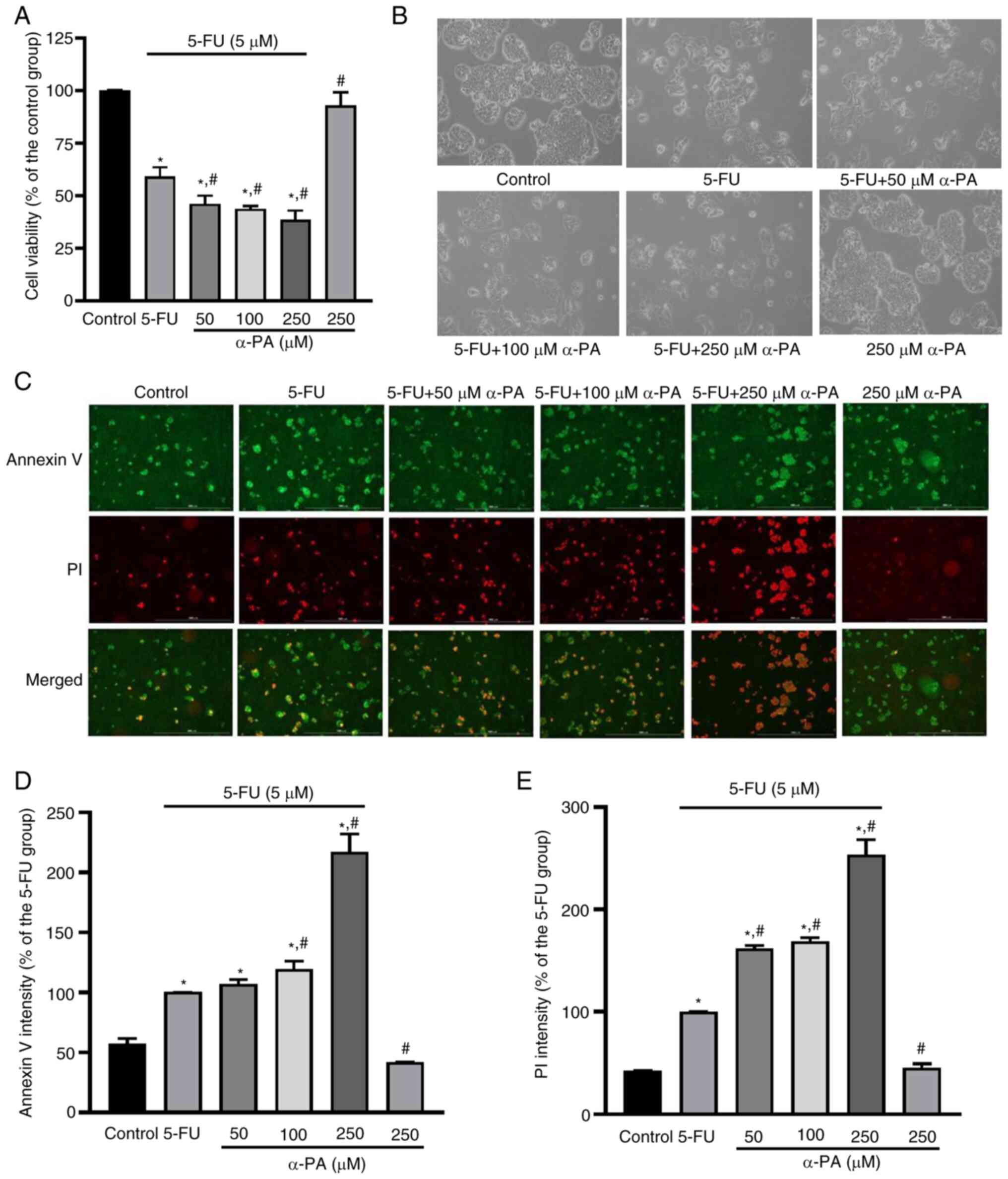
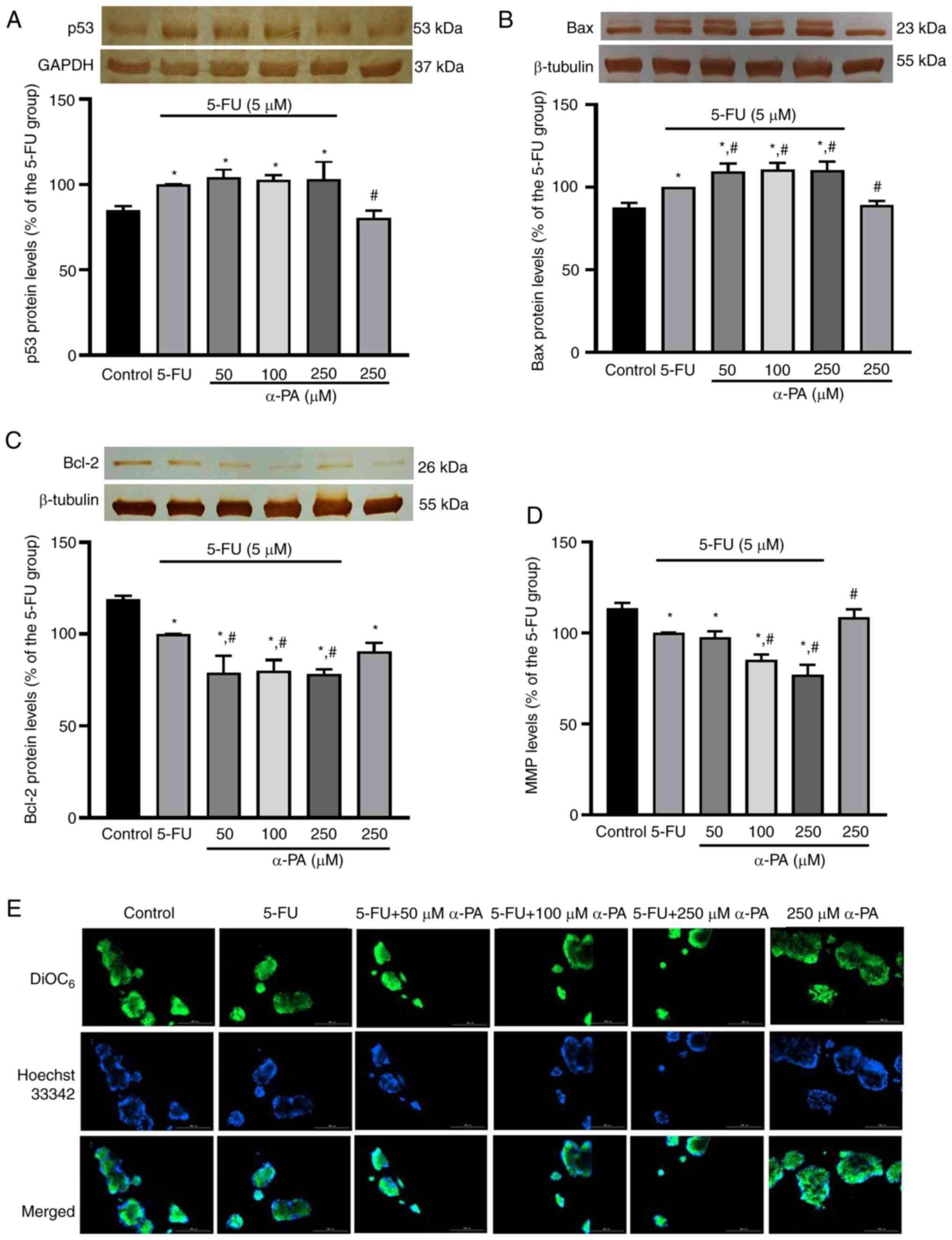
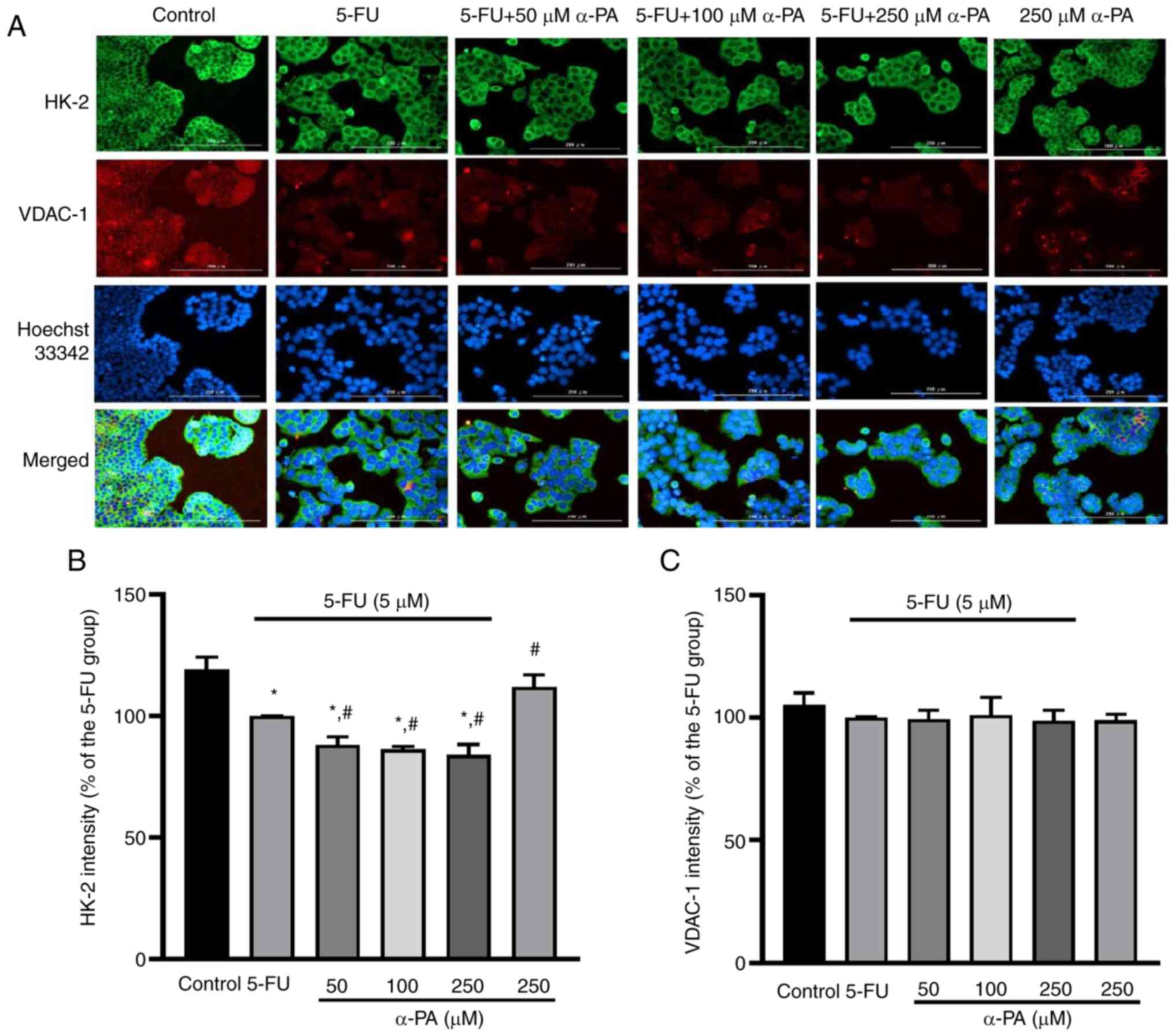
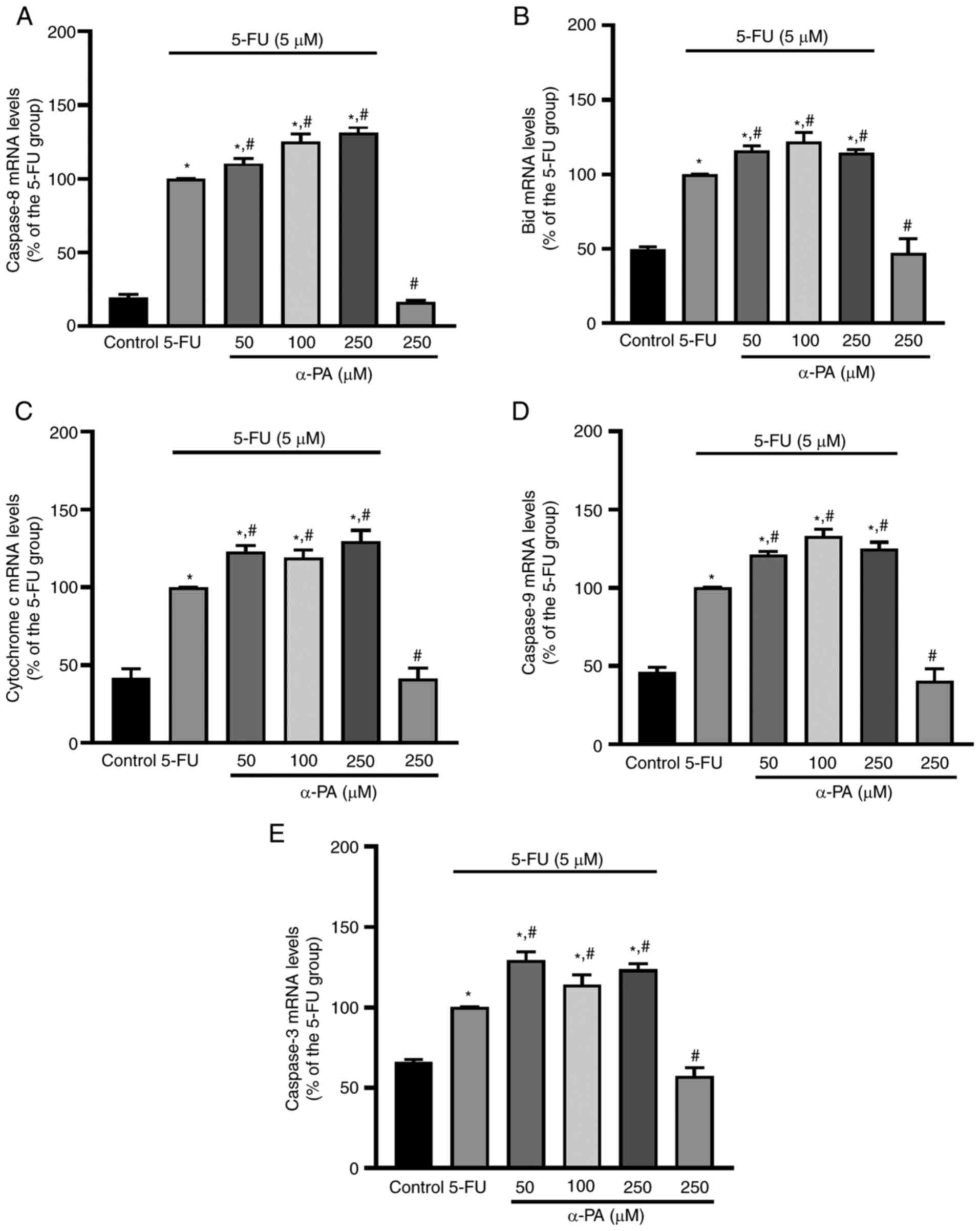
|
1
|
Asaro C, Sullivan BT, Dalusky MJ and
Berisford CW: Volatiles associated with preferred and nonpreferred
hosts of the Nantucket pine tip moth, Rhyacionia frustrana. J Chem
Ecol. 30:977–990. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Riyazi A, Hensel A, Bauer K, Geissler N,
Schaaf S and Verspohl EJ: The effect of the volatile oil from
ginger rhizomes (Zingiber officinale), its fractions and isolated
compounds on the 5-HT3 receptor complex and the serotoninergic
system of the rat ileum. Planta Med. 73:355–362. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dimov M, Petkova Z, Stoyanova M, Dobreva K
and Stoyanova A: Comparative chemical composition of dill fruits of
different origins. Bulg J Agric Sci. 26:696–700. 2020.
|
|
4
|
Prasannakumar NR, Jyothi N, Saroja S and
Lokesha AN: Insecticidal properties of Ocimum basilicum and Mentha
piperita essential oils against South American Tomato moth,
Phthorimaea absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelichiidae). Pestic
Biochem Physiol. 190:1053292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang Y, Long Y, Yu S, Li D, Yang M, Guan
Y, Zhang D, Wan J, Liu S, Shi A, et al: Natural volatile oils
derived from herbal medicines: A promising therapy way for treating
depressive disorder. Pharmacol Res. 164:1053762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Siqueira HDS, Neto BS, Sousa DP, Gomes BS,
da Silva FV, Cunha FVM, Wanderley CWS, Pinheiro G, Cândido AGF,
Wong DVT, et al: α-Phellandrene, a cyclic monoterpene, attenuates
inflammatory response through neutrophil migration inhibition and
mast cell degranulation. Life Sci. 160:27–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lin JJ, Lin JH, Hsu SC, Weng SW, Huang YP,
Tang NY, Lin JG and Chung JG: Alpha-phellandrene promotes immune
responses in normal mice through enhancing macrophage phagocytosis
and natural killer cell activities. In Vivo. 27:809–814.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hsieh LC, Hsieh SL, Chen CT, Chung JG,
Wang JJ and Wu CC: Induction of α-phellandrene on autophagy in
human liver tumor cells. Am J Chin Med. 43:121–136. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hsieh SL, Li YC, Chang WC, Chung JG, Hsieh
LC and Wu CC: Induction of necrosis in human liver tumor cells by
α-phellandrene. Nutr Cancer. 66:970–979. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin JJ, Wu CC, Hsu SC, Weng SW, Ma YS,
Huang YP, Lin JG and Chung JG: Alpha-phellandrene-induced DNA
damage and affect DNA repair protein expression in WEHI-3 murine
leukemia cells in vitro. Environ Toxicol. 30:1322–1330. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin JJ, Hsu SC, Lu KW, Ma YS, Wu CC, Lu
HF, Chen JC, Lin JG, Wu PP and Chung JG: Alpha-phellandrene-induced
apoptosis in mice leukemia WEHI-3 cells in vitro. Environ Toxicol.
31:1640–1651. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xi Y and Xu P: Global colorectal cancer
burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Transl Oncol.
14:1011742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Florescu-Ţenea RM, Kamal AM, Mitruţ P,
Mitruţ R, Ilie DS, Nicolaescu AC and Mogoantă L: Colorectal cancer:
An update on treatment options and future perspectives. Curr Health
Sci J. 45:134–141. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Longley DB, Harkin DP and Johnston PG:
5-Fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat
Rev Cance. 3:330–338. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Alzahrani SM, Al Doghaither HA, Al-Ghafari
AB and Pushparaj PN: 5-Fluorouracil and capecitabine therapies for
the treatment of colorectal cancer (review). Oncol Rep. 50:1752023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Debatin KM: Apoptosis pathways in cancer
and cancer therapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 53:153–159. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tsujimoto Y: Role of Bcl-2 family proteins
in apoptosis: Apoptosomes or mitochondria? Genes Cells. 3:697–707.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shoshan-Barmatz V, De S and Meir A: The
mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel 1, Ca2+
transport, apoptosis, and their regulation. Front Oncol. 7:602017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li J and Yuan J: Caspases in apoptosis and
beyond. Oncogene. 20:6194–6206. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Blondy S, David V, Verdier M, Mathonnet M,
Perraud A and Christou N: 5-Fluorouracil resistance mechanisms in
colorectal cancer: From classical pathways to promising processes.
Cancer Sci. 111:3142–3154. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mhaidat NM, Bouklihacene M and Thorne RF:
5-Fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells is
caspase-9-dependent and mediated by activation of protein kinase
C-δ. Oncol Lett. 8:699–704. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cordier PY, Nau A, Ciccolini J, Oliver M,
Mercier C, Lacarelle B and Peytel E: 5-FU-induced neurotoxicity in
cancer patients with profound DPD deficiency syndrome: A report of
two cases. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 68:823–826. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Baydar M, Dikilitas M, Sevinc A and
Aydogdu I: Prevention of oral mucositis due to 5-fluorouracil
treatment with oral cryotherapy. J Natl Med Assoc. 97:1161–1164.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
VanderVeen BN, Sougiannis AT, Velazquez
KT, Carson JA, Fan D and Murphy EA: The acute effects of 5
fluorouracil on skeletal muscle resident and infiltrating immune
cells in mice. Front Physiol. 11:5934682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nicolatou-Galitis O, Sarri T, Bowen J, Di
Palma M, Kouloulias VE, Niscola P, Riesenbeck D, Stokman M, Tissing
W, Yeoh E, et al: Systematic review of anti-inflammatory agents for
the management of oral mucositis in cancer patients. Support Care
Cancer. 21:3179–3189. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wong RSY: Role of nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in cancer prevention and cancer
promotion. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2019:34189752019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nautiyal J, Kanwar SS, Yu Y and Majumdar
AP: Combination of dasatinib and curcumin eliminates
chemo-resistant colon cancer cells. J Mol Signal. 6:72011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Denizot F and Lang R: Rapid colorimetric
assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the
tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and
reliability. J Immunol Methods. 89:271–277. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chou TC and Talalay P: Quantitative
analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of
multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 22:27–55.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rieger AM, Nelson KL, Konowalchuk JD and
Barreda DR: Modified annexin V/propidium iodide apoptosis assay for
accurate assessment of cell death. J Vis Exp. 50:e25972011.
|
|
31
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol
Chem. 193:265–275. 1951. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Towbin H, Staehelin T and Gordon J:
Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to
nitrocellulose sheets: Procedure and some applications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 76:4350–4354. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sakamuru S, Attene-Ramos MS and Xia M:
Mitochondrial membrane potential assay. Methods Mol Biol.
1473:17–22. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chomczynski P and Sacchi N: Single-step
method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium
thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem.
162:156–159. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
T-Johari SAT, Hashim F, Ismail WI and Ali
AM: Combinatorial cytotoxic effects of gelam honey and
5-fluorouracil against human adenocarcinoma colon cancer HT-29
cells in vitro. Int J Cell Biol. 2019:30596872019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yusefi M, Shameli K, Jahangirian H, Teow
SY, Umakoshi H, Saleh B, Rafiee-Moghaddam R and Webster TJ: The
potential anticancer activity of 5-fluorouracil loaded in cellulose
fibers isolated from rice straw. Int J Nanomedicine. 15:5417–5432.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang H, Huang S, Wei Y, Cao S, Pi C, Feng
T, Liang J, Zhao L and Ren G: Curcumin enhances the anticancer
effect of 5-fluorouracil against gastric cancer through
down-regulation of COX-2 and NF-κB signaling pathways. J Cancer.
8:3697–3706. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li Y, Fan L, Niu Y, Mian W, Zhang F, Xie
M, Sun Y and Mei Q: An apple oligogalactan enhances the growth
inhibitory effect of 5-fluorouracil on colorectal cancer. Eur J
Pharmacol. 804:13–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
de Sousa Fideles L, de Miranda JAL,
Martins CDS, Barbosa MLL, Pimenta HB, Pimentel PVS, Teixeira CS,
Scafuri MAS, Façanha SO, Barreto JEF, et al: Role of rutin in
5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis: Prevention of
histological damage and reduction of inflammation and oxidative
stress. Molecules. 25:27862020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kong L, Wang X, Zhang K, Yuan W, Yang Q,
Fan J, Wang P and Liu Q: Gypenosides synergistically enhances the
anti-tumor effect of 5-fluorouracil on colorectal cancer in vitro
and in vivo: A role for oxidative stress-mediated DNA damage and
p53 activation. PLoS One. 10:e01378882015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Țigu AB, Toma VA, Moț AC, Jurj A, Moldovan
CS, Fischer-Fodor E, Berindan-Neagoe I and Pârvu M: The synergistic
antitumor effect of 5-fluorouracil combined with allicin against
lung and colorectal carcinoma cells. Molecules. 25:19472020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jirovetz L, Buchbauer G, Stoyanova AS,
Georgiev EV and Damianova ST: Composition, quality control, and
antimicrobial activity of the essential oil of long-time stored
dill (Anethum graveolens L.) seeds from Bulgaria. J Agric Food
Chem. 51:3854–3857. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang H and Dou QP: Targeting apoptosis
pathway with natural terpenoids: Implications for treatment of
breast and prostate cancer. Curr Drug Targets. 11:733–744. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pratheeshkumar P and Kuttan G:
Vernolide-A, a sesquiterpene lactone from Vernonia cinerea, induces
apoptosis in B16F-10 melanoma cells by modulating p53 and caspase-3
gene expressions and regulating NF-κB-mediated bcl-2 activation.
Drug Chem Toxicol. 34:261–270. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Matt S and Hofmann TG: The DNA
damage-induced cell death response: A roadmap to kill cancer cells.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:2829–2850. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Czabotar PE and Garcia-Saez AJ: Mechanisms
of BCL-2 family proteins in mitochondrial apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 24:732–748. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bonora M, Patergnani S, Ramaccini D,
Morciano G, Pedriali G, Kahsay AE, Bouhamida E, Giorgi C,
Wieckowski MR and Pinton P: Physiopathology of the permeability
transition pore: Molecular mechanisms in human pathology.
Biomolecules. 10:9982020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Boice A and Bouchier-Hayes L: Targeting
apoptotic caspases in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res.
1867:1186882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Osaki M, Tatebe S, Goto A, Hayashi H,
Oshimura M and Ito H: 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) induced apoptosis in
gastric cancer cell lines: Role of the p53 gene. Apoptosis.
2:221–226. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Thangaraj K, Balasubramanian B, Park S,
Natesan K, Liu W and Manju V: Orientin induces G0/G1 cell cycle
arrest and mitochondria mediated intrinsic apoptosis in human
colorectal carcinoma HT29 cells. Biomolecules. 9:4182019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sionov RV and Haupt Y: The cellular
response to p53: The decision between life and death. Oncogene.
18:6145–6157. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Renault TT, Teijido O, Antonsson B, Dejean
LM and Manon S: Regulation of Bax mitochondrial localization by
Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L): Keep your friends close but your enemies
closer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:64–67. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chang W, Jiang XP, Jin S, Li PP, Song SS,
Yuan PF, Wei W and Lu JT: Synergistic effects of CP-25 and
5-fluorouracil on the hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo and in vitro
through regulating activating mitochondrial pathway. J Cancer.
13:1005–1018. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Schug ZT, Gonzalvez F, Houtkooper RH, Vaz
FM and Gottlieb E: BID is cleaved by caspase-8 within a native
complex on the mitochondrial membrane. Cell Death Differ.
18:538–548. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Vaseva AV and Moll UM: The mitochondrial
p53 pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1787:414–420. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Allavena G, Cuomo F, Baumgartner G, Bele
T, Sellgren AY, Oo KS, Johnson K, Gogvadze V, Zhivotovsky B and
Kaminskyy VO: Suppressed translation as a mechanism of initiation
of CASP8 (caspase 8)-dependent apoptosis in autophagy-deficient
NSCLC cells under nutrient limitation. Autophagy. 14:252–268. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Nikoletopoulou V, Markaki M, Palikaras K
and Tavernarakis N: Crosstalk between apoptosis, necrosis and
autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:3448–3459. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Shoshan-Barmatz V, Keinan N and Zaid H:
Uncovering the role of VDAC in the regulation of cell life and
death. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 40:183–191. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Klepinin A, Ounpuu L, Mado K, Truu L,
Chekulayev V, Puurand M, Shevchuk I, Tepp K, Planken A and Kaambre
T: The complexity of mitochondrial outer membrane permeability and
VDAC regulation by associated proteins. J Bioenerg Biomembr.
50:339–354. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Tewari D, Majumdar D, Vallabhaneni S and
Bera AK: Aspirin induces cell death by directly modulating
mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC). Sci Rep.
7:451842017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Sun G: Death and survival from executioner
caspase activation. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 156:66–73. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Su J, Cheng H, Zhang D, Wang M, Xie C, Hu
Y, Chang HCW and Li Q: Synergistic effects of 5-fluorouracil and
gambogenic acid on A549 cells: Activation of cell death caused by
apoptotic and necroptotic mechanisms via the ROS-mitochondria
pathway. Biol Pharm Bull. 37:1259–1268. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Cheng ZY, Chueh FS, Peng SF, Lin CH, Kuo
CL, Huang WW, Chen PY, Way TD and Chung JG: Combinational treatment
of 5-fluorouracil and casticin induces apoptosis in mouse leukemia
WEHI-3 cells in vitro. Environ Toxicol. 35:911–921. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|