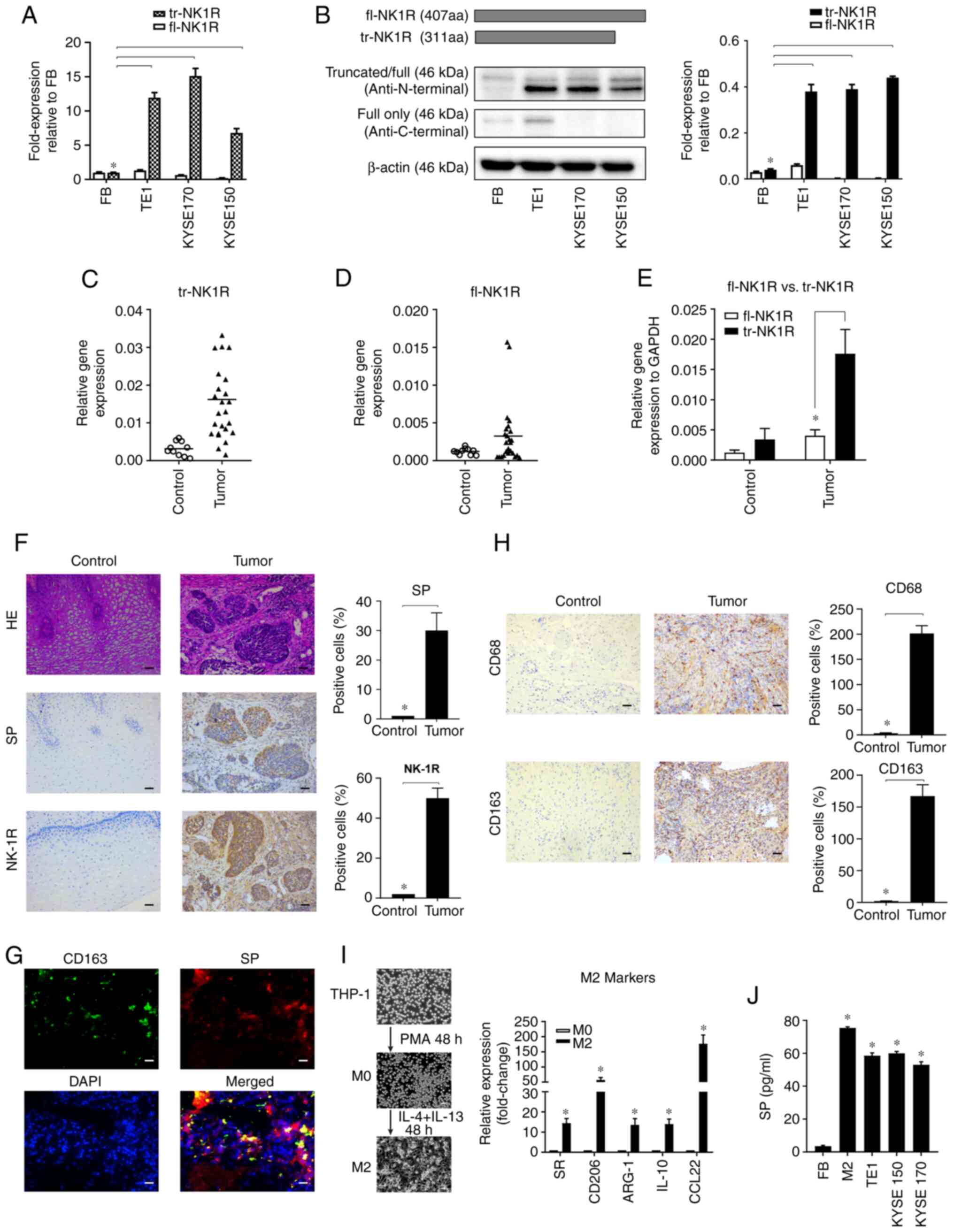
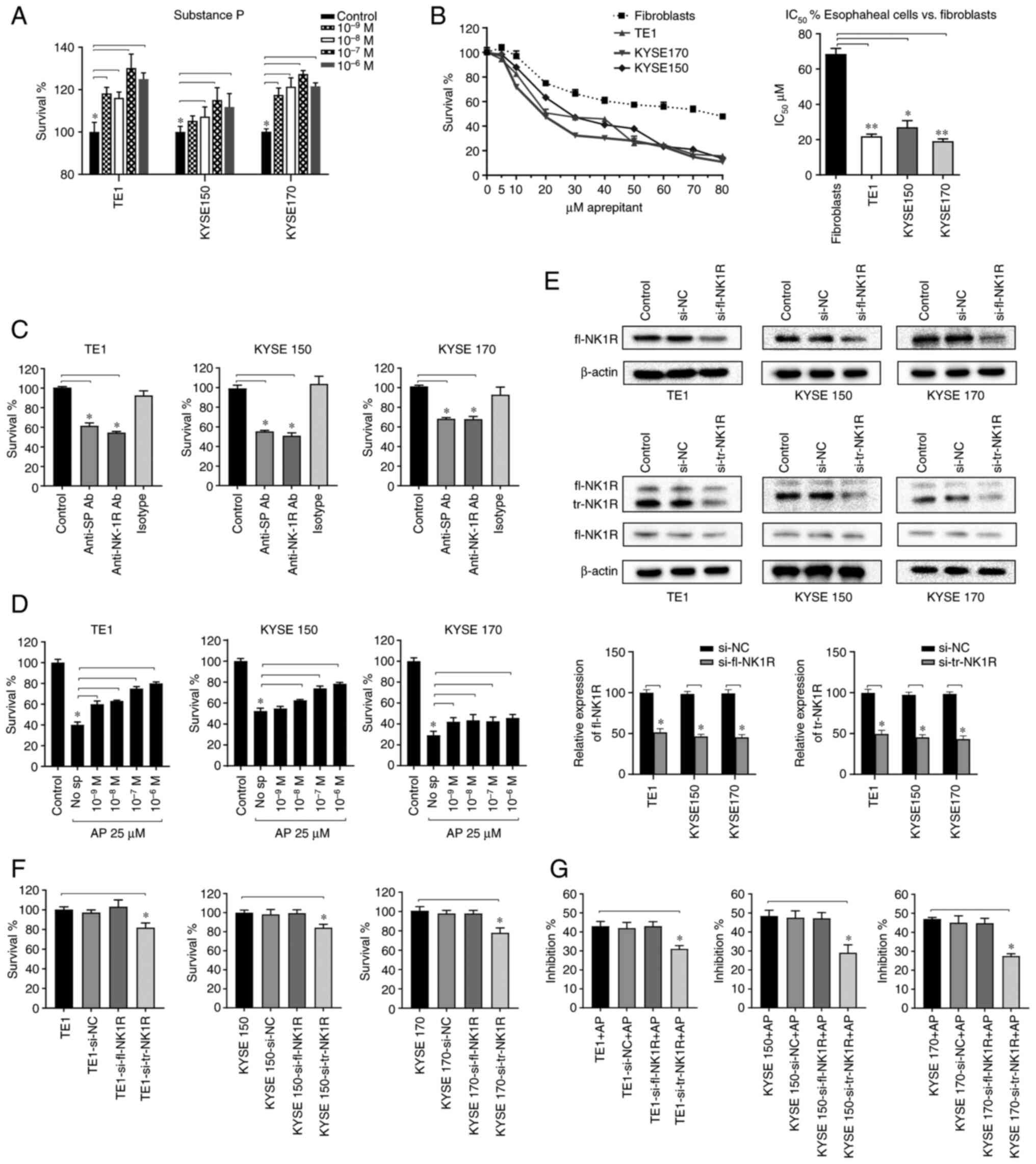
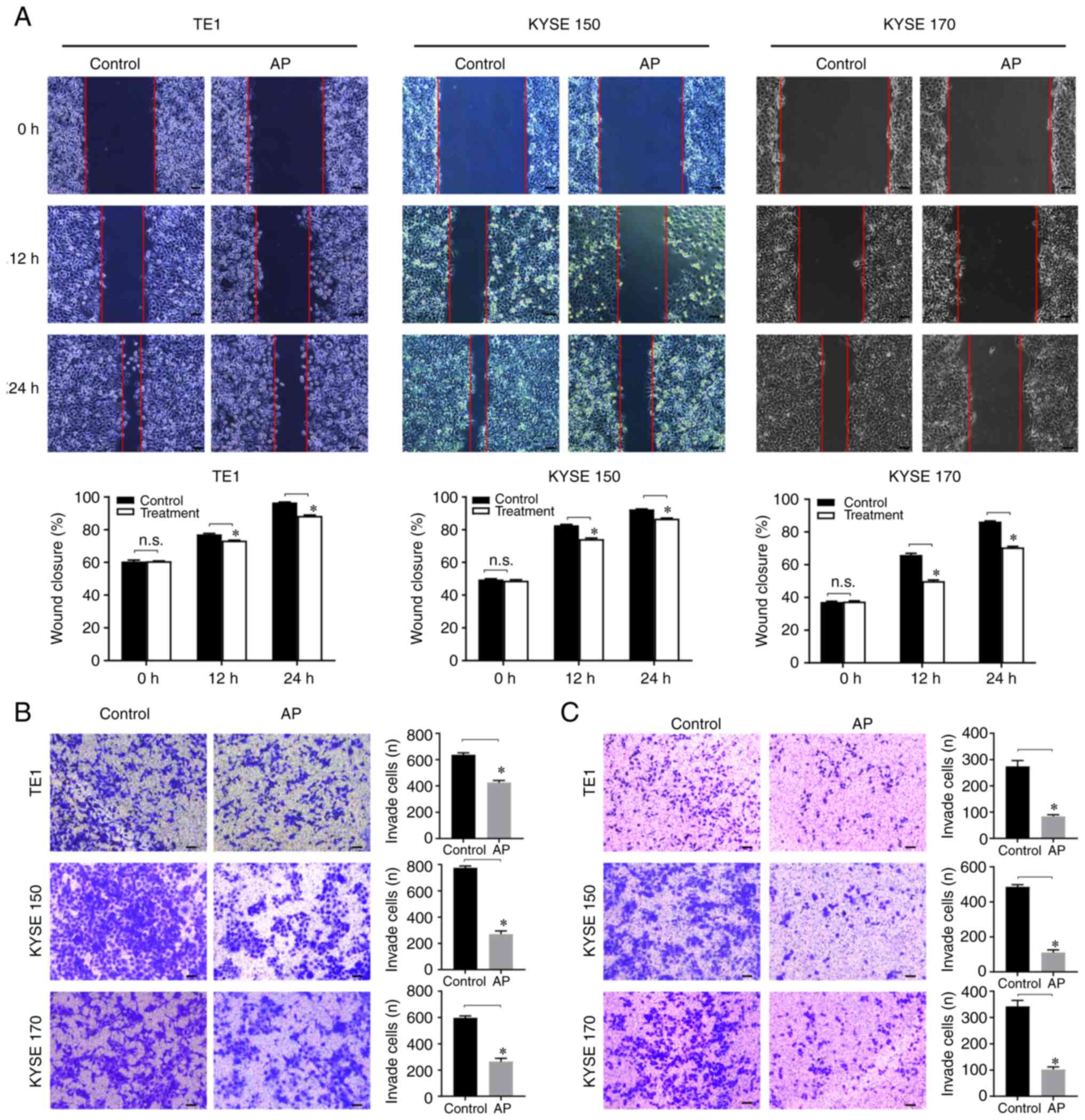
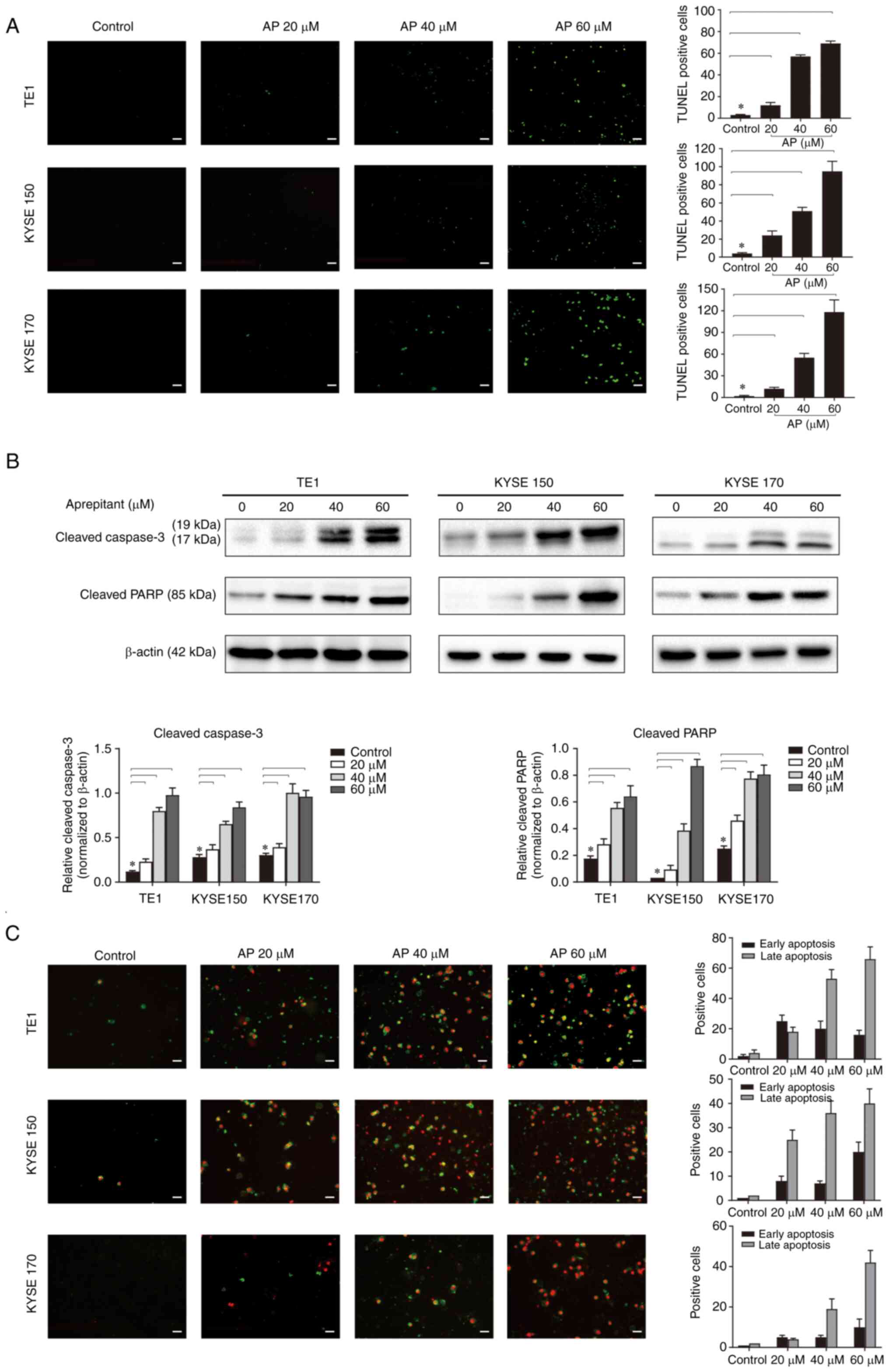
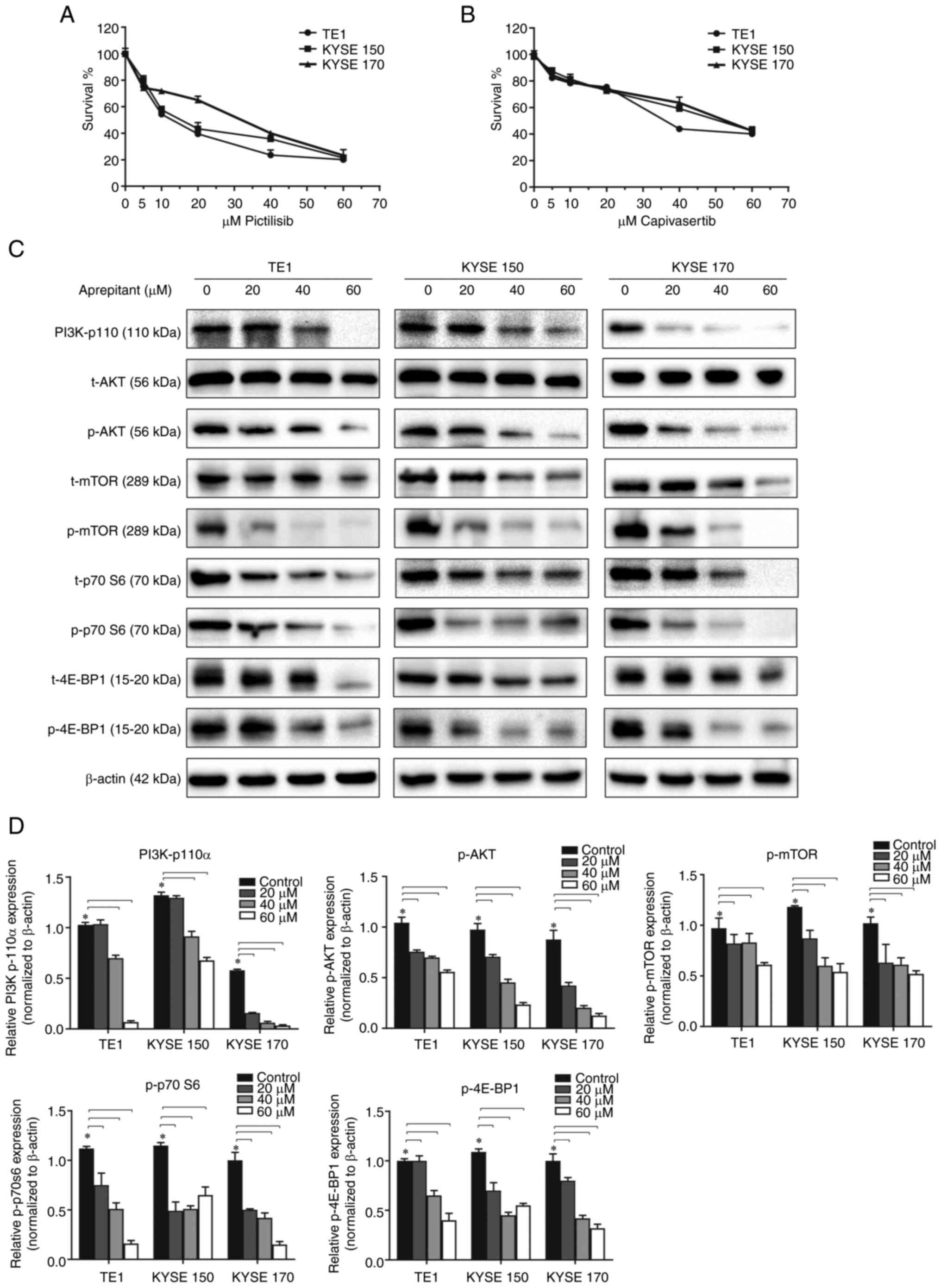
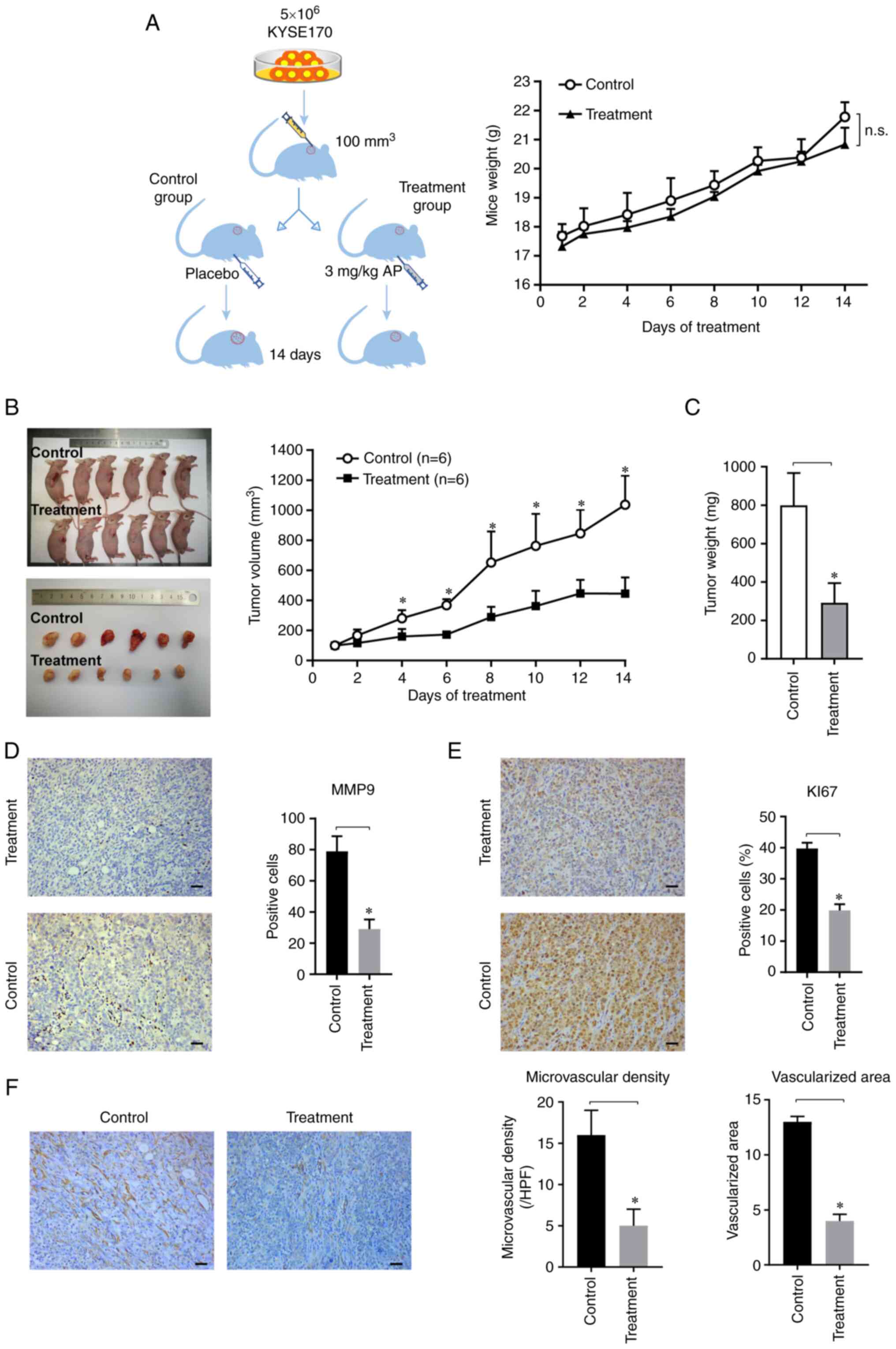
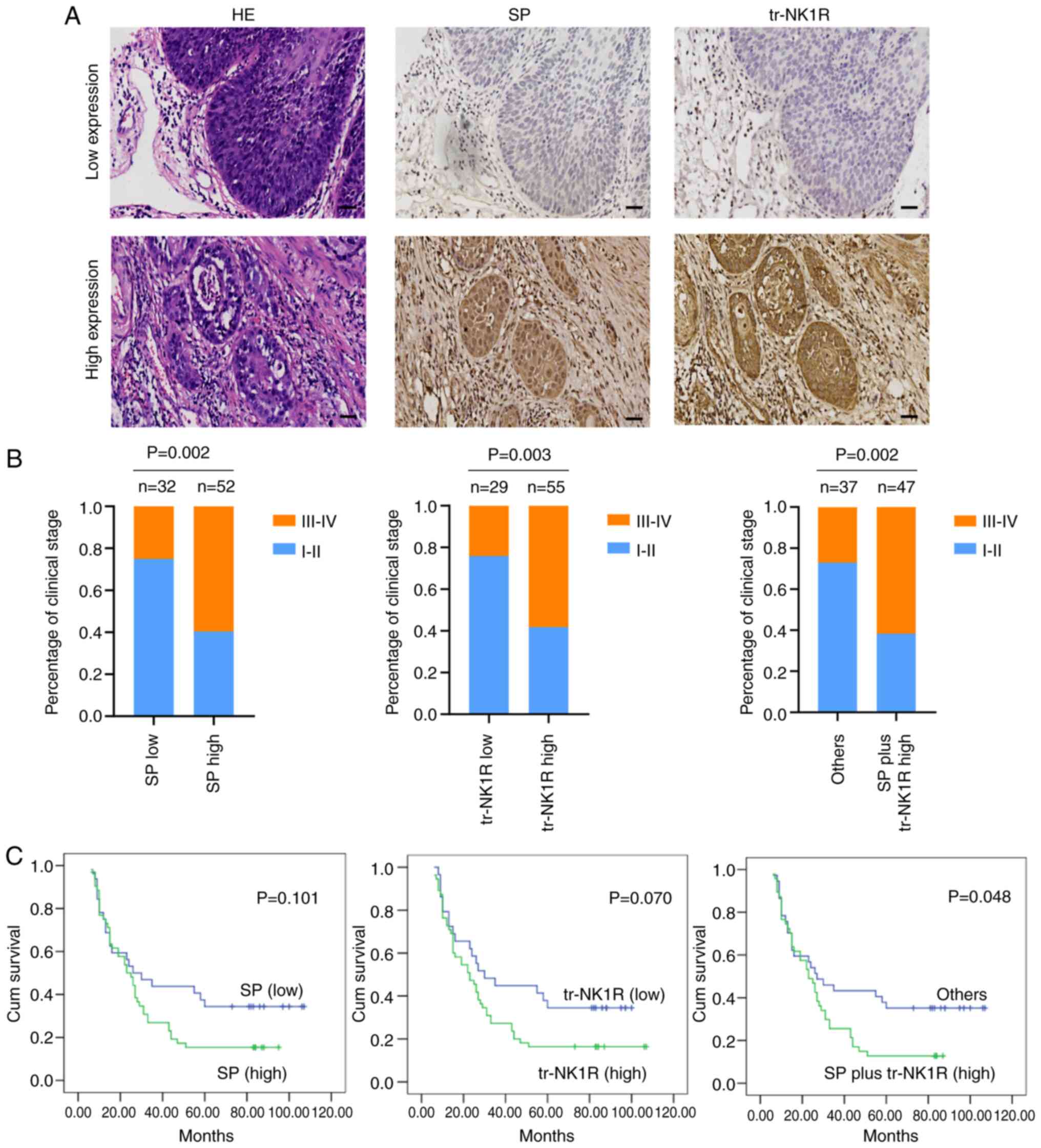
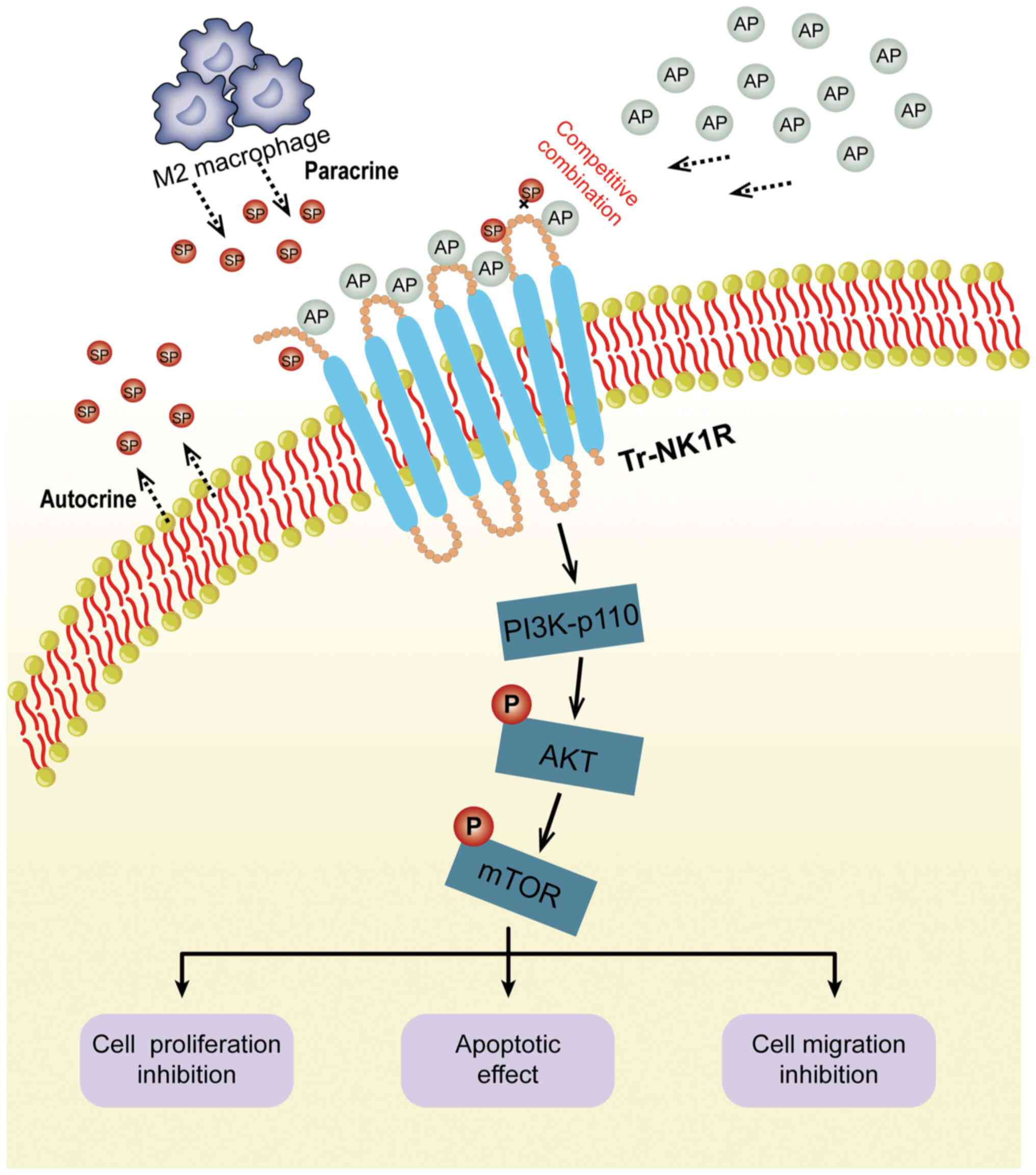
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 72:7–33. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Abnet CC, Arnold M and Wei WQ:
Epidemiology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 154:360–373. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Coveñas R and Muñoz M: Cancer progression
and substance P. Histol Histopathol. 29:881–890. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
González-Moles MÁ, Ramos-García P and
Esteban F: Significance of the overexpression of substance P and
its receptor NK-1R in head and neck carcinogenesis: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel). 13:13492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Patel HJ, Ramkissoon SH, Patel PS and
Rameshwar P: Transformation of breast cells by truncated
neurokinin-1 receptor is secondary to activation by
preprotachykinin-A peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:17436–17441. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gillespie E, Leeman SE, Watts LA, Coukos
JA, O'Brien MJ, Cerda SR, Farraye FA, Stucchi AF and Becker JM:
Truncated neurokinin-1 receptor is increased in colonic epithelial
cells from patients with colitis-associated cancer. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 108:17420–17425. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ramkissoon SH, Patel PS, Taborga M and
Rameshwar P: Nuclear factor-kappaB is central to the expression of
truncated neurokinin-1 receptor in breast cancer: Implication for
breast cancer cell quiescence within bone marrow stroma. Cancer
Res. 67:1653–1659. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Berger M, Neth O, Ilmer M, Garnier A,
Salinas-Martín MV, de Agustín Asencio JC, von Schweinitz D, Kappler
R and Muñoz M: Hepatoblastoma cells express truncated neurokinin-1
receptor and can be growth inhibited by aprepitant in vitro and in
vivo. J Hepatol. 60:985–994. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Deng XT, Tang SM, Wu PY, Li QP, Ge XX, Xu
BM, Wang HS and Miao L: SP/NK-1R promotes gallbladder cancer cell
proliferation and migration. J Cell Mol Med. 23:7961–7973. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Inoue T, Kimura M, Uchida J, Nishino K,
Kumagai T, Taniguchi J and Imamura F: Aprepitant for the treatment
of breakthrough chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in
patients receiving moderately emetogenic chemotherapy. Int J Clin
Oncol. 22:600–604. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yahata H, Kobayashi H, Sonoda K, Shimokawa
M, Ohgami T, Saito T, Ogawa S, Sakai K, Ichinoe A, Ueoka Y, et al:
Efficacy of aprepitant for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced
nausea and vomiting with a moderately emetogenic chemotherapy
regimen: A multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind,
randomized study in patients with gynecologic cancer receiving
paclitaxel and carboplatin. Int J Clin Oncol. 21:491–497. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Muñoz M and Coveñas R: Neurokinin-1
receptor antagonists as antitumor drugs in gastrointestinal cancer:
A new approach. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 22:260–268. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Douglas SD and Leeman SE: Neurokinin-1
receptor: Functional significance in the immune system in reference
to selected infections and inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1217:83–95. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ge C, Huang H, Huang F, Yang T, Zhang T,
Wu H, Zhou H, Chen Q, Shi Y, Sun Y, et al: Neurokinin-1 receptor is
an effective target for treating leukemia by inducing oxidative
stress through mitochondrial calcium overload. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 116:19635–19645. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chanmee T, Ontong P, Konno K and Itano N:
Tumor-associated macrophages as major players in the tumor
microenvironment. Cancers (Basel). 6:1670–1690. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou Y, Zhao L, Xiong T, Chen X, Zhang Y,
Yu M, Yang J and Yao Z: Roles of full-length and truncated
neurokinin-1 receptors on tumor progression and distant metastasis
in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 140:49–61. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lewis KM, Harford-Wright E, Vink R and
Ghabriel MN: NK1 receptor antagonists and dexamethasone as
anticancer agents in vitro and in a model of brain tumours
secondary to breast cancer. Anticancer Drugs. 24:344–354. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Javid H, Mohammadi F, Zahiri E and Hashemy
SI: The emerging role of substance P/neurokinin-1 receptor
signaling pathways in growth and development of tumor cells. J
Physiol Biochem. 75:415–421. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Garcia-Recio S, Fuster G,
Fernandez-Nogueira P, Pastor-Arroyo EM, Park SY, Mayordomo C,
Ametller E, Mancino M, Gonzalez-Farre X, Russnes HG, et al:
Substance P autocrine signaling contributes to persistent HER2
activation that drives malignant progression and drug resistance in
breast cancer. Cancer Res. 73:6424–6434. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ma J, Yuan S, Cheng J, Kang S, Zhao W and
Zhang J: Substance P promotes the progression of endometrial
adenocarcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 26:845–850. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Esteban F, Muñoz M, González-Moles MA and
Rosso M: A role for substance P in cancer promotion and
progression: A mechanism to counteract intracellular death signals
following oncogene activation or DNA damage. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
25:137–145. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mohammadi F, Javid H, Afshari AR, Mashkani
B and Hashemy SI: Substance P accelerates the progression of human
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via MMP-2, MMP-9, VEGF-A, and
VEGFR1 overexpression. Mol Biol Rep. 47:4263–4272. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mayordomo C, García-Recio S, Ametller E,
Fernández-Nogueira P, Pastor-Arroyo EM, Vinyals L, Casas I, Gascón
P and Almendro V: Targeting of substance P induces cancer cell
death and decreases the steady state of EGFR and Her2. J Cell
Physiol. 227:1358–1366. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cui Y, Zhang S, Hu X and Gao F:
Tumor-associated fibroblasts derived exosomes induce the
proliferation and cisplatin resistance in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma cells through RIG-I/IFN-β signaling. Bioengineered.
13:12462–12474. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ho WZ, Lai JP, Zhu XH, Uvaydova M and
Douglas SD: Human monocytes and macrophages express substance P and
neurokinin-1 receptor. J Immunol. 159:5654–5660. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dupuis LL, Lingertat-Walsh K and Walker
SE: Stability of an extemporaneous oral liquid aprepitant
formulation. Support Care Cancer. 17:701–706. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Munoz M, Covenas R, Esteban F and Redondo
M: The substance P/NK-1 receptor system: NK-1 receptor antagonists
as anti-cancer drugs. J Biosci. 40:441–463. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rapoport BL, Jordan K, Boice JA, Taylor A,
Brown C, Hardwick JS, Carides A, Webb T and Schmoll HJ: Aprepitant
for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting
associated with a broad range of moderately emetogenic
chemotherapies and tumor types: A randomized, double-blind study.
Support Care Cancer. 18:423–431. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Muñoz M and Rosso M: The NK-1 receptor
antagonist aprepitant as a broad spectrum antitumor drug. Invest
New Drugs. 28:187–193. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Palma C, Bigioni M, Irrissuto C, Nardelli
F, Maggi CA and Manzini S: Anti-tumour activity of tachykinin NK1
receptor antagonists on human glioma U373 MG xenograft. Br J
Cancer. 82:480–487. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bigioni M, Benzo A, Irrissuto C, Maggi CA
and Goso C: Role of NK-1 and NK-2 tachykinin receptor antagonism on
the growth of human breast carcinoma cell line MDA-MB-231.
Anticancer Drugs. 16:1083–1089. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|