
histologic subtypes in lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol.
15:1844–1856. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shi Q, Shao K, Jia H, Cao B, Li W, Dong S,
Liu J, Wu K, Liu M, Liu F, et al: Genomic alterations and evolution
of cell clusters in metastatic invasive micropapillary carcinoma of
the breast. Nat Commun. 13:1112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tavernari D, Battistello E, Dheilly E,
Petruzzella AS, Mina M, Sordet-Dessimoz J, Peters S, Krueger T,
Gfeller D, Riggi N, et al: Nongenetic evolution drives lung
adenocarcinoma spatial heterogeneity and progression. Cancer
Discov. 11:1490–1507. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sato R, Imamura K, Semba T, Tomita Y,
Saeki S, Ikeda K, Komohara Y, Suzuki M, Sakagami T, Saya H and
Arima Y: TGFβ signaling activated by cancer-associated fibroblasts
determines the histological signature of lung adenocarcinoma.
Cancer Res. 81:4751–4765. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang S, Xu Y, Zhao P, Bao H, Wang X, Liu
R, Xu R, Xiang J, Jiang H, Yan J, et al: Integrated analysis of
genomic and immunological features in lung adenocarcinoma with
micropapillary component. Front Oncol. 11:6521932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tang M, Abbas HA, Negrao MV, Ramineni M,
Hu X, Hubert SM, Fujimoto J, Reuben A, Varghese S, Zhang J, et al:
The histologic phenotype of lung cancers is associated with
transcriptomic features rather than genomic characteristics. Nat
Commun. 12:70812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nguyen TT, Lee HS, Burt BM, Wu J, Zhang J,
Amos CI and Cheng C: A lepidic gene signature predicts patient
prognosis and sensitivity to immunotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma.
Genome Med. 14:52022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen Z, Hu Z, Sui Q, Huang Y, Zhao M, Li
M, Liang J, Lu T, Zhan C, Lin Z, et al: LncRNA FAM83A-AS1
facilitates tumor proliferation and the migration via the
HIF-1α/glycolysis axis in lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Biol Sci.
18:522–535. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jia J, Li H, Chu J, Sheng J, Wang C, Jia
Z, Meng W, Yin H, Wan J and He F: LncRNA FAM83A-AS1 promotes ESCC
progression by regulating miR-214/CDC25B axis. J Cancer.
12:1200–1211. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He J and Yu J: Long noncoding RNA
FAM83A-AS1 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression by
binding with NOP58 to enhance the mRNA stability of FAM83A. Biosci
Rep. 39:BSR201925502019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang W, Zhao Z, Xu C, Li C, Ding C, Chen
J, Chen T and Zhao J: LncRNA FAM83A-AS1 promotes lung
adenocarcinoma progression by enhancing the pre-mRNA stability of
FAM83A. Thorac Cancer. 12:1495–1502. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xiao G, Wang P, Zheng X, Liu D and Sun X:
FAM83A-AS1 promotes lung adenocarcinoma cell migration and invasion
by targeting miR-150-5p and modifying MMP14. Cell Cycle.
18:2972–2985. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lunt SY and Vander Heiden MG: Aerobic
glycolysis: Meeting the metabolic requirements of cell
proliferation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:441–464. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou L, Li M, Yu X, Gao F and Li W:
Repression of hexokinases II-mediated glycolysis contributes to
piperlongumine-induced tumor suppression in non-small cell lung
cancer cells. Int J Biol Sci. 15:826–837. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tantai J, Pan X, Chen Y, Shen Y and Ji C:
TRIM46 activates AKT/HK2 signaling by modifying PHLPP2
ubiquitylation to promote glycolysis and chemoresistance of lung
cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 13:2852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li X, Li Y, Bai S, Zhang J, Liu Z and Yang
J: NR2F1-AS1/miR-140/HK2 axis regulates hypoxia-induced glycolysis
and migration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res.
13:427–437. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen J, Yu Y, Li H, Hu Q, Chen X, He Y,
Xue C, Ren F, Ren Z, Li J, et al: Long non-coding RNA PVT1 promotes
tumor progression by regulating the miR-143/HK2 axis in gallbladder
cancer. Mol Cancer. 18:332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yu T, Li G, Wang C, Gong G, Wang L, Li C,
Chen Y and Wang X: MIR210HG regulates glycolysis, cell
proliferation, and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells through
miR-125b-5p/HK2/PKM2 axis. RNA Biol. 18:2513–2530. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|