|
1
|
Becker T, Gerke V, Kube E and Weber K:
S100P, a novel Ca(2+)-binding protein from human placenta. cDNA
cloning, recombinant protein expression and Ca2+ binding
properties. Eur J Biochem. 207:541–547. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zimmer DB, Eubanks JO, Ramakrishnan D and
Criscitiello MF: Evolution of the S100 family of calcium sensor
proteins. Cell Calcium. 53:170–179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gonzalez LL, Garrie K and Turner MD: Role
of S100 proteins in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol
Cell Res. 1867:1186772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sapkota D, Costea DE, Blø M, Bruland O,
Lorens JB, Vasstrand EN and Ibrahim SO: S100A14 inhibits
proliferation of oral carcinoma derived cells through G1-arrest.
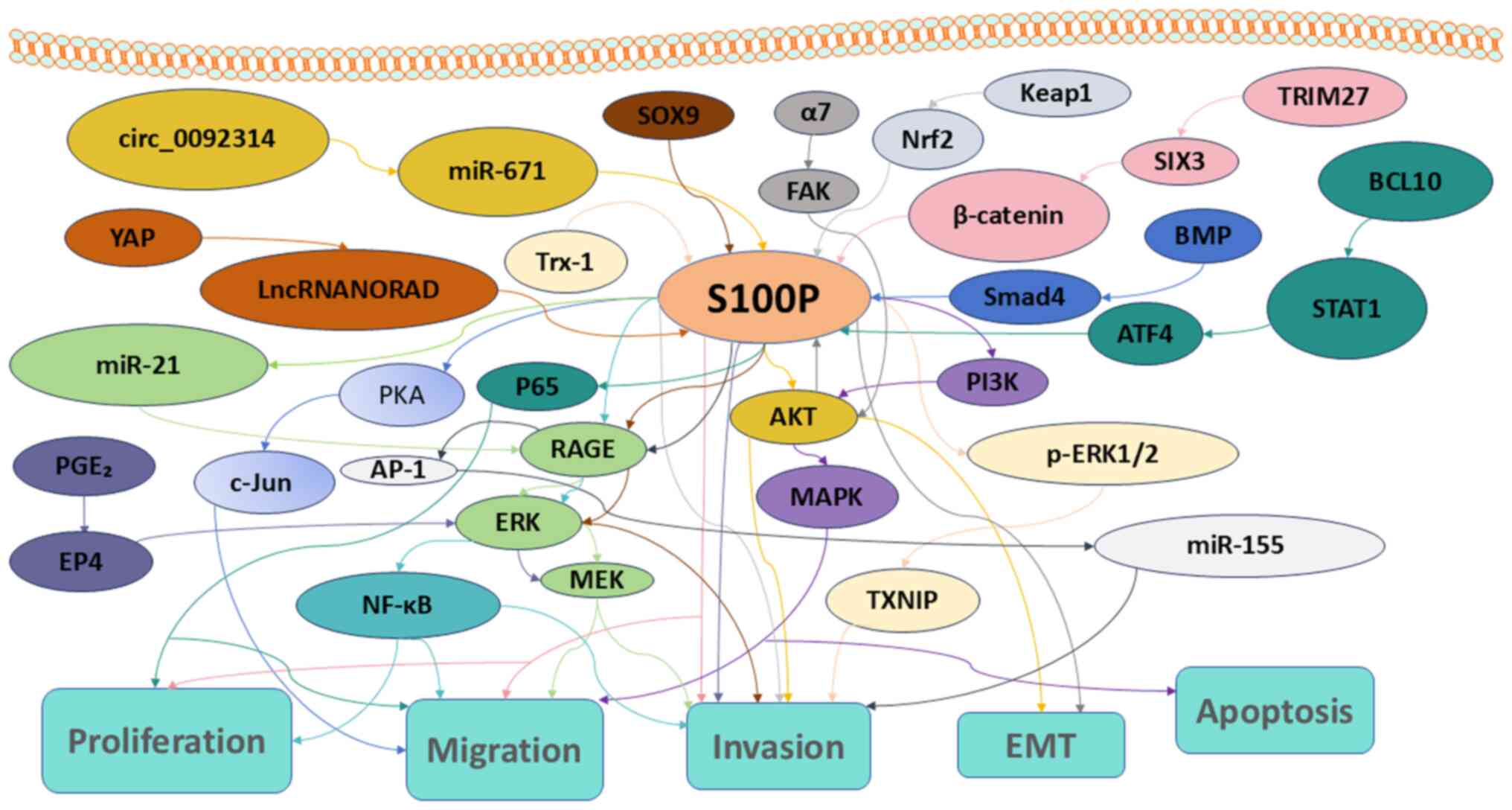
Oral Oncol. 48:219–225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang H, Wang G, Ding Y, Wang Z,
Barraclough R, Rudland PS, Fernig DG and Rao Z: The crystal
structure at 2A resolution of the Ca2+ -binding protein S100P. J
Mol Biol. 325:785–779. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Donato R: S100: A multigenic family of
calcium-modulated proteins of the EF-hand type with intracellular
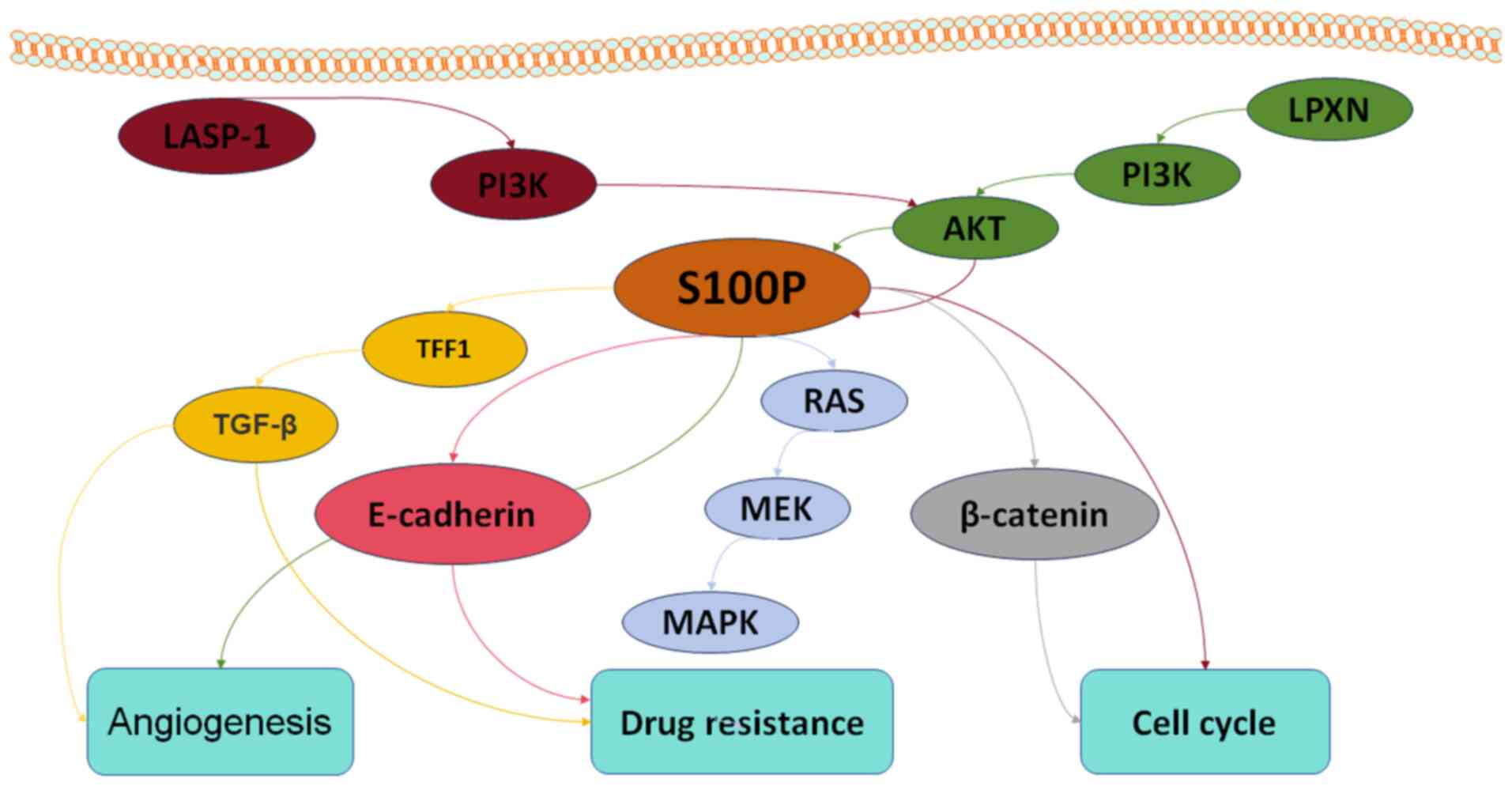
and extracellular functional roles. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
33:637–668. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shang X, Cheng H and Zhou R: Chromosomal
mapping, differential origin and evolution of the S100 gene family.
Genet Sel Evol. 40:449–464. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Prica F, Radon T, Cheng Y and
Crnogorac-Jurcevic T: The life and works of S100P-from conception
to cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 6:562–576. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu HY, Tong XM, Lin XN, Jiang LY, Wang JX
and Zhang SY: Expression and distribution of Calcium-Binding
protein S100P in human placenta during pregnancy. Int J Fertil
Steril. 8:445–452. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Arumugam T and Logsdon CD: S100P: A novel
therapeutic target for cancer. Amino Acids. 41:893–899. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gibadulinova A, Tothova V, Pastorek J and
Pastorekova S: Transcriptional regulation and functional
implication of S100P in cancer. Amino Acids. 41:885–892. 2011.
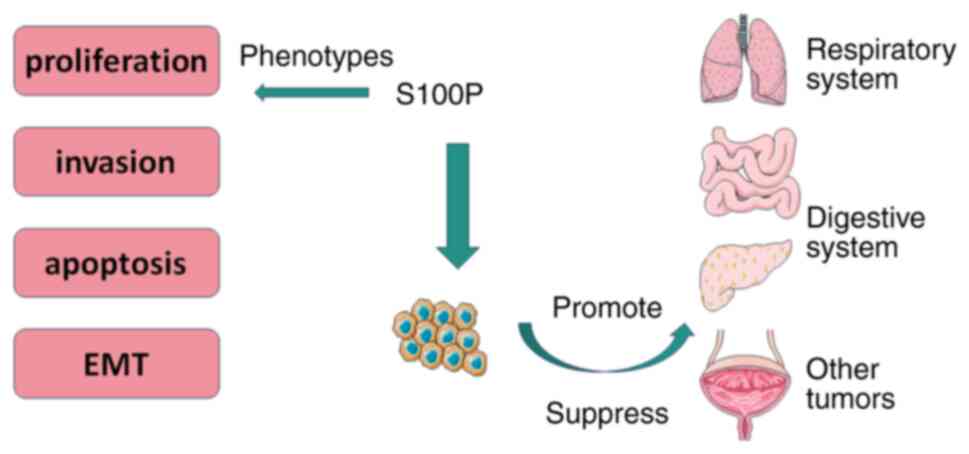
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fan G, Xie T, Yang M, Li L, Tang L, Han X
and Shi Y: Spatial analyses revealed S100P + TFF1 + tumor cells in
spread through air spaces samples correlated with undesirable
therapy response in non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl Med.
22:9172024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hao W, Zhang Y, Dou J, Cui P and Zhu J:
S100P as a potential biomarker for immunosuppressive
microenvironment in pancreatic cancer: A bioinformatics analysis
and in vitro study. BMC Cancer. 23:9972023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Srivastava K, Lines KE, Jach D and
Crnogorac-Jurcevic T: S100PBP is regulated by mutated KRAS and
plays a tumour suppressor role in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene.
42:3422–3434. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xuan Z, Liu L, Zhang G, Zheng X, Jiang J,
Wang K and Huang P: Novel cell subtypes of SPP1 + S100P+,
MS4A1-SPP1 + S100P+ were key subpopulations in intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 1867:1304202023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yoshizawa T, Uehara T, Iwaya M, Nakajima
T, Shimizu A, Kubota K, Notake T, Kitagawa N, Masuo H, Sakai H, et
al: An immunohistochemical analysis of osteopontin and S100
Calcium-binding protein P is useful for subclassifying Large- and
Small-duct type intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol.
48:751–760. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schmid F, Dahlmann M, Röhrich H, Kobelt D,
Hoffmann J, Burock S, Walther W and Stein U: Calcium-binding
protein S100P is a new target gene of MACC1, drives colorectal
cancer metastasis and serves as a prognostic biomarker. Br J
Cancer. 127:675–685. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang XY, Zhu WW, Wang Z, Huang JB, Wang
SH, Bai FM, Li TE, Zhu Y, Zhao J, Yang X, et al: Driver mutations
of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma shape clinically relevant
genomic clusters with distinct molecular features and therapeutic
vulnerabilities. Theranostics. 12:260–276. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sano N, Tabata K, Oda T, Yanagita M,
Suzuki T, Komatsubara T, Kawata H and Fukushima N: Bile cytology
diagnosis in challenging cases: Validation of diagnostic bile
cytology criteria and extensive study for immunocytochemical
markers. Diagn Cytopathol. 50:123–132. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ji L, Fu J, Hao J, Ji Y, Wang H, Wang Z,
Wang P and Xiao H: Proteomics analysis of tissue small
extracellular vesicles reveals protein panels for the reoccurrence
prediction of colorectal cancer. J Proteomics. 249:1043472021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hwang HS, An J, Kang HJ, Oh B, Oh YJ, Oh
JH, Kim W, Sung CO, Shim JH and Yu E: Prognostic molecular indices
of resectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Implications of S100P for
early recurrence. Ann Surg Oncol. 28:6466–6478. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qi LN, Ma L, Wu FX, Chen YY, Xing WT,
Jiang ZJ, Zhong JH, Chen ZS, Gong WF, Ye JZ, et al: S100P as a
novel biomarker of microvascular invasion and portal vein tumor
thrombus in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int. 15:114–126.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim BH, Kwon M, Lee D, Park SW and Shin E:
K-ras mutation detected by peptide nucleic acid-clamping polymerase
chain reaction, Ki-67, S100P, and SMAD4 expression can improve the
diagnostic accuracy of inconclusive pancreatic EUS-FNB specimens.
Pancreatology. 24:584–591. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hadjicharalambous MR and Lindsay MA: Long
Non-coding RNAs and the innate immune response. Noncoding RNA.
5:342019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ghafouri-Fard S, Majidpoor J, Shoorei H,
Hussen BM, Hadayat Jamal H, Baniahmad A, Taheri M and Mokhtari M:
The interaction between Non-Coding RNAs and calcium binding
proteins. Front Oncol. 12:8483762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lobera ES, Varela MA, Jimenez RL and
Moreno RB: miRNA as biomarker in lung cancer. Mol Biol Rep.
50:9521–9527. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang PF, Zhang XJ, Song CY, Zhang YX and
Wu Y: S100P acts as a target of miR-495 in pancreatic cancer
through bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification.
Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 37:562–571. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shen Q, Zheng G, Zhou Y, Tong J, Xu S, Gao
H, Zhang X and Fu Q: CircRNA circ_0092314 induces
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer cells via
elevating the expression of S100P by sponging miR-671. Front Oncol.
11:6754422021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hamada S, Masamune A, Miura S, Satoh K and
Shimosegawa T: MiR-365 induces gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic
cancer cells by targeting the adaptor protein SHC1 and
pro-apoptotic regulator BAX. Cell Signal. 26:179–185. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hidalgo M: Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J
Med. 362:1605–1617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Su KG, Savino C, Marracci G, Chaudhary P,
Yu X, Morris B, Galipeau D, Giorgio M, Forte M and Bourdette D:
Genetic inactivation of the p66 isoform of ShcA is neuroprotective
in a murine model of multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurosci.
35:562–571. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lin C, Zhao XY, Li L, Liu HY, Cao K, Wan
Y, Liu XY, Nie CL, Liu L, Tong AP, et al: NOXA-induced alterations
in the Bax/Smac axis enhance sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to
cisplatin. PLoS One. 7:e367222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Merry CR, McMahon S, Forrest ME, Bartels
CF, Saiakhova A, Bartel CA, Scacheri PC, Thompson CL, Jackson MW,
Harris LN and Khalil AM: Transcriptome-wide identification of mRNAs
and lincRNAs associated with trastuzumab-resistance in
HER2-positive breast cancer. Oncotarget. 7:53230–53244. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tan BS, Yang MC, Singh S, Chou YC, Chen
HY, Wang MY, Wang YC and Chen RH: LncRNA NORAD is repressed by the
YAP pathway and suppresses lung and breast cancer metastasis by
sequestering S100P. Oncogene. 38:5612–5626. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Williams ED, Gao D, Redfern A and Thompson
EW: Controversies around Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in
cancer metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 19:716–732. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Smith BN and Bhowmick NA: Role of EMT in
metastasis and therapy resistance. J Clin Med. 5:172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Brabletz T, Kalluri R, Nieto MA and
Weinberg RA: EMT in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:128–134. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ribatti D, Tamma R and Annese T:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: A historical overview.
Transl Oncol. 13:1007732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zuo Z, Zhang P, Lin F, Shang W, Bi R, Lu
F, Wu J and Jiang L: Interplay between Trx-1 and S100P promotes
colorectal cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition by
up-regulating S100A4 through AKT activation. J Cell Mol Med.
22:2430–2441. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shen ZY, Fang Y, Zhen L, Zhu XJ, Chen H,
Liu H, Jiang B, Li GX and Deng HJ: Analysis of the predictive
efficiency of S100P on adverse prognosis and the pathogenesis of
S100P-mediated invasion and metastasis of colon adenocarcinoma.
Cancer Genet. 209:143–153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shen Z, Deng H, Fang Y, Zhu X, Ye GT, Yan
L, Liu H and Li G: Identification of the interplay between SOX9 and
S100P in the metastasis and invasion of colon carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 6:20672–20684. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hsu YL, Hung JY, Liang YY, Lin YS, Tsai
MJ, Chou SH, Lu CY and Kuo PL: S100P interacts with integrin α7 and
increases cancer cell migration and invasion in lung cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:29585–29598. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hou T, Zhou L, Wang L, Kazobinka G, Chen
Y, Zhang X and Chen Z: Leupaxin promotes bladder cancer
proliferation, metastasis, and angiogenesis through the PI3K/AKT
pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 47:2250–2260. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li Z, Chen Y, Wang X, Zhang H, Zhang Y,
Gao Y, Weng M, Wang L, Liang H, Li M, et al: LASP-1 induces
proliferation, metastasis and cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase
in gallbladder cancer by down-regulating S100P via the PI3K/AKT
pathway. Cancer Lett. 372:239–250. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jiang H, Hu H, Lin F, Lim YP, Hua Y, Tong
X and Zhang S: S100P is overexpressed in squamous cell and
adenosquamous carcinoma subtypes of endometrial cancer and promotes
cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Cancer Invest. 34:477–488.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fuentes MK, Nigavekar SS, Arumugam T,
Logsdon CD, Schmidt AM, Park JC and Huang EH: RAGE activation by
S100P in colon cancer stimulates growth, migration, and cell
signaling pathways. Dis Colon Rectum. 50:1230–1240. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Onyeagucha BC, Mercado-Pimentel ME,
Hutchison J, Flemington EK and Nelson MA: S100P/RAGE signaling
regulates microRNA-155 expression via AP-1 activation in colon
cancer. Exp Cell Res. 319:2081–2090. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mercado-Pimentel ME, Onyeagucha BC, Li Q,
Pimentel AC, Jandova J and Nelson MA: The S100P/RAGE signaling
pathway regulates expression of microRNA-21 in colon cancer cells.
FEBS Lett. 589:2388–2393. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu S, Tian Y, Zheng Y, Cheng Y, Zhang D,
Jiang J and Li S: TRIM27 acts as an oncogene and regulates cell
proliferation and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer through
SIX3-β-catenin signaling. Aging (Albany NY). 12:25564–25580. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chien MH, Lee WJ, Hsieh FK, Li CF, Cheng
TY, Wang MY, Chen JS, Chow JM, Jan YH, Hsiao M, et al: Keap1-Nrf2
interaction suppresses cell motility in lung adenocarcinomas by
targeting the S100P protein. Clin Cancer Res. 21:4719–4732. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gao L, Bai Y, Zhou J, Liang C, Dong Y, Han
T, Liu Y, Guo J, Wu J and Hu D: S100P facilitates LUAD progression
via PKA/c-Jun-mediated tumor-associated macrophage recruitment and
polarization. Cell Signal. 120:1111792024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Carneiro P, Moreira AM, Figueiredo J,
Barros R, Oliveira P, Fernandes MS, Ferro A, Almeida R, Oliveira C,
Carneiro F, et al: S100P is a molecular determinant of E-cadherin
function in gastric cancer. Cell Commun Signal. 17:1552019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wu TS, Tan CT, Chang CC, Lin BR, Lai WT,
Chen ST, Kuo MY, Rau CL, Jaw FS and Chang HH: B-cell
lymphoma/leukemia 10 promotes oral cancer progression through
STAT1/ATF4/S100P signaling pathway. Oncogene. 34:1207–1219. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lin F, Zhang P, Zuo Z, Wang F, Bi R, Shang
W, Wu A, Ye J, Li S, Sun X, et al: Thioredoxin-1 promotes
colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis through crosstalk with
S100P. Cancer Lett. 401:1–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chandramouli A, Mercado-Pimentel ME,
Hutchinson A, Gibadulinová A, Olson ER, Dickinson S, Shañas R,
Davenport J, Owens J, Bhattacharyya AK, et al: The induction of
S100p expression by the Prostaglandin E2
(PGE2)/EP4 receptor signaling pathway in colon cancer
cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 10:1056–1066. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kumar A, Taghi Khani A, Sanchez Ortiz A
and Swaminathan S: GM-CSF: A Double-edged sword in cancer
immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 13:9012772022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kazakov AS, Rastrygina VA, Vologzhannikova
AA, Zemskova MY, Bobrova LA, Deryusheva EI, Permyakova ME, Sokolov
AS, Litus EA, Shevelyova MP, et al: Recognition of
granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor by specific S100
proteins. Cell Calcium. 119:1028692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kazakov AS, Deryusheva EI, Permyakova ME,
Sokolov AS, Rastrygina VA, Uversky VN, Permyakov EA and Permyakov
SE: Calcium-Bound S100P protein is a promiscuous binding partner of
the Four-helical cytokines. Int J Mol Sci. 23:120002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kazakov AS, Mayorov SA, Deryusheva EI,
Avkhacheva NV, Denessiouk KA, Denesyuk AI, Rastrygina VA, Permyakov
EA and Permyakov SE: Highly specific interaction of monomeric S100P
protein with interferon beta. Int J Biol Macromol. 143:633–639.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kazakov AS, Sofin AD, Avkhacheva NV,
Deryusheva EI, Rastrygina VA, Permyakova ME, Uversky VN, Permyakov
EA and Permyakov SE: Interferon-β activity is affected by S100B
protein. Int J Mol Sci. 23:19972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Angel MR, Séguin B, Löhr CV, Beer TM,
Feliciano J, Ramsey SA and Thomas GV: Comparative transcriptomes of
canine and human prostate cancers identify mediators of castration
resistance. Vet Comp Oncol. 22:629–640. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Sun W, Luo L, Fang D, Tang T, Ni W, Dai B,
Sun H and Jiang L: A Novel DNA aptamer targeting S100P induces
antitumor effects in colorectal cancer cells. Nucleic Acid Ther.
30:402–413. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Nedelkov D: Mass spectrometry-based
immunoassays for the next phase of clinical applications. Expert
Rev Proteomics. 3:631–640. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hussaini HM, Seo B and Rich AM:
Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence. Methods Mol Biol.
2588:439–450. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chen F, Huang Y, Liu Y, Zhuang Y, Cao X
and Qin X: SERS analysis platform based on aptamer
Recognition-release strategy for efficient and sensitive diagnosis
of colorectal precancerous lesions. Int J Nanomedicine.
19:10009–10021. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Cao X, Liu Z, Qin X, Gu Y, Huang Y, Qian
Y, Wang Z, Li H, Zhu Q and Wei W: LoC-SERS platform for rapid and
sensitive detection of colorectal cancer protein biomarkers.
Talanta. 270:1255632024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ahmed AA, Greenhalf W, Palmer DH, Williams
N, Worthington J, Arshad T, Haider S, Alexandrou E, Guneri D,
Waller ZAE and Neidle S: The potent G-Quadruplex-binding compound
QN-302 downregulates S100P gene expression in cells and in an in
vivo model of pancreatic cancer. Molecules. 28:24522023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Davoodi-Moghaddam Z, Jafari-Raddani F,
Kordasti S and Bashash D: Identification of an immune-related genes
signature in lung adenocarcinoma to predict survival and response
to immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 36:302024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Xu J, Zhang Y, Li M, Shao Z, Dong Y, Li Q,
Bai H, Duan J, Zhong J, Wan R, et al: A single-cell characterised
signature integrating heterogeneity and microenvironment of lung
adenocarcinoma for prognostic stratification. EBioMedicine.
102:1050922024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Shu J, Jiang J and Zhao G: Identification
of novel gene signature for lung adenocarcinoma by machine learning
to predict immunotherapy and prognosis. Front Immunol.
14:11778472023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Sun QY, Zhou Y, Du LJ, Zhang MK, Wang JL,
Ren YY and Liu F: Analysis between macrophage-related genes with
prognosis and tumor microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer.
Yi Chuan. 45:684–699. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wu J, Zhou J, Xu Q, Foley R, Guo J, Zhang
X, Tian C, Mu M, Xing Y, Liu Y, et al: Identification of key genes
driving tumor associated macrophage migration and polarization
based on immune fingerprints of lung adenocarcinoma. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 9:7518002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yu H, Zhang W, Xu XR and Chen S: Drug
resistance related genes in lung adenocarcinoma predict patient
prognosis and influence the tumor microenvironment. Sci Rep.
13:96822023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhou E, Wu F, Guo M, Yin Z, Li Y, Li M,
Xia H, Deng J, Yang G and Jin Y: Identification of a novel gene
signature of lung adenocarcinoma based on epidermal growth factor
receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance. Front Oncol.
12:10082832022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wu S, Pan J, Pan Q, Zeng L, Liang R and Li
Y: Multi-omics profiling and experimental verification of tertiary
lymphoid structure-related genes: Molecular subgroups, immune
infiltration, and prognostic implications in lung adenocarcinoma.
Front Immunol. 15:14532202024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Yu Y, Liu M, Wang Z, Liu Y, Yao M, Wang L
and Zhong L: Identification of oxidative stress signatures of lung
adenocarcinoma and prediction of patient prognosis or treatment
response with single-cell RNA sequencing and bulk RNA sequencing
data. Int Immunopharmacol. 137:1124952024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Li Y, Huang H, Jiang M, Yu N, Ye X, Huang
Z and Chen L: Identification and validation of a hypoxia-immune
signature for overall survival prediction in lung adenocarcinoma.
Front Genet. 13:9752792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Li Q, Xie D, Yao L, Qiu H, You P, Deng J,
Li C, Zhan W, Weng M, Wu S, et al: Combining autophagy and immune
characterizations to predict prognosis and therapeutic response in
lung adenocarcinoma. Front Immunol. 13:9443782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chen A, Jing W, Qiu J and Zhang R:
Prediction of cervical cancer outcome by identifying and validating
a NAD+ Metabolism-derived gene signature. J Pers Med. 12:20312022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Guo H, Wang Y, Gou L and Wang X, Tang Y
and Wang X: A novel prognostic model based on urea cycle-related
gene signature for colorectal cancer. Front Surg. 9:10276552022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhu L, Ito T, Nakahara T, Nagae K, Fuyuno
Y, Nakao M, Akahoshi M, Nakagawa R, Tu Y, Uchi H and Furue M:
Upregulation of S100P, receptor for advanced glycation end products
and ezrin in malignant melanoma. J Dermatol. 40:973–979. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Xiong TF, Pan FQ and Li D: Expression and
clinical significance of S100 family genes in patients with
melanoma. Melanoma Res. 29:23–29. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhu L, Okano S, Takahara M, Chiba T, Tu Y,
Oda Y and Furue M: Expression of S100 protein family members in
normal skin and sweat gland tumors. J Dermatol Sci. 70:211–219.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Li Q, Wang T, Tang Y, Zou X, Shen Z, Tang
Z, Zhou Y and Shi J: A novel prognostic signature based on
smoking-associated genes for predicting prognosis and immune
microenvironment in NSCLC smokers. Cancer Cell Int. 24:1712024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Wan R, Tan Z, Qian H, Li P, Zhang J, Zhu
X, Xie P and Ren L: Prognostic value of S100 family mRNA expression
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Turk J Gastroenterol. 35:316–334.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Li Z, Huang N, Du Q, Huang W, Wang B, Wang
B, Shen G, Zhang H, Shi S and Wang L: Role of immunophenotypic
characterisation in prognostic subtyping of intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Pathology. 55:979–988. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Rawal N, Hariprasad G, Bandyopadhyay S,
Ranjan Dash N, Kumar S, Das P, Dey S, Ahmad Khan M, Ranjan A,
Chopra A, et al: Molecular biomarkers involved in the progression
of gallbladder inflammatory lesions to invasive cancer: A proteomic
approach. Biomol Biomed. 25:115–143. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Mathai AM, Alexander J, Huang HY, Li CF,
Jeng YM, Fung KM, Harris WP, Swanson PE, Truong C and Yeh MM: S100P
as a marker for poor survival and advanced stage in gallbladder
carcinoma. Ann Diagn Pathol. 52:1517362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Tian Z, Tang J, Liao X, Yang Q, Wu Y and
Wu G: An immune-related prognostic signature for predicting breast
cancer recurrence. Cancer Med. 9:7672–7685. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Mirza Z, Ansari MS, Iqbal MS, Ahmad N,
Alganmi N, Banjar H, Al-Qahtani MH and Karim S: Identification of
novel diagnostic and prognostic gene signature biomarkers for
breast cancer using artificial intelligence and machine learning
assisted transcriptomics analysis. Cancers (Basel). 15:32372023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Peng C, Chen H, Wallwiener M, Modugno C,
Cuk K, Madhavan D, Trumpp A, Heil J, Marmé F, Nees J, et al: Plasma
S100P level as a novel prognostic marker of metastatic breast
cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 157:329–338. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Wang X, Tian T, Li X, Zhao M, Lou Y, Qian
J, Liu Z, Chen H and Cui Z: High expression of S100P is associated
with unfavorable prognosis and tumor progression in patients with
epithelial ovarian cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 5:2409–2421.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Umezaki Y, Ito M, Nakashima M, Mihara Y,
Naruke Y, Kurohama H, Yatsunami N and Yasuhi I: S100P is a useful
marker for differentiation of ovarian mucinous tumors. Eur J
Gynaecol Oncol. 36:138–141. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Guo L, Chen S, Jiang H, Huang J, Jin W and
Yao S: The expression of S100P increases and promotes cellular
proliferation by increasing nuclear translocation of β-catenin in
endometrial cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:2102–2112.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Hamada S, Satoh K, Hirota M, Fujibuchi W,
Kanno A, Umino J, Ito H, Satoh A, Kikuta K, Kume K, et al:
Expression of the calcium-binding protein S100P is regulated by
bone morphogenetic protein in pancreatic duct epithelial cell
lines. Cancer Sci. 100:103–110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|