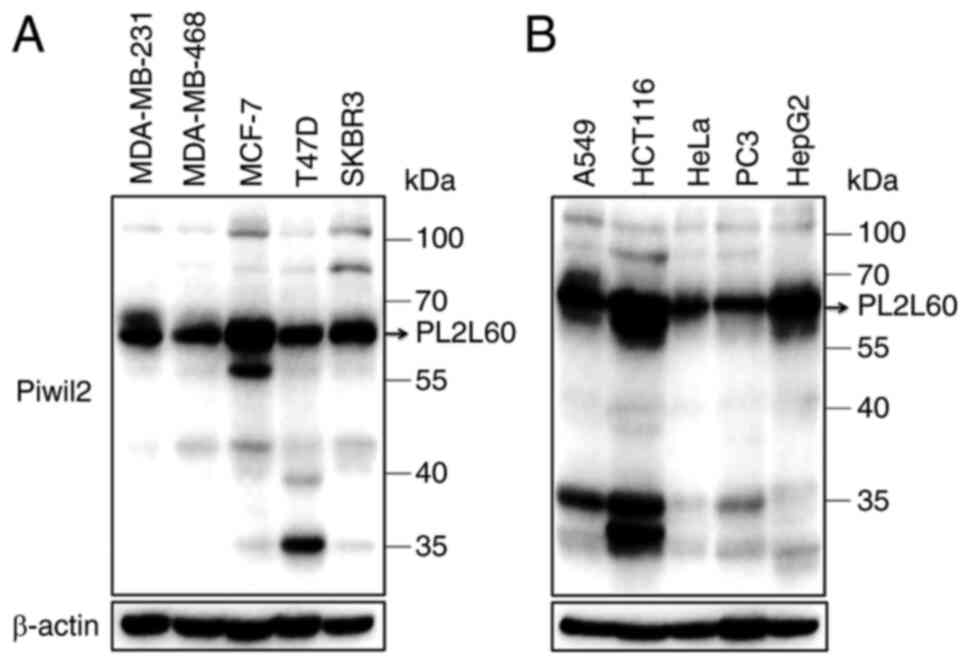
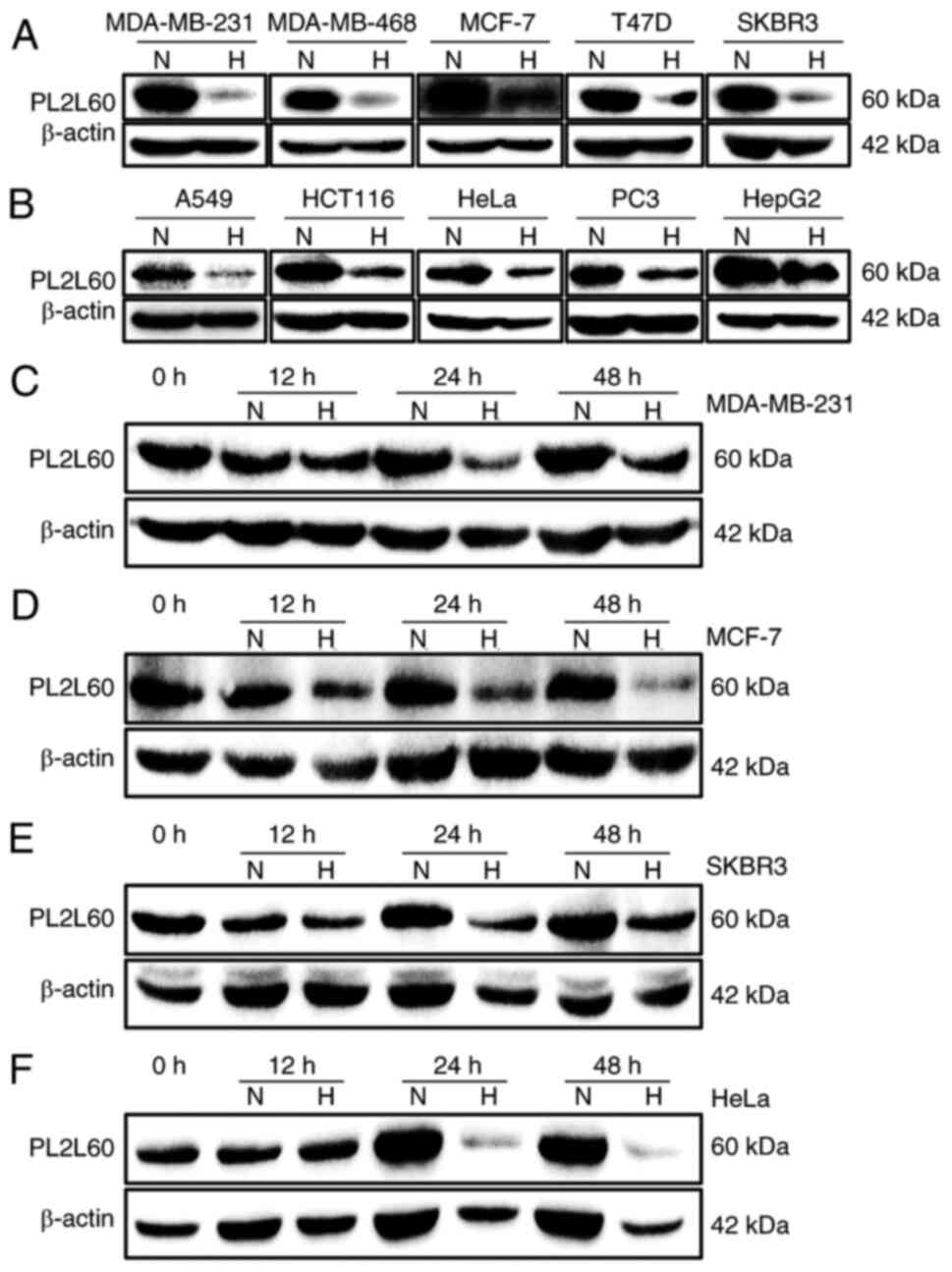
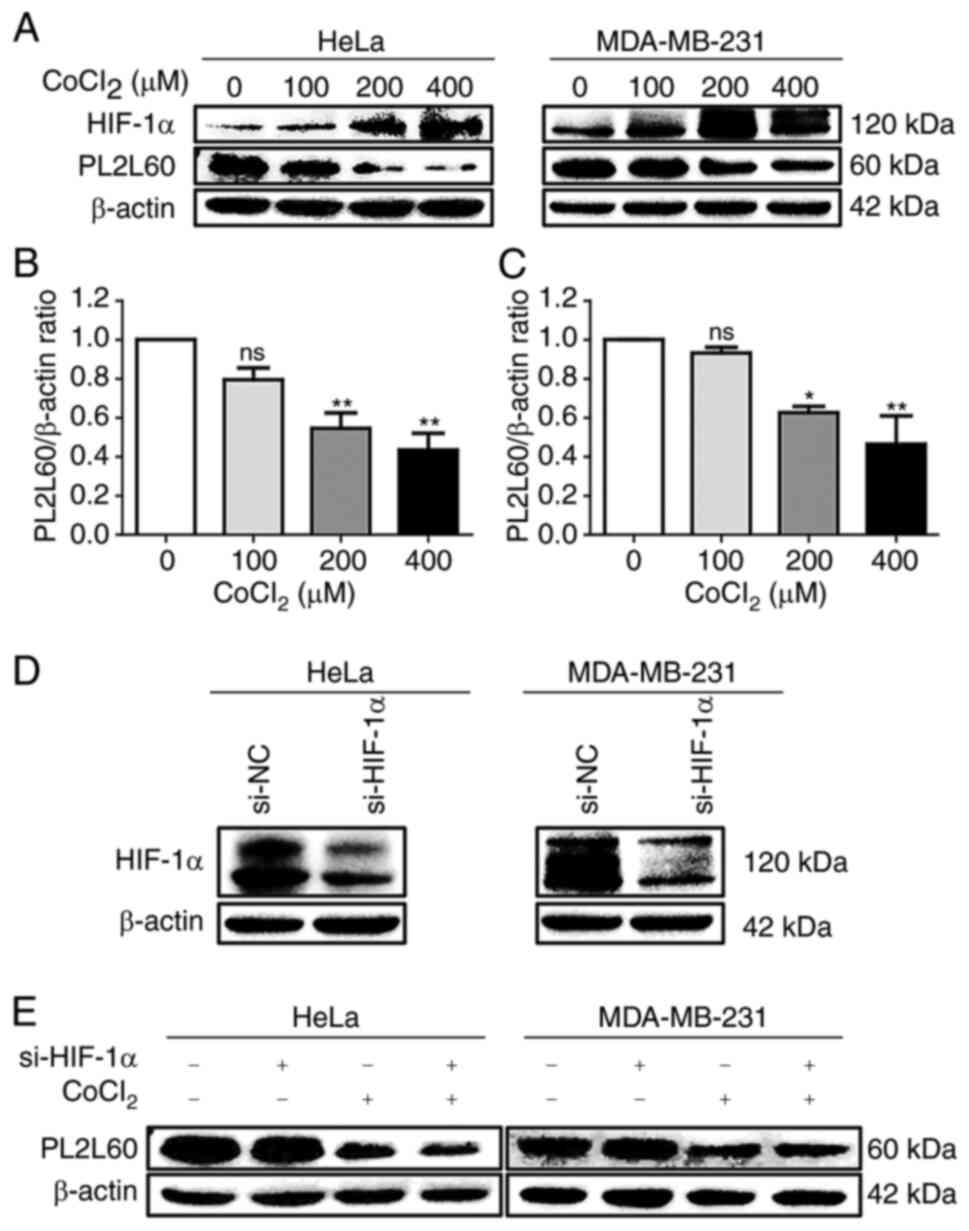
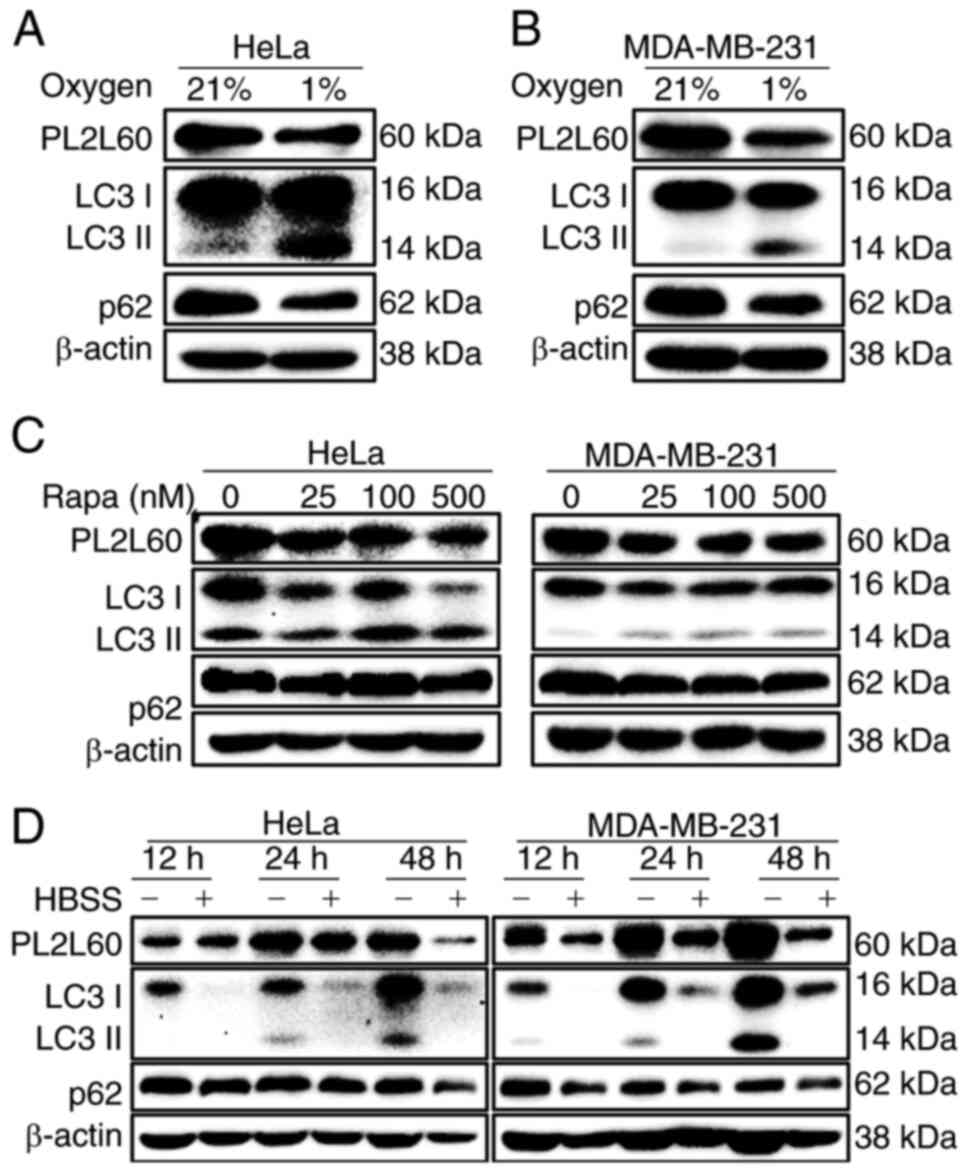
|
1
|
Chen L, Shen R, Ye Y, Pu XA, Liu X, Duan
W, Wen J, Zimmerer J, Wang Y, Liu Y, et al: Precancerous stem cells
have the potential for both benign and malignant differentiation.
PLoS One. 2:e2932007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ye Y, Yin DT, Chen L, Zhou Q, Shen R, He
G, Yan Q, Tong Z, Issekutz AC, Shapiro CL, et al: Identification of
Piwil2-like (PL2L) proteins that promote tumorigenesis. PLoS One.
5:e134062010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gainetdinov IV, Skvortsova YV, Stukacheva
EA, Bychenko OS, Kondratieva SA, Zinovieva MV and Azhikina TL:
Expression profiles of PIWIL2 short isoforms differ in testicular
germ cell tumors of various differentiation subtypes. PLoS One.
9:e1125282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu SS, Liu N, Liu MY, Sun L, Xia WY, Lu
HM, Fu YJ, Yang GL, Bo JJ, Liu XX, et al: An unusual intragenic
promoter of PIWIL2 contributes to aberrant activation of oncogenic
PL2L60. Oncotarget. 8:46104–46120. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li LF, Liu N, Liu MY and Gao JX: The
Functions of Piwil2 and Its Prospects in Tumorigenesis. Am J Transl
Med. 1:75–98. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gao JX, Liu N and Wu HL: PIWIL2 (piwi-like
RNA-mediated gene silencing 2). Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol
Haematol. 18:919–927. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Czech B and Hannon GJ: Small RNA sorting:
Matchmaking for Argonautes. Nat Rev Genet. 12:19–31. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang Z, Chen KM, Pandey RR, Homolka D,
Reuter M, Janeiro BK, Sachidanandam R, Fauvarque MO, McCarthy AA
and Pillai RS: PIWI slicing and EXD1 drive biogenesis of nuclear
piRNAs from cytosolic targets of the mouse piRNA pathway. Mol Cell.
61:138–152. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vourekas A and Mourelatos Z: HITS-CLIP
(CLIP-Seq) for mouse Piwi proteins. Methods Mol Biol. 1093:73–95.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vourekas A, Alexiou P, Vrettos N,
Maragkakis M and Mourelatos Z: Sequence-dependent but not
sequence-specific piRNA adhesion traps mRNAs to the germ plasm.
Nature. 531:390–394. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hirakata S and Siomi MC: piRNA biogenesis
in the germline: From transcription of piRNA genomic sources to
piRNA maturation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1859:82–92. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yin DT, Wang Q, Chen L, Liu MY, Han C, Yan
Q, Shen R, He G, Duan W, Li JJ, et al: Germline stem cell gene
PIWIL2 mediates DNA repair through relaxation of chromatin. PLoS
One. 6:e271542011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim E, Goren A and Ast G: Alternative
splicing: Current perspectives. Bioessays. 30:38–47. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xin D, Hu L and Kong X: Alternative
promoters influence alternative splicing at the genomic level. PLoS
One. 3:e23772008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang X, Coulombe-Huntington J, Kang S,
Sheynkman GM, Hao T, Richardson A, Sun S, Yang F, Shen YA, Murray
RR, et al: Widespread expansion of protein interaction capabilities
by alternative splicing. Cell. 164:805–817. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thadani-Mulero M, Portella L, Sun S, Sung
M, Matov A, Vessella RL, Corey E, Nanus DM, Plymate SR and
Giannakakou P: Androgen receptor splice variants determine taxane
sensitivity in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 74:2270–2282. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vaupel P, Kelleher DK and Höckel M: Oxygen
status of malignant tumors: Pathogenesis of hypoxia and
significance for tumor therapy. Semin Oncol. 28 (2 Suppl
8):S29–S35. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ueda S, Saeki T, Osaki A, Yamane T and
Kuji I: Bevacizumab induces acute hypoxia and cancer progression in
patients with refractory breast cancer: Multimodal functional
imaging and multiplex cytokine analysis. Clin Cancer Res.
23:5769–5778. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun L, Li T, Wei Q, Zhang Y, Jia X, Wan Z
and Han L: Upregulation of BNIP3 mediated by ERK/HIF-1α pathway
induces autophagy and contributes to anoikis resistance of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Future Oncol. 10:1387–1398. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Azad MB, Chen Y, Henson ES, Cizeau J,
McMillan-Ward E, Israels SJ and Gibson SB: Hypoxia induces
autophagic cell death in apoptosis-competent cells through a
mechanism involving BNIP3. Autophagy. 4:195–204. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Luo J, Solimini NL and Elledge SJ:
Principles of cancer therapy: Oncogene and non-oncogene addiction.
Cell. 136:823–837. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Klionsky DJ and Emr SD: Autophagy as a
regulated pathway of cellular degradation. Science. 290:1717–1721.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bellot G, Garcia-Medina R, Gounon P,
Chiche J, Roux D, Pouysségur J and Mazure NM: Hypoxia-induced
autophagy is mediated through hypoxia-inducible factor induction of
BNIP3 and BNIP3L via their BH3 domains. Mol Cell Biol.
29:2570–2581. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xie Z and Klionsky DJ: Autophagosome
formation: Core machinery and adaptations. Nat Cell Biol.
9:1102–1109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsujimoto Y and Shimizu S: Another way to
die: Autophagic programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ. 12 (Suppl
2):S1528–S1534. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gewirtz DA: The four faces of autophagy:
Implications for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 74:647–651. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Song J, Guo X, Xie X, Zhao X, Li D, Deng
W, Song Y, Shen F, Wu M and Wei L: Autophagy in hypoxia protects
cancer cells against apoptosis induced by nutrient deprivation
through a Beclin1-dependent way in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell
Biochem. 112:3406–3420. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun L, Liu N, Liu SS, Xia WY, Liu MY, Li
LF and Gao JX: Beclin-1-independent autophagy mediates programmed
cancer cell death through interplays with endoplasmic reticulum
and/or mitochondria in colbat chloride-induced hypoxia. Am J Cancer
Res. 5:2626–2642. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Philip B, Ito K, Moreno-Sánchez R and
Ralph SJ: HIF expression and the role of hypoxic microenvironments
within primary tumours as protective sites driving cancer stem cell
renewal and metastatic progression. Carcinogenesis. 34:1699–1707.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Majmundar AJ, Wong WJ and Simon MC:
Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol
Cell. 40:294–309. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando
J, Ohh M, Salic A, Asara JM, Lane WS and Kaelin WG Jr: HIFalpha
targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation:
Implications for O2 sensing. Science. 292:464–468. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kristensen AR, Schandorff S, Høyer-Hansen
M, Nielsen MO, Jäättelä M, Dengjel J and Andersen JS: Ordered
organelle degradation during starvation-induced autophagy. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 7:2419–2428. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li HY, Zhang J, Sun LL, Li BH, Gao HL, Xie
T, Zhang N and Ye ZM: Celastrol induces apoptosis and autophagy via
the ROS/JNK signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells: An in
vitro and in vivo study. Cell Death Dis. 6:e16042015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A and
Kroemer G: Self-eating and self-killing: Crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:741–752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liang XH, Jackson S, Seaman M, Brown K,
Kempkes B, Hibshoosh H and Levine B: Induction of autophagy and
inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature. 402:672–676. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liang C, Feng P, Ku B, Dotan I, Canaani D,
Oh BH and Jung JU: Autophagic and tumour suppressor activity of a
novel Beclin1-binding protein UVRAG. Nat Cell Biol. 8:688–699.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Johansen T and Lamark T: Selective
autophagy mediated by autophagic adapter proteins. Autophagy.
7:279–296. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kobayashi H and Tomari Y: RISC assembly:
Coordination between small RNAs and Argonaute proteins. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1859:71–81. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Da Ros M, Lehtiniemi T, Olotu O, Fischer
D, Zhang FP, Vihinen H, Jokitalo E, Sironen A, Toppari J and Kotaja
N: FYCO1 and autophagy control the integrity of the haploid male
germ cell-specific RNP granules. Autophagy. 13:302–321. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Link S, Grund SE and Diederichs S:
Alternative splicing affects the subcellular localization of
Drosha. Nucleic acids research. 44:5330–5343. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Olive PL, Vikse C and Trotter MJ:
Measurement of oxygen diffusion distance in tumor cubes using a
fluorescent hypoxia probe. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
22:397–402. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shimizu S, Eguchi Y, Kamiike W, Itoh Y,
Hasegawa J, Yamabe K, Otsuki Y, Matsuda H and Tsujimoto Y:
Induction of apoptosis as well as necrosis by hypoxia and
predominant prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL. Cancer
Res. 56:2161–2166. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rouschop KM, van den Beucken T, Dubois L,
Niessen H, Bussink J, Savelkouls K, Keulers T, Mujcic H, Landuyt W,
Voncken JW, et al: The unfolded protein response protects human
tumor cells during hypoxia through regulation of the autophagy
genes MAP1LC3B and ATG5. J Clin Invest. 120:127–141. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mariño G, Niso-Santano M, Baehrecke EH and
Kroemer G: Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and
apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:81–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Amaravadi R, Kimmelman AC and White E:
Recent insights into the function of autophagy in cancer. Genes
Dev. 30:1913–1930. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Goodwin JM, Dowdle WE, DeJesus R, Wang Z,
Bergman P, Kobylarz M, Lindeman A, Xavier RJ, McAllister G, Nyfeler
B, et al: Autophagy-independent lysosomal targeting regulated by
ULK1/2-FIP200 and ATG9. Cell Rep. 20:2341–2356. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Le Guerroué F, Eck F, Jung J, Starzetz T,
Mittelbronn M, Kaulich M and Behrends C: Autophagosomal content
profiling reveals an LC3C-dependent piecemeal mitophagy pathway.
Mol Cell. 68:786–796.e6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wild P, Farhan H, McEwan DG, Wagner S,
Rogov VV, Brady NR, Richter B, Korac J, Waidmann O, Choudhary C, et
al: Phosphorylation of the autophagy receptor optineurin restricts
Salmonella growth. Science. 333:228–233. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Newman AC, Kemp AJ, Drabsch Y, Behrends C
and Wilkinson S: Autophagy acts through TRAF3 and RELB to regulate
gene expression via antagonism of SMAD proteins. Nat Commun.
8:15372017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Jo C, Gundemir S, Pritchard S, Jin YN,
Rahman I and Johnson GVW: Nrf2 reduces levels of phosphorylated tau
protein by inducing autophagy adaptor protein NDP52. Nat Commun.
5:34962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Peng JC, Valouev A, Liu N and Lin H: Piwi
maintains germline stem cells and oogenesis in Drosophila through
negative regulation of Polycomb group proteins. Nat Genet.
48:283–291. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Reuter M, Chuma S, Tanaka T, Franz T,
Stark A and Pillai RS: Loss of the Mili-interacting Tudor
domain-containing protein-1 activates transposons and alters the
Mili-associated small RNA profile. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 16:639–646.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Aravin AA, van der Heijden GW, Castaneda
J, Vagin VV, Hannon GJ and Bortvin A: Cytoplasmic
compartmentalization of the fetal piRNA pathway in mice. PLoS
Genet. 5:e10007642009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mathioudakis N, Palencia A, Kadlec J,
Round A, Tripsianes K, Sattler M, Pillai RS and Cusack S: The
multiple Tudor domain-containing protein TDRD1 is a molecular
scaffold for mouse Piwi proteins and piRNA biogenesis factors. RNA.
18:2056–2072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Luo M, Zhao X, Song Y, Cheng H and Zhou R:
Nuclear autophagy: An evolutionarily conserved mechanism of nuclear
degradation in the cytoplasm. Autophagy. 12:1973–1983. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Dou Z, Xu C, Donahue G, Shimi T, Pan JA,
Zhu J, Ivanov A, Capell BC, Drake AM, Shah PP, et al: Autophagy
mediates degradation of nuclear lamina. Nature. 527:105–109. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Tan KP, Ho MY, Cho HC, Yu J, Hung JT and
Yu AL: Fucosylation of LAMP-1 and LAMP-2 by FUT1 correlates with
lysosomal positioning and autophagic flux of breast cancer cells.
Cell Death Dis. 7:e23472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kirino Y, Kim N, de Planell-Saguer M,
Khandros E, Chiorean S, Klein PS, Rigoutsos I, Jongens TA and
Mourelatos Z: Arginine methylation of Piwi proteins catalysed by
dPRMT5 is required for Ago3 and Aub stability. Nat Cell Biol.
11:652–658. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Sun L, Xia WY, Zhao SH, Liu N, Liu SS, Xiu
P, Li LF, Cao XL and Gao JX: An asymmetrically dimethylarginated
nuclear 90 kDa protein (p90aDMA) induced by interleukin (IL)-2,
IL-4 or IL-6 in the tumor microenvironment is selectively degraded
by autophagy. Int J Oncol. 48:2461–2471. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Li S, Yang P, Tian E and Zhang H: Arginine
methylation modulates autophagic degradation of PGL granules in C.
elegans. Mol Cell. 52:421–433. 2013.Ritio optatur sinvelignis ut
arum que lanturerum il et, quatio. Nam et et escia audi aciis nia
idis eum hilit volor molorat. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|