Gastrointestinal cancer accounts for one-quarter of
the global incidence rate of cancer and one-third of cancer-related
deaths (1). The efficacy of various
treatment approaches is restricted due to unidentified mechanisms,
adverse effects and cancer resistance. Therefore, it is crucial to
elucidate the pathogenesis and develop novel therapeutic targets
(2).
The cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)/stimulator of
interferon genes (STING) pathway has become a key regulatory
pathway for cancer (3,4). Once cGAS/STING binds to DNA, it can
stimulate various immune defense mechanisms and virtually influence
every facet of the development of cancer, such as the malignant
cell transformation, occurrence, development, drug resistance,
metastasis and recurrence (3,5).
Previous studies have reported that activation of the cGAS/STING
pathway is related to the maintenance of gastrointestinal
homeostasis (6,7). An increasing number of studies have
found that the cGAS/STING pathway serves an important regulatory
role in gastrointestinal cancer (7–11).
However, the exact role and molecular mechanisms of the cGAS/STING
pathway in gastrointestinal cancer, as well as its mechanistic
clinical applications, still need to be elucidated.
The present review discusses the critical role that
the cGAS/STING signal serves in the processes pertaining to the
occurrence, progression, diagnosis and treatment of
gastrointestinal cancer, as well as how cGAS/STING leads to
beneficial or harmful outcomes of gastrointestinal cancer. The
present review considers the current follow-up research directions
and challenges regarding the cGAS/STING axis in gastrointestinal
cancer, and emphasizes the novel frontiers of cGAS/STING biology to
inspire individuals to consider their association with
gastrointestinal cancer.
Gastrointestinal cancer includes gastric,
colorectal, esophageal, liver, gallbladder and pancreatic cancer.
Although the cGAS/STING pathway serves a crucial role in
maintaining gastrointestinal homeostasis, overactivation of the
cGAS/STING pathway can lead to gastrointestinal cancer and other
gastrointestinal diseases (7–11). The
development of novel treatment approaches for gastrointestinal
malignancies may benefit from elucidating the molecular mechanisms
and effects of the cGAS/STING pathway in gastrointestinal cancer
(7).
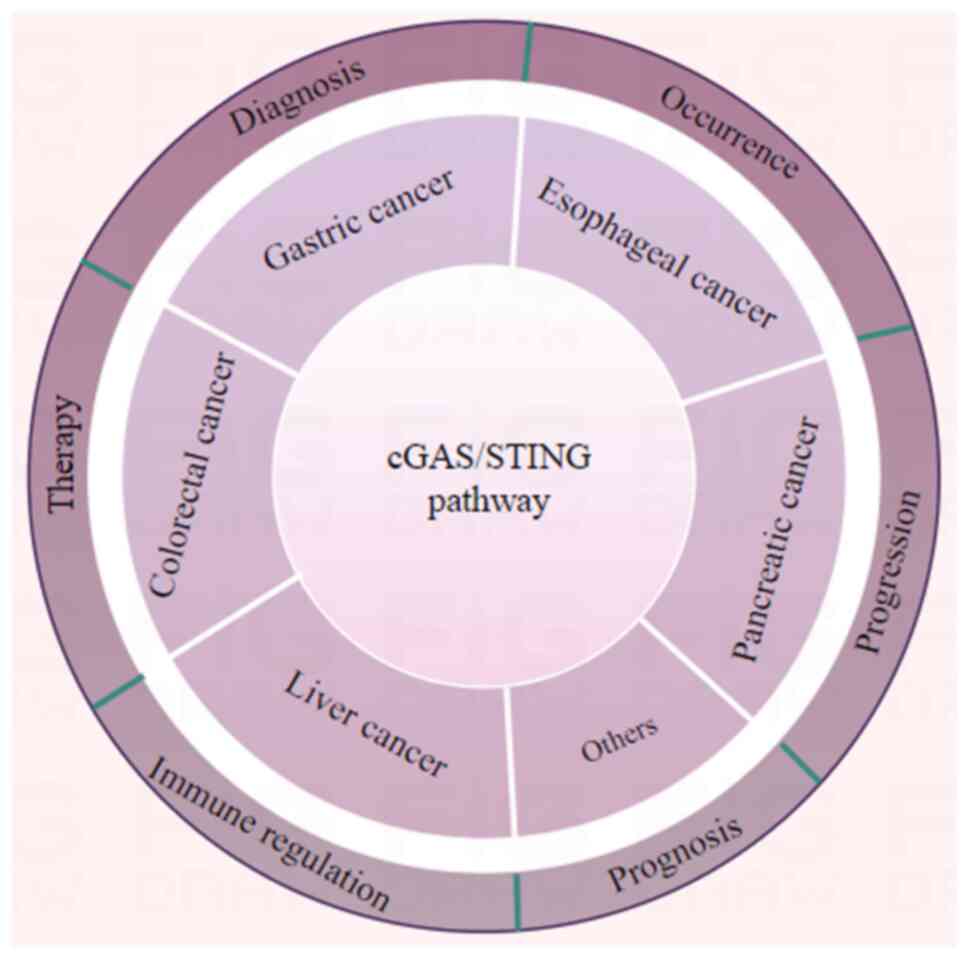
Increasing evidence suggests that the cGAS/STING
pathway serves a crucial role in the initiation, progression and
treatment of gastrointestinal cancer (7–11).
Fig. 1 briefly summarizes the scope
of the influence of this important pathway, and aims to visually
represent which cancer types are affected by the cGAS/STING
pathway, and the specific physiological and pathological processes
that are impacted. Numerous studies have shown that the cGAS/STING
pathway serves an important role in various gastrointestinal cancer
types, including gastric, colorectal, pancreatic, liver and
esophageal cancer (8–10). The occurrence, progression,
diagnosis, therapy, prognosis and immune regulation of these cancer
types are all influenced by the cGAS/STING pathway (8–10).
Further exploration of the role of the cGAS/STING pathway in these
cancer types may provide novel strategies for the diagnosis and
treatment of digestive tract cancers.
Gastric cancer is one of the most prevalent
malignant tumors of the digestive tract that primarily originates
from the gastric mucosa and is a danger to the health of
individuals. According to statistics for 2021, there were ~1.089
million new cases and 768,000 deaths worldwide each year (12). Due to the lack of obvious and
specific stage symptoms in the early stage of gastric cancer, the
majority of patients with gastric cancer are diagnosed in the
advanced stage and their prognosis is frequently poor (13,14).
It is imperative to investigate novel diagnostic and therapeutic
approaches and to clarify the processes underlying the onset and
progression of stomach cancer.
Although the cGAS/STING pathway exists and serves a
crucial role in various cell types, there may be differences in the
activation and response to this pathway among different cell types
(8,17). These differences may stem from
various factors such as genetic background, physiological state and
microenvironment among cells. In some cases, different cells may
require different ligands or stimulatory signals to activate the
cGAS/STING pathway and achieve the same effect (16,17).
This may be related to the distribution of receptors on the cell
surface, differences in signal transduction pathways and the
expression of downstream effector molecules. Even under the action
of the same ligand, different cells may produce different
biological effects through different signal transduction pathways
(9,17). This may be related to the complexity
of the intracellular signaling network and the interactions between
signaling molecules. For instance, during the activation of the
cGAS/STING pathway with additional dynamin-related protein 1
(Drp1), some esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell types may
shift to a proliferative state (8).
Conversely, HS746T cells inhibited by anlotinib, after returning
from a proliferative state to a reference state, also undergo
transitions during cGAS/STING activation (17). These changes may be related to
multiple factors such as intracellular signal transduction
pathways, gene expression regulation and cellular metabolic state
(8,17).
Future research needs to further explore the
specific mechanisms of the cGAS/STING pathway in different cell
types and how to utilize this pathway in disease treatment and
immunotherapy applications.
Gastric cancer lacks effective early diagnostic
markers and treatment methods. Research has revealed that the
cGAS/STING signal serves a crucial role in the initiation,
progression and treatment of gastric cancer. The cGAS/STING pathway
can influence the state of immune cells, the activation of immune
pathways, DNA damage repair, the proliferation and migration of
gastric cancer cells, and other processes during the initiation and
progression of gastric cancer by regulating the transduction of
various molecules and signaling pathways such as SOX2/Akt, C-X-C
motif chemokine ligand (CXCL)9/10/11 and IFN-β (Fig. 2). Effective diagnostic and
therapeutic methods based on the aforementioned roles of the
cGAS/STING pathway require targeted and in-depth research. Such
research can provide novel insights for the early diagnosis and
effective treatment of gastric cancer, thereby alleviating the
burden on patients with gastric cancer and improving their quality
of life.
Esophageal cancer is the eighth most common
malignant tumors and one of the leading causes of cancer-related
deaths worldwide (7). The 5-year
relative survival rate for patients with esophageal cancer is still
<20% despite progress in various treatment methods, including
surgical resection, immunotherapy, radiotherapy and chemotherapy
(7,23). Improved treatment strategies and
patient prognosis may be achieved by understanding the pathogenesis
of esophageal cancer.
Increasing evidence has demonstrated the regulatory
effect of the cGAS/STING pathway in esophageal cancer (27–30).
The mechanisms that dictate the function of the cGAS/STING pathway
vary in different contexts; for example, cGAS/STING can affect the
efficacy of radiotherapy, proliferation or immune regulation in
different situations (27–29). A deeper understanding of the roles
and mechanisms of the cGAS/STING pathway in different contexts will
aid the development of cGAS/STING signaling modulatory therapies.
Inhibiting the cGAS/STING pathway may be beneficial for the
treatment of esophageal cancer (28,29).
Future studies are required to enable medical professionals to
select the appropriate cGAS/STING modulators based on the
particular circumstances.
Colorectal cancer is a commonly diagnosed type of
cancer, with an estimated 592,232 new cases in 2022 worldwide, and
was the fifth most common cause of cancer deaths in China in 2022
(31,32). Despite the rapid development of
treatment methods for colorectal cancer, including immunotherapy,
chemotherapy and radiation therapy, there is still no cure. The
effectiveness of existing treatment methods is not satisfactory as
the median overall survival time of patients with colorectal cancer
is ~30 months (32). Understanding
the numerous processes involved in the initiation and progression
of colorectal cancer at the cellular and molecular levels is
crucial for developing precise and efficient therapeutic
strategies.
In some cases, local radiation therapy may produce T
cell-mediated abscopal effects on non-irradiated cancer lesions,
especially when combined with immune checkpoint blockade (33). However, this effect is still rare in
clinical practice, and improvements and further clarification are
highly desirable. The abscopal effect is dependent on cancer cell
mitochondrial DNA and cGAS/STING, which is enhanced by the addition
of liposome doxorubicin (33). Wang
et al (9) determined that
the germline polymorphism of STING and IFNB1 genes may predict the
efficacy of cetuximab treatment in patients with metastatic
colorectal cancer. The cGAS/STING pathway axis in colon
adenocarcinoma could regulate the m6A and m5C modifications of
glutathione peroxidase 4, which could be a promising target for
immunotherapy in colorectal cancer (34). Protecting the nuclear membrane and
genomic integrity of colorectal cancer cells delayed the
progression of colorectal cancer by preventing the activation of
the cGAS/STING axis via heterochromatin protein 1γ (35). Hu et al (36) found that the absence of cGAS in mice
exacerbated chemically induced colon cancer associated with
colitis. Mice lacking cGAS were more susceptible to
colitis-associated colon cancer infection than mice lacking STING
or type I interferon receptors under the same conditions (36). SH2 domain-containing tyrosine
phosphatase 2 (SHP2) regulates the dephosphorylation of
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) in colon cancer, thereby
inhibiting DNA repair and enhancing the anticancer immunity
mediated by the cGAS/STING pathway (37). This suggests that SHP2 may serve as
a promising therapeutic target for colon cancer treatment. It has
been reported that barrier to autointegration nuclear assembly
factor 1-knockout activated an anticancer immune response effect
regulated by the cGAS/STING pathway, resulting in immune activation
within the tumor microenvironment (38). This activation manifested as
increased infiltration of CD8+ T cells and decreased
accumulation of bone marrow-derived suppressive cells (38). The detection of the expression
levels of cGAS and STING indicated that the staging and metastasis
of colorectal cancer are closely related to the activation status
of the cGAS/STING signaling pathway (39). In multiple colorectal cancer models,
Vornholz et al (40) found
that the superior antitumor immune response in mismatch
repair-deficient colorectal cancer required activation of the
cGAS/STING signal in colorectal cancer cells. The research findings
introduced a reasonable strategy to forcibly regulate the intrinsic
program of cancer cells by engineering STING, making drug-resistant
tumors sensitive to immune checkpoint inhibitors (40).
Drug activation of cGAS/STING in the tumor
environment is considered an attractive and promising tumor therapy
for colorectal cancer; however, its efficacy is limited in clinical
practice (41). STING expression in
colorectal cancer cells was enhanced by lysine demethylase 5
inhibitors and inhibited cancer growth in immunocompromised mice
(41). HER2 is a protein that is
frequently upregulated in various cancer types, including
colorectal cancer (32). The
HER2-targeted antibody monomethyl auristatin E conjugate RC48 made
HER2-positive colon cancer cells more susceptible to immunotherapy
by activating the cGAS/STING signaling (32). A study involving 1,424 patients with
colorectal cancer revealed that the toll like receptor
3/cGAS/STING/IKKε/TANK binding kinase 1/IFN signal axis serves an
important role in the occurrence and development of colorectal
cancer (42). In the absence of
colon cancer cell-induced STING, higher doses of 5-fluorouracil are
needed to alleviate the tumor burden (43). In human colorectal specimens, higher
STING expression was associated with higher survival rates
(43). Liang et al (44) indicated that SIX homeobox 4 was the
main regulatory factor for STING expression in colon cancer cells.
This observation offers supplementary mechanisms and genetic
markers that can aid in predicting effective responses to immune
checkpoint blockade therapy. The combination of lovastatin and
cGAS/STING axis stimulation mediated by liposome delivery systems
enhanced colorectal cancer immunotherapy and chemotherapy,
providing a novel clinical diagnosis and treatment strategy for
combined immune checkpoint blockade treatment of ‘immune cold’
cancers (45). The immune
checkpoint inhibitor response in colorectal cancer is enhanced by
dietary methionine restriction, and the cGAS/STING pathway serves a
crucial regulatory role in this process (46). The cGAS/STING pathway could also be
triggered in combination with photothermal ablation therapy to
achieve improved therapeutic outcomes in colorectal cancer
(47).
Numerous studies have been conducted on the
molecular and cellular mechanisms of the relationship between
cGAS/STING and colorectal cancer (32,43–47)
(Table I), as well as the effects
of radiotherapy and chemotherapy, prognosis prediction, clinical
association analysis, and drug development. However, clinical
application of cGAS/STING in the diagnosis and treatment of
colorectal cancer is still limited, and researchers need to
strengthen related clinical research and drug development in later
research to benefit more patients with colorectal cancer.
Liver cancer is one of the most common malignant
tumors of the digestive system worldwide and a major cause of
cancer-related deaths (48).
Although scientists and medical professionals have performed
numerous studies investigating the diagnosis, management and
treatment of liver cancer, the prognosis is still poor and the
mortality rate is high, and thus, it is necessary to explore the
pathogenesis and novel treatment strategies (48,49).
The cGAS/STING pathway has a significant effect in liver physiology
and pathology, and is closely related to the occurrence,
progression and treatment of liver cancer (48,50).
The present review provides a summary highlighting the significance
of the cGAS/STING pathway in the occurrence and progression of
liver cancer, as well as the efficacy of targeting cGAS/STING in
liver cancer treatment and its synergistic potential with other
therapeutic modalities in clinical practice (Table II). The aim is to offer novel
insights for the diagnosis and management of liver cancer.
Hyperbaric oxygen promotes cGAS/STING activation
induced by teniposide to enhance the anticancer effect of PD-1
antibody in hepatocellular carcinoma (51). Enhancing DNA-activated STING
signaling by reducing hypoxia may be a possible direction to
improve the incidence of adverse reactions to PD-1 antibody in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Using a combination of
multiple therapies for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma has become a major trend. Wang et al (52) reported that sorafenib combined with
STAT3 knockdown triggered endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced
apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and that the cGAS/STING
pathway elicited antitumor immunity. Persistent DNA damage caused
by deficiencies in the BRCA pathway induces tumor immune
suppression and T lymphocyte infiltration in hepatocellular
carcinoma via the cGAS/STING pathway (53). This insight provides a more profound
understanding of the remodeling of the tumor immune
microenvironment, such as sustained DNA damage inducing tumor
immunosuppression and T lymphocyte infiltration, which could
potentially enhance the response of hepatocellular carcinoma to
PD-1 therapy. Intelligently responsive Fe/Mn nanovaccines could be
used for liver cancer immunotherapy and induced immunogenic cell
death by triggering pyroptosis-boosted cGAS/STING pathway activity
in cellular and mouse models (54).
The gut microbiota could regulate radiation-related anti-liver
cancer immune responses via the cGAS/STING pathway, which could
serve a key role in the treatment of liver cancer (55). RADA16-I (R) peptide was dissolved in
a mixture of lyOK-432 (O) and doxorubicin (D) to develop an ROD
hydrogel. The novel ROD peptide hydrogel could induce anticancer
immunity by activating the cGAS/STING/IFN-I pathway, which can
effectively treat residual liver cancer after incomplete
radiofrequency ablation of liver cancer (56). The cGAS/STING signaling pathway
serves an important regulatory role in the anticancer effect of
AZD6738, which enhances the tumor immune microenvironment of
hepatocellular carcinoma to enhance the antitumor activity of
radiotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors (57). A study has found that RecQ like
helicase 4 derived from hepatocellular carcinoma cells inhibited
the cGAS/STING pathway in dendritic cells by regulating the DNA
repair process, reducing the sensitivity of hepatocellular
carcinoma to radiation (58).
The regulation of the STING pathway has been found
to affect the development of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating
STAT1/programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1)/IFN in in vitro and
in vivo models (59). The
regulation of the STING pathway serves a crucial role in the
development of hepatocellular carcinoma and has been expected to be
used as a treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma, most likely in
combination with other immunomodulatory therapies or standard care
(59). By targeting eukaryotic
elongation factor 2 kinase blockade, it may be possible to activate
the cGAS/STING pathway, thereby enhancing the activity of natural
killer (NK) cells in hepatocellular carcinoma (60). This presents a novel strategy for
the treatment of this disease. Recombinant oncolytic influenza
virus expressing PD-L1 antibody induced activation of
CD8+ T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma mice via the
cGAS/STING pathway, thereby killing cancer cells (61). Isopentenyl-diphosphate δ isomerase 1
interacts with cGAS and recruits the E3 ligase tripartite motif
containing 41 to promote ubiquitination and degradation of cGAS,
thereby inhibiting the cGAS/STING signaling pathway (62). This process serves a crucial
regulatory role in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.
In-depth study of this mechanism holds promise for providing novel
ideas and strategies for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Olaparib, as a poly (ADP ribose) polymerase inhibitor, has been
shown to promote radiation-mediated systemic anticancer effects by
activating the STING chemokine pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma
(63). Hypoxia is one of the
characteristics of solid tumors, including hepatocellular carcinoma
(64). Hypoxia-induced ribonuclease
H2 subunit A inhibits the activation of the cGAS/STING pathway and
could predict the prognosis of liver cancer (64). The activation of the cGAS/STING
pathway is strongly associated with various immune biomarker sets
in hepatocellular carcinoma (65).
These findings suggest that members of the cGAS/STING pathway could
serve as prognostic biomarkers and immunotherapy targets for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Arsenic trioxide has become an effective
cytotoxic drug for the treatment of solid tumors, including liver
cancer (49). The cGAS/STING/IFN
pathway is induced by arsenic trioxide, which enhances immunogenic
cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma (49). In clinical hepatocellular carcinoma
tissues, cGAS has been demonstrated to be downregulated, and its
dysregulation leads to the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
(66). In cellular and animal
models, cGAS has been shown to inhibit the progression of
hepatocellular carcinoma by suppressing the PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 pathway
(66). Radiofrequency ablation has
been used as an alternative to surgical treatment for early
hepatocellular carcinoma (67).
Radiofrequency hyperthermia could enhance the therapeutic effect of
OK-432 on liver cancer by enhancing the activity of the cGAS/STING
pathway (67). The blockade of CD47
enhanced the capacity of CD103+ dendritic cells to
uptake cancer DNA, resulting in the stimulation of the cGAS/STING
axis (68). Consequently, this
enhancement promoted the activation of NK cells in hepatocellular
carcinoma (68). tet methylcytosine
dioxygenase 2-mediated cGAS-induced STING activation is required to
regulate vascular remodeling and anticancer immune effects in
hepatocellular carcinoma (69).
Hepatocellular ferroptosis-induced DNA oxidative damage promotes
the increase of STING activity in macrophages, thereby promoting
the occurrence and development of liver injury and liver cancer
(70). Du et al (71) identified an immune-cloaking
mechanism, specifically the cGAS/STING pathway, which was activated
by radiation therapy. Furthermore, their findings suggest that
radiation therapy augments the efficacy of immunotherapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma.
Pancreatic cancer is one of the major causes of
cancer-related deaths worldwide, reportedly ranking fourth, and
effective treatment options are limited (72). There are several treatment
strategies for pancreatic cancer, including surgical intervention,
immunotherapy, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy or
their combination; however, the effect is not satisfactory
(72–74). The cGAS/STING signal is considered
to serve a crucial regulatory role in the immune response and
immunotherapy of malignant tumors (72–77).
Therapies targeting cGAS/STING have been applied for the treatment
of pancreatic cancer by promoting the immune responses against
malignancy through different strategies, either as a monotherapy or
in combination with other immunotherapies for pancreatic cancer
(11). This section summarizes the
progress regarding the role of cGAS/STING in the occurrence,
progress and treatment of pancreatic cancer, and suggests improved
strategies for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
The therapeutic effect of disulfiram and
chemoimmunotherapy is enhanced by inhibiting PARP1 expression and
activating the cGAS/STING pathway in pancreatic cancer (72). Ectonucleotidase CD73 inhibits the
cGAS/STING pathway and cooperates with CD39 to promote the
occurrence of pancreatic cancer (73). POLQ is a key mediator in the
microhomology-mediated end joining pathway and is crucial for the
double-strand break repair of BRCA2 defect type pancreatic cancer
(74). POLQ inhibition triggers the
immune response in homologous recombination-deficient pancreatic
cancer via cGAS/STING signaling (74). The cGAS/STING pathway and
cancer-associated fibroblasts serve a pivotal role in overcoming
the cancer-associated fibroblast barrier and promoting immune cell
infiltration in pancreatic cancer (75). Activation of the cGAS/STING pathway
results in the upregulation of dual oxidase 2, as well as increased
expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and VEGF-A,
normoxic expression of HIF-1α and VEGF-A, and DNA double strand
cleavage (76). These findings
suggest that cGAS/STING signaling may contribute to the development
of an oxidative and pro-angiogenic microenvironment, potentially
leading to genetic instability associated with inflammation in
pancreatic cancer. The silencing of deltex E3 ubiquitin ligase 3L
(DTX3L) leads to enhanced activation of the cGAS/STING pathway and
improves the immune antitumor effect in pancreatic cancer (77). A novel promising treatment method
for pancreatic cancer may be a strategy based on the
DTX3L/cGAS/STING axis (77).
Due to extensive evidence indicating that the
cGAS/STING pathway regulates immune cells in the cancer
microenvironment, biological therapies based on cGAS/STING have
attracted widespread attention (72–77).
Pancreatic cancer and other cancer types have special tumor
microenvironments. Researchers have conducted in-depth research on
them and found that cGAS/STING serves a crucial role in the
progression of pancreatic cancer and in developing effective
strategies. cGAS/STING-based therapies have also been shown to work
in combination with other therapies, such as immune checkpoints,
vaccines and immune cell-targeting nanoparticles. Although the
present review aims to summarize the role of cGAS/STING signaling
in pancreatic cancer, in-depth investigations are still required to
clarify the various mechanisms by which STING may be activated and
to develop improved therapeutic approaches and drugs to enhance the
clinical care of patients with pancreatic cancer.
The early symptoms of most patients with
gastrointestinal cancer are not obvious and non-specific, and are
easy to overlook, and there are no good specific and effective
early diagnostic markers for clinical diagnosis (2). It is necessary to elucidate the
pathogenesis of gastrointestinal tumors and to find more effective
diagnostic and treatment strategies, as gastrointestinal cancer is
often diagnosed in the advanced stage. Increasing evidence suggests
that cGAS/STING is closely related to the occurrence, progression
and treatment of gastrointestinal cancer. Targeting the cGAS/STING
pathway is a promising approach for the treatment of
gastrointestinal cancer. Combining cGAS/STING pathway-based
therapeutic interventions with traditional chemotherapy, targeted
therapy or immunotherapy may be a commonly used and effective
strategy to treat gastrointestinal tumors. However, the exact
molecular mechanism of the cGAS/STING signaling pathway in
gastrointestinal cancer has not been fully revealed, and the safety
of treatment methods based on the cGAS/STING pathway also needs to
be comprehensively evaluated. Future translational research and
clinical trials necessitate the advancement of therapeutic
strategies based on the cGAS/STING pathway. Subsequent research
involves elucidating the molecular mechanisms and downstream
targets, evaluating safety and therapeutic efficacy, and exploring
the potential of combining cGAS/STING-based therapies with multiple
treatment modalities. Ultimately, such endeavors may be an
effective way to overcome gastrointestinal tumors and reduce the
social and patient burden.
In cancer, cancer-derived DNA, oncogenic viruses,
exosomes and DNA damage caused by radiotherapy can activate the
cGAS/STING pathway, thereby inducing cellular senescence,
inflammation and antitumor immunity. By contrast, CEA and CA19-9
reflect the presence and progression of cancer through blood tests
(78–80). Although there are differences in
their mechanisms of action, the cGAS/STING pathway, CEA and CA19-9
can all serve as important tools for the detection and treatment of
gastrointestinal cancers. Delving deeply into the mechanisms
underlying the role of the cGAS/STING pathway in the initiation and
progression of gastrointestinal cancer, as well as its application
prospects in cancer immunotherapy and radiotherapy can offer novel
insights into the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal
cancer. Investigating the interaction between the cGAS/STING
pathway and clinical biomarkers such as CEA and CA19-9, may provide
a theoretical basis for the development of more precise and
effective detection and treatment methods for gastrointestinal
cancer. In the future, by integrating the detection results of the
cGAS/STING pathway with clinical biomarkers such as CEA and CA19-9,
a more comprehensive risk assessment model for gastrointestinal
cancer can be established, which can offer patients more
personalized treatment plans and prognosis evaluations.
Not applicable.
The present study was supported by Project of Social Development
in Zhenjiang (grant no. SH2021045), Technology Development Project
of Jiangsu University (grant no. 20220516), the Foundation for
Excellent Young Teachers of Jiangsu University and the Practice
Innovation Training Program Projects of Jiangsu Province (grant no.
202410299093Z).
Not applicable.
ZL and JJ designed the research. CL, LT, WY and YG
analyzed data. ZL, CL, WX and JJ contributed to the writing and
revisions. Data authentication is not applicable. All authors have
read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
|
1
|
Wang S, Zheng R, Li J, Zeng H, Li L, Chen
R, Sun K, Han B, Bray F, Wei W and He J: Global, regional, and
national lifetime risks of developing and dying from
gastrointestinal cancers in 185 countries: A population-based
systematic analysis of GLOBOCAN. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol.
9:229–237. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang T, Jin Y, Wang M, Chen B, Sun J,
Zhang J, Yang H, Deng X, Cao X, Wang L and Tang Y: SALL4 in
gastrointestinal tract cancers: Upstream and downstream regulatory
mechanisms. Mol Med. 30:462024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Samson N and Ablasser A: The cGAS-STING
pathway and cancer. Nat Cancer. 3:1452–1463. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lv H, Zong Q, Chen C, Lv G, Xiang W, Xing
F, Jiang G, Yan B, Sun X, Ma Y, et al: TET2-mediated tumor cGAS
triggers endothelial STING activation to regulate vasculature
remodeling and anti-tumor immunity in liver cancer. Nat Commun.
15:62024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Y, Luo J, Alu A, Han X, Wei Y and Wei
X: cGAS-STING pathway in cancer biotherapy. Mol Cancer. 19:1362020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Canesso MCC, Lemos L, Neves TC, Marim FM,
Castro TBR, Veloso ÉS, Queiroz CP, Ahn J, Santiago HC, Martins FS,
et al: The cytosolic sensor STING is required for intestinal
homeostasis and control of inflammation. Mucosal Immunol.
11:820–834. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ke X, Hu T and Jiang M: cGAS-STING
signaling pathway in gastrointestinal inflammatory disease and
cancers. FASEB J. 36:e220292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li Y, Chen H, Yang Q, Wan L, Zhao J, Wu Y,
Wang J, Yang Y, Niu M, Liu H, et al: Increased Drp1 promotes
autophagy and ESCC progression by mtDNA stress mediated cGAS-STING
pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 41:762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang J, Xiao Y, Loupakis F, Stintzing S,
Yang Y, Arai H, Battaglin F, Kawanishi N, Jayachandran P, Soni S,
et al: Genetic variants involved in the cGAS-STING pathway predict
outcome in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: Data from
FIRE-3 and TRIBE trials. Eur J Cancer. 172:22–30. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu D, Tian Y, Xia Q and Ke B: The
cGAS-STING Pathway: Novel Perspectives in Liver Diseases. Front
Immunol. 12:6827362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mohseni G, Li J, Ariston Gabriel AN, Du L,
Wang YS and Wang C: The Function of cGAS-STING Pathway in Treatment
of Pancreatic Cancer. Front Immunol. 12:7810322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu Y, Han J, Zhang X, Zhang X, Song J, Gao
Z, Qian H, Jin J and Liang Z: Exosomal circRNAs in gastrointestinal
cancer: Role in occurrence, development, diagnosis and clinical
application (Review). Oncol Rep. 51:192024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lu L, Gao Z, Jin L, Geng H and Liang Z:
Novel role of circRNAs in the drug resistance of gastric cancer:
regulatory mechanisms and future for cancer therapy. Front
Pharmacol. 15:14352642024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shen Q, Yang L, Li C, Wang T, Lv J, Liu W,
Lin Y, Yin Y and Tao K: Metformin promotes cGAS/STING signaling
pathway activation by blocking AKT phosphorylation in gastric
cancer. Heliyon. 9:e189542023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li C, Shen Q, Zhang P, Wang T, Liu W, Li
R, Ma X, Zeng X, Yin Y and Tao K: Targeting MUS81 promotes the
anticancer effect of WEE1 inhibitor and immune checkpoint blocking
combination therapy via activating cGAS/STING signaling in gastric
cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40:3152021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yuan M, Guo XL, Chen JH, He Y, Liu ZQ,
Zhang HP, Ren J and Xu Q: Anlotinib suppresses proliferation,
migration, and immune escape of gastric cancer cells by activating
the cGAS-STING/IFN-beta pathway. Neoplasma. 69:807–819. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang KS, Xu CQ and Lv J: Identification
and validation of the prognostic value of cyclic GMP-AMP
synthase-stimulator of interferon (cGAS-STING) related genes in
gastric cancer. Bioengineered. 12:1238–1250. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fukai S, Nakajima S, Saito M, Saito K,
Kase K, Nakano H, Sato T, Sakuma M, Kaneta A, Okayama H, et al:
Down-regulation of stimulator of interferon genes (STING)
expression and CD8+ T-cell infiltration depending on
HER2 heterogeneity in HER2-positive gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer.
26:878–890. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Duan Y, Li S, Huang B, Dou Y, Kong P, Kang
W and Xu D: CD47-targeted immunotherapy unleashes antitumour
immunity in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer. Clin
Immunol. 247:1092382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hosseinzadeh S, Imani M, Pourfarzi F,
Jafari N, AbedianKenari S and Safarzadeh E: Combination of
IFN-gamma with STING agonist and PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade: A
potential immunotherapy for gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 41:1102024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liang L, Chai Y, Chai F, Liu H, Ma N,
Zhang H, Zhang S, Nong L, Li T and Zhang B: Expression of SASP, DNA
damage response, and cell proliferation factors in early gastric
neoplastic lesions: Correlations and clinical significance. Pathol
Oncol Res. 28:16104012022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Esophageal Cancer Treatment (PDQ(R)), .
Health Professional Version. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries
Bethesda (MD): 2002
|
|
24
|
Li Y, Yang Q, Chen H, Yang X, Han J, Yao
X, Wei X, Si J, Yao H, Liu H, et al: TFAM downregulation promotes
autophagy and ESCC survival through mtDNA stress-mediated STING
pathway. Oncogene. 41:3735–3746. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakajima S, Mimura K, Kaneta A, Saito K,
Katagata M, Okayama H, Saito M, Saze Z, Watanabe Y, Hanayama H, et
al: Radiation-induced remodeling of the tumor microenvironment
through tumor cell-intrinsic expression of cGAS-STING in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 115:957–971.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Matsuishi A, Nakajima S, Kaneta A, Saito
K, Fukai S, Sakuma M, Tsumuraya H, Okayama H, Saito M, Mimura K, et
al: The tumor cell-intrinsic cGAS-STING pathway is associated with
the high density of CD8+ T cells after chemotherapy in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Esophagus. 21:165–175. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakajima S, Mimura K, Kaneta A, Katagata
M, Okayama H, Saito M, Saze Z, Hanayama H, Tada T, Momma T and Kono
K: Remodeling of the tumor microenvironment by radiotherapy through
the cGAS-STING pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gan
To Kagaku Ryoho. 50:1099–1101. 2023.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li J, Ko JM, Dai W, Yu VZ, Ng HY, Hoffmann
JS and Lung ML: Depletion of DNA polymerase theta inhibits tumor
growth and promotes genome instability through the cGAS-STING-ISG
pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancers (Basel).
13:32042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Du J, Kageyama SI, Yamashita R, Hirata H,
Hakozaki Y, Okumura M, Motegi A, Hojo H, Nakamura M, Hirano Y, et
al: Impacts of the STING-IFNAR1-STAT1-IRF1 pathway on the cellular
immune reaction induced by fractionated irradiation. Cancer Sci.
113:1352–1361. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li X, Liu H, Gao W, Yang Q, Li X, Zhou X,
Wang L, Lu Z, Liu J, Luo A, et al: Octadecyl Gallate and
Lipid-modified MnSe2 nanoparticles enhance
radiosensitivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and promote
radioprotection in normal tissues. Adv Mater. 36:e23112912024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xia C, Dong X, Li H, Cao M, Sun D, He S,
Yang F, Yan X, Zhang S, Li N and Chen W: Cancer statistics in China
and United States, 2022: Profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin
Med J (Engl). 135:584–590. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu X, Xu L, Li X, Zhou Y, Han X, Zhang W,
Wang W, Guo W, Liu W, Xu Q and Gu Y: A HER2-targeting antibody-MMAE
conjugate RC48 sensitizes immunotherapy in HER2-positive colon
cancer by triggering the cGAS-STING pathway. Cell Death Dis.
14:5502023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang L, Luo R, Onyshchenko K, Rao X, Wang
M, Menz B, Gaedicke S, Grosu AL, Firat E and Niedermann G: Adding
liposomal doxorubicin enhances the abscopal effect induced by
radiation/αPD1 therapy depending on tumor cell mitochondrial DNA
and cGAS/STING. J Immunother Cancer. 11:e0062352023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen B, Hong Y, Zhai X, Deng Y, Hu H, Tian
S, Zhang Y, Ren X, Zhao J and Jiang C: m6A and m5C modification of
GPX4 facilitates anticancer immunity via STING activation. Cell
Death Dis. 14:8092023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mata-Garrido J, Frizzi L, Nguyen T, He X,
Chang-Marchand Y, Xiang Y, Reisacher C, Casafont I and Arbibe L:
HP1γ prevents activation of the cGAS/STING pathway by preserving
nuclear envelope and genomic integrity in colon adenocarcinoma
cells. Int J Mol Sci. 24:73472023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hu S, Fang Y, Chen X, Cheng T, Zhao M, Du
M, Li T, Li M, Zeng Z, Wei Y, et al: cGAS restricts colon cancer
development by protecting intestinal barrier integrity. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 118:e21057471182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wei B, Xu L, Guo W, Wang Y, Wu J, Li X,
Cai X, Hu J, Wang M, Xu Q, et al: SHP2-mediated inhibition of DNA
repair contributes to cGAS-STING activation and chemotherapeutic
sensitivity in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 81:3215–3228. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang M, Huang Y, Chen M, Wang W, Wu F,
Zhong T, Chen X, Wang F, Li Y, Yu J, et al: Inhibition of tumor
intrinsic BANF1 activates antitumor immune responses via cGAS-STING
and enhances the efficacy of PD-1 blockade. J Immunother Cancer.
11:e0070352023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kunac N, Degoricija M, Viculin J, Omerović
J, Terzić J, Vilović K and Korac-Prlic J: Activation of cGAS-STING
pathway is associated with MSI-H stage IV colorectal cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 15:2212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vornholz L, Isay SE, Kurgyis Z, Strobl DC,
Loll P, Mosa MH, Luecken MD, Sterr M, Lickert H, Winter C, et al:
Synthetic enforcement of STING signaling in cancer cells
appropriates the immune microenvironment for checkpoint inhibitor
therapy. Sci Adv. 9:eadd85642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zheng H, Wu L, Xiao Q, Meng X, Hafiz A,
Yan Q, Lu R and Cao J: Epigenetically suppressed tumor cell
intrinsic STING promotes tumor immune escape. Biomed Pharmacother.
157:1140332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Catalano C, da Silva Filho MI, Frank C, Lu
S, Jiraskova K, Vymetalkova V, Levy M, Liska V, Vycital O,
Naccarati A, et al: Epistatic effect of TLR3 and
cGAS-STING-IKKepsilon-TBK1-IFN signaling variants on colorectal
cancer risk. Cancer Med. 9:1473–1484. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tian J, Zhang D, Kurbatov V, Wang Q, Wang
Y, Fang D, Wu L, Bosenberg M, Muzumdar MD, Khan S, et al:
5-Fluorouracil efficacy requires anti-tumor immunity triggered by
cancer-cell-intrinsic STING. EMBO J. 40:e1060652021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liang B, Zhang EH, Ye Z, Storts H, Jin W,
Zheng X, Hylton H, Zaleski O, Xing X, Miles W and Wang JJ: SIX4
controls Anti-PD-1 efficacy by regulating STING expression. Cancer
Res Commun. 3:2412–2419. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang Y, Qi J, Hu J, Zhou Y, Zheng J, Deng
W, Inam M, Guo J, Xie Y, Li Y, et al: Lovastatin/SN38 co-loaded
liposomes amplified ICB therapeutic effect via remodeling the
immunologically-cold colon tumor and synergized stimulation of
cGAS-STING pathway. Cancer Lett. 588:2167652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Morehead LC, Garg S, Wallis KF, Simoes CC,
Siegel ER, Tackett AJ and Miousse IR: Increased response to immune
checkpoint inhibitors with dietary methionine restriction in a
colorectal cancer model. Cancers. 15:44672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xia J, Wang L, Shen T, Li P, Zhu P, Xie S,
Chen Z, Zhou F, Zhang J, Ling J, et al: Integrated manganese
(III)-doped nanosystem for optimizing photothermal ablation:
Amplifying hyperthermia-induced STING pathway and enhancing
antitumor immunity. Acta Biomater. 155:601–617. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ma J, Xin Y, Wang Q and Ding L: Roles of
cGAS-STING pathway in radiotherapy combined with immunotherapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 23:447–453. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li X, Pan YF, Chen YB, Wan QQ, Lin YK,
Shang TY, Xu MY, Jiang TY, Pei MM, Tan YX, et al: Arsenic trioxide
augments immunogenic cell death and induces cGAS-STING-IFN pathway
activation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 15:3002024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chen B, Rao X, Wang X, Luo Z, Wang J,
Sheng S, Liu Y, Zhang N, Jin S, Chen H, et al: cGAS-STING signaling
pathway and liver disease: From basic research to clinical
practice. Front Pharmacol. 12:7196442021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li K, Gong Y, Qiu D, Tang H, Zhang J, Yuan
Z, Huang Y, Qin Y, Ye L and Yang Y: Hyperbaric oxygen facilitates
Teniposide-induced cGAS-STING activation to enhance the antitumor
efficacy of PD-1 antibody in HCC. J Immunother Cancer.
10:e0040062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang X, Hu R, Song Z, Zhao H, Pan Z, Feng
Y, Yu Y, Han Q and Zhang J: Sorafenib combined with STAT3 knockdown
triggers ER stress-induced HCC apoptosis and cGAS-STING-mediated
anti-tumor immunity. Cancer Lett. 547:2158802022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ma H, Kang Z, Foo TK, Shen Z and Xia B:
Disrupted BRCA1-PALB2 interaction induces tumor immunosuppression
and T-lymphocyte infiltration in HCC through cGAS-STING pathway.
Hepatology. 77:33–47. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Du Q, Luo Y, Xu L, Du C, Zhang W, Xu J,
Liu Y, Liu B, Chen S, Wang Y, et al: Smart responsive Fe/Mn
nanovaccine triggers liver cancer immunotherapy via pyroptosis and
pyroptosis-boosted cGAS-STING activation. J Nanobiotechnol.
22:952024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Li Z, Zhang Y, Hong W, Wang B, Chen Y,
Yang P, Zhou J, Fan J, Zeng Z and Du S: Gut microbiota modulate
radiotherapy-associated antitumor immune responses against
hepatocellular carcinoma Via STING signaling. Gut Microbes.
14:21190552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cao Y, Sun T, Sun B, Zhang G, Liu J, Liang
B, Zheng C and Kan X: Injectable hydrogel loaded with lysed OK-432
and doxorubicin for residual liver cancer after incomplete
radiofrequency ablation. J Nanobiotechnol. 21:4042023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Sheng H, Huang Y, Xiao Y, Zhu Z, Shen M,
Zhou P, Guo Z, Wang J, Wang H, Dai W, et al: ATR inhibitor AZD6738
enhances the antitumor activity of radiotherapy and immune
checkpoint inhibitors by potentiating the tumor immune
microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer.
8:e0003402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hong W, Zhang Y, Wang S, Li Z, Zheng D,
Hsu S, Zhou J, Fan J, Chen Z, Xia X, et al: RECQL4 inhibits
radiation-induced tumor immune awakening via suppressing the
cGAS-STING pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Adv Sci (Weinh).
11:e23080092024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Thomsen MK, Skouboe MK, Boularan C,
Vernejoul F, Lioux T, Leknes SL, Berthelsen MF, Riedel M, Cai H,
Joseph JV, et al: The cGAS-STING pathway is a therapeutic target in
a preclinical model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene.
39:1652–1664. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Xu Y, Sun F, Tian Y, Zeng G, Lei G, Bai Z,
Wang Y, Ge X, Wang J, Xiao C, et al: Enhanced NK cell activation
via eEF2K-mediated potentiation of the cGAS-STING pathway in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int Immunopharmacol. 129:1116282024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sun F, Xu Y, Deng Z and Yang P: A
recombinant oncolytic influenza virus expressing a PD-L1 antibody
induces CD8+ T-cell activation via the cGas-STING
pathway in mice with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int Immunopharmacol.
120:1103232023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Fu L, Ding H, Bai Y, Cheng L, Hu S and Guo
Q: IDI1 inhibits the cGAS-Sting signaling pathway in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Heliyon. 10:e272052024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chen G, Zheng D, Zhou Y, Du S and Zeng Z:
Olaparib enhances radiation-induced systemic anti-tumor effects via
activating STING-chemokine signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer Lett. 582:2165072024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhao F, Liu A, Gong X, Chen H, Wei J, Chen
B, Chen S, Yang R, Fan Y and Mao R: Hypoxia-induced RNASEH2A limits
activation of cGAS-STING signaling in HCC and predicts poor
prognosis. Tumori. 108:63–76. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Qi Z, Yan F, Chen D, Xing W, Li Q, Zeng W,
Bi B and Xie J: Identification of prognostic biomarkers and
correlations with immune infiltrates among cGAS-STING in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Biosci Rep. 40:BSR202026032020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ma D, Yang M, Sun C, Cui X, Xiong G, Wang
Q, Jing W, Chen H, Lv X, Liu S, et al: cGAS suppresses
hepatocellular carcinoma independent of its cGAMP synthase
activity. Cell Death Differ. 31:722–737. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Sun B, Zhang Q, Sun T, Liu J, Cao Y, Liang
B, Zheng C and Kan X: Radiofrequency hyperthermia enhances the
effect of OK-432 for Hepatocellular carcinoma by activating of
TLR4-cGAS-STING pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 130:1117692024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wang S, Wu Q, Chen T, Su R, Pan C, Qian J,
Huang H, Yin S, Xie H, Zhou L and Zheng S: Blocking CD47 promotes
antitumour immunity through CD103+ dendritic cell-NK
cell axis in murine hepatocellular carcinoma model. J Hepatol.
77:467–478. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lv H, Zong Q, Chen C, Lv G, Xiang W, Xing
F, Jiang G, Yan B, Sun X, Ma Y, et al: TET2-mediated tumor cGAS
triggers endothelial STING activation to regulate vasculature
remodeling and anti-tumor immunity in liver cancer. Nat Commun.
15:62024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Su W, Gao W, Zhang R, Wang Q, Li L, Bu Q,
Xu Z, Liu Z, Wang M, Zhu Y, Wu G, et al: TAK1 deficiency promotes
liver injury and tumorigenesis via ferroptosis and macrophage
cGAS-STING signalling. JHEP Rep. 5:1006952023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Du SS, Chen GW, Yang P, Chen YX, Hu Y,
Zhao QQ, Zhang Y, Liu R, Zheng DX, Zhou J, et al: Radiation therapy
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma immune cloaking via PD-L1
Upregulation induced by cGAS-STING activation. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 112:1243–1255. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Huang S, Xie P, Huang X, Chen Z, Yang J,
Wang J, Liu C, Li H and Zhou B: Disulfiram combined with
chemoimmunotherapy potentiates pancreatic cancer treatment efficacy
through the activation of cGAS-STING signaling pathway via
suppressing PARP1 expression. Am J Cancer Res. 13:2055–2065.
2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Jacoberger-Foissac C, Cousineau I, Bareche
Y, Allard D, Chrobak P, Allard B, Pommey S, Messaoudi N, McNicoll
Y, Soucy G, et al: CD73 inhibits cGAS-STING and cooperates with
CD39 to promote pancreatic cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 11:56–71.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Oh G, Wang A, Wang L, Li J, Werba G,
Weissinger D, Zhao E, Dhara S, Hernandez RE, Ackermann A, et al:
POLQ inhibition elicits an immune response in homologous
recombination-deficient pancreatic adenocarcinoma via cGAS/STING
signaling. J Clin Invest. 133:e1659342023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kabashima A, Matsuo Y, Ito S, Akiyama Y,
Ishii T, Shimada S, Masamune A, Tanabe M and Tanaka S: cGAS-STING
signaling encourages immune cell overcoming of fibroblast
barricades in pancreatic cancer. Sci Rep. 12:104662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Wang SL, Wu Y, Konate M, Lu J, Mallick D,
Antony S, Meitzler JL, Jiang G, Dahan I, Juhasz A, et al: Exogenous
DNA enhances DUOX2 expression and function in human pancreatic
cancer cells by activating the cGAS-STING signaling pathway. Free
Radic Biol Med. 205:262–274. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Lin S: DTX3L mediated ubiquitination of
cGAS suppresses antitumor immunity in pancreatic cancer. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 681:106–110. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Yousef A, Yousef M, Zeineddine MA, More A,
Fanaeian M, Chowdhury S, Knafl M, Edelkamp P, Ito I, Gu Y, et al:
Serum tumor markers and outcomes in patients with appendiceal
adenocarcinoma. JAMA Netw Open. 7:e2402602024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Li R, Wang J, Xie Z, Tian X, Hou J, Wang
D, Qian H, Shen H and Xu W: CircUSP1 as a novel marker promotes
gastric cancer progression via stabilizing HuR to upregulate USP1
and Vimentin. Oncogene. 43:1033–1049. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Tian Y, Wang Y, Wen N, Wang S, Li B and
Liu G: Prognostic factors associated with early recurrence
following liver resection for colorectal liver metastases: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 24:4262024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|