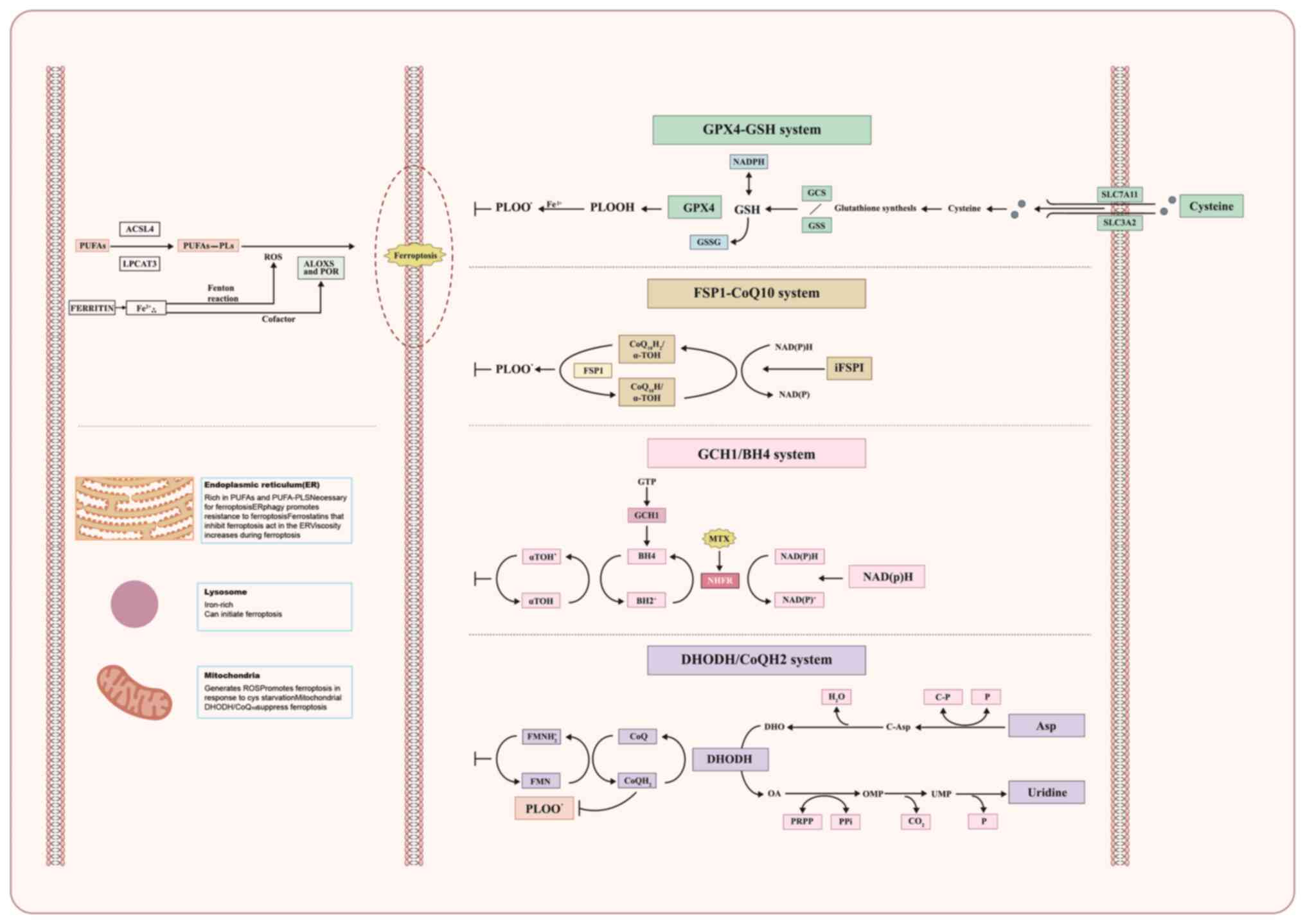
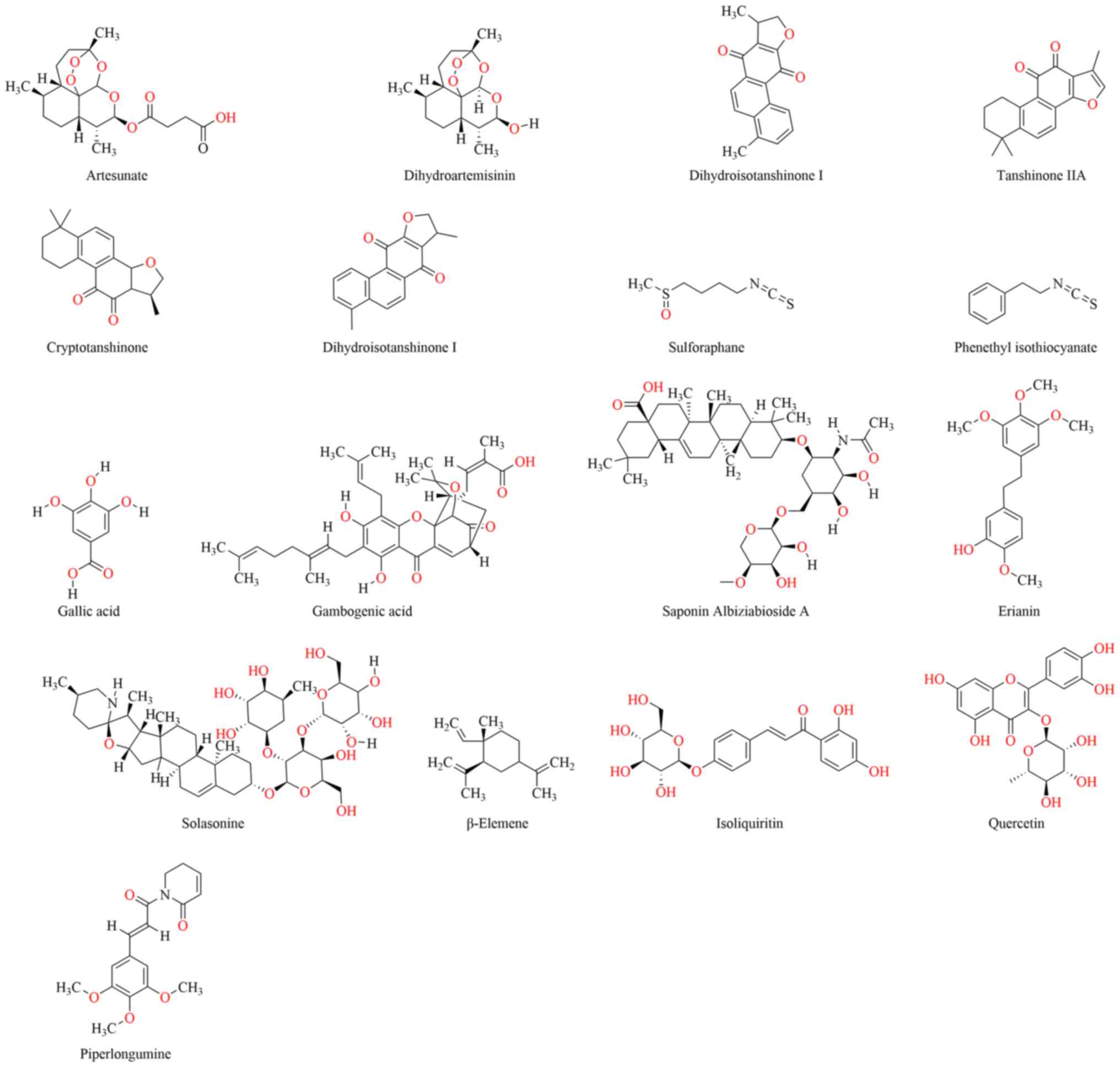
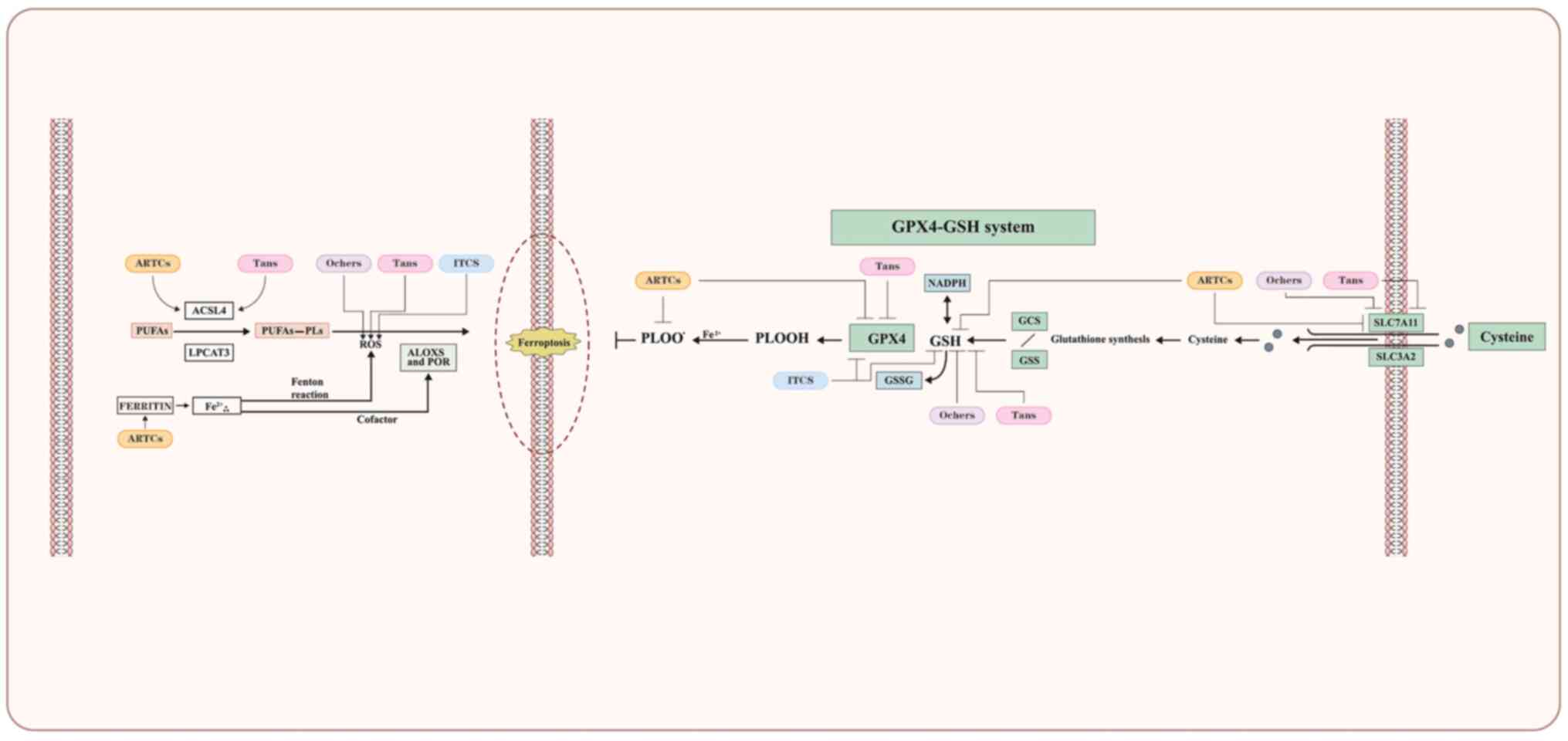
|
1
|
Ge C, Zhang S, Mu H, Zheng S, Tan Z, Huang
X, Xu C, Zou J, Zhu Y, Feng D and Aa J: Emerging mechanisms and
disease implications of ferroptosis: Potential applications of
natural products. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7749572022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stockwell BR, Jiang X and Gu W: Emerging
mechanisms and disesase relevance of ferroptosis. Trends Cell Biol.
30:478–490. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Doll S, Freitas FP, Shah R, Aldrovandi M,
da Silva MC, Ingold I, Goya Grocin A, Xavier da Silva TN, Panzilius
E, Scheel CH, et al: FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis
suppressor. Nature. 575:693–698. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ingold I, Berndt C, Schmitt S, Doll S,
Poschmann G, Buday K, Roveri A, Peng X, Porto Freitas F, Seibt T,
et al: Selenium utilization by GPX4 is required to prevent
hydroperoxide-induced ferroptosis. Cell. 172:409–422.e21. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kraft VAN, Bezjian CT, Pfeiffer S,
Ringelstetter L, Müller C, Zandkarimi F, Merl-Pham J, Bao X,
Anastasov N, Kössl J, et al: GTP cyclohydrolase
1/tetrahydrobiopterin counteract ferroptosis through lipid
remodeling. ACS Cent Sci. 6:41–53. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME,
Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, Cheah JH, Clemons PA, Shamji
AF, Clish CB, et al: Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by
GPX4. Cell. 156:317–331. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Doll S, Proneth B, Tyurina YY, Panzilius
E, Kobayashi S, Ingold I, Irmler M, Beckers J, Aichler M, Walch A,
et al: ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular
lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol. 13:91–98. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kagan VE, Mao G, Qu F, Angeli JP, Doll S,
Croix CS, Dar HH, Liu B, Tyurin VA, Ritov VB, et al: Oxidized
arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat Chem
Biol. 13:81–90. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li L, Sun S, Tan L, Wang Y, Wang L, Zhang
Z and Zhang L: Polystyrene nanoparticles reduced ROS and inhibited
ferroptosis by triggering lysosome stress and TFEB nucleus
translocation in a size-dependent manner. Nano Lett. 19:7781–7792.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Park E and Chung SW: ROS-mediated
autophagy increases intracellular iron levels and ferroptosis by
ferritin and transferrin receptor regulation. Cell Death Dis.
10:8222019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu J, Minikes AM, Gao M, Bian H, Li Y,
Stockwell BR, Chen ZN and Jiang X: Intercellular interaction
dictates cancer cell ferroptosis via NF2-YAP signalling. Nature.
572:402–406. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liang L, Liu Y, Wu X and Chen Y:
Artesunate induces ferroptosis by inhibiting the nuclear
localization of SREBP2 in myeloma cells. Int J Med Sci.
20:1535–1550. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu H, Gao L, Xie T, Li J, Zhai T and Xu
Y: Identification and validation of a prognostic signature for
prostate cancer based on ferroptosis-related genes. Front Oncol.
11:6233132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ma J, Hu X, Yao Y, Wu L, Sheng C, Chen K
and Liu B: Characterization of two ferroptosis subtypes with
distinct immune infiltration and gender difference in gastric
cancer. Front Nutr. 8:7561932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tang B, Zhu J, Li J, Fan K, Gao Y, Cheng
S, Kong C, Zheng L, Wu F, Weng Q, et al: The ferroptosis and
iron-metabolism signature robustly predicts clinical diagnosis,
prognosis and immune microenvironment for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cell Commun Signal. 18:1742020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Feng H, Schorpp K, Jin J, Yozwiak CE,
Hoffstrom BG, Decker AM, Rajbhandari P, Stokes ME, Bender HG, Csuka
JM, et al: Transferrin receptor is a specific ferroptosis marker.
Cell Rep. 30:3411–3423.e7. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hou W, Xie Y, Song X, Sun X, Lotze MT, Zeh
HJ III, Kang R and Tang D: Autophagy promotes ferroptosis by
degradation of ferritin. Autophagy. 12:1425–1428. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yanatori I and Kishi F: DMT1 and iron
transport. Free Radic Biol Med. 133:55–63. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mumbauer S, Pascual J, Kolotuev I and
Hamaratoglu F: Ferritin heavy chain protects the developing wing
from reactive oxygen species and ferroptosis. PLoS Genet.
15:e10083962019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gao M, Monian P, Pan Q, Zhang W, Xiang J
and Jiang X: Ferroptosis is an autophagic cell death process. Cell
Res. 26:1021–1032. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stockwell BR: Ferroptosis turns 10:
Emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic
applications. Cell. 185:2401–2421. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen P, Li X, Zhang R, Liu S, Xiang Y,
Zhang M, Chen X, Pan T, Yan L, Feng J, et al: Combinative treatment
of β-elemene and cetuximab is sensitive to KRAS mutant colorectal
cancer cells by inducing ferroptosis and inhibiting
epithelial-mesenchymal transformation. Theranostics. 10:5107–5119.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen GQ, Benthani FA, Wu J, Liang D, Bian
ZX and Jiang X: Artemisinin compounds sensitize cancer cells to
ferroptosis by regulating iron homeostasis. Cell Death Differ.
27:242–254. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu Y, Guo N, Yang T, Yan J, Wang W and Li
X: The potential mechanisms by which artemisinin and its
derivatives induce ferroptosis in the treatment of cancer. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2022:14581432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang WS, Kim KJ, Gaschler MM, Patel M,
Shchepinov MS and Stockwell BR: Peroxidation of polyunsaturated
fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 113:E4966–E4975. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Viswanathan VS, Ryan MJ, Dhruv HD, Gill S,
Eichhoff OM, Seashore-Ludlow B, Kaffenberger SD, Eaton JK, Shimada
K, Aguirre AJ, et al: Dependency of a therapy-resistant state of
cancer cells on a lipid peroxidase pathway. Nature. 547:453–457.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Conrad M and Pratt DA: The chemical basis
of ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol. 15:1137–1147. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang X, Stockwell BR and Conrad M:
Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 22:266–282. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sato H, Shiiya A, Kimata M, Maebara K,
Tamba M, Sakakura Y, Makino N, Sugiyama F, Yagami K, Moriguchi T,
et al: Redox imbalance in cystine/glutamate transporter-deficient
mice. J Biol Chem. 280:37423–37429. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Robert SM, Buckingham SC, Campbell SL,
Robel S, Holt KT, Ogunrinu-Babarinde T, Warren PP, White DM, Reid
MA, Eschbacher JM, et al: SLC7A11 expression is associated with
seizures and predicts poor survival in patients with malignant
glioma. Sci Transl Med. 7:289ra862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang W, Green M, Choi JE, Gijón M, Kennedy
PD, Johnson JK, Liao P, Lang X, Kryczek I, Sell A, et al:
CD8+ T cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer
immunotherapy. Nature. 569:270–274. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nie Z, Chen M, Gao Y, Huang D, Cao H, Peng
Y, Guo N, Wang F and Zhang S: Ferroptosis and tumor drug
resistance: Current status and major challenges. Front Pharmacol.
13:8793172022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kuang F, Liu J, Xie Y, Tang D and Kang R:
MGST1 is a redox-sensitive repressor of ferroptosis in pancreatic
cancer cells. Cell Chem Biol. 28:765–775.e5. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun X, Ou Z, Chen R, Niu X, Chen D, Kang R
and Tang D: Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects
against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology.
63:173–184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bersuker K, Hendricks JM, Li Z, Magtanong
L, Ford B, Tang PH, Roberts MA, Tong B, Maimone TJ, Zoncu R, et al:
The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit
ferroptosis. Nature. 575:688–692. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Stefely JA and Pagliarini DJ: Biochemistry
of mitochondrial coenzyme Q biosynthesis. Trends Biochem Sci.
42:824–843. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mao C, Liu X, Zhang Y, Lei G, Yan Y, Lee
H, Koppula P, Wu S, Zhuang L, Fang B, et al: DHODH-mediated
ferroptosis defence is a targetable vulnerability in cancer.
Nature. 593:586–590. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lei G, Zhuang L and Gan B: Targeting
ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
22:381–396. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Manogaran P, Beeraka NM, Paulraj RS,
Sathiyachandran P and Thammaiappa M: Impediment of cancer by
dietary plant-derived alkaloids through oxidative stress:
Implications of PI3K/AKT pathway in apoptosis, autophagy, and
ferroptosis. Curr Top Med Chem. 23:860–877. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Deng H, Jia Q, Ming X, Sun Y, Lu Y, Liu L
and Zhou J: Hippo pathway in intestinal diseases: Focusing on
ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 11:12916862023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu Z, Zhong M, Liu Y, Xiong Y, Gao Z, Ma
J, Zhuang G and Hong X: Application of natural products for
inducing ferroptosis in tumor cells. Biotechnol Appl Biochem.
69:190–197. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang N, Zeng GZ, Yin JL and Bian ZX:
Artesunate activates the ATF4-CHOP-CHAC1 pathway and affects
ferroptosis in Burkitt's lymphoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
519:533–539. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang K, Zhang Z, Wang M, Cao X, Qi J, Wang
D, Gong A and Zhu H: Role of GRP78 inhibiting artesunate-induced
ferroptosis in KRAS mutant pancreatic cancer cells. Drug Des Devel
Ther. 13:2135–2144. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li ZJ, Dai HQ, Huang XW, Feng J, Deng JH,
Wang ZX, Yang XM, Liu YJ, Wu Y, Chen PH, et al: Artesunate
synergizes with sorafenib to induce ferroptosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 42:301–310. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Roh JL, Kim EH, Jang H and Shin D: Nrf2
inhibition reverses the resistance of cisplatin-resistant head and
neck cancer cells to artesunate-induced ferroptosis. Redox Biol.
11:254–262. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Vakhrusheva O, Erb HHH, Bräunig V,
Markowitsch SD, Schupp P, Baer PC, Slade KS, Thomas A, Tsaur I,
Puhr M, et al: Artesunate inhibits the growth behavior of
docetaxel-resistant prostate cancer cells. Front Oncol.
12:7892842022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ye RR, Chen BC, Lu JJ, Ma XR and Li RT:
Phosphorescent rhenium(I) complexes conjugated with artesunate:
Mitochondrial targeting and apoptosis-ferroptosis dual induction. J
Inorg Biochem. 223:1115372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chen W, Xie L, Lv C, Song E, Zhu X and
Song Y: Transferrin-targeted cascade nanoplatform for inhibiting
transcription factor nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
and enhancing ferroptosis anticancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater
Interfaces. 15:28879–28890. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huang QF, Li YH, Huang ZJ, Jun M, Wang W,
Chen XL and Wang GH: Artesunate carriers induced ferroptosis to
overcome biological barriers for anti-cancer. Eur J Pharm Biopharm.
190:284–293. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Han N, Li LG, Peng XC, Ma QL, Yang ZY,
Wang XY, Li J, Li QR, Yu TT, Xu HZ, et al: Ferroptosis triggered by
dihydroartemisinin facilitates chlorin e6 induced photodynamic
therapy against lung cancerthrough inhibiting GPX4 and enhancing
ROS. Eur J Pharmacol. 919:1747972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yi R, Wang H, Deng C, Wang X, Yao L, Niu
W, Fei M and Zhaba W: Dihydroartemisinin initiates ferroptosis in
glioblastoma through GPX4 inhibition. Biosci Rep.
40:BSR201933142020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cui Z, Wang H, Li S, Qin T, Shi H, Ma J,
Li L, Yu G, Jiang T and Li C: Dihydroartemisinin enhances the
inhibitory effect of sorafenib on HepG2 cells by inducing
ferroptosis and inhibiting energy metabolism. J Pharmacol Sci.
148:73–85. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang X, Ai Z, Zhang Z, Dong R, Wang L,
Jin S and Wei H: Dihydroartemisinin triggers ferroptosis in
multidrug-resistant leukemia cells. DNA Cell Biol. 41:705–715.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Grignano E, Cantero-Aguilar L, Tuerdi Z,
Chabane T, Vazquez R, Johnson N, Zerbit J, Decroocq J, Birsen R,
Fontenay M, et al: Dihydroartemisinin-induced ferroptosis in acute
myeloid leukemia: Links to iron metabolism and metallothionein.
Cell Death Discov. 9:972023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang Y, Chen F, Zhou H, Huang L, Ye J, Liu
X, Sheng W, Gao W, Yu H and Wang F: Redox dyshomeostasis with dual
stimuli-activatable dihydroartemisinin nanoparticles to potentiate
ferroptotic therapy of pancreatic cancer. Small Methods.
7:e22008882023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Shi H, Xiong L, Yan G, Du S, Liu J and Shi
Y: Susceptibility of cervical cancer to dihydroartemisinin-induced
ferritinophagy-dependent ferroptosis. Front Mol Biosci.
10:11560622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lai X, Shi Y and Zhou M:
Dihydroartemisinin enhances gefitinib cytotoxicity against lung
adenocarcinoma cells by inducing ROS-dependent apoptosis and
ferroptosis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 39:699–709. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Antoszczak M, Müller S, Cañeque T,
Colombeau L, Dusetti N, Santofimia-Castaño P, Gaillet C, Puisieux
A, Iovanna JL and Rodriguez R: Iron-sensitive prodrugs that trigger
active ferroptosis in drug-tolerant pancreatic cancer cells. J Am
Chem Soc. 144:11536–11545. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Fan S, Yang Q, Song Q, Hong M, Liu X, Chen
H, Wang J, Li C and Cheng S: Multi-pathway inducing ferroptosis by
MnO2-based nanodrugs for targeted cancer therapy. Chem Commun
(Camb). 58:6486–6489. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lin R, Zhang Z, Chen L, Zhou Y, Zou P,
Feng C, Wang L and Liang G: Dihydroartemisinin (DHA) induces
ferroptosis and causes cell cycle arrest in head and neck carcinoma
cells. Cancer Lett. 381:165–175. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Du J, Wang T, Li Y, Zhou Y, Wang X, Yu X,
Ren X, An Y, Wu Y, Sun W, et al: DHA inhibits proliferation and
induces ferroptosis of leukemia cells through autophagy dependent
degradation of ferritin. Free Radic Biol Med. 131:356–369. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Du J, Wang X, Li Y, Ren X, Zhou Y, Hu W,
Zhou C, Jing Q, Yang C, Wang L, et al: DHA exhibits synergistic
therapeutic efficacy with cisplatin to induce ferroptosis in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via modulation of iron metabolism.
Cell Death Dis. 12:7052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yang XX, Xu X, Wang MF, Xu HZ, Peng XC,
Han N, Yu TT, Li LG, Li QR, Chen X, et al: A nanoreactor boosts
chemodynamic therapy and ferroptosis for synergistic cancer therapy
using molecular amplifier dihydroartemisinin. J Nanobiotechnology.
20:2302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Han W, Duan X, Ni K, Li Y, Chan C and Lin
W: Co-delivery of dihydroartemisinin and pyropheophorbide-iron
elicits ferroptosis to potentiate cancer immunotherapy.
Biomaterials. 280:1213152022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Lin YS, Shen YC, Wu CY, Tsai YY, Yang YH,
Lin YY, Kuan FC, Lu CN, Chang GH, Tsai MS, et al: Danshen improves
survival of patients with breast cancer and dihydroisotanshinone I
induces ferroptosis and apoptosis of breast cancer cells. Front
Pharmacol. 10:12262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Tan S, Hou X and Mei L: Dihydrotanshinone
I inhibits human glioma cell proliferation via the activation of
ferroptosis. Oncol Lett. 20:1222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Guan Z, Chen J, Li X and Dong N:
Tanshinone IIA induces ferroptosis in gastric cancer cells through
p53-mediated SLC7A11 down-regulation. Biosci Rep.
40:BSR202018072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ni H, Ruan G, Sun C, Yang X, Miao Z, Li J,
Chen Y, Qin H, Liu Y, Zheng L, et al: Tanshinone IIA inhibits
gastric cancer cell stemness through inducing ferroptosis. Environ
Toxicol. 37:192–200. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Li X, Li W, Yang P, Zhou H, Zhang W and Ma
L: Anticancer effects of cryptotanshinone against lung cancer cells
through ferroptosis. Arab J Chem. 14:1031772021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Wu CY, Yang YH, Lin YS, Chang GH, Tsai MS,
Hsu CM, Yeh RA, Shu LH, Cheng YC and Liu HT: Dihydroisotanshinone I
induced ferroptosis and apoptosis of lung cancer cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 139:1115852021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zheng K, Dong Y, Yang R, Liang Y, Wu H and
He Z: Regulation of ferroptosis by bioactive phytochemicals:
Implications for medical nutritional therapy. Pharmacol Res.
168:1055802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lv H, Zhen C, Liu J and Shang P: PEITC
triggers multiple forms of cell death by GSH-iron-ROS regulation in
K7M2 murine osteosarcoma cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 41:1119–1132.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Iida Y, Okamoto-Κatsuyama M, Maruoka S,
Mizumura K, Shimizu T, Shikano S, Hikichi M, Takahashi M, Tsuya K,
Okamoto S, et al: Effective ferroptotic small-cell lung cancer cell
death from SLC7A11 inhibition by sulforaphane. Oncol Lett.
21:712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kasukabe T, Honma Y, Okabe-Kado J, Higuchi
Y, Kato N and Kumakura S: Combined treatment with cotylenin A and
phenethyl isothiocyanate induces strong antitumor activity mainly
through the induction of ferroptotic cell death in human pancreatic
cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 36:968–976. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Qin Z, Ou S, Xu L, Sorensen K, Zhang Y, Hu
DP, Yang Z, Hu WY, Chen F and Prins GS: Design and synthesis of
isothiocyanate-containing hybrid androgen receptor (AR) antagonist
to downregulate AR and induce ferroptosis in GSH-deficient prostate
cancer cells. Chem Biol Drug Des. 97:1059–1078. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Tang HM and Cheung PCK: Gallic acid
triggers iron-dependent cell death with apoptotic, ferroptotic, and
necroptotic features. Toxins (Basel). 11:4922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Khorsandi K, Kianmehr Z, Hosseinmardi Z
and Hosseinzadeh R: Anti-cancer effect of gallic acid in presence
of low level laser irradiation: ROS production and induction of
apoptosis and ferroptosis. Cancer Cell Int. 20:182020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Yamaguchi Y, Kasukabe T and Kumakura S:
Piperlongumine rapidly induces the death of human pancreatic cancer
cells mainly through the induction of ferroptosis. Int J Oncol.
52:1011–1022. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Wei G, Sun J, Hou Z, Luan W, Wang S, Cui
S, Cheng M and Liu Y: Novel antitumor compound optimized from
natural saponin Albiziabioside A induced caspase-dependent
apoptosis and ferroptosis as a p53 activator through the
mitochondrial pathway. Eur J Med Chem. 157:759–772. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Liang X, Hu C, Han M, Yan L, Sun Y, Liu S,
Xiang Y, Zhang M, Pan T, Chen X, et al: Erianin, a novel dibenzyl
compound in Dendrobium extract, inhibits lung cancer cell
growth and migration via calcium/calmodulin-dependent ferroptosis.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:512020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Xiang Y, Chen X, Wang W, Zhai L, Sun X,
Feng J, Duan T, Zhang M, Pan T, Yan L, et al: Natural product
erianin inhibits bladder cancer cell growth by inducing ferroptosis
via NRF2 inactivation. Front Pharmacol. 12:7755062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Xu C, Jiang ZB, Shao L, Zhao ZM, Fan XX,
Sui X, Yu LL, Wang XR, Zhang RN, Wang WJ, et al: β-Elemene enhances
erlotinib sensitivity through induction of ferroptosis by
upregulating lncRNA H19 in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer.
Pharmacol Res. 191:1067392023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Wang J, Li Y, Zhang J and Luo C:
Isoliquiritin modulates ferroptosis via NF-κB signaling inhibition
and alleviates doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 45:443–454. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
An S and Hu M: Quercetin promotes TFEB
nuclear translocation and activates lysosomal degradation of
ferritin to induce ferroptosis in breast cancer cells. Comput
Intell Neurosci. 2022:52992182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Zeng YY, Luo YB, Ju XD, Wu Y, Shi H, Chen
Y, Lu G, Shen HM, Lu GD and Zhou J: Quercetin induces
p53-independent cancer cell death through lysosome activation by
the transcription factor EB and reactive oxygen species-dependent
ferroptosis. Br J Pharmacol. 178:1133–1148. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Kannan R, Kumar K, Sahal D, Kukreti S and
Chauhan VS: Reaction of artemisinin with haemoglobin: Implications
for antimalarial activity. Biochem J. 385:409–418. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Beekman A, Wierenga P, Woerdenbag H, Van
Uden W, Pras N, Konings AW, el-Feraly FS, Galal AM and Wikström HV:
Artemisinin-derived sesquiterpene lactones as potential antitumour
compounds: Cytotoxic action against bone marrow and tumour cells.
Planta Med. 64:615–619. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Zheng GQ: Cytotoxic Terpenoids and
Flavonoids from Artemisia annua. Planta Med. 60:54–57. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Zhao Y, Jiang W, Li B, Yao Q, Dong J, Cen
Y, Pan X, Li J, Zheng J, Pang X and Zhou H: Artesunate enhances
radiosensitivity of human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells via
increasing NO production to induce cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase.
Int Immunopharmacol. 11:2039–2046. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Dell'Eva R, Pfeffer U, Vené R, Anfosso L,
Forlani A, Albini A and Efferth T: Inhibition of angiogenesis in
vivo and growth of Kaposi's sarcoma xenograft tumors by the
anti-malarial artesunate. Biochem Pharmacol. 68:2359–2366. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Rasheed SAK, Efferth T, Asangani IA and
Allgayer H: First evidence that the antimalarial drug artesunate
inhibits invasion and in vivo metastasis in lung cancer by
targeting essential extracellular proteases. Int J Cancer.
127:1475–1485. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Wang B, Hou D, Liu Q, Wu T, Guo H, Zhang
X, Zou Y, Liu Z, Liu J, Wei J, et al: Artesunate sensitizes ovarian
cancer cells to cisplatin by downregulating RAD51. Cancer Biol
Ther. 16:1548–1556. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Zhou C, Pan W, Wang XP and Chen TS:
Artesunate induces apoptosis via a Bak-mediated caspase-independent
intrinsic pathway in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. J Cell
Physiol. 227:3778–3786. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Efferth T, Dunstan H, Sauerbrey A, Miyachi
H and Chitambar CR: The anti-malarial artesunate is also active
against cancer. Int J Oncol. 18:767–773. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Disbrow GL, Baege AC, Kierpiec KA, Yuan H,
Centeno JA, Thibodeaux CA, Hartmann D and Schlegel R:
Dihydroartemisinin Is cytotoxic to papillomavirus-expressing
epithelial cells in vitro and In vivo. Cancer Res. 65:10854–10861.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Kelter G, Steinbach D, Konkimalla VB,
Tahara T, Taketani S, Fiebig HH and Efferth T: Role of transferrin
receptor and the ABC transporters ABCB6 and ABCB7 for resistance
and differentiation of tumor cells towards artesunate. PLoS One.
2:e7982007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Lai H, Nakase I, Lacoste E, Singh NP and
Sasaki T: Artemisinin-transferrin conjugate retards growth of
breast tumors in the rat. Anticancer Res. 29:3807–3810.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Mercer AE, Maggs JL, Sun XM, Cohen GM,
Chadwick J, O'Neill PM and Park BK: Evidence for the involvement of
carbon-centered radicals in the induction of apoptotic cell death
by artemisinin compounds. J Biol Chem. 282:9372–9382. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Eling N, Reuter L, Hazin J, Hamacher-Brady
A and Brady NR: Identification of artesunate as a specific
activator of ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncoscience.
2:517–532. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Yan G, Dawood M, Böckers M, Klauck SM,
Fottner C, Weber MM and Efferth T: Multiple modes of cell death in
neuroendocrine tumors induced by artesunate. Phytomedicine.
79:1533322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Song Q, Peng S, Che F and Zhu X:
Artesunate induces ferroptosis via modulation of p38 and ERK
signaling pathway in glioblastoma cells. J Pharmacol Sci.
148:300–306. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Koike T, Takenaka M, Suzuki N, Ueda Y,
Mori M, Hirayama T, Nagasawa H and Morishige KI: Intracellular
ferritin heavy chain plays the key role in artesunate-induced
ferroptosis in ovarian serous carcinoma cells. J Clin Biochem Nutr.
71:34–40. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Morris CA, Duparc S, Borghini-Fuhrer I,
Jung D, Shin CS and Fleckenstein L: Review of the clinical
pharmacokinetics of artesunate and its active metabolite
dihydroartemisinin following intravenous, intramuscular, oral or
rectal administration. Malar J. 10:2632011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Valashedi MR, Nikoo A, Najafi-Ghalehlou N,
Tomita K, Kuwahara Y, Sato T, Roushandeh AM and Roudkenar MH:
Pharmacological targeting of ferroptosis in cancer treatment. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 22:108–125. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Li Y, Shi N, Zhang W, Zhang H, Song Y, Zhu
W and Feng X: Supramolecular hybrids of carbon dots and
dihydroartemisinin for enhanced anticancer activity and mechanism
analysis. J Mater Chem B. 8:9777–9784. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Shterman N, Kupfer B and Moroz C:
Comparison of transferrin receptors, iron content and isoferritin
profile in normal and malignant human breast cell lines.
Pathobiology. 59:19–25. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Torti SV and Torti FM: Iron and cancer:
More ore to be mined. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:342–355. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Cao JY and Dixon SJ: Mechanisms of
ferroptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:2195–2209. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Yang ND, Tan SH, Ng S, Shi Y, Zhou J, Tan
KS, Wong WS and Shen HM: Artesunate induces cell death in human
cancer cells via enhancing lysosomal function and lysosomal
degradation of ferritin. J Biol Chem. 289:33425–33441. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Dowdle WE, Nyfeler B, Nagel J, Elling RA,
Liu S, Triantafellow E, Menon S, Wang Z, Honda A, Pardee G, et al:
Selective VPS34 inhibitor blocks autophagy and uncovers a role for
NCOA4 in ferritin degradation and iron homeostasis in vivo. Nat
Cell Biol. 16:1069–1079. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Mancias JD, Wang X, Gygi SP, Harper JW and
Kimmelman AC: Quantitative proteomics identifies NCOA4 as the cargo
receptor mediating ferritinophagy. Nature. 509:105–109. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Abrams RP, Carroll WL and Woerpel KA:
Five-membered ring peroxide selectively initiates ferroptosis in
cancer cells. ACS Chem Biol. 11:1305–1312. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Efferth T and Oesch F: Oxidative stress
response of tumor cells: Microarray-based comparison between
artemisinins and anthracyclines. Biochem Pharmacol. 68:3–10. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Horwedel C, Tsogoeva SB, Wei S and Efferth
T: Cytotoxicity of artesunic acid homo- and heterodimer molecules
toward sensitive and multidrug-resistant CCRF-CEM leukemia cells. J
Med Chem. 53:4842–4848. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Lee YS, Lee DH, Choudry HA, Bartlett DL
and Lee YJ: Ferroptosis-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress:
Crosstalk between ferroptosis and apoptosis. Mol Cancer Res.
16:1073–1076. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Ooko E, Saeed ME, Kadioglu O, Sarvi S,
Colak M, Elmasaoudi K, Janah R, Greten HJ and Efferth T:
Artemisinin derivatives induce iron-dependent cell death
(ferroptosis) in tumor cells. Phytomedicine. 22:1045–1054. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Amable L: Cisplatin resistance and
opportunities for precision medicine. Pharmacol Res. 106:27–36.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Zhao F, Vakhrusheva O, Markowitsch SD,
Slade KS, Tsaur I, Cinatl J Jr, Michaelis M, Efferth T, Haferkamp A
and Juengel E: Artesunate impairs growth in cisplatin-resistant
bladder cancer cells by cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and autophagy
induction. Cells. 9:26432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Wong KH, Yang D, Chen S, He C and Chen M:
Development of nanoscale drug delivery systems of
dihydroartemisinin for cancer therapy: A review. Asian J Pharm Sci.
17:475–490. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Efferth T: From ancient herb to modern
drug: Artemisia annua and artemisinin for cancer therapy.
Semin Cancer Biol. 46:65–83. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Zhang C and Zhang F: Iron homeostasis and
tumorigenesis: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities.
Protein Cell. 6:88–100. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Xu M, Zha H, Han R, Cheng Y, Chen J, Yue
L, Wang R and Zheng Y: Cyclodextrin-derived ROS-generating
nanomedicine with pH-modulated degradability to enhance tumor
ferroptosis therapy and chemotherapy. Small. 18:e22003302022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Huang D, Xu D, Chen W, Wu R, Wen Y, Liu A,
Lin L, Lin X and Wang X: Fe-MnO2 nanosheets loading
dihydroartemisinin for ferroptosis and immunotherapy. Biomed
Pharmacother. 161:1144312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Li L, Yang X, Xu H, Yu TT, Li QR, Hu J,
Peng XC, Han N, Xu X, Chen NN, et al: A dihydroartemisinin-loaded
nanoreactor motivates anti-cancer immunotherapy by synergy-induced
ferroptosis to activate Cgas/STING for reprogramming of macrophage.
Adv Healthc Mater. 12:e23015612023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Liang J, Li L, Tian H, Wang Z, Liu G, Duan
X, Guo M, Liu J, Zhang W, Nice EC, et al: Drug repurposing-based
brain-targeting self-assembly nanoplatform using enhanced
ferroptosis against glioblastoma. Small. 19:e23030732023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Zhang X, Liu H, Li N, Li J, Wang M and Ren
X: A (Traditional Chinese Medicine) TCM-inspired doxorubicin
resistance reversing strategy: Preparation, characterization, and
application of a co-loaded pH-sensitive liposome. AAPS
PharmSciTech. 24:1812023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Zheng Y, Zheng J, Du M, Yang Y, Li X, Chen
H and Gao Y: An iron-containing ferritin-based nanosensitizer for
synergistic ferroptosis/sono-photodynamic cancer therapy. J Mater
Chem B. 11:4958–4971. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Jiang Z, Gao W and Huang L: Tanshinones,
critical pharmacological components in Salvia miltiorrhiza.
Front Pharmacol. 10:2022019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Pang H, Wu L, Tang Y, Zhou G, Qu C and
Duan J: Chemical analysis of the herbal medicine salviae
miltiorrhizae radix et Rhizoma (Danshen). Molecules. 21:512016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Huang X, Jin L, Deng H, Wu D, Shen QK,
Quan ZS, Zhang CH and Guo HY: Research and development of natural
product tanshinone I: Pharmacology, total synthesis, and structure
modifications. Front Pharmacol. 13:9204112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Li W, Huang T, Xu S, Che B, Yu Y, Zhang W
and Tang K: Molecular mechanism of tanshinone against prostate
cancer. Molecules. 27:55942022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Dong Y, Morris-Natschke SL and Lee KH:
Biosynthesis, total syntheses, and antitumor activity of
tanshinones and their analogs as potential therapeutic agents. Nat
Prod Rep. 28:529–542. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Fu L, Han B, Zhou Y, Ren J, Cao W, Patel
G, Kai G and Zhang J: The anticancer properties of tanshinones and
the pharmacological effects of their active ingredients. Front
Pharmacol. 11:1932020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Yang H, Gao Y, Fan X, Liu X, Peng L and Ci
X: Oridonin sensitizes cisplatin-induced apoptosis via
AMPK/Akt/mTOR-dependent autophagosome accumulation in A549 cells.
Front Oncol. 9:7692019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Yang W, Zhao J, Wang Y, Xu H, Wu Z, Hu Y,
Jiang K, Shen P, Ma C, Guan Z, et al: In vivo inhibitory activity
of andrographolide derivative ADN-9 against liver cancer and its
mechanisms involved in inhibition of tumor angiogenesis. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 327:1–12. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Yu J, Wang X, Li Y and Tang B: Tanshinone
IIA suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration by
downregulation of FOXM1. Oncol Rep. 37:1394–1400. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Zhang Y, Wei R, Zhu X, Cai L, Jin W and Hu
H: Tanshinone IIA induces apoptosis and inhibits the proliferation,
migration, and invasion of the osteosarcoma MG-63 cell line in
vitro. Anticancer Drugs. 23:212–219. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Zhou M, Zhou G, Hu S and Zhang L:
Tanshinone IIA suppress the proliferation of HNE-1 nasopharyngeal
carcinoma an in vitro study. Saudi J Biol Sci. 25:267–272. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Wu WL, Chang WL and Chen CF: Cytotoxic
activities of tanshinones against human carcinoma cell lines. Am J
Chin Med. 19:207–216. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Cao Y, Huang B and Gao C: Salvia
miltiorrhiza extract dihydrotanshinone induces apoptosis and
inhibits proliferation of glioma cells. Bosn J of Basic Med Sci.
17:235–240. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Li Q, Hu K, Tang S, Xu LF and Luo YC:
Anti-tumor activity of tanshinone IIA in combined with
cyclophosphamide against Lewis mice with lung cancer. Asian Pac J
Trop Med. 9:1084–1088. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Lv C, Zeng HW, Wang JX, Yuan X, Zhang C,
Fang T, Yang PM, Wu T, Zhou YD, Nagle DG and Zhang WD: The
antitumor natural product tanshinone IIA inhibits protein kinase C
and acts synergistically with 17-AAG. Cell Death Dis. 9:1652018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Ma K, Zhang C, Huang MY, Guo YX and Hu GQ:
Crosstalk between beclin-1-dependent autophagy and
caspase-dependent apoptosis induced by tanshinone IIA in human
osteosarcoma MG-63 cells. Oncol Rep. 36:1807–1818. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Qiu W, Sun B, He F and Zhang Y:
MTA-induced notch activation enhances the proliferation of human
dental pulp cells by inhibiting autophagic flux. Int Endod J. 50
(Suppl 2):e52–e62. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Su CC, Chien SY, Kuo SJ, Chen YL, Cheng CY
and Chen DR: Tanshinone IIA inhibits human breast cancer MDA-MB-231
cells by decreasing LC3-II, Erb-B2 and NF-κBp65. Mol Med Rep.
5:1019–1022. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Zhang K, Li J, Meng W, Xing H and Yang Y:
Tanshinone IIA inhibits acute promyelocytic leukemia cell
proliferation and induces their apoptosis in vivo. Blood Cells Mol
Dis. 56:46–52. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Zhang Y, Guo S, Fang J, Peng B, Zhang Y
and Cao T: Tanshinone IIA inhibits cell proliferation and tumor
growth by downregulating STAT3 in human gastric cancer. Exp Ther
Med. 16:2931–2937. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Jiang L, Kon N, Li T, Wang SJ, Su T,
Hibshoosh H, Baer R and Gu W: Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated
activity during tumour suppression. Nature. 520:57–62. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Radif Y, Ndiaye H, Kalantzi V, Jacobs R,
Hall A, Minogue S and Waugh MG: The endogenous subcellular
localisations of the long chain fatty acid-activating enzymes ACSL3
and ACSL4 in sarcoma and breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
448:275–286. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Yuan H, Li X, Zhang X, Kang R and Tang D:
Identification of ACSL4 as a biomarker and contributor of
ferroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 478:1338–1343. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Mao W, Ding J, Li Y, Huang R and Wang B:
Inhibition of cell survival and invasion by Tanshinone IIA via
FTH1: A key therapeutic target and biomarker in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 24:5212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Wang TX, Duan KL, Huang ZX, Xue ZA, Liang
JY, Dang Y, Zhang A, Xiong Y, Ding C, Guan KL and Yuan HX:
Tanshinone functions as a coenzyme that confers gain of function of
NQO1 to suppress ferroptosis. Life Sci Alliance. 6:e2022016672022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Zhao H, Han B, Li X, Sun C, Zhai Y, Li M,
Jiang M, Zhang W, Liang Y and Kai G: Salvia miltiorrhiza in
breast cancer treatment: A review of its phytochemistry,
derivatives, nanoparticles, and potential mechanisms. Front
Pharmacol. 13:8720852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Zhang YF, Zhang M, Huang XL, Fu YJ, Jiang
YH, Bao LL, Maimaitiyiming Y, Zhang GJ, Wang QQ and Naranmandura H:
The combination of arsenic and cryptotanshinone induces apoptosis
through induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress-reactive oxygen
species in breast cancer cells. Metallomics. 7:165–173. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Lin H, Zheng L, Li S, Xie B, Cui B, Xia A,
Lin Z and Zhou P: Cytotoxicity of tanshinone IIA combined with
Taxol on drug-resist breast cancer cells MCF-7 through inhibition
of Tau. Phytother Res. 32:667–671. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Li K and Lai H: TanshinoneIIA enhances the
chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells to doxorubicin through
down-regulating the expression of MDR-related ABC transporters.
Biomed Pharmacother. 96:371–377. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Li S, Wu C, Fan C, Zhang P, Yu G and Li K:
Tanshinone II A improves the chemosensitivity of breast cancer
cells to doxorubicin by inhibiting β-catenin nuclear translocation.
J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 35:e226202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Hu T, To KKW, Wang L, Zhang L, Lu L, Shen
J, Chan RL, Li M, Yeung JH and Cho CH: Reversal of P-glycoprotein
(P-gp) mediated multidrug resistance in colon cancer cells by
cryptotanshinone and dihydrotanshinone of Salvia
miltiorrhiza. Phytomedicine. 21:1264–1272. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Hu T, Wang L, Zhang L, Lu L, Shen J, Chan
RL, Li M, Wu WK, To KK and Cho CH: Sensitivity of
apoptosis-resistant colon cancer cells to tanshinones is mediated
by autophagic cell death and p53-independent cytotoxicity.
Phytomedicine. 22:536–544. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Tian HL, Yu T, Xu NN, Feng C, Zhou LY, Luo
HW, Chang DC, Le XF and Luo KQ: A novel compound modified from
tanshinone inhibits tumor growth in vivo via activation of the
intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Cancer Lett. 297:18–30. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Guerram M, Jiang ZZ, Yousef BA, Hamdi AM,
Hassan HM, Yuan ZQ, Luo HW, Zhu X and Zhang LY: The potential
utility of acetyltanshinone IIA in the treatment of
HER2-overexpressed breast cancer: Induction of cancer cell death by
targeting apoptotic and metabolic signaling pathways. Oncotarget.
6:21865–21877. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Wu Q, Zheng K, Huang X, Li L and Mei W:
Tanshinone-IIA-based analogues of imidazole alkaloid Act as potent
inhibitors to block breast cancer invasion and metastasis in vivo.
J Med Chem. 61:10488–10501. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Liu Y, Xie X, Hou X, Shen J, Shi J, Chen
H, He Y, Wang Z and Feng N: Functional oral nanoparticles for
delivering silibinin and cryptotanshinone against breast cancer
lung metastasis. J Nanobiotechnology. 18:832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Ngo SNT and Williams DB: Protective effect
of isothiocyanates from cruciferous vegetables on breast cancer:
Epidemiological and preclinical perspectives. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 21:1413–1430. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Fimognari C, Turrini E, Ferruzzi L, Lenzi
M and Hrelia P: Natural isothiocyanates: Genotoxic potential versus
chemoprevention. Mutat Res. 750:107–131. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Palliyaguru DL, Yuan JM, Kensler TW and
Fahey JW: Isothiocyanates: Translating the power of plants to
people. Mol Nutr Food Res. 62:17009652018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Greco G, Schnekenburger M, Catanzaro E,
Turrini E, Ferrini F, Sestili P, Diederich M and Fimognari C:
Discovery of sulforaphane as an inducer of ferroptosis in U-937
leukemia cells: Expanding its anticancer potential. Cancers
(Basel). 14:762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Chen PY, Lin KC, Lin JP, Tang NY, Yang JS,
Lu KW and Chung JG: Phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) inhibits the
growth of human oral squamous carcinoma HSC-3 Cells through
G(0)/G(1) phase arrest and mitochondria-mediated apoptotic cell
death. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:7183202012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Hwang ES and Lee HJ: Effects of
phenylethyl isothiocyanate and its metabolite on cell-cycle arrest
and apoptosis in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. Int J Food Sci
Nutr. 61:324–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Lv H, Zhen C, Liu J and Shang P:
β-Phenethyl isothiocyanate induces cell death in human osteosarcoma
through altering iron metabolism, disturbing the redox balance, and
activating the MAPK signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2020:50219832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Pappa G, Lichtenberg M, Iori R, Barillari
J, Bartsch H and Gerhäuser C: Comparison of growth inhibition
profiles and mechanisms of apoptosis induction in human colon
cancer cell lines by isothiocyanates and indoles from Brassicaceae.
Mutat Res. 599:76–87. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Wu CL, Huang AC, Yang JS, Liao CL, Lu HF,
Chou ST, Ma CY, Hsia TC, Ko YC and Chung JG: Benzyl isothiocyanate
(BITC) and phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC)-mediated generation of
reactive oxygen species causes cell cycle arrest and induces
apoptosis via activation of caspase-3, mitochondria dysfunction and
nitric oxide (NO) in human osteogenic sarcoma U-2 OS cells. J
Orthop Res. 29:1199–1209. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Mitsiogianni M, Koutsidis G, Mavroudis N,
Trafalis DT, Botaitis S, Franco R, Zoumpourlis V, Amery T, Galanis
A, Pappa A and Panayiotidis MI: The role of isothiocyanates as
cancer chemo-preventive, chemo-therapeutic and anti-melanoma
agents. Antioxidants (Basel). 8:1062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Subramanian AP, John AA, Vellayappan MV,
Balaji A, Jaganathan SK, Supriyanto E and Yusof M: Gallic acid:
Prospects and molecular mechanisms of its anticancer activity. RSC
Adv. 5:35608–35621. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
You BR and Park WH: Gallic acid-induced
lung cancer cell death is related to glutathione depletion as well
as reactive oxygen species increase. Toxicol In Vitro.
24:1356–1362. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Liu KC, Ho HC, Huang AC, Ji BC, Lin HY,
Chueh FS, Yang JS, Lu CC, Chiang JH, Meng M and Chung JG: Gallic
acid provokes DNA damage and suppresses DNA repair gene expression
in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Environ Toxicol. 28:579–587.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Subramanian V, Venkatesan B, Tumala A and
Vellaichamy E: Topical application of Gallic acid suppresses the
7,12-DMBA/Croton oil induced two-step skin carcinogenesis by
modulating anti-oxidants and MMP-2/MMP-9 in Swiss albino mice. Food
Chem Toxicol. 66:44–55. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Teng CLJ, Han SM, Wu WC, Hsueh CM, Tsai
JR, Hwang WL and Hsu SL: Mechanistic aspects of lauryl
gallate-induced differentiation and apoptosis in human acute
myeloid leukemia cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 71:197–206. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Kim NS, Jeong SI, Hwang BS, Lee YE, Kang
SH, Lee HC and Oh CH: Gallic acid inhibits cell viability and
induces apoptosis in human monocytic cell line U937. J Med Food.
14:240–246. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Zhao B and Hu M: Gallic acid reduces cell
viability, proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis in human
cervical cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 6:1749–1755. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Asano J, Chiba K, Tada M and Yoshii T:
Cytotoxic xanthones from Garcinia hanburyi. Phytochemistry.
41:815–820. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Su J, Xu T, Jiang G, Hou M, Liang M, Cheng
H and Li Q: Gambogenic acid triggers apoptosis in human
nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE-2Z cells by activating
volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying chloride channel.
Fitoterapia. 133:150–158. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Mei W, Dong C, Hui C, Bin L, Fenggen Y,
Jingjing S, Cheng P, Meiling S, Yawen H, Xiaoshan W, et al:
Gambogenic acid kills lung cancer cells through aberrant autophagy.
PLoS One. 9:e836042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Yan F, Wang M, Chen H, Su J, Wang X, Wang
F, Xia L and Li Q: Gambogenic acid mediated apoptosis through the
mitochondrial oxidative stress and inactivation of Akt signaling
pathway in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE-1 cells. Eur J
Pharmacol. 652:23–32. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Wang M, Li S, Wang Y, Cheng H, Su J and Li
Q: Gambogenic acid induces ferroptosis in melanoma cells undergoing
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
401:1151102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Wang M, Cheng H, Wu H, Liu C, Li S, Li B,
Su J, Luo S and Li Q: Gambogenic acid antagonizes the expression
and effects of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 and triggers autophagy and
ferroptosis in melanoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 154:1136362022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Dhillon H, Mamidi S, McClean P and Reindl
KM: Transcriptome analysis of piperlongumine-treated human
pancreatic cancer cells reveals involvement of oxidative stress and
endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways. J Med Food. 19:578–585.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Jin HO, Park JA, Kim HA, Chang YH, Hong
YJ, Park IC and Lee JK: Piperlongumine downregulates the expression
of HER family in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
486:1083–1089. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Alpay M, Yurdakok-Dikmen B, Kismali G and
Sel T: Antileukemic effects of piperlongumine and alpha lipoic acid
combination on Jurkat, MEC1 and NB4 cells in vitro. J Can Res Ther.
12:556–560. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Wei G, Wang S, Cui S, Guo J, Liu Y, Liu Y
and Cheng M: Synthesis and evaluation of the anticancer activity of
albiziabioside A and its analogues as apoptosis inducers against
human melanoma cells. Org Biomol Chem. 12:5928–5935. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Wei G, Sun J, Luan W, Hou Z, Wang S, Cui
S, Cheng M and Liu Y: Natural product albiziabioside A conjugated
with pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase inhibitor dichloroacetate to
induce apoptosis-ferroptosis-M2-TAMs polarization for combined
cancer therapy. J Med Chem. 62:8760–8772. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Wang H, Zhang T, Sun W, Wang Z, Zuo D,
Zhou Z, Li S, Xu J, Yin F, Hua Y and Cai Z: Erianin induces
G2/M-phase arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via the ROS/JNK
signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells in vitro and in vivo.
Cell Death Dis. 7:e22472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Xie Y, Zhou X, Li J, Yao XC, Liu WL, Kang
FH, Zou ZX, Xu KP, Xu PS and Tan GS: Identification of a new
natural biflavonoids against breast cancer cells induced
ferroptosis via the mitochondrial pathway. Bioorg Chem.
109:1047442021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Liang X, Hu C, Han M, Liu C, Sun X, Yu K,
Gu H and Zhang J: Solasonine inhibits pancreatic cancer progression
with involvement of ferroptosis induction. Front Oncol.
12:8347292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Jin M, Shi C, Li T, Wu Y, Hu C and Huang
G: Solasonine promotes ferroptosis of hepatoma carcinoma cells via
glutathione peroxidase 4-induced destruction of the glutathione
redox system. Biomed Pharmacother. 129:1102822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Kim DH, Khan H, Ullah H, Hassan STS,
Šmejkal K, Efferth T, Mahomoodally MF, Xu S, Habtemariam S, Filosa
R, et al: MicroRNA targeting by quercetin in cancer treatment and
chemoprotection. Pharmacol Res. 147:1043462019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|