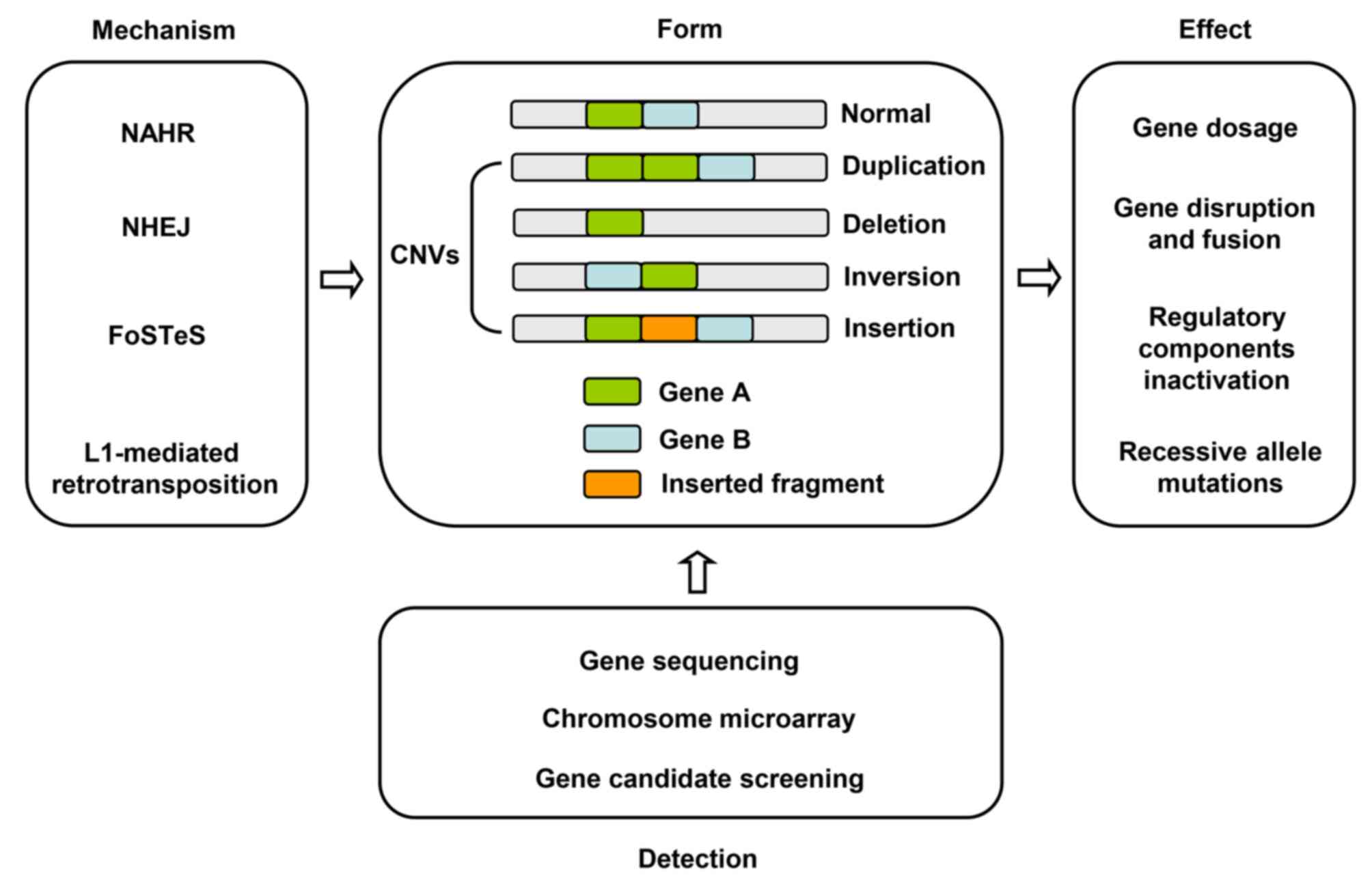
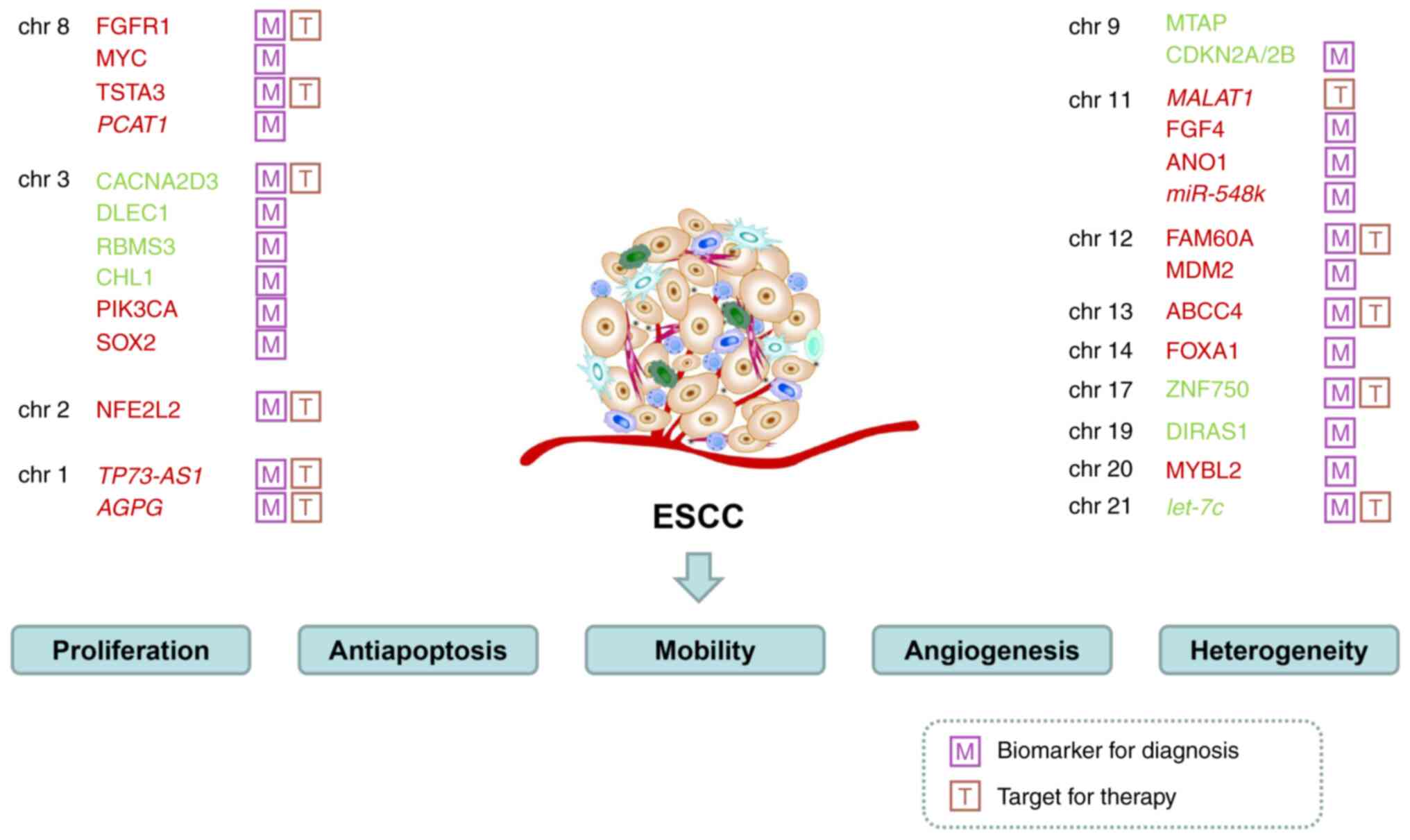
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smyth EC, Lagergren J, Fitzgerald RC,
Lordick F, Shah MA, Lagergren P and Cunningham D: Oesophageal
cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 3:170482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA and
Luketich JD: Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 381:400–412. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chang J, Tan W, Ling Z, Xi R, Shao M, Chen
M, Luo Y, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Huang X, et al: Genomic analysis of
oesophageal squamous-cell carcinoma identifies alcohol
drinking-related mutation signature and genomic alterations. Nat
Commun. 8:152902017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen XX, Zhong Q, Liu Y, Yan SM, Chen ZH,
Jin SZ, Xia TL, Li RY, Zhou AJ, Su Z, et al: Genomic comparison of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its precursor lesions by
multi-region whole-exome sequencing. Nat Commun. 8:5242017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Song Y, Li L, Ou Y, Gao Z, Li E, Li X,
Zhang W, Wang J, Xu L, Zhou Y, et al: Identification of genomic
alterations in oesophageal squamous cell cancer. Nature. 509:91–95.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang L, Zhou Y, Cheng C, Cui H, Cheng L,
Kong P, Wang J, Li Y, Chen W, Song B, et al: Genomic analyses
reveal mutational signatures and frequently altered genes in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Hum Genet. 96:597–611.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cheng C, Zhou Y, Li H, Xiong T, Li S, Bi
Y, Kong P, Wang F, Cui H, Li Y, et al: Whole-genome sequencing
reveals diverse models of structural variations in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Hum Genet. 98:256–274. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng C, Cui H, Zhang L, Jia Z, Song B,
Wang F, Li Y, Liu J, Kong P, Shi R, et al: Genomic analyses reveal
FAM84B and the NOTCH pathway are associated with the progression of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gigascience. 5:12016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cui Y, Chen H, Xi R, Cui H, Zhao Y, Xu E,
Yan T, Lu X, Huang F, Kong P, et al: Whole-genome sequencing of 508
patients identifies key molecular features associated with poor
prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Res.
30:902–913. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lian Y, Niu X, Cai H, Yang X, Ma H, Ma S,
Zhang Y and Chen Y: Clinicopathological significance of c-MYC in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177158042017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yan T, Cui H, Zhou Y, Yang B, Kong P,
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Wang B, Cheng Y, Li J, et al: Multi-region
sequencing unveils novel actionable targets and spatial
heterogeneity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Commun.
10:16702019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin DC, Wang MR and Koeffler HP: Targeting
genetic lesions in esophageal cancer. Cell Cycle. 13:2013–2014.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Almal SH and Padh H: Implications of gene
copy-number variation in health and diseases. J Hum Genet. 57:6–13.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Conrad DF, Pinto D, Redon R, Feuk L,
Gokcumen O, Zhang Y, Aerts J, Andrews TD, Barnes C, Campbell P, et
al: Origins and functional impact of copy number variation in the
human genome. Nature. 464:704–712. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Redon R, Ishikawa S, Fitch KR, Feuk L,
Perry GH, Andrews TD, Fiegler H, Shapero MH, Carson AR, Chen W, et
al: Global variation in copy number in the human genome. Nature.
444:444–454. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang F, Gu W, Hurles ME and Lupski JR:
Copy number variation in human health, disease, and evolution. Annu
Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 10:451–481. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lupski JR and Stankiewicz P: Genomic
disorders: Molecular mechanisms for rearrangements and conveyed
phenotypes. PLoS Genet. 1:e492005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lieber MR, Ma Y, Pannicke U and Schwarz K:
Mechanism and regulation of human non-homologous DNA end-joining.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 4:712–720. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lieber MR: The mechanism of human
nonhomologous DNA end joining. J Biol Chem. 283:1–5. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee JA, Carvalho CMB and Lupski JR: A DNA
replication mechanism for generating nonrecurrent rearrangements
associated with genomic disorders. Cell. 131:1235–1247. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kazazian HH Jr and Moran JV: The impact of
L1 retrotransposons on the human genome. Nat Genet. 19:19–24. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang S, Lu Z, Unruh AK, Ivan C, Baggerly
KA, Calin GA, Li Z, Bast RC Jr and Le XF: Clinically relevant
microRNAs in ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 13:393–401. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zucman-Rossi J, Villanueva A, Nault JC and
Llovet JM: Genetic landscape and biomarkers of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 149:1226–1239.e4. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang H, Liang L, Fang JY and Xu J: Somatic
gene copy number alterations in colorectal cancer: New quest for
cancer drivers and biomarkers. Oncogene. 35:2011–2019. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Choi W, Ochoa A, McConkey DJ, Aine M,
Höglund M, Kim WY, Real FX, Kiltie AE, Milsom I, Dyrskjøt L and
Lerner SP: Genetic alterations in the molecular subtypes of bladder
cancer: Illustration in the cancer genome atlas dataset. Eur Urol.
72:354–365. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Berger AC, Korkut A, Kanchi RS, Hegde AM,
Lenoir W, Liu W, Liu Y, Fan H, Shen H, Ravikumar V, et al: A
comprehensive pan-cancer molecular study of gynecologic and breast
cancers. Cancer Cell. 33:690–705.e9. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kleinjan DA and van Heyningen V:
Long-range control of gene expression: Emerging mechanisms and
disruption in disease. Am J Hum Genet. 76:8–32. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Girirajan S, Campbell CD and Eichler EE:
Human copy number variation and complex genetic disease. Annu Rev
Genet. 45:203–226. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Meyerson M, Gabriel S and Getz G: Advances
in understanding cancer genomes through second-generation
sequencing. Nat Rev Genet. 11:685–696. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Alkan C, Coe BP and Eichler EE: Genome
structural variation discovery and genotyping. Nat Rev Genet.
12:363–376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mamanova L, Coffey AJ, Scott CE, Kozarewa
I, Turner EH, Kumar A, Howard E, Shendure J and Turner DJ:
Target-enrichment strategies for next-generation sequencing. Nat
Methods. 7:111–118. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ari Å and Arikan M: Next-generation
sequencing: Advantages, disadvantages, and future. In: Plant omics:
Trends and applications. Springer; Berlin: pp. 109–135. 2016
|
|
34
|
Ogawa A, Celikkol-Aydin S, Gaylarde C,
Baptista-Neto JA and Beech I: Microbiomes of biofilms on decorative
siliceous stone: Drawbacks and advantages of next generation
sequencing. Curr Microbiol. 74:848–853. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Berná L, Rodriguez M, Chiribao ML,
Parodi-Talice A, Pita S, Rijo G, Alvarez-Valin F and Robello C:
Expanding an expanded genome: Long-read sequencing of Trypanosoma
cruzi. Microb Genom. 4:e0001772018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lin DC, Hao JJ, Nagata Y, Xu L, Shang L,
Meng X, Sato Y, Okuno Y, Varela AM, Ding LW, et al: Genomic and
molecular characterization of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Nat Genet. 46:467–473. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shi ZZ, Shang L, Jiang YY, Hao JJ, Zhang
Y, Zhang TT, Lin DC, Liu SG, Wang BS, Gong T, et al: Consistent and
differential genetic aberrations between esophageal dysplasia and
squamous cell carcinoma detected by array comparative genomic
hybridization. Clin Cancer Res. 19:5867–5878. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Qin HD, Liao XY, Chen YB, Huang SY, Xue
WQ, Li FF, Ge XS, Liu DQ, Cai Q, Long J, et al: Genomic
characterization of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma reveals
critical genes underlying tumorigenesis and poor prognosis. Am J
Hum Genet. 98:709–727. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lin DC, Wang MR and Koeffler HP: Genomic
and epigenomic aberrations in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
and implications for patients. Gastroenterology. 154:374–389. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang R, Dai Q, Yang R, Duan Y, Zhao Q,
Haybaeck J and Yang Z: A review: PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
and its regulated eukaryotic translation initiation factors may be
a potential therapeutic target in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Front Oncol. 12:8179162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zang W, Wang T, Wang Y, Chen X, Du Y, Sun
Q, Li M, Dong Z and Zhao G: Knockdown of long non-coding RNA
TP73-AS1 inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:19960–19974.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu J, Liu ZX, Wu QN, Lu YX, Wong CW, Miao
L, Wang Y, Wang Z, Jin Y, He MM, et al: Long noncoding RNA AGPG
regulates PFKFB3-mediated tumor glycolytic reprogramming. Nat
Commun. 11:15072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu X, Zhang M, Ying S, Zhang C, Lin R,
Zheng J, Zhang G, Tian D, Guo Y, Du C, et al: Genetic alterations
in esophageal tissues from squamous dysplasia to carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 153:166–177. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ma S, Paiboonrungruan C, Yan T, Williams
KP, Major MB and Chen XL: Targeted therapy of esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma: The NRF2 signaling pathway as target. Ann N Y Acad
Sci. 1434:164–172. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shen H, Yang Y, Xia S, Rao B, Zhang J and
Wang J: Blockage of Nrf2 suppresses the migration and invasion of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells in hypoxic
microenvironment. Dis Esophagus. 27:685–692. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kawasaki Y, Okumura H, Uchikado Y, Kita Y,
Sasaki K, Owaki T, Ishigami S and Natsugoe S: Nrf2 is useful for
predicting the effect of chemoradiation therapy on esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 21:2347–2352. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shibata T, Kokubu A, Saito S,
Narisawa-Saito M, Sasaki H, Aoyagi K, Yoshimatsu Y, Tachimori Y,
Kushima R, Kiyono T and Yamamoto M: NRF2 mutation confers malignant
potential and resistance to chemoradiation therapy in advanced
esophageal squamous cancer. Neoplasia. 13:864–873. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bollong MJ, Yun H, Sherwood L, Woods AK,
Lairson LL and Schultz PG: A small molecule inhibits deregulated
NRF2 transcriptional activity in cancer. ACS Chem Biol.
10:2193–2198. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Singh A, Venkannagari S, Oh KH, Zhang YQ,
Rohde JM, Liu L, Nimmagadda S, Sudini K, Brimacombe KR, Gajghate S,
et al: Small molecule inhibitor of NRF2 selectively intervenes
therapeutic resistance in KEAP1-deficient NSCLC tumors. ACS Chem
Biol. 11:3214–3225. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li Y, Zhu CL, Nie CJ, Li JC, Zeng TT, Zhou
J, Chen J, Chen K, Fu L, Liu H, et al: Investigation of tumor
suppressing function of CACNA2D3 in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e600272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nie C, Qin X, Li X, Tian B, Zhao Y, Jin Y,
Li Y, Wang Q, Zeng D, Hong A and Chen X: CACNA2D3 enhances the
chemosensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to cisplatin
via inducing Ca2+-mediated apoptosis and suppressing
PI3K/Akt pathways. Front Oncol. 9:1852019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li L, Xu J, Qiu G, Ying J, Du Z, Xiang T,
Wong KY, Srivastava G, Zhu XF, Mok TS, et al: Epigenomic
characterization of a p53-regulated 3p22.2 tumor suppressor that
inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation via protein docking and is
frequently methylated in esophageal and other carcinomas.
Theranostics. 8:61–77. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li Y, Chen L, Nie CJ, Zeng TT, Liu H, Mao
X, Qin Y, Zhu YH, Fu L and Guan XY: Downregulation of RBMS3 is
associated with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 71:6106–6115. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tang H, Jiang L, Zhu C, Liu R, Wu Y, Yan
Q, Liu M, Jia Y, Chen J, Qin Y, et al: Loss of cell adhesion
molecule L1 like promotes tumor growth and metastasis in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 38:3119–3133. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sugita M, Tanaka N, Davidson S, Sekiya S,
Varella-Garcia M, West J, Drabkin HA and Gemmill RM: Molecular
definition of a small amplification domain within 3q26 in tumors of
cervix, ovary, and lung. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 117:9–18. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yang YL, Chu JY, Luo ML, Wu YP, Zhang Y,
Feng YB, Shi ZZ, Xu X, Han YL, Cai Y, et al: Amplification of
PRKCI, located in 3q26, is associated with lymph node metastasis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
47:127–136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wu Y, Liu X, Hu L, Tao H, Guan X, Zhang K,
Bai Y and Yang K: Copy number loss of variation_91720 in PIK3CA
predicts risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:14479–14485. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wang P, Shan L, Xue L, Zheng B and Lu N:
Genome wide copy number analyses of superficial esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma with and without metastasis. Oncotarget.
8:5069–5080. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li B, Cheung PY, Wang X, Tsao SW, Ling MT,
Wong YC and Cheung AL: Id-1 activation of PI3K/Akt/NFkappaB
signaling pathway and its significance in promoting survival of
esophageal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 28:2313–2320. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Gen Y, Yasui K, Zen Y, Zen K, Dohi O, Endo
M, Tsuji K, Wakabayashi N, Itoh Y, Naito Y, et al: SOX2 identified
as a target gene for the amplification at 3q26 that is frequently
detected in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Genet
Cytogenet. 202:82–93. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Gen Y, Yasui K, Nishikawa T and Yoshikawa
T: SOX2 promotes tumor growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
through the AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 signaling
pathway. Cancer Sci. 104:810–816. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang X, Ge X, Wang H, Huang J, Song Q, Xu
C, Jiang Z, Su J, Wang H, Tan L, et al: SOX2 amplification and
chromosome 3 gain significantly impact prognosis in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Transl Med. 9:3212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Gao H, Teng C, Huang W, Peng J and Wang C:
SOX2 promotes the epithelial to mesenchymal transition of
esophageal squamous cells by modulating slug expression through the
activation of STAT3/HIF-α Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 16:21643–21657.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Chen B, Liu S, Gan L, Wang J, Hu B, Xu H,
Tong R, Yang H, Cristina I, Xue J, et al: FGFR1 signaling
potentiates tumor growth and predicts poor prognosis in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma patients. Cancer Biol Ther. 19:76–86. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Guagnano V, Kauffmann A, Wöhrle S, Stamm
C, Ito M, Barys L, Pornon A, Yao Y, Li F, Zhang Y, et al: FGFR
genetic alterations predict for sensitivity to NVP-BGJ398, a
selective pan-FGFR inhibitor. Cancer Discov. 2:1118–1133. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
von Loga K, Kohlhaussen J, Burkhardt L,
Simon R, Steurer S, Burdak-Rothkamm S, Jacobsen F, Sauter G and
Krech T: FGFR1 amplification is often homogeneous and strongly
linked to the squamous cell carcinoma subtype in esophageal
carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01418672015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Luo H, Quan J, Xiao H, Luo J, Zhang Q, Pi
G, Ye Y, He R, Liu Y, Su X, et al: FGFR inhibitor AZD4547 can
enhance sensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells
with epithelial-mesenchymal transition to gefitinib. Oncol Rep.
39:2270–2278. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Huang J, Jiang D, Zhu T, Wang Y, Wang H,
Wang Q, Tan L, Zhu H, Yao J and Hou Y: Prognostic significance of
c-MYC amplification in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann
Thorac Surg. 107:436–443. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhang HF, Wu C, Alshareef A, Gupta N, Zhao
Q, Xu XE, Jiao JW, Li EM, Xu LY and Lai R: The PI3K/AKT/c-MYC axis
promotes the acquisition of cancer stem-like features in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Stem Cells. 34:2040–2051. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Li W, Zhang L, Guo B, Deng J, Wu S, Li F,
Wang Y, Lu J and Zhou Y: Exosomal FMR1-AS1 facilitates maintaining
cancer stem-like cell dynamic equilibrium via TLR7/NFκB/c-Myc
signaling in female esophageal carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 18:222019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wang Y, Cheng J, Xie D, Ding X, Hou H,
Chen X, Er P, Zhang F, Zhao L, Yuan Z, et al: NS1-binding protein
radiosensitizes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by
transcriptionally suppressing c-Myc. Cancer Commun (Lond).
38:332018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yang J, Kong P, Yang J, Jia Z, Hu X, Wang
Z, Cui H, Bi Y, Qian Y, Li H, et al: High TSTA3 expression as a
candidate biomarker for poor prognosis of patients with ESCC.
Technol Cancer Res Treat. 17:5330338187814052018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Zhang L, Gao Y, Zhang X, Guo M, Yang J,
Cui H, Kong P, Niu X, Bi Y, Xu J, et al: TSTA3 facilitates
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through regulating
fucosylation of LAMP2 and ERBB2. Theranostics. 10:11339–11358.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Lin X, Yan C, Gao Y, Du J, Zhu X, Yu F,
Huang T, Dai J, Ma H, Jiang Y, et al: Genetic variants at 9p21.3
are associated with risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in a
Chinese population. Cancer Sci. 108:250–255. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Shen TY, Mei LL, Qiu YT and Shi ZZ:
Identification of candidate target genes of genomic aberrations in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 12:2956–2961. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Wang Q, Bai J, Abliz A, Liu Y, Gong K, Li
J, Shi W, Pan Y, Liu F, Lai S, et al: An old story retold: Loss of
G1 control defines a distinct genomic subtype of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics.
13:258–270. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Su D, Zhang D, Jin J, Ying L, Han M, Chen
K, Li B, Wu J, Xie Z, Zhang F, et al: Identification of predictors
of drug sensitivity using patient-derived models of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Commun. 10:50762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Clark ES, Brown B, Whigham AS,
Kochaishvili A, Yarbrough WG and Weaver AM: Aggressiveness of HNSCC
tumors depends on expression levels of cortactin, a gene in the
11q13 amplicon. Oncogene. 28:431–444. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Kwek SS, Roy R, Zhou H, Climent J,
Martinez-Climent JA, Fridlyand J and Albertson DG: Co-amplified
genes at 8p12 and 11q13 in breast tumors cooperate with two major
pathways in oncogenesis. Oncogene. 28:1892–1903. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Huang J, Song Q, Wang H, Wang H, Xu C,
Wang X, Jiang Z, Wang Y, Xu Y, Su J, et al: Poor prognostic impact
of FGF4 amplification in patients with esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 80:210–218. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Yu Y, Cao J, Wu W, Zhu Q, Tang Y, Zhu C,
Dai J, Li Z, Wang J, Xue L, et al: Genome-wide copy number
variation analysis identified ANO1 as a novel oncogene and
prognostic biomarker in esophageal squamous cell cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 40:1198–1208. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Shang L, Hao JJ, Zhao XK, He JZ, Shi ZZ,
Liu HJ, Wu LF, Jiang YY, Shi F, Yang H, et al: ANO1 protein as a
potential biomarker for esophageal cancer prognosis and
precancerous lesion development prediction. Oncotarget.
7:24374–24382. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhang W, Hong R, Li L, Wang Y, Du P, Ou Y,
Zhao Z, Liu X, Xiao W, Dong D, et al: The chromosome 11q13.3
amplification associated lymph node metastasis is driven by
miR-548k through modulating tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer.
17:1252018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Dong G, Mao Q, Yu D, Zhang Y, Qiu M, Dong
G, Chen Q, Xia W, Wang J, Xu L and Jiang F: Integrative analysis of
copy number and transcriptional expression profiles in esophageal
cancer to identify a novel driver gene for therapy. Sci Rep.
7:420602017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Sawada R, Maehara R, Oshikiri T, Nakamura
T, Itoh T, Kodama Y, Kakeji Y and Zen Y: MDM2 copy number increase:
A poor prognostic, molecular event in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 89:1–9. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Xiao FK, Guo S, Yang F, Zhao LS and Wang
LD: MDM2 and its functional polymorphism SNP309 contribute to the
development of esophageal carcinoma. J Gene Med. 21:e30862019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
He T, Guo J, Song H, Zhu H, Di X, Min H,
Wang Y, Chen G, Dai W, Ma J, et al: Nutlin-3, an antagonist of
MDM2, enhances the radiosensitivity of esophageal squamous cancer
with wild-type p53. Pathol Oncol Res. 24:75–81. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Okamoto H, Fujishima F, Kamei T, Nakamura
Y, Ozawa Y, Miyata G, Nakano T, Katsura K, Abe S, Taniyama Y, et
al: Murine double minute 2 predicts response of advanced esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma to definitive chemoradiotherapy. BMC
Cancer. 15:2082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Sun Y, Shi N, Lu H, Zhang J, Ma Y, Qiao Y,
Mao Y, Jia K, Han L, Liu F, et al: ABCC4 copy number variation is
associated with susceptibility to esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 35:1941–1950. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Yasui K, Imoto I, Fukuda Y, Pimkhaokham A,
Yang ZQ, Naruto T, Shimada Y, Nakamura Y and Inazawa J:
Identification of target genes within an amplicon at 14q12-q13 in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
32:112–118. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Sano M, Aoyagi K, Takahashi H, Kawamura T,
Mabuchi T, Igaki H, Tachimori Y, Kato H, Ochiai A, Honda H, et al:
Forkhead box A1 transcriptional pathway in KRT7-expressing
esophageal squamous cell carcinomas with extensive lymph node
metastasis. Int J Oncol. 36:321–330. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Xu Y, Wang W, Li L, Liu J, Wu X, Yu J,
Wang H, Cui W and Zhang R: FOXA1 and CK7 expression in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma and its prognostic significance. Neoplasma.
65:469–476. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Bi Y, Guo S, Xu X, Kong P, Cui H, Yan T,
Ma Y, Cheng Y, Chen Y, Liu X, et al: Decreased ZNF750 promotes
angiogenesis in a paracrine manner via activating
DANCR/miR-4707-3p/FOXC2 axis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Cell Death Dis. 11:2962020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Kong P, Xu E, Bi Y, Xu X, Liu X, Song B,
Zhang L, Cheng C, Yan T, Qian Y, et al: Novel ESCC-related gene
ZNF750 as potential prognostic biomarker and inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through directly depressing SNAI1
promoter in ESCC. Theranostics. 10:1798–1813. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Du Plessis L, Dietzsch E, Van Gele M, Van
Roy N, Van Helden P, Parker MI, Mugwanya DK, De Groot M, Marx MP,
Kotze MJ and Speleman F: Mapping of novel regions of DNA gain and
loss by comparative genomic hybridization in esophageal carcinoma
in the black and colored populations of South Africa. Cancer Res.
59:1877–1883. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Gorringe KL, Ramakrishna M, Williams LH,
Sridhar A, Boyle SE, Bearfoot JL, Li J, Anglesio MS and Campbell
IG: Are there any more ovarian tumor suppressor genes? A new
perspective using ultra high-resolution copy number and loss of
heterozygosity analysis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 48:931–942.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Girard L, Zöchbauer-Müller S, Virmani AK,
Gazdar AF and Minna JD: Genome-wide allelotyping of lung cancer
identifies new regions of allelic loss, differences between small
cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer, and loci
clustering. Cancer Res. 60:4894–4906. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Zhu YH, Fu L, Chen L, Qin YR, Liu H, Xie
F, Zeng T, Dong SS, Li J, Li Y, et al: Downregulation of the novel
tumor suppressor DIRAS1 predicts poor prognosis in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 73:2298–2309. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Qin H, Li Y, Zhang H, Wang F, He H, Bai X
and Li S: Prognostic implications and oncogenic roles of MYBL2
protein expression in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. Onco
Targets Ther. 12:1917–1927. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Chong CR and Jänne PA: The quest to
overcome resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in cancer. Nat Med.
19:1389–1400. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Ciardiello F and Tortora G: EGFR
antagonists in cancer treatment. N Engl J Med. 358:1160–1174. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Ruhstaller T, Thuss-Patience P, Hayoz S,
Schacher S, Knorrenschild JR, Schnider A, Plasswilm L, Budach W,
Eisterer W, Hawle H, et al: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by
chemoradiation and surgery with and without cetuximab in patients
with resectable esophageal cancer: A randomized, open-label, phase
III trial (SAKK 75/08). Ann Oncol. 29:1386–1393. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Han X, Lu N, Pan Y and Xu J: Nimotuzumab
combined with chemotherapy is a promising treatment for locally
advanced and metastatic esophageal cancer. Med Sci Monit.
23:412–418. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J and
Claesson-Welsh L: VEGF receptor signalling-in control of vascular
function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:359–371. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Li J and Wang L: Efficacy and safety of
apatinib treatment for advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Onco Targets Ther. 10:3965–3969. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Zhang B, Qi L, Wang X, Xu J, Liu Y, Mu L,
Wang X, Bai L and Huang J: Phase II clinical trial using
camrelizumab combined with apatinib and chemotherapy as the
first-line treatment of advanced esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Commun (Lond). 40:711–720. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Xu M, Huang H, Xiong Y, Peng B, Zhou Z,
Wang D and Yang X: Combined chemotherapy plus endostar with
sequential stereotactic radiotherapy as salvage treatment for
recurrent esophageal cancer with severe dyspnea: A case report and
review of the literature. Oncol Lett. 8:291–294. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Waks AG and Winer EP: Breast cancer
treatment: A review. JAMA. 321:288–300. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Hecht JR, Bang YJ, Qin SK, Chung HC, Xu
JM, Park JO, Jeziorski K, Shparyk Y, Hoff PM, Sobrero A, et al:
Lapatinib in combination with capecitabine plus oxaliplatin in
human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive advanced or
metastatic gastric, esophageal, or gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma:
TRIO-013/LOGiC-a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol.
34:443–451. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Hirata H, Niida A, Kakiuchi N, Uchi R,
Sugimachi K, Masuda T, Saito T, Kageyama SI, Motomura Y, Ito S, et
al: The evolving genomic landscape of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma under chemoradiotherapy. Cancer Res. 81:4926–4938. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Batista PJ and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell.
152:1298–1307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Flynn RA and Chang HY: Long noncoding RNAs
in cell-fate programming and reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell.
14:752–761. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Sugimura K, Miyata H, Tanaka K, Hamano R,
Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y, Yamasaki M, Nakajima K, Takiguchi S, Mori
M and Doki Y: Let-7 expression is a significant determinant of
response to chemotherapy through the regulation of IL-6/STAT3
pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
18:5144–5153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Huang L, Wang Y, Chen J, Wang Y, Zhao Y,
Wang Y, Ma Y, Chen X, Liu W, Li Z, et al: Long noncoding RNA PCAT1,
a novel serum-based biomarker, enhances cell growth by sponging
miR-326 in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis.
10:5132019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Hu L, Wu Y, Tan D, Meng H, Wang K, Bai Y
and Yang K: Up-regulation of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 contributes
to proliferation and metastasis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:72015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Li Z, Zhou Y, Tu B, Bu Y, Liu A and Kong
J: Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 affects the efficacy of radiotherapy
for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating Cks1
expression. J Oral Pathol Med. 46:583–590. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Azizi E, Carr AJ, Plitas G, Cornish AE,
Konopacki C, Prabhakaran S, Nainys J, Wu K, Kiseliovas V, Setty M,
et al: Single-cell map of diverse immune phenotypes in the breast
tumor microenvironment. Cell. 174:1293–1308.e36. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Gao S, Yan L, Wang R, Li J, Yong J, Zhou
X, Wei Y, Wu X, Wang X, Fan X, et al: Tracing the temporal-spatial
transcriptome landscapes of the human fetal digestive tract using
single-cell RNA-sequencing. Nat Cell Biol. 20:721–734. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Xiao Z, Dai Z and Locasale JW: Metabolic
landscape of the tumor microenvironment at single cell resolution.
Nat Commun. 10:37632019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Zong C, Lu S, Chapman AR and Xie XS:
Genome-wide detection of single-nucleotide and copy-number
variations of a single human cell. Science. 338:1622–1626. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Vitak SA, Torkenczy KA, Rosenkrantz JL,
Fields AJ, Christiansen L, Wong MH, Carbone L, Steemers FJ and Adey
A: Sequencing thousands of single-cell genomes with combinatorial
indexing. Nat Methods. 14:302–308. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Chen Z, Zhao M, Liang J, Hu Z, Huang Y, Li
M, Pang Y, Lu T, Sui Q, Zhan C, et al: Dissecting the single-cell
transcriptome network underlying esophagus non-malignant tissues
and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. EBioMedicine.
69:1034592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|