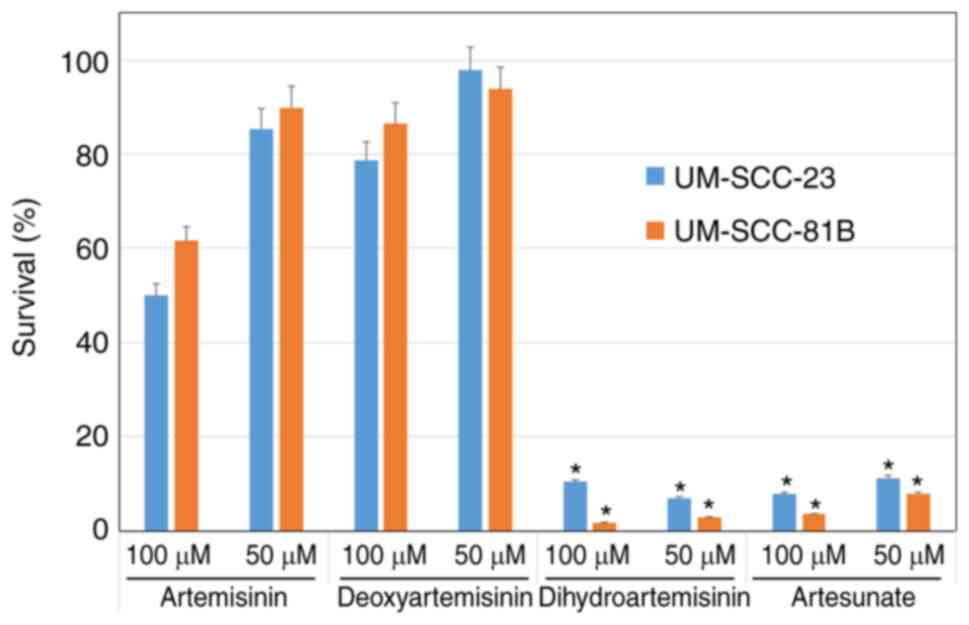
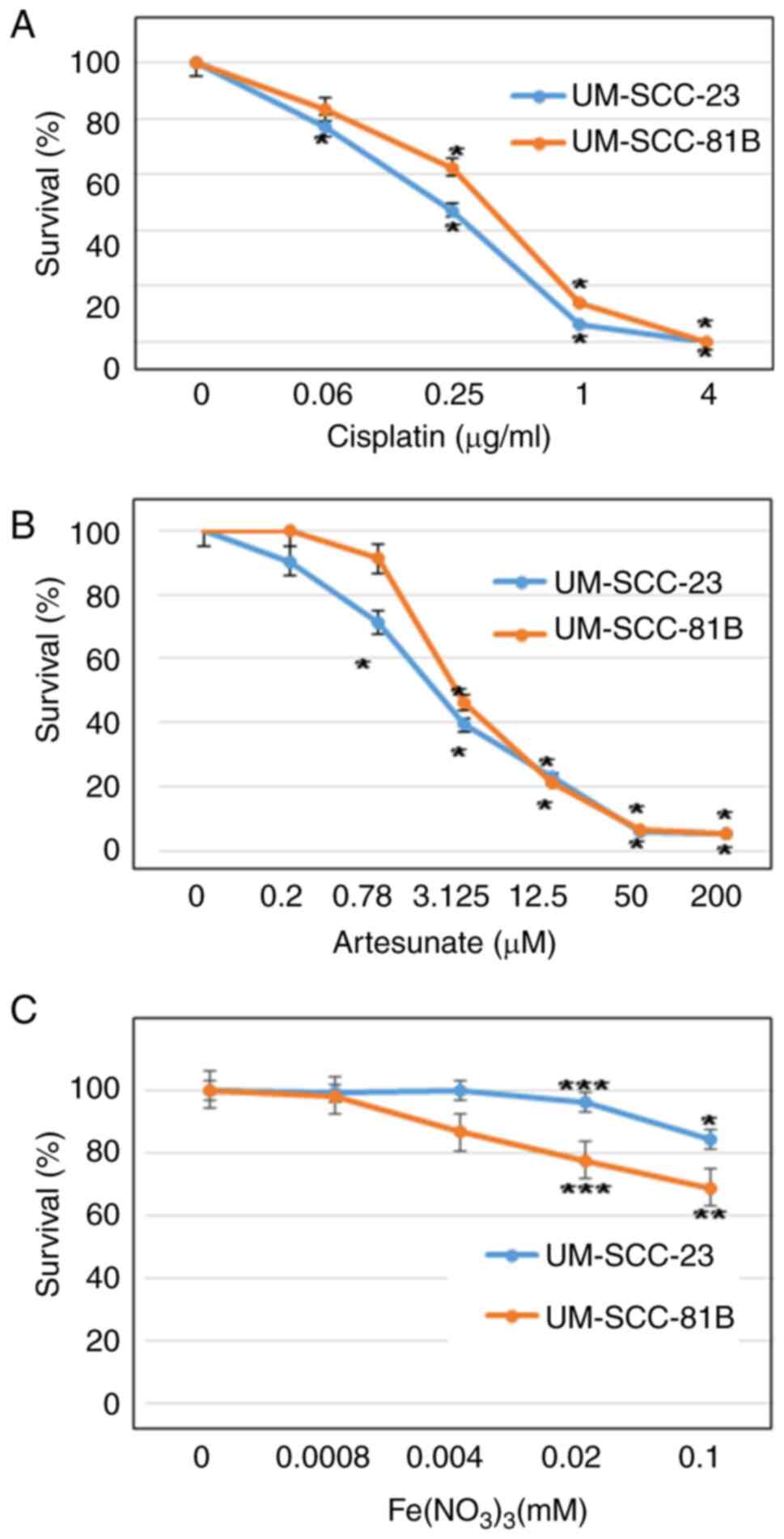
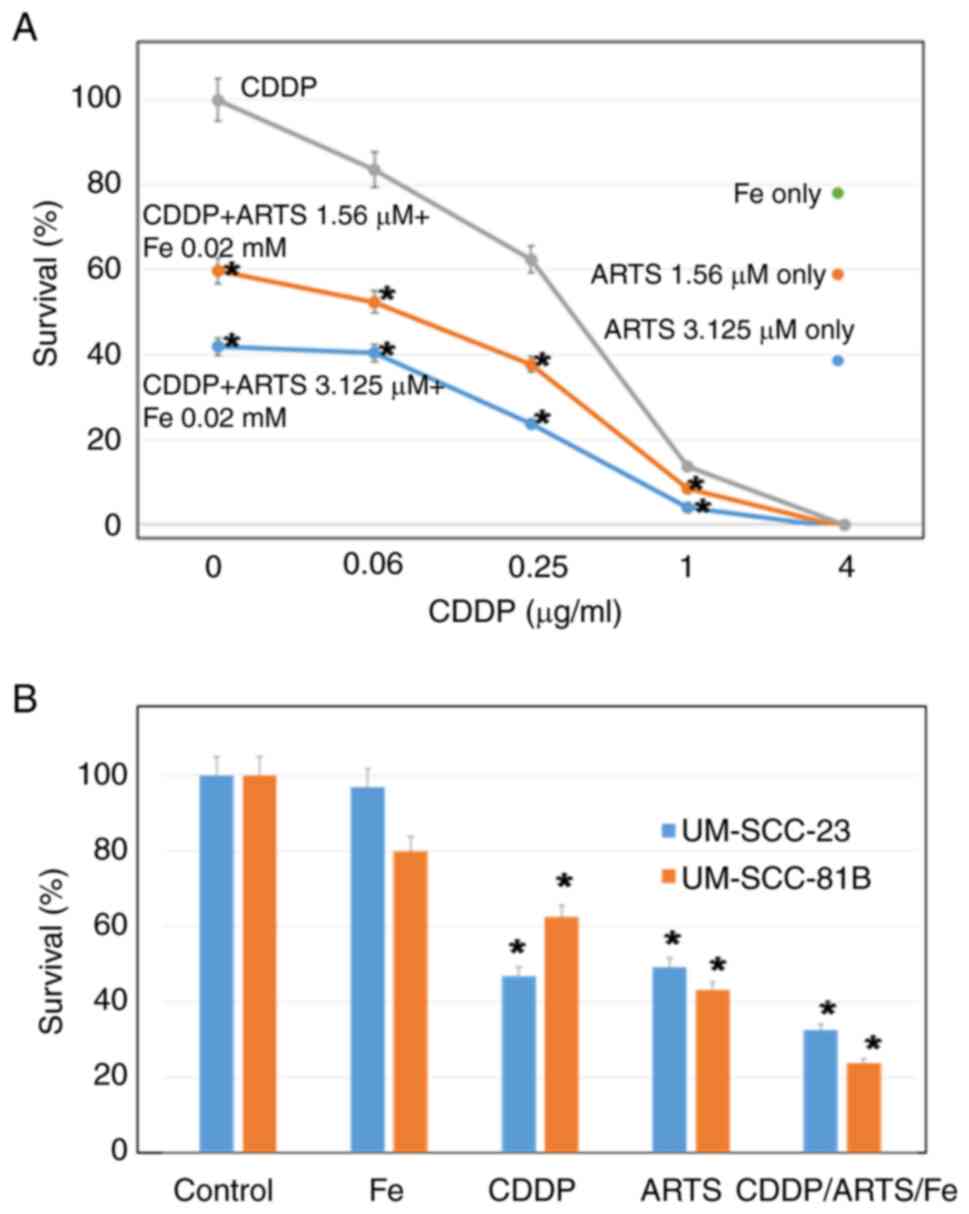
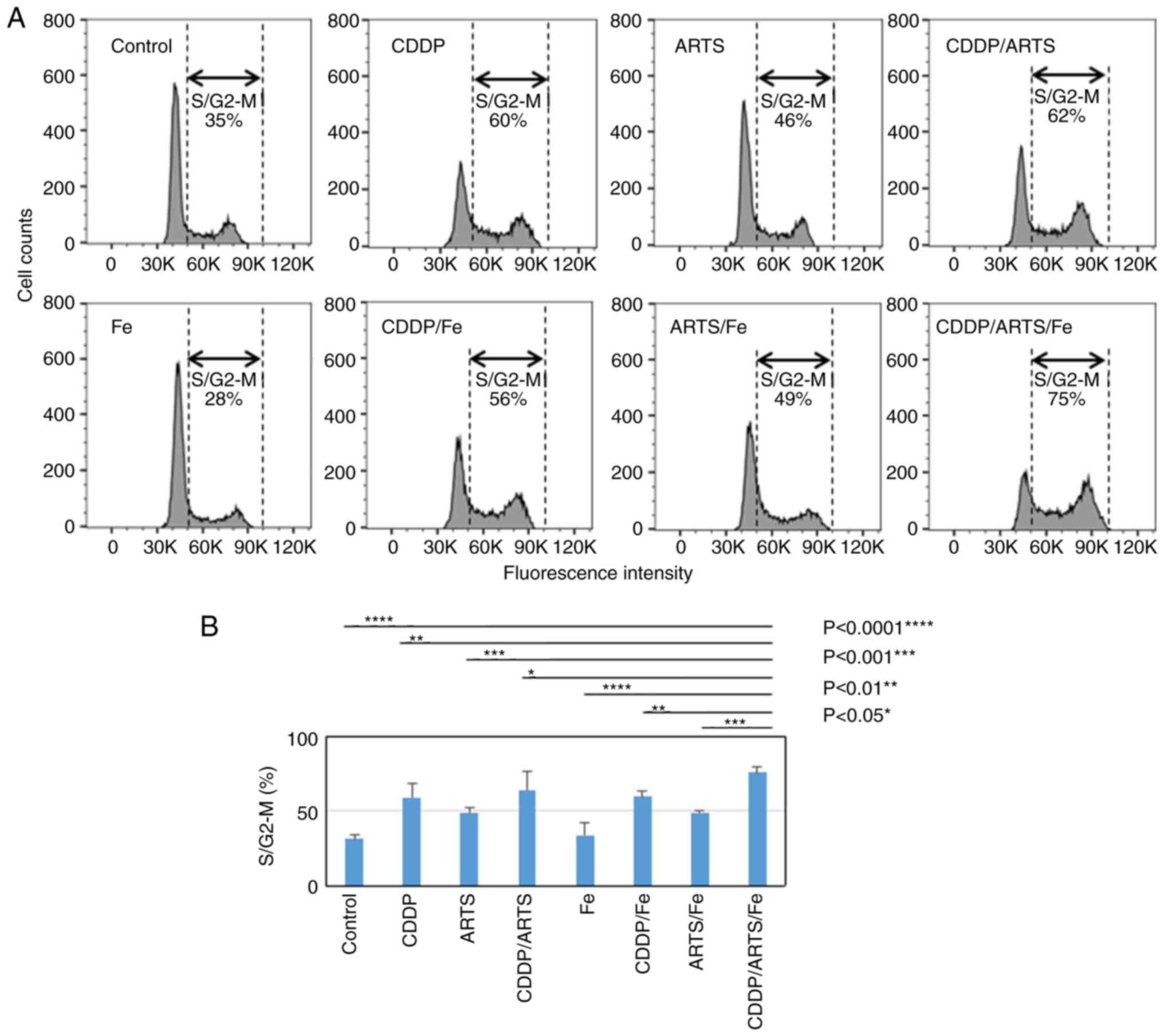
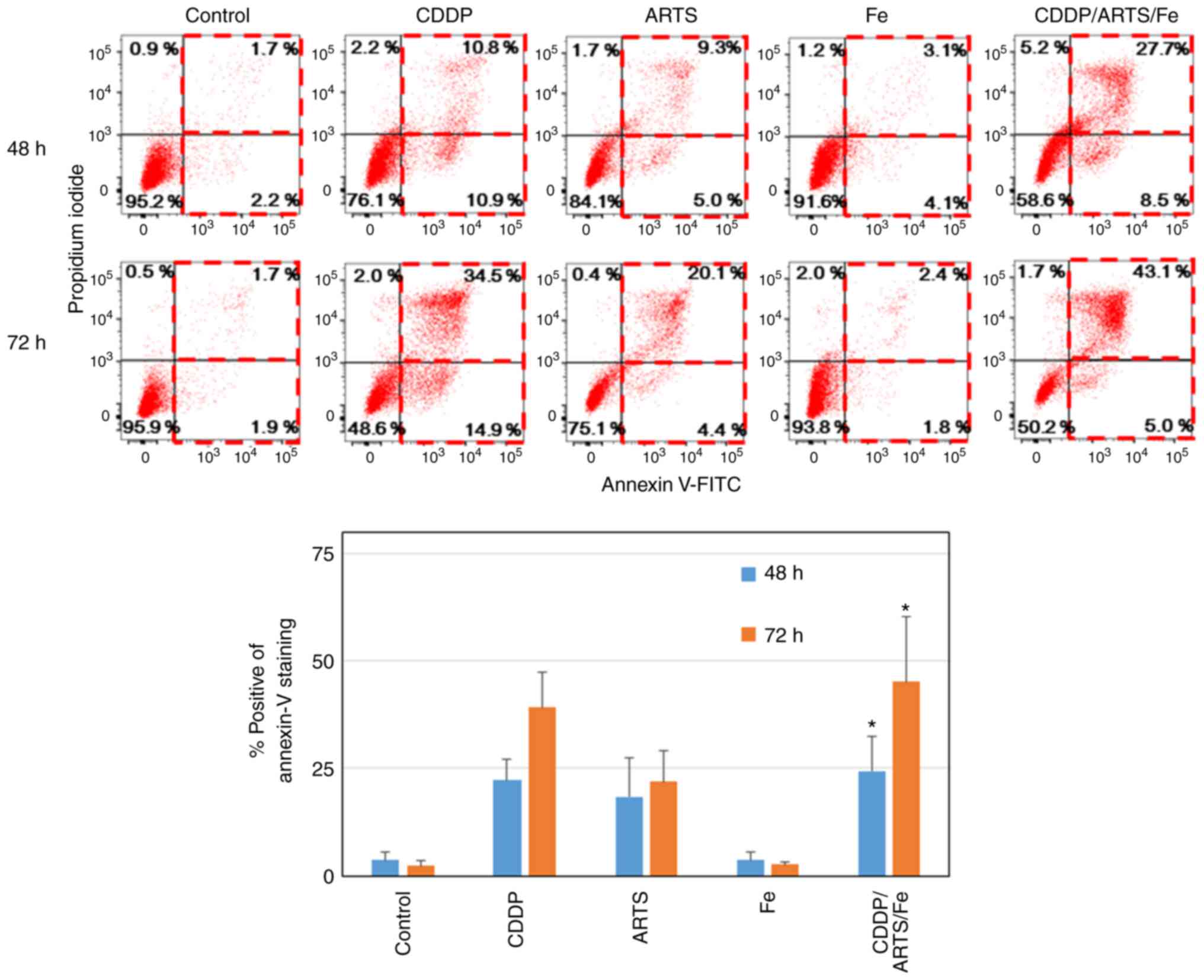
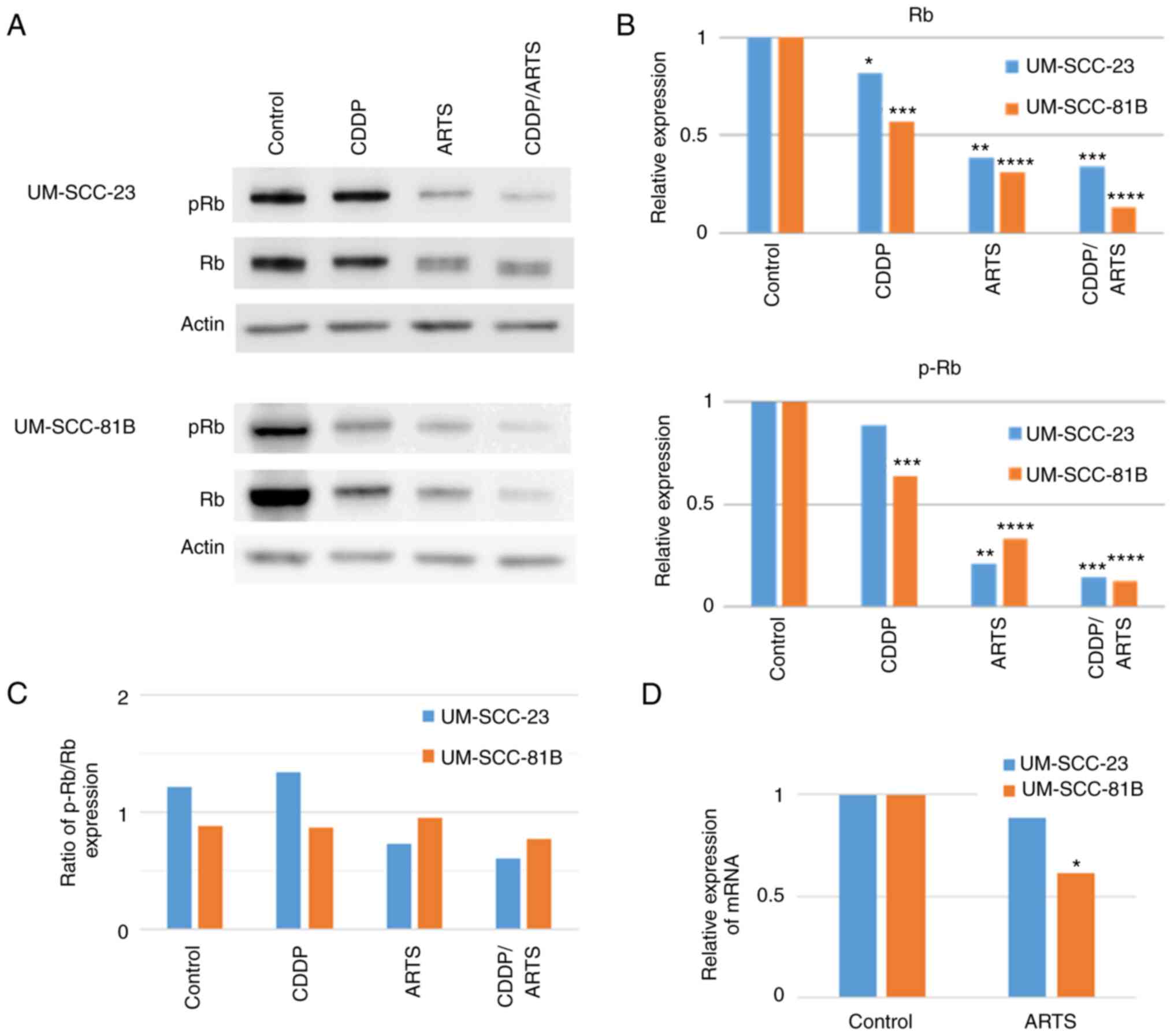
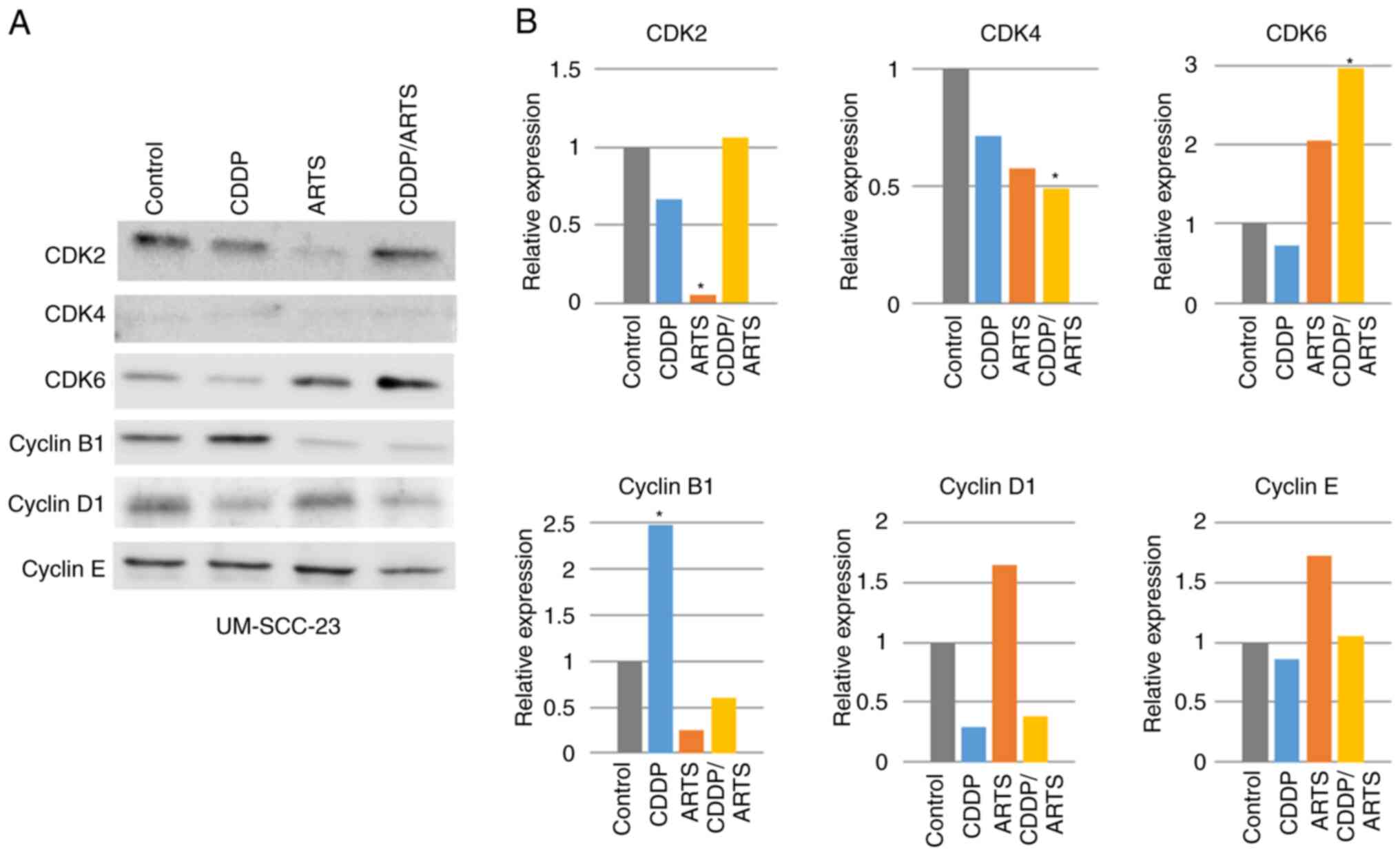
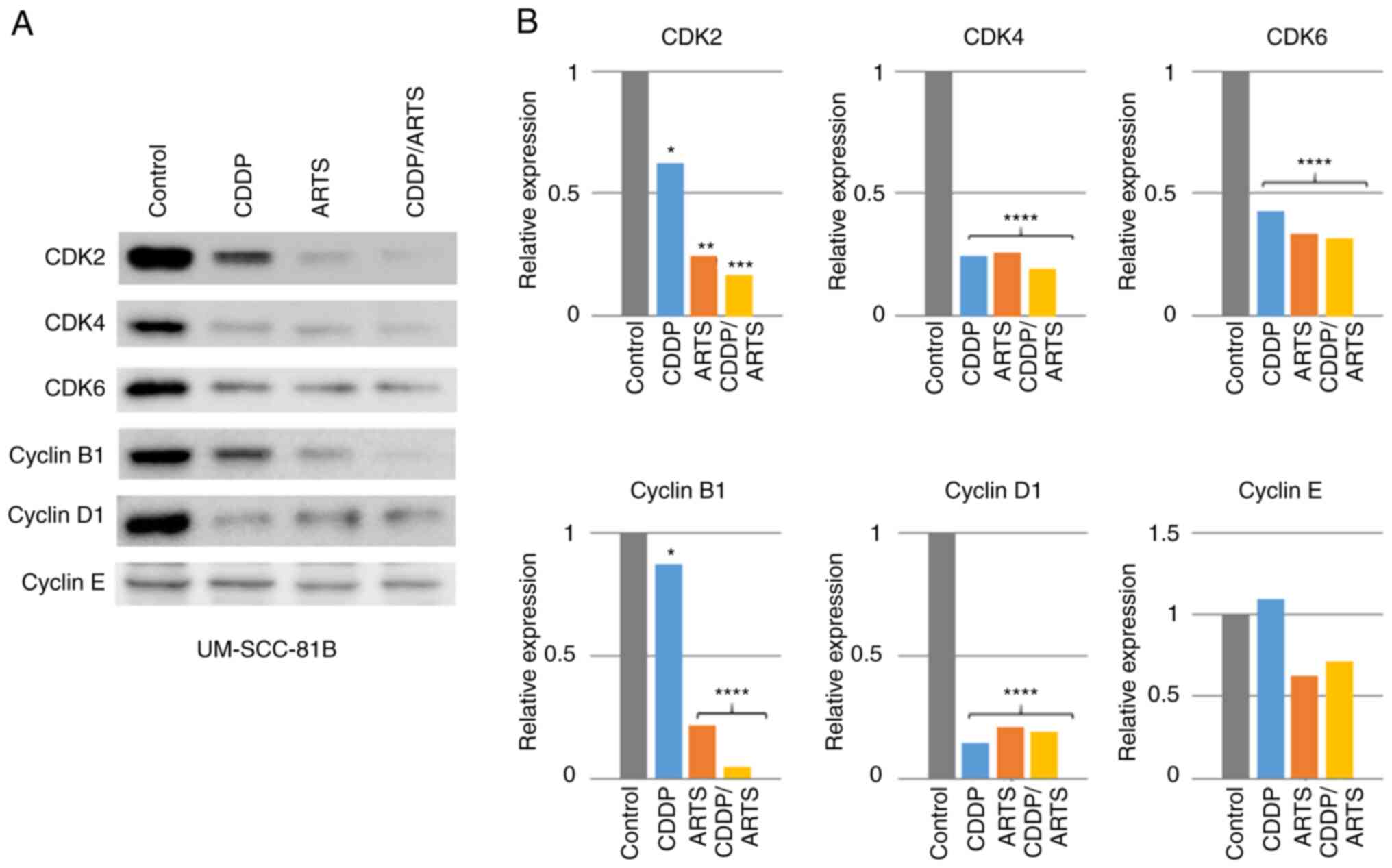
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Morton RP, Rugman F, Dorman EB, Stoney PJ,
Wilson JA, McCormick M, Veevers A and Stell PM: Cisplatinum and
bleomycin for advanced or recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the
head and neck: A randomised factorial phase III controlled trial.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 15:283–289. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kish JA, Weaver A, Jacobs J, Cummings G
and Al-Sarraf M: Cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil infusion in patients
with recurrent and disseminated epidermoid cancer of the head and
neck. Cancer. 53:1819–1824. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kish J, Drelichman A, Jacobs J, Hoschner
J, Kinzie J, Loh J, Weaver A and Al-Sarraf M: Clinical trial of
cisplatin and 5-FU infusion as initial treatment for advanced
squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer Treat Rep.
66:471–474. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ogawa T, Niho S, Nagai S, Kojima T,
Nishimura Y, Ohe Y, Kondo N, Yamaguchi T, Endo K, Izumi K and
Minami H: Moderate renal dysfunction may not require a cisplatin
dose reduction: A retrospective study of cancer patients with renal
impairment. Int J Clin Oncol. 18:977–982. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rosenthal PJ: Artesunate for the treatment
of severe falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 358:1829–1836. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ho WE, Peh HY, Chan TK and Wong WS:
Artemisinins: Pharmacological actions beyond anti-malarial.
Pharmacol Ther. 142:126–139. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun WC, Han JX, Yang WY, Deng DA and Yue
XF: Antitumor activities of 4 derivatives of artemisic acid and
artemisinin B in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 13:541–543. 1992.
|
|
9
|
Efferth T, Dunstan H, Sauerbrey A, Miyachi
H and Chitambar CR: The anti-malarial artesunate is also active
against cancer. Int J Oncol. 18:767–773. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Efferth T, Sauerbrey A, Olbrich A, Gebhart
E, Rauch P, Weber HO, Hengstler JG, Halatsch ME, Volm M, Tew KD, et
al: Molecular modes of action of artesunate in tumor cell lines.
Mol Pharmacol. 64:382–394. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Våtsveen TK, Myhre MR, Steen CB, Wälchli
S, Lingjærde OC, Bai B, Dillard P, Theodossiou TA, Holien T, Sundan
A, et al: Artesunate shows potent anti-tumor activity in B-cell
lymphoma. J Hematol Oncol. 11:232018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Berte N, Lokan S, Eich M, Kim E and Kaina
B: Artesunate enhances the therapeutic response of glioma cells to
temozolomide by inhibition of homologous recombination and
senescence. Oncotarget. 7:67235–67250. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hou J, Wang D, Zhang R and Wang H:
Experimental therapy of hepatoma with artemisinin and its
derivatives: In vitro and in vivo activity, chemosensitization, and
mechanisms of action. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5519–5530. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Roh JL, Kim EH, Jang H and Shin D: Nrf2
inhibition reverses the resistance of cisplatin-resistant head and
neck cancer cells to artesunate-induced ferroptosis. Redox Biol.
11:254–262. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jia J, Qin Y, Zhang L, Guo C, Wang Y, Yue
X and Qian J: Artemisinin inhibits gallbladder cancer cell lines
through triggering cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Mol Med Rep.
13:4461–4468. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen S, Gan S, Han L, Li X, Xie X, Zou D
and Sun H: Artesunate induces apoptosis and inhibits the
proliferation, stemness, and tumorigenesis of leukemia. Ann Transl
Med. 8:7672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dell'Eva R, Pfeffer U, Vené R, Anfosso L,
Forlani A, Albini A and Efferth T: Inhibition of angiogenesis in
vivo and growth of Kaposi's sarcoma xenograft tumors by the
anti-malarial artesunate. Biochem Pharmacol. 68:2359–2366. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim SJ, Kim MS, Lee JW, Lee CH, Yoo H,
Shin SH, Park MJ and Lee SH: Dihydroartemisinin enhances
radiosensitivity of human glioma cells in vitro. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 132:129–135. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Efferth T: From ancient herb to modern
drug: Artemisia annua and artemisinin for cancer therapy.
Semin Cancer Biol. 46:65–83. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wong YK, Xu C, Kalesh KA, He Y, Lin Q,
Wong WSF, Shen HM and Wang J: Artemisinin as an anticancer drug:
Recent advances in target profiling and mechanisms of action. Med
Res Rev. 37:1492–1517. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu C, Zhang H, Mu L and Yang X:
Artemisinins as anticancer drugs: Novel therapeutic approaches,
molecular mechanisms, and clinical trials. Front Pharmacol.
11:5298812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nishimura K, Tsuchiya Y, Okamoto H, Ijichi
K, Gosho M, Fukayama M, Yoshikawa K, Ueda H, Bradford CR, Carey TE
and Ogawa T: Identification of chemoresistant factors by protein
expression analysis with iTRAQ for head and neck carcinoma. Br J
Cancer. 111:799–806. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Muramatsu H, Sumitomo M, Morinaga S,
Kajikawa K, Kobayashi I, Nishikawa G, Kato Y, Watanabe M, Zennami
K, Kanao K, et al: Targeting lactate dehydrogenase-A promotes
docetaxel-induced cytotoxicity predominantly in
castration-resistant prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 42:224–230.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang JL, Wang Z, Hu W, Chen SS, Lou XE
and Zhou HJ: DHA regulates angiogenesis and improves the efficiency
of CDDP for the treatment of lung carcinoma. Microvasc Res.
87:14–24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Razavi A, Nouri HR, Mehrabian F and
Mirshafiey A: Treatment of experimental nephrotic syndrome with
artesunate. Int J Toxicol. 26:373–380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang SJ, Gao Y, Chen H, Kong R, Jiang HC,
Pan SH, Xue DB, Bai XW and Sun B: Dihydroartemisinin inactivates
NF-kappaB and potentiates the anti-tumor effect of gemcitabine on
pancreatic cancer both in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett.
293:99–108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao F, Vakhrusheva O, Markowitsch SD,
Slade KS, Tsaur I, Cinatl J Jr, Michaelis M, Efferth T, Haferkamp A
and Juengel E: Artesunate impairs growth in cisplatin-resistant
bladder cancer cells by cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and autophagy
induction. Cells. 9:26432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tran KQ, Tin AS and Firestone GL:
Artemisinin triggers a G1 cell cycle arrest of human Ishikawa
endometrial cancer cells and inhibits cyclin-dependent kinase-4
promoter activity and expression by disrupting nuclear factor-κB
transcriptional signaling. Anticancer Drugs. 25:270–281. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ji Y, Zhang YC, Pei LB, Shi LL, Yan JL and
Ma XH: Anti-tumor effects of dihydroartemisinin on human
osteosarcoma. Mol and Cell Biochem. 351:99–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen K, Shou LM, Lin F, Duan WM, Wu MY,
Xie X, Xie YF, Li W and Tao M: Artesunate induces G2/M cell cycle
arrest through autophagy induction in breast cancer cells.
Anticancer Drugs. 25:652–662. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
An B and Dou QP: Cleavage of
retinoblastoma protein during apoptosis: An interleukin 1
beta-converting enzyme-like protease as candidate. Cancer Res.
56:438–442. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen WD, Otterson GA, Lipkowitz S, Khleif
SN, Coxon AB and Kaye FJ: Apoptosis is associated with cleavage of
a 5 kDa fragment from RB which mimics dephosphorylation and
modulates E2F binding. Oncogene. 14:1243–1248. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tan X and Wang JY: The caspase-RB
connection in cell death. Trends Cell Biol. 8:116–120. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fan HN, Zhu MY, Peng SQ, Zhu JS, Zhang J
and Qu GQ: Dihydroartemisinin inhibits the growth and invasion of
gastric cancer cells by regulating cyclin D1-CDK4-Rb signaling.
Pathol Res Pract. 216:1527952020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Almasan A, Yin Y, Kelly RE, Lee EY,
Bradley A, Li W, Bertino JR and Wahl GM: Deficiency of
retinoblastoma protein leads to inappropriate S-phase entry,
activation of E2F-responsive genes, and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 92:5436–5440. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|