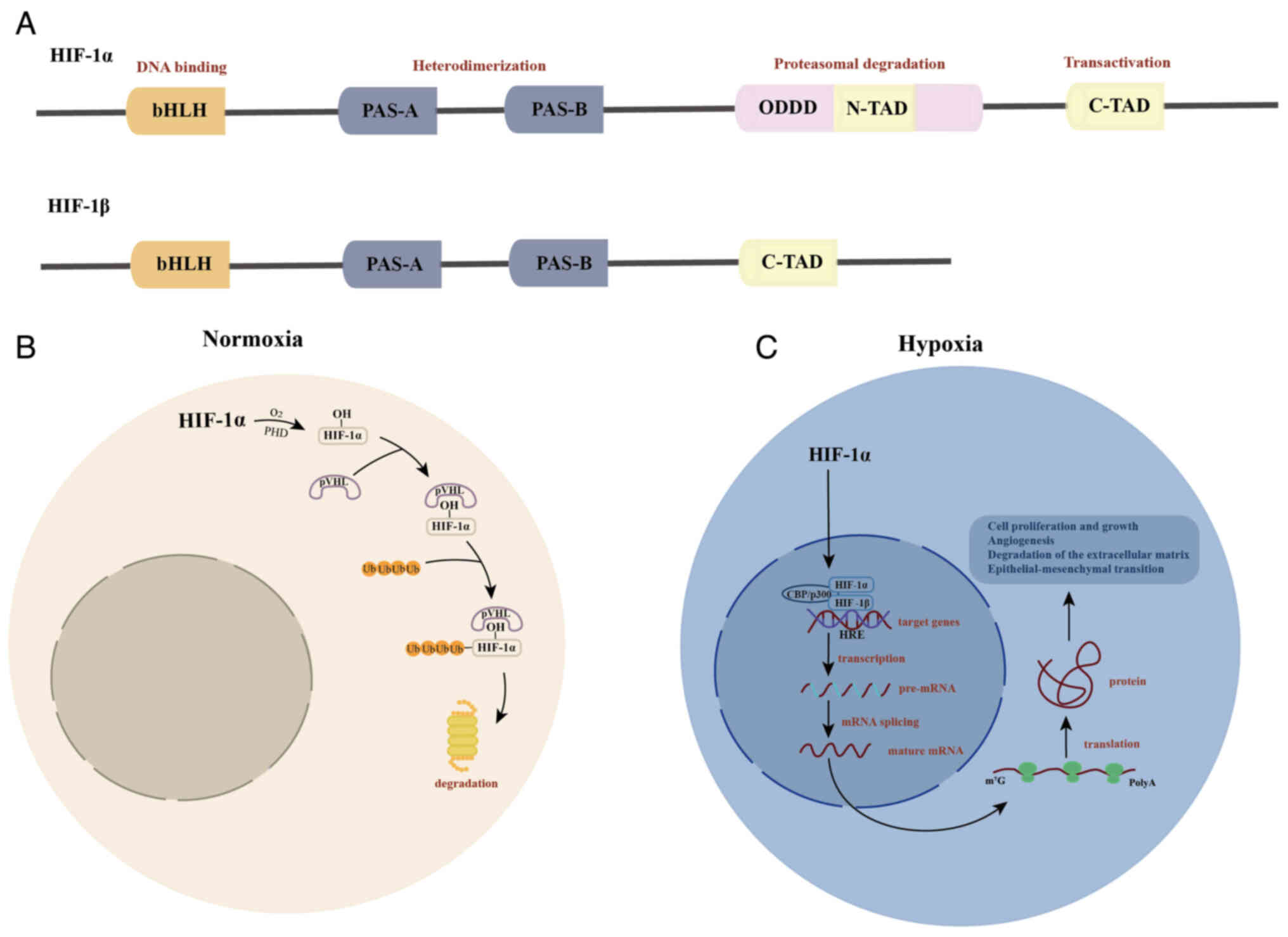
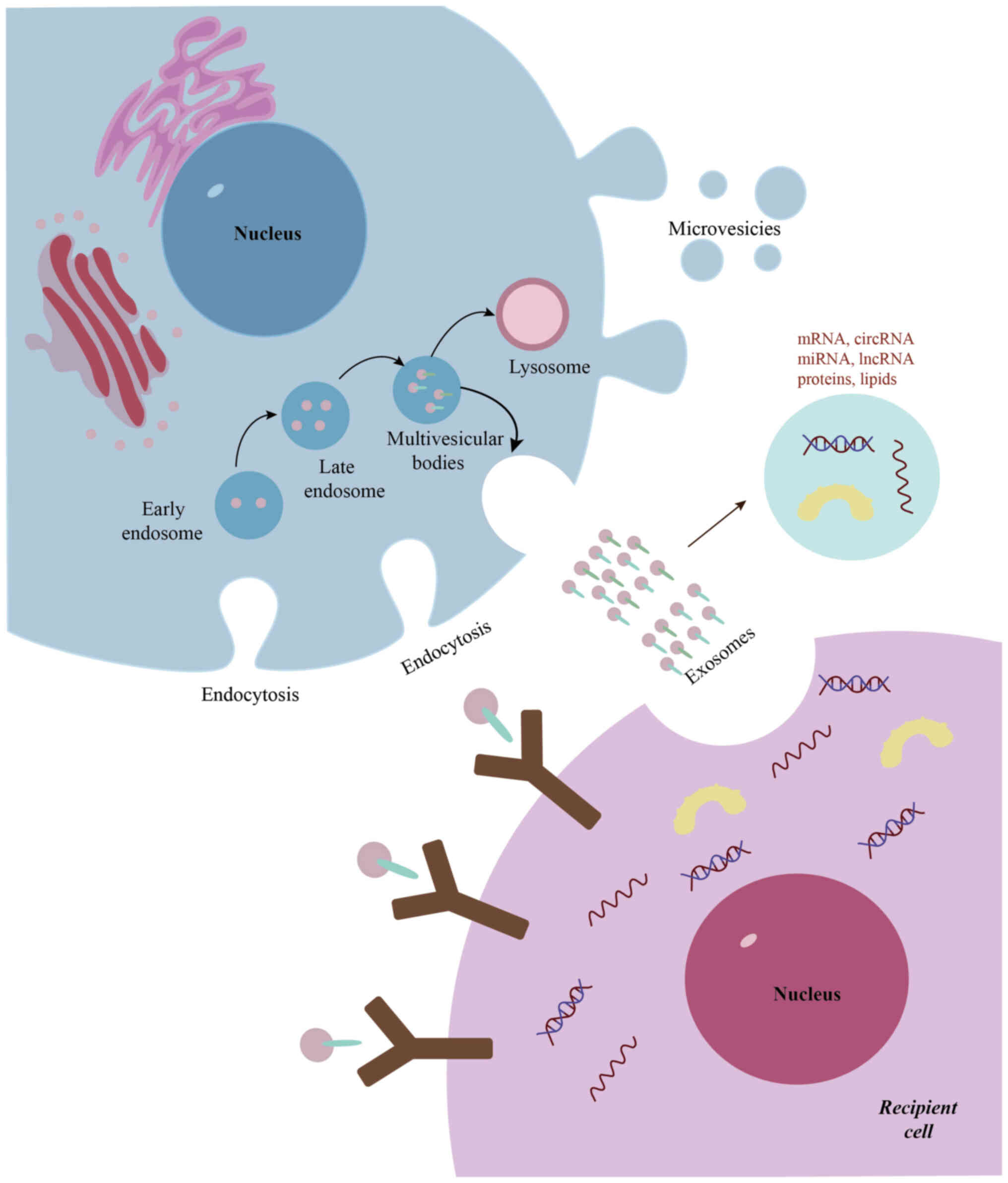
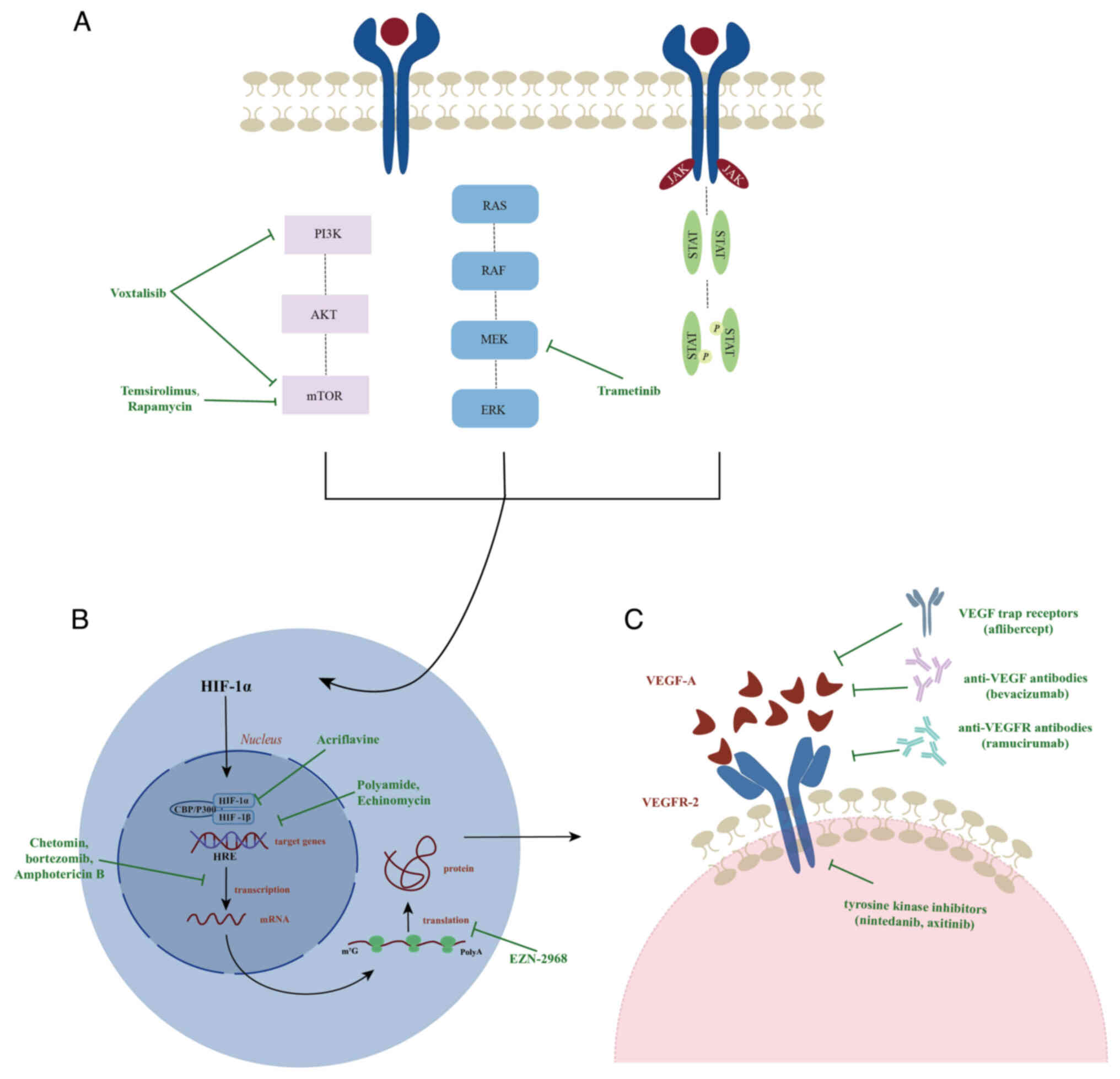
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Steeg PS: Targeting metastasis. Nat Rev
Cancer. 16:201–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 72:7–33. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xu FX, Zhang YL, Liu JJ, Zhang DD and Chen
HB: Hypoxic markers in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)-A review.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:849–852. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Saxena K and Jolly MK: Acute vs. chronic
vs. cyclic hypoxia: Their differential dynamics, molecular
mechanisms, and effects on tumor progression. Biomolecules.
9:3392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bertout JA, Patel SA and Simon MC: The
impact of O2 availability on human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:967–975. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Meng X, Kong FM and Yu J: Implementation
of hypoxia measurement into lung cancer therapy. Lung Cancer.
75:146–150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Challapalli A, Carroll L and Aboagye EO:
Molecular mechanisms of hypoxia in cancer. Clin Transl Imaging.
5:225–253. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hinshaw DC and Shevde LA: The tumor
microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression. Cancer Res.
79:4557–4566. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Desai P, Takahashi N, Kumar R, Nichols S,
Malin J, Hunt A, Schultz C, Cao Y, Tillo D, Nousome D, et al:
Microenvironment shapes small-cell lung cancer neuroendocrine
states and presents therapeutic opportunities. Cell Rep Med.
5:1016102024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tam FF, Ning KL, Lee M, Dumlao JM and Choy
JC: Cytokine induction of HIF-1α during normoxia in A549 human lung
carcinoma cells is regulated by STAT1 and JNK signalling pathways.
Mol Immunol. 160:12–19. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tirpe AA, Gulei D, Ciortea SM, Crivii C
and Berindan-Neagoe I: Hypoxia: Overview on hypoxia-mediated
mechanisms with a focus on the role of HIF genes. Int J Mol Sci.
20:61402019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rankin EB and Giaccia AJ: The role of
hypoxia-inducible factors in tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ.
15:678–685. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Masoud GN and Li W: HIF-1α pathway: Role,
regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B.
5:378–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Della Rocca Y, Fonticoli L, Rajan TS,
Trubiani O, Caputi S, Diomede F, Pizzicannella J and Marconi GD:
Hypoxia: molecular pathophysiological mechanisms in human diseases.
J Physiol Biochem. 78:739–752. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zeng SG, Lin X, Liu JC and Zhou J:
Hypoxia-induced internalization of connexin 26 and connexin 43 in
pulmonary epithelial cells is involved in the occurrence of
non-small cell lung cancer via the P53/MDM2 signaling pathway. Int
J Oncol. 55:845–859. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hapke RY and Haake SM: Hypoxia-induced
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in cancer. Cancer Lett.
487:10–20. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Musleh Ud Din S, Streit SG, Huynh BT, Hana
C, Abraham AN and Hussein A: Therapeutic targeting of
hypoxia-inducible factors in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 25:20602024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu S, Zhan Y, Luo J, Feng J, Lu J, Zheng
H, Wen Q and Fan S: Roles of exosomes in the carcinogenesis and
clinical therapy of non-small cell lung cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 111:338–346. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang C, Xu S and Yang X: Hypoxia-driven
changes in tumor microenvironment: Insights into exosome-mediated
cell interactions. Int J Nanomedicine. 19:8211–8236. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Luo W, Hu H, Chang R, Zhong J, Knabel M,
O'Meally R, Cole RN, Pandey A and Semenza GL: Pyruvate kinase M2 is
a PHD3-stimulated coactivator for hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell.
145:732–744. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wei Y, Wang D, Jin F, Bian Z, Li L, Liang
H, Li M, Shi L, Pan C, Zhu D, et al: Pyruvate kinase type M2
promotes tumour cell exosome release via phosphorylating
synaptosome-associated protein 23. Nat Commun. 8:140412017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ji X, Zhu R, Gao C, Xie H, Gong X and Luo
J: Hypoxia-derived exosomes promote lung adenocarcinoma by
regulating HS3ST1-GPC4-mediated glycolysis. Cancers (Basel).
16:6952024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang H, Zhao H, Zhang M, He Y, Li X, Xu Y
and Liu X: Hypoxia induced changes of exosome cargo and subsequent
biological effects. Front Immunol. 13:8241882022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang S, Wang R, Yan H, Jin L, Dou X and
Chen D: MicroRNA-21 modulates radiation resistance through
upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-promoted glycolysis in
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 13:4101–4107. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Becker V, Yuan X, Boewe AS, Ampofo E,
Ebert E, Hohneck J, Bohle RM, Meese E, Zhao Y, Menger MD, et al:
Hypoxia-induced downregulation of microRNA-186-5p in endothelial
cells promotes non-small cell lung cancer angiogenesis by
upregulating protein kinase C alpha. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
31:421–436. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao J, Qiao CR, Ding Z, Sheng YL, Li XN,
Yang Y, Zhu DY, Zhang CY, Liu DL, Wu K and Zhao S: A novel pathway
in NSCLC cells: miR-191, targeting NFIA, is induced by chronic
hypoxia, and promotes cell proliferation and migration. Mol Med
Rep. 15:1319–1325. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang C, Han C, Zhang Y and Liu F: LncRNA
PVT1 regulate expression of HIF1α via functioning as ceRNA for
miR-199a-5p in non-small cell lung cancer under hypoxia. Mol Med
Rep. 17:1105–1110. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ren J: Intermittent hypoxia BMSCs-derived
exosomal miR-31-5p promotes lung adenocarcinoma development via
WDR5-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition. Sleep Breath.
27:1399–1409. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yin HL, Xu HW and Lin QY: miR129-1
regulates protein phosphatase 1D protein expression under hypoxic
conditions in non-small cell lung cancer cells harboring a TP53
mutation. Oncol Lett. 20:2239–2247. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leone RD and Powell JD: Metabolism of
immune cells in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 20:516–531. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu Z, Zou J and Xu F: Tumor-associated
macrophages affect the treatment of lung cancer. Heliyon.
10:e293322024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jin J and Yu G: Hypoxic lung cancer
cell-derived exosomal miR-21 mediates macrophage M2 polarization
and promotes cancer cell proliferation through targeting IRF1.
World J Surg Oncol. 20:2412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gu J, Yang S, Wang X, Wu Y, Wei J and Xu
J: Hypoxic lung adenocarcinoma-derived exosomal miR-1290 induces M2
macrophage polarization by targeting SOCS3. Cancer Med.
12:12639–12652. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jackson AL, Zhou B and Kim WY: HIF,
hypoxia and the role of angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 14:1047–1057. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Eales KL, Hollinshead KER and Tennant DA:
Hypoxia and metabolic adaptation of cancer cells. Oncogenesis.
5:e1902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dai E, Wang W and Li Y, Ye D and Li Y:
Lactate and lactylation: Behind the development of tumors. Cancer
Lett. 591:2168962024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Courtnay R, Ngo DC, Malik N, Ververis K,
Tortorella SM and Karagiannis TC: Cancer metabolism and the Warburg
effect: the role of HIF-1 and PI3K. Mol Biol Rep. 42:841–851. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Luo F, Liu X, Yan N, Li S, Cao G, Cheng Q,
Xia Q and Wang H: Hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1α
promotes hypoxia-induced A549 apoptosis via a mechanism that
involves the glycolysis pathway. BMC Cancer. 6:262006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shang S, Wang MZ, Xing Z, He N and Li S:
Lactate regulators contribute to tumor microenvironment and predict
prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Front Immunol. 13:10249252022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nisar H, Sanchidrián González PM, Brauny
M, Labonté FM, Schmitz C, Roggan MD, Konda B and Hellweg CE:
Hypoxia changes energy metabolism and growth rate in non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Cancers (Basel). 15:24722023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Guo Z, Hu L, Wang Q, Wang Y, Liu XP, Chen
C, Li S and Hu W: Molecular characterization and prognosis of
lactate-related genes in lung adenocarcinoma. Curr Oncol.
30:2845–2861. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang X, Liang C, Wu C, Wan S and Xu L,
Wang S, Wang J, Huang X and Xu L: A rising star involved in tumour
immunity: Lactylation. J Cell Mol Med. 28:e701462024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang C, Zhou L, Zhang M, Du Y, Li C, Ren
H and Zheng L: H3K18 lactylation potentiates immune escape of
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 84:3589–3601. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Porporato PE, Filigheddu N, Pedro JMB,
Kroemer G and Galluzzi L: Mitochondrial metabolism and cancer. Cell
Res. 28:265–280. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Brustugun OT: Hypoxia as a cause of
treatment failure in non-small cell carcinoma of the lung. Semin
Radiat Oncol. 25:87–92. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Huang RX and Zhou PK: DNA damage response
signaling pathways and targets for radiotherapy sensitization in
cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen H, Han Z, Luo Q, Wang Y, Li Q, Zhou L
and Zuo H: Radiotherapy modulates tumor cell fate decisions: A
review. Radiat Oncol. 17:1962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gong L, Zhang Y, Liu C, Zhang M and Han S:
Application of radiosensitizers in cancer radiotherapy. Int J
Nanomedicine. 16:1083–1102. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhou T, Zhang LY, He JZ, Miao ZM, Li YY,
Zhang YM, Liu ZW, Zhang SZ, Chen Y, Zhou GC and Liu YQ: Review:
Mechanisms and perspective treatment of radioresistance in
non-small cell lung cancer. Front Immunol. 14:11338992023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gray LH, Conger AD, Ebert M, Hornsey S and
Scott OC: The concentration of oxygen dissolved in tissues at the
time of irradiation as a factor in radiotherapy. Br J Radiol.
26:638–648. 1953. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Herrera-Campos AB, Zamudio-Martinez E,
Delgado-Bellido D, Fernández-Cortés M, Montuenga LM, Oliver FJ and
Garcia-Diaz A: Implications of hyperoxia over the tumor
microenvironment: An overview highlighting the importance of the
immune system. Cancers (Basel). 14:27402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Guo Q, Lan F, Yan X, Xiao Z, Wu Y and
Zhang Q: Hypoxia exposure induced cisplatin resistance partially
via activating p53 and hypoxia inducible factor-1α in non-small
cell lung cancer A549 cells. Oncol Lett. 16:801–808.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Roy S, Kumaravel S, Sharma A, Duran CL,
Bayless KJ and Chakraborty S: Hypoxic tumor microenvironment:
Implications for cancer therapy. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
245:1073–1086. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hu CY, Hung CF, Chen PC, Hsu JY, Wang CT,
Lai MD, Tsai YS, Shiau AL, Shieh GS and Wu CL: Oct4 and hypoxia
dual-regulated oncolytic adenovirus armed with shRNA-targeting
dendritic cell immunoreceptor exerts potent antitumor activity
against bladder cancer. Biomedicines. 11:25982023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mancino A, Schioppa T, Larghi P,
Pasqualini F, Nebuloni M, Chen IH, Sozzani S, Austyn JM, Mantovani
A and Sica A: Divergent effects of hypoxia on dendritic cell
functions. Blood. 112:3723–3734. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Peng X, He Y, Huang J, Tao Y and Liu S:
Metabolism of dendritic cells in tumor microenvironment: For
immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 12:6134922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Eltzschig HK, Thompson LF, Karhausen J,
Cotta RJ, Ibla JC, Robson SC and Colgan SP: Endogenous adenosine
produced during hypoxia attenuates neutrophil accumulation:
Coordination by extracellular nucleotide metabolism. Blood.
104:3986–3992. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li J, Wang L, Chen X, Li L, Li Y, Ping Y,
Huang L, Yue D, Zhang Z, Wang F, et al: CD39/CD73 upregulation on
myeloid-derived suppressor cells via TGF-β-mTOR-HIF-1 signaling in
patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncoimmunology.
6:e13200112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
An SM, Lei HM, Ding XP, Sun F, Zhang C,
Tang YB, Chen HZ, Shen Y and Zhu L: Interleukin-6 identified as an
important factor in hypoxia- and aldehyde dehydrogenase-based
gefitinib adaptive resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Oncol Lett. 14:3445–3454. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kogita A, Togashi Y, Hayashi H, Sogabe S,
Terashima M, De Velasco MA, Sakai K, Fujita Y, Tomida S, Takeyama
Y, et al: Hypoxia induces resistance to ALK inhibitors in the H3122
non-small cell lung cancer cell line with an ALK rearrangement via
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Oncol. 45:1430–1436. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Karan S, Cho MY, Lee H, Lee H, Park HS,
Sundararajan M, Sessler JL and Hong KS: Near-infrared fluorescent
probe activated by nitroreductase for in vitro and in vivo hypoxic
tumor detection. J Med Chem. 64:2971–2981. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Cheng MHY, Mo Y and Zheng G: Nano versus
molecular: Optical imaging approaches to detect and monitor tumor
hypoxia. Adv Healthc Mater. 10:e20015492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Clark LC Jr, Wolf R, Granger D and Taylor
Z: Continuous recording of blood oxygen tensions by polarography. J
Appl Physiol. 6:189–193. 1953. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sun X, Niu G, Chan N, Shen B and Chen X:
Tumor hypoxia imaging. Mol Imaging Biol. 13:399–410. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Shirmanova MV, Lukina MM, Sirotkina MA,
Shimolina LE, Dudenkova VV, Ignatova NI, Tobita S, Shcheslavskiy VI
and Zagaynova EV: Effects of photodynamic therapy on tumor
metabolism and oxygenation revealed by fluorescence and
phosphorescence lifetime imaging. Int J Mol Sci. 25:17032024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Vanderkooi JM, Maniara G, Green TJ and
Wilson DF: An optical method for measurement of dioxygen
concentration based upon quenching of phosphorescence. J Biol Chem.
262:5476–5482. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Koch CJ and Evans SM: Optimizing hypoxia
detection and treatment strategies. Semin Nucl Med. 45:163–176.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Horsman MR, Sørensen BS, Busk M and
Siemann DW: Therapeutic modification of hypoxia. Clin Oncol (R Coll
Radiol). 33:e492–e509. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Huang C, Liang J, Lei X, Xu X, Xiao Z and
Luo L: Diagnostic performance of perfusion computed tomography for
differentiating lung cancer from benign lesions: A meta-analysis.
Med Sci Monit. 25:3485–3494. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Hu X, Gou J, Wang L, Lin W, Li W and Yang
F: Diagnostic accuracy of low-dose dual-input computed tomography
perfusion in the differential diagnosis of pulmonary benign and
malignant ground-glass nodules. Sci Rep. 14:170982024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Liao C, Liu X, Zhang C and Zhang Q: Tumor
hypoxia: From basic knowledge to therapeutic implications. Semin
Cancer Biol. 88:172–186. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Nasri D, Manwar R, Kaushik A, Er EE and
Avanaki K: Photoacoustic imaging for investigating tumor hypoxia: A
strategic assessment. Theranostics. 13:3346–3367. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Krohn KA, Link JM and Mason RP: Molecular
imaging of hypoxia. J Nucl Med. 49 (Suppl 2):129S–148S. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Brender JR, Saida Y, Devasahayam N,
Krishna MC and Kishimoto S: Hypoxia imaging as a guide for
hypoxia-modulated and hypoxia-activated therapy. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 36:144–159. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Godet I, Doctorman S, Wu F and Gilkes DM:
Detection of hypoxia in cancer models: Significance, challenges,
and advances. Cells. 11:6862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Matsumoto K, Mitchell JB and Krishna MC:
Multimodal functional imaging for cancer/tumor microenvironments
based on MRI, EPRI, and PET. Molecules. 26:16142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Qin W, Xu C, Zhao Y, Yu C, Shen S, Li L
and Huang W: Recent progress in small molecule fluorescent probes
for nitroreductase. Chin Chem Lett. 29:1451–1455. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Vikram DS, Zweier JL and Kuppusamy P:
Methods for noninvasive imaging of tissue hypoxia. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 9:1745–1756. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Epel B, Bowman MK, Mailer C and Halpern
HJ: Absolute oxygen R1e imaging in vivo with pulse electron
paramagnetic resonance. Magn Reson Med. 72:362–368. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Hao B, Dong H, Xiong R, Song C, Xu C, Li N
and Geng Q: Identification of SLC2A1 as a predictive biomarker for
survival and response to immunotherapy in lung squamous cell
carcinoma. Comput Biol Med. 171:1081832024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhang R, Lai L, He J, Chen C, You D, Duan
W, Dong X, Zhu Y, Lin L, Shen S, et al: EGLN2 DNA methylation and
expression interact with HIF1A to affect survival of early-stage
NSCLC. Epigenetics. 14:118–129. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ostheimer C, Bache M, Güttler A, Kotzsch M
and Vordermark D: A pilot study on potential plasma hypoxia markers
in the radiotherapy of non-small cell lung cancer. Osteopontin,
carbonic anhydrase IX and vascular endothelial growth factor.
Strahlenther Onkol. 190:276–282. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Giatromanolaki A, Harris AL, Banham AH,
Contrafouris CA and Koukourakis MI: Carbonic anhydrase 9 (CA9)
expression in non-small-cell lung cancer: Correlation with
regulatory FOXP3+T-cell tumour stroma infiltration. Br J Cancer.
122:1205–1210. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Geng H, Chen L, Lv S, Li M, Huang X, Li M
and Liu C and Liu C: Photochemically controlled release of the
glucose transporter 1 inhibitor for glucose deprivation responses
and cancer suppression research. J Proteome Res. 23:653–662. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Kim SJ, Rabbani ZN, Vollmer RT, Schreiber
EG, Oosterwijk E, Dewhirst MW, Vujaskovic Z and Kelley MJ: Carbonic
anhydrase IX in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 10:7925–7933. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Coppola D, Szabo M, Boulware D, Muraca P,
Alsarraj M, Chambers AF and Yeatman TJ: Correlation of osteopontin
protein expression and pathological stage across a wide variety of
tumor histologies. Clin Cancer Res. 10((1 Pt 1)): 184–190. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Ostheimer C, Bache M, Güttler A, Reese T
and Vordermark D: Prognostic information of serial plasma
osteopontin measurement in radiotherapy of non-small-cell lung
cancer. BMC Cancer. 14:8582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Stępień K, Ostrowski RP and Matyja E:
Hyperbaric oxygen as an adjunctive therapy in treatment of
malignancies, including brain tumours. Med Oncol. 33:1012016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Kim SW, Kim IK, Ha JH, Yeo CD, Kang HH,
Kim JW and Lee SH: Normobaric hyperoxia inhibits the progression of
lung cancer by inducing apoptosis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
243:739–748. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Thews O and Vaupel P: Spatial oxygenation
profiles in tumors during normo- and hyperbaric hyperoxia.
Strahlenther Onkol. 191:875–882. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Heyboer M III, Sharma D, Santiago W and
McCulloch N: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: Side effects defined and
quantified. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 6:210–224. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Jones LW, Viglianti BL, Tashjian JA,
Kothadia SM, Keir ST, Freedland SJ, Potter MQ, Moon EJ, Schroeder
T, Herndon JE II and Dewhirst MW: Effect of aerobic exercise on
tumor physiology in an animal model of human breast cancer. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 108:343–348. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Jo S, Jeon J, Park G, Do HK, Kang J, Ahn
KJ, Ma SY, Choi YM, Kim D, Youn B and Ki Y: Aerobic exercise
improves radiation therapy efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer:
Preclinical study using a xenograft mouse model. Int J Mol Sci.
25:27572024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Ghosh P, Vidal C, Dey S and Zhang L:
Mitochondria targeting as an effective strategy for cancer therapy.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:33632020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Ashton TM, McKenna WG, Kunz-Schughart LA
and Higgins GS: Oxidative phosphorylation as an emerging target in
cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 24:2482–2490. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Kalyanaraman B, Cheng G, Hardy M and You
M: OXPHOS-targeting drugs in oncology: New perspectives. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 27:939–952. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Shameem M, Bagherpoor AJ, Nakhi A, Dosa P,
Georg G and Kassie F: Mitochondria-targeted metformin (mitomet)
inhibits lung cancer in cellular models and in mice by enhancing
the generation of reactive oxygen species. Mol Carcinog.
62:1619–1629. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Skwarski M, McGowan DR, Belcher E, Di
Chiara F, Stavroulias D, McCole M, Derham JL, Chu KY, Teoh E,
Chauhan J, et al: Mitochondrial inhibitor atovaquone increases
tumor oxygenation and inhibits hypoxic gene expression in patients
with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 27:2459–2469.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Benej M, Hong X, Vibhute S, Scott S, Wu J,
Graves E, Le QT, Koong AC, Giaccia AJ, Yu B, et al: Papaverine and
its derivatives radiosensitize solid tumors by inhibiting
mitochondrial metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:10756–10761.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Sohoni S, Ghosh P, Wang T, Kalainayakan
SP, Vidal C, Dey S, Konduri PC and Zhang L: Elevated heme synthesis
and uptake underpin intensified oxidative metabolism and
tumorigenic functions in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 79:2511–2525. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Wang T, Ashrafi A, Konduri PC, Ghosh P,
Dey S, Modareszadeh P, Salamat N, Alemi PS, Berisha E and Zhang L:
Heme sequestration as an effective strategy for the suppression of
tumor growth and progression. Mol Cancer Ther. 20:2506–2518. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Dewhirst MW and Secomb TW: Transport of
drugs from blood vessels to tumour tissue. Nat Rev Cancer.
17:738–750. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Sukhatme V, Bouche G, Meheus L, Sukhatme
VP and Pantziarka P: Repurposing drugs in oncology
(ReDO)-nitroglycerin as an anti-cancer agent.
Ecancermedicalscience. 9:5682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Reymen BJT, van Gisbergen MW, Even AJG,
Zegers CML, Das M, Vegt E, Wildberger JE, Mottaghy FM, Yaromina A,
Dubois LJ, et al: Nitroglycerin as a radiosensitizer in non-small
cell lung cancer: Results of a prospective imaging-based phase II
trial. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 21:49–55. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Wong PP, Bodrug N and Hodivala-Dilke KM:
Exploring novel methods for modulating tumor blood vessels in
cancer treatment. Curr Biol. 26:R1161–R1166. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Guelfi S, Hodivala-Dilke K and Bergers G:
Targeting the tumour vasculature: From vessel destruction to
promotion. Nat Rev Cancer. 24:655–675. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Wigerup C, Påhlman S and Bexell D:
Therapeutic targeting of hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in
cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 164:152–169. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Xia Y, Choi HK and Lee K: Recent advances
in hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem.
49:24–40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Iommarini L, Porcelli AM, Gasparre G and
Kurelac I: Non-canonical mechanisms regulating hypoxia-inducible
factor 1 alpha in cancer. Front Oncol. 7:2862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Albadari N, Deng S and Li W: The
transcriptional factors HIF-1 and HIF-2 and their novel inhibitors
in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 14:667–682. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Ma J, Cao K, Ling X, Zhang P and Zhu J:
LncRNA HAR1A suppresses the development of non-small cell lung
cancer by inactivating the STAT3 pathway. Cancers (Basel).
14:28452022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Deng H, Chen Y, Li P, Hang Q, Zhang P, Jin
Y and Chen M: PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, hypoxia, and glucose
metabolism: Potential targets to overcome radioresistance in small
cell lung cancer. Cancer Pathog Ther. 1:56–66. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Lara MS, Blakely CM and Riess JW:
Targeting MEK in non-small cell lung cancer. Curr Probl Cancer.
49:1010652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zhu H and Zhang S: Hypoxia inducible
factor-1α/vascular endothelial growth factor signaling activation
correlates with response to radiotherapy and its inhibition reduces
hypoxia-induced angiogenesis in lung cancer. J Cell Biochem.
119:7707–7718. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Tian W, Cao C, Shu L and Wu F:
Anti-angiogenic therapy in the treatment of non-small cell lung
cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 13:12113–12129. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Mahdi A, Darvishi B, Majidzadeh-A K,
Salehi M and Farahmand L: Challenges facing antiangiogenesis
therapy: The significant role of hypoxia-inducible factor and MET
in development of resistance to anti-vascular endothelial growth
factor-targeted therapies. J Cell Physiol. 234:5655–5663. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Yuan X, Xie Z and Zou T: Recent advances
in hypoxia-activated compounds for cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Bioorg Chem. 144:1071612024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Bryant JL, Meredith SL, Williams KJ and
White A: Targeting hypoxia in the treatment of small cell lung
cancer. Lung Cancer. 86:126–132. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Wilson WR and Hay MP: Targeting hypoxia in
cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:393–410. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Chen SX, Zhang J, Xue F, Liu W, Kuang Y,
Gu B, Song S and Chen H: In situ forming oxygen/ROS-responsive
niche-like hydrogel enabling gelation-triggered chemotherapy and
inhibition of metastasis. Bioact Mater. 21:86–96. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Shepherd F, Koschel G, Von Pawel J,
Gatzmeier U, Van Zandwiyk N, Woll P, Van Klavren R, Krasko P,
Desimone P, Nicolson M, et al: Comparison of Tirazone
(Tirapazamine) and cisplatin vs. etoposide and cisplatin in
advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Final results of the
International phase III CATAPULT II trial. Lung Cancer. 29:282000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Marcu L and Olver I: Tirapazamine: From
bench to clinical trials. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 1:71–79. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Graham K and Unger E: Overcoming tumor
hypoxia as a barrier to radiotherapy, chemotherapy and
immunotherapy in cancer treatment. Int J Nanomedicine.
13:6049–6058. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Lindsay D, Garvey CM, Mumenthaler SM and
Foo J: Leveraging hypoxia-activated prodrugs to prevent drug
resistance in solid tumors. PLoS Comput Biol. 12:e10050772016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Meaney C, Powathil GG, Yaromina A, Dubois
LJ, Lambin P and Kohandel M: Role of hypoxia-activated prodrugs in
combination with radiation therapy: An in silico approach. Math
Biosci Eng. 16:6257–6273. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Oronsky BT, Knox SJ and Scicinski JJ: Is
nitric oxide (NO) the last word in radiosensitization? A review.
Transl Oncol. 5:66–71. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Oronsky B, Scicinski J, Ning S, Peehl D,
Oronsky A, Cabrales P, Bednarski M and Knox S: RRx-001, A novel
dinitroazetidine radiosensitizer. Invest New Drugs. 34:371–377.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Zhao L, Li M, Shen C and Luo Y, Hou X, Qi
Y, Huang Z, Li W, Gao L, Wu M and Luo Y: Nano-assisted radiotherapy
strategies: New opportunities for treatment of non-small cell lung
cancer. Research (Wash D C). 7:04292024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Chen Y, Zhou Y, Feng X, Wu Z, Yang Y, Rao
X, Zhou R, Meng R, Dong X, Xu S, et al: Targeting FBXO22 enhances
radiosensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting the
FOXM1/Rad51 axis. Cell Death Dis. 15:1042024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Dey P, Das R, Chatterjee S, Paul R and
Ghosh U: Combined effects of carbon ion radiation and PARP
inhibitor on non-small cell lung carcinoma cells: Insights into DNA
repair pathways and cell death mechanisms. DNA Repair (Amst).
144:1037782024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Demizu Y, Fujii O, Iwata H and Fuwa N:
Carbon ion therapy for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer.
Biomed Res Int. 2014:7279622014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Bentzen SM and Gregoire V:
Molecular-imaging-based dose painting: A novel paradigm for
radiation therapy prescription. Semin Radiat Oncol. 21:101–110.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Meijer G, Steenhuijsen J, Bal M, De Jaeger
K, Schuring D and Theuws J: Dose painting by contours versus dose
painting by numbers for stage II/III lung cancer: Practical
implications of using a broad or sharp brush. Radiother Oncol.
100:396–401. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|