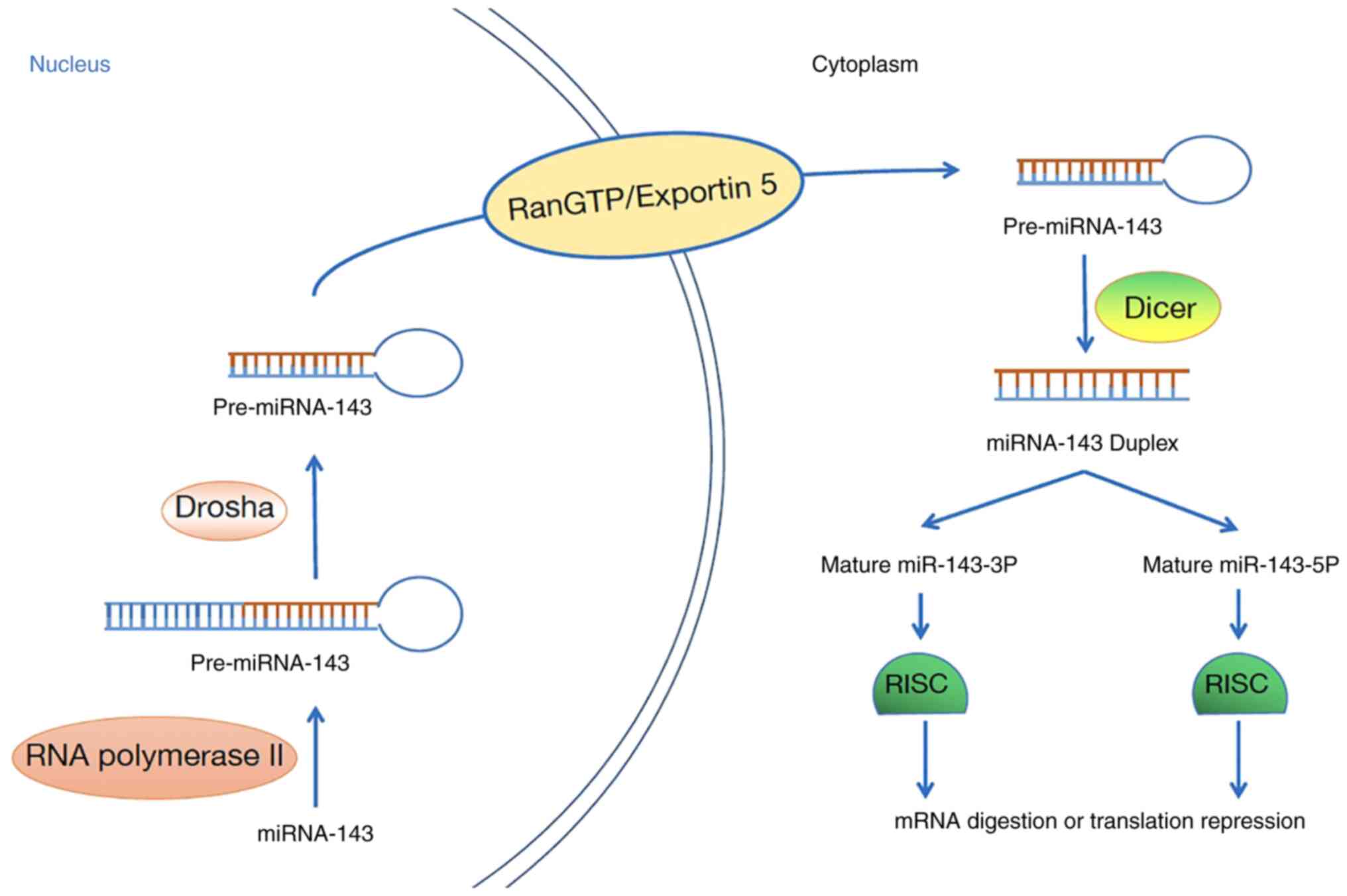
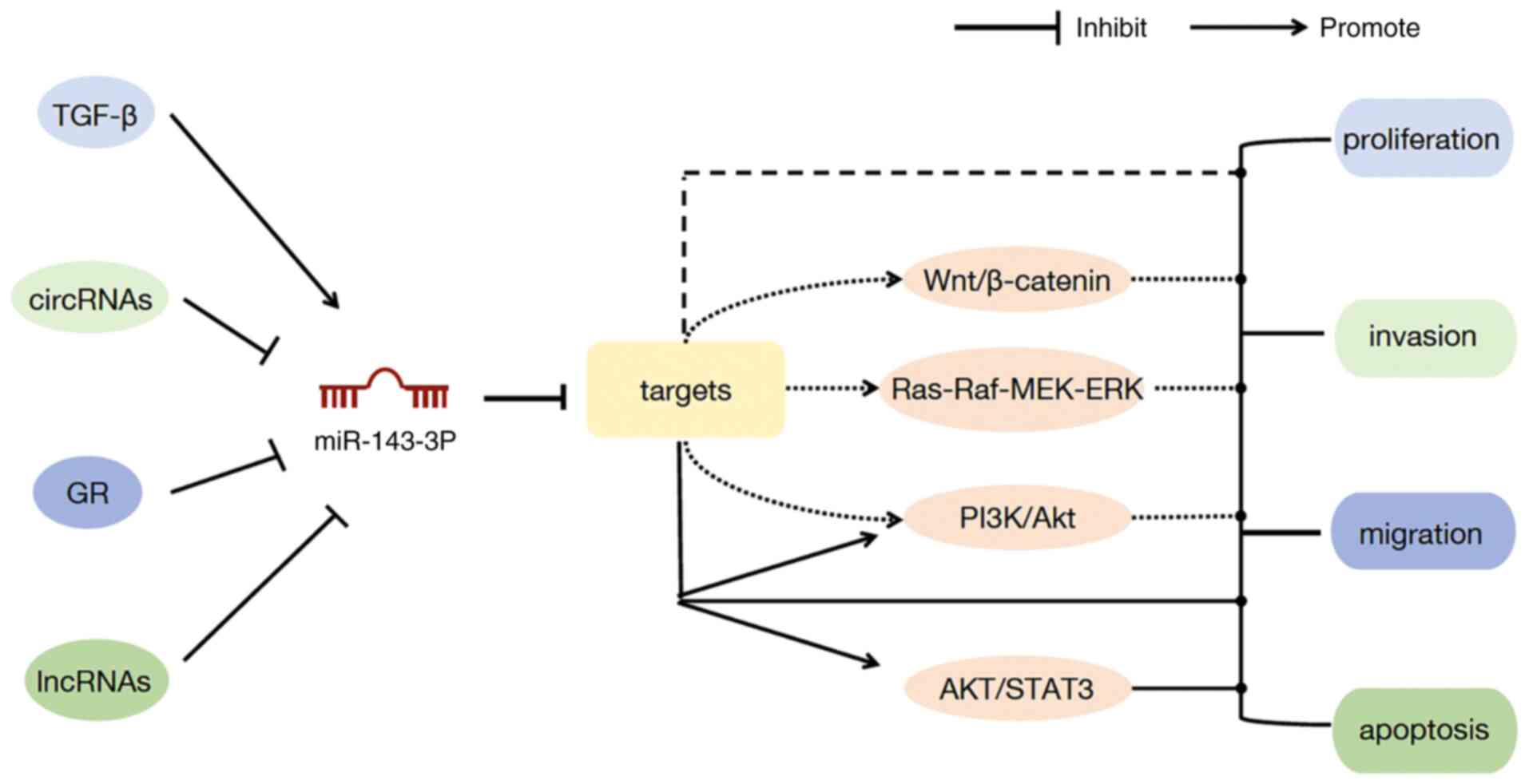
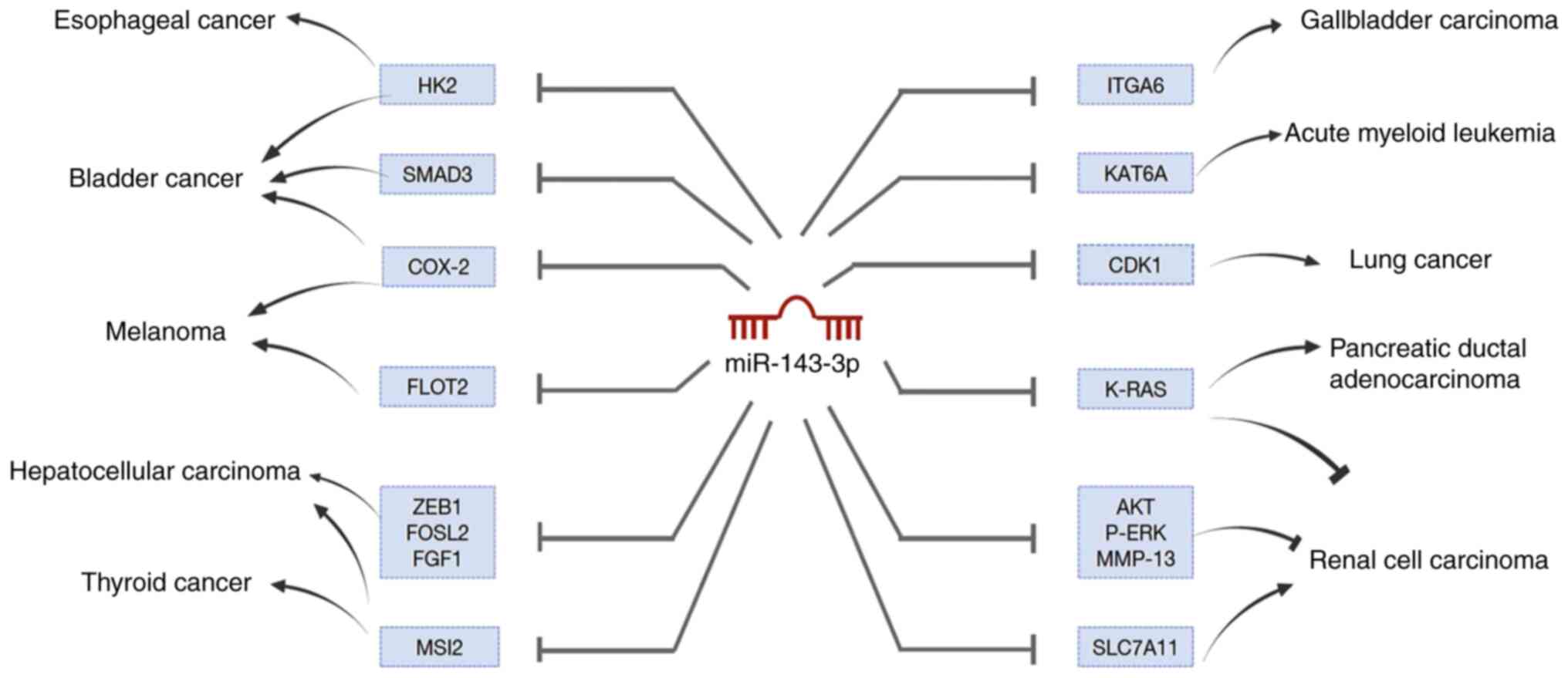
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Jemal A, Grey N, Ferlay J and
Forman D: Global cancer transitions according to the human
development index (2008–2030): A population-based study. Lancet
Oncol. 13:790–801. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Farmer P, Frenk J, Knaul FM, Shulman LN,
Alleyne G, Armstrong L, Atun R, Blayney D, Chen L, Feachem R, et
al: Expansion of cancer care and control in countries of low and
middle income: A call to action. Lancet. 376:1186–1193. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maskalenko NA, Zhigarev D and Campbell KS:
Harnessing natural killer cells for cancer immunotherapy:
Dispatching the first responders. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 21:559–577.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Punekar SR, Velcheti V, Neel BG and Wong
KK: The current state of the art and future trends in RAS-targeted
cancer therapies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 19:637–655. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Y, Zhang H, Liu C, Wang Z, Wu W,
Zhang N, Zhang L, Hu J, Luo P, Zhang J, et al: Immune checkpoint
modulators in cancer immunotherapy: Recent advances and emerging
concepts. J Hematol Oncol. 15:1112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kozomara A, Birgaoanu M and
Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function.
Nucleic Acids Res. 47(D1): D155–D162. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chang Y, Lin J and Tsung A: Manipulation
of autophagy by MIR375 generates antitumor effects in liver cancer.
Autophagy. 8:1833–1834. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNAs in
cancer: Small molecules with a huge impact. J Clin Oncol.
27:5848–5856. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao J, Chen P, Tan C, Cheng X, Zhang W,
Shen C and Zhang D: LncRNA LINC00667 gets involved in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma development and chemoresistance by regulating
the miR-143-3p/ZEB1 axis. Aging (Albany NY). 15:10057–10071. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Panza E, Ercolano G, De Cicco P, Armogida
C, Scognamiglio G, Botti G, Cirino G and Ianaro A: MicroRNA-143-3p
inhibits growth and invasiveness of melanoma cells by targeting
cyclooxygenase-2 and inversely correlates with malignant melanoma
progression. Biochem Pharmacol. 156:52–59. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou JH, Yao ZX, Zheng Z, Yang J, Wang R,
Fu SJ, Pan XF, Liu ZH and Wu K: G-MDSCs-derived exosomal
miRNA-143-3p promotes proliferation via targeting of ITM2B in lung
cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 13:9701–9719. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee Y, Jeon K, Lee JT, Kim S and Kim VN:
MicroRNA maturation: Stepwise processing and subcellular
localization. EMBO J. 21:4663–4670. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen
S, Bateman A and Enright AJ: miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets
and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 34((Database Issue)):
D140–D144. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee Y, Ahn C, Han J, Choi H, Kim J, Yim J,
Lee J, Provost P, Rådmark O, Kim S and Kim VN: The nuclear RNase
III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature. 425:415–419.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Morales-Martinez M and Vega MI: Role of
MicroRNA-7 (MiR-7) in cancer physiopathology. Int J Mol Sci.
23:90912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu XL, Cheng B, Li PY, Huang HJ, Zhao Q,
Dan ZL, Tian DA and Zhang P: MicroRNA-143 suppresses gastric cancer
cell growth and induces apoptosis by targeting COX-2. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:7758–7765. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu T, Qiu T, Han B, Wang Y, Sun X, Qin Y,
Liu A, Ge N and Jiao W: Circular RNA circCSNK1G3 induces HOXA10
signaling and promotes the growth and metastasis of lung
adenocarcinoma cells through hsa-miR-143-3p sponging. Cell Oncol
(Dordr). 44:297–310. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang X, Song Z, Meng Q, Xia S, Wang C and
Huang X: Circular RNA circ_0006089 regulates the IGF1R expression
by targeting miR-143-3p to promote gastric cancer proliferation,
migration and invasion. Cell Cycle. May 11;1–14. 2022.(Epub ahead
of print). doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2075197. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Huang CS, Tsai CH, Yu CP, Wu YS, Yee MF,
Ho JY and Yu DS: Long Noncoding RNA LINC02470 sponges
MicroRNA-143-3p and enhances SMAD3-mediated
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition to promote the aggressive
properties of bladder cancer. Cancers (Basel). 14:9682022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu XX, Bao QX, Li YM and Zhang YH: The
promotion of cervical cancer progression by signal transducer and
activator of transcription 1-induced up-regulation of lncRNA
MEOX2-AS1 as a competing endogenous RNA through miR-143-3p/VDAC1
pathway. Bioengineered. 12:3322–3335. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang ZL, Wang C, Liu W and Ai ZL:
Upregulation of microRNA-143-3p induces apoptosis and suppresses
proliferation, invasion, and migration of papillary thyroid
carcinoma cells by targeting MSI2. Exp Mol Pathol. 112:1043422020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen R, Zhang CF, Cheng YD, Wang SQ, Lin H
and Zhang H: LncRNA UCC promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition
via the miR-143-3p/SOX5 axis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lab
Invest. 101:1153–1165. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li Q, Bian Y and Li QL: Down-regulation of
TMPO-AS1 induces apoptosis in lung carcinoma cells by regulating
miR-143-3p/CDK1 axis. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
20:15330338209488802021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang Y, Li S, Cao J, Li Y, Hu H and Wu Z:
RRM2 regulated by LINC00667/miR-143-3p signal is responsible for
non-small cell lung cancer cell progression. Onco Targets Ther.
12:9927–9939. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang J, Jia Y, Wang B, Yang S, Du K, Luo
Y, Li Y and Zhu B: Circular RNA TUBA1C accelerates the progression
of non-small-cell lung cancer by sponging miR-143-3p. Cell Signal.
74:1096932020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tang X, Hua X, Peng X, Pei Y and Chen Z:
Integrated dissection of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA pairs and potential
regulatory role of lncRNA PCAT19 in lung adenocarcinoma. Front
Genet. 12:7652752022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang H, Deng Q, Lv Z, Ling Y, Hou X, Chen
Z, Dinglin X, Ma S, Li D, Wu Y, et al: N6-methyladenosine induced
miR-143-3p promotes the brain metastasis of lung cancer via
regulation of VASH1. Mol Cancer. 18:1812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Song LN, Qiao GL, Yu J, Yang CM, Chen Y,
Deng ZF, Song LH, Ma LJ and Yan HL: Hsa_circ_0003998 promotes
epithelial to mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by
sponging miR-143-3p and PCBP1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:1142020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao H, Bi M, Lou M, Yang X and Sun L:
Downregulation of SOX2-OT prevents hepatocellular carcinoma
progression through miR-143-3p/MSI2. Front Oncol. 11:6859122021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen L, Yao H, Wang K and Liu X: Long
non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates ZEB1 expression by sponging
miR-143-3p and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression. J
Cell Biochem. 118:4836–4843. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang J, Huang J, Chen W, Hu Z and Wang X:
miR-143-3p targets lncRNA PSMG3-AS1 to inhibit the proliferation of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Manag Res. 12:6303–6309.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Peng J, Wu HJ, Zhang HF, Fang SQ and Zeng
R: miR-143-3p inhibits proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells by regulating its target gene FGF1. Clin Transl
Oncol. 23:468–480. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fan H, Ge Y, Ma X, Li Z, Shi L, Lin L,
Xiao J, Chen W, Ni P, Yang L and Xu Z: Long non-coding RNA
CCDC144NL-AS1 sponges miR-143-3p and regulates MAP3K7 by acting as
a competing endogenous RNA in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis.
11:5212020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
He W, Zhang D, Li D, Zhu D, Geng Y, Wang
Q, He J and Wu J: Knockdown of long non-coding RNA LINC00200
inhibits gastric cancer progression by regulating
miR-143-3p/SERPINE1 axis. Dig Dis Sci. 66:3404–3414. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lin GR, Chen WR, Zheng PH, Chen WS and Cai
GY: Circular RNA circ_0006089 promotes the progression of gastric
cancer by regulating the miR-143-3p/PTBP3 axis and PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. J Dig Dis. 23:376–387. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xiang T, Jiang HS, Zhang BT and Liu G:
CircFOXO3 functions as a molecular sponge for miR-143-3p to promote
the progression of gastric carcinoma via upregulating USP44. Gene.
753:1447982020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim JK, Qu X, Chen CT, Smith JJ,
Sanchez-Vega F and Garcia-Aguilar J: Identifying diagnostic
MicroRNAs and investigating their biological implications in rectal
cancer. JAMA Netw Open. 4:e21369132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Moreno EC, Pascual A, Prieto-Cuadra D,
Laza VF, Molina-Cerrillo J, Ramos-Muñoz ME, Rodríguez-Serrano EM,
Soto JL, Carrato A, García-Bermejo ML and Guillén-Ponce C: Novel
molecular characterization of colorectal primary tumors based on
miRNAs. Cancers (Basel). 11:3462019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang G, Liu Z, Zhong J and Lin L:
Circ-ACAP2 facilitates the progression of colorectal cancer through
mediating miR-143-3p/FZD4 axis. Eur J Clin Invest. 51:e136072021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhao L, Li Y and Song A: Inhibition of
lncRNA TMPO-AS1 suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion of
colorectal cancer cells by targeting miR-143-3p. Mol Med Rep.
22:3245–3254. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shan TD, Tian ZB, Li Q, Jiang YP, Liu FG,
Sun XG, Han Y, Sun LJ and Chen L: Long intergenic noncoding RNA
00908 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of colorectal
cancer cells by regulating KLF5 expression. J Cell Physiol.
236:889–899. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Abd El Fattah YK, Abulsoud AI, AbdelHamid
SG, AbdelHalim S and Hamdy NM: CCDC144NL-AS1/hsa-miR-143-3p/HMGA2
interaction: In-silico and clinically implicated in CRC
progression, correlated to tumor stage and size in case-controlled
study; step toward ncRNA precision. Int J Biol Macromol.
253:1267392023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Guo L, Fu J, Sun S, Zhu M, Zhang L, Niu H,
Chen Z, Zhang Y, Guo L and Wang S: MicroRNA-143-3p inhibits
colorectal cancer metastases by targeting ITGA6 and ASAP3. Cancer
Sci. 110:805–816. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ding X, Du J, Mao K, Wang X, Ding Y and
Wang F: MicroRNA-143-3p suppresses tumorigenesis by targeting
catenin-delta1 in colorectal cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
12:3255–3265. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shu YJ, Bao RF, Jiang L, Wang Z, Wang XA,
Zhang F, Liang HB, Li HF, Ye YY, Xiang SS, et al: MicroRNA-29c-5p
suppresses gallbladder carcinoma progression by directly targeting
CPEB4 and inhibiting the MAPK pathway. Cell Death Differ.
24:445–457. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jin YP, Hu YP, Wu XS, Wu YS, Ye YY, Li HF,
Liu YC, Jiang L, Liu FT, Zhang YJ, et al: miR-143-3p targeting of
ITGA6 suppresses tumour growth and angiogenesis by downregulating
PLGF expression via the PI3K/AKT pathway in gallbladder carcinoma.
Cell Death Dis. 9:1822018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li J, Zhang H and Luo H: Long non-coding
RNA OIP5-AS1 contributes to gallbladder cancer cell invasion and
migration by miR-143-3p suppression. Cancer Manag Res.
12:12983–12992. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang B, Xu Y, Wei Y, Lv L, Liu N, Lin R,
Wang X and Shi B: Human mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal
microRNA-143 promotes apoptosis and suppresses cell growth in
pancreatic cancer via target gene regulation. Front Genet.
12:5816942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Xie F, Li C, Zhang X, Peng W and Wen T:
MiR-143-3p suppresses tumorigenesis in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma by targeting KRAS. Biomed Pharmacother.
119:1094242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sun W, Wang D, Zu Y and Deng Y: Long
noncoding RNA CASC7 is a novel regulator of glycolysis in
oesophageal cancer via a miR-143-3p-mediated HK2 signalling
pathway. Cell Death Discov. 8:2312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Dong LM, Zhang XL, Mao MH, Li YP, Zhang
XY, Xue DW and Liu YL: LINC00511/miRNA-143-3p modulates apoptosis
and malignant phenotype of bladder carcinoma cells via PCMT1. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 9:6509992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhou H, Huang J and Wang F: Increased
transcription of hsa_circ_0000644 upon RUNX family transcription
factor 3 downregulation participates in the malignant development
of bladder cancer. Cell Signal. 104:1105902023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Xiang W, Lyu L, Huang T, Zheng F, Yuan J,
Zhang C and Jiang G: The long non-coding RNA SNHG1 promotes bladder
cancer progression by interacting with miR-143-3p and EZH2. J Cell
Mol Med. 24:11858–11873. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li D, Zhong S, Zhu Z, Jiang X, Zhang J, Gu
J and Chen F: LncRNA MAFG-AS1 promotes the progression of bladder
cancer by targeting the miR-143-3p/COX-2 axis. Pathobiology.
87:345–355. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang Y, Chen L and Luo G: Long non-coding
RNA PCAT6 regulates bladder cancer progression via the
microRNA-143-3p/PDIA6 axis. Exp Ther Med. 22:9472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Huang K and Tang Y: SChLAP1 promotes
prostate cancer development through interacting with EZH2 to
mediate promoter methylation modification of multiple miRNAs of
chromosome 5 with a DNMT3a-feedback loop. Cell Death Dis.
12:1882021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Sun F, Wu K, Yao Z, Mu X, Zheng Z, Sun M,
Wang Y, Liu Z and Zhu Y: Long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes prostate
cancer metastasis by increasing NOP2 expression via targeting tumor
suppressor MicroRNAs. Onco Targets Ther. 13:6755–6765. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yang X, Wang L, Li R, Zhao Y, Gu Y, Liu S,
Cheng T, Huang K, Yuan Y, Song D and Gao S: The long non-coding RNA
PCSEAT exhibits an oncogenic property in prostate cancer and
functions as a competing endogenous RNA that associates with EZH2.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 502:262–268. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Armstrong L, Willoughby CE and McKenna DJ:
Targeting of AKT1 by miR-143-3p suppresses
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer. Cells.
12:22072023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang L, Jiang H, Zhang Y, Wang C, Xia X
and Sun Y: GR silencing impedes the progression of
castration-resistant prostate cancer through the JAG1/NOTCH2
pathway via up-regulation of microRNA-143-3p. Cancer Biomark.
28:483–497. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y,
Bedke J, Capitanio U, Dabestani S, Fernández-Pello S, Giles RH,
Hofmann F, Hora M, et al: European association of urology
guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: The 2022 update. Eur Urol.
82:399–410. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhai W, Sun Y, Guo C, Hu G, Wang M, Zheng
J, Lin W, Huang Q, Li G, Zheng J and Chang C: LncRNA-SARCC
suppresses renal cell carcinoma (RCC) progression via altering the
androgen receptor(AR)/miRNA-143-3p signals. Cell Death Differ.
24:1502–1517. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Li YZ, Zhu HC, Du Y, Zhao HC and Wang L:
Silencing lncRNA SLC16A1-AS1 induced ferroptosis in renal cell
carcinoma through miR-143-3p/SLC7A11 signaling. Technol Cancer Res
Treat. 21:153303382210778032022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Chen X, Xiong D, Yang H, Ye L, Mei S, Wu
J, Chen S, Shang X, Wang K and Huang L: Long noncoding RNA
OPA-interacting protein 5 antisense transcript 1 upregulated SMAD3
expression to contribute to metastasis of cervical cancer by
sponging miR-143-3p. J Cell Physiol. 234:5264–5275. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yang J, Jiang B, Hai J, Duan S, Dong X and
Chen C: Long noncoding RNA opa-interacting protein 5 antisense
transcript 1 promotes proliferation and invasion through elevating
integrin α6 expression by sponging miR-143-3p in cervical cancer. J
Cell Biochem. 120:907–916. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Song L, Wang L, Pan X and Yang C: lncRNA
OIP5-AS1 targets ROCK1 to promote cell proliferation and inhibit
cell apoptosis through a mechanism involving miR-143-3p in cervical
cancer. Braz J Med Biol Res. 53:e88832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Luo L, Wang M, Li X, Luo C, Tan S, Yin S,
Liu L and Zhu X: A novel mechanism by which ACTA2-AS1 promotes
cervical cancer progression: acting as a ceRNA of miR-143-3p to
regulate SMAD3 expression. Cancer Cell Int. 20:3722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Liu M, Jia J, Wang X, Liu Y, Wang C and
Fan R: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes cervical cancer
progression through regulating BCL2 via targeting miR-143-3p.
Cancer Biol Ther. 19:391–399. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Gang X, Yuan M and Zhang J: Long
non-coding RNA TMPO-AS1 promotes cervical cancer cell
proliferation, migration, and invasion by regulating
miR-143-3p/ZEB1 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 12:1587–1599. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Tang J, Pan H, Wang W, Qi C, Gu C, Shang A
and Zhu J: MiR-495-3p and miR-143-3p co-target CDK1 to inhibit the
development of cervical cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 23:2323–2334.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhang L, Zhou D, Guan W, Ren W, Sun W, Shi
J, Lin Q, Zhang J, Qiao T, Ye Y, et al: Pyridoxine 5′-phosphate
oxidase is a novel therapeutic target and regulated by the TGF-β
signalling pathway in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cell Death Dis.
8:32142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Guan W, Wang X, Lin Q, Zhang J, Ren W and
Xu G: Transforming growth factor-β/miR-143-3p/cystatin B axis is a
therapeutic target in human ovarian cancer. Int J Oncol.
55:267–276. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Shi J, Zhang L, Zhou D, Zhang J, Lin Q,
Guan W, Zhang J, Ren W and Xu G: Biological Function of ribosomal
protein L10 on cell behavior in human epithelial ovarian cancer. J
Cancer. 9:745–756. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhang H and Li W: Dysregulation of
micro-143-3p and BALBP1 contributes to the pathogenesis of the
development of ovarian carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 36:3605–3610. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Shi H, Shen H, Xu J, Zhao S, Yao S and
Jiang N: MiR-143-3p suppresses the progression of ovarian cancer.
Am J Transl Res. 10:866–874. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Tan X, Shao Y, Teng Y, Liu S, Li W, Xue L,
Cao Y, Sun C, Zhang J, Han J, et al: The cancer-testis long
non-coding RNA PCAT6 facilitates the malignant phenotype of ovarian
cancer by sponging miR-143-3p. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:5936772021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Lin Q, Guan W, Ren W, Zhang L, Zhang J and
Xu G: MALAT1 affects ovarian cancer cell behavior and patient
survival. Oncol Rep. 39:2644–2652. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Xu C, Zhai J and Fu Y: LncRNA CDKN2B-AS1
promotes the progression of ovarian cancer by miR-143-3p/SMAD3 axis
and predicts a poor prognosis. Neoplasma. 67:782–793. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Liu T, Wang X, Zhai J, Wang Q and Zhang B:
Long noncoding RNA UCA1 facilitates endometrial cancer development
by regulating KLF5 and RXFP1 gene expressions. Cancer Biother
Radiopharm. 36:521–533. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wang ZL, Wang C, Liu W and Ai ZL: Emerging
roles of the long non-coding RNA 01296/microRNA-143-3p/MSI2 axis in
development of thyroid cancer. Biosci Rep. 39:BSR201823762019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhang F and Cao H: MicroRNA-143-3p
suppresses cell growth and invasion in laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma via targeting the k-Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway.
Int J Oncol. 54:689–701. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Han L, Tang M, Xu X, Jiang B, Wei Y, Qian
H and Lu X: MiR-143-3p suppresses cell proliferation, migration,
and invasion by targeting melanoma-associated antigen A9 in
laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cell Biochem. 120:1245–1257.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Qian Y, Teng Y, Li Y, Lin X, Guan M, Li Y,
Cao X and Gao Y: MiR-143-3p suppresses the progression of nasal
squamous cell carcinoma by targeting Bcl-2 and IGF1R. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 518:492–499. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Chen J and Chen X: MYBL2 is targeted by
miR-143-3p and regulates breast cancer cell proliferation and
apoptosis. Oncol Res. 26:913–922. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Xia C, Yang Y, Kong F, Kong Q and Shan C:
MiR-143-3p inhibits the proliferation, cell migration and invasion
of human breast cancer cells by modulating the expression of MAPK7.
Biochimie. 147:98–104. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Li D, Hu J, Song H, Xu H, Wu C, Zhao B,
Xie D, Wu T, Zhao J and Fang L: miR-143-3p targeting LIM domain
kinase 1 suppresses the progression of triple-negative breast
cancer cells. Am J Transl Res. 9:2276–2285. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Cui Y, Fan Y, Zhao G, Zhang Q, Bao Y, Cui
Y, Ye Z, Chen G, Piao X, Guo F, et al: Novel lncRNA PSMG3-AS1
functions as a miR-143-3p sponge to increase the proliferation and
migration of breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 43:229–239.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Li GH, Yu JH, Yang B, Gong FC and Zhang
KW: LncRNA LOXL1-AS1 inhibited cell proliferation, migration and
invasion as well as induced apoptosis in breast cancer via
regulating miR-143-3p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:10400–10409.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhu J, Xiang XL, Cai P, Jiang YL, Zhu ZW,
Hu FL and Wang J: CircRNA-ACAP2 contributes to the invasion,
migration, and anti-apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells through
targeting the miRNA-143-3p-hexokinase 2 axis. Transl Pediatr.
10:3237–3247. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Xu D, Jiang J, He G, Zhou H and Ji C:
miR-143-3p represses leukemia cell proliferation by inhibiting
KAT6A expression. Anticancer Drugs. 33:e662–e669. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Hou Y, Feng H, Jiao J, Qian L, Sun B, Chen
P, Li Q and Liang Z: Mechanism of miR-143-3p inhibiting
proliferation, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by
targeting MAPK7. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47:2065–2071.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Sun X, Dai G, Yu L, Hu Q, Chen J and Guo
W: miR-143-3p inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion in
osteosarcoma by targeting FOSL2. Sci Rep. 8:6062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wu K, Feng Q, Li L, Xiong Y, Liu S, Liu J
and Wu Q: Long-noncoding RNA PCAT6 aggravates osteosarcoma
tumourigenesis via the MiR-143-3p/ZEB1 axis. Onco Targets Ther.
13:8705–8714. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Tian S, Han G, Lu L and Meng X: Circ-FOXM1
contributes to cell proliferation, invasion, and glycolysis and
represses apoptosis in melanoma by regulating miR-143-3p/FLOT2
axis. World J Surg Oncol. 18:562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Duan Q, Xu M, Wu M, Zhang X, Gan M and
Jiang H: Long noncoding RNA UCA1 promotes cell growth, migration,
and invasion by targeting miR-143-3p in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Med. 9:3115–3129. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Wang S, Li W, Yang L, Yuan J, Wang L, Li N
and Zhao H: CircPVT1 facilitates the progression of oral squamous
cell carcinoma by regulating miR-143-3p/SLC7A11 axis through MAPK
signaling pathway. Funct Integr Genomics. 22:891–903. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Yu L, Shao X, Huo L and Zhang T: Long
non-coding RNA (lncRNA) metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma
transcript 1 (MALAT1) promotes cell proliferation and migration by
regulating miR-143-3p and MAGE family member A9 (MAGEA9) in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Med Sci Monit. 26:e9241872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Liu J, Xiao Q, Xiao J, Niu C, Li Y, Zhang
X, Zhou Z, Shu G and Yin G: Wnt/β-catenin signalling: Function,
biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 7:32022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Abdelhamed S, Ogura K, Yokoyama S, Saiki I
and Hayakawa Y: AKT-STAT3 pathway as a downstream target of EGFR
signaling to regulate PD-L1 expression on NSCLC cells. J Cancer.
7:1579–1586. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Mei J, Zhu C, Pan L and Li M: MACC1
regulates the AKT/STAT3 signaling pathway to induce migration,
invasion, cancer stemness, and suppress apoptosis in cervical
cancer cells. Bioengineered. 13:61–70. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Zhao J and Luo Z: Discovery of raf family
is a milestone in deciphering the ras-mediated intracellular
signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 23:51582022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Baglio SR, Rooijers K, Koppers-Lalic D,
Verweij FJ, Pérez Lanzón M, Zini N, Naaijkens B, Perut F, Niessen
HW, Baldini N and Pegtel DM: Human bone marrow- and
adipose-mesenchymal stem cells secrete exosomes enriched in
distinctive miRNA and tRNA species. Stem Cell Res Ther. 6:1272015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Lin Z, Wu Y, Xu Y, Li G, Li Z and Liu T:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in cancer therapy
resistance: Recent advances and therapeutic potential. Mol Cancer.
21:1792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|